Polyketides as Secondary Metabolites from the Genus Aspergillus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Aspergillus-Derived Polyketides as Secondary Metabolites
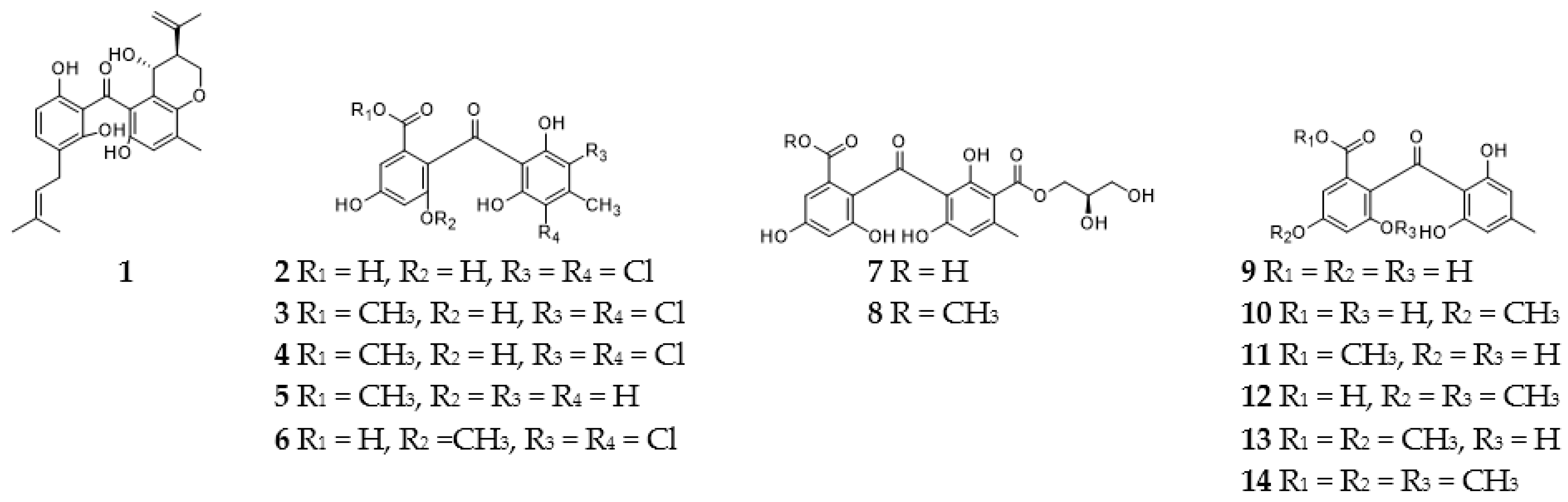
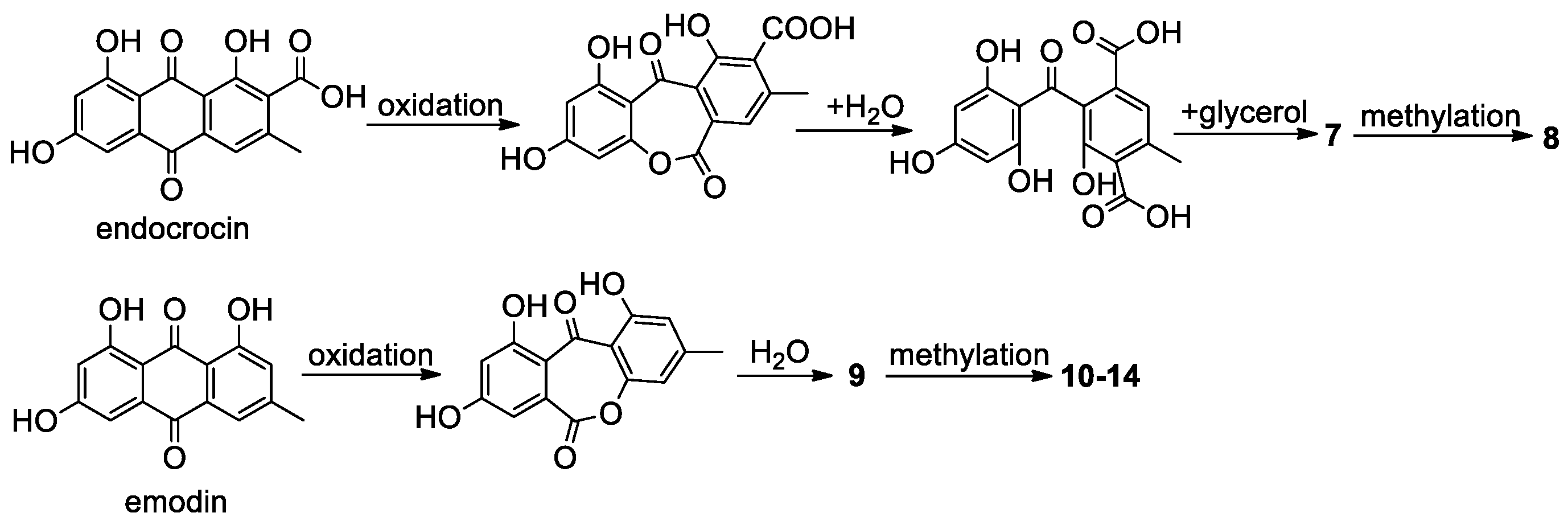
2.1. Benzophenones
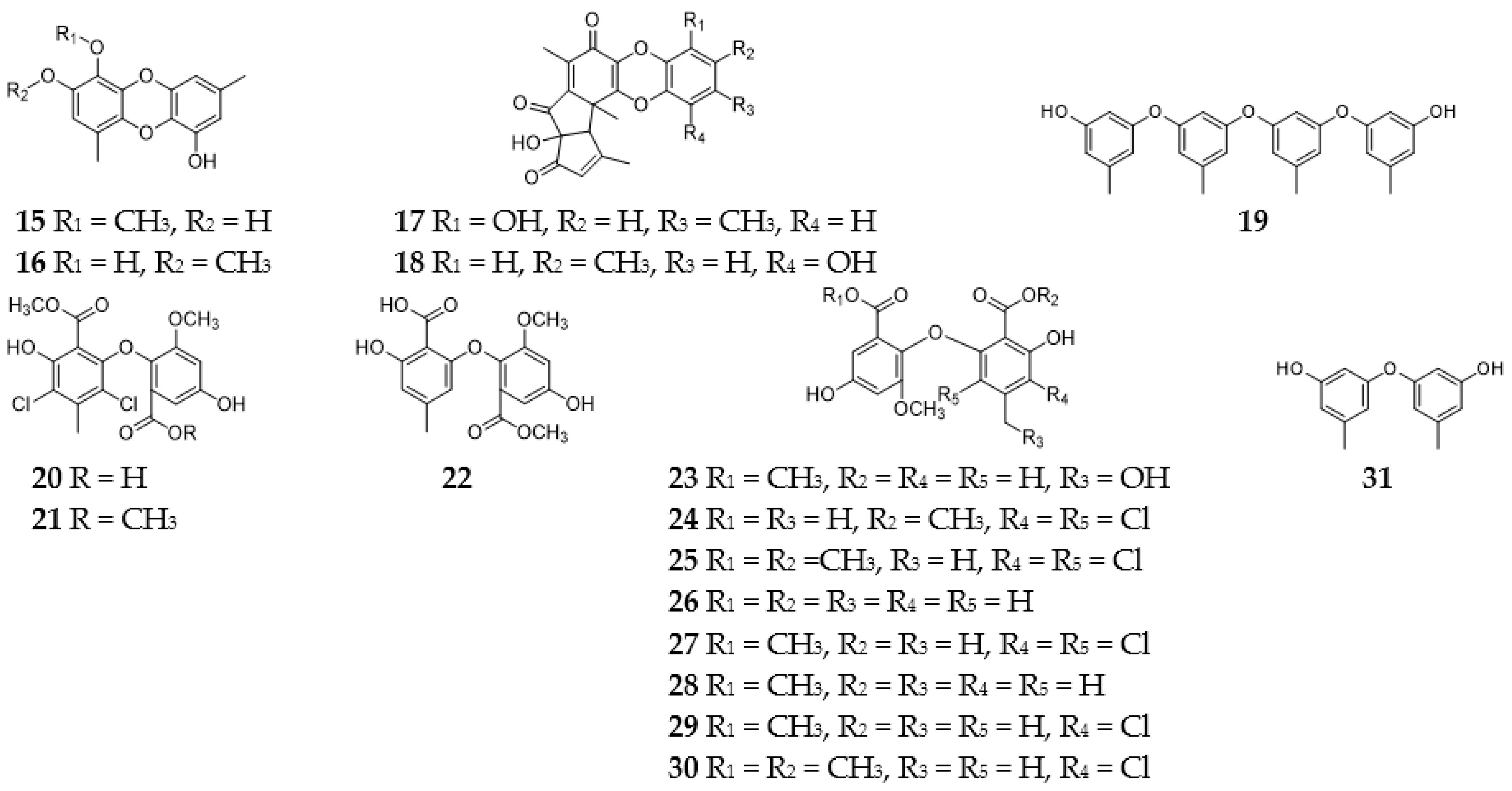
2.2. Diphenyl Ethers
2.3. Furans and Furanones
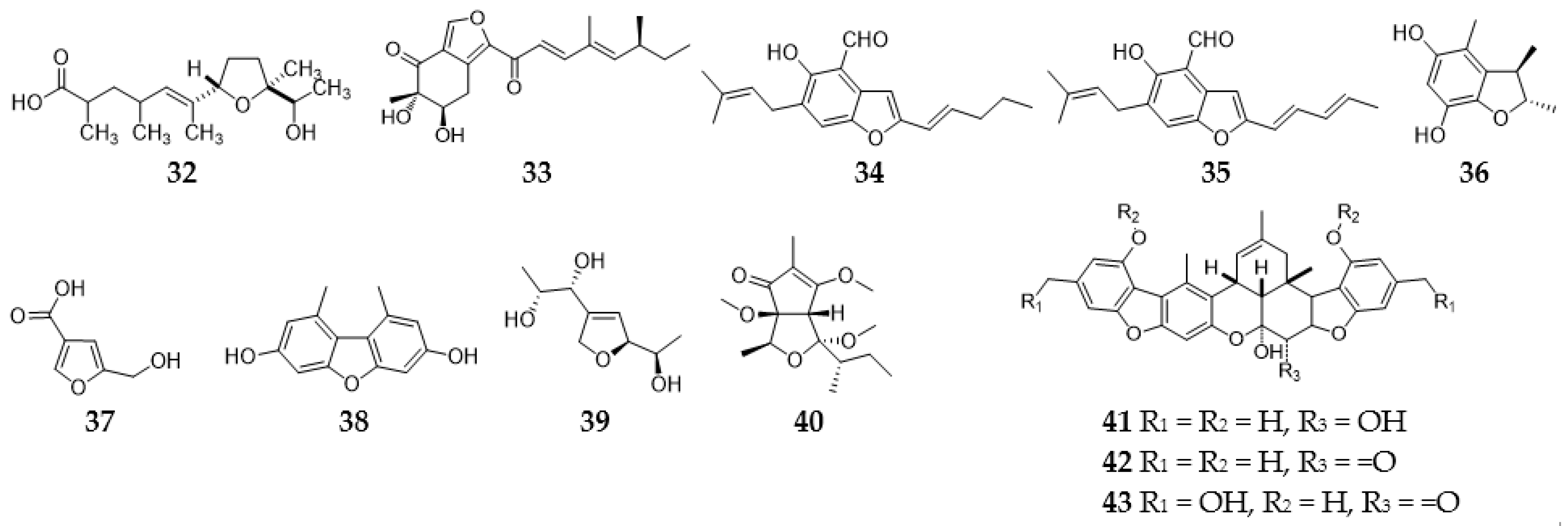
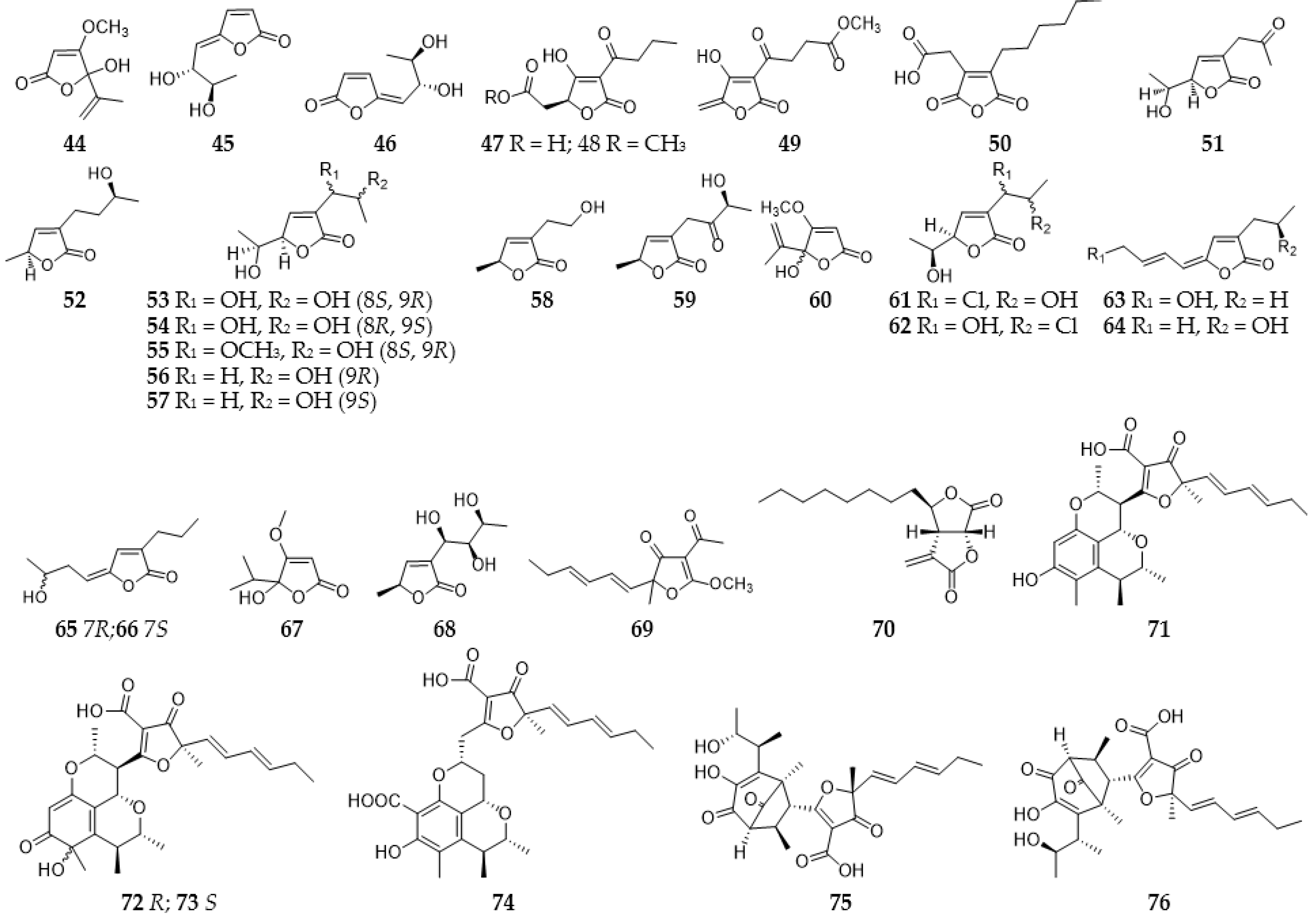
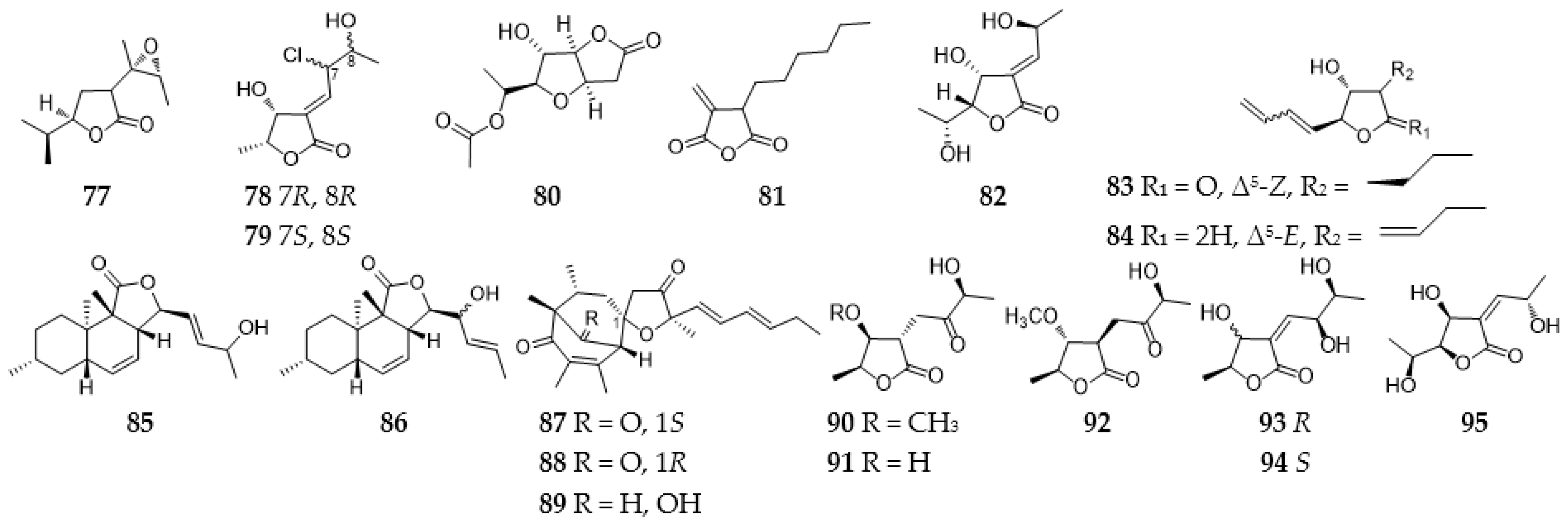
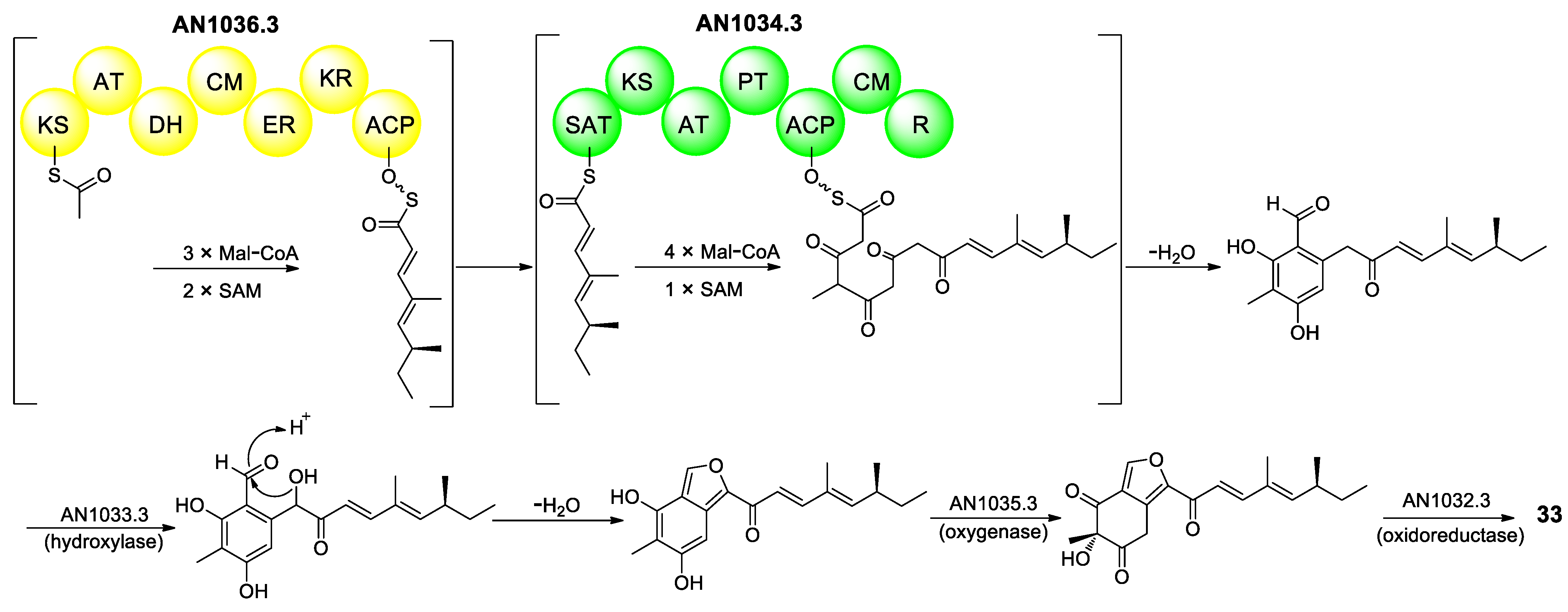
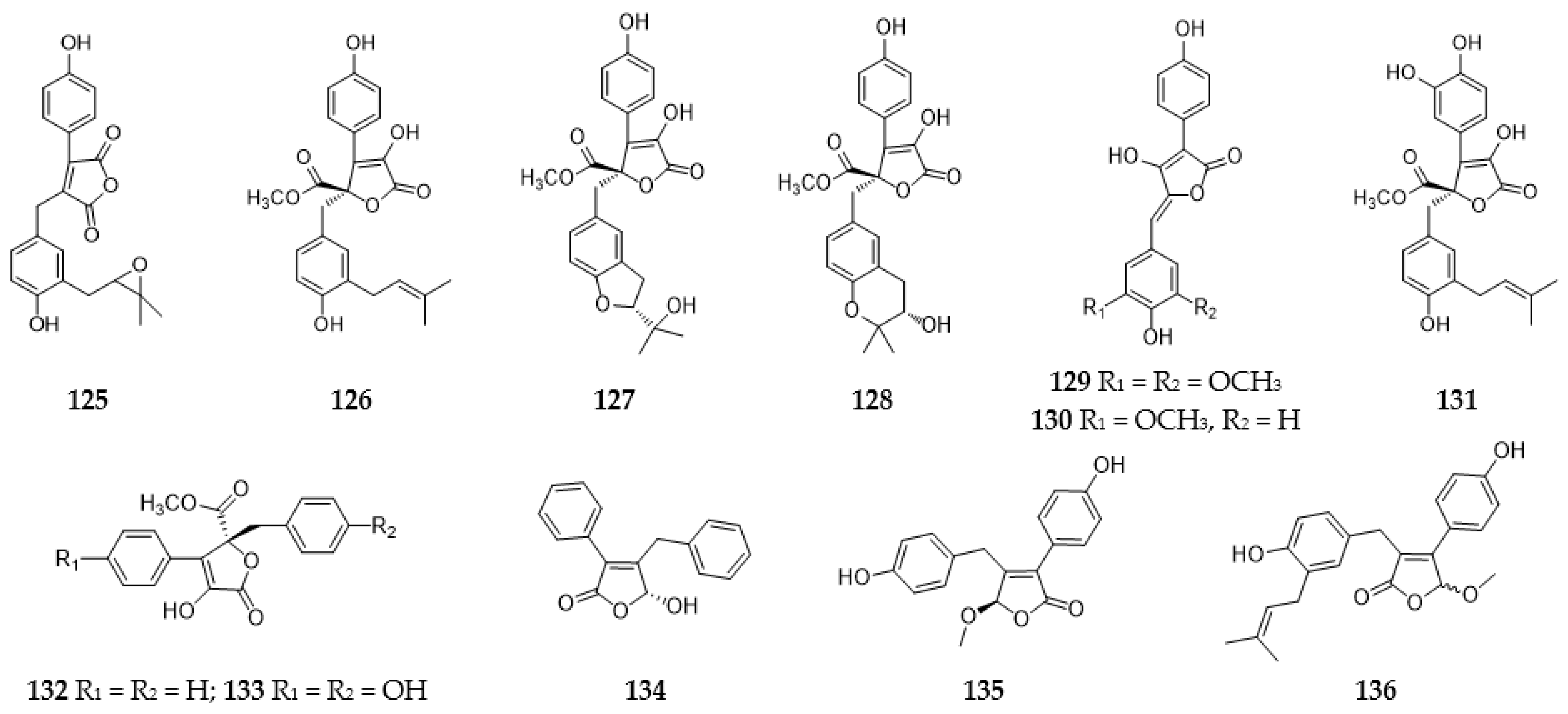
2.3.1. Furans and Benzofurans
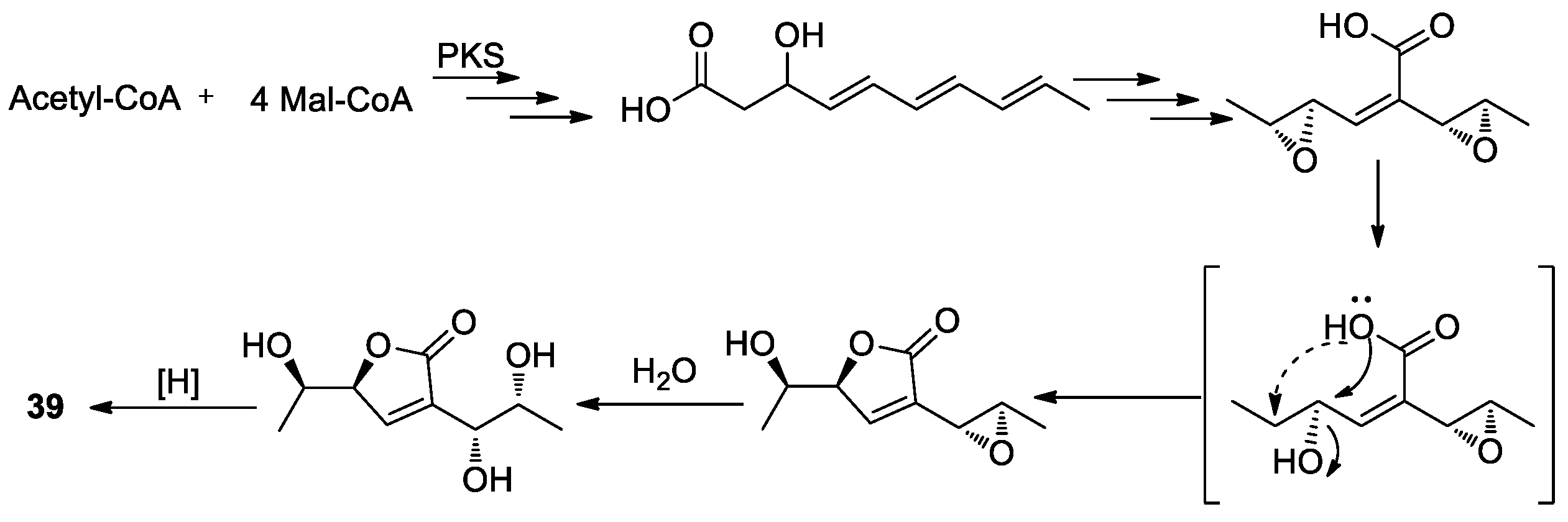
2.3.2. Furanones and Benzofuranones
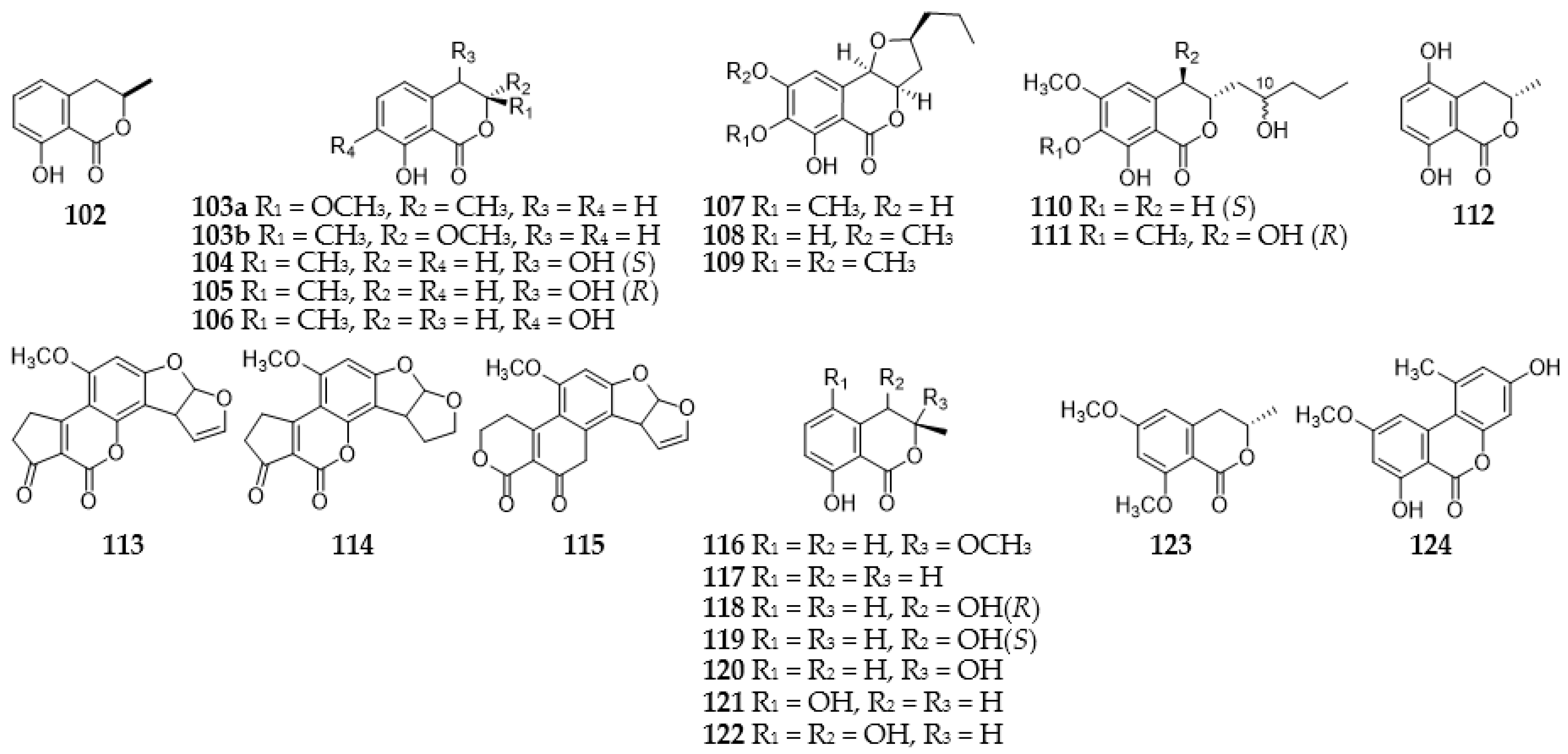
2.4. Isocoumarins
2.5. Lignans
2.6. Naphthalenes
2.7. Phenolics
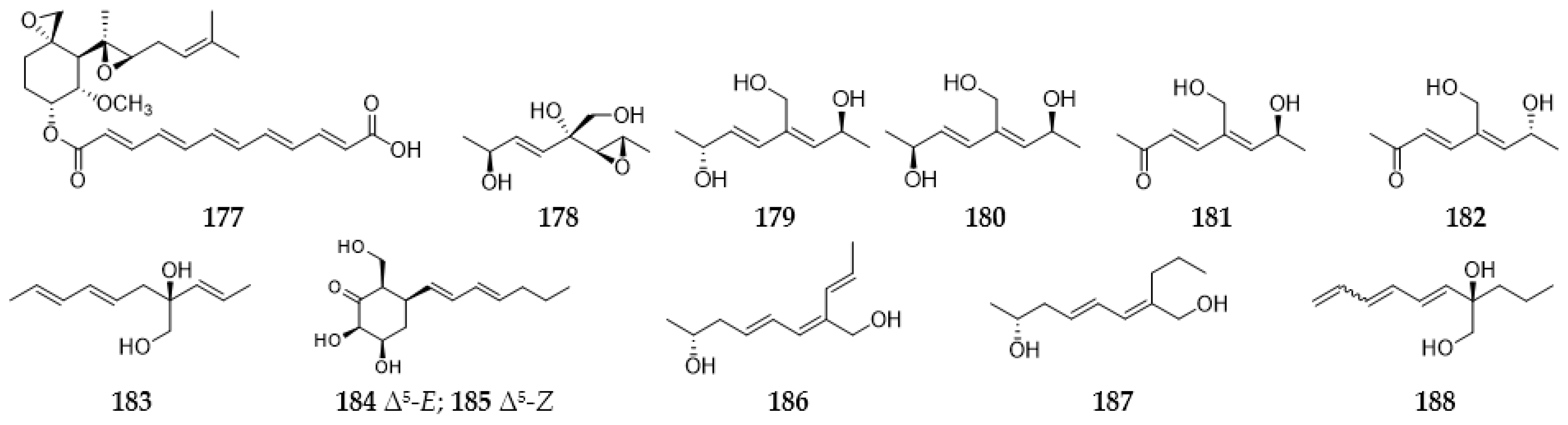
2.8. Polyenes
2.9. Pyrans and Pyranones
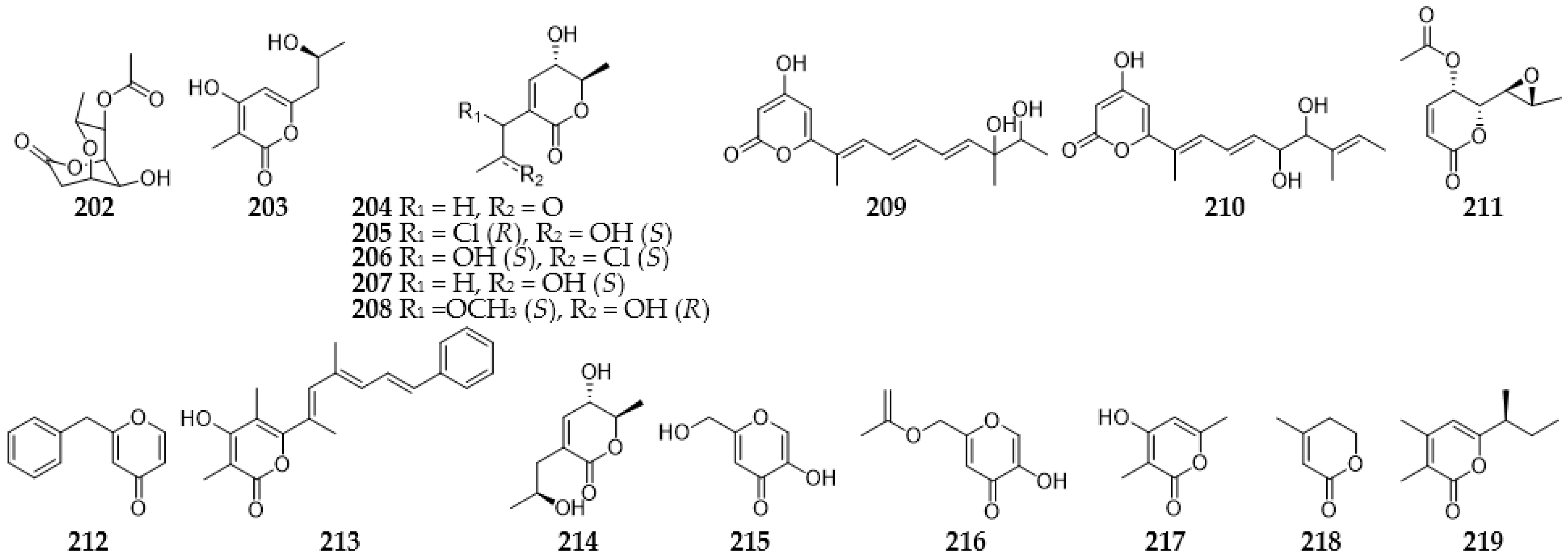
2.9.1. Pyrans
2.9.2. Pyranones
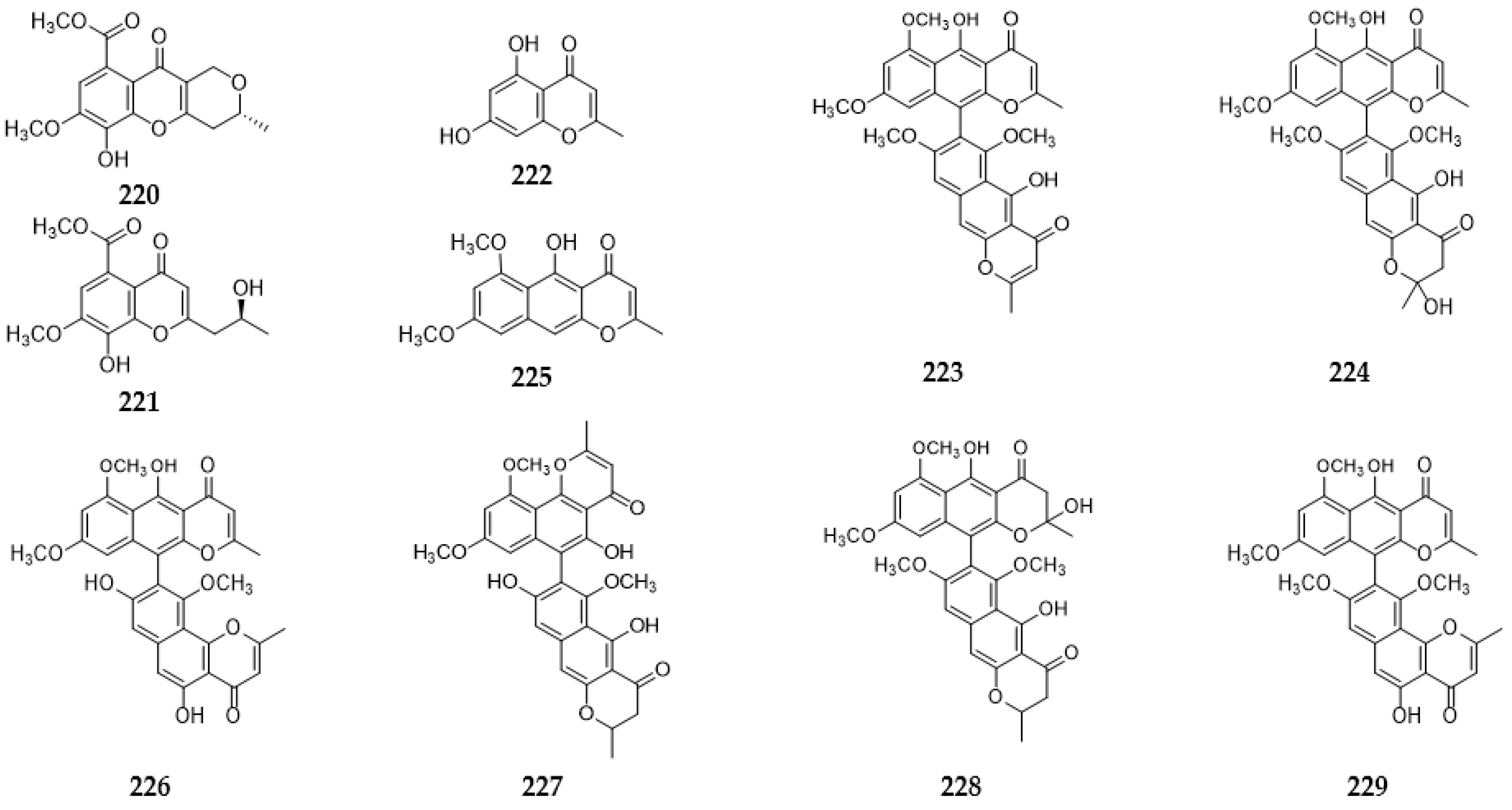
2.9.3. Benzopyranones and Naphthopyranones
2.10. Quinones
2.10.1. Anthraquinones
2.10.2. Benzoquinones and Naphthoquinones
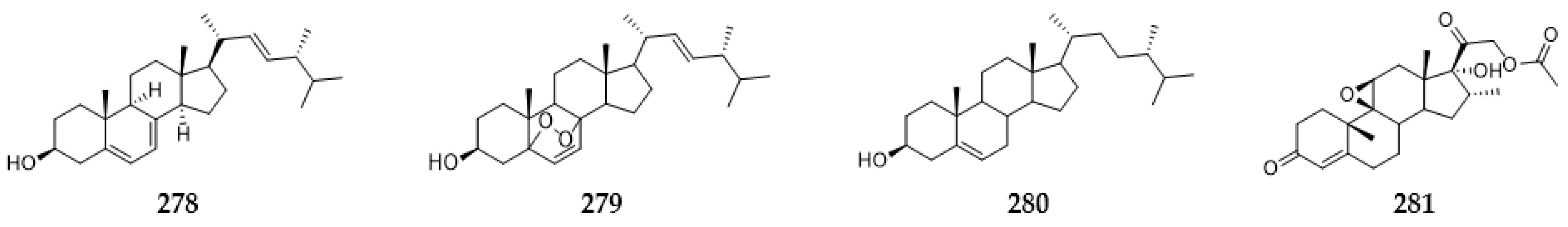
2.11. Steroids
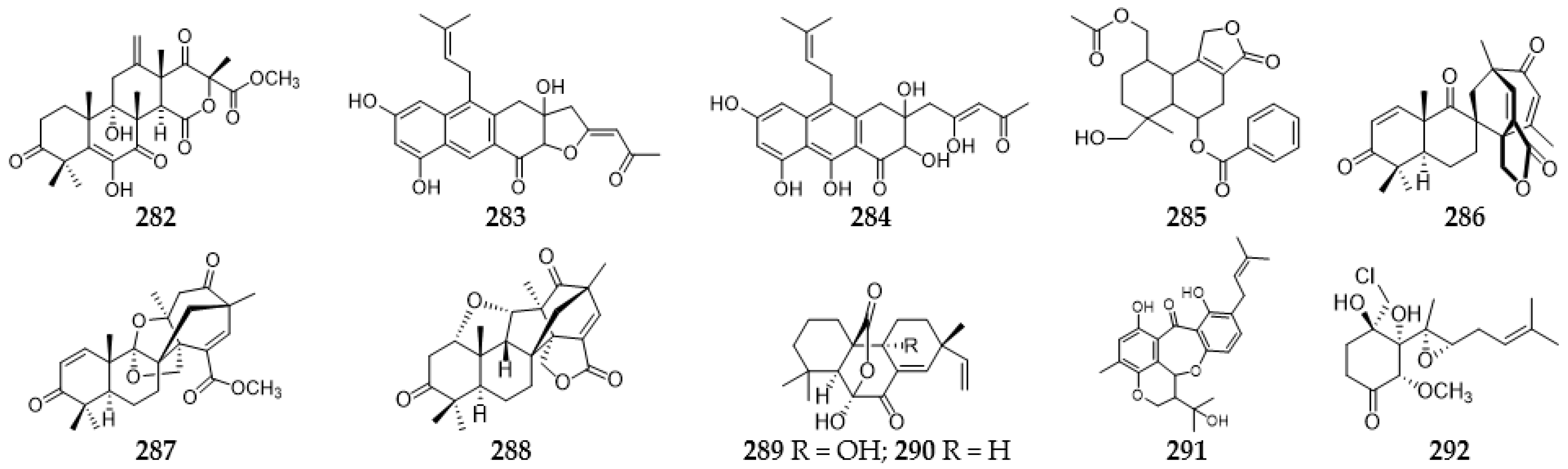
2.12. Meroterpenoids
2.13. Xanthones
2.14. Miscellaneous
3. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alberti, F.; Foster, G.D.; Bailey, A.M. Natural products from filamentous fungi and production by heterologous expression. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 101, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bills, G.F.; Gloer, J.B. Biologically active secondary metabolites from the fungi. Microbiol. Spectr. 2016, 4, 1087–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theobald, S.; Vesth, T.C.; Rendsvig, J.K.; Nielsen, K.F.; Riley, R.; de Abreu, L.M.; Salamov, A.; Frisvad, J.C.; Larsen, T.O.; Andersen, M.R.; et al. Uncovering secondary metabolite evolution and biosynthesis using gene cluster networks and genetic dereplication. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Cao, X.H.; Wen, Q.Y.; Chen, Z.T.; Cheng, Z.X.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Long, C.N.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z. An overview of the bioactivity of monacolin K/lovastatin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubel-Sadron, G.; Londos-Gagliardi, D. Daunorubicin and doxorubicin, anthracycline antibiotics, a physicochemical and biological review. Biochimie 1984, 66, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkyard, C.V.; Koerner, R.J. The use of erythromycin as a gastrointestinal prokinetic agent in adult critical care: Benefits versus risks. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 59, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chooi, Y.-H.; Tang, Y. Navigating the fungal polyketide chemical space: From genes to molecules. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 9933–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H. Aspergillus niger as a Secondary Metabolite Factory. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 701022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dictionary of Natural Products. Available online: https://dnp.chemnetbase.com/faces/chemical/ChemicalSearch.xhtml (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- Mihai, D.M.; Hall, S.; Deng, H.; Welch, C.J.; Kawamura, A. Benzophenone and its analogs bind to human glyoxalase 1. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5349–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkara, A.; Funka, A.N.; Scherlach, K.; Horn, F.; Schroeckh, V.; Chankhamjon, P.; Westermann, M.; Roth, M.; Brakhage, A.A.; Hertweck, C.; et al. Differential expression of silent polyketide biosynthesis gene clusters in chemostat cultures of As-pergillus nidulans. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 160, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wu, C.M.; Long, H.L.; Chen, R.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Guo, P.; Lin, W.H. Varioxiranols A-G and 19-o-methyl-22-methoxypre-shamixanthone, PKS and hybrid PKS-derived metabolites from a sponge-associated Emericella variecolor fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.-Y.; Shen, C.-N.; Lin, L.-H.; Yang, Y.-L.; Han, H.-Y.; Chen, J.-W.; Kuo, S.-C.; Wu, S.-H.; Liaw, C.-C. Asperjinone, a nor-neolignan, and terrein, a suppressor of ABCG2-expressing breast cancer cells, from thermophilic Aspergillus terreus. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, A.; Ismail, M.; Shaaban, M. X-ray, structural assignment and molecular docking study of dihydrogeodin from As-pergillus terreus TM8. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-H.; Feng, B.-M.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Sun, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, F.; Chen, G.; Bai, J.; Hua, H.-M.; Wang, H.-F.; et al. Polyketide butenolide, diphenyl ether, and benzophenone derivatives from the fungus Aspergillus flavipes PJ03-11. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Zhang, C.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Polyketide derivatives from the sponge associated fungus Aspergillus europaeus with antioxidant and no inhibitory activities. Fitoterapia 2018, 130, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, S.G.; Rathi, E.; Kumar, A.; Bhat, V. Potentials of diphenyl ether scaffold as a therapeutic agent: A review. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1392–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Lyu, H.N.; Zhou, S.; Yu, J.W.; Keller, N.P.; Chen, L.; Yin, W.B. Deletion of a global regulator LaeB leads to the discovery of novel polyketides in Aspergillus nidulans. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 4973–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeckh, V.; Scherlach, K.; Nützmann, H.-W.; Shelest, E.; Schmidt-Heck, W.; Schuemann, J.; Martin, K.; Hertweck, C.; Brakhage, A.A. Intimate bacterial–fungal interaction triggers biosynthesis of archetypal polyketides in Aspergillus nidulans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14558–14563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Y.B.; Teng, X.C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.P.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Li, G.Q.; Zhu, W.M. Cyclopeptides and polyketides from coral-associated fungus, Aspergillus versicolor LCJ-5-4. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 7085–7089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, H.; Akiyama, H.; Nishikori, K.; Mochizuki, J.-I. Asterric acid, a new endothelin binding inhibitor. J. Antibiot. 1992, 45, 1684–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawfike, A.F.; Romli, M.; Clements, C.; Abbott, G.; Young, L.; Schumacher, M.; Diederich, M.; Farag, M.; Edrada-Ebel, R. Isolation of anticancer and anti-trypanosome secondary metabolites from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus flocculus via bioactivity guided isolation and MS based metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1106–1107, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanlall, V.; Odhav, B. Furans and furanones with antimycotoxigenic activity isolated from Warburgia salutaris (Canel-laceae). J. Med. Plants Res. 2009, 3, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varoglu, M.; Crews, P. Biosynthetically diverse compounds from a saltwater culture of sponge-derived Aspergillus niger. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 63, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettit, G.R.; Du, J.; Pettit, R.K.; Knight, J.C.; Doubek, D.L. Antineoplastic agents. 575. The Fungus Aspergillus phoenicis. Heterocycles 2009, 79, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.-M.; Szewczyk, E.; Davidson, A.D.; Keller, N.; Oakley, B.R.; Wang, C.C.C. A gene cluster containing two fungal polyketide synthases encodes the biosynthetic pathway for a polyketide, asperfuranone, in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2965–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.C.; Chiang, Y.-M.; Praseuth, M.B.; Kuo, P.-L.; Liang, H.-L.; Hsu, Y.-L. Asperfuranone from Aspergillus nidulans inhibits proliferation of human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells via blocking cell cycle progression and inducing apoptosis. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 107, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.-W.; Ji, C.-Z.; Gu, Q.-Q.; Li, D.-H.; Zhu, T.-J. Three new polyketides from marine-derived fungus Aspergillus glaucus HB1-19. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-L.; Cao, F.; Tian, S.-S.; Zhu, H.-J. Alkaloids and polyketides from the soil fungus Aspergillus terreus and their antibacterial activities. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2017, 53, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldan, N.C.; Almeida, R.T.R.; Avíncola, A.; Porto, C.; Galuch, M.B.; Magon, T.F.S.; Pilau, E.J.; Svidzinski, T.I.E.; Oliveira, C.C. Development of an analytical method for identification of Aspergillus flavus based on chemical markers using HPLC-MS. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evidente, A.; Cristinzio, G.; Punzo, B.; Andolfi, A.; Testa, A.; Melck, D. ChemInform abstract: Flufuran, an antifungal 3,5-Disubstituted furan produced by Aspergillus flavus link. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, T.; Takenaka, Y.; Nagakura, N.; Hamada, N. Dibenzofurans from the cultured lichen mycobionts of Lecanora ci-nereocarnea. Phytochemistry 2001, 58, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Peng, S.; Yang, J.; Cong, Z.; Lin, X.; Liao, S.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Structurally diverse sesquiterpenoids and polyketides from a sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus sydowii SCSIO41301. Fitoterapia 2019, 135, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.-B.; Zhang, G.; Li, S.-M.; He, Z.-H.; Yan, Q.-X.; Lin, Y.-K.; Xie, C.-L.; Xia, J.-M.; Luo, Z.-H.; Luo, L.-Z.; et al. Asperochratides A–J, ten new polyketides from the deep-sea-derived Aspergillus ochraceus. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 105, 104349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Liu, H.; Long, J.; Tao, H.; Lin, X.; Liao, S.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. Asperpentenone A, a novel polyketide isolated from the deep-sea derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41024. Phytochem. Lett. 2019, 35, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, P.S.; Vleggaar, R.; Simpson, T.J. Stable isotope labelling studies on the biosynthesis of asticolorin C by Aspergillus multicolor. Evidence for a symmetrical intermediate. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1984, 12, 765–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabie, C.J.; Simpson, T.J.; Steyn, P.S.; van Rooyen, P.H.; Vleggaar, R. Structure and absolute configuration of the asticolorins, toxic metabolites from Aspergillus multicolor. