Reprogramming of Fundamental miRNA and Gene Expression during the Barley-Piriformospora indica Interaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. P. indica and Barley Cultivation and Inoculation
2.2. Small RNA Library Construction and Sequencing
2.3. Novel miRNA Prediction
2.4. Co-Expression Analysis of mRNA-miRNA
2.5. GO and KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
2.6. Quantitative Real Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) and Stem-Loop PCR for Validation of Sequencing Results
3. Results
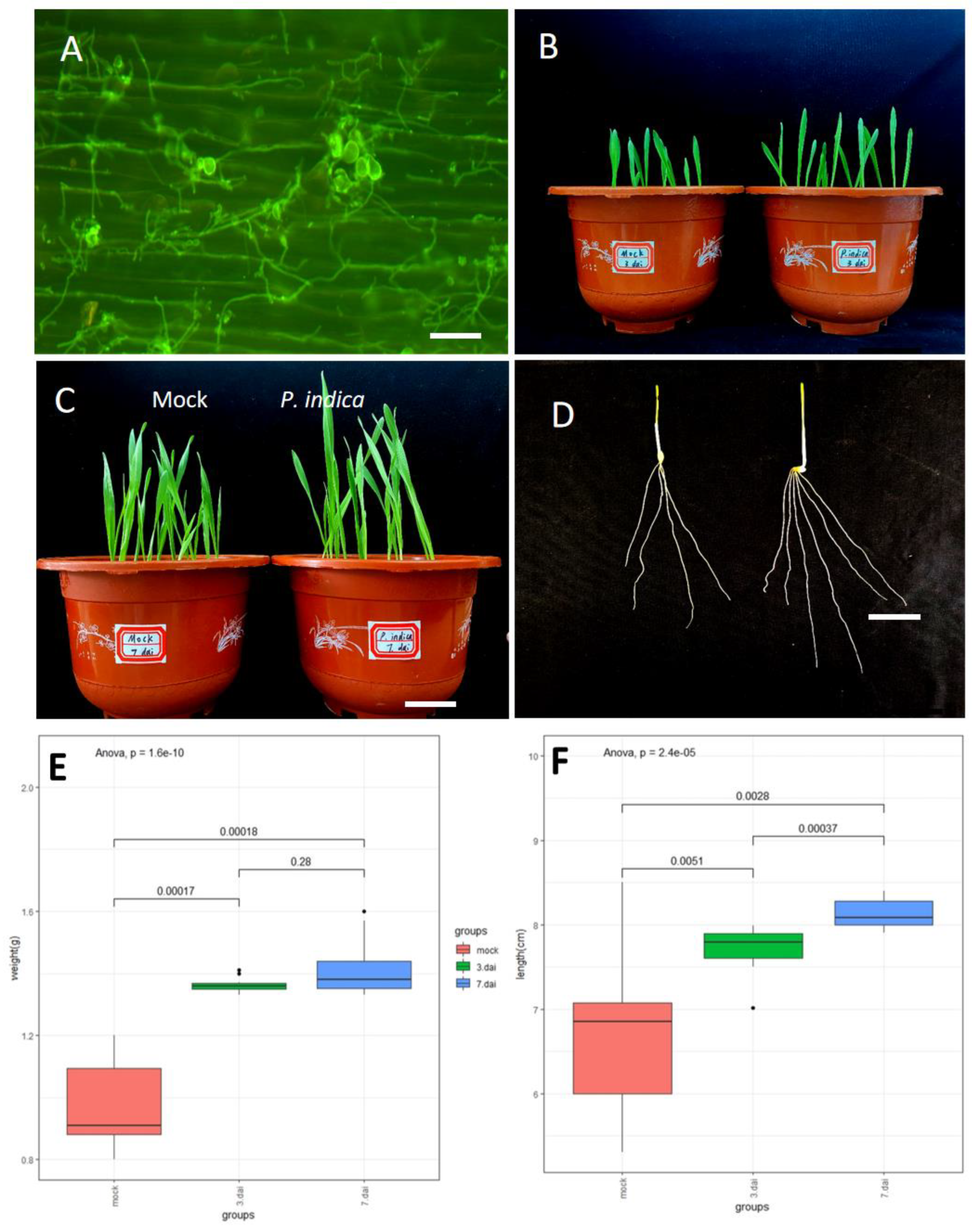
3.1. P. indica Promote Root Growth and Plant Development
3.2. Establishment of the Barley–P. indica Interaction Is Associated with Extensive Transcriptional Reprogramming
3.3. Differentially Expressed miRNAs
3.4. Expression Patterns of miRNAs and Their Putative Targets in P. indica—Colonized Roots
3.5. Prediction of miRNA Target Genes
3.6. Identification of miRNAs Related to Transcription Factor and Other Key Pathway Regulation in Barley Roots Colonization by P. indica
3.7. MiRNA–mRNA Interaction
4. Discussion
4.1. Transcriptional Changes Detected during the Barley–P. indica Interaction
4.2. Barley miRNAs Detected in the Barley–P. indica Interaction
4.3. MiRNA and Target mRNA
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fesel, P.H.; Zuccaro, A. Dissecting endophytic lifestyle along the parasitism/ mutualism continuum in Arabidopsis. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 32, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lagunas, B.; Schäfer, P.; Gifford, M.L. Housing helpful invaders: The evolutionary and molecular architecture underlying plant root-mutualist microbe interactions. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vishwakarma, K.; Kumar, N.; Shandilya, C.; Mohapatra, S.; Bhayana, S.; Varma, A. Revisiting plant-microbe interactions and microbial consortia application for enhancing sustainable agriculture: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Guo, N.; Feng, Y.; Duan, M.; Li, C. Effect of Piriformospora indica-induced systemic resistance and basal immunity against Rhizoctonia cerealis and Fusarium graminearum in wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 836940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Huckelhoven, R.; Schäfer, P.; Imani, J.; Sharma, M.; Weiss, M.; Waller, F.; Kogel, K.-H. The root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica requires host cell death for proliferation during mutualistic symbiosis with barley. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18450–18457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Bodjrenou, D.M.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Pan, H.; Yeh, K.W.; Lai, Z.; Cheng, C. The endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica reprograms banana to cold resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagonda, T.; Adil, M.F.; Sehar, S.; Rasheed, A.; Joan, H.I.; Ouyang, Y.; Shamsi, I.H. Physio-ultrastructural footprints and iTRAQ-based proteomic approach unravel the role of Piriformospora indica-colonization in counteracting cadmium toxicity in rice. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, A.; Mishra, S.; Kundu, P.; Jogawat, A.; Vadassery, J. Piriformospora indica recruits host-derived putrescine for growth promotion in plants. Plant Physiol. 2022, 188, 2289–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.D.; Senthil Kumar, R.; Shyur, L.F.; Cheng, Y.B.; Tian, Z.; Oelmüller, R.; Yeh, K.W. Metabolomic compounds identified in Piriformospora indica-colonized Chinese cabbage roots delineate symbiotic functions of the interaction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atia, M.A.M.; Abdeldaym, E.A.; Abdelsattar, M.; Ibrahim, D.S.S.; Saleh, I.; Elwahab, M.A.; Osman, G.H.; Arif, I.A.; Abdelaziz, M.E. Piriformospora indica promotes cucumber tolerance against Root-knot nematode by modulating photosynthesis and innate responsive genes. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, A.; Vadassery, J. Molecular mechanisms of Piriformospora indica mediated growth promotion in plants. Plant Signal Behav. 2022, 17, 2096785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Cao, J.L.; Zou, Y.N.; Wu, Q.S.; Kuca, K. Piriformospora indica: A root endophytic fungus and its roles in plants. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobo. 2020, 48, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simon, S.A.; Meyers, B.C.; Sherrier, D.J. MicroRNAs in the rhizobia legume symbiosis. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lai, E.C. miRNAs: Whys and wherefores of miRNA-mediated regulation. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.L.; Wang, M.Z.; Qiu, X.X.; Zhou, H.; Lu, S.F. Noncoding RNAs in medicinal plants and their regulatory roles in bioactive compound production. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2020, 22, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.Z. Computational detection of microRNAs targeting transcription factor genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2005, 29, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szittya, G.; Moxon, S.; Santos, D.M.; Jing, R.; Fevereiro, M.P.; Moulton, V.; Dalmay, T. High throughput sequencing of Medicago truncatula short RNAs identifies eight new miRNA families. BMC Genomics. 2008, 9, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voinnet, O. Origin, biogenesis, and activity of plant microRNAs. Cell 2008, 136, 669–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, S.; Fu, Y.; Sunkar, R.; Barbazuk, W.B.; Zhu, J.K.; Yu, O. Novel and nodulation-regulated microRNAs in soybean roots. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lelandais-Briere, C.; Naya, L.; Sallet, E.; Calenge, F.; Frugier, F.; Hartmann, C.; Gouzy, J.; Crespi, M. Genome-wide Medicago truncatula small RNA analysis revealed novel microRNAs and isoforms differentially regulated in roots and nodules. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2780–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branscheid, A.; Sieh, D.; Pant, B.D.; May, P.; Devers, E.A.; Elkrog, A.; Schauser, L.; Scheible, W.R.; Krajinski, F. Expression pattern suggests a role of MiR399 in the regulation of the cellular response to local Pi increase during arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Mol. Plant Microbe. Interact. 2010, 23, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devers, E.A.; Branscheid, A.; May, P.; Krajinski, F. Stars and symbiosis: microRNA and microRNA-mediated transcript cleavage involved in arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1990–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Combier, J.P.; Frugier, F.; de Billy, F.; Boualem, A.; El-Yahyaoui, F.; Moreau, S.; Vernié, T.; Ott, T.; Gamas, P.; Crespi, M.; et al. MtHAP2-1 is a key transcriptional regulator of symbiotic nodule development regulated by microRNA169 in Medicago truncatula. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 3084–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Duan, Y.J.; Sun, N.L.; Wang, L.; Feng, S.S.; Fang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.P. The miR169n-NF-YA8 regulation module involved in drought resistance in Brassica napus L. Plant Sci. 2021, 313, 111062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.J.; Zhu, M.; Luan, M.D.; Zhang, M.; Jin, L.; Liu, Y.P.; Zou, J.J.; Wang, L.; Xu, M.Y. miR169q and nuclear factor YA8 enhance salt tolerance by activating PEROXIDASE1 expression in response to ROS. Plant Physiol. 2022, 188, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Hong, Y.H.; Liu, Y.R.; Cui, J.; Luan, Y.S. Function identification of miR394 in tomato resistance to Phytophthora infestans. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomkowiak, A.; Jędrzejewski, T.; Spychała, J.; Kuczyński, J.; Kwiatek, M.T.; Tyczewska, A.; Skowrońska, R.; Twardowski, T. Analysis of miRNA expression associated with the Lr46 gene responsible for APR resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Appl. Genet. 2020, 61, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Wu, J.D.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Xu, W.J.; Li, Y.; Xie, J.B. Genome-wide analysis of coding and non-coding RNA reveals a conserved miR164-NAC-mRNA regulatory pathway for disease defense in Populus. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 668940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Shen, C.H.; Lin, Y.; Chen, P.J.; Xu, X.; Oelmuller, R.; Yeh, K.W.; Lai, Z.X. Growth promotion-related miRNAs in Oncidium Orchid roots colonized by the endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica. PLoS ONE. 2014, 9, e84920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šečić, E.; Zanini, S.; Wibberg, D.; Jelonek, L.; Busche, T.; Kalinowski, J.; Nasfi, S.; Thielmann, J.; Imani, J.; Steinbrenner, J.; et al. A novel plant-fungal association reveals fundamental sRNA and gene expression reprogramming at the onset of symbiosis. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, A.; Verma, S.; Sudha, X.; Sahay, N.; Bu¨tehorn, B.; Franken, P. Piriformospora indica, a cultivable plant-growth-promoting root endophyte. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 2741–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. DEGseq: An R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedländer, M.R.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Li, N.; Chen, W.; Rajewsky, N. miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 40, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wani, N.; Barh, D.; Raza, K. Modular network inference between miRNA-mRNA expression profiles using weighted co-expression network analysis. J. Integr. Bioinform. 2021, 18, 20210029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavorgna, G.; Guffanti, A.; Borsani, G.; Ballabio, A.; Boncinelli, E. TargetFinder: Searching annotated sequence databases for target genes of transcription factors. Bioinformatics 1999, 15, 172–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cline, M.S.; Smoot, M.; Cerami, E.; Kuchinsky, A.; Landys, N.; Workman, C.; Christmas, R.; Avila-Campilo, I.; Creech, M.; Gross, B.; et al. Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using Cytoscape. Nature Protocol. 2007, 2, 2366–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Xiao, C.; Li, H.; Wu, W.; Du, W.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, C. SYBR Green real-time qPCR method: Diagnose drowning more rapidly and accurately. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2021, 321, 110720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ridzon, D.A.; Broomer, A.J.; Zhou, Z.; Lee, D.H.; Nguyen, J.T.; Barbisin, M.; Xu, N.; Mahuvakar, V.R.; Andersen, M.R.; et al. Realtime quantification of microRNAs by stem–loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.F. Stem-loop RT-qPCR for miRNAs. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2011, 95, Unit 15.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, A.H.; Akgül, B. Endogenous miRNA sponges. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2257, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bologna, N.G.; Voinnet, O. The diversity, biogenesis, and activities of endogenous silencing small RNAs in Arabidopsis. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 473–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ario, M.; Griffifiths-Jones, S.; Kim, M. Small RNAs: Big impact on plant development. Trends Plant Sci. 2017, 22, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khraiwesh, B.; Zhu, J.K.; Zhu, J. Role of miRNAs and siRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses of plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012, 1819, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, V.; Kumar, M.; Deep, D. A phosphate transporter from the root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica plays a role in phosphate transport to the host plant. J. Biol.Chem. 2010, 285, 26532–26544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narayan, O.P.; Verma, N.; Jogawat, A.; Dua, M.; Johri, A.K. Sulfur transfer from the endophytic fungus Serendipita indica improves maize growth andrequires the sulfate transporter SiSulT. Plant Cell 2021, 33, 1268–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baulcombe, D. RNA silencing in plants. Nature 2004, 431, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdarpasic, A.; Ruggenthaler, P. Analysis of miRNA expression under stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2012, 12, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X. Small RNAs in development—Insights from plants. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2012, 22, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, G.; Declerck, M.; Sorin, C.; Hartmann, C.; Crespi, M.; Lelandais-Brière, C. MicroRNAs as regulators of root development and architecture. Plant Mol. Bio. 2011, 177, 1573–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhang, Z.M.; Gao, J.; Zeng, X.; Pan, G.T. The role of miR319 in plant development regulation. Yi Chuan. 2011, 33, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunkar, R.; Li, Y.F.; Jagadeeswaran, G. Functions of microRNAs in plant stress responses. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, J.R.; Dalmay, T.; Bartels, D. The role of small RNAs in abiotic stress. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3592–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guleria, P.; Mahajan, M.; Bhardwaj, J.; Yadav, S.K. Plant small RNAs: Biogenesis, mode of action and their roles in abiotic stresses. Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2011, 9, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.J.; Zhong, Y.Q.; Qi, X. LncRNA TCONS_00021861 is functionally associated with drought tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) via competing endogenous RNA regulation. BMC Plant SBiol. 2021, 21, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Gene | Description | Log2FC | EXP |
|---|---|---|---|
| PIIN_mito_NAD4 | oxidoreductase activity | 16.468 | up |
| PIIN_mito_NAD2 | oxidoreductase activity | 11.841 | up |
| PIIN_mito_COX3 | membrane | 14.225 | up |
| PIIN_mito_ATP9 | ion transport | 13.467 | up |
| PIIN_mito_NAD5 | oxidoreductase activity | 13.356 | up |
| PIIN_mito_COX1 | Ion transmembrane transporter activity | 13.053 | up |
| PIIN_mito_NAD3 | oxidoreductase activity | 12.363 | up |
| PIIN_mito_COX2 | ion transmembrane transporter activity | 12.764 | up |
| PIIN_mito_COB | membrane | 12.641 | up |
| PIIN_mit_GIY1 | molecular_function | 12.236 | up |
| PIIN_mit_LAG4 | endonuclease activity | 11.708 | up |
| PIIN_mit_NAD2 | oxidoreductase activity | 11.65 | up |
| PIIN_08131 | phosphate transporter | 8.031 | up |
| PIIN_mit_LAG8 PIIN_mito_NAD6 PIIN_mito_NAD1 PIIN_mit_LAG7 PIIN_mito_ATP6 PIIN_05864 PIIN_03862 PIIN_mito_RPS3 | None oxidoreductase activity membrane endonuclease activity ion transport ion transport tRNA THr modification None | 11.505 11.444 11.201 11.166 11.087 10.883 10.583 10.045 | up up up up up up up up |
| Gene | Description | FC | EXP |
|---|---|---|---|
| PIIN_mito_NAD4 | cellular respiration | 16.297 | up |
| PIIN_09240 | None | 14.972 | up |
| PIIN_mito_COX3 | membrane | 13.926 | up |
| PIIN_mito_ATP9 | ion transport | 13.449 | up |
| PIIN_mito_NAD5 | cellular respiration | 13.182 | up |
| PIIN_mito_COX1 | Ion transmembrane transporter activity | 12.757 | up |
| PIIN_mito_NAD3 | oxidoreductase activity | 12.645 | up |
