Abstract
Between 2020 and 2023, rust fungus specimens were collected from the primary forested regions of the Sanjiangyuan area in Qinghai Province, resulting in over 300 samples. A taxonomic and phylogenetic study of the rust fungi from these forests was conducted using morphological and molecular biological techniques. The investigation identified rust fungi from 7 families, 12 genera, 56 species and varieties, including 10 new host records, 1 new record for China, and 2 novel species. The host plants involved belonged to 26 families, 48 genera, and 78 species. Pucciniaceae and Coleosporiaceae were the dominant families, with the genera Puccinia, Melampsora, and Gymnosporangium being prevalent. The rust fungi in the Sanjiangyuan forests showed a biogeographical affinity with the North Temperate Zone. Floristic comparisons revealed a higher similarity with rust fungi from Inner Mongolia, Gansu, and Tibet and a lower similarity with those from Hainan. An analysis of the life forms of rust fungus host plants indicated that herbaceous plants were the most common, followed by shrubs and trees. In different regions of Sanjiangyuan, rust fungi were found as follows: Golog Prefecture with 6 families, 9 genera, and 28 species; Yushu Prefecture with 5 families, 8 genera, and 31 species; Huangnan Prefecture with 5 families, 9 genera, and 26 species; and Hainan Prefecture with 4 families, 5 genera, and 10 species. The families Pucciniaceae, Melampsoraceae, and Coleosporiaceae were common across all four regions. Moreover, the families Rosaceae, Asteraceae, Ranunculaceae, Salicaceae, and Caprifoliaceae were shared among the host plants in these regions.
1. Introduction
Rust fungi (Pucciniales) belong to the phylum Basidiomycota, class Pucciniomycetes, and order Pucciniales [1]. To date, there are 14 families, 166 genera, and over 7000 species of rust fungi recorded worldwide [2], with a broad distribution and a wide range of hosts, posing significant threats as pathogens to many plants. Infected plants often display noticeable symptoms such as deformities, clustering, overgrowth, or enlargement [3]. Rust diseases severely impact the growth and development of dominant tree species within forests and understory vegetation, and can even destroy young plantations, reducing the biomass and seed yields of trees and economic crops, thereby seriously impacting the ecological functions of forestry systems, as exemplified by pine gall rust [4], mulberry rust [5], and poplar leaf rust [6]. On the other hand, rust fungi play an essential role in forest ecosystems as living decomposers, crucial for maintaining the material cycle and ecological balance of forests [7]. Historically, numerous domestic scholars have published regional rust fungi checklists or treatises, covering areas including Jilin [8,9,10], Tibet [11,12], Fujian [13,14], Hubei [15,16], the Qinling Mountains [17,18,19], Xinjiang [20,21,22,23], Gansu [24], and Inner Mongolia [25], among others. These publications meticulously list the rust fungi species and systematically analyze the rust fungi of those regions. The present study conducted a survey and sampling of rust fungi in the main forest regions of the Sanjiangyuan area in Qinghai Province, employing both morphological and molecular systematic methods to classify the collected rust fungi, determine the regional rust fungi characteristics, and compile a checklist of rust fungi in the main forest regions of Sanjiangyuan. This research provides a foundation for further studies on rust fungi taxonomy and offers a scientific basis for the prevention and control of rust diseases in the main forest regions of the Sanjiangyuan area.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
The primary forest region of the Sanjiangyuan area is situated in the hinterland of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, in the southern part of Qinghai Province, between the geographical coordinates of 89°24′ E to 102°23′ E longitude and 31°39′ N to 36°16′ N latitude. The Sanjiangyuan region’s altitude ranges from 3836 to 6500 m [26]. The annual mean temperature is between −5.6 °C and 3.8 °C, with most areas experiencing an annual mean temperature below 0 °C, decreasing from southeast to northwest. The highest and lowest temperatures occur in July and January, respectively. Precipitation is primarily concentrated between June and September, accounting for approximately 80% of the annual total. The annual average precipitation ranges from 262.2 to 772.8 mm [27,28]. Field investigations were carried out and specimens were collected from the main forest areas of the Sanjiangyuan region from 2020 to 2023. Plant specimens infected by rust fungi should be collected during the growing season of the plant leaves, typically from April to October each year. The collection date, location, altitude, and host information were recorded. Specimens are stored at the Plant Pathology Laboratory of the College of Agriculture and Animal Husbandry, Qinghai University. Collect the number of specimens as shown in Appendix A.
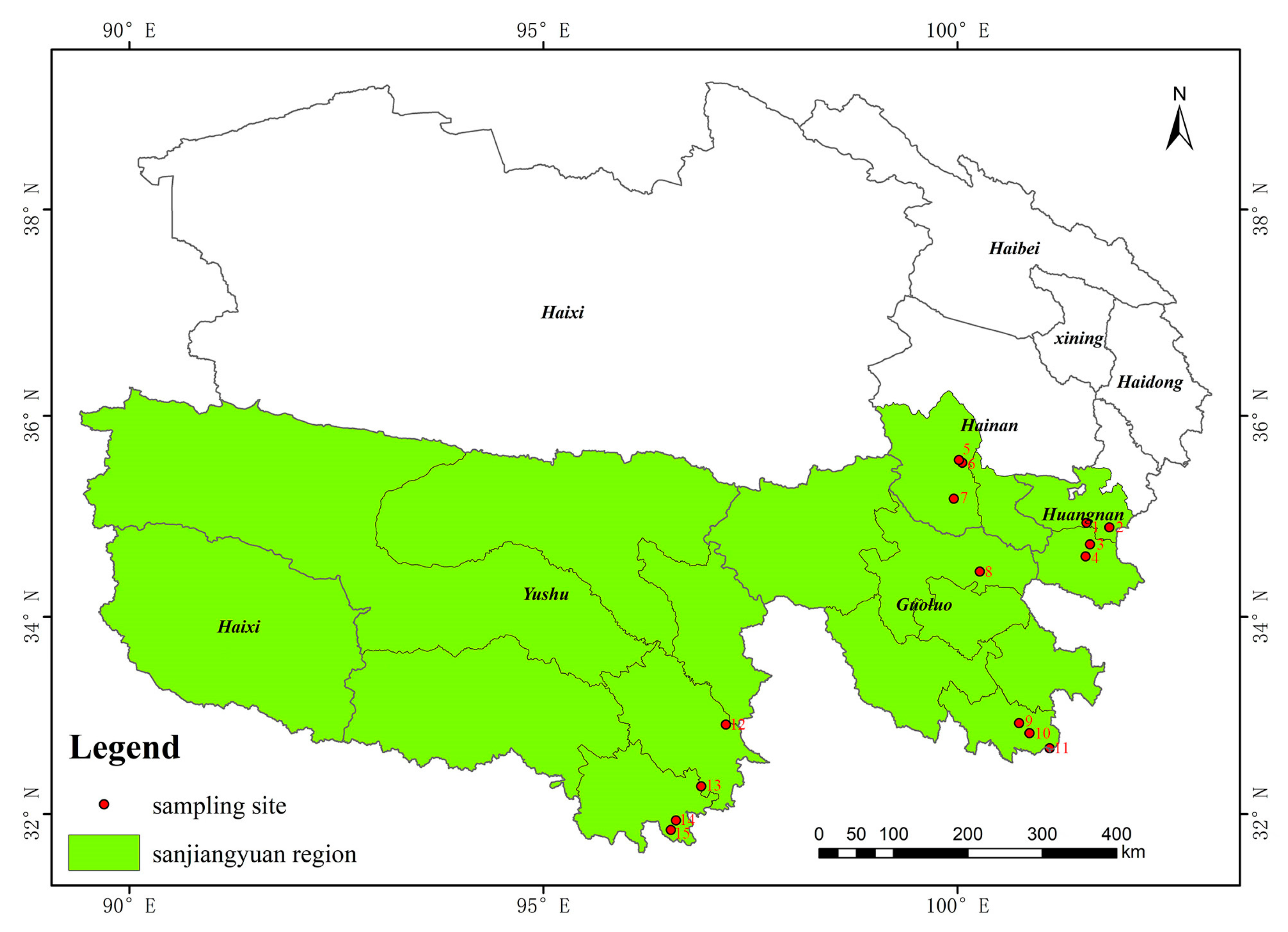
The main forest areas of Sanjiangyuan include Maixiu Forest Area, Xibosha Forestry Farm, Shuangpengxi Forestry Farm, Lanci Forestry Farm, Makehe River Forest Area, Yangyu Forest Area, Duoke River Forestry Farm, Friendship Bridge Forestry Farm, Dongzhong Forest Area, Jiangxi Forestry Farm, Leba Forestry Farm, Baizha Forestry Farm, Dongshan Forestry Farm, Xihe Forestry Farm, and Jiangla Forestry Farm. The distribution of sampling sites is illustrated in Figure 1.
