Three New Species of Hypoxylon (Xylariales, Ascomycota) on a Multigene Phylogeny from Medog in Southwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Specimens
2.2. Morphological Observations
2.3. DNA Extraction, Amplification, and Sequencing
2.4. Molecular Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
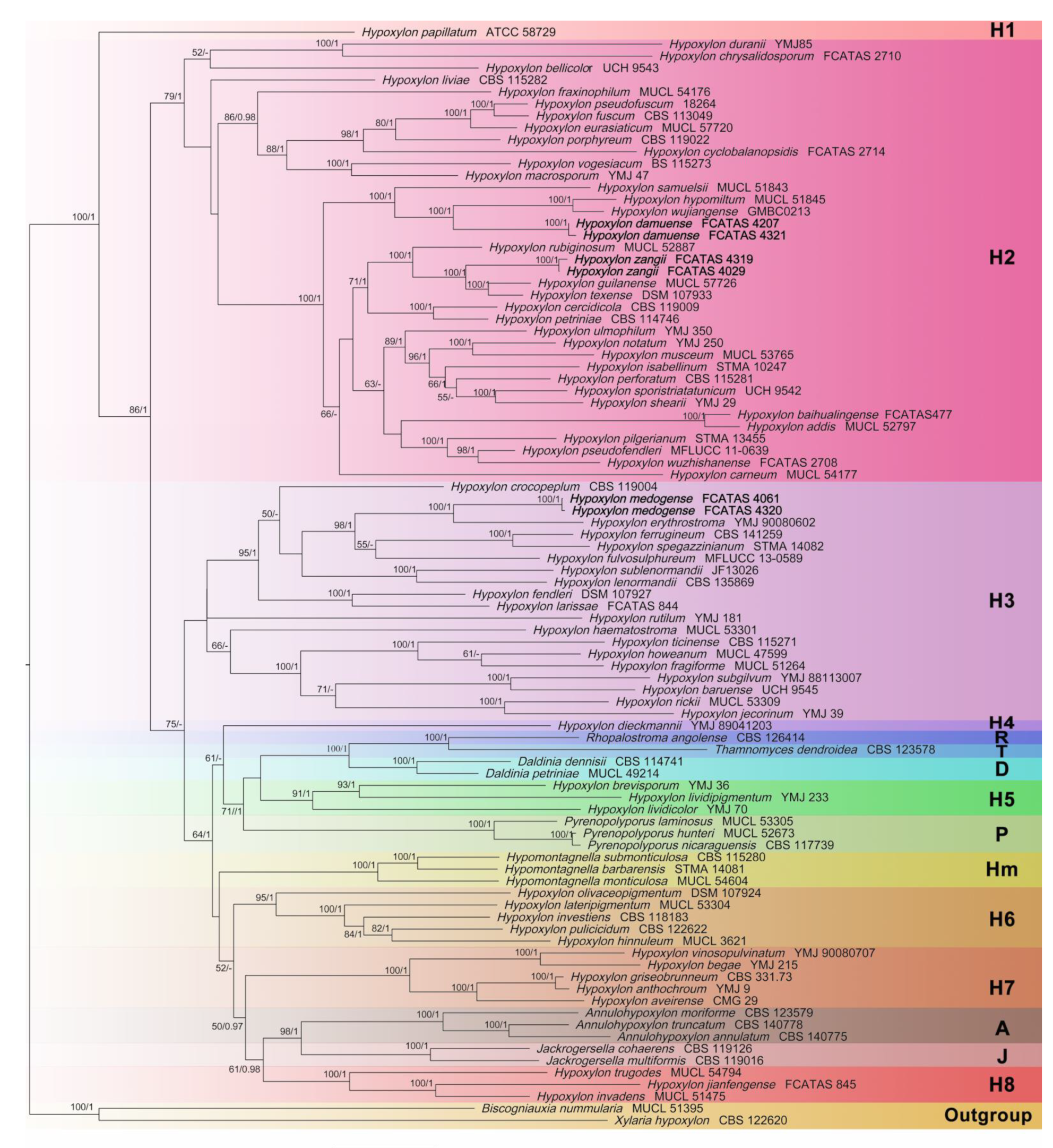
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis
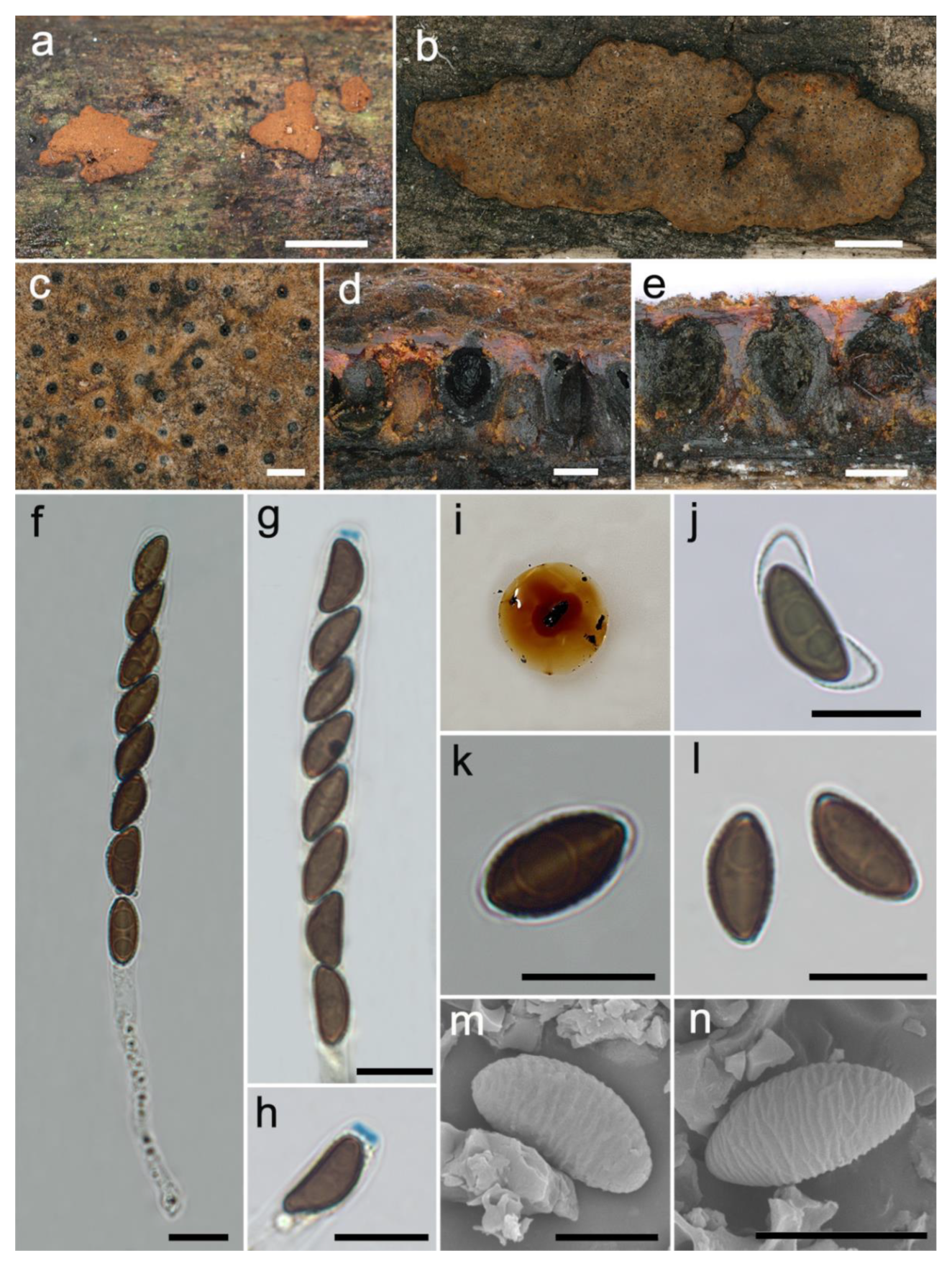
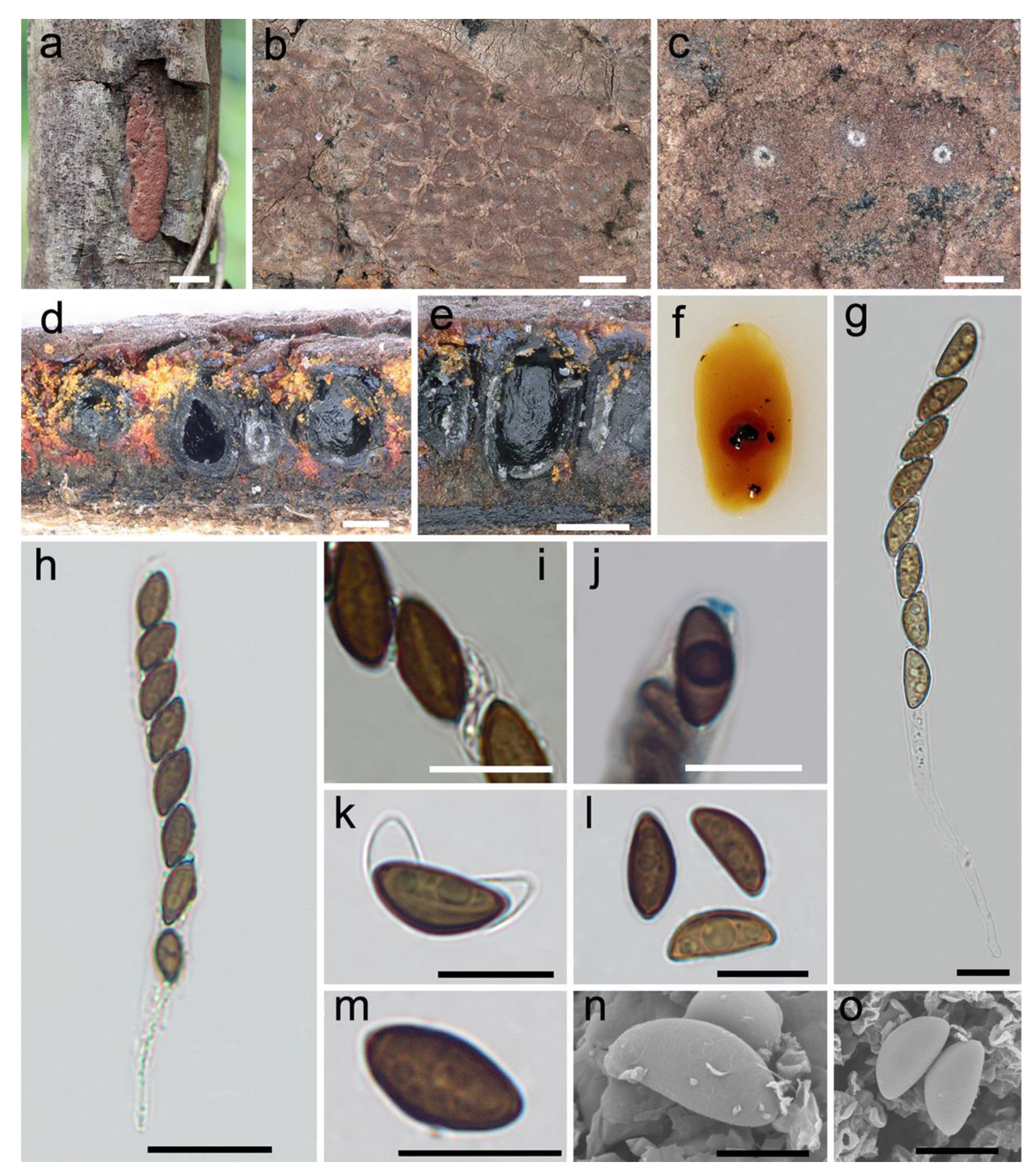
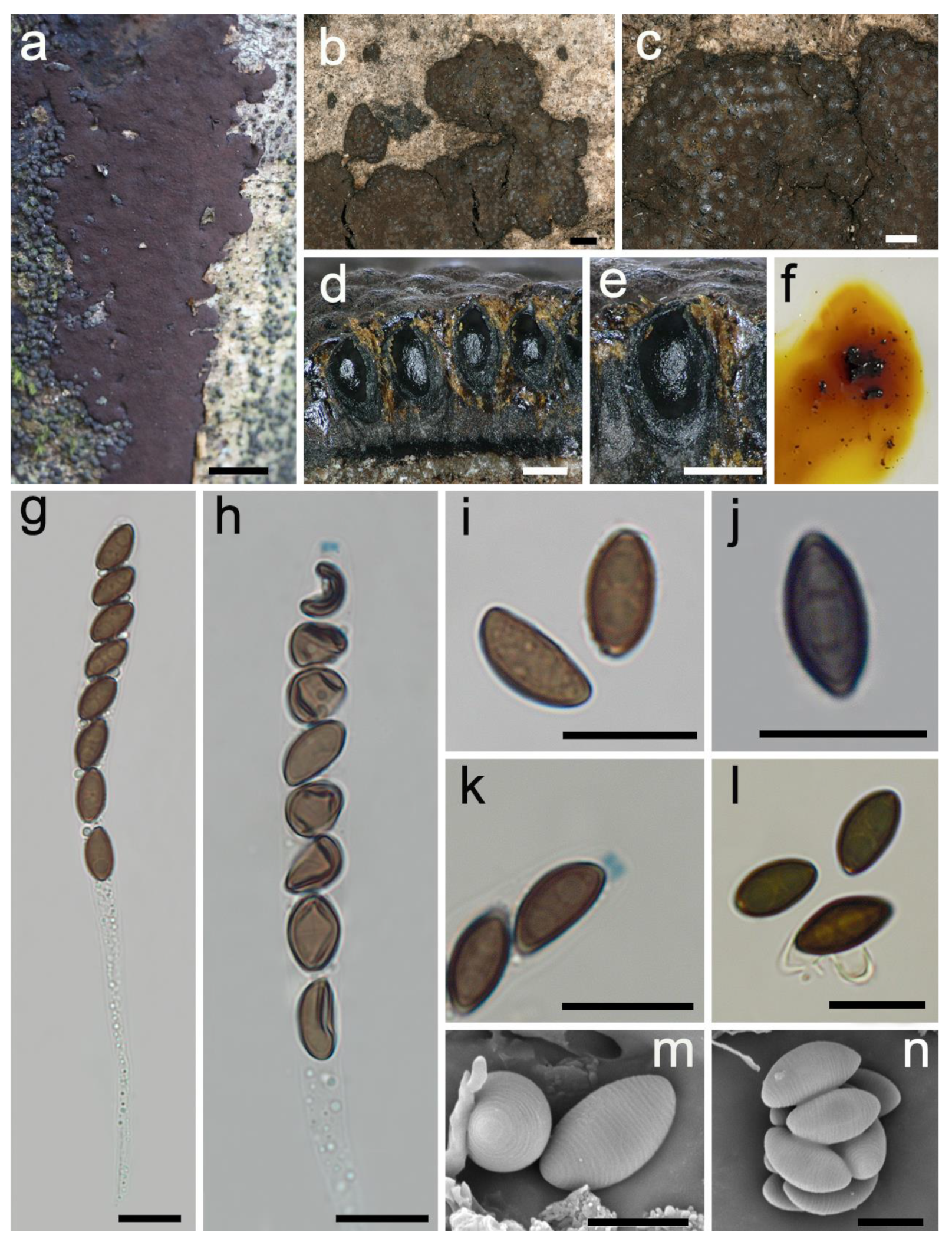
3.2. Taxonomy
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stadler, M.; Fournier, J. Pigment chemistry, taxonomy and phylogeny of the Hypoxyloideae (Xylariaceae). Rev. Iberoam. Micol. 2006, 23, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendt, L.; Sir, E.B.; Kuhnert, E.; Heitkämper, S.; Lambert, C.; Hladki, A.I.; Romero, A.I.; Luangsaard, J.J.; Srikitikulchai, P.; Per, D.; et al. Resurrection and emendation of the Hypoxylaceae, recognised from a multigene phylogeny of the Xylariales. Mycol. Prog. 2018, 17, 115–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhnert, E.; Navarro-Muñoz, J.C.; Becker, K.; Stadler, M.; Collemare, J.; Cox, R.J. Secondary metabolite biosynthetic diversity in the fungal family Hypoxylaceae and Xylaria hypoxylon. Stud. Mycol. 2021, 99, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyde, K.D.; Norphanphoun, C.; Maharachchikumbura, S.S.N.; Bhat, D.J.; Jones, E.B.G.; Bundhun, D.; Chen, Y.J.; Bao, D.-F.; Boonmee, S.; Calabon, M.; et al. Refined families of Sordariomycetes. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 305–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pažoutová, S.; Follert, S.; Bitzer, J.; Keck, M.; Surup, F.; Šrůtka, P.; Holuša, J.; Stadler, M. A new endophytic insect-associated Daldinia species, recognised from a comparison of secondary metabolite profiles and molecular phylogeny. Fungal Divers. 2013, 60, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pažoutová, S.; Šrůtka, P.; Holuša, J.; Chudickova, M.; Kolarik, M. The phylogenetic position of Obolarina dryophila (Xylariales). Mycol. Prog. 2010, 9, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pažoutová, S.; Šrůtka, P.; Holuša, J.; Chudíčková, M.; Kolařík, M. Diversity of xylariaceous symbionts in Xiphydria woodwasps: Role of vector and a host tree. Fungal Ecol. 2010, 3, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.D. Thoughts and musings on tropical Xylariaceae. Mycol. Res. 2000, 104, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnert, E.; Fournier, J.; Per, D.; Luangsaard, J.J.D.; Stadler, M. New Hypoxylon species from Martinique and new evidence on the molecular phylogeny of Hypoxylon based on ITS rDNA and β-tubulin data. Fungal Divers. 2014, 64, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, J.; Lechat, C.; Courtecuisse, R. The genus Hypoxylon (Xylariaceae) in Guadeloupe and Martinique (French West Indies). Ascomycete. Org. 2016, 7, 145–212. [Google Scholar]
