Efficacy of LD Bio Aspergillus ICT Lateral Flow Assay for Serodiagnosis of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kosmidis, C.; Denning, D.W. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Thorax 2015, 70, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swain, S.; Ray, A.; Sarda, R.; Vyas, S.; Singh, G.; Jorwal, P.; Kodan, P.; Khanna, P.; Xess, I.; Sinha, S.; et al. COVID-19-associated subacute invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses 2022, 65, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweer, K.E.; Bangard, C.; Hekmat, K.; Cornely, O.A. Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses 2014, 57, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denning, D.W.; Cadranel, J.; Beigelman-Aubry, C.; Ader, F.; Chakrabarti, A.; Blot, S.; Ullmann, A.J.; Dimopoulos, G.; Lange, C. Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: Rationale and clinical guidelines for diagnosis and management. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, C.B.; Davidsen, J.R.; Van Acker, L.; Salzer, H.J.F.; Seidel, D.; Cornely, O.A.; Hoenigl, M.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Hennequin, C.; Godet, C.; et al. CPAnet Registry—An International Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis Registry. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Denning, D.W.; Chakrabarti, A. Estimation of the Burden of Chronic and Allergic Pulmonary Aspergillosis in India. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singla, R.; Singhal, R.; Rathore, R.; Gupta, A.; Sethi, P.; Myneedu, V.P.; Chakraborty, A.; Kumar, V. Risk factors for chronic pulmonary aspergillosis in post-TB patients. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. Off. J. Int. Union Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2021, 25, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucky Hunter, E.; Richardson, M.D.; Denning, D.W. Evaluation of LDBio Aspergillus ICT Lateral Flow Assay for IgG and IgM Antibody Detection in Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e00538-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unusual Case of Chronic Cavitary Pulmonary Aspergillosis Presenting as Spontaneous Pneumothorax in an Immunocompromised Man. BMJ Case Reports. Available online: https://casereports.bmj.com/content/14/8/e241655 (accessed on 15 February 2022).
- Sarda, R.; Ray, A. TB and chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: A few relevant points. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. Off. J. Int. Union Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2021, 25, 1042–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragesh, R.; Ray, A.; Mian, A.; Vyas, S.; Sharma, S.K. Cavitary Lung Lesions in a Difficult-To-Treat Asthma Patient. