Biodiversity, Distribution and Functional Differences of Fungi in Four Species of Corals from the South China Sea, Elucidated by High-Throughput Sequencing Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
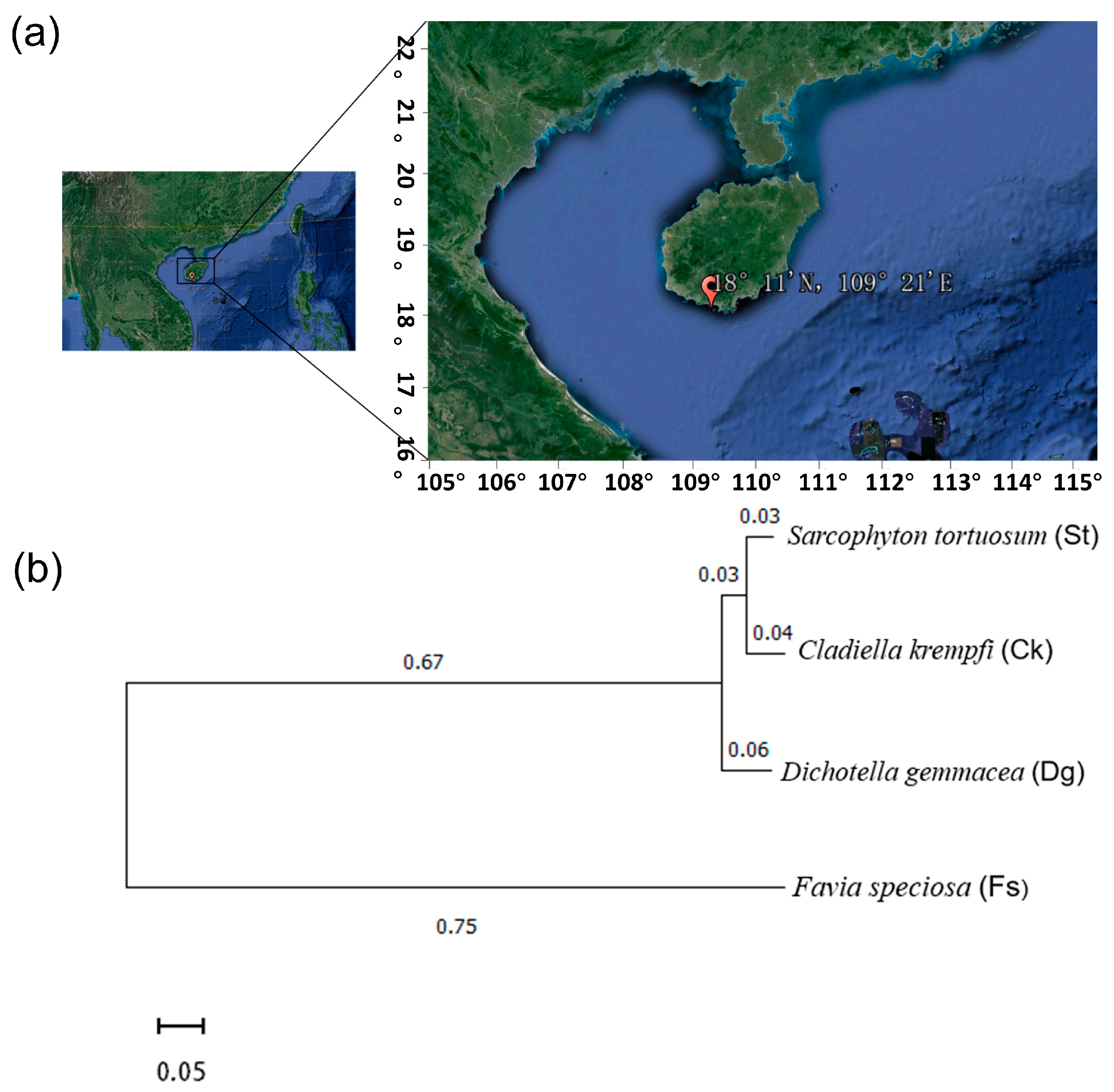
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.3. Sequence Analysis
2.4. Diversity Analysis
2.5. Taxonomic and Functional Classification
2.6. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Number
3. Results
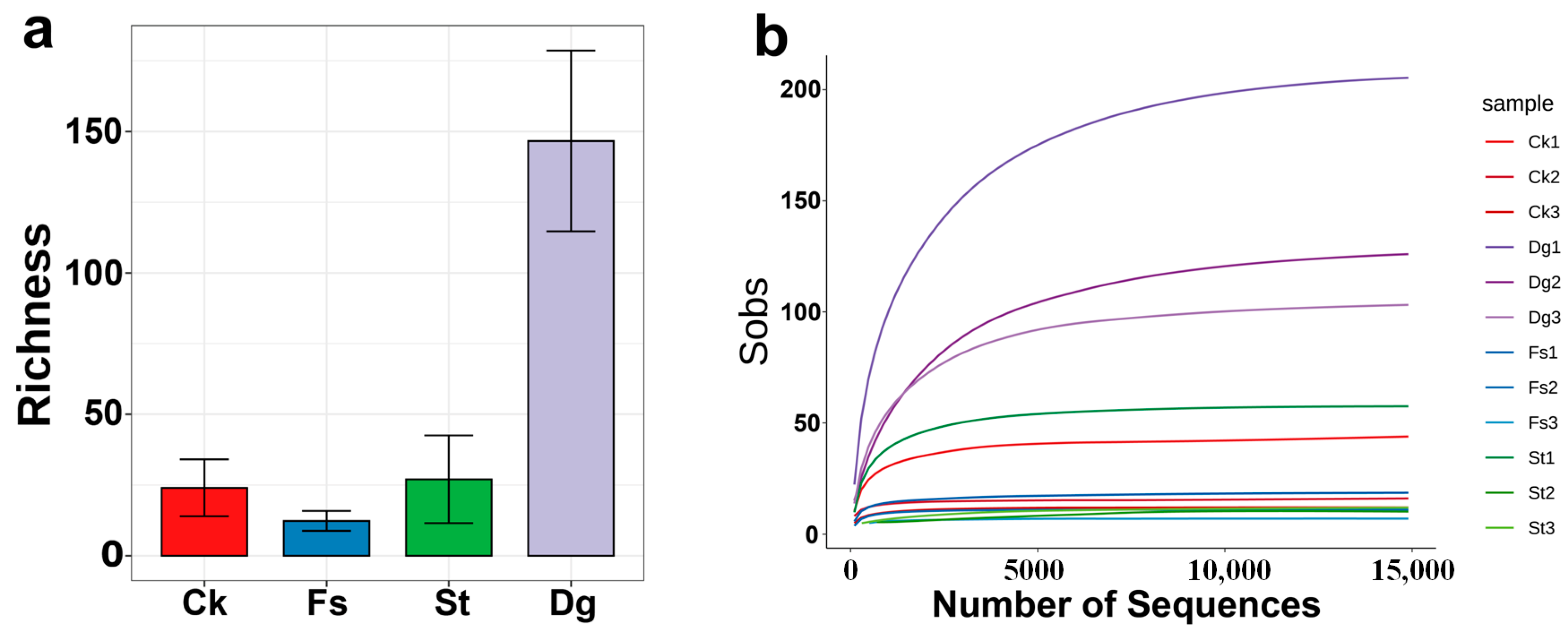
3.1. High-Throughput Sequencing and Sequence Analysis
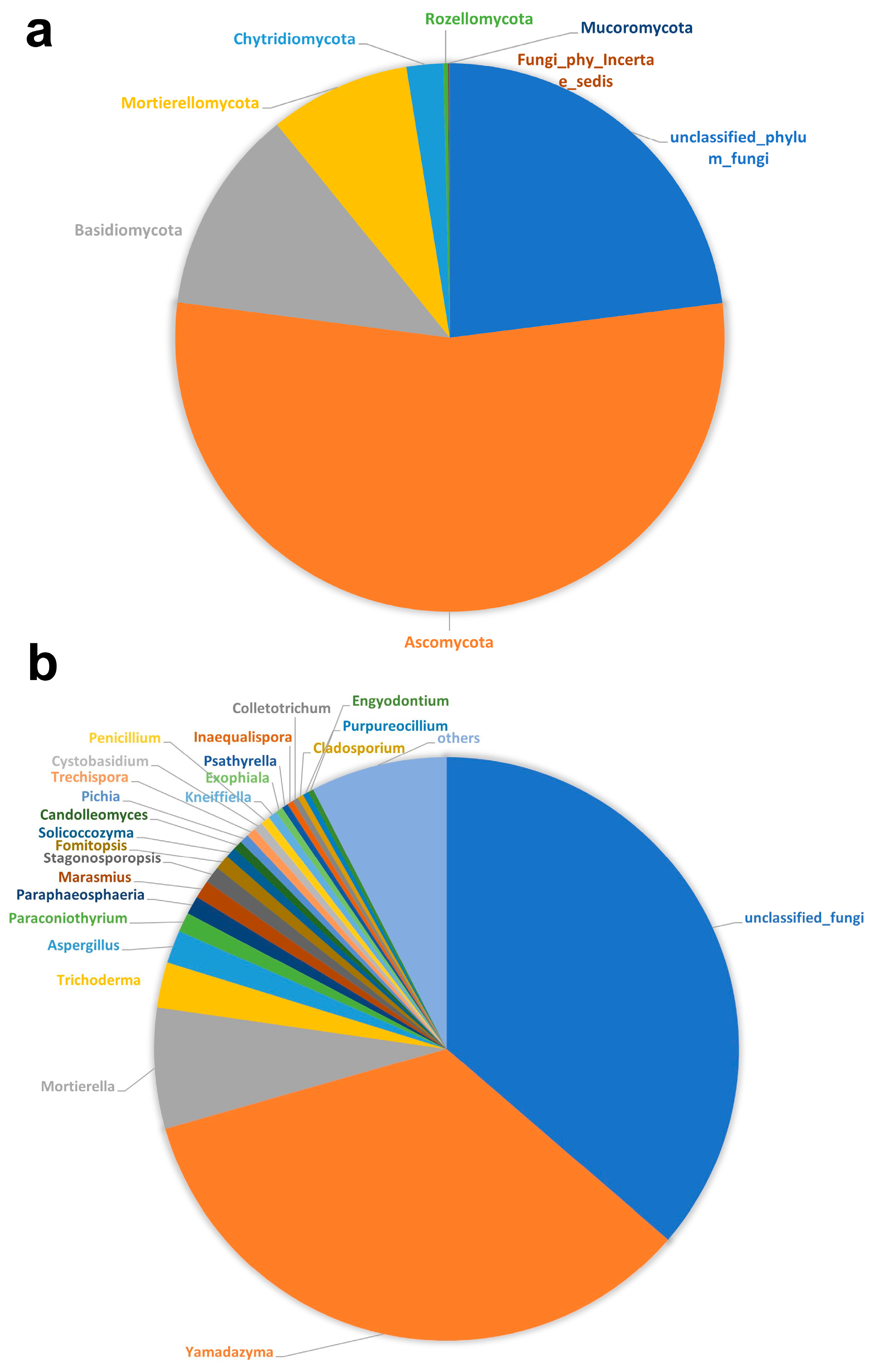
3.2. Fungal Diversity and Composition
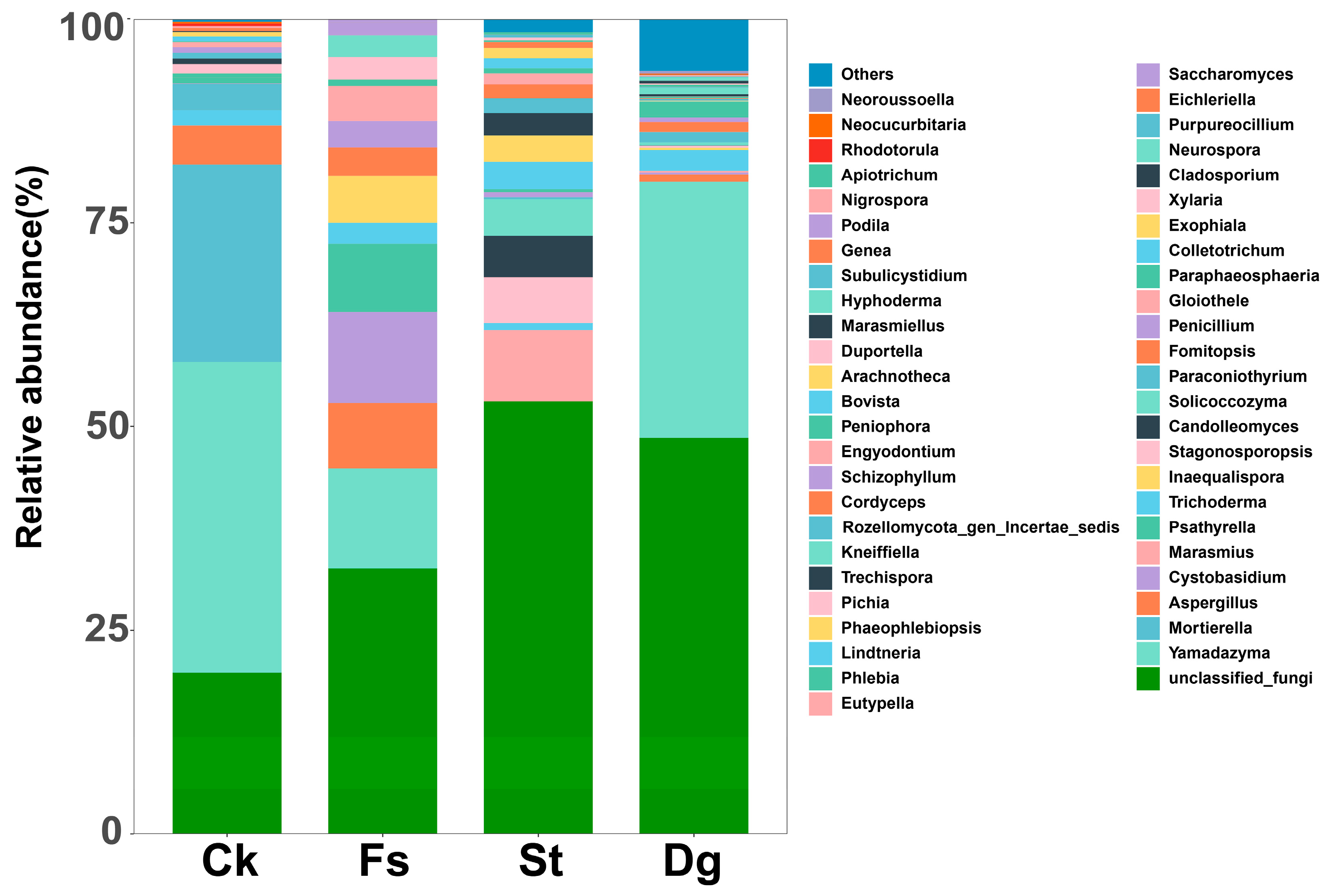
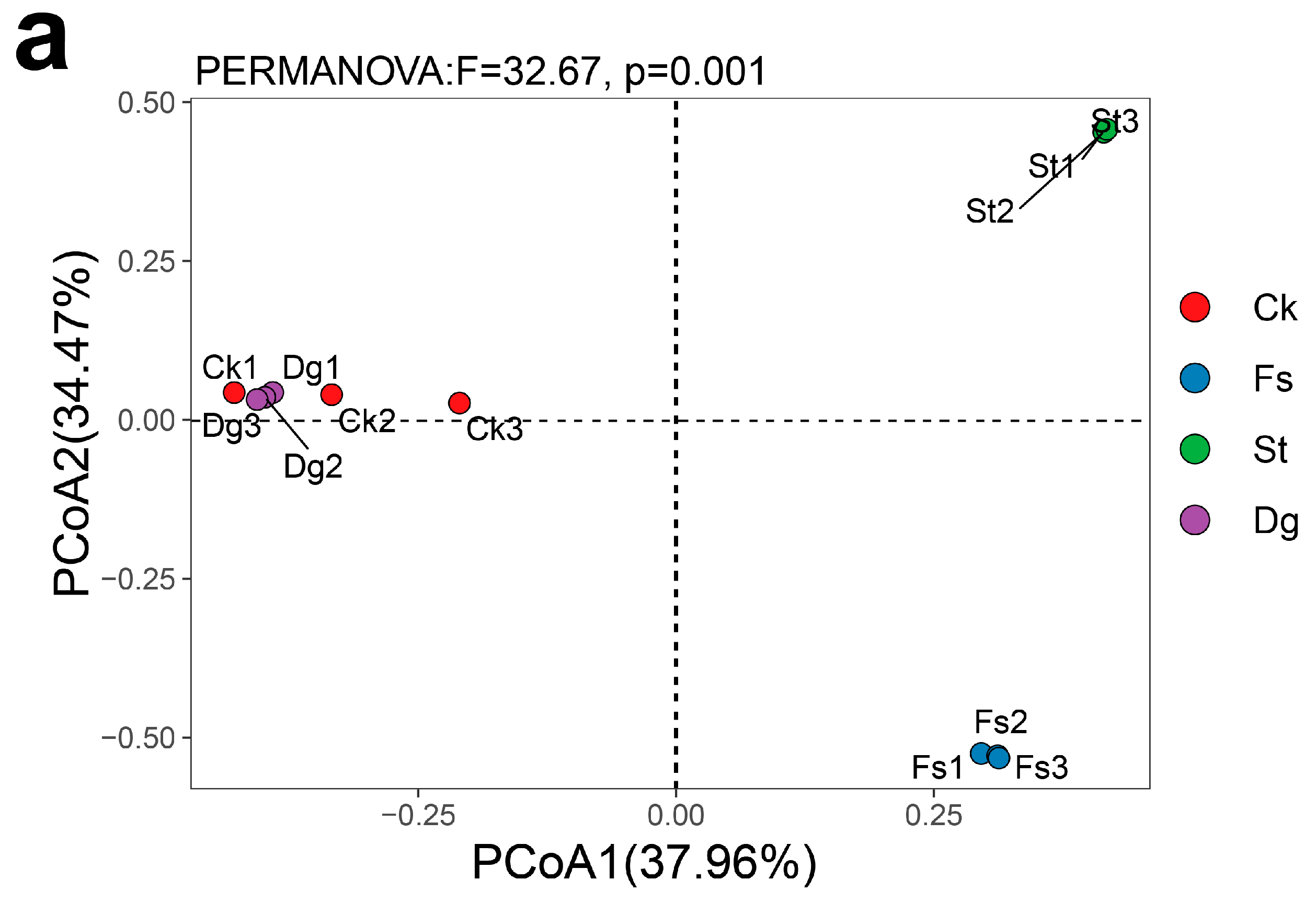
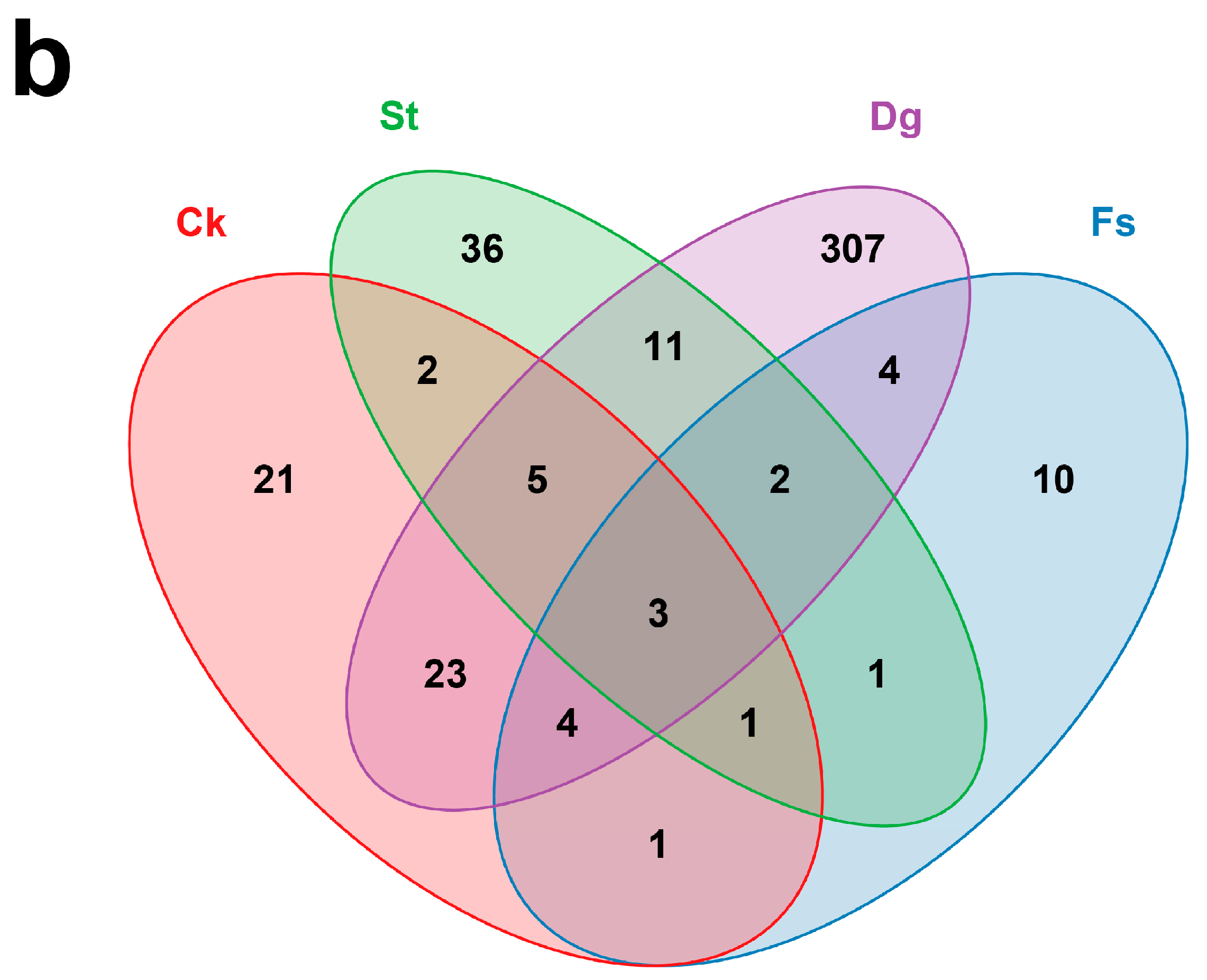
3.3. Comparison of Fungal Communities in Different Species of Corals
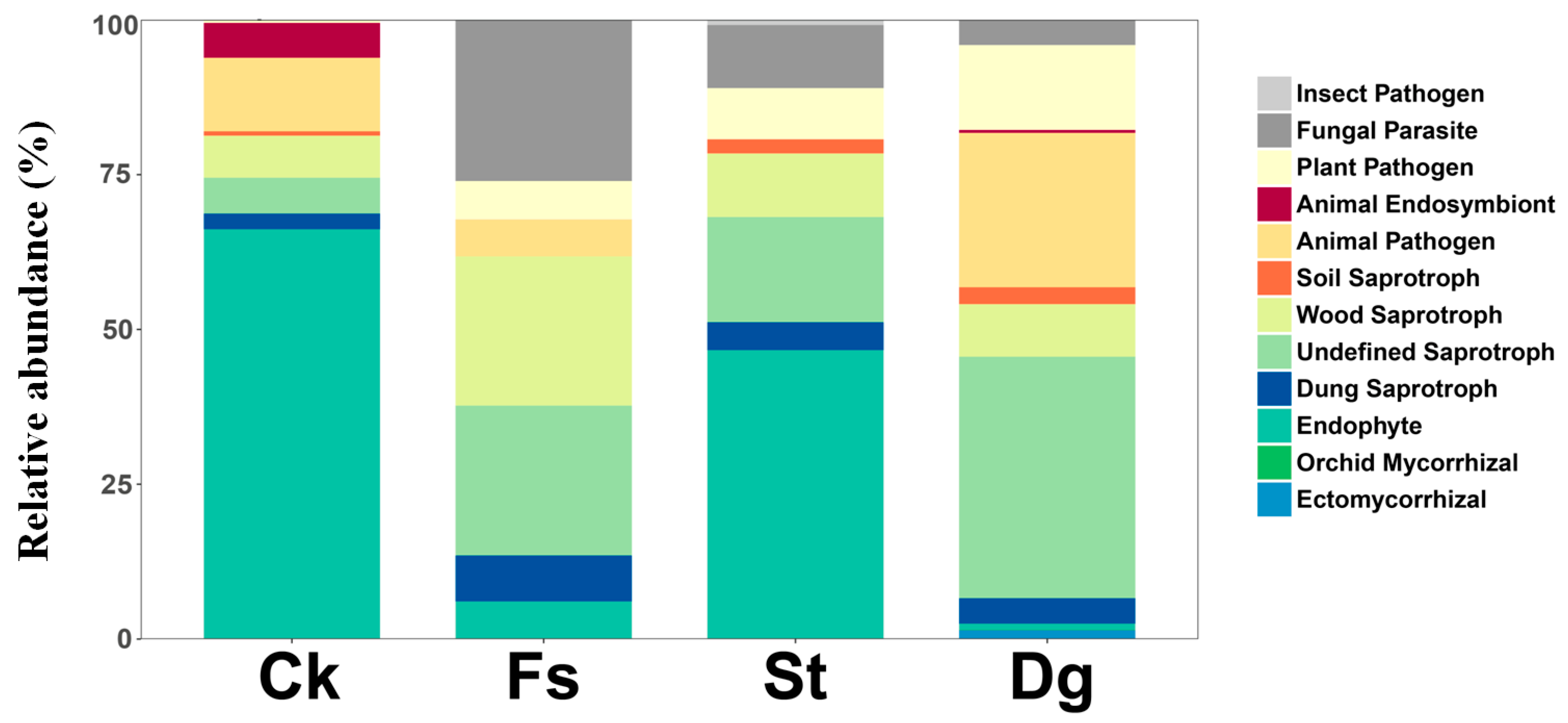
3.4. Prediction of Fungal Functional Groups
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harrison, P.L.; Booth, D.J. Coral reefs: Naturally dynamic and increasingly disturbed ecosystems. In Marine Ecology; Connell, S.D., Gillanders, B.M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 316–377. [Google Scholar]
- Earp, H.S.; Prinz, N.; Cziesielski, M.J.; Andskog, M. For a world without boundaries: Connectivity between marine tropical ecosystems in times of change. In YOUMARES 8–Oceans Across Boundaries: Learning from each other: Proceedings of the 2017 Conference for YOUng MARine RESearchers in Kiel, Germany; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 125–144. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.C.; Huang, R.M.; Bao, J.; Wu, K.Y.; Wu, H.Y.; Gao, X.Y.; Zhang, X. The unexpected diversity of microbial communities associated with black corals revealed by high-throughput Illumina sequencing. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 35, fny167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, D.G.; Garren, M.; Work, T.M.; Rosenberg, E.; Smith, G.W.; Harvell, C.D. Microbial disease and the coral holobiont. Trends Microbiol. 2009, 17, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, N.A.; Nash, K.L. The importance of structural complexity in coral reef ecosystems. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, J.; Xu, D.; Yang, Q.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, X. Diversity and antimicrobial activity of intestinal fungi from three species of coral reef fish. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, G.R.; Rizzari, J.R.; Abesamis, R.A.; Alcala, A.C. Coral cover a stronger driver of reef fish trophic biomass than fishing. Ecol. Appl. 2021, 31, e02224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.G.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.L.; Tian, P.; Niu, W.T. Recent deterioration of coral reefs in the South China Sea due to multiple disturbances. Peer J. 2022, 10, e13634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richmond, R.H. Coral reefs: Present problems and future concerns resulting from anthropogenic disturbance. Am. Zool. 1993, 33, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasl, B.; Webster, N.S.; Bourne, D.G. Microbial indicators as a diagnostic tool for assessing water quality and climate stress in coral reef ecosystems. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumby, P.J.; Steneck, R.S. Coral reef management and conservation in light of rapidly evolving ecological paradigms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glasl, B.; Bourne, D.G.; Frade, P.R.; Thomas, T.; Schaffelke, B.; Webster, N.S. Microbial indicators of environmental perturbations in coral reef ecosystems. Microbiome 2019, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Pang, X.; He, Y.; Lin, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, B. Secondary metabolites from coral-associated fungi: Source, chemistry and bioactivities. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modolon, F.; Barno, A.R.; Villela, H.D.M.; Peixoto, R.S. Ecological and biotechnological importance of secondary metabolites produced by coral-associated bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1441–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, R.S.; Rosado, P.M.; Leite, D.C.D.A.; Rosado, A.S.; Bourne, D.G. Beneficial microorganisms for corals (BMC): Proposed mechanisms for coral health and resilience. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 236713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krediet, C.J.; Ritchie, K.B.; Paul, V.J.; Teplitski, M. Coral-associated microorganisms and their roles in promoting coral health and thwarting diseases. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20122328. [Google Scholar]
- Van Oppen, M.J.; Medina, M. Coral evolutionary responses to microbial symbioses. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2020, 375, 20190591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Ospina, J.; Molina-Hernández, J.B.; Chaves-López, C.; Romanazzi, G.; Paparella, A. The role of fungi in the cocoa production chain and the challenge of climate change. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Anbuchezhian, R.; Li, Z. Association of coral-microbes, and the ecological roles of microbial symbionts in corals. In Medusa and Her Sisters: The Cnidaria, Past, Present and Future; Goffredo, S., Dubinsky, Z., Eds.; Springer Press: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 347–357. [Google Scholar]
- Putnam, H.M.; Barott, K.L.; Ainsworth, T.D.; Gates, R.D. The vulnerability and resilience of reef-building corals. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R528–R540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Zhang, F.L.; Feng, T. Sesquiterpenoids specially produced by fungi: Structures, biological activities, chemical and biosynthesis (2015–2020). J. Fungi 2021, 7, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amend, A.S.; Barshis, D.J.; Oliver, T.A. Coral-associated marine fungi form novel lineages and heterogeneous assemblages. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1291–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amend, A.; Burgaud, G.; Cunliffe, M.; Edgcomb, V.P.; Ettinger, C.L.; Gutiérrez, M.H.; Heitman, J.; Hom, E.F.Y.; Ianiri, G.; Jones, A.C.; et al. Fungi in the marine environment: Open questions and unsolved problems. MBio 2019, 10, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Bao, J.; Wang, G.H.; He, F.; Xu, X.Y.; Qi, S.H. Diversity and antimicrobial activity of culturable fungi isolated from six species of the South China Sea gorgonians. