Climate Change Influences Basidiome Emergence of Leaf-Cutting Ant Cultivars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
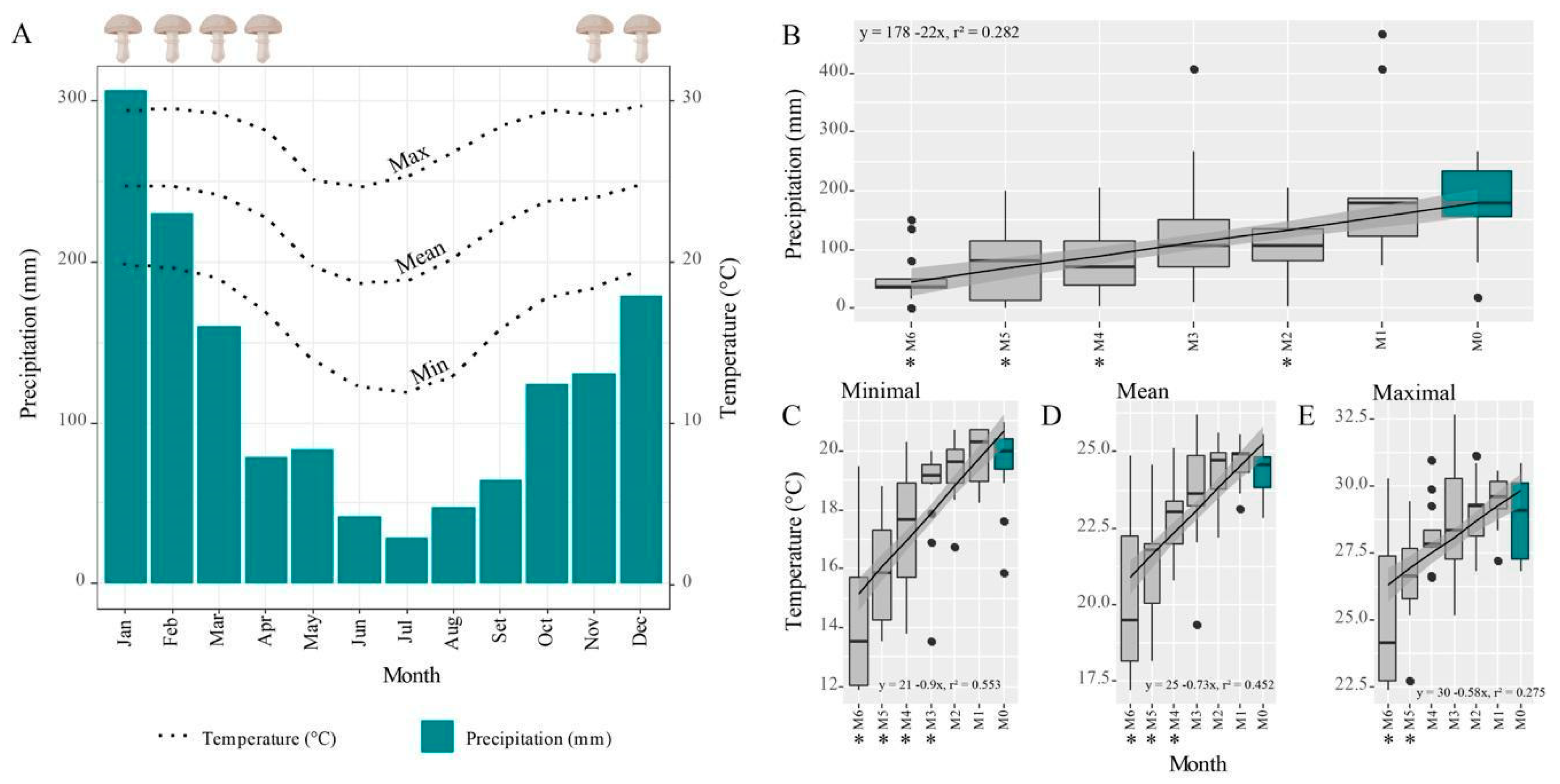
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Accessibility Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Branstetter, M.G.; Ješovnik, A.; Sosa-Calvo, J.; Lloyd, M.W.; Faircloth, B.C.; Brady, S.G.; Schultz, T.R. Dry habitats were crucibles of domestication in the evolution of agriculture in ants. Proc. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20170095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nygaard, S.; Hu, H.; Li, C.; Schiøtt, M.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Ma, C.; Deng, Y.; Dikow, R.B.; et al. Reciprocal genomic evolution in the ant–fungus agricultural symbiosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schultz, T.R.; Brady, S.G. Major evolutionary transitions in ant agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5435–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bollazzi, M.; Roces, F. To build or not to build: Circulating dry air organizes collective building for climate control in the leaf-cutting ant Acromyrmex ambiguus. Anim. Behav. 2007, 74, 1349–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollazzi, M.; Roces, F. Leaf-cutting ant workers (Acromyrmex heyeri) trade off nest thermoregulation for humidity control. J. Ethol. 2010, 28, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleineidam, C.; Roces, F. Carbon dioxide concentrations and nest ventilation in nests of the leaf-cutting ant Atta vollenweideri. Insect. Soc. 2000, 47, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, R.; Herz, H.; Ryel, R.J.; Beyschlag, W.; Hölldobler, B. Herbivory of Leaf-Cutting Ants: A Case Study on Atta Colombica in the Tropical Rainforest of Panama (Vol. 164); Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Cristiano, M.P.; Cardoso, D.C.; Sandoval-Gómez, V.E.; Simões-Gomes, F.C. Amoimyrmex Cristiano, Cardoso & Sandoval, gen. nov. (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): A new genus of leaf-cutting ants revealed by multilocus molecular phylogenetic and morphological analyses. Austral. Entomol. 2020, 59, 643–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, R. The Agaricales in Modern Taxonomy, 4th ed.; Koeltz Scientific Books: Koenigstein, Germany, 1986; p. 981. [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa, M.M.; Silva, P.S.; Wirth, R.; Tabarelli, M.; Leal, I.R. How leaf-cutting ants impact forests: Drastic nest effects on light environment and plant assemblages. Oecologia 2010, 162, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.T.; Leal, I.R.; Tabarelli, M.; Wirth, R. Ecosystem engineering by leaf-cutting ants: Nests of Atta cephalotes drastically alter forest structure and microclimate. Ecol. Entomol. 2011, 36, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, A.C.; Schwendenmann, L.; Allen, M.F.; Aronson, E.L.; Artavia-León, A.; Dierick, D.; Fernandez-Bou, A.S.; Harmon, T.C.; Murillo-Cruz, C.; Oberbauer, S.F.; et al. Welcome to the Atta world: A framework for understanding the effects of leaf-cutter ants on ecosystem functions. Funct. Ecol. 2019, 33, 1386–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sternberg, L.D.S.; Pinzon, M.C.; Moreira, M.Z.; Moutinho, P.; Rojas, E.I.; Herre, E.A. Plants use macronutrients accumulated in leaf-cutting ant nests. Proc. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leal, I.R.; Oliveira, P.S. Interactions between fungus-growing ants (Attini), Fruits and Seeds in cerrado vegetation in southeast Brazil. Biotropica 1998, 30, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farji-Brener, A.G.; Werenkraut, V. A meta-analysis of leaf-cutting ant nest effects on soil fertility and plant performance. Ecol. Entomol. 2015, 40, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, N.A. Fungus-growing ants. Science 1966, 153, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, R.J.; Cherrett, J.M. Aspects of the symbiosis of the leaf-cutting ant Acromyrmex octospinosus (Reich) and its food fungus. Ecol. Entomol. 1978, 3, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapela, I.H.; Rehner, S.A.; Schultz, T.R.; Mueller, U.G. Evolutionary history of the symbiosis between fungus-growing ants and their fungi. Science 1994, 266, 1691–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, U.G. Ant versus fungus versus mutualism: Ant-cultivar conflict and the deconstruction of the attine ant-fungus symbiosis. Am. Nat. 2002, 160, S67–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, A. Die Pilzgärten Einiger Südamerikanischer Ameisen, 1st ed.; Verlag von Gustav Fischer: Jena, Germany, 1893; Volume 6, pp. 1–127. [Google Scholar]
- Stahel, G.; Geijskes, D.C. Weitere Untersuchungen über den Nestbau und Gartenpilz von. Atta Cephalotes. Rev. Entomol. 1941, 12, 243–268. [Google Scholar]
- Pagnocca, F.C.; Bacci, M., Jr.; Fungaro, M.H.; Bueno, O.C.; Hebling, M.J.; Sant’Anna, A.; Capelari, M. RAPD analysis of the sexual state and sterile mycelium of the fungus cultivated by the leaf-cutting ant Acromyrmex hispidus fallax. Mycol. Res. 2001, 105, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autuori, M. Algumas observações sobre formigas cultivadoras de fungo (Hym. Formicidae). Rev. Bras. Entomol. 1940, 11, 215–226. [Google Scholar]
- Muchovej, J.J.; Della Lucia, T.M.; Muchovej, R.M.C. Leucoagaricus weberi sp. nov. from a live nest of leaf-cutting ants. Mycol. Res. 1991, 95, 1308–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, P.J.; Stradling, D.J.; Pegler, D.N. Leaf cutting ants, their fungus gardens and the formation of basidiomata of Leucoagaricus Gongylophorus. Mycologist 1994, 8, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, P.J.; Stradling, D.J.; Pegler, D.N. Leucoagaricus basidiomata from a live nest of the leaf-cutting ant Atta cephalotes. Mycol. Res. 1994, 98, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielmann, A.A.; Putzke, J. Leucoagaricus gongylophorus (Agaricales, Basidiomycota) em ninho ativo de formigas Attini (Acromyrmex aspersus). Cad. Pesq. Sér. Botânica 1998, 10, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, C.R. O gênero Acromyrmex no Brasil (Hym. Formicidae). Stud. Entomol. 1961, 4, 113–180. [Google Scholar]
- Luederwaldt, H. Observações biológicas sobre formigas brasileiras especialmente do estado de São Paulo. Rev. Museu Paul. 1926, 14, 185–303. [Google Scholar]
- Heim, R. A propos du Rozites gongylophora A. Möller. Rev. Mycol. 1957, 22, 293–299. [Google Scholar]
