Fungal Biodegradation of Polyurethanes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biodiversity of Fungi Involved in Polyurethane Degradation
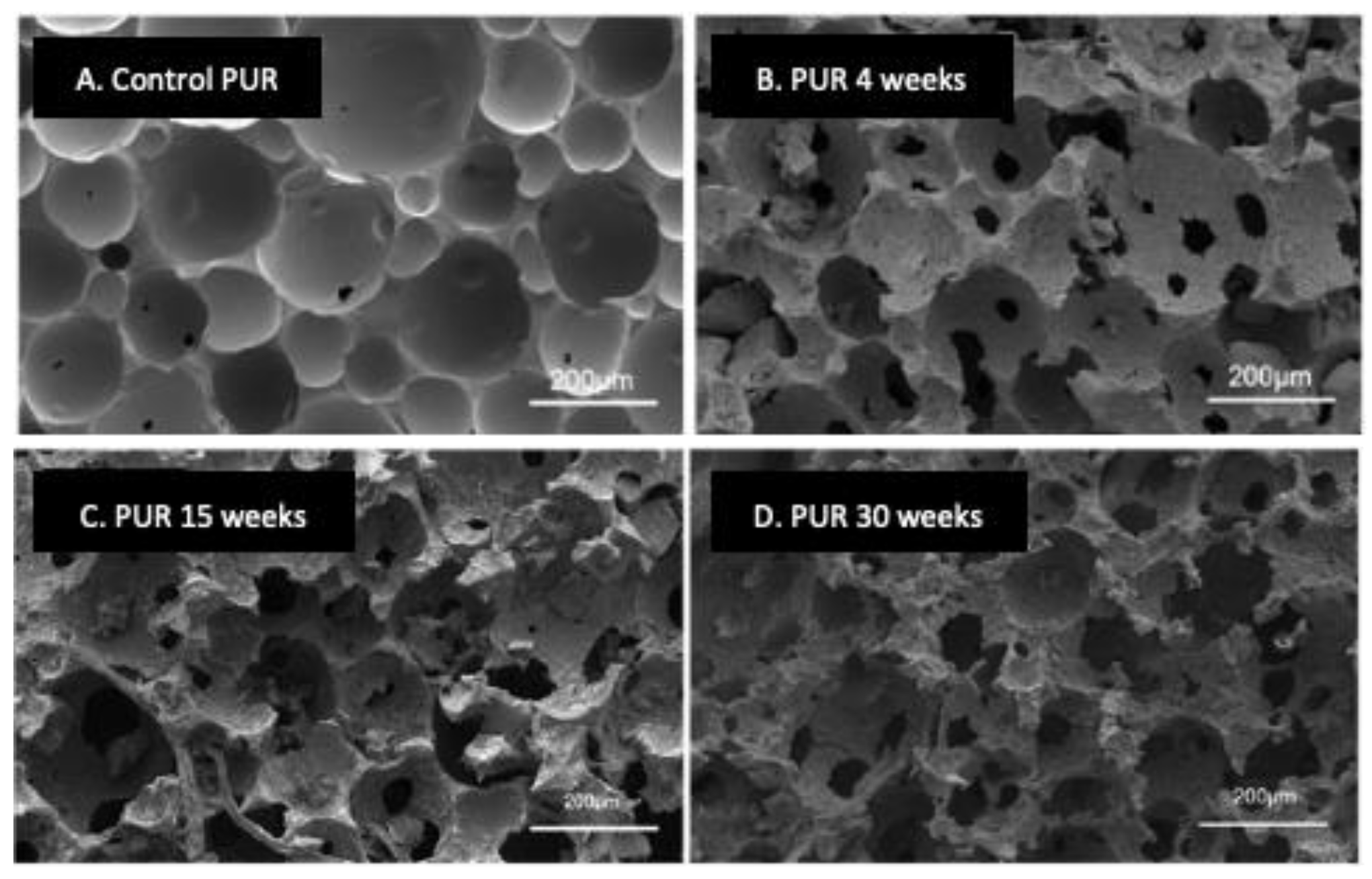
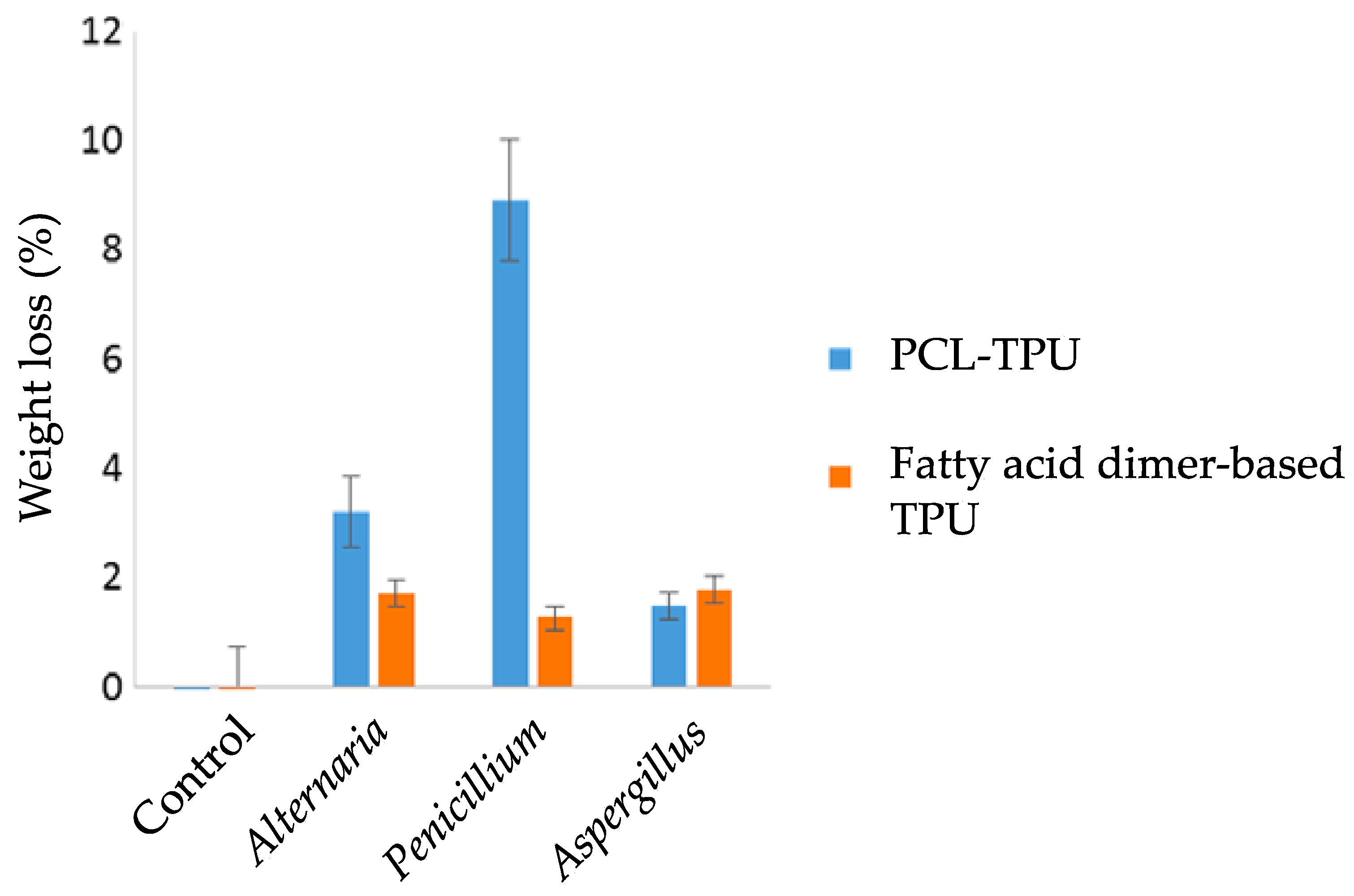
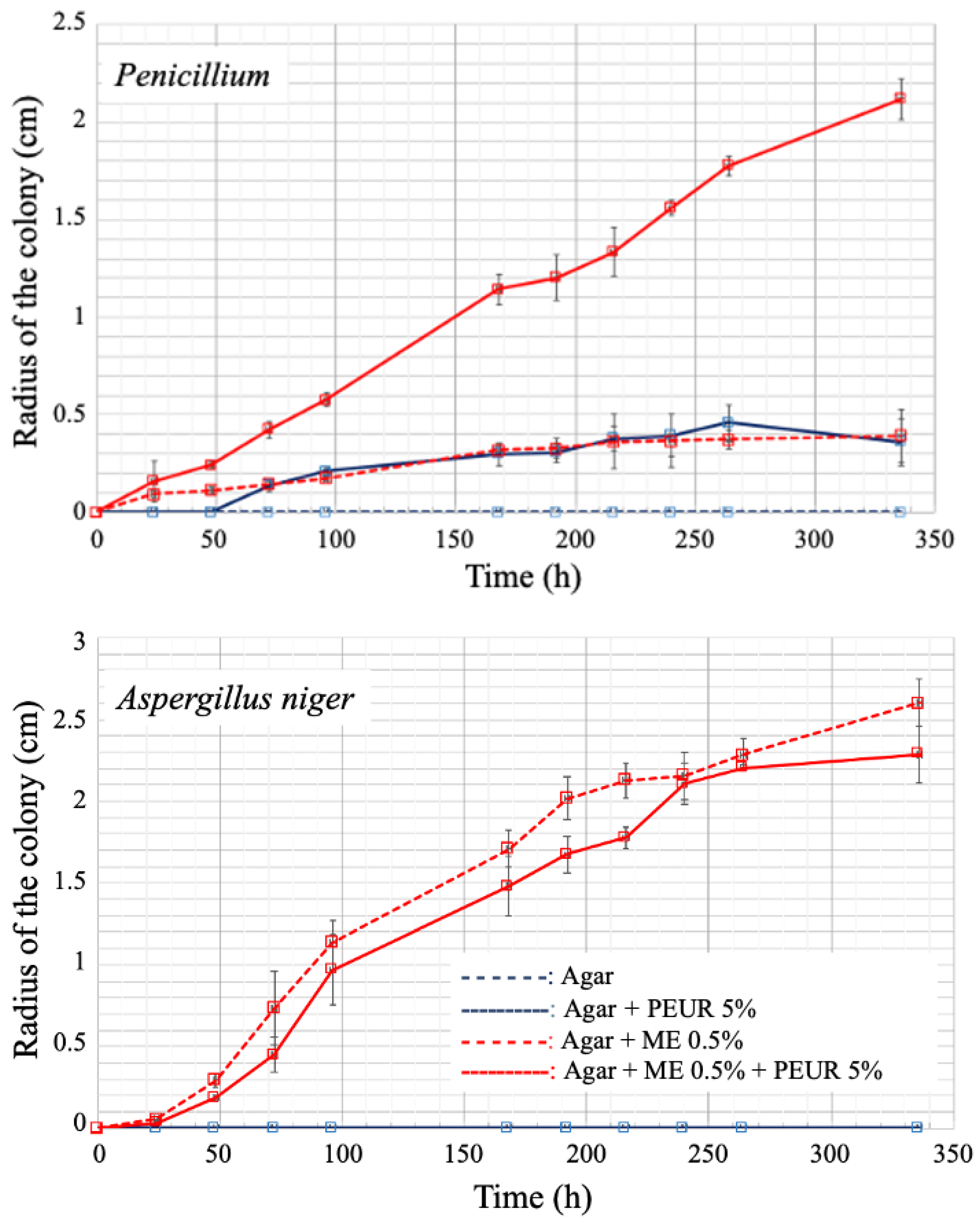
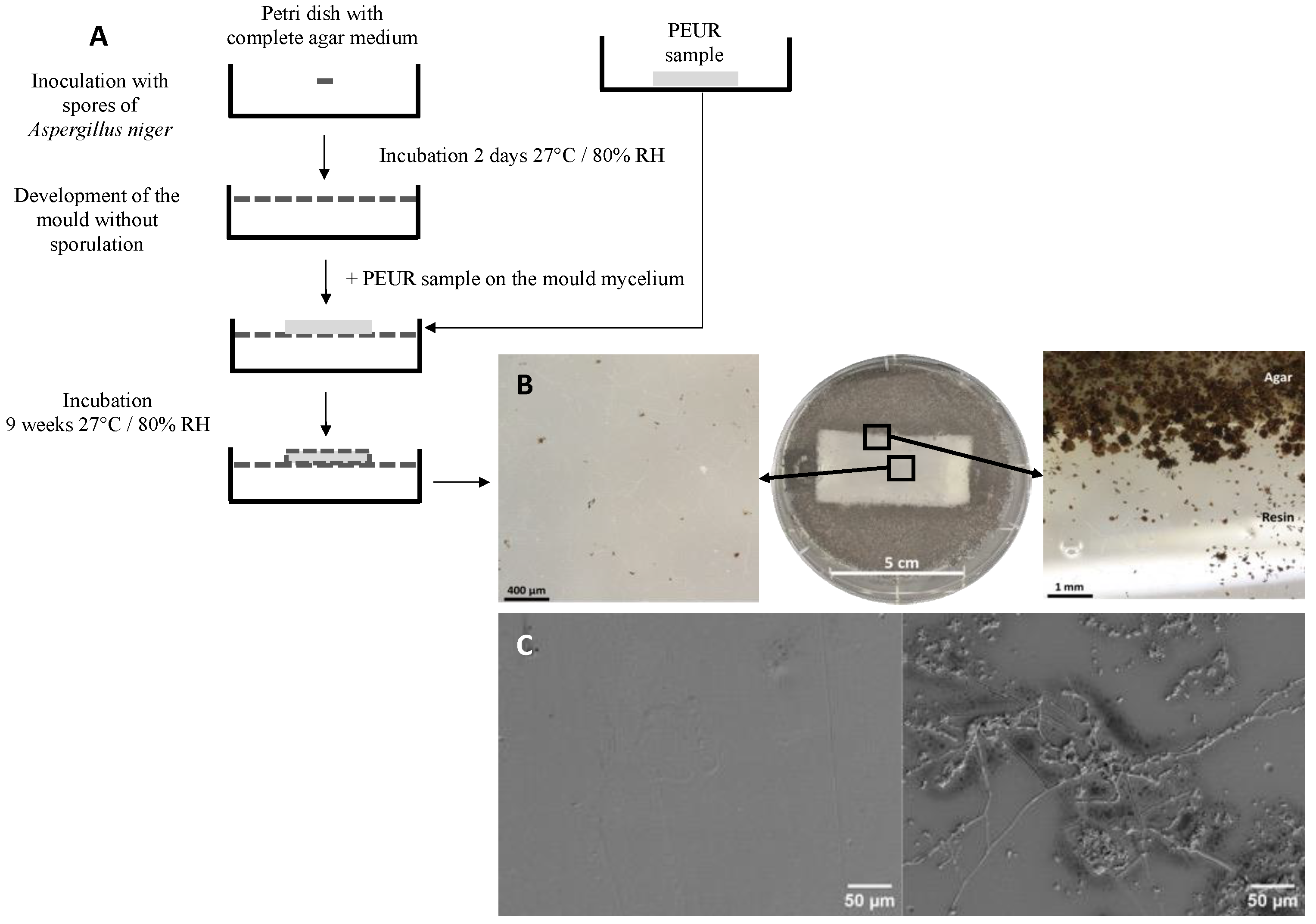
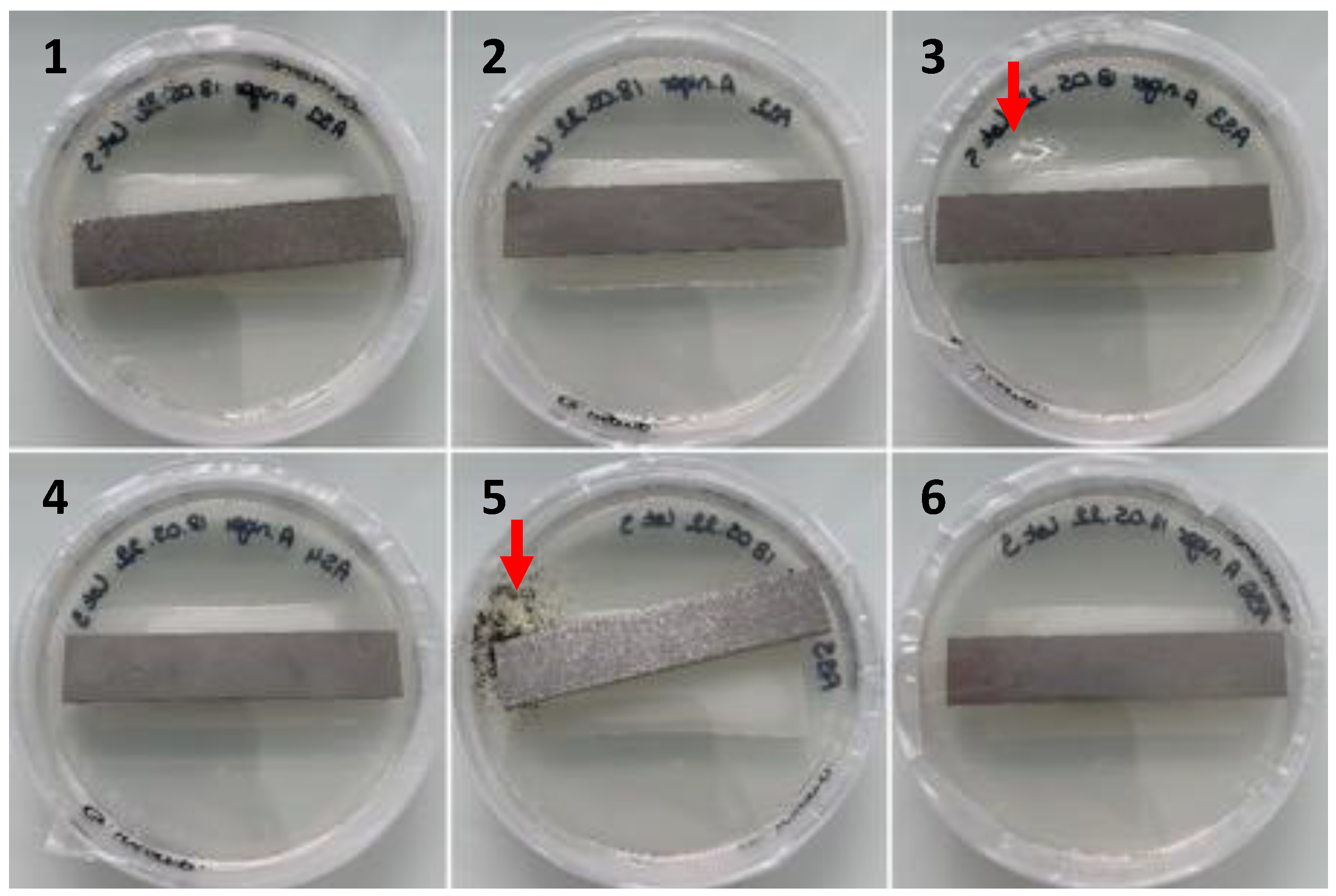
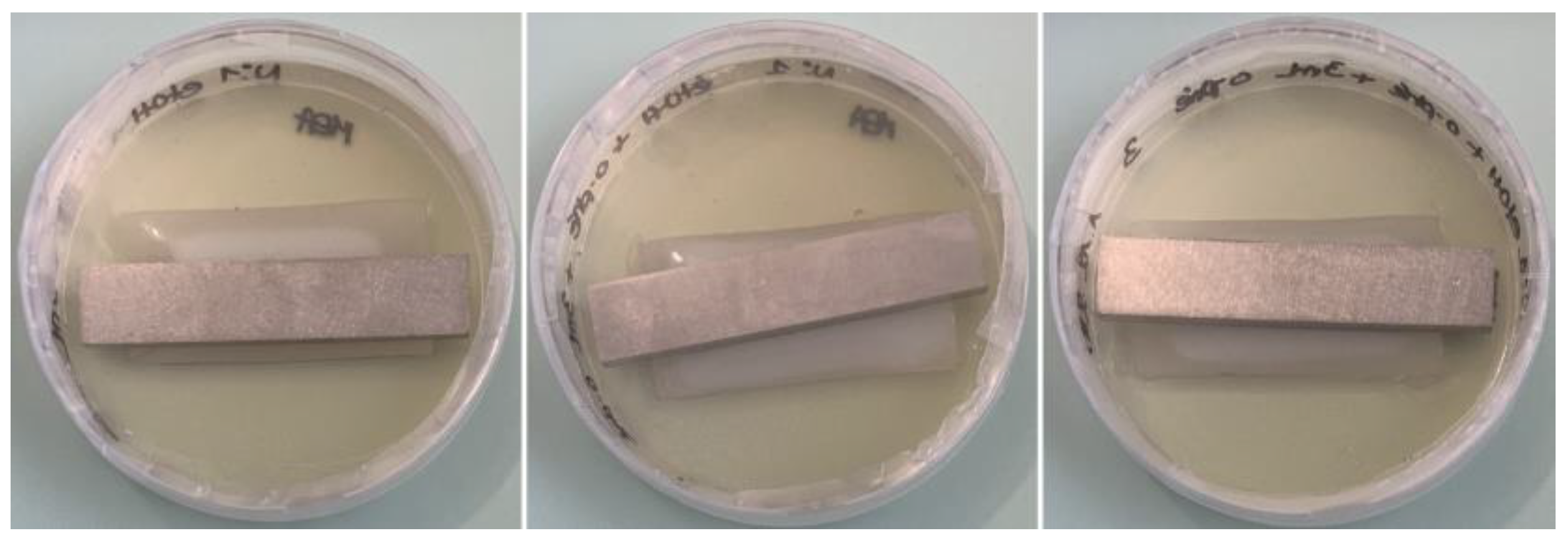
3. Experimental Analysis of Polyurethane Biodegradation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Das, A.; Mahanwar, P. A brief discussion on advances in polyurethane applications. Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2020, 3, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, J.R. Polymer science and technology. Mater. Des. 1995, 16, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhang, T.; Bryant, P.; Kurusingal, V.; Colwell, J.M.; Laycock, B. Degradation and stabilization of polyurethane elastomers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 90, 211–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Wang, L.; Luo, H.; Fan, H.; Xiang, J.; Yan, J.; Li, C.; Chen, Z. Photodegradation behavior and blocking strategy of waterborne polyurethane under UV and Xenon irradiation. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, U.; Nzeram, P.; Langarica-Fuentes, A.; Houlden, A.; Heyworth, A.; Saiani, A.; Robson, G.D. Biodegradation of polyester polyurethane during commercial composting and analysis of associated fungal communities. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 158, 374–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trhlíková, O.; Vlčková, V.; Abbrent, S.; Valešová, K.; Kanizsová, L.; Skleničková, K.; Paruzel, A.; Bujok, S.; Walterová, Z.; Innemanová, P.; et al. Microbial and abiotic degradation of fully aliphatic polyurethane foam suitable for biotechnologies. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2021, 194, 109764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashoua, Y.; Peydaei, A.; Mortensen, M.N.; Kanstrup, A.B.; Gregory, D.J. Real time degradation studies on polyurethane household sponges in Danish weather and marine environments. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 184, 114128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.J.; Roby, M.S. Biodegradable Polymers Poly(amide-urethanes). J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 1986, 1, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima-Kambe, T.; Shigeno-Akutsu, Y.; Nomura, N.; Onuma, F.; Nakahara, T. Microbial degradation of polyurethane, polyester polyurethanes and polyether polyurethanes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 51, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Nadir, S.; Shah, Z.U.; Shah, A.A.; Karunarathna, S.C.; Xu, J.; Khan, A.; Munir, S.; Hasan, F. Biodegradation of polyester polyurethane by Aspergillus tubingensis. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehrei, F. Biodegradation of Synthetic and Natural Plastic by Microorganisms. J. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 5, 8–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, C.-S.; Barlow, D.E.; Varaljay, V.A.; Drake, C.A.; Crouch, A.L.; Russell, J.N.; Nadeau, L.J.; Crookes-Goodson, W.J.; Biffinger, J.C. The biodegradation of polyester and polyester polyurethane coatings using Papiliotrema laurentii. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 139, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, F. Biodegradation of Polyethers and Polyacrylate. In Studies in Polymer Science; Biodegradable Plastics and Polymers; Doi, Y., Fukuda, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; Volume 12, pp. 24–38. [Google Scholar]
- Mohan, S.K.; Srivastava, T. Microbial deterioration and degradation of Polymeric materials. J. Biochem. Tech. 2010, 2, 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Delacuvellerie, A.; Benali, S.; Cyriaque, V.; Moins, S.; Raquez, J.-M.; Gobert, S.; Wattiez, R. Microbial biofilm composition and polymer degradation of compostable and non-compostable plastics immersed in the marine environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 419, 126526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiontek Brzezinska, M.; Walczak, M.; Kalwasińska, A.; Richert, A.; Świątczak, J.; Deja-Sikora, E.; Burkowska-But, A. Biofilm formation during biodegradation of polylactide, poly (3,4 hydroxybutyrate) and poly(ε-caprolactone) in activated sludge. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Hasan, F.