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2016, 64, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Volpe Chaves, C.E.; do Valle Leone de Oliveira, S.M.; Venturini, J.; Grande, A.J.; Sylvestre, T.F.; Poncio Mendes, R.; Mello Miranda Paniago, A. Accuracy of serological tests for diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0222738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richardson, M.D.; Page, I.D. Aspergillus serology: Have we arrived yet? Med. Mycol. 2017, 55, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rozaliyani, A.; Rosianawati, H.; Handayani, D.; Agustin, H.; Zaini, J.; Syam, R.; Adawiyah, R.; Tugiran, M.; Setianingrum, F.; Burhan, E.; et al. Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Post Tuberculosis Patients in Indonesia and the Role of LDBio Aspergillus ICT as Part of the Diagnosis Scheme. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piarroux, R.P.; Romain, T.; Martin, A.; Vainqueur, D.; Vitte, J.; Lachaud, L.; Gangneux, J.-P.; Gabriel, F.; Fillaux, J.; Ranque, S. Multicenter Evaluation of a Novel Immunochromatographic Test for Anti-aspergillus IgG Detection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denning, D.W.; Page, I.D.; Chakaya, J.; Jabeen, K.; Jude, C.M.; Cornet, M.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Bongomin, F.; Bowyer, P.; Chakrabarti, A.; et al. Case Definition of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Resource-Constrained Settings. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, e171312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, I.D.; Richardson, M.D.; Denning, D.W. Comparison of six Aspergillus-specific IgG assays for the diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA). J. Infect. 2016, 72, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-R.; Huang, H.-L.; Keng, L.-T.; Chang, H.-L.; Sheu, C.-C.; Fu, P.-K.; Wang, J.-Y.; Chong, I.-W.; Shih, J.-Y.; Yu, C.-J. Establishing Aspergillus-Specific IgG Cut-Off Level for Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis Diagnosis: Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozaliyani, A.; Setianingrum, F.; Azahra, S.; Abdullah, A.; Fatril, A.E.; Rosianawati, H.; Burhan, E.; Handayani, D.; Arifin, A.R.; Zaini, J.; et al. Performance of LDBio Aspergillus WB and ICT Antibody Detection in Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, I.S.; Choudhary, H.; Dhooria, S.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Garg, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Agarwal, R. Diagnostic cut-off of Aspergillus fumigatus-specific IgG in the diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses 2018, 61, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.-H.; Lai, H.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Sun, K.-S.; Chen, C.-Y. Investigating Factors of False-Positive Results of Aspergillus Galactomannan Assay: A Case-Control Study in Intensive Care Units. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 747280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.