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 64, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.N.; Shao, C.L.; Zheng, C.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, C.Y. Diversity and antibacterial activities of fungi derived from the gorgonian Echinogorgia rebekka from the South China Sea. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Hao, H.L.; Lau, S.C.K.; Wang, H.Y.; Han, Y.; Dong, L.M.; Huang, R.M. Biodiversity and antifouling activity of fungi associated with two soft corals from the South China Sea. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, S.D. Diagnostic applications of high-throughput DNA sequencing. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2013, 8, 381–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClenny, N. Laboratory detection and identification of Aspergillus species by microscopic observation and culture: The traditional approach. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43 (Suppl. S1), S125–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galkiewicz, J.P.; Stellick, S.H.; Gray, M.A.; Kellogg, C.A. Cultured fungal associates from the deep-sea coral Lophelia pertusa. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2012, 67, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, A.J.; Purahong, W.; Wubet, T.; Hyde, K.D.; Zhang, W.; Xu, H.; Zhang, G.; Fu, C.; Liu, M.; Xing, Q.; et al. Direct comparison of culture-dependent and culture-independent molecular approaches reveal the diversity of fungal endophytic communi-ties in stems of grapevine (Vitis vinifera). Fungal Divers. 2018, 90, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, L.; DeForce, E.; Apprill, A. Optimization of DNA extraction for advancing coral microbiota investiga-tions. Microbiome 2017, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawardene, N.N.; Dai, D.Q.; Jayasinghe, P.K.; Gunasekara, S.S.; Nagano, Y.; Tribromo, S.; Suwannarach, N.; Boonyuen, N. Ecological and oceanographic perspectives in future marine fungal taxonomy. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Gastélum, L.; Chong-Robles, J.; Lago-Lestón, A.; Darcy, J.L.; Amend, A.S.; Riquelme, M. Targeted ITS1 sequencing unravels the mycodiversity of deep-sea sediments from the Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 4046–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.J.; Rygiewicz, P.T. Fungal-specific PCR primers developed for analysis of the ITS region of environmental DNA extracts. BMC Microbial. 2005, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bolen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; O’Hara, B.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Oksanen, M.J.; Suggests, M.A.S.S. The vegan package. Community Ecol. Package 2020, 10, 719. [Google Scholar]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Song, C.; Wu, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Li, J. GPR clutter removal based on weighted nuclear norm minimization for nonparallel cases. Sensors 2023, 23, 5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, N.E.; Ferry, M. ggtern: Ternary diagrams using ggplot2. J. Stat. Softw. 2018, 87, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.V.; Hoss, A.G.; Kolde, R.; van Aggelen, H.C.; Loving, J.; Smith, S.A.; Mack, D.A.; Kathirvel, R.; Halperin, J.A.; Buell, D.J.; et al. Integration of genomic and clinical data augments surveillance of healthcare-acquired infections. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2019, 40, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.H.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Jeppesen, T.S.; Schigel, D.; Kennedy, P.; Picard, K.; Glöckner, F.O.; Tedersoo, L.; et al. The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi: Handling dark taxa and parallel taxonomic classifications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D259–D264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarenkov, K.; Nilsson, R.H.; Larsson, K.H.; Alexander, I.J.; Eberhardt, U.; Erland, S.; Høiland, K.; Kjøller, R.; Larsson, E.; Pennanen, T.; et al. The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi–recent updates and future perspectives. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Song, Z.; Bates, S.T.; Branco, S.; Tedersoo, L.; Menke, J.; Schilling, J.S.; Kennedy, P.G. FUNGuild: An open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 20, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valderrama, B.; Ruiz, J.J.; Gutiérrez, M.S.; Alveal, K.; Caruffo, M.; Oliva, M.; Flores, H.; Silva, A.; Toro, M.; Reyes-Jara, A.; et al. Cultivable yeast microbiota from the marine fish species Genypterus chilensis and Seriolella violacea. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejesvi, M.V.; Turunen, J.; Salmi, S.; Reunanen, J.; Paalanne, N.; Tapiainen, T. Delivery mode and perinatal antibiotics influence the infant gut bacteriome and mycobiome: A network analysis. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertout, S.; Gouveia, T.; Krasteva, D.; Pierru, J.; Pottier, C.; Bellet, V.; Arianiello, E.; Salipante, F.; Roger, F.; Drakulovski, P. Search for cryptococcus neoformans/gattii complexes and related genera (Filobasidium, Holtermanniella, Naganishia, Papiliotrema, Solicoccozyma, Vishniacozyma) spp. Biotope: Two years surveillance of wild avian fauna in southern France. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.L.; Lin, J.Y.; Li, G.M.; Yang, Z.L. Mushrooms adapted to seawater: Two new species of Candolleomyces (Basidiomycota, Agaricales) from China. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thitla, T.; Kumla, J.; Khuna, S.; Lumyong, S.; Suwannarach, N. Species diversity, distribution, and phylogeny of Exophiala with the addition of four new species from Thailand. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.L.; Feng, T. Diterpenes specially produced by fungi: Structures, biological activities, and biosynthesis (2010–2020). J. Fungi 2022, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Xing, Y.; Liu, G.; Hu, C.; Wang, X.; Yan, G.; Wang, Q. Changes in soil bacterial and fungal community composition and functional groups during the succession of boreal forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 161, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicek, C.P.; Steindorff, A.S.; Chenthamara, K.; Manganiello, G.; Henrissat, B.; Zhang, J.; Cai, F.; Kopchinskiy, A.G.; Kubicek, E.M.; Kuo, A.; et al. Evolution and comparative genomics of the most common Trichoderma species. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozimek, E.; Hanaka, A. Mortierella species as the plant growth-promoting fungi present in the agricultural soils. Agriculture 2020, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, A.; Schmoll, M. Biology and biotechnology of Trichoderma. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, E.; Dunn-Coleman, N.; Frisvad, J.C.; Van Dijck, P.W. On the safety of Aspergillus niger–A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 59, 426–435. [Google Scholar]