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1984, 12, 764–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrell, L.M.; Borgeson, B.; Crews, P. Chloro polyketides from the cultured fungus (Aspergillus) separated from a marine sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 2331–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Yu, N.; Jeon, S.; Lee, H.; Bae, C.-H.; Yeo, J.; Kim, I.-S.; Park, H.; Kim, J.-C. Antibacterial activities of penicillic acid isolated from Aspergillus persii against various plant pathogenic bacteria. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Gao, W.; Guan, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Chen, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Lai, Y.; Hu, Z.; et al. Butenolides from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus with antitumor activities against pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 5903–5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-L.; Awakawa, T.; Wakimoto, T.; Abe, I. Three acyltetronic acid derivatives: Noncanonical cryptic polyketides from Aspergillus niger identified by genome mining. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, L.; Lodin, A.; Herold, I.; Ilan, M.; Carmeli, S.; Yarden, O. Sensitivity of Neurospora crassa to a marine-derived Aspergillus tubingensis anhydride exhibiting antifungal activity that is mediated by the mas1 protein. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4713–4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-W.; Li, C.-W.; Cui, C.-B.; Hua, W.; Zhu, T.-J.; Gu, Q.-Q. Nine new and five known polyketides derived from a deep sea-sourced Aspergillus sp. 16-02-1. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3116–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.-M.; Meng, L.-H.; Wang, B.-G. Polyketides from the marine mangrove-derived fungus Aspergillus ochraceus MA-15 and their activity against aquatic pathogenic bacteria. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 12, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.D.; Zhao, C.Y.; Hao, J.J.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.L.; Zhu, W.M. New α-glucosidase inhibitors from a marine sponge-derived fungus, Aspergillus sp. OUCMDZ-1583. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 68852–68863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phainuphong, P.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Tadpetch, K.; Sukpondma, Y.; Saithong, S.; Phongpaichit, S.; Preedanon, S.; Sakayaroj, J. Gamma-butenolide and furanone derivatives from the soil-derived fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PSU-RSPG178. Phytochemistry 2017, 137, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijeratne, E.M.K.; Xu, Y.M.; Arnold, A.E.; Gunatilaka, A.A.L. Pulvinulin A, graminin C, and cis-gregatin B—new natural furanones from Pulvinula sp. 11120, a fungal endophyte of cupressus arizonica. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, D.; Tidd, B.K.; Turne, W.B. Avenaciolide, an antifuingal lactone from Aspergillus avenaceus. J. Chem. Soc. 1963, 68, 5385–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelo-branco, P.A.; Rubinger, M.M.M.; Alves, L.D.C.; de Barros, P.M.; Pereira, S.G.; de Melo, V.J.; Pilo-Veloso, D.; Zambolim, L. Synthesis and antifungal activity of aromatic bis-gamma-lactones analogous to avenaciolide. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 2745–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.P.; Wu, Y.R.; Yang, M.H.; Li, T.X.; Wang, X.B.; Zhou, M.M.; Lei, J.L.; Kong, L.Y. Citrifurans A-D, four dimeric aromatic polyketides with new carbon skeletons from the fungus Aspergillus sp. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4058–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.P.; Wu, Y.R.; Han, C.; Wang, X.B.; Gao, H.L.; Yin, Y.; Kong, L.Y.; Yang, M.H. Asperones A–E, five dimeric polyketides with new carbon skeletons from the fungus Aspergillus sp AWG 1–15. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 2432–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garson, M.J.; Staunton, J.; Jones, P.G. New polyketide metabolites from Aspergillus melleus: Structural and stereochemical studies. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1984, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhri, A.; Chaouche, N.K.; Catania, M.R.; Ritieni, A.; Santini, A. Chemical composition of Aspergillus creber extract and evaluation of its antimicrobial and antioxidant activities. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2019, 68, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, J.-H.; Oh, H.-C. Protulactones A and B: Two new polyketides from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SF-5044. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadorn, K.; Saepua, S.; Boonyuen, N.; Laksanacharoen, P.; Rachtawee, P.; Prabpai, S.; Kongsaeree, P.; Pittayakhajonwut, P. Allahabadolactones A and B from the endophytic fungus, Aspergillus allahabadii BCC45335. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruta, T.; Bizukojc, M. Culture-based and sequence-based insights into biosynthesis of secondary metabolites by Aspergillus terreus ATCC 20542. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 175, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Okusa, N.; Ogawa, A.; Ikenoue, T.; Seki, T.; Tsuji, T. Identification and preliminary SAR studies of (+)-geodin as a glucose uptake stimulator for rat adipocytes. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.B.; Tu, K.; Feng, W.Y.; Liu, J.J.; Xu, Q.Q.; Tao, L.; Zhu, H.C.; Chen, C.M.; Wang, J.P.; Xue, Y.B.; et al. Polyketide and prenylxanthone derivatives from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. TJ23. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1800395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suemitsu, R.; Ohnishi, K.; Horiuchi, M.; Morikawa, Y.; Sakaki, Y.; Matsumoto, Y. Structure of porriolide, a new metabolite from Alternaria porri. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 1993, 57, 334–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-L.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Q.-B.; Luo, D.-Q.; Zhang, Y. Phthalide derivatives with antifungal activities against the plant pathogens isolated from the liquid culture of Pestalotiopsis photiniae. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frédérick, R.; Masereel, B. Coumarin and isocoumarin as serine protease inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 3781–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederic, C.; Costa Cristine, A.; Erwan, A.; David, A.; Cecile, D.; Michael, F.; Jean-Francois, H.; Martinez, J.; Solveig, L.J.; Philippe, M.; et al. JLK inhibitors: Isocoumarin compounds as putative probes to selectively target the gamma-secretase pathway. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2005, 2, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, H.; Green, I.R. A patent review of two fruitful decades (1997–2016) of isocoumarin research. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2017, 27, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cimmino, A.; Maddau, L.; Masi, M.; Linaldeddu, B.T.; Evidente, A. Secondary metabolites produced by Sardiniella urbana, a new emerging pathogen on European hackberry. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 1862–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, X.P.; Ju, Z.R.; Liao, X.J.; Huang, X.J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, B.X.; Xu, S.H. Aspergchromones A and B, two new polyketides from the marine sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO XWS03F03. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 19, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.-M.; Bi, X.-B.; Zhao, Q.-R.; Fang, A.; Chen, Y.-G. Dihydroisocoumarins from the Fungus Cephalosporium sp. AL031. Pol. J. Chem. 2006, 80, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.B.; Abdel Kader, M.M.; Wick, E.L.; Wogan, G.N. Aflatoxin B2: Chemical identity and biological activity. Science 1963, 142, 1191–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klich, M.A. Aspergillus flavus: The major producer of aflatoxin. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-W.; Lin, Y.; Lu, Y.-J.; Zhou, X.F.; Liu, Y.H. Peptides and polyketides isolated from the marine sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus terreus SCSIO 41008. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Y.; Pan, R.; Bai, X.L.; Wei, B.; Chen, J.W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.W. Aromatic polyketides from a symbiotic strain Asper-gillus fumigatus D and characterization of their biosynthetic gene D8.t287. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runeberg, P.A.; Brusentsev, Y.; Rendon, S.M.K.; Eklund, P.C. Oxidative transformations of lignans. Molecules 2019, 24, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.V.; Sadhukhan, A.K.; Veerender, M.; Ravikumar, V.; Mohan, E.V.S.; Dhanvantri, S.D.; Sitaramkumar, M.; Babu, J.M.; Vyas, K.; Reddy, G.O. Butyrolactones from Aspergillus terreus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Lu, C.; Shen, Y. Secondary metabolites of Aspergillus sp. F1, a commensal fungal strain of Trewia nudiflora. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritakun, R.; Rachtawee, P.; Chanthaket, R.; Boonyuen, N.; Isaka, M. Butyrolactones from the fungus Aspergillus terreus BCC 4651. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T.; Fukuda, T.; Nagai, K.; Uchida, R.; Tomoda, H. Helvafuranone produced by the fungus Aspergillus nidulans BF0142 isolated from hot spring-derived soil. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.-L.; Wu, X.; Ye, K.; Lv, X.; Ai, H.-L.; Liu, J.-K. Bioactive polyketides from the potato endophytic fungus Aspergillus carneus. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Schreiner, C. Genetic toxicity of naphthalene: A review. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. Part B 2003, 6, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preuss, R.; Drexler, H. Naphthalene—An environmental and occupational toxicant. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Heal. 2003, 76, 556–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Zhu, T.; Liu, H.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Gu, Q. Cytotoxic polyketides from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus glaucus. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1837–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.-B.; Chooi, Y.H.; Smith, A.R.; Cacho, R.A.; Hu, Y.; White, T.C.; Tang, Y. Discovery of cryptic polyketide metabolites from dermatophytes using heterologous expression in Aspergillus nidulans. ACS Synth. Biol. 2013, 2, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inokoshi, J.; Shiomi, K.; Masuma, R.; Tanaka, H.; Yamada, H.; Omura, S. ChemInform abstract: Funalenone, a novel collagenase inhibitor produced by Aspergillus Niger. J. Antibiot. 