- Stahel, G. Sobre o fungo cultivado pela formiga Atta cephalotes L. An. Prim. Reun. Sul-Am. Bot. 1938, 1, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Stahel, G.; Geijskes, D.C. Ueber den bau der nester von Atta cephalotes L. und Atta sexdens L. (Hym. Formicidae). Rev. Entomol. 1939, 10, 27–78. [Google Scholar]
- Stahel, G.; Geijskes, D.C. De parasolmieren en hunne bestrijding. Bull. Depart. Landbouw. 1940, 56, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, D.M.; Freeman, C.J.; Wong, J.C.; Fogel, M.L.; Knowlton, N. Climate change promotes parasitism in a coral symbiosis. ISME J. 2018, 12, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brosi, G.B.; McCulley, R.L.; Bush, L.P.; Nelson, J.A.; Classen, A.T.; Norby, R.J. Effects of multiple climate change factors on the tall fescue–fungal endophyte symbiosis: Infection frequency and tissue chemistry. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, C.J.; Coppins, B.J. Contrasting functional traits maintain lichen epiphyte diversity in response to climate and autogenic succession. J. Biogeogr. 2006, 33, 1643–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersch, M.F.; Fonseca, C.R. Abiotic factors and the conditional outcome of an ant–plant mutualism. Ecology 2005, 86, 2117–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Büntgen, U.; Egli, S.; Camarero, J.J.; Fischer, E.M.; Stobbe, U.; Kauserud, H.; Tegel, W.; Sproll, L.; Stenseth, N.C. Drought-induced decline in Mediterranean truffle harvest. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2012, 2, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büntgen, U.; Egli, S.; Tegel, W.; Stobbe, U.; Sproll, L.; Elburg, R.; Peter, M.; Nievergelt, D.; Cherubini, P.; Stenseth, N.C. Illuminating the mysterious world of truffles. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, M.L.; 2021 URM—Herbário Pe. Camille Torrand. Version 1.84. Universidade Federal de Pernambuco. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/2464956731 (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Ueda, K. 2021 iNaturalist Research-Grade Observations. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/occurrence/1986496332 (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Lacerda, L.T.; Gusmão, L.F.; Rodrigues, A. Diversity of endophytic fungi in Eucalyptus microcorys assessed by complementary isolation methods. Mycol. Prog. 2018, 17, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.J.W.T.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Innis, M.A., Gelfand, D.H., Sninsky, J.J., White, T.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; Volume 18, pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Rehner, S.A.; Samuels, G.J. Taxonomy and phylogeny of Gliocladium analysed from nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycol. Res. 1994, 98, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, T. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R.; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2021; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing.; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. Available online: https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Kucheryavskiy, S. mdatools—R package for chemometrics. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2020, 198, 103937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikheyev, A.S.; Mueller, U.G.; Abbot, P. Cryptic sex and many-to-one coevolution in the fungus-growing ant symbiosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10702–10706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butlin, R. The costs and benefits of sex: New insights from old asexual lineages. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koné, N.A.; Dosso, K.; Konaté, S.; Kouadio, J.Y.; Linsenmair, K.E. Environmental and biological determinants of Termitomyces species seasonal fructification in central and southern Côte d’Ivoire. Insect. Soc. 2011, 58, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Luedeling, E.; Chen, G.; Hyde, K.D.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Xu, J.; Yang, Y. Climate change effects fruiting of the prize matsutake mushroom in China. Fungal Divers. 2012, 56, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eveling, D.W.; Wilson, R.N.; Gillespie, E.S.; Bataille, A. Environmental effects on sporocarp counts over fourteen years in a forest area. Mycol. Res. 1990, 94, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, C.J.; Carrier, P.; Boutin, S.; Boonstra, R.; Hofer, E. Mushroom crops in relation to weather in the southwestern Yukon. Botany 2008, 86, 1497–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecl, G.T.; Araújo, M.B.; Bell, J.D.; Blanchard, J.; Bonebrake, T.C.; Chen, I.C.; Clark, T.D.; Colwell, R.K.; Danielsen, F.; Evengård, B.; et al. Biodiversity redistribution under climate change: Impacts on ecosystems and human well-being. Science 2017, 355, eaai9214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffers, B.R.; De Meester, L.; Bridge, T.C.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Pandolfi, J.M.; Corlett, R.T.; Butchart, S.H.; Pearce-Kelly, P.; Kovacs, K.M.; Dudgeon, D.; et al. The broad footprint of climate change from genes to biomes to people. Science 2016, 354, aaf7671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ant Species | Fungal Species | Occurrence Data | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acromyrmex aspersus | Leucoagaricus gongylophorus | Basidiomes found on 29 November 1995 in an active nest in a native forest in Santa Cruz do Sul-RS (Rio Pardinho), Brazil. | [27] |
| Acromyrmex coronatus | Leucoagaricus gongylophorus | Basidiomes observed on 23 March 2006, in Rio Claro-SP (UNESP Campus), Brazil. | Bacci M. (personal communication) |
| Acromyrmex coronatus | Leucoagaricus gongylophorus | Basidiomes observed on 5 and 27 January 2018 in Rio Claro-SP, Brazil (Colony ID: BLS170701-01). | This study |
| Acromyrmex coronatus | Leucoagaricus gongylophorus | Basidiomes observed on 5 April and 27 November 2018, 28 January 2019, 10 February 2020, in Rio Claro-SP, Brazil (Colony ID: RB181203-01). One specimen is deposited in the herbarium of the Federal University of Santa Catarina # FLOR0068416). | This study |
| Acromyrmex coronatus | Leucoagaricus gongylophorus | Basidiome observed on 29 December 2019 in Mogi-Guaçu-SP, Brazil (colony ID: RB200104-01). | This study |
| Acromyrmex coronatus | Leucoagaricus gongylophorus | Basidiomes observed on 2 and 10 January 2020, 5 and 7 February, 12 November, and 13 and 18 December 2020 in Rio Claro-SP, Brazil (Colony ID: RB190909-01). | This study |