- Nardo, V.G.; Otero, I.V.; Giovanella, P.; SANTOS, J.A.D.; Pellizzer, E.P.; Dovigo, D.R.; Paes, E.C.; Sette, L.D. Biobank of fungi from marine and terrestrial Antarctic environments. An. Acad. Bras. Ciências 2023, 95, e20230603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Kim, W.; Wang, Y.W.; Yakubovich, E.; Dong, C.; Trail, F.; Townsend, J.P.; Yarden, O. The Sordariomycetes: An expanding resource with Big Data for mining in evolutionary genomics and transcriptomics. Front. Fungal Biol. 2023, 4, 1214537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Dong, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhang, K.; Shi, X.; Yang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, D.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; et al. Maize/peanut intercrop** improves nutrient uptake of side-row maize and system microbial community diversity. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, N.S.; Doni, F.; Mispan, M.S.; Saiman, M.Z.; Yusuf, Y.M.; Oke, M.A.; Suhaimi, N.S.M. Harnessing Trichoderma in agriculture for productivity and sustainability. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.N.; Monteiro, V.N.; Steindorff, A.S.; Gomes, E.V.; Noronha, E.F.; Ulhoa, C.J. Trichoderma/pathogen/plant interaction in pre-harvest food security. Fungal Biol. 2019, 123, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mašínová, T.; Yurkov, A.; Baldrian, P. Forest soil yeasts: Decomposition potential and the utilization of carbon sources. Fungal Ecol. 2018, 34, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, X.; Wu, W.; Hou, J.; Zhang, W.; Tang, D.K.H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Y.; et al. Biotic and abiotic effects of manganese salt and apple branch biochar co-application on humification in the co-composting of hog manure and sawdust. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 149077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gutiérrez, K.N.; Ragazzo-Sánchez, J.A.; Barros-Castillo, J.C.; Narváez-Zapata, J.A.; Calderón-Santoyo, M. Yeasts with potential biocontrol of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in avocado (Persea americana Mill. cv. Hass) and characterization of Yamadazyma mexicana mechanisms. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2023, 165, 525–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgaud, G.; Coton, M.; Jacques, N.; Debaets, S.; Maciel, N.O.P.; Rosa, C.A.; Gadanho, M.; Sampaio, J.P.; Casaregola, S. Yamadazyma barbieri f.a. sp. nov., an ascomycetous anamorphic yeast isolated from a Mid-Atlantic Ridge hydrothermal site (−2300 m) and marine coastal waters. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3600–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shi, B.; Peng, Y.; Dai, D.; Sha, Z.; Zheng, J. Microbe-driven elemental cycling enables microbial adaptation to deep-sea ferromanganese nodule sediment fields. Microbiome 2023, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Hu, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhong, H.; Kong, Z.; Wu, L. Linking bacterial and fungal assemblages to soil nutrient cycling within different aggregate sizes in agroecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1038536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramss, G. Aspects determining the dominance of Fomitopsis pinicola in the colonization of deadwood and the role of the pathogenicity factor oxalate. Forests 2020, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, T.A.; McCutcheon, J.P. Coral symbiosis is a three-player game. Nature 2019, 568, 41–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pan, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.Z. Global assembly of microbial communities. mSystems 2023, 8, e01289-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayanthan, A.; Ordoñez, P.A.C.; Oresnik, I.J. The role of synthetic microbial communities (SynCom) in sustainable agriculture. Front. Agron. 2022, 4, 896307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Q.; Liu, D.; Hu, C.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Liang, G.; Zhou, W. Composition, predicted functions, and co-occurrence networks of fungal and bacterial communities links to soil organic carbon under long-term fertilization in a rice-wheat crop system. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 100, 103226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubartova, A.; Ottosson, E.; Stenlid, J. Linking fungal communities to wood density loss after 12 years of log decay. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, fiv032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adarsh, C.K.; Kumar, V.; Vidyasagaran, K.; Ganesh, P.N. Decomposition of wood by polypore fungi in tropics-biological, ecological and environmental factors-a case study. Res. J. Agric. For. Sci. 2015, 2320, 6063. [Google Scholar]
- Davy, S.K.; Allemand, D.; Weis, V.M. Cell biology of cnidarian-dinoflagellate symbiosis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2012, 76, 229–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladner, J.T.; Barshis, D.J.; Palumbi, S.R. P evolution in two co-occurring types of Symbiodinium: An ex-ploration into the genetic basis of thermal tolerance in Symbiodinium clade D rotein. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesser, M.P.; Stat, M.; Gates, R.D. The endosymbiotic dinoflagellates (Symbiodinium sp.) of corals are parasites and mutualists. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega Thurber, R.; Mydlarz, L.D.; Brandt, M.; Harvell, D.; Weil, E.; Raymundo, L.; Willis, B.L.; Langevin, S.; Tracy, A.M.; Littman, R.; et al. Deciphering coral disease dynamics: Integrating host, microbiome, and the changing environment. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 575927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carturan, B.S.; Parrott, L.; Pither, J. Functional richness and resilience in coral reef communities. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 780406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, T.W.; Maynard, D.S.; Crowther, T.R.; Peccia, J.; Smith, J.R.; Bradford, M.A. Untangling the fungal niche: The trait-based approach. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leray, M.; Wilkins, L.G.; Apprill, A.; Bik, H.M.; Clever, F.; Connolly, S.R.; De Leon, M.E.; Duffy, J.E.; Ezzat, L.; Gignoux-Wolfsohn, S.; et al. Natural experiments and long-term monitoring are critical to understand and predict marine host–microbe ecology and evolution. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabina, N.S.; Putnam, H.M.; Franklin, E.C.; Stat, M.; Gates, R.D. Symbiotic specificity, association patterns, and function determine community responses to global changes: Defining critical research areas for coral-Symbiodinium symbioses. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 3306–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, M.; Schmitt, I.; Weber, D.; Dal Grande, F. Fungal host affects photosynthesis in a lichen holobiont. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackall, L.L.; Wilson, B.; Van Oppen, M.J. Coral—The world’s most diverse symbiotic ecosystem. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 5330–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanó de Orte, M.; Koweek, D.A.; Cyronak, T.; Takeshita, Y.; Griffin, A.; Wolfe, K.; Szmant, A.; Whitehead, R.; Albright, R.; Caldeira, K. Unexpected role of communities colonizing dead coral substrate in the calcification of coral reefs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2021, 66, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, F.; Saalmann, F.; Thomson, T.; Coker, D.J.; Villalobos, R.; Jones, B.H.; Wild, C.; Carvalho, S. Coral reef degradation affects the potential for reef recovery after disturbance. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 142, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Campion-Alsumard, T.; Golubic, S.; Priess, K. Fungi in corals: Symbiosis or disease? Interaction between polyps and fungi causes pearl-like skeleton biomineralization. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 117, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Rahman, T.M.; Tharwat, N.A.; Abo El-Souad, S.M.; El-Beih, A.A.; El-Diwany, A.I. Biological activities and variation of symbiotic fungi isolated from coral reefs collected from Red Sea in Egypt. Mycology 2020, 11, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, E.C. Diseases of coral reef organisms. In Coral Reefs in the Anthropocene; Birkeland, C., Ed.; Springer Press: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 147–178. [Google Scholar]
- Glynn, P.W.; Manzello, D.P. Bioerosion and coral reef growth: A dynamic balance. In Coral Reefs in the Anthropocene; Birkeland, C., Ed.; Springer Press: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 67–97. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Orlandi, C.B.; Sardi, J.C.; Pitangui, N.S.; De Oliveira, H.C.; Scorzoni, L.; Galeane, M.C.; Medina-Alarcón, K.P.; Melo, W.C.M.A.; Marcelino, M.Y.; Braz, J.D.; et al. Fungal biofilms and polymicrobial diseases. J. Fungi 2015, 3, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, N.S.; Reusch, T.B. Microbial contributions to the persistence of coral reefs. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2167–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghukumar, C.; Ravindran, J. Fungi and their role in corals and coral reef ecosystems. In Biology of Marine Fungi; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 89–113. [Google Scholar]