- Sir, E.B.; Kuhnert, E.; Lambert, C.; Hladki, A.I.; Romero, A.I.; Stadler, M. New species and reports of Hypoxylon from Argentina recognized by a polyphasic approach. Mycol. Prog. 2016, 15, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.M.; Rogers, J.D. A Revision of the Genus Hypoxylon; American Phytopathological Society Press: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1996; p. 365. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, H.; Ju, Y.M.; Rogers, J.D. Molecular phylogeny of Hypoxylon and closely related genera. Mycologia 2005, 97, 844–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, M. Importance of secondary metabolites in the Xylariaceae as parameters for assessment of their taxonomy, phylogeny, and functional biodiversity. Curr. Res. Envion. Appl. Mycol. 2011, 1, 75–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourmoghaddam, M.J.; Lambert, C.; Surup, F.; Khodaparast, S.A.; Krisai-Greilhuber, I.; Voglmayr, H.; Stadler, M. Discovery of a new species of the Hypoxylon rubiginosum complex from Iran and antagonistic activities of Hypoxylon spp. Against the Ash Dieback pathogen, Hymenoscyphus fraxineus, in dual culture. MycoKeys 2020, 66, 105–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Index Fungorum. Available online: http://www.indexfungorum.org/names/names.asp (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- Chi, S.Q.; Xu, J.; Lu, B.S. Three New Chinese Records of Hypoxylon. J. Fungal Res. 2016, 14, 218–221. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.X.; Qiu, J.Z.; Xu, B.; Li, Y. Two Hypoxylon species from Yunnan Province based on morphological and molecular characters. Phytotaxa 2018, 376, 027–036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, Y.H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.L.; Long, Q.D.; Shen, X.C.; Kang, Y.Q.; Hyde, K.D.; Boonmee, S.; Kang, J.C.; Li, Q.R. Contributions to species of Xylariales in China—4 Hypoxylon wujiangensis sp. nov. Phytotaxa 2020, 455, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Song, Z.; Pan, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Qu, Z. Multi-gene phylogeny and taxonomy of Hypoxylon (Hypoxylaceae, Ascomycota) from China. Diversity 2022, 14, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.K.; Pan, X.Y.; Li, C.T.; Ma, H.X.; Li, Y. Two new species of Hypoxylon (Hypoxylaceae) from China based on morphological and DNA sequence data analyses. Phytotaxa 2022, 538, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Zhu, R.J.; Zhao, G.F. Utilization of wild plant resources and development suggestions of agricultural industry in Motuo tropical area of Tibet. Chin. J. Trop. Agric. 