Distinct Roles of Ena ATP Family Proteins in Sodium Accumulation, Invasive Growth, and Full Virulence in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
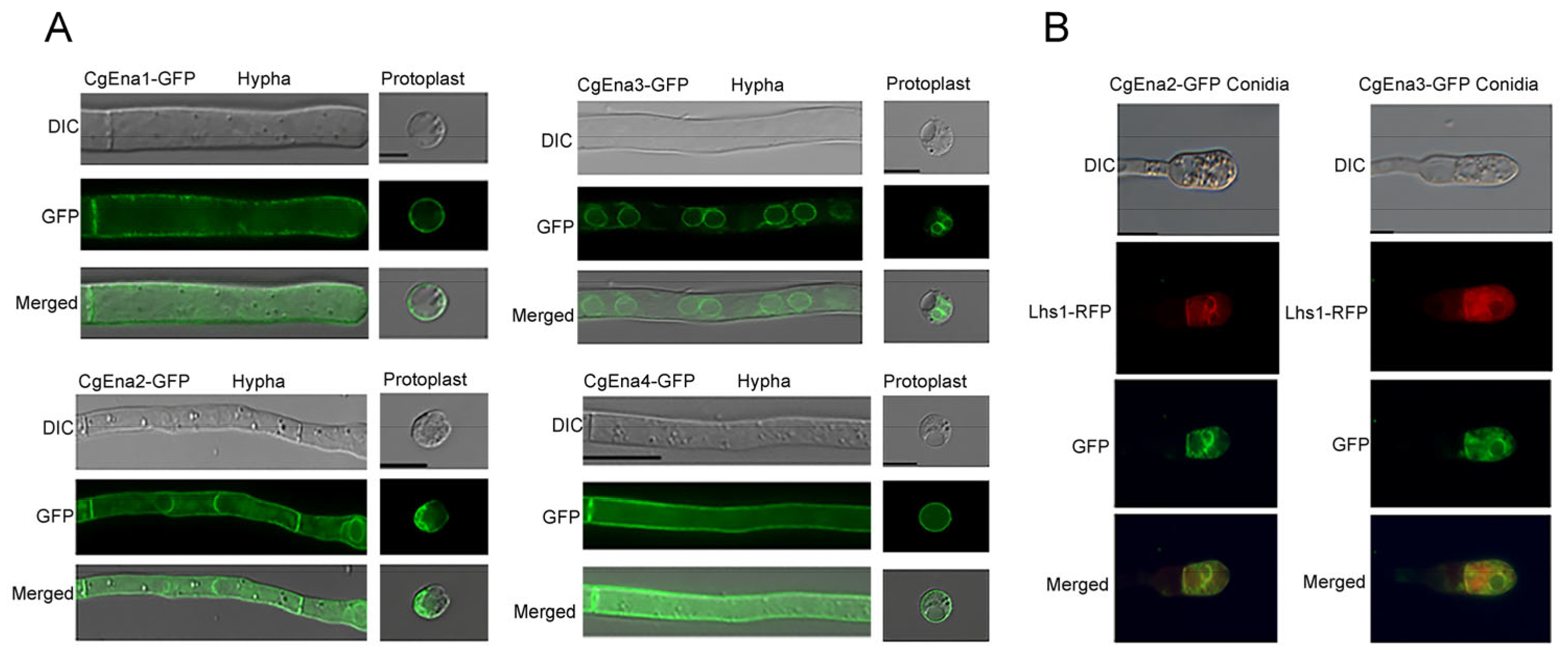
2.1. Ena Family Proteins in C. gloeosporioides and Their Localization Pattern
2.2. Ena Family Proteins Expressed at the Early Stage of Plant Infection
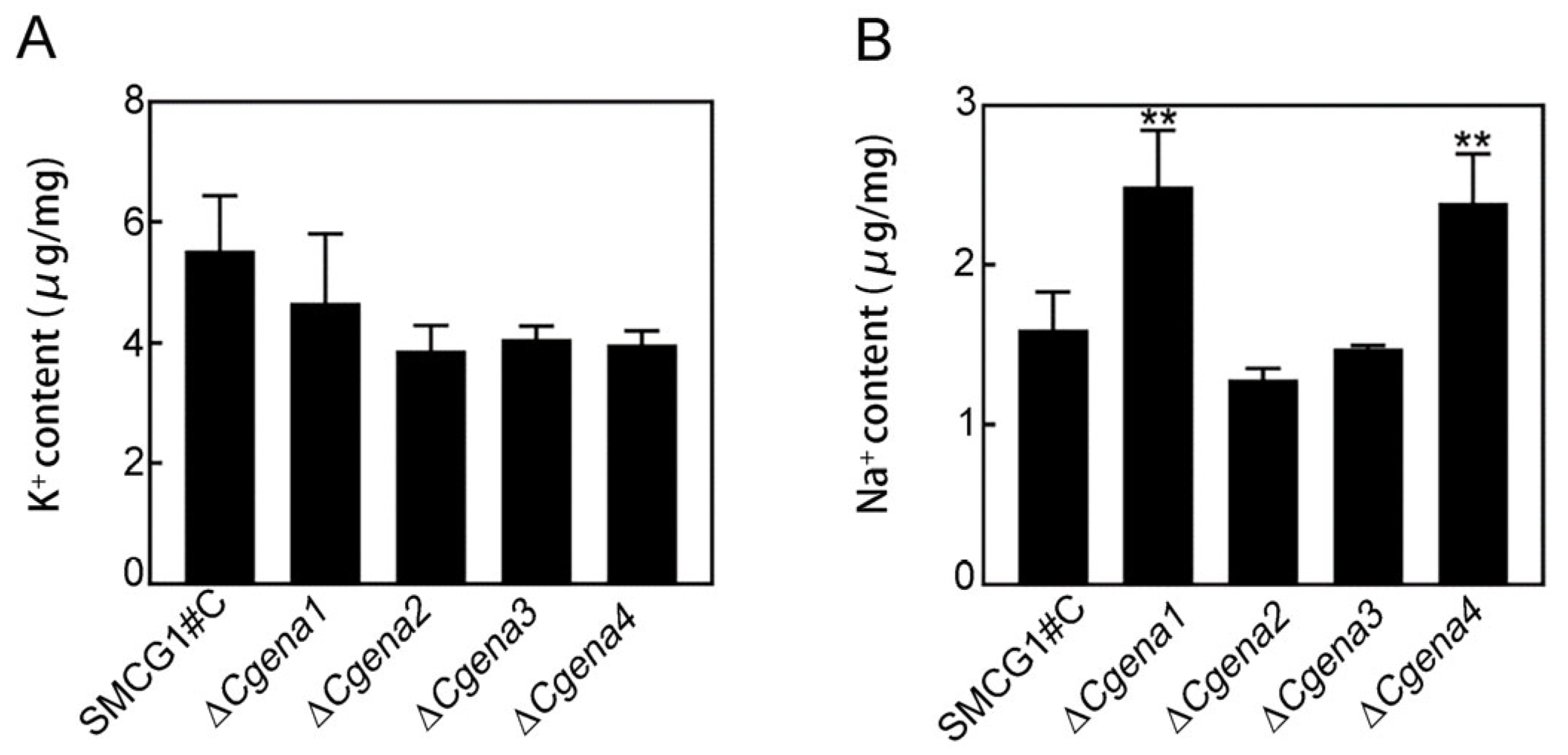
2.3. CgEna1 and CgEna4 Are Involved in Sodium Accumulation
2.4. CgEna1 and CgEna3 Indispensable for Full Virulence
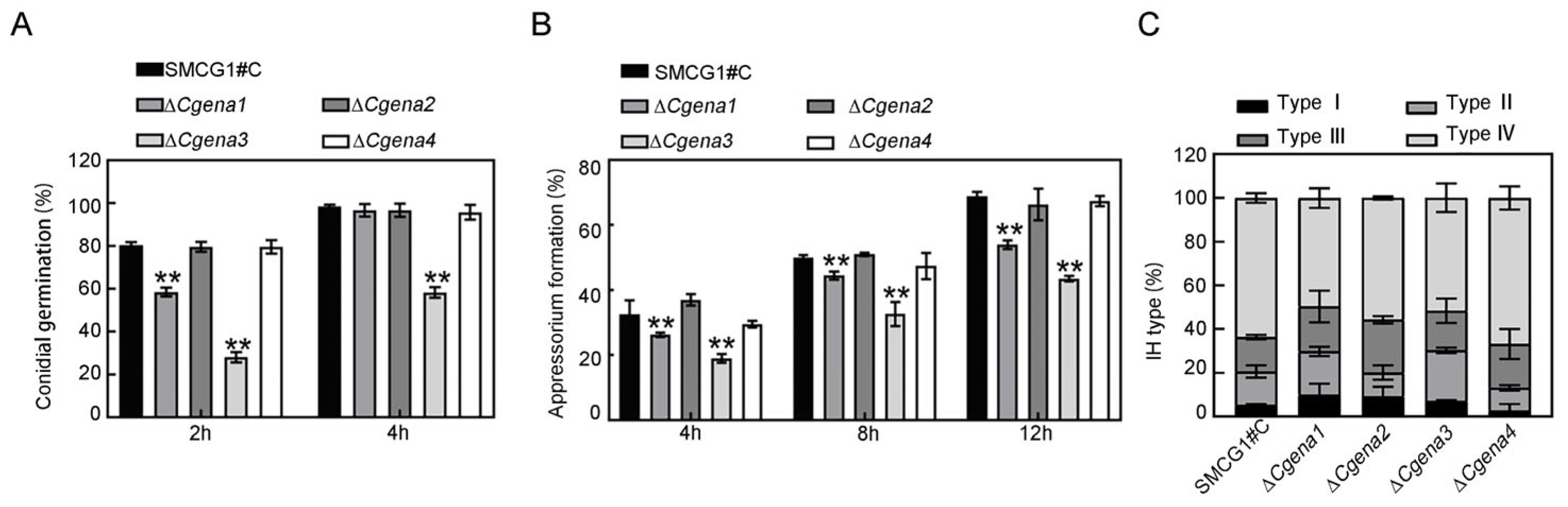
2.5. CgEna1 and CgEna3 Regulate Conidial Germination, Appressorium Formation and Invasive Hypha Development
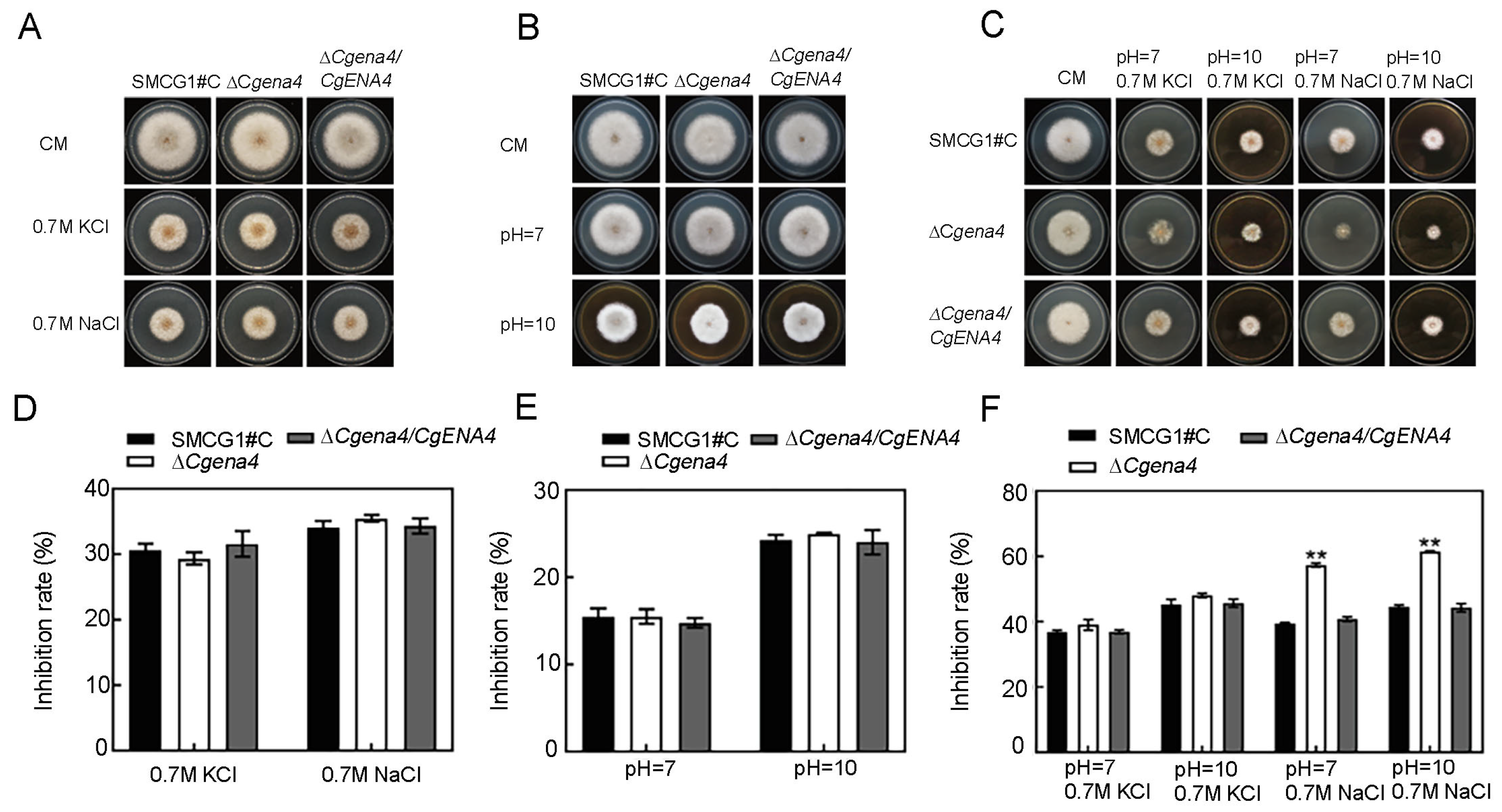
2.6. CgEna4 Is Required for Ion Stress Response under Certain Extracellular Conditions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Fungal Strains and Culture Conditions
3.2. Gene Deletion of CgENA1, CgENA2, CgENA3, and CgENA4
3.3. Complementation of Targeted Gene Mutants
3.4. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
3.5. Assays for Vegetative Growth
3.6. Assays of Stress Resistance and Sodium/Potassium Accumulation
3.7. Pathogenicity Tests
3.8. Observation of Conidial Germination, Appressorium Formation and Invasive Hyphal Development
3.9. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clausen, M.J.; Poulsen, H. Sodium/Potassium homeostasis in the cell. Met. Ions Life Sci. 2013, 12, 41–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adler, V.; Yin, Z.; Fuchs, S.Y.; Benezra, M.; Rosario, L.; Tew, K.D.; Pincus, M.R.; Sardana, M.; Henderson, C.J.; Wolf, C.R.; et al. Regulation of JNK signaling by GSTp. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Navarro, A.; Benito, B. Sodium or potassium efflux ATPase a fungal, bryophyte, and protozoal ATPase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1798, 1841–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catty, P.; de Kerchove d Exaerde, A.; Goffeau, A. The complete inventory of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae P-type transport ATPases. FEBS