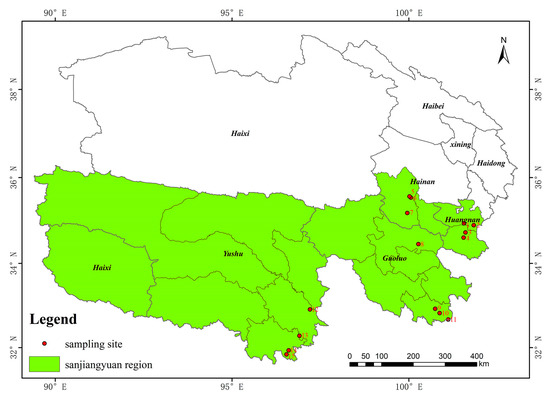
Figure 1.
Sampling point distribution map. (1: Lanci; 2: Shuangpengxi; 3: Xibosha; 4: Maixiu; 5: Jiangla; 6: Dongshan; 7: Xihe; 8: Yangyu; 9: Duoke; 10: Makehe; 11: Friendship; 12: Leba; 13: Dongzhong; 14: Jiangxi; 15: Baizha).
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Morphological Study
Morphological classification follows the systems in “Fungi of China”, “Manual of Fungal Identification”, and “Dictionary of Fungi”.
(1) Symptom Observation: Using a stereo microscope (Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) to observe the type, morphological characteristics, location on the host plant, color, shape, and distribution of spore heaps (spore structures). Measurements and photographs of the spore heaps (spore structures) are taken.
(2) Spore Structures Observation: Longitudinally sectioned spore heaps (spore structures) are observed for internal structure using an optical microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
(3) Spore Characteristics Observation: Mature spore heaps (spore structures) are selected, and spores are randomly picked to observe morphological characteristics using an optical microscope.
(4) Spore Electron Microscopy (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) Observation: Conductive adhesive is placed on the sample stage of the scanning electron microscope. Leaves containing spore bodies are placed on the stage and coated with gold using a sputter coater. Surface structure and ornamentation of the spores are observed using a field emission scanning electron microscope, with photographs and records taken.
2.2.2. Molecular Phylogenetic Study
DNA extraction is performed using a modified CTAB method [29]. Amplification of gene sequences for rust fungi ITS and LSU fragments is performed, specifically using primers ITS1F (5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′), ITS4 (5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′), NL1 (5′-GCATATCAATAAGCGGAGGAAAAG-3′), and NL4 (5′-GGTCCGTGTTTCAAGACGG-3′). Qualified sequencing sequences are submitted to GenBank to obtain accession numbers. An ML phylogenetic tree is constructed with support rates obtained by bootstrapping (BT) repeated 1000 times, and the phylogenetic relationships between sequences are analyzed.
2.2.3. Floristic Analysis
The floristic geographical characteristics mainly followed the principles of plant floristic division as described by Wu Zhengyi (2003) [30]. The analysis was conducted from the following aspects:
- (1)
- Composition of rust fungi in the main forest areas of Sanjiangyuan
The genera and species of rust fungi and their host plants were enumerated to analyze the proportion of each genus, thereby determining the dominant families and genera. The calculation method was based on the formula proposed by Dong Xueyun et al. [31]:
Above formula: Fa represents the dominant family, Fc represents the number of species in a family, St is the total number of species, Ft is the total number of families, Ga represents the dominant genus, Gc represents the number of species in a genus, and Gt is the total number of genera.
- (2)
- Geographic Component Analysis
The geographic distribution of host plant genera and species was examined to clarify the geographical characteristics of the rust fungi flora in the main forest areas of Sanjiangyuan. The known species of rust fungi in the area were listed and compared with those in adjacent regions to calculate their similarity.
- (3)
- Analysis of Host Plant Life Forms: Within the host plants, categorization was made according to their ecological types into trees, shrubs, and grasses. The ecological types of host plants were investigated and analyzed.
- (4)
- Diversity Analysis of Rust Fungi in Different Research Areas: The study areas were divided into four regions based on provincial divisions and forest distribution in the Sanjiangyuan area: Golog Prefecture, Yushu Prefecture, Huangnan Prefecture, and Hainan Prefecture.
① Diversity Calculation of Rust Fungi: The species, number, and frequency of rust fungi in each area were recorded, and the diversity index of rust fungi in different regions was calculated. When assessing species richness, indices such as weighted average number of species, Shannon-Wiener diversity index (H′), and richness index (E) were calculated to analyze the relationship between rust fungi diversity in different regions [32], with the following formulas:
- Shannon-Wiener diversity index: ;
- Maximum diversity index: ;
- Evenness index: ;
Above formula: , is the proportion of the ith species, n is the number of individuals of the ith species; N is the total number of all species; S is the number of species.
② Similarity Determination of Rust Fungi: The similarity between different regions was determined by qualitative or quantitative comparisons of species presence, which reflect their relationship and identify the environmental factors or combinations of factors that influence this relationship [32], with the following formula:
Above formula: S1 and S2 are the number of species in community 1 and community 2, respectively; C represents the number of common species between communities 1 and 2.
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Identification of Rust Fungi Species in the Main Forest Area of Sanjiang Source
Following years of continuous fixed-point surveys and collections in the major forest regions of the Sanjiangyuan area, over 300 rust fungus specimens were collected. A total of 7 families, 12 genera, 56 species, and varieties of rust fungi were identified within these regions, including 1 new record for China and 2 proposed new species, involving 26 families, 48 genera, and 78 species of host plants, with 10 plant species being new records as hosts for rust fungi (Table 1). In this study, two new rust fungi were discovered, parasitic on Ligularia przewalskii and Rheum pumilum, respectively. The morphological characteristics of the parasitic rust spores on L. przewalskii were compared with those of known species, revealing certain differences from other rust spores. Molecular systematics studies of the rust fungi were conducted using molecular biology techniques, showing their affinity with rust fungi of the genus Puccinia (GenBank accession number PP469520). Considering that only one species of rust fungus, P. ligulicola, has been reported on the host plant L. przewalskii, and after consulting relevant literature, we believe that this species is a new one awaiting publication. Similarly, the rust fungus parasitic on R. pumilum was identified as Puccinia sp. (GenBank accession number PP469561), pending publication. Based on the ITS and LSU segments, an ML system was constructed to build phylogenetic trees, both of which divided the rust fungi in the Three Rivers Source main forest area into seven families, consistent with morphological identification results. The Pucciniaceae family diverges significantly, with genera Puccinia and Uromyces clustering together in a major branch, while Gymnosporangium is dispersed in another well-supported branch. Genera Ochropsora and Nyssopsora are incorporated into Gymnosporangium. Additionally, Hyalopsora, Melampsora, Coleosporium, Chrysomyxa, and Uredo are grouped into another major branch.

Table 1.
Rust Fungus Catalogue of the Major Forest Regions in the Sanjiangyuan Area.
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.2.1. Rust Fungi Composition in the Sanjiangyuan RegionIn
In the primary forest areas of the Sanjiangyuan region, the dominant family of rust fungi is Pucciniaceae, accounting for 36.36% of the total number of rust genera, followed by Coleosporiaceae, representing 18.18% of the genera. The prevalent genera are Puccinia, constituting 50% of the total species count; Melampsora, comprising 12% of the species; and Gymnosporangium, making up 11% of the species (Table 2). The host plants’ dominant families are Rosaceae, which represent 16% of the total host species; Asteraceae, accounting for 9%; Ranunculaceae, also at 9%; Polygonaceae, at 8%; Salicaceae, at 8%; Berberidaceae, at 6%; Fabaceae, at 6%; Poaceae, at 5%; and Grossulariaceae, also at 5%.

Table 2.
Composition of Rust Fungi families, genera, and species in Sanjiangyuan.