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, S. Biological degradation of plastics: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2008, 26, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NF EN ISO 846-Plastiques-Évaluation de l’action des Micro-Organismes. Available online: https://www.boutique.afnor.org/fr-fr/norme/nf-en-iso-846/plastiques-evaluation-de-laction-des-microorganismes/fa193962/83371 (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- OECD. Test No. 301: Ready Biodegradability; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Paris, France, 1992; Available online: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-301-ready-biodegradability_9789264070349-en (accessed on 27 June 2023).
- Barratt, S.R.; Ennos, A.R.; Greenhalgh, M.; Robson, G.D.; Handley, P.S. Fungi are the predominant micro-organisms responsible for degradation of soil-buried polyester polyurethane over a range of soil water holding capacities. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 95, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darby, R.T.; Kaplan, A.M. Fungal Susceptibility of Polyurethanes. Appl. Microbiol. 1968, 16, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathirana, R.A.; Seal, J. Studies on polyurethane deteriorating fungi. Part 2. An examination of their enzyme activities. Int. Biodeterior. 1984, 20, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Crabbe, J.R.; Campbell, J.R.; Thompson, L.; Walz, S.L.; Schultz, W.W. Biodegradation of a colloidal ester-based polyurethane by soil fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1994, 33, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, L.; McGeechan, P.L.; Robson, G.D.; Handley, P.S. Fungal Communities Associated with Degradation of Polyester Polyurethane in Soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5817–5824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumiya, Y.; Murata, N.; Tanabe, E.; Kubota, K.; Kubo, M. Isolation and characterization of an ether-type polyurethane-degrading micro-organism and analysis of degradation mechanism by Alternaria sp. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.R.; Huang, J.; Anand, P.; Kucera, K.; Sandoval, A.G.; Dantzler, K.W.; Hickman, D.; Jee, J.; Kimovec, F.M.; Koppstein, D.; et al. Biodegradation of Polyester Polyurethane by Endophytic Fungi. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 6076–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, G.; Prasad, R. Degradation of Polyurethane by Aspergillus flavus (ITCC 6051) Isolated from Soil. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Barragán, J.; Domínguez-Malfavón, L.; Vargas-Suárez, M.; González-Hernández, R.; Aguilar-Osorio, G.; Loza-Tavera, H. Biodegradative Activities of Selected Environmental Fungi on a Polyester Polyurethane Varnish and Polyether Polyurethane Foams. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5225–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Hu, J.; Yang, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhuang, P.; Grossart, H.-P.; Luo, Z. Biodegradation of polyester polyurethane by the marine fungus Cladosporium halotolerans 6UPA1. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filip, Z. Polyurethane as the sole nutrient source for Aspergillus niger and Cladosporium herbarum. Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1979, 7, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plancher, L.; Nguyen, G.T.M.; Hébert, R.; Maestri, C.; Mélinge, Y.; Ledésert, B.; Di Martino, P. Oxidative biodegradation of a solid-solid polyether-urethane phase change material by Penicillium and Aspergillus. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, S.; Otani, T.; Masaoka, S.; Ohe, T. The Biodegradation of Low-molecular-weight Urethane Compounds by a Strain of Exophiala jeanselmei. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1996, 60, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taxeidis, G.; Nikolaivits, E.; Siaperas, R.; Gkountela, C.; Vouyiouka, S.; Pantelic, B.; Nikodinovic-Runic, J.; Topakas, E. Triggering and identifying the polyurethane and polyethylene-degrading machinery of filamentous fungi secretomes. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 325, 121460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnin, A.; Entzmann, L.; Pollet, E.; Avérous, L. Breakthrough in polyurethane bio-recycling: An efficient laccase-mediated system for the degradation of different types of polyurethanes. Waste Manag. 2021, 132, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burelo, M.; Gaytán, I.; Loza-Tavera, H.; Cruz-Morales, J.A.; Zárate-Saldaña, D.; Cruz-Gómez, M.J.; Gutiérrez, S. Synthesis, characterization and biodegradation studies of polyurethanes: Effect of unsaturation on biodegradability. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.D.; Kim, S.C. Effect of chemical structure on the biodegradation of polyurethanes under composting conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1998, 62, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.; Kalita, H.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Degradation Study of Biobased Polyester–Polyurethane and its Nanocomposite Under Natural Soil Burial, UV Radiation and Hydrolytic-Salt Water Circumstances. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 1528–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, N.R.; Tessman, M.; Schreiman, A.C.; Simkovsky, R.; Samoylov, A.A.; Neelakantan, N.K.; Bemis, T.A.; Burkart, M.D.; Pomeroy, R.S.; Mayfield, S.P. Rapid biodegradation of renewable polyurethane foams with identification of associated microorganisms and decomposition products. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2020, 11, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, N.R.; Tessman, M.; Zhen, D.; Johnson, L.; Evans, P.; Clements, S.M.; Pomeroy, R.S.; Burkart, M.D.; Simkovsky, R.; Mayfield, S.P. Biodegradation of renewable polyurethane foams in marine environments occurs through depolymerization by marine microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, N.L.; Adhikari, R.; Shanks, R.; Adhikari, B. Aerobic biodegradation of starch–polyurethane flexible films under soil burial condition: Changes in physical structure and chemical composition. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 145, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Xu, L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, G. Degradable polyurethane for marine anti-biofouling. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 3099–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Xiao, Y.; Song, L.; Hu, J.; Rao, Q.; Shoaib, M.; Amin, B.U.; Zhan, X.; Zhang, Q. Biodegradable polyurethane based clay composite and their anti-biofouling properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weintraub, S.; Harris, L.G.; Thevissen, K.; Lewitus, D.Y. Polyastaxanthin-based coatings reduce bacterial colonization in vivo. Materialia 2018, 3, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Franier, B.; Asker, D.; van den Berg, D.; Hatton, B.; Thompson, M. Reduction of microbial adhesion on polyurethane by a sub-nanometer covalently-attached surface modifier. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 200, 111579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, S.; Blaszykowski, C.; Nolan, R.; Thompson, D.; Thompson, M. On the hydration of subnanometric antifouling organosilane adlayers: A molecular dynamics simulation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 437, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnin, A.; Hoornaert, L.; Pollet, E.; Laurichesse, S.; Phalip, V.; Avérous, L. Isolation and characterization of different promising fungi for biological waste management of polyurethanes. Microb. Biotechnol. 2018, 12, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardelli, G.; Rechichi, A.; Cerrai, P.; Tricoli, M.; Barbani, N.; Giusti, P. Segmented Polyurethanes for Medical Applications: Synthesis, Characterization and in vitro Enzymatic Degradation Studies. Macromol. Symp. 2004, 218, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffinger, J.C.; Barlow, D.E.; Cockrell, A.L.; Cusick, K.D.; Hervey, W.J.; Fitzgerald, L.A.; Nadeau, L.J.; Hung, C.S.; Crookes-Goodson, W.J.; Russell, J.N. The applicability of Impranil®DLN for gauging the biodegradation of polyurethanes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 120, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, J.; Xue, R.; Xu, B.; Qian, X.; Xin, F.; Blank, L.M.; Zhou, J.; Wei, R.; Dong, W.; et al. Biodegradation and up-cycling of polyurethanes: Progress, challenges, and prospects. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 48, 107730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattuati-Derieux, A.; Thao-Heu, S.; Lavédrine, B. Assessment of the degradation of polyurethane foams after artificial and natural ageing by using pyrolysis-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry and headspace-solid phase microextraction-gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4498–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Lopina, S.T. Oxidative and enzymatic degradations of l-tyrosine based polyurethanes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 1994–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, S. Dependence of fungal biodegradation of PEG/castor oil-based polyurethane elastomers on the hard-segment structure. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 2396–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, A.E.; Zebrowski, J.; Piszczyk, Ł.; Boyko, V.V.; Riabov, S.V.; Dmitrieva, T.; Bortnitskiy, V.I.; Gonchar, M.; Wojnarowska-Nowak, R.; Ryszkowska, J. Assessment of the impact of bacteria Pseudomonas denitrificans, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Bacillus subtilis and yeast Yarrowia lipolytica on commercial poly(ether urethanes). Polym. Test. 2017, 63, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harussani, M.M.; Sapuan, S.M.; Firdaus, A.H.M.; El-Badry, Y.A.; Hussein, E.E.; El-Bahy, Z.M. Determination of the Tensile Properties and Biodegradability of Cornstarch-Based Biopolymers Plasticized with Sorbitol and Glycerol. Polymers 2021, 13, 3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrzejewska, A. One Year Evaluation of Material Properties Changes of Polylactide Parts in Various Hydrolytic Degradation Conditions. Polymers 2019, 11, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NF EN ISO 527-2-Plastiques-Détermination des Propriétés en Traction-Partie 2: Conditions d’essai des Plastiques Pour Moulage et Extrusion. Available online: https://www.boutique.afnor.org/fr-fr/norme/nf-en-iso-5272/plastiques-determination-des-proprietes-en-traction-partie-2-conditions-des/fa154013/39223 (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- Rafiemanzelat, F.; Jafari, M.; Emtiazi, G. Study of Biological Degradation of New Poly(Ether-Urethane-Urea)s Containing Cyclopeptide Moiety and PEG by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Isolated from Soil. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 177, 842–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuka, E.; Cirule, D.; Andersone, I.; Andersons, B.; Antons, A.; Kevers, M.; Danieks, M. Photodegradation risk evaluation of polyurethane gluelines in wood products by infrared spectroscopy and mechanical tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 379, 131251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, M.; Springthorpe, V.S.; Sattar, S.A. Feasibility of a combined carrier test for disinfectants: Studies with a mixture of five types of microorganisms. Am. J. Infect. Control. 