1999, 52, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machrafi, Y.; Prévost, D.; Beauchamp, C.J. Toxicity of phenolic compounds extracted from bark residues of different ages. J. Chem. Ecol. 2006, 32, 2595–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lünne, F.; Niehaus, E.-M.; Lipinski, S.; Kunigkeit, J.; Kalinina, S.A.; Humpf, H.-U. Identification of the polyketide synthase PKS7 responsible for the production of lecanoric acid and ethyl lecanorate in Claviceps purpurea. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2020, 145, 103481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogo, D.; Matos, M.D.C.; Honda, N.K.; Pontes, E.C.; Oguma, P.M.; Santos, E.C.D.; de Carvalho, J.E.; Nomizo, A. In vitro an-titumour activity of orsellinates. Z. Nat. C 2010, 65, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Li, H.; Hong, J.; Cho, H.Y.; Bae, K.S.; Kim, M.A.; Kim, D.-K.; Jung, J.H. Bioactive metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2010, 33, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flewelling, A.J.; Bishop, A.L.; Johnson, J.A.; Gray, C.A. Polyketides from an endophytic Aspergillus fumigatus Isolate inhibit the growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and MRSA. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 1661–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, G.F.; Adpressa, D.A.; Bruhn, T.; Loesgen, S. Polyketides from marine-derived Aspergillus porosus: Challenges and opportunities for determining absolute configuration. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2780–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamasaki, T.; Nagayama, K.; Hatsuda, Y. Two new metabolites, sydonic acid and hydroxysydonic acid, from Aspergillus sydowi. Agri. Biol. Chem. 1978, 42, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, T.H.; Phong, N.V.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Cuong, N.X.; Ngan, N.T.T.; Oh, H.; Nam, N.H.; Minh, C.V. Cytotoxic and im-munomodulatory phenol derivatives from a marine sponge-derived fungus Ascomycota sp. VK12. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 5153–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.-Q.; Lin, S.-T.; Kumaravel, K.; Zhou, H.; Wang, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.-H. Polyketide-derived metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. F40. Phytochem. Lett. 2018, 27, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.S.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.Y.; He, H.T.; Dai, H.Q.; Xia, X.K.; Liu, C.H.; Zhang, L.X.; Song, F.H. New diketopiperazines from a ma-rine-derived fungus strain Aspergillus versicolor MF180151. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, S.; Murakami, T.; Miyanishi, J.; Tanaka, K.; Takada, N.; Hashimoto, M. Isolation and absolute stereochemistry of op-tically active sydonic acid from Glonium sp. (Hysteriales, Ascomycota). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Q.A.; Shao, C.L.; She, Z.G.; Lin, Y.C. Five sesquiterpenoids from a marine-derived fungus Asper-Gillus sp. isolated from a gorgonian Dichotella gemmacea. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, B.; Chen, Q.; Lian, X.-Y. Synthesis and biological evaluation of caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhani, P.; Patil, A.; Majumdar, S. Challenges in the polyene- and azole-based pharmacotherapy of ocular fungal infections. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 35, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, F.R.; Eble, T.E. AN antiphage agent isolated from Aspergillus sp. J. Bacteriol. 1949, 58, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchser, J.; Grabley, S.; Noltemeyer, M.; Philipps, S.; Thiericke, R.; Zeeck, A. Secondary metabolites by chemical-screening, 28. Aspinonene, a new multifunctional fungal metabolite. Liebigs Ann. Der Chem. 1994, 8, 831–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kito, K.; Ookura, R.; Yoshida, S.; Namikoshi, M.; Ooi, T.; Kusumi, T. Pentaketides relating to aspinonene and dihydroaspyrone from a marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus ostianus. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 2022–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ola, A.R.B.; Tawo, B.D.; Belli, H.L.L.; Proksch, P.; Tommy, D.; Hakim, E.H. A new antibacterial polyketide from the endophytic fungi Aspergillus fumigatiaffinis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 1573–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Yin, P.; Li, J.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Qu, D.; Li, Z.; Xue, X.; Luo, X.; Li, M. In vitro and in vivo anti-biofilm activity of pyran derivative against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Infect. Public Heal. 2019, 13, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, B.R.; Scheidt, K.A. Pyranone Natural products as inspirations for catalytic reaction discovery and development. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabala, A.O.; Xu, W.; Chooi, Y.-H.; Tang, Y. Characterization of a silent azaphilone gene cluster from Aspergillus niger ATCC 1015 reveals a hydroxylation-mediated pyran-ring formation. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filho, J.W.G.D.O.; Islam, M.T.; Ali, E.S.; Uddin, S.J.; Santos, J.V.D.O.; de Alencar, M.V.O.B.; Júnior, A.L.G.; Paz, M.F.C.J.; Brito, M.D.R.M.D.; Sousa, J.M.D.C.E.; et al. A comprehensive review on biological properties of citrinin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 110, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, M.; Mathieu, M.; Anastopoulos, I.P.; Martínez, M.G.; Rousseau, F.; Dotto, G.L.; de Oliveira, H.P.; Lima, E.C.; Thyrel, M.; Larsson, S.H.; et al. Process parameters optimization, characterization, and application of KOH-activated norway spruce bark graphitic biochars for efficient azo dye adsorption. Molecules 2022, 27, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Bakeer, W.; Marshall, J.W.; Yakasai, A.A.; Khalid, R.M.; Collemare, J.; Skellam, E.; Tharreau, D.; Lebrun, M.-H.; Lazarus, C.M.; et al. Heterologous expression of the avirulence gene ACE1 from the fungal rice pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4837–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, M.F.; Entwistle, R.; Chiang, Y.-M.; Ahuja, M.; Oakley, C.E.; Akashi, T.; Wang, C.C.C.; Todd, R.B.; Oakley, B.R. Hybrid transcription factor engineering activates the silent secondary metabolite gene cluster for (+)-asperlin in Aspergillus nidulans. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 3193–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, X.; Yu, D.; Chen, X.; Tabudravu, J.; Deng, H.; Pan, L. Deletion of the epigenetic regulator GcnE in Aspergillus niger FGSC A1279 activates the production of multiple polyketide metabolites. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 217, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Takahashi, K.; Iwakura, N.; Abe, T.; Akaishi, M.; Chiba, S.; Namikoshi, M.; Uchida, R. A new protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory α-pyrone-type polyketide from Okinawan plant-associated Aspergillus sp. TMPU1623. J. Antibiot. 2018, 71, 745–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardane, A.M.; Kumar, N.S.; Jayasinghe, L.; Fujimoto, Y. Chemical investigation of metabolites produced by an endo-phytic Aspergillus sp. isolated from Limonia acidissima. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 1384–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, T.J.; Jones, D.C. The metabolism and toxicity of quinones, quinonimines, quinone methides, and quinone-thioethers. Curr. Drug Metab. 2002, 3, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa-Bustos, C.; Vázquez, K.; Varela, J.; Cerecetto, H.; Paulino, M.; Segura, R.; Pizarro, J.; Vera, B.; González, M.; Zarate, A.M.; et al. New aryloxy-quinone derivatives with promising activity on Trypanosoma cruzi. Arch. Pharm. 2019, 353, e1900213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Jiang, X.; Liu, X.; He, C.; Di, Y.; Lu, S.; Huang, H.; Lin, B.; Wang, D.; Fan, B. Antibacterial anthraquinone dimers from marine derived fungus Aspergillus sp. Fitoterapia 2018, 133, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, E.M.; Müller, C.E. Anthraquinones as pharmacological tools and drugs. Med. Res. Rev. 2016, 36, 705–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhu, T.; Fang, Y.; Liu, H.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Aspergiolide A, a novel anthraquinone derivative with naphtho[1,2,3-de]chromene-2,7-dione skeleton isolated from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus glaucus. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Ai, J.; Li, D.; Zhu, T.; Wang, Y.; Knauer, M.; Bruhn, T.; Liu, H.; Geng, M.; Gu, Q.; et al. Aspergiolides C and D: Spirocyclic aromatic polyketides with potent protein kinase c-met inhibitory effects. Chem. A Eur. J. 2010, 17, 1319–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherlach, K.; Sarkar, A.; Schroeckh, V.; Dahse, H.-M.; Roth, M.; Brakhage, A.A.; Horn, U.; Hertweck, C. Two Induced fungal polyketide pathways converge into antiproliferative spiroanthrones. Chembiochem 2011, 12, 1836–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Tang, H.; Song, J.; Long, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, X. Chrysophanol: A review of its pharmacology, toxicity and pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paranjape, S.R.; Chiang, Y.M.; Sanchez, J.F.; Entwistle, R.; Wang, C.C.C.; Oakley, B.R.; Gamblin, T.C. Inhibition of tau ag-gregation by three Aspergillus nidulans secondary metabolites: 2,omega-dihydroxyemodin, asperthecin, and asperbenzal -dehyde. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Zhu, A.O.; Bai, X.; Zhu, H.J.; Cao, F. Alkaloids and polyketides from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus ver-sicolor. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2020, 56, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisvad, J.C.; Larsen, T.O. Extrolites of Aspergillus fumigatus and Other Pathogenic Species in Aspergillus section fumigati. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Fujioka, S.; Nukina, M.; Kawano, T.; Shimada, A.; Kimura, Y. Fumiquinones A and B, nematicidal quinones produced by Aspergillus fumigatus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Huang, H.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. Heterologous pathway assembly reveals molecular steps of fungal terreic acid biosynthesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seshime, Y.; Juvvadi, P.R.; Kitamoto, K.; Ebizuka, Y.; Fujii, I. Identification of csypyrone B1 as the novel product of Aspergillus oryzae type III polyketide synthase CsyB. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 4542–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Xiong, B.; Xu, J. Chemical investigation of secondary metabolites produced by mangrove endophytic fungus phyl-losticta capitalensis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, J.; Pozo, J.O. Current LC-MS methods and procedures applied to the identification of new steroid metabolites. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 162, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmi, C.; Brunel, J.M. Therapeutic potential of cationic steroid antibacterials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobot, V.; Opletal, L.; Jahodar, L.; Patel, A.V.; Dacke, C.G.; Blunden, G. Ergosta-4,6,8,22-tetraen-3-one from the edible fungus, Pleurotus ostreatus (oyster fungus). Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 1669–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Lee, S.J.; Kwak, H.Y.; Jung, L.K.; Heo, J.; Hong, S.; Kim, G.W.; Baek, N.I. Sterols isolated from nuruk (rhizopus oryzae KSD-815) inhibit the migration of cancer cells. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 19, 1328–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salendra, L.; Lin, X.; Chen, W.; Pang, X.; Luo, X.; Long, J.; Liao, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Cytotoxicity of polyketides and steroids isolated from the sponge-associated fungus Penicillium citrinum SCSIO 41017. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 35, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.; Saleem, M.; Tousif, M.I.; Anwar, M.A.; Surup, F.; Ali, I.; Wang, D.; Mamadalieva, N.Z.; Alshammari, E.; Ashour, M.L.; et al. Meroterpenoids: A comprehensive ipdate insight on structural di-versity and biology. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, J.P.; Dorner, J.W.; Cole, R.J.; Cox, R.H. Terretonin, a toxic compound from Aspergillus terreus. J. Org. Chem. 1979, 44, 4852–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, C.C.; Scherlach, K.; Schroeckh, V.; Horn, F.; Nietzsche, S.; Brakhage, A.A.; Hertweck, C. Bacterium induces cryptic meroterpenoid pathway in the pathogenic fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Chembiochem 2013, 14, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamasaki, T.; Kuwano, H.; Isono, K.; Hatsuda, Y.; Fukuyama, K.; Tsukihara, T.; Katsube, Y. A new metabolite, parasiticolide A, from Aspergillus parasiticus. Agric. Biol. Chem. 2014, 39, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.X.; Sun, W.G.; Li, Q.; Li, X.N.; Zhu, H.C.; Huang, J.F.; Liu, J.J.; Wang, J.P.; Xue, Y.B.; Zhang, Y.H. Spiroaspertrione A, a bridged spirocyclic meroterpenoid, as a potent potentiator of oxacillin against methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus from Aspergillus sp. TJ23. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 3125–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, Y.; Sun, W.; Feng, W.; Liu, J.; Hu, Z.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Aspermerodione, a novel fungal metabolite with an unusual 2,6-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane skeleton, as an inhibitor of penicillin-binding protein 2a. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Guo, Z.K.; Jiang, R.; Wei, W.; Wang, T.; Guo, Y.; Song, Y.C.; Jiao, R.H.; Tan, R.X.; Ge, H.M. New flavonol and diterpenoids from the endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp. YXf3. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawas, U.W.; El-Beih, A.A.; El-Halawany, A.M. Bioactive anthraquinones from endophytic fungus Aspergillus versicolor iso-lated from red sea algae. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 1749–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchoa, P.K.S.; Pimenta, A.T.A.; Braz-Filho, R.; de Oliveira, M.D.C.F.; Saraiva, N.N.; Rodrigues, B.S.F.; Pfenning, L.H.; Abreu, L.M.; Wilke, D.V.; Florêncio, K.G.D.; et al. New cytotoxic furan from the marine sediment-derived fungi Aspergillus niger. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2599–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoiprommarat, S.; Kongthong, S.; Choowong, W.; Boonyuen, N.; Isaka, M.; Bunyapaiboonsri, T. Xanthones from a lignicolous freshwater fungus (BCC 28210). Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 34, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-H.; Liu, D.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J.-L.; Lin, W.-H. Antioxidant xanthones and anthraquinones isolated from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khattab, A.R.; Farag, M.A. Current status and perspectives of xanthones production using cultured plant biocatalyst models aided by in-silico tools for its optimization. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.; Ardalani, H.; Anam, S.; McNair, L.M.; Kromphardt, K.J.; Frandsen, R.J.N.; Franzyk, H.; Staerk, D.; Kongstad, K.T. Antidiabetic xanthones with α-glucosidase inhibitory activities from an endophytic penicillium canescens. Fitoterapia 2020, 142, 104522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masters, K.-S.; Bräse, S. Xanthones from fungi, lichens, and bacteria: The natural products and their synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3717–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pornpakakul, S.; Liangsakul, J.; Ngamrojanavanich, N.; Roengsumran, S.; Silhanonth, P.; Piapukiew, J.; Sangvichien, E.; Puthong, S.; Petsom, A. Cytotoxic activity of four xanthones from Emericella variecolor, an endophytic fungus isolated from Croton oblongifolius. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2006, 29, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, R.; Buechi, G.; Kobbe, B.; Demain, A.L. Secalonic acids D and F are toxic metabolites of Aspergillus aculeatus. J. Org. Chem. 1977, 42, 352–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, A.W.; Chen, J.; Kuron, G.; Hunt, V.; Huff, J.; Hoffman, C.; Rothrock, J.; Lopez, M.; Joshua, H.; Harris, E.; et al. Mevinolin: A highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 3957–3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Miura, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ohta, T. Aspermytin A: A New neurotrophic polyketide isolated from a marine-derived fungus of the genus Aspergillus. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 35, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravleva, O.I.; Afiyatullov, S.S.; Vishchuk, O.M.; Denisenko, V.A.; Slinkina, N.N.; Smetanina, O.F. Decumbenone C, a new cytotoxic decaline derivative from the marine fungus Aspergillus sulphureus KMM 4640. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2012, 35, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravleva, O.I.; Kirichuk, N.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Pivkin, M.V.; Afiyatullov, S.S. New kipukasin from marine isolate of the fungus Aspergillus flavus. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.M.; Hoeck, C.; Frisvad, J.C.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Larsen, T.O. Dereplication guided discovery of secondary metabo-lites of mixed biosynthetic origin from Aspergillus aculeatus. Molecules 2014, 19, 10898–10921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Karwowski, J.P.; Humphrey, P.E.; Kohl, W.L.; Barlow, G.J.; Tanaka, S.K. Calbistrins, novel antifungal agents produced by Penicillium restrictum. I. Production, taxonomy of the producing organism and biological activity. J. Antibiot. 1993, 46, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, P.; Xue, J.H.; Wei, X.Y.; Li, H.X. Versicorin, a new lovastatin analogue from the fungus Aspergillus versicolor SC0156. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Yoshida, T.; Hosono, H.; Ohta, T.; Yokosawa, H. Hexylitaconic acid: A new inhibitor of p53-HDM2 interaction isolated from a marine-derived fungus, Arthrinium sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 69–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaaniche, F.; Hamed, A.; Abdel-Razek, A.S.; Wibberg, D.; Abdissa, N.; El Euch, I.Z.; Allouche, N.; Mellouli, L.; Shaaban, M.; Sewald, N. Bioactive secondary metabolites from new endophytic fungus Curvularia sp. isolated from Rauwolfia macrophylla. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, M.; Someno, T.; Kawada, M.; Ikeda, D. A New Terrein Glucoside, a Novel Inhibitor of Angiogenin Secretion in Tumor Angiogenesis. J. Antibiot. 2008, 61, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.B.; Jayasuriya, H.; Zink, D.L.; Polishook, J.D.; Dombrowski, A.W.; Zweerink, H. Aspercyclide A–C, three novel fungal metabolites from Aspergillus sp. as inhibitors of high-affinity IgE receptor. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 7605–7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.Q.; Espinosa-Artiles, P.; Schubert, V.; Xu, Y.M.; Zhang, W.; Lin, M.; Gunatilaka, A.A.L.; Sussmuth, R.; Molnar, I. Char-acterization of the biosynthetic genes for 10,11-dehydrocurvularin, a heat shock response-modulating anticancer fungal polyketide from Aspergillus terreus. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2013, 79, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagata, S.; Xu, Y.-M.; Wijeratne, E.M.K.; Kontnik, R.; Rooney, C.; Perley, C.C.; Kwon, H.; Clardy, J.; Kesari, S.; Whitesell, L.; et al. Using the heat-shock response to discover anticancer compounds that target protein homeostasis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-S.; Jun, S.-C.; Han, K.-H.; Hong, S.-B.; Yu, J.-H. Diversity, application, and synthetic biology of industrially important Aspergillus fungi. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 100, 161–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfannenstiel, B.T.; Greco, C.; Sukowaty, A.T.; Keller, N.P. The epigenetic reader SntB regulates secondary metabolism, de-velopment and global histone modifications in Aspergillus flavus. Fung. Genet. Biol. 2018, 120, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Li, H.; Geng, C.; Huang, X.; Lu, X. Discovery and characterization of a PKS–NRPS hybrid in Aspergillus terreus by genome mining. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, X.; Sheng, Y.; Tang, Z.; Pan, J.; Wang, S.; Tang, B.; Zhou, T.; Shi, L.; Zhang, H. Polyketides as Secondary Metabolites from the Genus Aspergillus. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020261
Bai X, Sheng Y, Tang Z, Pan J, Wang S, Tang B, Zhou T, Shi L, Zhang H. Polyketides as Secondary Metabolites from the Genus Aspergillus. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(2):261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020261
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Xuelian, Yue Sheng, Zhenxing Tang, Jingyi Pan, Shigui Wang, Bin Tang, Ting Zhou, Lu’e Shi, and Huawei Zhang. 2023. "Polyketides as Secondary Metabolites from the Genus Aspergillus" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 2: 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020261
APA StyleBai, X., Sheng, Y., Tang, Z., Pan, J., Wang, S., Tang, B., Zhou, T., Shi, L., & Zhang, H. (2023). Polyketides as Secondary Metabolites from the Genus Aspergillus. Journal of Fungi, 9(2), 261. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9020261






