The Effect of the Application of Chemical Fertilizer and Arbuscular MyCorrhizal Fungi on Maize Yield and Soil Microbiota in Saline Agricultural Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Sites and Study Design
2.2. Makings
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Analysis of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
2.3.2. Analysis of Maize Production
2.3.3. Analysis of Mycorrhizal Infestation
2.3.4. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequence Analysis
2.3.5. Data Processing
2.3.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Fertilization Practices on Soil Chemical Properties
3.2. Effect of Fertilization Practices on Maize Yield
3.3. Alpha Diversity of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Fertilization Treatments
3.4. Beta Diversity of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Fertilization Treatments
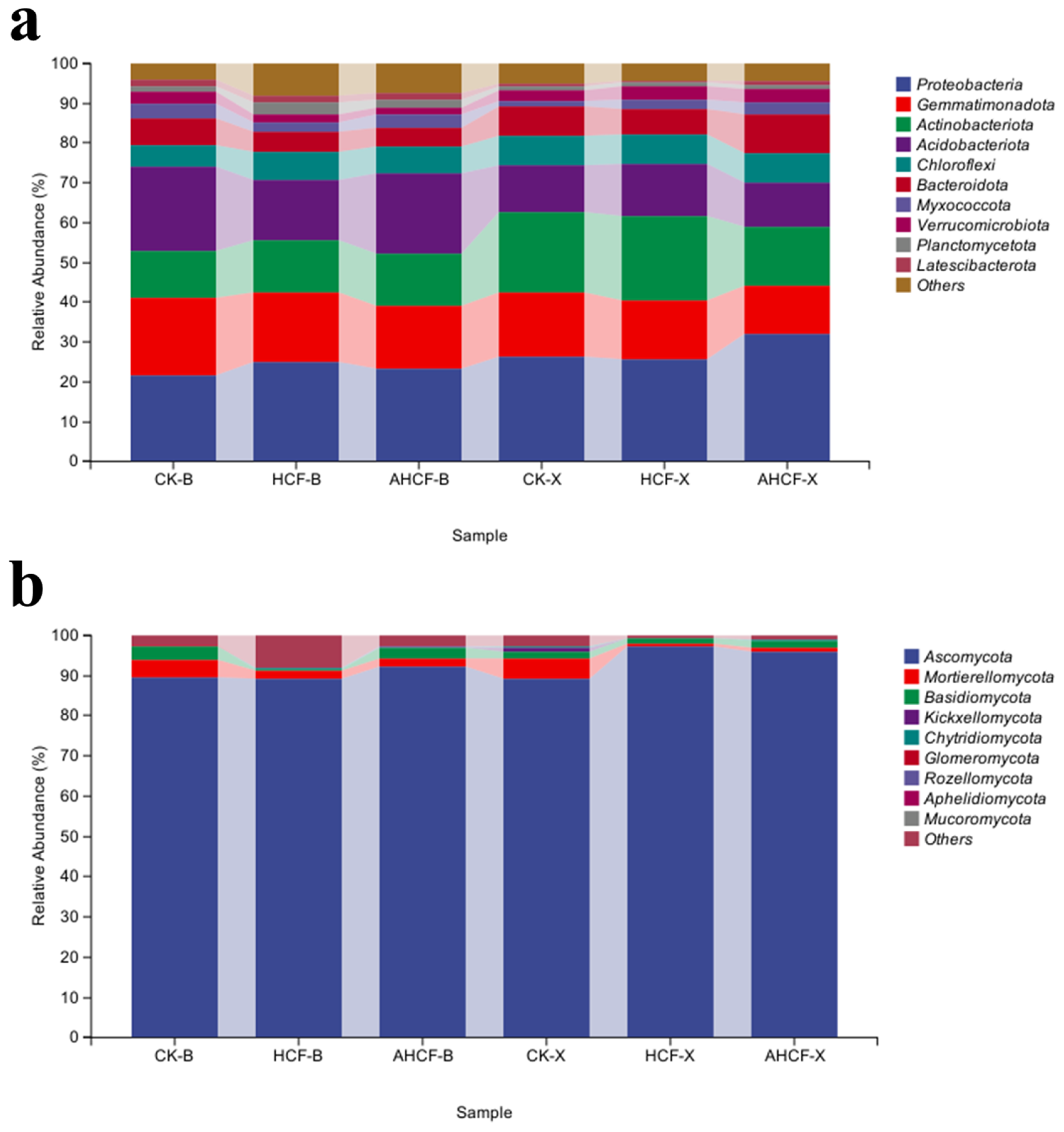
3.5. Soil Bacterial and Fungal Community Composition and Relative Abundance in Fertilizer Treatments
3.6. Analysis of Microbial Community Species Variation and Marker Species
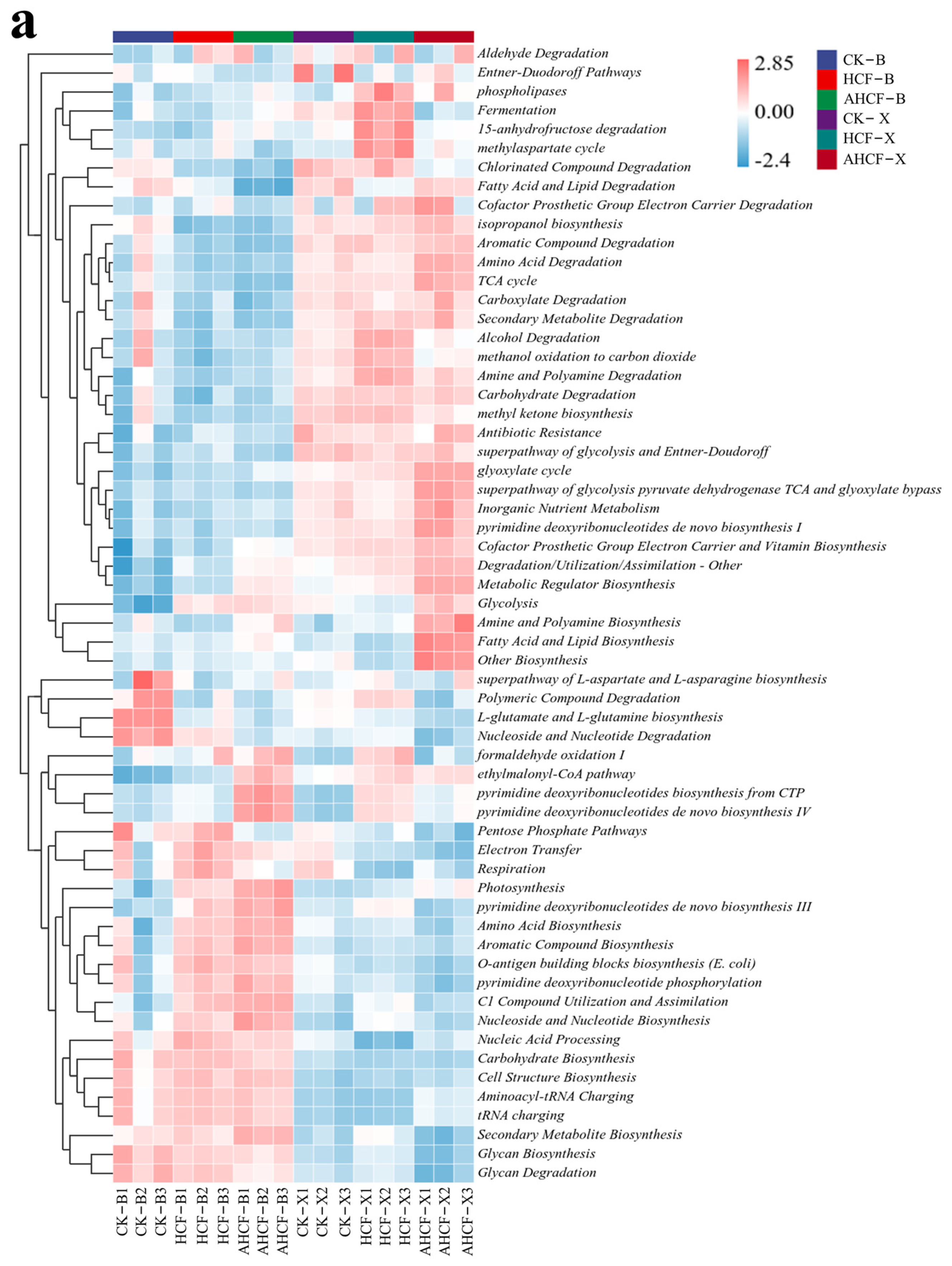
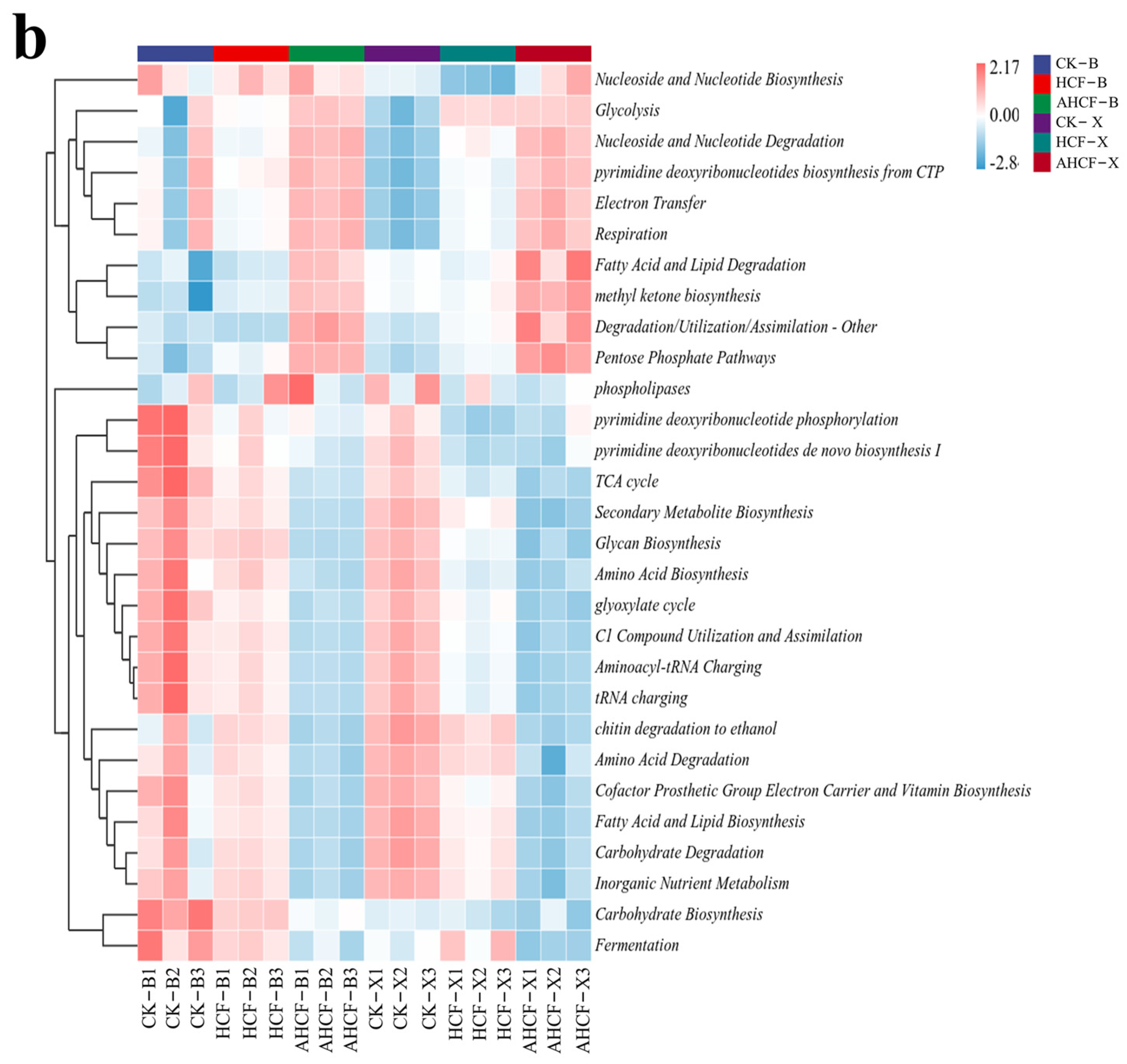
3.7. Differences in Metabolic Pathways of Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Fertilization Treatments
3.8. Relationship Between Microbial Community Structure and Soil Chemical Properties
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMF | arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi |
| ECe | electrical conductivity of saturated soil extracts |
| SOM | soil organic matter |
| AN | available nitrogen |
| AK | available potassium |
| AP | available phosphorus |
| CK | conventional fertilization |
| CF | chemical fertilizer at 600 kg/ha |
| HCF | chemical fertilizer at 300 kg/ha |
| ACF | chemical fertilizer at 600 kg/ha and AMF at 157.5 kg/ha |
| AHCF | chemical fertilizer at 300 kg/ha and AMF at 157.5 kg/ha |
| B | BeiWuLao |
| X | XuJiaZhen |
Appendix A
| Plan | pH | ECe (ds/m) | SOM (mg/kg) | AN (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BeiWuLao | CK | 8.34 ± 0.01 a | 2.414 ± 0.21 ab | 23.91 ± 2.06 d | 40.83 ± 2.02 c | 8.14 ± 1.23 d | 39.33 ± 0.15 d |
| CF | 8.24 ± 0.01 b | 2.348 ± 0.32 abc | 39.41 ± 3.63 b | 47.83 ± 2.02 b | 12.08 ± 0.57 c | 55.77 ± 0.55 b | |
| HCF | 8.22 ± 0.01 b | 2.427 ± 0.24 a | 32.56 ± 0.83 c | 45.50 ± 3.50 bc | 11.73 ± 0.44 c | 44.17 ± 2.89 c | |
| ACF | 8.11 ± 0.02 c | 2.301 ± 0.16 c | 46.98 ± 1.19 a | 59.50 ± 3.50 a | 15.50 ± 0.64 b | 60.37 ± 0.21 a | |
| AHCF | 8.23 ± 0.02 b | 2.333 ± 0.19 bc | 43.54 ± 4.96 ab | 64.17 ± 2.02 a | 20.50 ± 0.45 a | 61.35 ± 0.23 a | |