3.2.2. Rust Fungi Geographical Components of the Sanjiangyuan Region
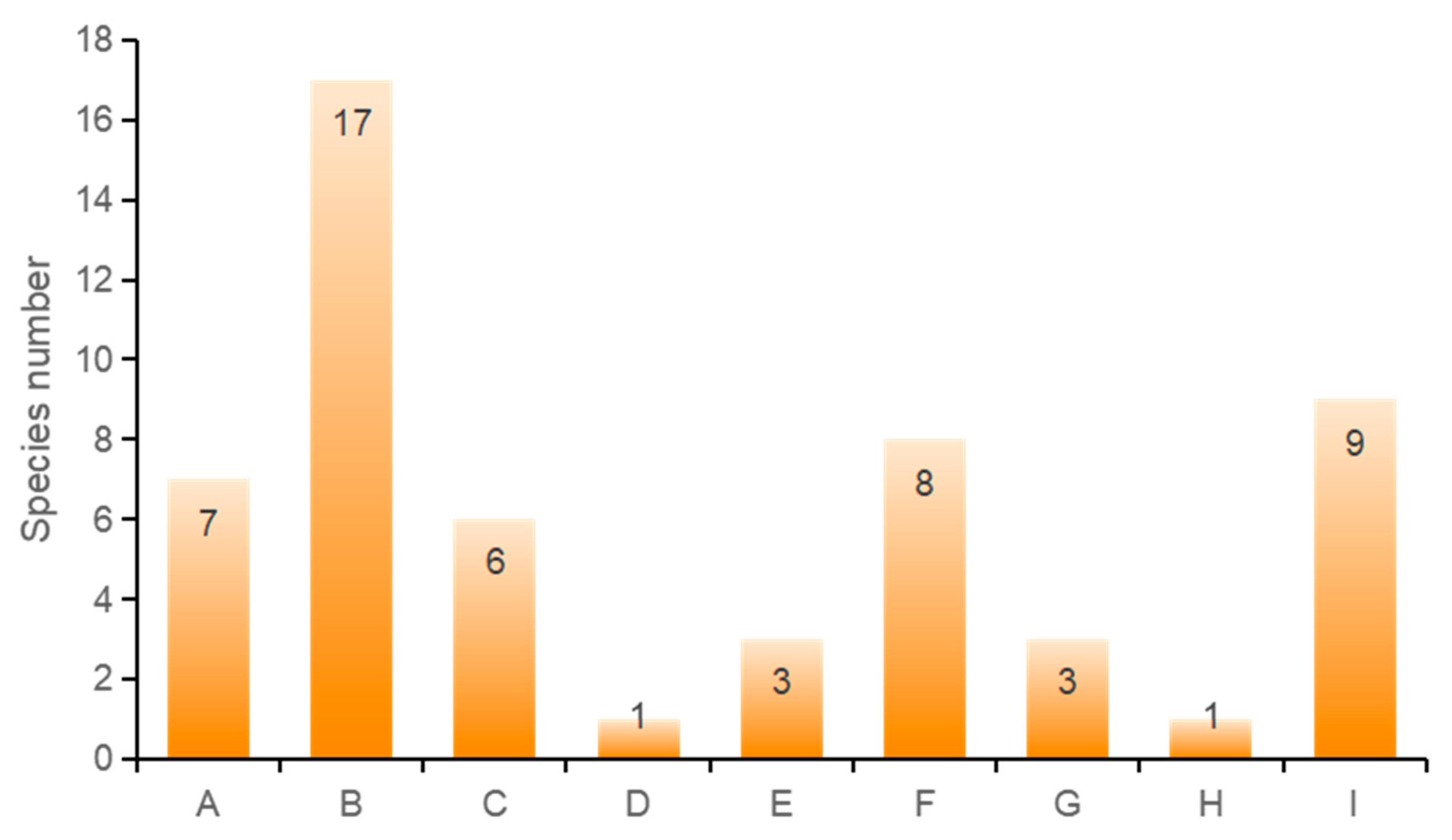
The floristic geographical features primarily adhered to Wu Zhengyi’s plant floristic division principles [31]. The rust fungi of the forest plants in the Sanjiangyuan region have been preliminarily divided into nine geographical components. Cosmopolitan species account for 12.1%, North Temperate widespread species represent 30.9%, Eurasian Temperate widespread species comprise 10.9%, species widespread in both the cold and temperate zones of the Northern Hemisphere make up 1.8%, Central European components constitute 5.5%, East Asian components 14.5%, Central Asian components 5.5%, South Central Asian components 1.8%, and species endemic to China 16.4% (Figure 2).
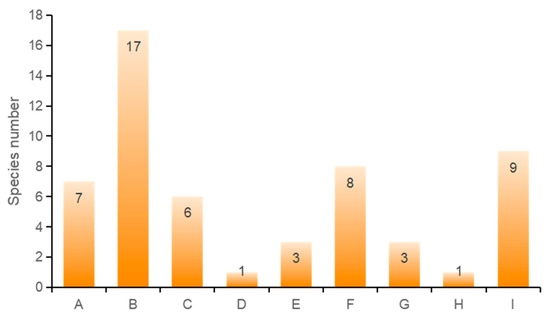
Figure 2.
Analysis of geographic components of rust fungi in Sanjiangyuan. (A: Worldwide; B: Widely distributed in the northern temperate zone; C: The eurasian temperate zone is widespread; D: The northern hemisphere is cold and temperate; E: Central European component; F: East Asian elements; G: Central Asian component; H: Central and south Asian components; I: Chinese endemic).
3.2.3. Comparative Analysis of Rust Fungi in the Sanjiangyuan Forests and Adjacent Regions
To ascertain the geographical composition of the rust fungi flora in the main forested areas of the Sanjiangyuan region, a comparison was made with rust fungi lists from neighboring areas (Table 3). The floristic elements of the rust fungi in the major forested areas of Sanjiangyuan show a higher similarity with those of Inner Mongolia, Gansu, and Tibet, with similarity coefficients of 49.6, 45.9, and 41.6, respectively. There is a moderate resemblance to the rust fungi flora of the Qinling Mountains, the Altai region in Xinjiang, and Jilin, with similarity coefficients of 38.2, 24.6, and 13.3, respectively. The disparity between the rust fungi flora of Hainan and the Sanjiangyuan region is substantial, with a coefficient of only 2.

Table 3.
Comparison of rust flora in the main forest areas of Sanjiangyuan with adjacent areas.
3.3. Analysis of Life Forms of Rust Fungus Host Plants in the Sanjiangyuan
For the main forest regions, following the classification method of the “Flora of China”, the rust fungus host plants in the main forest regions of Sanjiangyuan are broadly categorized into three life forms: trees, shrubs, and herbaceous plants. The herbaceous plants dominate, comprising 17 families, 32 genera, and 44 species, accounting for 56.41% of the total species count; shrubs consist of 6 families, 11 genera, and 24 species, representing 30.77% of the total; trees include 4 families, 5 genera, and 8 species, making up 12.82%, as shown in Table 3, Table 4 and Table 5. It has been observed that the rust fungi parasitizing tree vegetation belong to three families, three genera, and six species, with the most diverse being the genus Melampsora, which primarily infects plants of the Salicaceae family. Those infecting shrub vegetation comprise 4 families, 5 genera, and 14 species, with the genus Gymnosporangium being the most diverse, affecting plants of the Rosaceae family. The species diversity of rust fungi parasitizing herbaceous vegetation is the highest, with 6 families, 8 genera, and 40 species, predominantly from the genus Puccinia, which afflicts plants of the Poaceae, Asteraceae, Gentianaceae, Polygonaceae, Ranunculaceae, Urticaceae, Rubiaceae, Onagraceae, Apiaceae, and Lamiaceae families.

Table 4.
Analysis of host plant life form.

Table 5.
Rust population diversity in four regions.