Lett. 1997, 409, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedelsberger, J.; Obando, P.A.; Gonzalez, W. Yeast strain Saccharomyces cerevisiae BYT45 lacking the cation extrusion systems ENA1-5 and NHA1 is suitable for the characterization of TASK-3 potassium channel antagonists. FEMS Yeast Res. 2019, 19, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Huang, L. Enhanced expression of vacuolar H+-ATPase subunit E in the roots is associated with the adaptation of Broussonetia papyrifera to salt stress. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaton, A.F.; Merkulova, M.; Brown, D. The H+-ATPase (V-ATPase): From proton pump to signaling complex in health and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, 392–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, B.; Garciadeblas, B.; Rodrıguez-Navarro, A. Potassium- or sodium-efflux ATPase, a key enzyme in the evolution of fungi. Microbiology 2002, 148, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Jin, K.; Peng, G.; Xia, Y. An Ena ATPase, MaEna1, of metarhizium acridum influences the Na+, thermo and UV tolerances of conidia and is involved in multiple mechanisms of stress tolerance. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015, 83, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Ariño, J. Function and regulation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ena sodium ATPase system. Eukaryot. Cell 2007, 6, 2175–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, H.K.; Antebi, A.; Fink, G.R.; Buckley, C.M.; Moir, D.T. The yeast secretory pathway is perturbed by mutations in PMR1, a member of a Ca2+ ATPase family. Cell 1989, 58, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraile-Escanciano, A.; Garciadeblás, B.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A.; Benito, B. Role of Ena ATPase in Na+ efflux at high pH in bryophytes. Plant. Mol. Biol. 2009, 71, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haro, R.; Garciadeblas, B.