| XuJianZhen | CK | 8.43 ± 0.01 a | 4.431 ± 0.11 b | 14.19 ± 2.86 d | 17.33 ± 3.81 c | 9.55 ± 1.37 c | 44.17 ± 0.95 e |
| CF | 8.44 ± 0.02 a | 5.043 ± 0.22 a | 26.20 ± 1.73 b | 32.00 ± 3.00 b | 10.61 ± 1.13 abc | 59.07 ± 0.65 c | |
| HCF | 8.41 ± 0.03 ab | 5.055 ± 0.09 a | 19.72 ± 1.31 c | 29.17 ± 2.02 b | 10.14 ± 1.17 bc | 49.02 ± 0.38 d | |
| ACF | 8.38 ± 0.02 b | 5.046 ± 0.21 a | 31.86 ± 2.66 a | 32.67 ± 2.02 b | 12.20 ± 0.36 ab | 67.83 ± 0.75 b | |
| AHCF | 8.30 ± 0.04 c | 5.075 ± 0.14 a | 28.32 ± 0.58 ab | 38.67 ± 3.25 a | 12.79 ± 1.06 a | 78.50 ± 0.40 a |
References
- Sun, H.; Lu, H.; Chu, L.; Shao, H.; Shi, W. Biochar applied with appropriate rates can reduce N leaching, keep N retention and not increase NH(3) volatilization in a coastal saline soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, S.P.; Winnik, F.M.; Mwale, F.; Gong, Y.K. Group reorientation and migration of amphiphilic polymer bearing phosphorylcholine functionalities on surface of cellular membrane mimicking coating. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 84, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir, M.; Schubert, S. Degradation processes and nutrient constraints in sodic soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2002, 13, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasfar, A.; Bargaz, A.; Yaakoubi, K.; Hilali, A.; Bennis, I.; Zeroual, Y.; Meftah Kadmiri, I. Nitrogen Fixing Azotobacter Species as Potential Soil Biological Enhancers for Crop Nutrition and Yield Stability. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 628379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.; Ren, M.; Zhao, P.; Huang, Z.; Jia, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, A. Comprehensive evaluation of the risk system for heavy metals in the rehabilitated saline-alkali land. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Yang, Y.; Guan, P.; Geng, L.; Ma, L.; Di, H.; Liu, W.; Li, B. Remediation of organic amendments on soil salinization: Focusing on the relationship between soil salts and microbial communities. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Shen, M.; Dang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, Q.; et al. Organic fertilizer enhances rice growth in severe saline–alkali soil by increasing soil bacterial diversity. Soil Use Manag. 2021, 38, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Zhao, L.; Huang, M.L.; Chen, L.; Jin, S. Application of a vertical ‘electric sieve’ to mitigate and prevent salinization in coastal soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 2477–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mony, C.; Vannier, N.; Burel, F.; Ernoult, A.; Vandenkoornhuyse, P. The root microlandscape of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 2024, 244, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ci, D.; Qin, F.