3.4. Analysis of Rust Fungi in Different Regions of the Sanjiangyuan Area
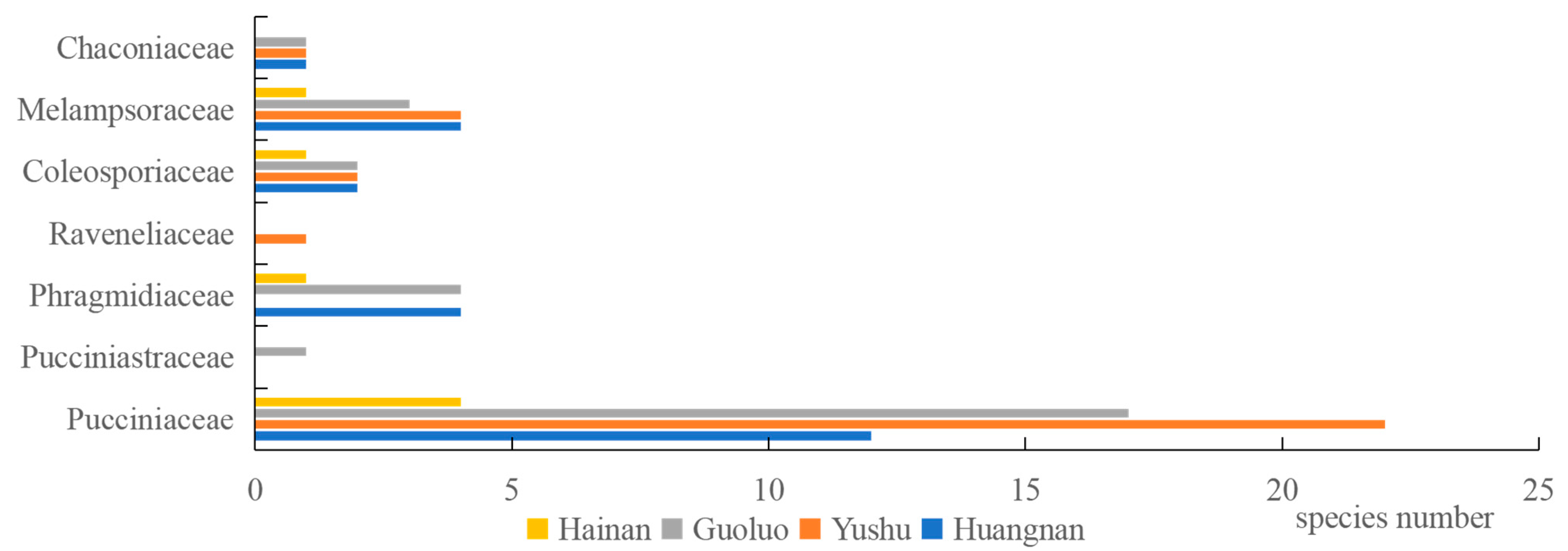
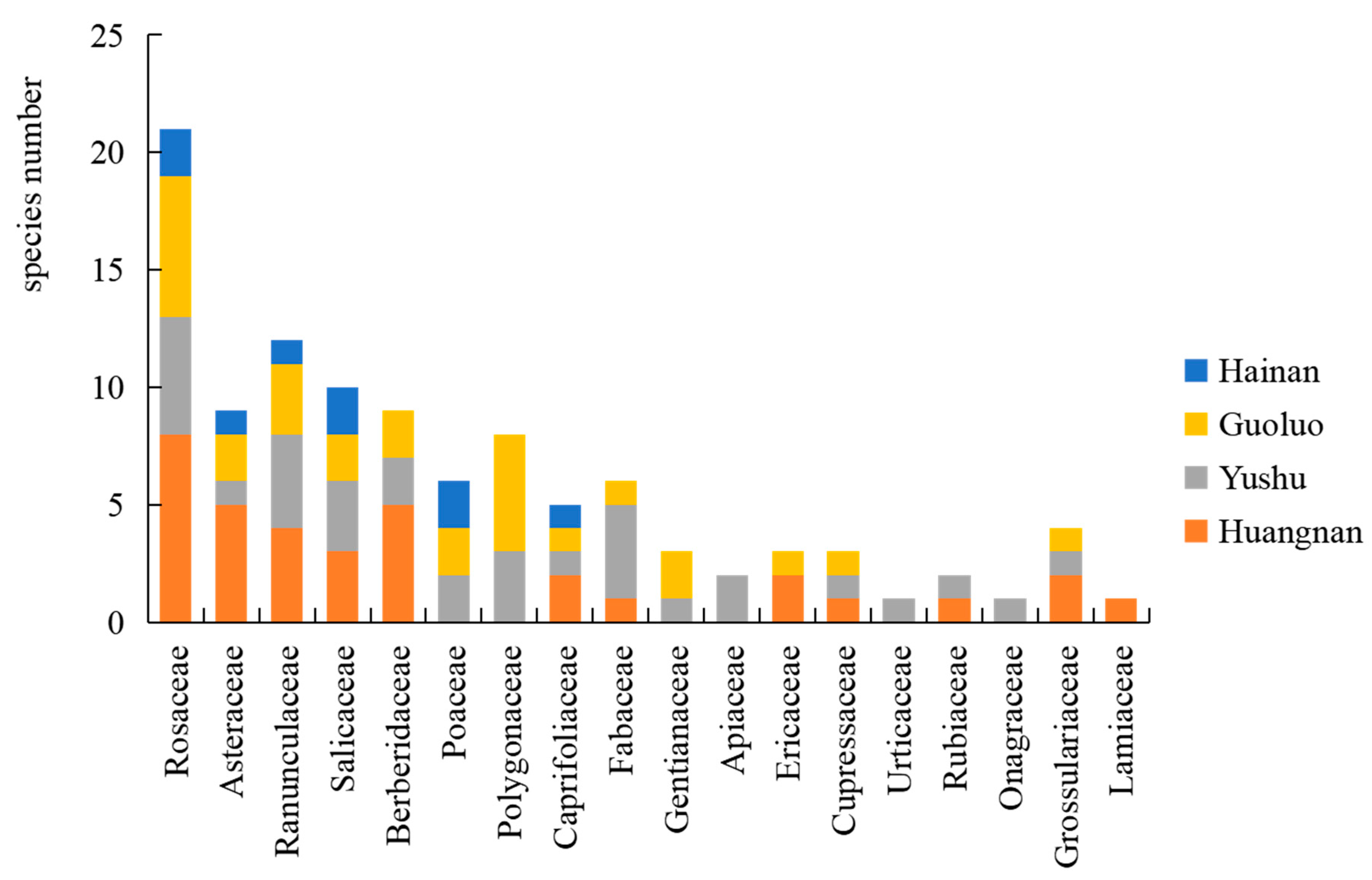
An investigation and analysis of rust fungi were conducted within four regions of the Sanjiangyuan area, revealing 7 families, 12 genera, and 56 species in total. Specifically, Golog Prefecture harbored 7 families, 9 genera, and 28 species; Yushu Prefecture was home to 6 families, 8 genera, and 31 species; Huangnan Prefecture contained 6 families, 9 genera, and 26 species; and Hainan Prefecture had 4 families, 5 genera, and 10 species. The families Pucciniaceae, Melampsoraceae, and Coleosporiaceae were common to rust fungi across all four regions (Figure 3), while the host plant families Rosaceae, Asteraceae, Ranunculaceae, Salicaceae, and Caprifoliaceae were shared among the regions (Figure 4).
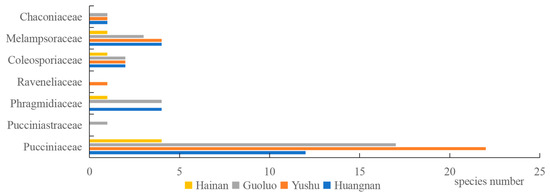
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of rust fungi in the main forest areas in Sanjiangyuan.
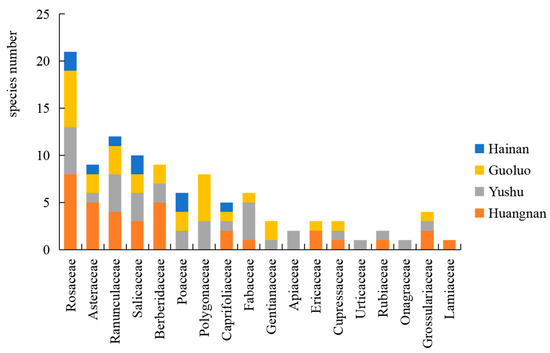
Figure 4.
Spatial distribution of rust host plants in the main forest areas of Sanjiangyuan.
3.4.1. Rust Fungus Species Diversity
Upon collation and computation of the data, it was revealed that Yushu Prefecture boasts the richest diversity of rust fungus species, with a diversity index of 3.10. Within the four regions of the Sanjiangyuan area, the diversity indices of rust fungi, in descending order, are as follows: Yushu Prefecture, Guoluo Prefecture, Huangnan Prefecture, and Hainan Prefecture (Table 5).