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A. A novel P-type ATPase from yeast involved in sodium transport. FEBS Lett. 1991, 291, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garciadeblas, B.; Rubio, F.; Quintero, F.J.; Bañuelos, M.A.; Haro, R.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A. Differential expression of two genes encoding isoforms of the ATPase involved in sodium efflux in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1993, 236, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banuelos, M.A.; Rodriguez-Navarro, A. P-type ATPases Mediate Sodium and Potassium Effluxes in Schwanniomyces occidentalis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enjalbert, B.; Moran, G.P.; Vaughan, C.; Yeomans, T.; Maccallum, D.M.; Quinn, J.; Coleman, D.C.; Brown, A.J.P.; Sullivan, D.J. Genome-wide gene expression profiling and a forward genetic screen show that differential expression of the sodium ion transporter Ena21 contributes to the differential tolerance of Candida albicans and Candida dubliniensis to osmotic stress. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 72, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idnurm, A.; Walton, F.J.; Floyd, A.; Reedy, J.L.; Heitman, J. Identification of ENA1 as a virulence gene of the human pathogenic fungus Cryptococcus neoformans through signature-tagged insertional mutagenesis. Eukaryot. Cell 2009, 8, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinyu, E.; Varga, J.; Ferenczy, L. Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of variability in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2567–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.B.; Park, J.Y.; Jung, H.S. First report of leaf anthracnose caused by Colletotrichum boninense on spindle trees. Plant Pathol. 2010, 54, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Kim, K.T.; Yang, J.Y.; Song, H.; Choi, G.; Jeon, J.; Cheong, K.; Ko, J.; Xu, H.; Lee, Y.H. A High-Quality draft genome sequence of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides sensu stricto SMCG1#C, a causal agent of anthracnose on Cunninghamia lanceolata in China. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 32, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Fang, Y.L.; Wang, P.; Ye, J.R.; Huang, L. Pleiotropic Roles of ChSat4 in Asexual Development, Cell Wall Integrity Maintenance, and Pathogenicity in Colletotrichum higginsianum. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Li, B.; Pan, Y.T.; Fang, Y.L.; Li, D.W.; Huang, L. Protein phosphatase CgPpz1 regulates potassium uptake, stress responses, and plant infection in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Phytopathology 2022, 112, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, M.; Chi, M.H.; Khang, C.H.; Park, S.Y.; Kang, S.; Valent, B.; Lee, Y.H. The ER chaperone Lhs1 is involved in asexual development and rice infection by the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.L.; Xia, L.M.; Wang, P.; Zhu, L.H.; Ye, J.R.; Huang, L. The MAPKKK CgMck1 is required for cell wall integrity, appressorium development, and pathogenicity in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Genes 2018, 9, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Li, B.; Pan, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Li, D.W.; Huang, L. Calcineurin-responsive transcription factor CgCrzA is required for cell wall integrity and infection-related morphogenesis in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Plant Pathol. J. 2020, 36, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, Z. The FgVps39-FgVam7-FgSso1 complex mediates vesicle trafficking and is important for the development and virulence of Fusarium graminearum. Plant Microbe Interact. 2017, 30, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Xu, J.R.; Xu, Q.; Ding, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, X. A MADS-box transcription factor MoMcm1 is required for male fertility, microconidium production and virulence in Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 80, 33–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, C.; Su, Z.; Yi, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z. MoTup1 is required for growth, conidiogenesis and pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 16, 799–810. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, Y.T.; Li, L.; Yang, J.Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Wang, P.; Huang, L. Involvement of protein kinase CgSat4 in potassium uptake, cation tolerance, and full virulence in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 773–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, B.; Garciadeblás, B.; Pérez-Martín, J.; Rodríguez-Navarro, A. Growth at high pH and sodium and potassium tolerance in media above the cytoplasmic pH depend on Ena ATPases in Ustilago maydis. Eukaryot. Cell 2009, 8, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, M.; Haro, R.; Conchillo, L.B.; Benito, B. The endophyte Serendipita indica reduces the sodium content of Arabidopsis plants exposed to salt stress: Fungal Ena ATPases are expressed and regulated at high pH and during plant co-cultivation in salinity. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 3364–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markina-Iñarrairaegui, A.; Spielvogel, A.; Etxebeste, O.; Ugalde, U.; Espeso, E.A. Tolerance to alkaline ambient pH in Aspergillus nidulans depends on the activity of Ena proteins. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brett, C.L.; Donowitz, M.; Rao, R. Evolutionary origins of eukaryotic sodium/proton exchangers. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2005, 288, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, R.; Ruiz, A.; Bernal, D.; Chambers, J.R.; Ariño, J. The transcriptional response to alkaline pH in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Evidence for calcium-mediated signalling. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 46, 1319–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibalova-Culakova, H.; Alonso-Del-Real, J.; Querol, A.; Sychrova, H. Expression of heterologous transporters in Saccharomyces kudriavzevii: A strategy for improving yeast salt tolerance and fermentation performance. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 268, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spielvogel, A.; Findon, H.; Arst, H.N.; Araújo-Bazán, L.; Hernández-Ortíz, P.; Stahl, U.; Meyer, V.; Espeso, E.A. Two zinc finger transcription factors, CrzA and SltA, are involved in cation homoeostasis and detoxification in Aspergillus nidulans. Biochem. J. 2008, 414, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirasaki, M.; Horiguchi, M.; Numamoto, M.; Sugiyama, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Nogi, Y.; Harashima, S. Saccharomyces cerevisiae protein phosphatase Ppz1 and protein kinases Sat4 and Hal5 are involved in the control of subcellular localization of Gln3 by likely regulating its phosphorylation state. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, T.-C.; Yang, J.-Y.; Sun, M.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Pan, Y.-T.; Huang, L. Distinct Roles of Ena ATP Family Proteins in Sodium Accumulation, Invasive Growth, and Full Virulence in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9050566
Deng T-C, Yang J-Y, Sun M-L, Zhang Y-Z, Pan Y-T, Huang L. Distinct Roles of Ena ATP Family Proteins in Sodium Accumulation, Invasive Growth, and Full Virulence in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(5):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9050566
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Tian-Ci, Ji-Yun Yang, Mei-Ling Sun, Yun-Zhao Zhang, Yun-Ting Pan, and Lin Huang. 2023. "Distinct Roles of Ena ATP Family Proteins in Sodium Accumulation, Invasive Growth, and Full Virulence in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 5: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9050566
APA StyleDeng, T.-C., Yang, J.-Y., Sun, M.-L., Zhang, Y.-Z., Pan, Y.-T., & Huang, L. (2023). Distinct Roles of Ena ATP Family Proteins in Sodium Accumulation, Invasive Growth, and Full Virulence in Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Journal of Fungi, 9(5), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9050566