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Si, T.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Yu, T.; Xu, M.; et al. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Restored the Saline-Alkali Soil and Promoted the Growth of Peanut Roots. Plants 2023, 12, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, M.; Boughattas, S.; Hu, S.; Oh, S.H.; Sa, T. A meta-analysis of arbuscular mycorrhizal effects on plants grown under salt stress. Mycorrhiza 2014, 24, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.-J.; Zhang, N.-L.; Zhang, L.-L.; Zhang, X.-L.; Wu, A.-P.; Huang, J.-Y.; Yu, S.-Q.; Wang, Y.-H. Mediation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and biochemical parameters of Ligustrum vicaryi in response to salinity. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2020, 112, 101522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Xue, R.; Cao, J.; Li, S.; Guo, M.; Huang, H. Earthworms and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Alleviated Salt Stress in Maize Seedlings by Regulating the Root Endodermis Diffusion Barrier. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 43, 3490–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludemann, C.I.; Gruere, A.; Heffer, P.; Dobermann, A. Global data on fertilizer use by crop and by country. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Peng, H.; Ji, X.; Li, C.; Li, S. Effects of reduced inorganic fertilization and rice straw recovery on soil enzyme activities and bacterial community in double-rice paddy soils. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2019, 94, 103116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ti, C.; Luo, Y.; Yan, X. Characteristics of nitrogen balance in open-air and greenhouse vegetable cropping systems of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 18508–18518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B.; Teng, Y. Soil environmental quality in greenhouse vegetable production systems in eastern China: Current status and management strategies. Chemosphere 2017, 170, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Niu, X.; Wang, P. Effect of AMF Inoculation on Reducing Excessive Fertilizer Use. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J.; Zou, P.; Yu, Q.; Jiang, L. Fungal community composition change and heavy metal accumulation in response to the long-term application of anaerobically digested slurry in a paddy soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Ali, S.; Shahid, M.A.; Mustafa, A.; Sayyed, R.Z.; Cura, J.A. Insights into the Interactions among Roots, Rhizosphere, and Rhizobacteria for Improving Plant Growth and Tolerance to Abiotic Stresses: A Review. Cells 2021, 10, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Gu, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Lin, X.; Huang, Q.; Shen, W. The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant Soil 2009, 326, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Miao, Q.; Shi, H.; Feng, Z.; Feng, W. Effects of Combined Application of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers on Physical and Chemical Properties in Saline–Alkali Soil. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, M.D.; Joshi, P.K.; Jat, H.S.; Chinchmalatpure, A.R.; Narjary, B.; Sheoran, P.; Sharma, D.K. Changes in biological and chemical properties of saline soil amended with municipal solid waste compost and chemical fertilizers in a mustard–pearl millet cropping system. Catena 2016, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svenningsen, N.B.; Watts-Williams, S.J.; Joner, E.J.; Battini, F.; Efthymiou, A.; Cruz-Paredes, C.; Nybroe, O.; Jakobsen, I. Suppression of the activity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi by the soil microbiota. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Nie, H.; Zhu, L. Intercropping of Echinochloa frumentacea with Leguminous Forages Improves Hay Yields, Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Diversity, and Soil Enzyme Activities in Saline–Alkali Soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Yang, W.; Liu, S.; Xuan, N.; Shao, Y.; Geng, Y.; Afzal, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yue, S.; Mushtaq, R.; et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi increased peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) yield by changing the rhizosphere microbial community structure in saline-alkali soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1303979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, J.D.; Manteghi, N.A.; Shouse, P.J.; Alves, W.J. Estimating Soil Salinity from Saturated Soil-Paste Electrical Conductivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1989, 53, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhu, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Han, L.; Ma, X.; Xu, D. Bivariate empirical mode decomposition of the spatial variation in the soil organic matter content: A case study from NW China. Catena 2021, 206, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivell, P.; Ahmed, O.H.; Omar, L.; Abdul Majid, N.M. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Adsorption and Desorption Improvement and Soil Buffering Capacity Using Clinoptilolite Zeolite. Agronomy 2021, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, M.; Mosse, B. An Evaluation of Techniques for Measuring Vesicular Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Infection in Roots. New Phytol. 2006, 84, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, A.O.; Ejue, W.S.; Olayanju, A.; Dunsin, O.; Aboyeji, C.M.; Aremu, C.; Adegbite, K.; Akinpelu, O. Different organic manure sources and NPK fertilizer on soil chemical properties, growth, yield and quality of okra. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Dobbie, S.; Zhang, X.; Deng, A.; Qian, H.; Zhang, W. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on crop growth and soil N2O emissions in the legume system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chu, C.; Ding, S.; Wei, H.; Wu, S.; Xie, B. Insight into how fertilization strategies increase quality of grape (Kyoho) and shift microbial community. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 27182–27194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhan, A.; Chen, H.; Luo, S.; Bu, L.; Chen, X.; Li, S. Response of nitrogen use efficiency and soil nitrate dynamics to soil mulching in dryland maize (Zea mays L.) fields. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2015, 101, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Johnson, N.C.; Jansa, J.; Han, J.; Fang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xi, H.; Mao, L.; Pan, J.; et al. Mycorrhizal effects on crop yield and soil ecosystem functions in a long-term tillage and fertilization experiment. New Phytol. 2023, 242, 1798–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, W.; Zhu, C.; Luo, G.; Kong, Y.; Ling, N.; Wang, M.; Dai, J.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. Bacterial rather than fungal community composition is associated with microbial activities and nutrient-use efficiencies in a paddy soil with short-term organic amendments. Plant Soil 2017, 424, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Ren, Y.; Chen, A.; Yang, C.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Hu, S.; Xu, G. Plant nitrogen nutrition: The roles of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 269, 153591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ma, J.; Rong, Z.; Zeng, D.; Wang, Y.; Hu, S.; Ye, W.; Zheng, X. Wheat Straw Return Influences Nitrogen-Cycling and Pathogen Associated Soil Microbiota in a Wheat–Soybean Rotation System. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, D.; Zampieri, E.; Ioannou, A.; Spanos, A.; Sillo, F.; Giovannini, L.; Fotopoulos, V.; Brunetti, C.; Lumini, E.; Balestrini, R. Impact of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal inoculation on growth and biochemical parameters in Rosmarinus officinalis and Lavandula angustifolia. Symbiosis 2023, 91, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada, B.; Aroca, R.; Maathuis, F.J.M.; Barea, J.M.; Ruiz-Lozano, J.M. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi native from a Mediterranean saline area enhance maize tolerance to salinity through improved ion homeostasis. Plant Cell Environ. 2013, 36, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón, A.; Delgadillo-Martínez, J.; Franco-Ramírez, A.; Davies, F.T.; Ferrera-Cerrato, R. Influence of two Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons on Spore Germination, and Phytoremediation Potential of Gigaspora margarita—Echynochloa polystachya Symbiosis in Benzo(a)Pyrene-Polluted Substrate. Rev. Int. Contam. Ambient. 2010, 22, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Geng, Q.; Zhang, H.; Bian, C.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Jiang, D.; Xu, X. Global negative effects of nutrient enrichment on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, plant diversity and ecosystem multifunctionality. New Phytol. 2020, 229, 2957–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Bai, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, G.; Cui, B. Shifts in the soil bacterial community along a salinity gradient in the Yellow River Delta. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 2255–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, T.; Mao, X.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhou, J.; He, Y.; Ma, Q.; Wu, L. Long-term fertilizer application alters microbial resource limitations in soil aggregates via nutrient and microbial resource allocation. Plant Soil 2024, 508, 971–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.-P.; Zhang, L.-M.; Guo, J.-F.; Ray, J.L.; He, J.-Z. Impact of long-term fertilization practices on the abundance and composition of soil bacterial communities in Northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 46, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Lin, Y.; Luo, J.; Di, H.J.; Lindsey, S.; Liu, D.; Fan, J.; Ding, W. Responses of soil fungal diversity and community composition to long-term fertilization: Field experiment in an acidic Ultisol and literature synthesis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 145, 103305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Shi, X.