- Rädecker, N.; Pogoreutz, C.; Gegner, H.M.; Cárdenas, A.; Roth, F.; Bougoure, J.; Guagliardo, P.; Wild, C.; Pernice, M.; Raina, J.B.; et al. Heat stress destabilizes symbiotic nutrient cycling in corals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022653118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Wang, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Peng, S.; Ge, Z.; Mao, L.; et al. Long-term nitrogen deposition alters ectomycorrhizal community composition and function in a poplar plantation. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedersoo, L.; Bahram, M.; Zobel, M. How mycorrhizal associations drive plant population and community biology. Science 2020, 367, eaba1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Shannon | Simpson | Richness | Chao1 | Ace |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ck1 | 1.74 | 0.74 | 44 | 44 | 44.48 |
| Ck2 | 1.23 | 0.48 | 45 | 45 | 45.31 |
| Ck3 | 0.69 | 0.24 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Mean of Ck | 1.22 | 0.49 | 38 | 38 | 38.26 |
| Fs1 | 0.89 | 0.41 | 24 | 24 | 24.44 |
| Fs2 | 0.55 | 0.24 | 15 | 15 | 16.08 |
| Fs3 | 0.65 | 0.34 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| Mean of Fs | 0.70 | 0.33 | 17.67 | 17.67 | 18.17 |
| St1 | 1.51 | 0.60 | 58 | 58 | 58 |
| St2 | 1.24 | 0.59 | 37 | 37 | 37 |
| St3 | 1.05 | 0.49 | 37 | 37 | 37.44 |
| Mean of St | 1.26 | 0.56 | 44 | 44 | 44.15 |
| Dg1 | 2.68 | 0.82 | 208 | 208.38 | 209.02 |
| Dg2 | 1.79 | 0.65 | 128 | 128.13 | 128.442 |
| Dg3 | 2.06 | 0.73 | 103 | 103.75 | 103.65 |
| Mean of Dg | 2.18 | 0.73 | 146.33 | 146.75 | 147.038 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, W.; Chen, J.; Liao, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, J.; Huang, R.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, X. Biodiversity, Distribution and Functional Differences of Fungi in Four Species of Corals from the South China Sea, Elucidated by High-Throughput Sequencing Technology. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10070452
Dong W, Chen J, Liao X, Chen X, Huang L, Huang J, Huang R, Zhong S, Zhang X. Biodiversity, Distribution and Functional Differences of Fungi in Four Species of Corals from the South China Sea, Elucidated by High-Throughput Sequencing Technology. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(7):452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10070452
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Wenyu, Jiatao Chen, Xinyu Liao, Xinye Chen, Liyu Huang, Jiayu Huang, Riming Huang, Saiyi Zhong, and Xiaoyong Zhang. 2024. "Biodiversity, Distribution and Functional Differences of Fungi in Four Species of Corals from the South China Sea, Elucidated by High-Throughput Sequencing Technology" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 7: 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10070452
APA StyleDong, W., Chen, J., Liao, X., Chen, X., Huang, L., Huang, J., Huang, R., Zhong, S., & Zhang, X. (2024). Biodiversity, Distribution and Functional Differences of Fungi in Four Species of Corals from the South China Sea, Elucidated by High-Throughput Sequencing Technology. Journal of Fungi, 10(7), 452. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10070452