2022, 42, 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Friebes, G.; Wendelin, I. Studies on Hypoxylon ferrugineum (Xylariaceae), a rarely reported species collected in the urban area of Graz (Austria). Ascomycete. Org. 2016, 8, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Rayner, R.W. A Mycological Colour Chart; Cmi. & British Mycological Society Kew: London, UK, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhnert, E.; Sir, E.B.; Lambert, C.; Hyde, K.D.; Hladki, A.I.; Romero, A.I.; Rohde, M.; Stadler, M. Phylogenetic and chemotaxonomic resolution of the genus Annulohypoxylon (Xylariaceae) including four new species. Fungal Divers. 2017, 85, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS primers with enhanced specificity for basidiomycetes-application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol. Eco. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O‘donnell, K.; Cigelnik, E. Two divergent intragenomic rDNA ITS2 types within a monophyletic lineage of the fungus Fusarium are nonorthologous. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1997, 7, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.D.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J.W. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics—science direct. PCR Protoc. 1990, 18, 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Vilgalys, R.; Hester, M. Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 4238–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.J.; Whelen, S.; Hall, B.D. Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetes: Evidence from an RNA polymerse II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: A maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 1981, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedeño-Sanchez, M.; Wendt, L.; Stadler, M.; Mejía, L.C. Three new species of Hypoxylon and new records of Xylariales from Panama. Mycosphere 2020, 11, 1457–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stadler, M.; Læssøe, T.; Fournier, J.; Decock, C.; Schmieschek, B.; Tichy, H.V.; Peršoh, D. A polyphasic taxonomy of Daldinia (Xylariaceae). Stud. Mycol. 2014, 77, 1–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambert, C.; Wendt, L.; Hladki, A.I.; Stadler, M.; Sir, E.B. Hypomontagnella (Hypoxylaceae): A new genus segregated from Hypoxylon by a polyphasic taxonomic approach. Mycol. Prog. 2019, 18, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, T.F.L.; Goncalves, M.F.M.; Brandao, C.; Fidalgo, C.; Alves, A. Diversity of fungi associated with macroalgae from an estuarine environment and description of Cladosporium rubrum sp. nov. and