1994, 22, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penna, T.C.V.; Mazzola, P.G.; Silva Martins, A.M. The efficacy of chemical agents in cleaning and disinfection programs. BMC Infect. Dis. 2001, 1, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, G.; Russell, A.D. Antiseptics and Disinfectants: Activity, Action, and Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 147–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Diol | Diisocyanate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tolylene-2,4-Diisocyanate | Diphenylmethane-4,4′-Diisocyanate | 3,3′-Bitolylene-4,4′-Diisocyanate | 1,6-Hexamethylene-Diisocyanate | ||
| 1,5-Pentanediol | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | Polyurethane |
| 3-Methyl-2,4-pentanediol | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Polyurethane |
| 2-Methyl-2,4-pentanediol | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Polyurethane |
| Diethylene glycol | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | Polyurethane |
| Dipropylene glycol | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Polyurethane |
| Polypropylene glycol 400 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | Polyether urethane |
| Polypropylene glycol 1020 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | Polyether urethane |
| Polypropylene glycol 1320 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | Polyether urethane |
| Polyethylene glycol adipate | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Polyester urethane |
| Poly-1,3-propanediol adipate | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | Polyester urethane |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maestri, C.; Plancher, L.; Duthoit, A.; Hébert, R.L.; Di Martino, P. Fungal Biodegradation of Polyurethanes. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9070760
Maestri C, Plancher L, Duthoit A, Hébert RL, Di Martino P. Fungal Biodegradation of Polyurethanes. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(7):760. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9070760
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaestri, Clotilde, Lionel Plancher, Alexis Duthoit, Ronan L. Hébert, and Patrick Di Martino. 2023. "Fungal Biodegradation of Polyurethanes" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 7: 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9070760
APA StyleMaestri, C., Plancher, L., Duthoit, A., Hébert, R. L., & Di Martino, P. (2023). Fungal Biodegradation of Polyurethanes. Journal of Fungi, 9(7), 760. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9070760