| PIIN_08131 | phosphate transporter | 12.531 | up |
| PIIN_mito_COX2 | ion transmembrane transporter activity | 12.391 | up |
| PIIN_mito_COB | membrane | 12.268 | up |
| PIIN_mito_NAD3 PIIN_mito_ATP6 PIIN_mit_GIY1 PIIN_03862 PIIN_mito_NAD6 PIIN_mit_NAD2 PIIN_mit_LAG7 PIIN_mito_NAD1 PIIN_mit_LAG8 PIIN_05864 PIIN_mito_RPS3 | oxidoreductase activity ion transport molecular_function tRNA THr modification oxidoreductase activity oxidoreductase activity endonuclease activity membrane None ion transport None | 12.363 11.975 11.899 11.875 11.858 11.841 11.62 11.379 10.883 10.596 10.353 | up up up up up up up up up up up |
| Gene | Description | FC | EXP |
|---|---|---|---|
| PIIN_09391 | copper ion transmembrane transporter activity | 4.543 | up |
| PIIN_07598 | serine-type endopeptidase activity | 5.0228 | up |
| PIIN_04659 | None | 2.796 | up |
| PIIN_07107 | plasma membrane | 3.8174 | up |
| PIIN_05757 | None | 2.1593 | up |
| PIIN_08262 | lyase activity | 1.7341 | up |
| PIIN_08836 | pathogenesis | 2.4633 | up |
| PIIN_08345 | None | 2.9089 | up |
| PIIN_06899 | single-organism process | 2.3964 | up |
| PIIN_08131 | lyase activity | 1.8848 | up |
| miRNA | Target mRNA | Score | The Function of mRNA |
|---|---|---|---|
| hvu-miR5049a | HORVU1Hr1G020490 | 0 | uncharacterized protein LOC123407470 |
| HORVU1Hr1G091240 | 0 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase STY13 | |
| HORVU1Hr1G041440 | 1 | uncharacterized protein LOC123431160 | |
| HORVU2Hr1G084120 | 0 | uncharacterized membrane protein YuiD | |
| HORVU2Hr1G078270 | 0 | protein LURP-one-related 6 | |
| HORVU2Hr1G096290 | 0 | thioredoxin-like 3-3 isoform X1 | |
| HORVU5Hr1G060310 | 0 | putative transcription factor RL9 | |
| HORVU6Hr1G018530 | 0 | uncharacterized protein LOC123402714 | |
| HORVU6Hr1G025780 | 0 | protein argonaute 1B | |
| HORVU5Hr1G112710 | 0 | leucine rich repeat family expressed | |
| HORVU7Hr1G096360 | 0 | uncharacterized protein LOC123411193 | |
| HORVU6Hr1G083120 | 0.5 | 60S ribosomal protein L35a-1 | |
| novel_22 | HORVU3Hr1G094730 | 1 | squamosa promoter-binding-like protein 2 |
| HORVU6Hr1G028980 | 1 | cinnamoyI-CoA reductase 1 | |
| HORVU6Hr1G031450 | 1 | squamosa promoter-binding-like protein 4 | |
| HORVU0Hr1G039170 | 1 | squamosa promoter-binding-like protein 16 | |
| hvu-miR171-3p | HORVU4Hr1G010490 | 0 | protein MIZU-KUSSEI 1 |
| HORVU4Hr1G087700 | 0 | scarecrow-like protein 6 | |
| HORVU6Hr1G063650 | 1 | scarecrow-like protein 27 | |
| HORVU7Hr1G001300 | 1 | scarecrow-like protein 22 |
| miRNA | Target mRNA | Score | The Function of Target mRNA |
|---|---|---|---|
| hvu-miR397a | HORVU6Hr1G025830 | 0 | Uncharacterized protein LOC123403149 |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU6Hr1G073040 | 1 | MADS-box transcription factor 57 |
| hvu-miR1120 | HORVU1Hr1G080480 | 1 | 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase |
| HORVU3Hr1G039220 | 0 | pyruvate kinase, cytosolic. Isozyme | |
| HORVU3Hr1G067470 | 1 | 26S proteasome regulatory subunit 6B homolog | |
| HORVU4Hr1G002170 | 1 | general negative regulator of transcription subunit 3 isoform X4 | |
| HORVU7Hr1G030930 | 1 | AUGMIN subunit 3 | |
| novel_1 | HORVU2Hr1G101770 | 1 | growth-regulating factor 3-like |
| HORVU6Hr1G068370 | 1 | growth-regulating factor 4-like isoform X1 | |
| HORVU7Hr1G034610 | 1 | growth-regulating factor 2-like | |
| HORVU6Hr1G081210 | 1 | growth-regulating factor 1-like | |
| HORVU7Hr1G008680 | 1 | growth-regulating factor 5-like isoform X1 | |
| HORVU0Hr1G016610 | 1 | growth-regulating factor 4-like isoform X2 | |
| HORVU0Hr1G026650 | 1 | predicted protein | |
| HORVU0Hr1G016590 | 1 | predicted protein |
| miRNA | Gene_names | GO_accession | pval | Description | log2FoldChange | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 dai vs.mock | hvu-miR6189 | HORVU3Hr1G055830 | GO:0008134 | 3.0700 × 10−7 | transcription factor binding | 0.94830 |