Hypoxylon aveirense sp. nov. Int. J Syst. Evol. Micr. 2021, 71, 004630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, C.; Pourmoghaddam, M.J.; Cedeño‒Sanchez, M.; Surup, F.; Khodaparast, S.A.; Krisai-Greilhuber, I.; Voglmayr, H.; Stradal, T.E.B.; Stadler, M. Resolution of the Hypoxylon fuscum complex (Hypoxylaceae, Xylariales) and discovery and biological characterization of two of its prominent secondary metabolites. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sir, E.B.; Becker, K.; Lambert, C.; Bills, G.F.; Kuhnert, E. Observations on Texas hypoxylons, including two new Hypoxylon species and widespread environmental isolates of the H. croceum complex identified by a polyphasic approach. Mycologia 2019, 11, 832–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sir, E.B.; Kuhnert, E.; Surup, F.; Hyde, K.D.; Stadler, M. Discovery of new mitorubrin derivatives from Hypoxylon fulvosulphureum sp. nov. (Ascomycota, Xylariales). Mycol. Prog. 2015, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.; Groenewald, M.; Vries, M.; Gehrmann, T.; Stielow, B.; Eberhardt, U.; Al-Hatmi, A.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Cardinali, G.; Houbraken, J.; et al. Large-scale generation and analysis of filamentous fungal DNA barcodes boosts coverage for kingdom fungi and reveals thresholds for fungal species and higher taxon delimitation. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 92, 135–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitzer, J.; Læssøe, T.; Fournier, J.; Kummer, V.; Decock, C.; Tichy, H.V.; Piepenbring, M.; Peršoh, D.; Stadler, M. Affinities of Phylacia and the daldinoid Xylariaceae, inferred from chemotypes of cultures and ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycol. Res. 2008, 112, 251–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Lambert, C.; Wieschhaus, J.; Stadler, M. Phylogenetic assignment of the fungicolous Hypoxylon invadens (Ascomycota, Xylariales) and investigation of its secondary metabolites. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhnert, E.; Surup, F.; Sir, E.B.; Lambert, C.; Hyde, K.D.; Hladki, A.I.; Romero, A.I.; Stadler, M. Lenormandins A—G, new azaphilones from Hypoxylon lenormandii and Hypoxylon jaklitschii sp. nov., recognised by chemotaxonomic data. Fungal Divers. 2015, 71, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.Q.; Phookamsak, R.; Wijayawardene, N.N.; Li, W.J.; Bhat, D.J.; Xu, J.C.; Taylor, J.E.; Hyde, K.D.; Chukeatirote, E. Bambusicolous fungi. Fungal Divers. 2017, 82, 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bills, G.F.; González-Menéndez, V.; Martín, J.; Platas, G.; Fournier, J.; Peršoh, D.; Stadler, M. Hypoxylon pulicicidum sp. nov. (Ascomycota, Xylariales), a pantropical insecticide-producing endophyte. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, M.; Kuhnert, E.; Peršoh, D.; Fournier, J. The Xylariaceae as model example for a unified nomenclature following the “One Fungus-One Name” (1F1N) concept. Mycology 2013, 4, 5–21. [Google Scholar]