-Y.; Kang, M.-L.; Tan, B.-H.; Ngan, C.C.-L. Case report: Enteral nutritional supplement as a likely cause of false-positive galactomannan testing. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2014, 3, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.F.; Petrie, A. Method agreement analysis: A review of correct methodology. Theriogenology 2010, 73, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camuset, J.; Nunes, H.; Dombret, M.-C.; Bergeron, A.; Henno, P.; Philippe, B.; Dauriat, G.; Mangiapan, G.; Rabbat, A.; Cadranel, J. Treatment of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis by voriconazole in nonimmunocompromised patients. Chest 2007, 131, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergidis, P.; Moore, C.B.; Novak-Frazer, L.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R.; Walker, A.; Denning, D.W.; Richardson, M.D. High-volume culture and quantitative real-time PCR for the detection of Aspergillus in sputum. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, I.D.; Byanyima, R.; Hosmane, S.; Onyachi, N.; Opira, C.; Richardson, M.; Sawyer, R.; Sharman, A.; Denning, D.W. Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis commonly complicates treated pulmonary tuberculosis with residual cavitation. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, I.S.; Dhooria, S.; Choudhary, H.; Aggarwal, A.N.; Garg, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Agarwal, R. Utility of Serum and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Galactomannan in Diagnosis of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, e01821-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, B.; Koh, W.-J.; Jeong, B.-H.; Yoo, H.; Park, H.Y.; Suh, G.Y.; Kwon, O.J.; Jeon, K. Serum galactomannan antigen test for the diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Infect. 2014, 68, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumikawa, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Mihara, T.; Takazono, T.; Morinaga, Y.; Kurihara, S.; Nakamura, S.; Imamura, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Nishino, T.; et al. Bronchoalveolar lavage galactomannan for the diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwizera, R.; Katende, A.; Teu, A.; Apolot, D.; Worodria, W.; Kirenga, B.J.; Bongomin, F. Algorithm-aided diagnosis of chronic pulmonary aspergillosis in low- and middle-income countries by use of a lateral flow device. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 39, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oladele, R.O.; Irurhe, N.K.; Foden, P.; Akanmu, A.S.; Gbaja-Biamila, T.; Nwosu, A.; Ekundayo, H.A.; Ogunsola, F.T.; Richardson, M.D.; Denning, D.W. Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis as a cause of smear-negative TB and/or TB treatment failure in Nigerians. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. Off. J. Int. Union Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2017, 21, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