3.4.2. Rust Fungus Similarity Assessment across Different Regions
As analyzed in Table 6, the similarity coefficients for rust fungus species between Huangnan Prefecture and Guoluo Prefecture, Yushu Prefecture, and Hainan Prefecture are 0.5185, 0.4561, and 0.3333, respectively; between Guoluo Prefecture and Yushu Prefecture, Hainan Prefecture are 0.6102, and 0.2632, respectively; and between Yushu Prefecture and Hainan Prefecture is 0.1951. It is thus evident that the similarity in rust fungus species is highest between Yushu Prefecture and Guoluo Prefecture, and lowest between Yushu Prefecture and Hainan Prefecture.

Table 6.
Scale factor.
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Upon surveying the forest mycoflora within the primary forests of the Sanjiangyuan region, a total of 56 rust fungus species and varieties across 7 families and 12 genera were identified. This inventory includes 1 new record for China, 2 proposed new species, and spans 26 families, 48 genera, and 78 species of host plants, with 10 plants being newly recorded hosts for these rust fungi. The dominant rust fungi families in the Sanjiangyuan forests are Pucciniaceae and Coleosporiaceae, and the prevalent genera include Puccinia, Melampsora, and Gymnosporangium. The host plants are predominantly from the Rosaceae, Asteraceae, Ranunculaceae, Polygonaceae, Salicaceae, Berberidaceae, Fabaceae, Poaceae, and Grossulariaceae families.
The phytoflora of this region is chiefly of the North Temperate Zone, and the discovery of the primitive rust fungus Hyalopsora adianti-capilli-veneris, which parasitizes on ferns, underscores the antiquity of the local flora. The geographic distribution of rust fungi in the Sanjiangyuan primary forests primarily consists of widespread North Temperate species, representing 17 species (30.9%). Followed by nine endemic Chinese species (16.4%), including Gymnosporangium Huanglongense and Gymnosporangium pleoporum, exclusive to the Sanjiangyuan region. There are eight East Asian species (14.5%), seven cosmopolitan species (12.7%), seix Eurasian Temperate widespread species (10.9%), and three each of the Central European and Central Asian components (5.5%, respectively). There are one species each (1.8%) from the North Hemisphere cold and temperate zones and the South and Central Asia components.
The Sanjiangyuan rust fungus flora shows high similarity coefficients with Inner Mongolia, Gansu, and Tibet, at 49.6, 45.9, and 41.6, respectively. This is likely due to geographical proximity and similar species composition, richness, and abundance. The similarity coefficient with the Qinling Mountains is 38.2, which may be attributed to its location between North and Southwest China, serving as a climatic divide, and its complex mountainous terrain with rich precipitation that supports a diverse ecosystem, hence a high diversity of fungi. The high altitude and harsh climatic conditions of the Sanjiangyuan region, characterized by plateaus, mountains, an arid climate, and low precipitation, result in relatively limited biodiversity. The similarity coefficient with Altai, Xinjiang is 24.6, possibly due to the diverse climate ranging from arid desert to temperate mountainous weather with clear seasonal changes and varied precipitation. The typical plateau climate of the Sanjiangyuan region has a significant impact on the survival and distribution of biota due to its cold climate, thin oxygen, low precipitation, and high evaporation. The dissimilarities in fungal diversity between the two regions are attributed to their different climatic conditions. With Jilin, the similarity coefficient is 13.3, likely because Jilin has a rich variety of ecosystems, including forests, wetlands, and grasslands, which support a wide range of plants, animals, and microorganisms. In contrast, the Sanjiangyuan region predominantly features plateau meadows, wetlands, and glaciers, hosting many endemic species but overall having less biodiversity than Jilin Province due to the severe climate. The rust fungi flora of Hainan shows a stark contrast with a similarity coefficient of only 2, as Hainan has a tropical monsoon climate with year-round warmth and moisture, abundant rainfall conducive to tropical rainforests, and other tropical ecosystems. The humid environment is ideal for many fungi species, unlike the typically fewer fungi found in the stark plateau climate of the Sanjiangyuan region.
In the Sanjiangyuan primary forests, herbaceous plants dominate the host plants for rust fungi, with 17 families, 32 genera, and 44 species (56.41%); shrubs comprise 6 families, 11 genera, and 24 species (30.77%); and trees make up 4 families, 5 genera, and 8 species (12.82%). It has been observed that rust fungi parasitizing arboreal vegetation include three families and three genera with six species, with Melampsora affecting the most species, particularly the Salicaceae plants. The shrub layer hosts 4 families, 5 genera, and 14 species of rust fungi, predominantly from Gymnosporangium, impacting the Rosaceae plants. The herbaceous layer carries the highest number of rust fungus species, with 6 families, 8 genera, and 40 species, with Puccinia being the most diverse, affecting Poaceae, Asteraceae, Gentianaceae, Polygonaceae, Ranunculaceae, Urticaceae, Rubiaceae, Onagraceae, Apiaceae, and Lamiaceae plants.
Diversity surveys of forest plant rust fungi across four distinct regions within the Sanjiangyuan revealed that biodiversity indices decreased in the order of Yushu Prefecture, Golog Prefecture, Huangnan Prefecture, and Hainan Prefecture. This pattern is attributed to the high coverage of pristine forests in Yushu Prefecture, offering complex and undisturbed natural habitats that provide rich conditions and biomass resources for a variety of fungi. The primeval forests of Yushu Prefecture, connected to the Hengduan Mountains in Tibet, furnish a diverse range of conditions and isolated environments for the distribution and evolution of species, favoring the maintenance of biodiversity and the emergence of endemic species. The highest similarity in rust fungi between Yushu and Golog Prefectures may be due to their shared primitive forests and similar altitudes, likely harboring comparable habitat types.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft, Q.X.; Writing—review & editing, L.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Qinghai Province Key Research and Development and Transformation Plan (2023-SF-119).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Number of Rust Fungus Specimens Collected
| Order | Rust Fungi Species Name | Host Plants | Collection Sample Site | The Gatherer | Collection Number |
| 1 | Chrysomyxa woroninii | Rhododendron thymifolium | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°56′08″ E, 35°54′35″ N) | Qi Xu; Hailan LI | QHU2022004, QHU2021135 |
| 2 | Coleosporium pedicularis | Pedicularis croizatiana | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°45′19″ E, 32°27′09″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022203, QHU2022219 |
| Pedicularis croizatiana | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°21′53″ E, 32°17′56″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022237 | ||
| Pedicularis croizatiana | Dongzhong Forest Farm (97°27′20″ E, 32°40′22”) | Qi Xu; Yuying Li | QHU2023065 | ||
| Pedicularis croizatiana | Yangyu Forest Farm (100°16′13″ E, 34°27′15″ N) | Qi Xu; Hailan LI | QHU2021007 | ||
| 3 | Gymnosporangium annulatum | Cotoneaster sp. | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°56′08″ E, 35°54′35″ N) | Qi Xu; Hezhua Xiji | QHU2022134, QHU2021138, QHU2021129, QHU2021137, QHU2021131, QHU2021128 |
| 4 | G. cornutum | Sorbus koehneana | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°15′28″ E, 32°27′17″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022223 |
| Sorbus koehneana | Dongzhong Forest Farm (97°27′20″ E, 32°40′24″ N) | Qi Xu; Zihan Tan | QHU2023060 | ||
| Sorbus koehneana | Makehe Forest Farm (100°52′09″ E, 32°49′28″ N) | Qi Xu; Zihan Tan | QHU2023085 | ||
| 5 | G. confusum | Cotoneaster adpressus | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°15′28″ E, 32°27′18″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022217, QHU2022254, QHU2022255, QHU2021120 |
| Cotoneaster multiflorus | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°15′28″ E, 32°27′35″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022244, QHU2022256, QHU2022257, QHU2021121, QHU2021122 | ||
| 6 | G. Huanglongense | Juniperus przewalskii | Makehe Forest Farm (100°58′08″ E, 34°31′07″ N) | Qinen He | QHU2023023 |