- Stadler, M.; Fournier, J.; Laessøe, T.; Chlebicki, A.; Lechat, C.; Flessa, F.; Rambold, G.; Peršoh, D. Chemotaxonomic and phylogenetic studies of Thamnomyces (Xylariaceae). Mycoscience 2010, 51, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, M.; Fournier, J.; Beltrán-Tejera, E.; Granmo, A. The “red Hypoxylons” of the temperate and subtropical Northern Hemisphere. N. Am. Fungi 2008, 3, 73–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.C.; Yang, Z.L.; Cui, B.K.; Wu, G.; Yuan, H.S.; Zhou, L.W.; He, S.H.; Ge, Z.W.; Wu, F.; Wei, Y.L.; et al. Diversity and systematics of the important macrofungi in Chinese forests. Mycosystema 2021, 40, 770–805. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Chen, S.L.; Dai, Y.C.; Jia, Z.F.; Li, T.H.; Liu, T.Z.; Phurbu, D.; Mamut, R.; Sun, G.Y.; Bau, T.; et al. Overview of China’ s nomenclature novelties of fungi in the new century (2000–2020). Mycosystema 2021, 40, 822–833. [Google Scholar]


| Species Name | Specimen No. | Locality | GenBank Accession No. | References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | LSU | RPB2 | β-Tubulin | Status | ||||
| Annulohypoxylon annulatum | CBS 140775 | USA | KU604559 | KY610418 | KY624263 | KX376353 | ET | [2,11,25] |
| A. moriforme | CBS 123579 | Martinique | KX376321 | KY610425 | KY624289 | KX271261 | [25] | |
| A. truncatum | CBS 140778 | USA | KX376329 | KY610419 | KY624277 | KX376352 | ET | [2,25] |
| Daldinia dennisii | CBS 114741 | Australia | JX658477 | KY610435 | KY624244 | KC977262 | T | [2,9,34] |
| D. petriniae | MUCL 49214 | Austria | JX658512 | KY610439 | KY624248 | KC977261 | ET | [2,9,34] |
| Hypomontagnella barbarensis | STMA 14081 | Argentina | MK131720 | MK131718 | MK135891 | MK135893 | T | [35] |
| Hypom. monticulosa | MUCL 54604 | French Guiana | KY610404 | KY610487 | KY624305 | KX271273 | ET | [2] |
| Hypom. submonticulosa | CBS 115280 | France | KC968923 | KY610457 | KY624226 | KC977267 | [2,9] | |
| Hypoxylon addis | MUCL 52797 | Ethiopia | KC968931 | N/A | N/A | KC977287 | T | [9] |
| H. anthochroum | YMJ 9 | Mexico | JN660819 | N/A | N/A | AY951703 | [13] | |
| H. aveirense | CMG 29 | Portugal | MN053021 | N/A | N/A | MN066636 | T | [36] |
| H.baihualingense | FCATAS 477 | China | MG490190 | N/A | N/A | MH790276 | T | [18] |
| H.baruense | UCH 9545 | Panama | MN056428 | N/A | N/A | MK908142 | [32] | |
| H. begae | YMJ 215 | USA | JN660820 | N/A | N/A | AY951704 | [13] | |
| H. bellicolor | UCH 9543 | Panama | MN056425 | N/A | N/A | MK908139 | [32] | |