| hvu-miR6189 | HORVU5Hr1G021690 | GO:0001071 | 3.0700 × 10−7 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | 0.94830 | |
| hvu-miR6189 | HORVU3Hr1G086270 | GO:0001071 | 3.0700 × 10−7 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | 0.94830 | |
| hvu-miR6189 | HORVU1Hr1G095410 | GO:0098531 | 3.0700 × 10−7 | transcription factor activity, direct ligand regulated sequence-specific DNA binding | 0.94830 | |
| hvu-miR6189 | HORVU3Hr1G089580 | GO:0000989 | 3.0700 × 10−7 | transcription factor activity, transcription factor binding | 0.94830 | |
| hvu-miR6189 | HORVU3Hr1G026990 | GO:0001071 | 3.0700 × 10−7 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | 0.94830 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU6Hr1G057060 | GO:0003700 | 1.3136 × 10−2 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −1.41320 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU1Hr1G051970 | GO:0001071 | 1.3136 × 10−2 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −1.41320 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU7Hr1G036130 | GO:0003700 | 1.3136 × 10−2 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −1.41320 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU1Hr1G020620 | GO:0001071 | 1.3136 × 10−2 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −1.41320 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU6Hr1G081340 | GO:0003700 | 1.3136 × 10−2 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −1.41320 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU0Hr1G032300 | GO:0001071 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU2Hr1G079610 | GO:0001071 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU2Hr1G080490 | GO:0001071 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU3Hr1G055960 | GO:0001071 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU1Hr1G051370 | GO:0001076 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II transcription factor binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU0Hr1G030830 | GO:0003700 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU4Hr1G069340 | GO:0003700 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU5Hr1G055470 | GO:0001071 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU5Hr1G092310 | GO:0001071 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU5Hr1G119220 | GO:0008134 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU4Hr1G087360 | GO:0000989 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor activity, transcription factor binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU2Hr1G108210 | GO:0000988 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor activity, protein binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU4Hr1G028610 | GO:0044798 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | nuclear transcription factor complex | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU5Hr1G000370 | GO:0001071 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU3Hr1G054770 | GO:0008134 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU6Hr1G062340 | GO:0090575 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | RNA polymerase II transcription factor complex | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU6Hr1G066140 | GO:0003700 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU5Hr1G123770 | GO:0003700 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU5Hr1G000370 | GO:0003700 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU7Hr1G024000 | GO:0003700 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU7Hr1G023940 | GO:0001071 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU6Hr1G073040 | GO:0001071 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU7Hr1G026940 | GO:0003700 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU4Hr1G087570 | GO:0008134 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU6Hr1G034130 | GO:0000989 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | transcription factor activity, transcription factor binding | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR6190 | HORVU1Hr1G082910 | GO:0003700 | 4.6930 × 10−2 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | 4.59780 | |