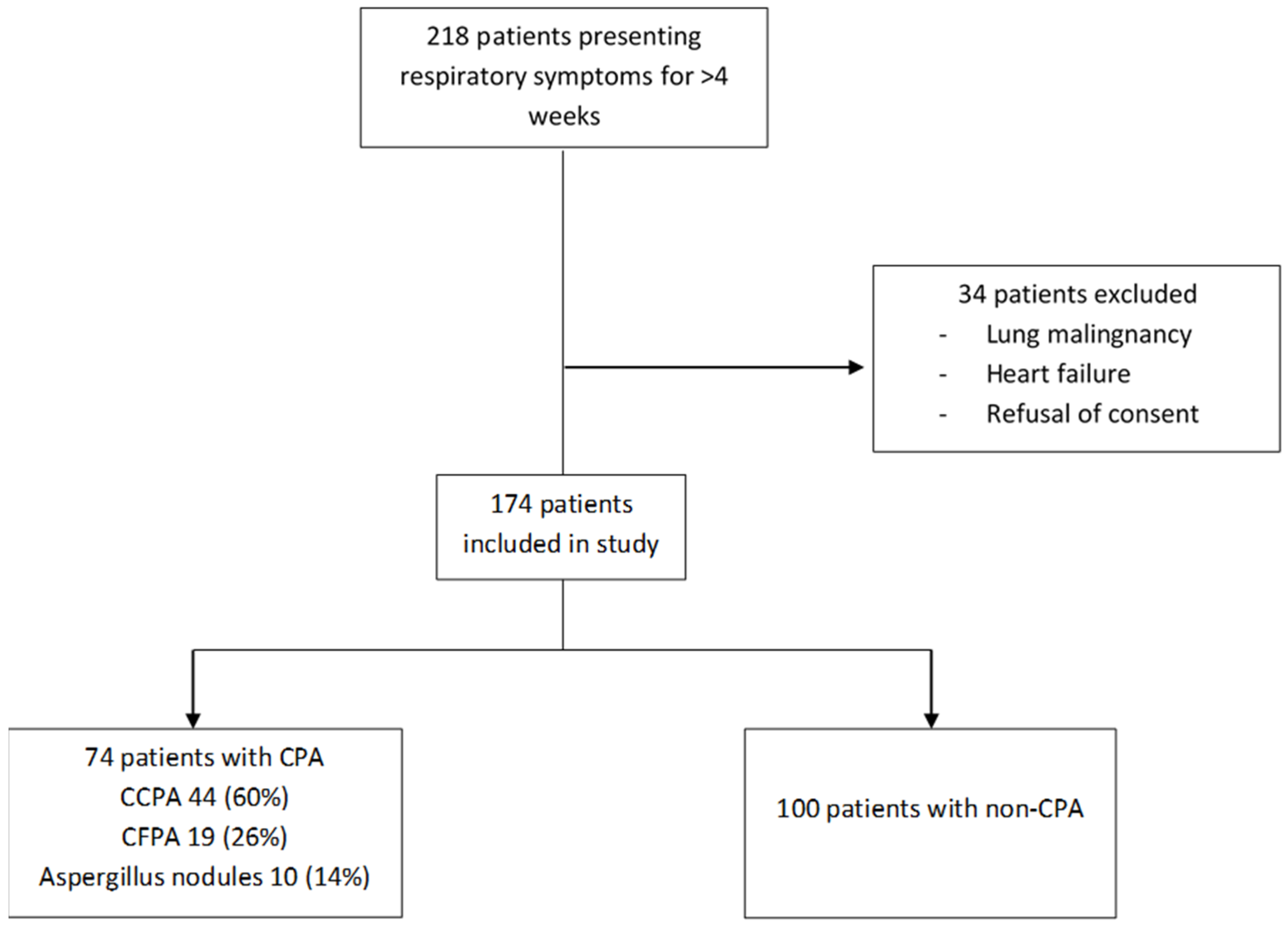

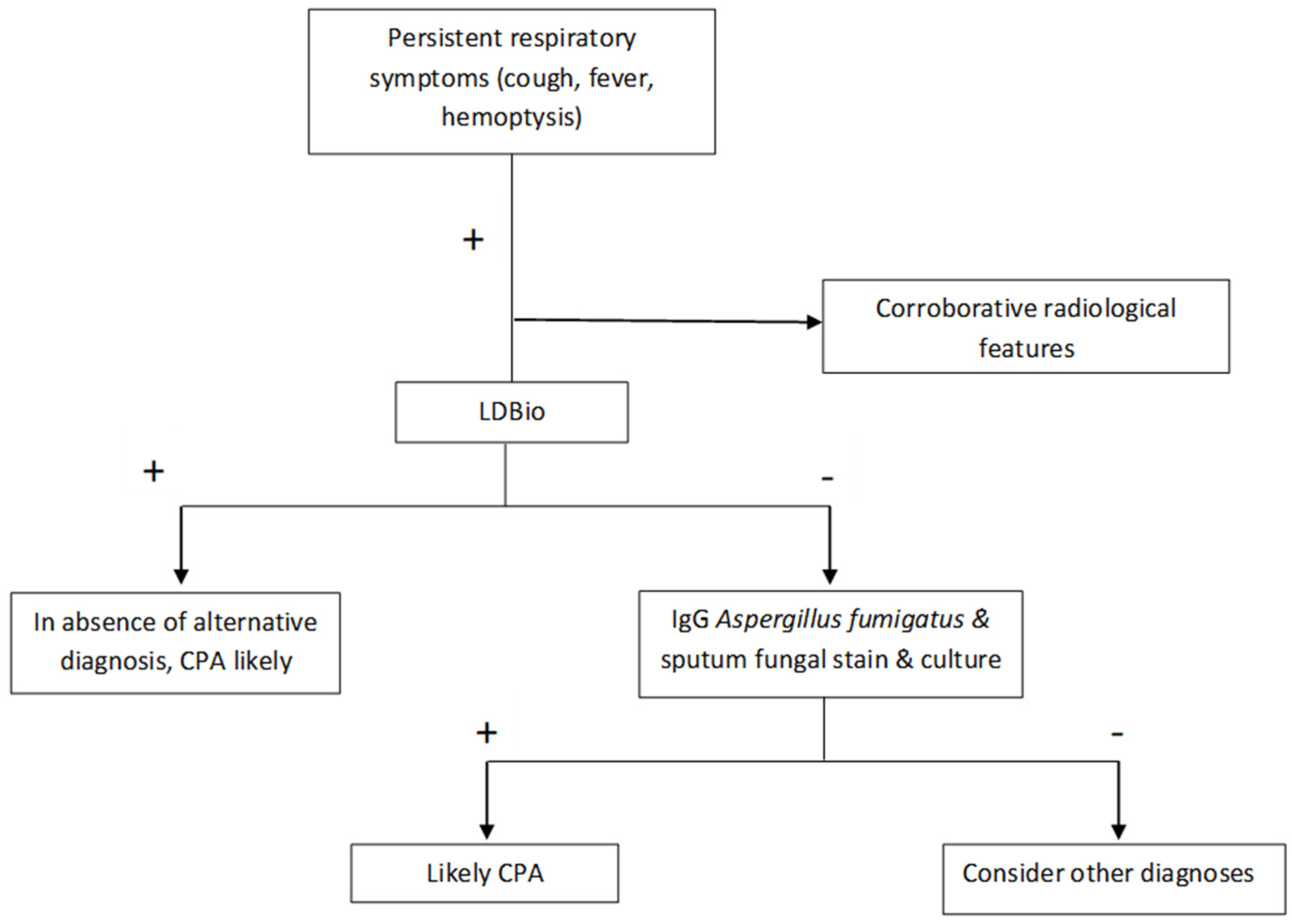
| Variables | Non-CPA (n = 100) | CPA (n = 74) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (±SD) | 41.4 (±14.57) | 39.68 (±13.05) | 0.42 | |
| Sex | Male | 66 (66.0%) | 42 (56.8%) | 0.21 |
| Female | 34 (34.0%) | 32 (43.2%) | ||
| Past History | ||||
| Tuberculosis | 56 (56.0%) | 60 (81.1%) | 0.001 | |
| HIV | 2 (2.0%) | 1 (1.35%) | >0.99 | |
| ABPA | 12 (12.0%) | 1 (1.35%) | 0.008 | |
| MDI use | 28 (28%) | 18 (24.3%) | 0.67 | |
| Symptoms & Mycobacterial Workup | ||||
| Fever | 10 (10%) | 13 (17.6%) | 0.16 | |
| Cough | 53 (53%) | 53 (71.6%) | 0.02 | |
| Weight loss | 25 (25%) | 25 (33.8%) | 0.24 | |
| Breathlessness | 46 (46%) | 31 (41.9%) | 0.51 | |
| Haemoptysis | 17(17%) | 34 (46%) | <0.001 | |
| Fatigue | 0 (0%) | 2 (100%) | 0.33 | |
| Any symptom | 84 (84.0%) | 68 (91.9%) | 0.12 | |
| No. (%) with Post-TB sequelae | 29 (29%) | 52 (70.3%) | ||
| No. (%) with pulmonary/disseminated TB | 21 (21%) | 9 (12.2%) | ||
| No. (%) with ABPA | 11 (11%) | 1 (1.4%) | ||
| No. (%) with obstructive airway disease | 13 (13%) | 2 (2.7%) | ||
| No. (%) with sarcoidosis | 5 (5%) | 0 (0%) | ||
| No. (%) with ILD | 1 (1%) | 1 (1.4%) | ||
| No. (%) with others - Lung malignancy/metastasis - Lung mass under evaluation - Pulmonary/disseminated cryptococcosis - Pulmonary/disseminated mucormycosis - Post COVID sequelae - Gujjar’s lung - Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis - PUO - Bronchiectasis under evaluation - Diabetes mellitus - CML - Unclassified | 4 (4%) 4 (4%) 1 (1%) 1 (1%) 2 (2%) 1 (1%) 1 (1%) 1 (1%) 5 (5%) 2 (2%) 0 (0%) 11 (11%) | 0 (0%) 1 (1.4%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 2 (2.7%) 1 (1.4%) 8 (10.8%) | ||
| Features | Non-CPA (n = 100) | CPA (n = 74) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consolidation | 33 (33%) | 35 (47.3%) | 0.33 |
| Cavity | 22 (22%) | 61 (82.4%) | <0.001 |
| Nodules | 40 (40%) | 42 (56.8%) | 0.14 |
| Ground glass opacities | 22 (22%) | 26 (35.1%) | 0.21 |
| Pleural effusion | 16 (16%) | 5 (6.8%) | 0.06 |
| Pleural thickening | 10 (10%) | 24 (32.4%) | <0.001 |
| Bronchiectasis | 36 (36%) | 46 (62.2%) | 0.001 |
| Variables | Non-CPA (n = 100) | CPA (n = 74) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDBio LFA positive Weakly positive | 19 (19%) 2 (2%) | 50 (67.6%) 1 (1.4%) | <0.001 0.6 |
| Specific IgE (IQR) | 0.11 (0.02–0.37) | 0.34 (0.04–1.5) | 0.2 |
| Total IgE (IQR) | 328 (66.9–1465) | 406 (119–1035) | 0.8 |
| Specific IgG (IQR) | 11.5 (6.40–20.1) | 53.85 (30–91) | <0.001 |
| AEC (IQR) | 162.07 (49.6–341.66) | 162.32 (15.19–371.46) | 0.93 |
| Specific IgE (≥0.1 KVA/L) | 16 (16/28, 57.1%) | 30 (30/46, 65.2%) | 0.49 |