| H. brevisporum | YMJ 36 | Puerto Rico | JN660821 | N/A | N/A | AY951705 | [13] | |
| H. carneum | MUCL 54177 | France | KY610400 | KY610480 | KY624297 | KX271270 | [2] | |
| H. cercidicola | CBS 119009 | France | KC968908 | KY610444 | KY624254 | KX271270 | [2,9] | |
| H. chrysalidosporum | FCATAS 2710 | China | OL467294 | OL615106 | OL584222 | OL584229 | T | [20] |
| H. crocopeplum | CBS 119004 | France | KC968907 | KY610445 | KY624255 | KC977268 | [2] | |
| H. cyclobalanopsidis | FCATAS 2714 | China | OL467298 | OL615108 | OL584225 | OL584232 | T | [20] |
| H. damuense | FCATAS4207 | China | ON075427 | ON075433 | ON093251 | ON093245 | T | This study |
| H. damuense | FCATAS4321 | China | ON075428 | ON075434 | ON093252 | ON093246 | This study | |
| H. dieckmannii | YMJ 89041203 | China | JN979413 | N/A | N/A | AY951713 | [13] | |
| H. duranii | YMJ 85 | China | JN979414 | N/A | N/A | AY951714 | [13] | |
| H. erythrostroma | YMJ 90080602 | China | JN979416 | N/A | N/A | AY951716 | [13] | |
| H. eurasiaticum | MUCL 57720 | Iran | MW367851 | N/A | MW373852 | MW373861 | [37] | |
| H. fendleri | DSM 107927 | USA | MK287533 | MK287545 | MK287558 | MK287571 | [38] | |
| H. ferrugineum | CBS 141259 | Austria | KX090079 | N/A | N/A | KX090080 | [23] | |
| H. fragiforme | MUCL 51264 | Germany | KM186294 | KM186295 | KM186296 | KM186293 | ET | [38] |
| H. fraxinophilum | MUCL 54176 | France | KC968938 | N/A | N/A | KC977301 | ET | [9] |
| H. fulvosulphureum | MFLUCC 13-0589 | Thailand | KP401576 | N/A | N/A | KP401584 | T | [39] |
| H. fuscum | CBS 113049 | France | KY610401 | KY610482 | KY624299 | KX271271 | ET | [2] |
| H. griseobrunneum | CBS 331.73 | India | KY610402 | MH872399 | KY624300 | KC977303 | T | [2,9,40] |
| H. guilanense | MUCL 57726 | Iran | MT214997 | MT214992 | MT212235 | MT212239 | T | [15] |
| H. haematostroma | MUCL 53301 | Martinique | KC968911 | KY610484 | KY624301 | KC977291 | ET | [35] |
| H. hinnuleum | MUCL 3621 | USA | MK287537 | MK287549 | MK287562 | MK287575 | T | [38] |
| H. howeanum | MUCL 47599 | Germany | AM749928 | KY610448 | KY624258 | KC977277 | [2,9,41] | |
| H. hypomiltum | MUCL 51845 | Guadeloupe | KY610403 | KY610449 | KY624302 | KX271249 | [2] | |
| H. invadens | MUCL 51475 | France | MT809133 | MT809132 | MT813037 | MT813038 | T | [42] |
| H. investiens | CBS 118183 | Malaysia | KC968925 | KY610450 | KY624259 | KC977270 | [2,9] | |
| H. isabellinum | STMA 10247 | Martinique | KC968935 | N/A | N/A | KC977295 | T | [9] |
| H. jecorinum | YMJ 39 | Mexico | JN979429 | N/A | N/A | AY951731 | [13] | |
| H.jianfengense | FACATAS845 | China | MW984546 | MZ029707 | MZ047260 | MZ047264 | T | [21] |
| H. larissae | FACATAS844 | China | MW984548 | MZ029706 | MZ047258 | MZ047262 | T | [21] |