| hvu-miR6190 | HORVU1Hr1G063610 | GO:0003700 | 4.6930 × 10−2 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | 4.59780 | |
| hvu-miR6190 | HORVU6Hr1G008320 | GO:0090575 | 4.6930 × 10−2 | RNA polymerase II transcription factor complex | 4.59780 | |
| hvu-miR6190 | HORVU7Hr1G091040 | GO:0003700 | 4.6930 × 10−2 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | 4.59780 | |
| hvu-miR6190 | HORVU5Hr1G120230 | GO:0001071 | 4.6930 × 10−2 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | 4.59780 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU0Hr1G012230 | GO:0000988 | 4.0994 × 10−3 | transcription factor activity, protein binding | −3.97730 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU1Hr1G047110 | GO:0000989 | 4.0994 × 10−3 | transcription factor activity, transcription factor binding | −3.97730 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU7Hr1G001070 | GO:0000989 | 4.0994 × 10−3 | transcription factor activity, transcription factor binding | −3.97730 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU3Hr1G024950 | GO:0003700 | 4.0994 × 10−3 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −3.97730 | |
| hvu-miR6184 | HORVU7Hr1G114030 | GO:0001071 | 3.6984 × 10−2 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −4.76840 | |
| hvu-miR397a | HORVU2Hr1G059320 | GO:0000989 | 1.8131 × 10−2 | transcription factor activity, transcription factor binding | −5.24440 | |
| hvu-miR397a | HORVU4Hr1G080350 | GO:0003700 | 1.8131 × 10−2 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −5.24440 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU1Hr1G020620 | GO:0001071 | 3.0948 × 10−2 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | 0.78887 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU7Hr1G117010 | GO:0003700 | 3.0948 × 10−2 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | 0.78887 | |
| hvu-miR6180 | HORVU2Hr1G035310 | GO:0000989 | 4.8474 × 10−2 | transcription factor activity, transcription factor binding | −1.65400 | |
| hvu-miR6180 | HORVU5Hr1G046390 | GO:0001071 | 4.8474 × 10−2 | nucleic acid binding transcription factor activity | −1.65400 | |
| hvu-miR6180 | HORVU5Hr1G070260 | GO:0003700 | 4.8474 × 10−2 | transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | −1.64310 |
| miRNA | Target_ Gene | p-Value | GO Term Accession | Function Description | log2 Fold Change | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 dai vs. 3 dai | hvu-miR6214 | HORVU7Hr1G036130 | 3.0948 × 10−2 | GO:0005179 | hormone activity | 0.78887 |
| hvu-miR6180 | HORVU1Hr1G037250 | 4.8474 × 10−2 | GO:0005179 | hormone activity | −1.65400 | |
| hvu-miR6180 | HORVU3Hr1G068970 | 4.8474 × 10−2 | GO:0005184 | neuropeptide hormone activity | −1.65400 | |
| hvu-miR6189 | HORVU5Hr1G067480 | 3.0700 × 10−7 | GO:0051301 | cell division | 0.94830 | |
| hvu-miR6189 | HORVU4Hr1G036120 | 3.0700 × 10−7 | GO:0009725 | response to hormone | 0.94830 | |
| hvu-miR6189 | HORVU3Hr1G089580 | 3.0700 × 10−7 | GO:0035257 | nuclear hormone receptor binding | 0.94830 | |
| hvu-miR6189 | HORVU1Hr1G095410 | 3.0700 × 10−7 | GO:0015979 | photosynthesis | 0.94830 | |
| hvu-miR6189 | HORVU6Hr1G056490 | 3.0700 × 10−7 | GO:0015979 | photosynthesis | 0.94830 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU2Hr1G021110 | 1.3136 × 10−2 | GO:0051301 | cell division | −1.41320 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU5Hr1G051090 | 1.3136 × 10−2 | GO:0051301 | cell division | −1.41320 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU4Hr1G009990 | 1.3136 × 10−2 | GO:0015979 | photosynthesis | −1.41320 | |