| Total IgE (≥500 KVA/L) | 14 (14/31, 45.2%) | 20 (20/47, 42.6%) | 0.82 |
| Specific IgG (≥27 MgA/L) | 18 (18.0%) | 61 (82.4%) | <0.001 |
| AEC (≥500 cells/mm3) | 13 (13/60, 21.7%) | 10 (10/50, 20%) | 0.83 |
| Positive direct KOH | 4 (4/55, 7.3%) | 6 (6/53, 11.3%) | 0.52 |
| Positive fungal culture Aspergillus fumigatus Aspergillus flavus Aspergillus niger Aspergillus spp. | 2 (2/70, 2.9%) - 2 * 1 * - | 7 (7/61, 11.5%) 2 3 1 1 | 0.08 |
| Serum galactomannan (≥1.0) | 10 (10/28, 35.7%) | 16 (16/39, 41%) | 0.66 |
| BAL galactomannan (≥1.0) | 7 (7/30, 23.3%) | 17 (17/28, 60.7%) | 0.004 |
| ZN AFB + ve | 2 (2/48, 4.2%) | 0 (0/41, 0%) | 0.49 |
| MGIT + ve | 5 (5/30, 16.7%) | 0 (0/25, 0%) | 0.06 |
| GeneXpert | 9 (9/55, 16.4%) | 4 (4/54, 7.4%) | 0.24 |
| Any TB investigation + ve | 12 (12/100, 12.0%) | 4 (4/74, 5.4%) | 0.19 |
| Population/Test | No of Observations | Sensitivity | Specificity | Diagnostic Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms > 4 weeks | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 67.6% (55.7–78%) | 81% (71.9–88.2%) | 75.3% (68.19–81.50%) | |
| LDBio neg | 24 | 81 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 50 | 19 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 82.4% (71.8–90.3%) | 82% (73.1–89%) | 82.2% (75.68–87.56%) | |
| IgG neg | 13 | 82 | ||||
| IgG pos | 61 | 18 | ||||
| Symptoms > 4 weeks with past history of PTB | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 73.3% (60.3–83.9%) | 83.9% (71.7–92.4%) | 78.5% (69.9–85.5%) | |
| LDBio neg | 16 | 47 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 44 | 9 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 86.7% (75.4–94.1%) | 80.4% (67.6–89.8%) | 83.6% (75.6–89.8%) | |
| IgG neg | 8 | 45 | ||||
| IgG pos | 52 | 11 | ||||
| Symptoms > 3 months with past history of PTB | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 74.1% (60.3–85%) | 85% (70.2–94.3%) | 78.7% (69.1–86.5%) | |
| LDBio neg | 14 | 34 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 40 | 6 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 85.2% (72.9–93.4% | 82.5% (67.2–92.7%) | 84% (75.1–90.8%) | |
| IgG neg | 8 | 33 | ||||
| IgG pos | 46 | 7 | ||||
| Symptoms > 4 weeks with lung cavity | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 68.9% (55.7–80.1%) | 81.82% (59.7–94.8%) | 72.3% (61.4–81.6%) | |
| LDBio neg | 19 | 18 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 42 | 4 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 82% (70–90.6%) | 86.4% (65.1–97.1%) | 83.1% (73.3–90.5%) | |
| IgG neg | 11 | 19 | ||||
| IgG pos | 50 | 3 | ||||
| Symptoms > 4 weeks excluding abpa | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 67.12% (55.1–77.7%) | 89.77% (81.5–95.2%) | 79.5% (72.4–85.5%) | |
| LDBio neg | 24 | 79 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 49 | 9 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 82.19% (71.5–90.2%) | 87.50% (78.7–93.4%) | 85.1% (78.6–90.2%) | |