| H. lateripigmentum | MUCL 53304 | Martinique | KC968933 | KY610486 | KY624304 | KC977290 | T | [2,9] |
| H. lenormandii | CBS 135869 | Cameroon | KY610390 | KY610453 | KY624262 | KM610295 | [2,43] | |
| H. liviae | CBS 115282 | Norway | NR155154 | N/A | N/A | KC977265 | ET | [9] |
| H. lividicolor | YMJ 70 | China | JN979432 | N/A | N/A | AY951734 | [13] | |
| H. lividipigmentum | YMJ 233 | Mexico | JN979433 | N/A | N/A | AY951735 | [13] | |
| H. macrosporum | YMJ 47 | Canada | JN979434 | N/A | N/A | AY951736 | [13] | |
| H. medogense | FCATAS4061 | China | ON075425 | ON075431 | ON093249 | ON093243 | T | This study |
| H. medogense | FCATAS4320 | China | ON075426 | ON075432 | ON093250 | ON093244 | This study | |
| H. musceum | MUCL 53765 | Guadeloupe | KC968926 | KY610488 | KY624306 | KC977280 | [2,9] | |
| H. notatum | YMJ 250 | USA | JQ009305 | N/A | N/A | AY951739 | [13] | |
| H. olivaceopigmentum | DSM 10792 | USA | MK287530 | MK287542 | MK287555 | MK287568 | T | [38] |
| H. papillatum | ATCC 58729 | USA | NR155153 | KY610454 | KY624223 | KC977258 | T | [2,9] |
| H. perforatum | CBS 115281 | France | KY610391 | KY610455 | KY624224 | KX271250 | [2] | |
| H. petriniae | CBS 114746 | France | NR155185 | KY610491 | KY624279 | KX271274 | T | [2] |
| H. pilgerianum | STMA 13455 | Martinique | KY610412 | N/A | KY624308 | KY624315 | [2] | |
| H. porphyreum | CBS 119022 | France | KC968921 | KY610456 | KY624225 | KC977264 | [2,9] | |
| H. pseudofendleri | MFLUCC 11-0639 | Thailand | KU940156 | KU863144 | N/A | N/A | [44] | |
| H. pseudofuscum | 18264 | Germany | MW367857 | MW367848 | MW373858 | MW373867 | T | [37] |
| H. pulicicidum | CBS 122622 | Martinique | JX183075 | KY610492 | KY624280 | JX183072 | T | [2,45] |
| H. rickii | MUCL 53309 | Martinique | KC968932 | KY610416 | KY624281 | KC977288 | ET | [2] |
| H. rubiginosum | MUCL 52887 | Germany | KC477232 | KY610469 | KY624266 | KY624311 | ET | [2,46] |
| H. rutilum | YMJ 181 | France | N/A | N/A | N/A | AY951752 | [13] | |
| H. samuelsii | MUCL 51843 | Guadeloupe | KC968916 | KY610466 | KY624269 | KC977286 | ET | [2,9] |
| H. shearii | YMJ 29 | Mexico | EF026142 | N/A | N/A | AY951753 | [13] | |
| H. spegazzinianum | STMA 14082 | Argentina | KU604573 | N/A | N/A | KU604582 | T | [11] |
| H. sporistriatatunicum | UCH 9542 | Panama | MN056426 | N/A | N/A | MK908140 | T | [32] |
| H. subgilvum | YMJ 88113007 | China | JQ009315 | N/A | N/A | AY951755 | [13] | |
| H. sublenormandii | JF 13026 | Sri Lanka | KM610291 | N/A | N/A | KM610303 | T | [43] |
| H. texense | DSM 107933 | USA | MK287536 | MK287548 | MK287561 | MK287574 | T | [38] |
| H. ticinense | CBS 115271 | France | JQ009317 | KY610471 | KY624272 | AY951757 | [2,13] | |
| H. trugodes | MUCL 54794 | Sri Lanka | KF234422 | NG066380 | KY624282 | KF300548 | ET | [2,9] |