| Juniperus przewalskii | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°16′59″ E, 35°28′42″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2023024 | ||
| 7 | G. pleoporum | Cotoneaster acutifolius | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°15′33″ E, 32°27′30″ N) | Qinen He; Taijun Fang | QHU2022215 |
| Cotoneaster acutifolius | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°16′59″ E, 35°35′27″ N) | Fengying He; Hailan LI | QHU2022145, QHU2022162 | ||
| Cotoneaster acutifolius | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°09′41″ E, 35°27′56″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022014 | ||
| Juniperus przewalskii | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°21′56″ E, 32°12′07″ N) | Qinen He; Hailan LI | QHU2023025, QHU2022252, QHU2022253, QHU2021124, QHU2021118, QHU2021126 | ||
| 8 | G. yamadae | Pyrus sp. | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°56′08″ E, 35°54′35″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022244, QHU2021123, QHU2021117, QHU2021125, QHU2021119, QHU2021127 |
| 9 | Hyalopsora adianti-capilli-veneris | Adiantum capillus-veneris | Makehe Forest Farm (101°49′27″ E, 32°46′05″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2023078, QHU2021133, QHU2021134, QHU2021139 |
| 10 | Melampsorella caryophyllacearum | Stellaria media | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°29′16″ E, 35°20′18″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022111, QHU2021140, QHU2021144 |
| 11 | M. euphorbiae | Euphorbia micractina | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°21′46″ E, 32°12′27″ N) | Fengying He; Shengshan Gan | QHU2022231, QHU2021146 |
| 12 | M. epitea | Salix sinica | Jiangxi Forest Farm (98°46′42″ E, 36°37′29″ N) | Qi Xu; Hailan LI | QHU2022201 |
| Salix sinica | Jiangxi Forest Farm (98°46′42″ E, 36°37′30″ N) | Hezhua Xiji; Shengshan Gan | QHU2022226 | ||
| Salix sinica | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°21′38″ E, 32°12′07″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022242, QHU2021021 | ||
| Salix sinica | Dongzhong Forest Farm (96°29′33″ E, 31°49′12″ N) | Qi Xu; Zihan Tan | QHU2023064 | ||
| Salix paraplesia | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°09′38″ E, 35°27′05″ N) | Qinen He; Taijun Fang | QHU2022013, QHU2021037 | ||
| Salix paraplesia | Xihe Forest Farm (101°24′10″ E, 36°01′57″ N) | Qi Xu; Xiaoning Mao | QHU2023108 | ||
| Salix oritrepha | Lebagou Forestry Farm (97°20′16″ E, 32°13′02″ N) | Fengying He | QHU2022243 | ||
| Salix oritrepha | Yangyu Forest Farm (100°16′13″ E, 34°26′35″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021005, QHU2021016, QHU2021020 | ||
| Salix oritrepha | Yangyu Forest Farm (100°16′13″ E, 34°26′35″ N) | Qi Xu; Zihan Tan | QHU2023112, QHU2023113 | ||
| Salix oritrepha | Makehe Forest Farm (101°49′27″ E, 32°46′05″ N) | Qi Xu; Zihan Tan | QHU2023087 | ||
| 13 | M. kusanoi | Hypericum przewalskii | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°22′08″ E, 35°25′17″ N) | Haixia Mu | QHU2022123, QHU2022194 |
| 14 | M. laricis-populina | Populus cathayana | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°19′28″ E, 35°23′57″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022141, QHU2021038 |
| Populus cathayana | Jiangla Forest Farm (101°30′22″ E, 35°52′33″ N) | Qi Xu; Xiaoning Mao | QHU2023100, QHU2023107 | ||
| 15 | M. salicis-albae | Salix matsudana | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°29′18″ E, 35°37′07″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022200, QHU2021143, QHU2021141 |
| 16 | M. stellerae | Stellera chamaejasme | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°14′02″ E, 32°27′49″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022205 |
| Stellera chamaejasme | Dongzhong Forest Farm (97°27′21″ E, 32°40′20″ N) | Qi Xu; Yuying Li | QHU2023062 | ||
| Stellera chamaejasme | Makehe Forest Farm (100°52′04″ E, 32°49′19″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021014 | ||
| 17 | Miyagia anaphalidis | Anaphalis lactea | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°27′59″ E, 35°35′42″ N) | Qi Xu; Hailan LI | QHU2022136, QHU2022164 |
| Anaphalis flavescens | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°17′28″ E, 35°35′05″ N) | Qi Xu; Shengshan Gan | QHU2022158, QHU2021118, QHU2021119, QHU2021120, QHU2021121, QHU2021112 | ||
| 18 | Nyssopsora asiatica | Eleutherococcus wilsonii | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°09′47″ E, 32°29′38″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022221, QHU2021132 |
| 19 | Ochropsora ariae | Anemone rivularis var. flore-minore | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′34″ E, 35°16′19″ N) | Qi Xu; Shengshan Gan | QHU2022146 |
| Anemone rivularis var. flore-minore | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°55′45″ E, 32°15′36″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022206 | ||
| Anemone rivularis var. flore-minore | Dongzhong Forest Farm (97°27′19″ E, 32°40′19″ N) | Qi Xu; Yuying Li | QHU2023055 | ||
| Anemone rivularis var. flore-minore | Makehe Forest Farm (100°52′04″ E, 32°49′19″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021032, QHU2021078 | ||
| 20 | Phragmidium andersoni | Dasiphora fruticosa | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°55′18″ E, 35°53′35″ N) | Qinen He; Hezhua Xiji | QHU2023105, QHU2021136, QHU2021130 |
| 21 | P. potentillae | Potentilla saundersiana | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°56′18″ E, 35°25′51″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022019 |
| Potentilla saundersiana | Makehe Forest Farm (100°52′12″ E, 32°49′33″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021054 | ||
| Potentilla multifida | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°09′27″ E, 35°26′53″ N) | Taijun Fang; Hailan LI | QHU2022037 | ||
| Potentilla multifida | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°14′47″ E, 32°27′15″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022202, QHU2022229 | ||
| 22 | P. rubi-idaei | Rubus sachalinensis | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°26′16″ E, 35°26′52″ N) | Qinen He; Taijun Fang | QHU2022151 |
| Rubus sachalinensis | Makehe Forest Farm (100°52′09″ E, 32°49′30″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2023084 | ||
| Rubus sachalinensis | Xihe Forest Farm (101°34′34″ E, 36°15′26″ N) | Qi Xu; Xiaoning Mao | QHU2023102 | ||
| 23 | P. tuberculatum | Rosa omeiensis | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°22′46″ E, 35°24′46″ N) | Qinen He; Taijun Fang | QHU2022012, QHU2022036 |
| Rosa omeiensis | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°43′44″ E, 36°29′41″ N) | Qi Xu; Shengshan Gan | QHU2022144, QHU2022170 | ||
| Rosa omeiensis | Makehe Forest Farm (100°52′15″ E, 32°49′29″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021026 | ||
| Rosa giraldii | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°03′13″ E, 35°24′06″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022024, QHU2022001, QHU2022066, QHU2022094 | ||
| Rosa sp. | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°52′20″ E, 35°21′14″ N) | Qi Xu; Hezhua Xiji | QHU2022157 | ||
| Rosa sp. | Yangyu Forest Farm (100°16′11″ E, 34°27′21″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021010 | ||
| Rosa sp. | Makehe Forest Farm (100°49′28″ E, 32°46′06″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2023079 | ||
| Rosa sp. | Makehe Forest Farm (100°49′28″ E, 32°46′05″ N) | Qi Xu; Liming Zhang | QHU2023081 | ||
| Rosa sp. | Makehe Forest Farm (100°57′32″ E, 32°40′55″ N) | Qi Xu; Zihan Tan | QHU2023089 | ||
| Rosa sp. | Xihe Forest Farm (101°34′32″ E, 36°15′30″ N) | Qi Xu; Xiaoning Mao | QHU2023099 | ||
| 24 | Puccinia atragenes | Clematis rehderiana | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°54′33″ E, 32°16′29″ N) | Haixia Mu; Hezhua Xiji | QHU2022208, QHU2021090, QHU2021087, QHU2021091 |
| 25 | P. bistortae | Bistorta vivipara | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°50′31″ E, 35°26′25″ N) | Qi Xu; Shengshan Gan | QHU2023070 |
| Bistorta vivipara | Dongzhong Forest Farm (96°29′34″ E, 31°49′12″ N) | Qi Xu; Yuying Li | QHU2023046 | ||
| Bistorta vivipara | Makehe Forest Farm (100°44′28″ E, 32°56′03″ N) | Qi Xu; Zihan Tan | QHU2022238 | ||
| Bistorta vivipara | Yangyu Forest Farm (100°33′36″ E, 34°32′57″ N) | Qi Xu; Yuying Li | QHU2022207 | ||
| 26 | P. calumnata | Koenigia divaricata | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°16′26″ E, 32°55′21″ N) | Taijun Fang | QHU2022232 |
| Koenigia divaricata | Dongzhong Forest Farm (97°27′19″ E, 32°40′24″ N) | Qi Xu; Yuying Li | QHU2023063 | ||