| Acromyrmex coronatus | Leucoagaricus gongylophorus | Basidiome observed on 4 January 2020 in Mogi-Guaçu-SP, Brazil (Colony ID: RB200104-03). | This study |
| Acromyrmex coronatus | Leucoagaricus gongylophorus | Basidiome observed on 21 February 2020, in Rio Claro-SP, Brazil (Colony ID: RB200507-03). | This study |
| Acromyrmex crassispinus | Rozites gongylophora (=Leucoagaricus gongylophorus) | As mentioned in Gonçalves (1961, page 117) “Luederwaldt 1926 observed basidiomes on nests of A. crassispinus (cited as A. nigra). | [19,28,29] |
| Acromyrmex disciger | Leucocoprinus gongylophorus (=Leucoagaricus gongylophorus) | Basidiomes observed in November 1891, 19 February, and 17 and 30 March 1892 in Blumenau-SC, Brazil. | [19,20,30] |
| Acromyrmex hispidus fallax | Rozites gongylophora (=Leucoagaricus gongylophorus) | Observation from 11 November 1944 in Curitiba-PR, Brazil (see page 143). | [19,28] |
| Acromyrmex hispidus fallax | Leucoagaricus gongylophorus | Last week of February 1996 (dozen of basidiomes) and April (ten basidiomes) in Rio Claro-SP, Brazil. Colony found under a peach tree. | [19,22] |
| Atta cephalotes | Unidentified | No data/not sure | [19,31] |
| Atta cephalotes | Unidentified | Lelydorp, 20 km near Paramaribo, Suriname. | [19,32,33] |
| Atta cephalotes | Rozites gongylophora (=Leucoagaricus gongylophorus) | 8 and 9 November 1939 in Paramaribo, Suriname (see pages 253–254, and 258–266). | [19,21] |
| Atta cephalotes | Rozites gongylophora (=Leucoagaricus gongylophorus) | 13 January 1940, in Paramaribo, Suriname (see page 260). | [19,21] |
| Atta colombica | Leucocoprinus cf. gongylophorus | No data/not sure | Collection PA-236, U.G. Mueller, unpublished data |
| Not informed | Rozites gongylophora | Basidiome observed on 29 May 1957. | gbif.org/occurrence/2464956731, last accessed on 25 June 2021 |
| We assumed Acromyrmex sp. on the basis of the collector’s ant-colony descriptions | Leucoagaricus gongylophorus | Basidiome observed on 22 December 2010 in Brasília-DF, Brazil. Sh Jardim Botânico/Condomínio Quintas Bela Vista Conjunto e—Jardim Botânico, Brasília—DF, 70297-400, Brasil (Coordinates: 15.9 S and 47.8 W). | gbif.org/occurrence/1986496332, last accessed on 25 June 2021 |
| We assumed Acromyrmex sp. on the basis of collector’s ant-colony descriptions | Leucoagaricus gongylophorus | Basidiome observed on 11 November 2017 in Parque Nacional da Serra dos Órgãos—Parnaso, Teresópolis-RJ, Brazil. | Heisecke C., Duque J. and Venegas M. (personal communication) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bizarria, R., Jr.; Kooij, P.W.; Rodrigues, A. Climate Change Influences Basidiome Emergence of Leaf-Cutting Ant Cultivars. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7110912
Bizarria R Jr., Kooij PW, Rodrigues A. Climate Change Influences Basidiome Emergence of Leaf-Cutting Ant Cultivars. Journal of Fungi. 2021; 7(11):912. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7110912
Chicago/Turabian StyleBizarria, Rodolfo, Jr., Pepijn W. Kooij, and Andre Rodrigues. 2021. "Climate Change Influences Basidiome Emergence of Leaf-Cutting Ant Cultivars" Journal of Fungi 7, no. 11: 912. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7110912