| IgG neg | 13 | 77 | ||||
| IgG pos | 60 | 11 | ||||
| Symptoms > 4 weeks with bronchiectasis and excluding abpa | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 80% (65.4–90.4%) | 86.67% (69.28–96.2%) | 82.7% (72.2–90.4%) | |
| LDBio neg | 9 | 26 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 36 | 4 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 86.7% (73.2–95%) | 86.7% (69.3–96.2%) | 86.7% (76.8–93.4%) | |
| IgG neg | 6 | 26 | ||||
| IgG pos | 39 | 4 | ||||
| Population/Test | No of Observations | Sensitivity | Specificity | Diagnostic Accuracy | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symptoms > 4 weeks | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 68.3% (55.04–79.74%) | 75.4% (66.49–83.02%) | 72.99% (65.75–79.43%) | |
| LDBio neg | 19 | 86 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 41 | 28 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 75% (62.14–85.28%) | 90.35% (83.39–95.08%) | 85.06% (78.88–90.00%) | |
| IgG neg | 15 | 103 | ||||
| IgG pos | 45 | 11 | ||||
| Symptoms > 4 weeks and prior history of PTB | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 75.51% (61.13–86.66%) | 76.12% (64.14–85.69%) | 75.86% (67.04–83.32%) | |
| LDBio neg | 12 | 51 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 37 | 16 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 79.59% (65.66–89.76%) | 91.04% (81.52–96.64%) | 86.21% (78.57–91.91%) | |
| IgG neg | 10 | 61 | ||||
| IgG pos | 39 | 6 | ||||
| Symptoms > 3 months with past history of tuberculosis | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 75.00% (59.66–86.81%) | 74.00% (59.66–85.37%) | 74.47% (64.43–82.91%) | |
| LDBio neg | 11 | 37 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 33 | 13 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 77.27% (62.16–88.53%) | 94.00% (83.45–98.75%) | 86.17% (77.51–92.43%) | |
| IgG neg | 10 | 47 | ||||
| IgG pos | 34 | 3 | ||||
| Symptoms > 4 weeks with lung cavity | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 69.23% (54.90–81.28%) | 67.74% (48.63–83.32%) | 68.67% (57.56–78.41%) | |
| LDBio neg | 16 | 21 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 36 | 10 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 76.92% (63.16–87.47%) | 96.77% (83.30–99.92%) | 84.34% (74.71–91.39%) | |
| IgG neg | 12 | 30 | ||||
| IgG pos | 40 | 1 | ||||
| Symptoms > 4 weeks excluding abpa | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 67.80% (54.36–79.38%) | 82.35% (73.55–89.19%) | 77.02% (69.74–83.27%) | |
| LDBio neg | 19 | 84 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 40 | 18 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 76.27% (63.41–86.38%) | 95.10% (88.93–98.39%) | 88.20% (82.19–92.74%) | |
| IgG neg | 14 | 97 | ||||
| IgG pos | 45 | 5 | ||||
| Symptoms > 4 weeks with bronchiectasis and excluding abpa | ||||||