| 27 | P. caricina | Urtica triangularis | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°12′50″ E, 32°54′44″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022007, QHU2022067, QHU2022241, QHU2021099 |
| Ribes himalense | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′35″ E, 35°16′19″ N) | Qi Xu; Shengshan Gan | QHU2022010, QHU2022152 | ||
| Ribes stenocarpum | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′36″ E, 35°16′19″ N) | Qi Xu; Wenbo Leng | QHU2022011 | ||
| Ribes stenocarpum | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°52′39″ E, 35°15′50″ N) | Haixia Mu; Hezhua Xiji | QHU2022153 | ||
| Ribes sp. | Makehe Forest Farm (100°49′26″ E, 32°45′11″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022010, QHU2022135, QHU2022152, QHU2021004 | ||
| 28 | P. chaerophylli | Anthriscus sylvestris | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°27′11″ E, 32°15′18″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022228, QHU2021113, QHU2021114, QHU2021107, QHU2021115, QHU2021109 |
| 29 | P. circaeae | Circaea alpina | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°27′08″ E, 32°15′28″ N) | Taijun Fang; Shengshan Gan | QHU2022218, QHU2022220 |
| Circaea alpina | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°32′26″ E, 31°50′07″ N) | Qi Xu; Yuying Li | QHU2023117 | ||
| 30 | P. cnici-oleracei | Saussurea sp. | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°52′11″ E, 35°24′17″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022060, QHU2022062, QHU2022106, QHU2022143 |
| 31 | P. coronata var. coronata | Clematis sp. | Dongzhong Forest Farm (97°27′19″ E, 32°40′24″ N) | Qi Xu; Zihan Tan | QHU2022059, QHU2023068 |
| 32 | P. dioicae | Asteraceae | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°52′13″ E, 35°14′59″ N) | Qi Xu; Fengying He | QHU2022022, QHU2022038, QHU2022040 |
| 33 | P. festucae | Lonicera sp. | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′35″ E, 35°16′21″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022009, QHU2022023, QHU2022029, QHU2022032 |
| Lonicera sp. | Dongshan Forest Farm (101°36′57″ E, 36°13′50″ N) | Qi Xu; Xiaoning Mao | QHU2023011 | ||
| Lonicera sp. | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°16′31″ E, 32°55′22″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021025 | ||
| Lonicera hispida | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°54′53″ E, 32°16′40″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022209 | ||
| Lonicera hispida | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°16′33″ E, 32°55′18″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022234, QHU2023020 | ||
| Lonicera hispida | Dongzhong Forest Farm (96°30′59″ E, 31°48′42″ N) | Qi Xu; Zihan Tan | QHU2023058 | ||
| Lonicera hispida | Makehe Forest Farm (100°52′03″ E, 32°49′30″ N) | Qi Xu; Zihan Tan | QHU2023018, QHU2022134 | ||
| Lonicera tangutica | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′36″ E, 35°16′09″ N) | Qi Xu; Fengying He | QHU2022009, QHU2022023 | ||
| 34 | P. gentianae | Gentiana straminea | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°20′18″ E, 32°13′08″ N) | Qi Xu; Taijun Fang | QHU2022233, QHU2021102, QHU2021100, QHU2021104 |
| 35 | P. graminis | Berberis dasystachya | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′31″ E, 35°16′21″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022008, QHU2022031, QHU2022070, QHU2022110, 2021097 |
| Berberis poiretii | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′36″ E, 35°15′20″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022026, QHU2022077, QHU2022188, QHU2022017 | ||
| Berberis diaphana | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′41″ E, 35°15′22″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022169 | ||
| Berberis diaphana | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°54′36″ E, 32°17′38″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022230, QHU2022239 | ||
| Berberis vulgaris | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′41″ E, 35°15′26″ N) | Qi Xu; Wenbo Leng | QHU2022168 | ||
| Berberis vulgaris | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°55′33″ E, 32°47′04″ N) | Qi Xu; Fengying He | QHU2022213 | ||
| Berberis vulgaris | Makehe Forest Farm (100°49′27″ E, 32°46′07″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021098, QHU2021101, QHU2021103 | ||
| 36 | P. haleniae | Halenia elliptica | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°54′ 55″ E, 32°16′39″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2023123, QHU2021095 |
| 37 | P. helianthi | Helianthus annuus | Jiangla Forest Farm (101°30′27″ E, 35°51′55″ N) | Qi Xu; Xiaoning Mao | QHU2023095, QHU2021094, QHU2021086 |
| 38 | P. heraclei-nepalensis | Heracleum candicans | Dongzhong Forest Farm (96°32′31″ E, 31°50′12″ N) | Qinen He; Liming Zhang | QHU2023053 |
| Heracleum candicans | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°12′12″ E, 32°54′46″ N) | Qinen He; Taijun Fang | QHU2021019 | ||
| 39 | P. magnusiana | Phragmites australis | Xihe Forest Farm (101°24′07″ E, 36°01′53″ N) | Qi Xu; Xiaoning Mao | QHU2023098, QHU2021083, QHU2021070 |
| 40 | P. polygoni-cyanandri | Koenigia cyanandra | Makehe Forest Farm (100°52′07″ E, 32°49′31″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2023082, QHU2023001, QHU2021080, QHU2021081 |
| 41 | P. ribis | Ribes glaciale | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°15′28″ E, 32°27′53″ N) | Qi Xu; Fengying He | QHU2022224, QHU2023116, QHU2021110, QHU2021111 |
| 42 | P. recondita | Aquilegia viridiflora | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°52′17″ E, 35°21′06″ N) | Qi Xu; Shengshan Gan | QHU2022160, QHU2021085, QHU2021096, QHU2021092 |
| Thalictrum alpinum | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°52′22″ E, 35°21′13″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022199 | ||
| Thalictrum alpinum | Makehe Forest Farm (100°51′13″ E, 32°49′10″ N) | Qinen He; Taijun Fang | QHU2021051 | ||
| Thalictrum aquilegiifolium var. sibiricum | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′37″ E, 35°16′08″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022016, QHU2022167, QHU2022210 | ||
| Thalictrum aquilegiifolium var. sibiricum | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°54′12″ E, 32°16′33″ N) | Qi Xu; Shengshan Gan | QHU2022225, QHU2023067, QHU2021027 | ||
| Thalictrum aquilegiifolium var. sibiricum | Dongzhong Forest Farm (96°32′27″ E, 31°50′07″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021082 | ||
| Thalictrum aquilegiifolium var. sibiricum | Makehe Forest Farm (100°51′33″ E, 32°49′19″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021060, QHU2021089, QHU2021070 | ||
| Agropyron cristatum | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°54′19″ E, 32°16′59″ N) | Qi Xu; Fengying He | QHU2022222 | ||
| Agropyron cristatum | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°12′16″ E, 32°54′44″ N) | Haixia Mu; Hezhua Xiji | QHU2022240 | ||
| Agropyron cristatum | Dongzhong Forest Farm (96°32′25″ E, 31°50′06″ N) | Qi Xu; Yuying Li | QHU2023054 | ||
| Agropyron cristatum | Makehe Forest Farm (100°52′10″ E, 32°49′29″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022183, QHU2022212, QHU2023074 | ||
| Agropyron cristatum | Yangyu Forest Farm (100°16′12″ E, 34°27′19″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2023021, QHU20210093 | ||
| 43 | P. rhei-palmati | Rheum tanguticum | Makehe Forest Farm (100°52′10″ E, 32°49′27″ N) | Qi Xu; Liming Zhang | QHU2023086, QHU2021088, QHU2021084 |
| 44 | P. rubiae-tataricae | Rubia cordifolia | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°50′29″ E, 35°26′31″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022112, QHU2022119 |
| Rubia cordifolia | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°14′11″ E, 32°27′12″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022211 | ||
| 45 | P. rupestris | Saussurea sp. | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°52′11″ E, 35°24′17″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2022041, QHU2021170 |
| 46 | P. sorghi | Zea mays | Jiangla Forest Farm (101°30′21″ E, 35°51′21″ N) | Qi Xu; Xiaoning Mao | QHU2023096, QHU2023097 |
| 47 | P. striiformis | Berberis circumserrata | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′30″ E, 35°16′21″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022018, QHU2022028 |
| Berberis circumserrata | Makehe Forest Farm (100°49′27″ E, 32°46′16″ N) | Qinen He; Hailan LI | QHU2022097 | ||
| Leymus secalinus | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°54′53″ E, 32°16′40″ N) | Qi Xu; Fengying He | QHU2022204, QHU2021023 | ||