| 3 dai vs. mock | hvu-miR6214 | HORVU5Hr1G070630 | 1.3136 × 10−2 | GO:0019684 | photosynthesis, light reaction | −1.41320 |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU6Hr1G074220 | 1.3136 × 10−2 | GO:0015979 | photosynthesis | −1.41320 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU5Hr1G092310 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | GO:0051301 | cell division | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU6Hr1G009230 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | GO:0051301 | cell division | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU5Hr1G069040 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | GO:0047746 | chlorophyllase activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | ENSRNA049488557 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | GO:0007059 | chromosome segregation | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU2Hr1G124270 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | GO:0098813 | nuclear chromosome segregation | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU1Hr1G047730 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | GO:0005185 | neurohypophyseal hormone activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU3Hr1G061700 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | GO:0005184 | neuropeptide hormone activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU7Hr1G048310 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | GO:0005179 | hormone activity | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU2Hr1G090100 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | GO:0015979 | photosynthesis | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR444b | HORVU4Hr1G087360 | 5.2200 × 10−6 | GO:0015979 | photosynthesis | −2.59460 | |
| hvu-miR6190 | HORVU7Hr1G040960 | 4.6930 × 10−2 | GO:0005179 | hormone activity | 4.59780 | |
| hvu-miR6190 | HORVU7Hr1G068230 | 4.6930 × 10−2 | GO:0005179 | hormone activity | 4.59780 | |
| hvu-miR6190 | HORVU2Hr1G057700 | 4.6930 × 10−2 | GO:0042548 | regulation of photosynthesis, light reaction | 4.59780 | |
| hvu-miR6190 | HORVU3Hr1G016330 | 4.6930 × 10−2 | GO:0015979 | photosynthesis | 4.59780 | |
| 7 dai vs. mock | hvu-miR6214 | HORVU3Hr1G021610 | 4.0994 × 10−3 | GO:0051301 | cell division | −3.97730 |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU5Hr1G051090 | 4.0994 × 10−3 | GO:0051301 | cell division | −3.97730 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU3Hr1G078090 | 4.0994 × 10−3 | GO:0005179 | hormone activity | −3.97730 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU5Hr1G070630 | 4.0994 × 10−3 | GO:0005179 | hormone activity | −3.97730 | |
| hvu-miR6214 | HORVU7Hr1G036130 | 4.0994 × 10−3 | GO:0005179 | hormone activity | −3.97730 | |
| hvu-miR397a | HORVU4Hr1G036120 | 1.8131 × 10−2 | GO:0009733 | response to auxin | −5.24440 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Guo, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Lu, A.; Li, S.; Wang, Z. Reprogramming of Fundamental miRNA and Gene Expression during the Barley-Piriformospora indica Interaction. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9010024
Li L, Guo N, Zhang Y, Yuan Z, Lu A, Li S, Wang Z. Reprogramming of Fundamental miRNA and Gene Expression during the Barley-Piriformospora indica Interaction. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Liang, Nannan Guo, Yanze Zhang, Zhi Yuan, Aidang Lu, Si Li, and Ziwen Wang. 2023. "Reprogramming of Fundamental miRNA and Gene Expression during the Barley-Piriformospora indica Interaction" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9010024
APA StyleLi, L., Guo, N., Zhang, Y., Yuan, Z., Lu, A., Li, S., & Wang, Z. (2023). Reprogramming of Fundamental miRNA and Gene Expression during the Barley-Piriformospora indica Interaction. Journal of Fungi, 9(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9010024