| H. ulmophilum | YMJ 350 | Russia | JQ009320 | N/A | N/A | AY951760 | [13] | |
| H. vogesiacum | CBS 115273 | France | KC968920 | KY610417 | KY624283 | KX271275 | [2] | |
| H. wujiangense | GMBC0213 | China | MT568854 | MT568853 | MT585802 | MT572481 | T | [19] |
| H. wuzhishanense | FCATAS2708 | China | OL467292 | OL615104 | OL584220 | OL584227 | T | [20] |
| H. zangii | FCATAS4029 | China | ON075423 | ON075429 | ON093247 | ON093241 | T | This study |
| H. zangii | FCATAS4319 | China | ON075424 | ON075430 | ON093248 | ON093242 | This study | |
| Jackrogersella cohaerens | CBS 119126 | Germany | KY610396 | KY610497 | KY624270 | KY624314 | [2] | |
| J. multiformis | CBS 119016 | Germany | KC477234 | KY610473 | KY624290 | KX271262 | ET | [2,9] |
| Pyrenopolyporus hunteri | MUCL 52673 | Ivory Coast | KY610421 | KY610472 | KY624309 | KU159530 | ET | [2,25] |
| P. laminosus | MUCL 53305 | Martinique | KC968934 | KY610485 | KY624303 | KC977292 | T | [2,9] |
| P. nicaraguensis | CBS 117739 | Burkina Faso | AM749922 | KY610489 | KY624307 | KC977272 | [2,9,41] | |
| Rhopalostroma angolense | CBS 126414 | Ivory Coas | KY610420 | KY610459 | KY624228 | KX271277 | [2] | |
| Thamnomyces dendroidea | CBS 123578 | French Guiana | FN428831 | KY610467 | KY624232 | KY624313 | T | [2,47] |
| Xylaria hypoxylon | CBS 122620 | Sweden | KY610407 | KY610495 | KY624231 | KX271279 | ET | [2] |
| Biscogniauxia nummularia | MUCL 51395 | France | KY610382 | KY610427 | KY624236 | KX271241 | [2] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Z.-K.; Zhu, A.-H.; Liu, Z.-D.; Qu, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.-X. Three New Species of Hypoxylon (Xylariales, Ascomycota) on a Multigene Phylogeny from Medog in Southwest China. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8050500
Song Z-K, Zhu A-H, Liu Z-D, Qu Z, Li Y, Ma H-X. Three New Species of Hypoxylon (Xylariales, Ascomycota) on a Multigene Phylogeny from Medog in Southwest China. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(5):500. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8050500
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Zi-Kun, An-Hong Zhu, Zhen-Dong Liu, Zhi Qu, Yu Li, and Hai-Xia Ma. 2022. "Three New Species of Hypoxylon (Xylariales, Ascomycota) on a Multigene Phylogeny from Medog in Southwest China" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 5: 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8050500
APA StyleSong, Z.-K., Zhu, A.-H., Liu, Z.-D., Qu, Z., Li, Y., & Ma, H.-X. (2022). Three New Species of Hypoxylon (Xylariales, Ascomycota) on a Multigene Phylogeny from Medog in Southwest China. Journal of Fungi, 8(5), 500. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8050500