| Leymus secalinus | Makehe Forest Farm (100°49′26″ E, 32°45′07″ N) | Qi Xu | QHU2021008 | ||
| 48 | P. stipina | Dracocephalum heterophyllum | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°08′28″ E, 35°27′26″ N) | Qi Xu; Taijun Fang | QHU2022130, QHU202110105, QHU2021106, QHU2021112, QHU2021108 |
| 49 | Puccinia sp. | Ligularia przewalskii | Makehe Forest Farm (100°57′33″ E, 32°40′54″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022139, QHU2023090, QHU2021116 |
| 50 | Puccinia sp. | Rheum pumilum | Yangyu Forest Farm (100°33′37″ E, 34°32′56″ N) | Qi Xu; Hailan LI | QHU2023094, QHU2021055 |
| 51 | P. vomica | Saussurea epilobioides | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°54′37″ E, 35°16′21″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022143, QHU2022148, QHU2022155, QHU2022158 |
| Saussurea epilobioides | Makehe Forest Farm (100°52′08″ E, 32°49′29″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022159, QHU2022164, QHU2023077 | ||
| 52 | P. vivipari | Bistorta vivipara | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°23′14″ E, 32°22′45″ N) | Qi Xu; Shengshan Gan | QHU2021029 |
| Bistorta vivipara | Jiangxi Forest Farm (96°14′02″ E, 32°27′18″ N) | Qi Xu; Fengying He | QHU2023091 | ||
| Bistorta vivipara | Makehe Forest Farm (100°49′31″ E, 32°45′16″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2023071 | ||
| 53 | Uromyces hedysari-obscuri | Hedysarum sikkimense | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°22′46″ E, 32°13′42″ N) | Qi Xu; Fengying He | QHU2022235, QHU2022236 |
| Hedysarum polybotrys var. alaschanicum | Yangyu Forest Farm (100°33′37″ E, 34°32′52″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021003 | ||
| Hedysarum polybotrys var. alaschanicum | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°22′45″ E, 32°13′39″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2023120 | ||
| Astragalus sp. | Dongzhong Forest Farm (97°27′19″ E, 32°40′24″ N) | Qi Xu; Yuying Li | QHU2023057 | ||
| Astragalus sp. | Lebagou Forest Farm (97°22′36″ E, 32°13′47″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2021024, QHU2021022 | ||
| 54 | U. lapponicus | Astragalus sp. | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°26′19″ E, 35°26′52″ N) | Qi Xu; Qinen He | QHU2022150, QHU2022249, QHU2022250, QHU2021113, QHU2021114 |
| Oxytropis sp. | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°10′31″ E, 35°26′25″ N) | Shengshan Gan; Haixia Mu | QHU2022080, QHU2022251, QHU2021115, QHU2021117 | ||
| 55 | U. lycoctoni | Aconitum sinomontanum | Jiangla Forest Farm (101°36′57″ E, 36°13′50″ N) | Qi Xu; Xiaoning Mao | QHU2023003, QHU2023104 |
| 56 | Uredo rhododendri-capitati | Rhododendron capitatum | Maixiu Forest Farm (101°57′08″ E, 35°54′35″ N) | Qi Xu; Hailan LI | QHU2022003, QHU2021142, QHU2021145, QHU2021147 |
References
- Aime, M.C.; Bell, C.D.; Wilson, A.W. Deconstructing the evolutionary complexity between rust fungi (Pucciniales) and their plant hosts. Stud. Mycol. 2018, 89, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, P.M.; Cannon, P.F.; Minter, D.W.; Stalpers, J.A. Dictionary of the Fungi, 10th ed.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2008; pp. 1–784. [Google Scholar]
- Cummins, G.B.; Hiratsuka, Y. Illustrated Genera of Rust Fungi, 3rd ed.; American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Di, S.L. Risk Analysis Report of Two-Needle Pine Blister Rust Pathogen. Shanxi For. Sci. Technol. 2020, 49, 36–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.; Tang, L.; Cheng, X.Q.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Tang, M.Y.; Huang, S.H.; Jiang, M.G. Progress and Prospects of Mulberry Rust Research. Guangxi Seric. 2022, 59, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Occurrence and Control Measures of Yang Leaf Rust Disease. Hortic. Seed 2018, 6, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.M. Classification evolution and progress of rust fungi. J. Northwest For. Univ. 2000, 2, 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.G. Fungi of Jilin Province (Vol.1 Basidiomycota); Northeast Normal University Press: Changchun, China, 1991; pp. 1–528. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.X. Investigation of Rust Flora in Jilin Province and Study on Life History of Six Rust Fungi. Master’s Thesis, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, J.X. Study on Taxonomy and Life Cycle of Unclear Rust Fungi in Jilin Province. Ph.D. Thesis, Jilin Agricultural University, Changchun, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Han, S.J.; Wei, S.X.; Cheng, M.M.; Ma, Q.M.; Guo, L.; Cheng, G.Q.; Xu, L.W.; Tang, G.R.; Zhang, X.Q.; et al. Tibetan Fungi; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1983; pp. 31–61. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Z.M. Study on Virulence Variation and Population Genetic Diversity of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. hordei and P. striiformis f. sp. tritici in Tibet. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J.Y. Aprovisional list of Uredinales of Fujian province, China. Acta Mycol. Sin. 1983, 2, 146–158. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J.Y. Rust fungi in Wuyi Mountain, Fujian. J. Mycol. 1983, 2, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L. Shennongjia Fungi and Lichens; World Book Publishing Company: Beijing, China, 1989; pp. 107–156. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.X.; Zhuang, J.Y. Fungi in Xiaowutai Mountain, Hebei; China Agricultural Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 103–133. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.X.; Zhuang, J.Y. Qinling Fungi; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1997; pp. 24–83. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.M.; Li, Z.Q. Rust fungi of Qinling Mountains; China Forestry Publishing House Co., Ltd.: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 1–188. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.M.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhuang, J.Y. Uredinales from the Qinling Mountains (Continued I). Mycosystema 2000, 9, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, M.H.; Lv, Z.H.; Zheng, M.Y.; Huang, Q.N.; Wu, W.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J. Genetic Structure Analysis of Wheat Stripe Rust Pathogen Populations in the Ili Region of Xinjiang. J. Triticeae Crops 2024, 44, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L. Construction of Selfed Progeny and Inheritance of Xinjiang Isolate BGTB-1 of Puccinia striiformis f. sp. Tritici. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, J.Y. Rust fungi from the Altai. J. Anhui Agric. Univ. 1999, 6, 261–265. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, L.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Bai, J.K.; Lv, X.X.; Fan, Z.T. Research on the classification of rust fungi in the Asteraceae family in Xinjiang. J. August First Agric. Coll. 1991, 3, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.T. Investigation and Identification of Rust Fungi in Southern Gansu. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.Z. Rust Fungi of Inner Mongolia; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 1–393. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.P.; Ye, H.; Wang, J.B.; Zhan, X.L.; Zuo, C.; Lu, G.X.; Zhang, F.W.; Li, Y.N. Change of surface albedo of alpine vegetation and its radiation temperature effect in Sanjiangyuan region of Qinghai Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 5630–5641. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C. Study on Stitability of Snow Leopard Habitat Based on Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation. Master’s Thesis, Shandong Agricultural University, Tai’an, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.Q. Ecological Planning in Ethnic Minority Areas-Sanjiangyuan Area System Protection Planning Research; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Halling, R.E. A synopsis of Marasmius section Globulares (Tricholomataceae) in the United States. Brittonia 1983, 35, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.J.; Zhou, Z.K.; Li, D.Z.; Peng, H.; Sun, H. The distribution type system of seed plants in the world. Acta Bot. Yunnan 2003, 25, 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.Y.; Wang, H.F.; Zhang, J.W. A comparative study on the flora of Maoershan National Forest Park before and after 30 years. Acta Bot. Boreali Occident. Sin. 2017, 37, 2290–2299. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.H. Several vegetation analysis methods are introduced. J. North-East. For. Inst. 1982, 1, 142–159. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).