| LDBio LFA | CPA | Non-CPA | 80.56% (63.98–91.81%) | 71.79% (55.13–85.00%) | 76.00% (64.75–85.11%) | |
| LDBio neg | 7 | 28 | ||||
| LDBio pos | 29 | 11 | ||||
| ImmunoCAP Asp IgG | CPA | Non-CPA | 80.56% (63.98–91.81%) | 94.87% (82.68–99.37%) | 88.00% (78.44–94.36%) | |
| IgG neg | 7 | 37 | ||||
| IgG pos | 29 | 2 | ||||
| Author | Country/Year | Study Type | Population | Comparator | Sensitivity | Specificity | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piarroux et al. [15] | France/2019 | Both retrospective and prospective | All samples received for Aspergillus serology (ABPA, CPA, IA SAIA *). Retrospective: 262 cases (68 CPA) & 188 controls. Prospective: 44 cases (11 CPA) & 213 non-cases | Who did not correspond to case definition of CPA | 88.9% | 96.3% | Definition of CPA as per ERS/ESCMID |
| Hunter et al. [8] | UK/2019 | Cross sectional | CPA patient sera. 154 CPA patients, 150 healthy controls. | Healthy control | 91.6% | 98% | Definition of CPA as per ERS/ESCMID |
| Rozaliyani et al. [19] | Indonesia/2020 | Prospective | Adults with symptoms after completing tuberculosis therapy. | Patients without diagnosis CPA | 80% | 70% | Sputum for fungal culture was used as an essential diagnostic criterion. |
| Ray et al. (present study) | India/2021–22 present study | Prospective | Patients presenting with respiratory symptoms > 4 weeks. 74 CPA & 100 non-CPA patients | Patients being tested who did not have CPA | 67.6% | 81% | Definition of CPA as per ERS/ESCMID |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ray, A.; Chowdhury, M.; Sachdev, J.; Sethi, P.; Meena, V.P.; Singh, G.; Xess, I.; Vyas, S.; Khan, M.A.; Sinha, S.; et al. Efficacy of LD Bio Aspergillus ICT Lateral Flow Assay for Serodiagnosis of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8040400
Ray A, Chowdhury M, Sachdev J, Sethi P, Meena VP, Singh G, Xess I, Vyas S, Khan MA, Sinha S, et al. Efficacy of LD Bio Aspergillus ICT Lateral Flow Assay for Serodiagnosis of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(4):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8040400
Chicago/Turabian StyleRay, Animesh, Mohit Chowdhury, Janya Sachdev, Prayas Sethi, Ved Prakash Meena, Gagandeep Singh, Immaculata Xess, Surabhi Vyas, Maroof Ahmad Khan, Sanjeev Sinha, and et al. 2022. "Efficacy of LD Bio Aspergillus ICT Lateral Flow Assay for Serodiagnosis of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 4: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8040400
APA StyleRay, A., Chowdhury, M., Sachdev, J., Sethi, P., Meena, V. P., Singh, G., Xess, I., Vyas, S., Khan, M. A., Sinha, S., Denning, D. W., Wig, N., & Kabra, S. K. (2022). Efficacy of LD Bio Aspergillus ICT Lateral Flow Assay for Serodiagnosis of Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis. Journal of Fungi, 8(4), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8040400