-R.; Yuan, Z.-Y.; Yuan, L.Y.; Lock, T.R.; Kallenbach, R.L. Changes in rhizosphere bacterial and fungal community composition with vegetation restoration in planted forests. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.J.; Overmann, J. Vicinamibacteraceae fam. nov., the first described family within the subdivision 6 Acidobacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2331–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensch, K.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Meijer, M.; Dijksterhuis, J.; Jurjević, Ž.; Andersen, B.; Houbraken, J.; Crous, P.W.; Samson, R.A. Cladosporium species in indoor environments. Stud. Mycol. 2018, 89, 177–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Duan, W.; Zhang, W.; Peng, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Qi, X.; Pi, H.; Chen, K.; Yan, L. Integrative analysis of microbiome and metabolome revealed the effect of microbial inoculant on microbial community diversity and function in rhizospheric soil under tobacco monoculture. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e04046-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choreño-Parra, E.M.; Treseder, K.K. Mycorrhizal fungi modify decomposition: A meta-analysis. New Phytol. 2024, 242, 2763–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, R.; Paszkowski, U. Plant carbon nourishment of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2017, 39, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, M.A.; Crowther, T.W.; van der Linde, S.; Suz, L.M.; Bidartondo, M.I.; Cox, F.; Schaub, M.; Rautio, P.; Ferretti, M.; Vesterdal, L.; et al. Forest tree growth is linked to mycorrhizal fungal composition and function across Europe. ISME J. 2022, 16, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemergut, D.R.; Cleveland, C.C.; Wieder, W.R.; Washenberger, C.L.; Townsend, A.R. Plot-scale manipulations of organic matter inputs to soils correlate with shifts in microbial community composition in a lowland tropical rain forest. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 2153–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Forslund, S.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; Bodegom, P.M.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Anslan, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Harend, H.; et al. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature 2018, 560, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sui, Y.; Yu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Soil carbon content drives the biogeographical distribution of fungal communities in the black soil zone of northeast China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 83, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Xiang, X.; Yang, J.; Adams, J.M.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y. Effects of Slope Aspects on Soil Bacterial and Arbuscular Fungal Communities in a Boreal Forest in China. Pedosphere 2016, 26, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Op De Beeck, M.; Lievens, B.; Busschaert, P.; Rineau, F.; Smits, M.; Vangronsveld, J.; Colpaert, J.V. Impact of metal pollution on fungal diversity and community structures. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 17, 2035–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
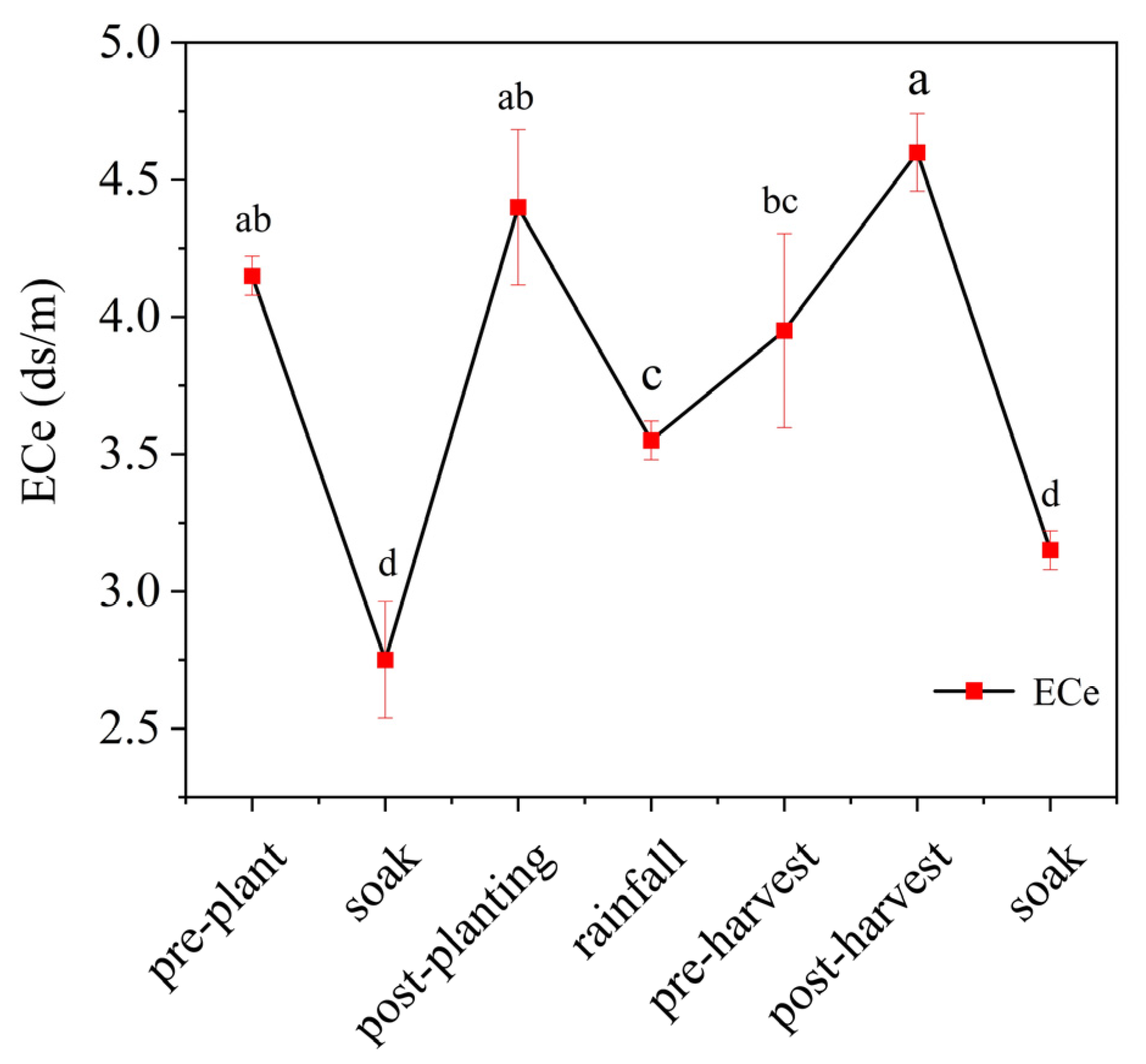
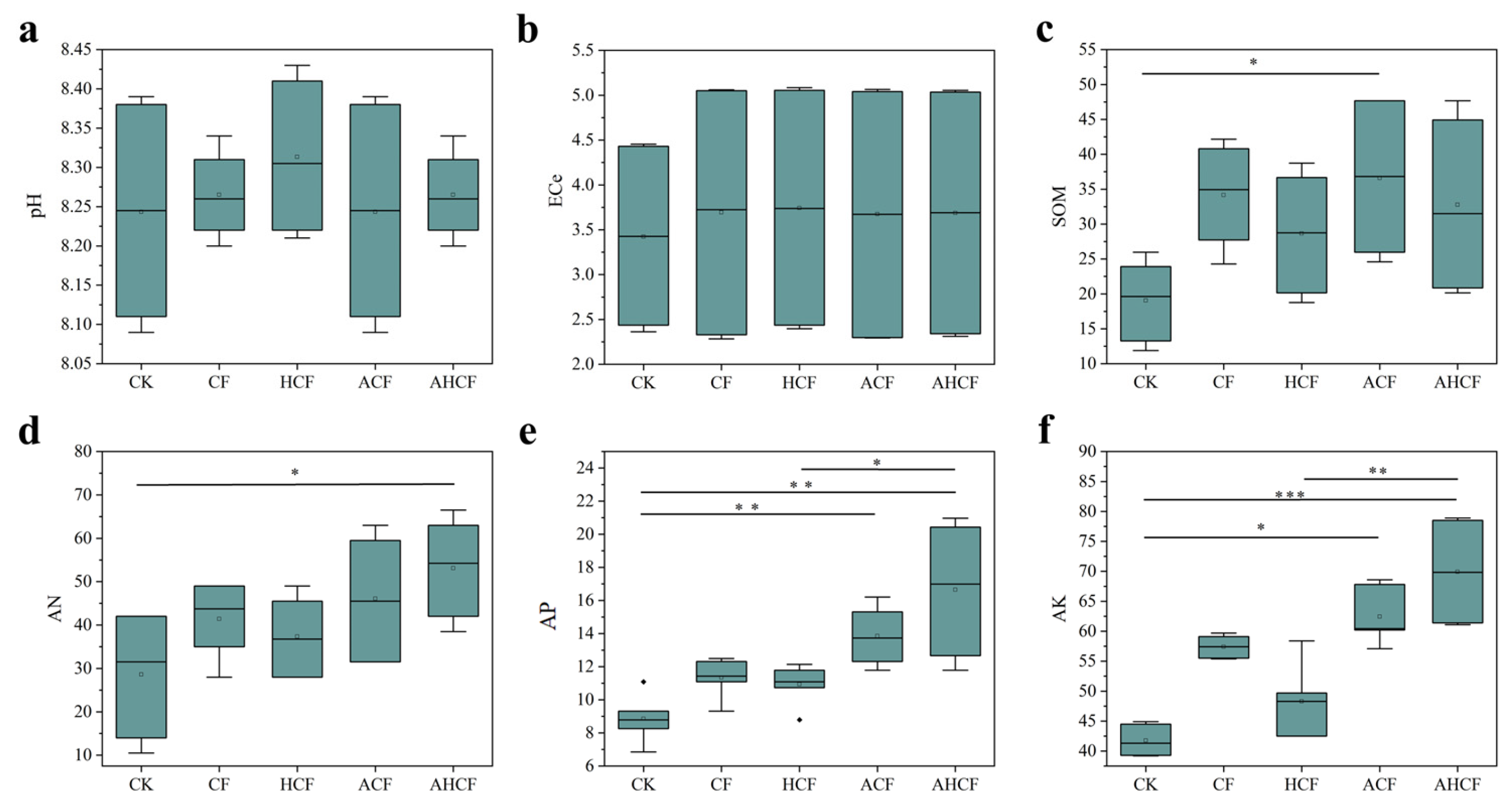
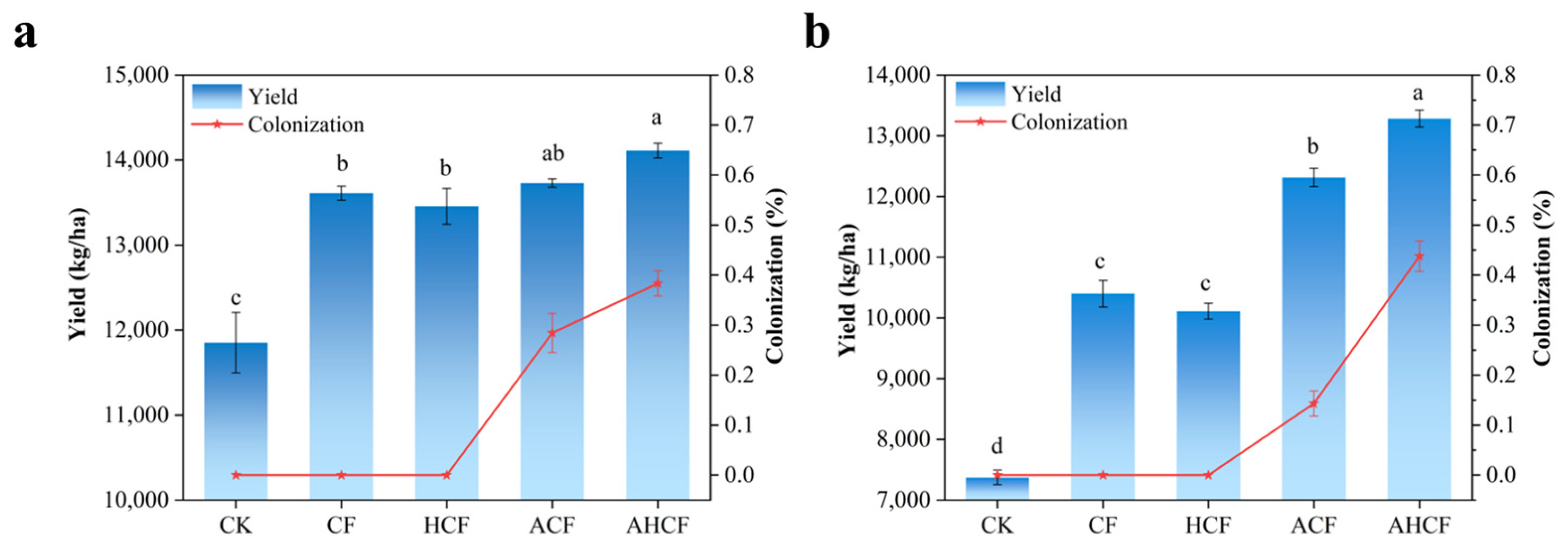
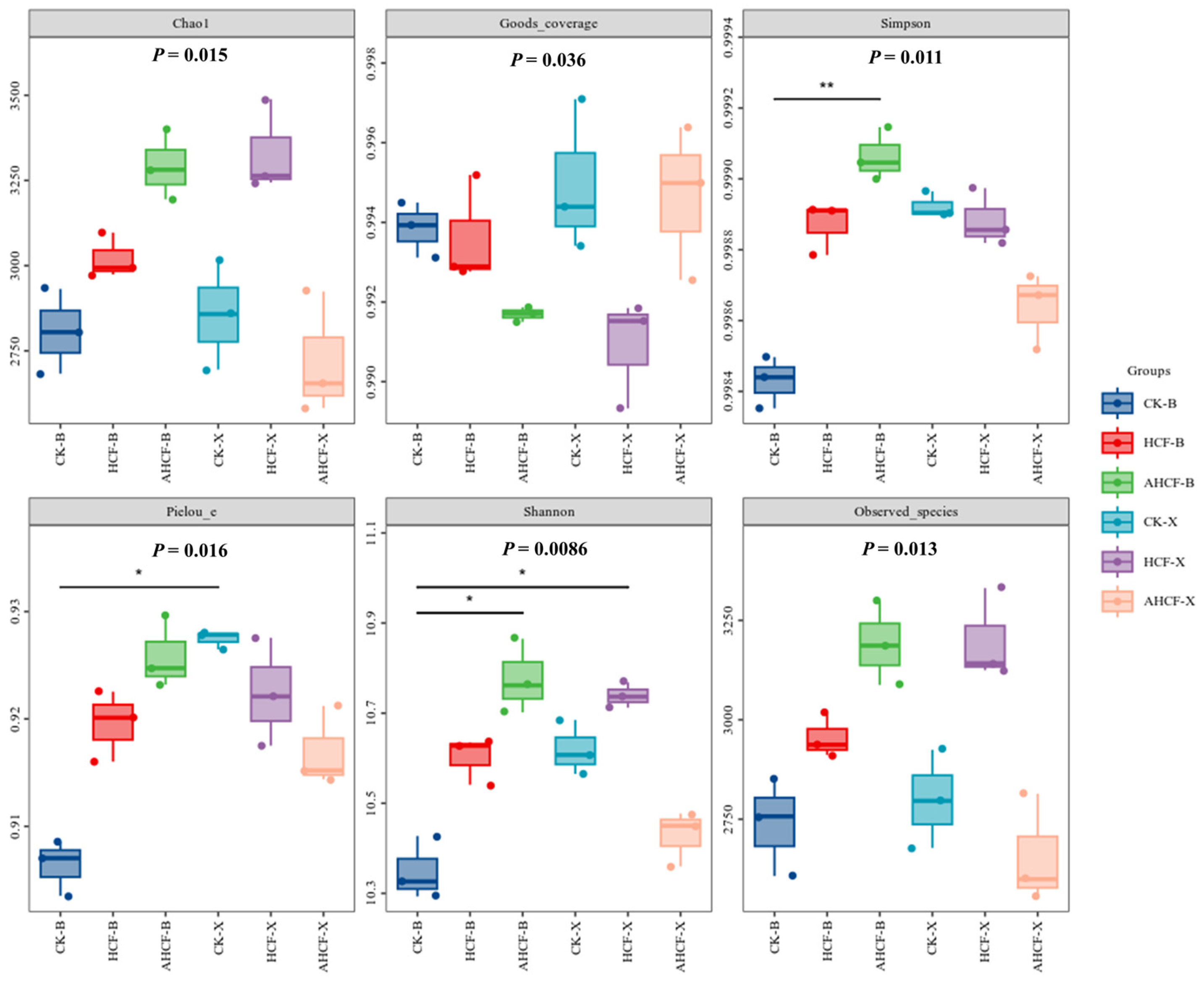




| Test Site | pH | Ece (ds/m) | SOM (mg/kg) | AN (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BeiWuLao | 8.44 | 4.1 ± 0.25 | 25.42 ± 1.32 | 41.42 ± 2.11 | 9.22 ± 0.84 | 41.52 ± 0.84 |
| XuJiaZhen | 8.34 | 4.4 ± 0.41 | 15.76 ± 2.46 | 18.69 ± 2.43 | 9.43 ± 1.47 | 46.43 ± 0.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, Y.; Feng, Z.; Yan, S.; Zhang, J.; Song, H.; Zou, Y.; Jin, D. The Effect of the Application of Chemical Fertilizer and Arbuscular MyCorrhizal Fungi on Maize Yield and Soil Microbiota in Saline Agricultural Soil. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040319
Yuan Y, Feng Z, Yan S, Zhang J, Song H, Zou Y, Jin D. The Effect of the Application of Chemical Fertilizer and Arbuscular MyCorrhizal Fungi on Maize Yield and Soil Microbiota in Saline Agricultural Soil. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(4):319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040319
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Ye, Zhengjun Feng, Shengxin Yan, Junjie Zhang, Huiping Song, Yan Zou, and Dapeng Jin. 2025. "The Effect of the Application of Chemical Fertilizer and Arbuscular MyCorrhizal Fungi on Maize Yield and Soil Microbiota in Saline Agricultural Soil" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 4: 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040319
APA StyleYuan, Y., Feng, Z., Yan, S., Zhang, J., Song, H., Zou, Y., & Jin, D. (2025). The Effect of the Application of Chemical Fertilizer and Arbuscular MyCorrhizal Fungi on Maize Yield and Soil Microbiota in Saline Agricultural Soil. Journal of Fungi, 11(4), 319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040319






