From Lab to Shelf: Gelatin-Based pH Sensors Revolutionizing Food Packaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Classification, Sources and Functional Properties of Gelatin
2.1. Sources of Gelatin
2.2. Classification of Gelatin
2.3. Properties of Gelatin
2.4. Biodegradation of Gelatin-Based Film
3. Development of Gelatin-Based pH Sensors
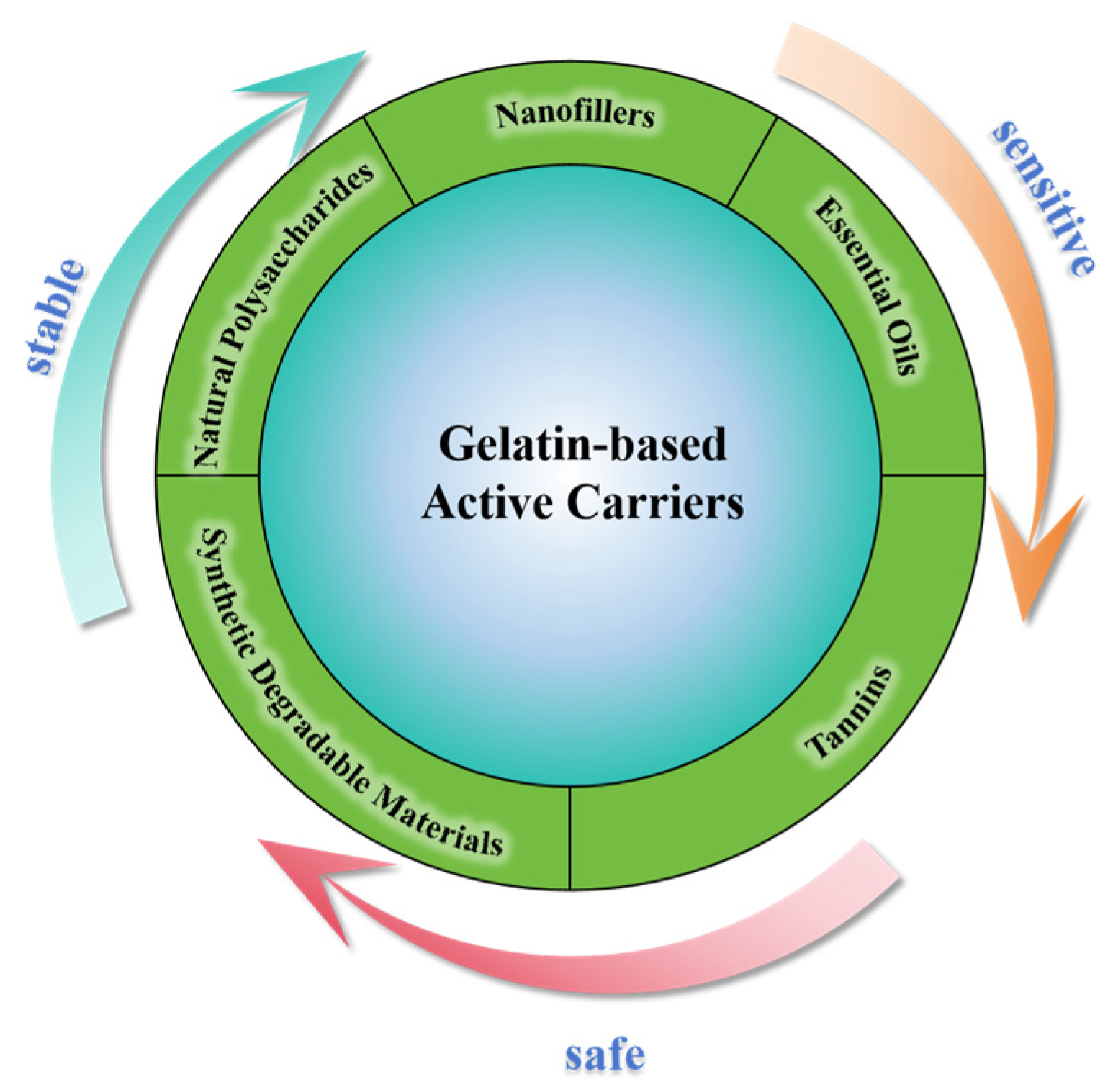
3.1. Active Carriers
3.1.1. Natural Polysaccharides
3.1.2. Nanofillers
3.1.3. Essential Oils
3.1.4. Tannins
3.1.5. Synthetic Degradable Materials
3.2. Intelligent Indicators
3.2.1. Synthetic Dyes
3.2.2. Natural Dyes
4. Summary and Outlook
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fung, F.; Wang, H.S.; Menon, S. Food safety in the 21st century. Biomed. J. 2018, 41, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halonen, N.; Pálvölgyi, P.S.; Bassani, A.; Fiorentini, C.; Nair, R.; Spigno, G.; Kordas, K. Bio-based smart materials for food packaging and sensors—A review. Front. Mater. 2020, 7, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, T.; Cole, M.; Farber, J.M.; Eisenbrand, G.; Zabaras, D.; Fox, E.M.; Hill, J.P. Food safety for food security: Relationship between global megatrends and developments in food safety. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 68, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, M.; Ferrara, L.; Calogero, A.; Montesano, D.; Naviglio, D. Relationships between food and diseases: What to know to ensure food safety. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, M.; Zhao, X.; Wei, X.; Luo, Z.; Gu, W.; Du, D.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, C. Single-atom materials for food safety. Mater. Today 2023, 64, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, M.A.; Azizi-Lalabadi, M.; Tavassoli, M.; Mohammadi, K.; McClements, D.J. Recent advances in the development of smart and active biodegradable packaging materials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, S.; Gholizadeh, S.; Hamishehkar, H.; Moghaddam, T.N.; Haghi, P.B.; Bakhshizadeh, M. Development of an intelligent packaging system based on gelatin/chitosan nanofibers and containing β-Cyclodextrin/Viola odorata L. anthocyanins complex. J. Polym. Environ. 2024, 32, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebel, F.S.; Roufegarinejad, L.; Alizadeh, A.; Amjadi, S. Development and characterization of a double-layer smart packaging system consisting of polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers and gelatin film for fish fillet. Food Chem. 2025, 462, 140985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Peng, Q.; Wang, J.; Deng, J.; Li, W.; Lin, Q.; Zhong, F.; Xia, X. An intelligent thymol/alizarin-loaded polycaprolactone/gelatin/zein nanofibrous film with pH-responsive and antibacterial properties for shrimp freshness monitoring and preservation. Food Chem. 2025, 471, 142812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaslan, D. Use of colorimetric hydrogel as an indicator for food packaging applications. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2019, 42, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, M.A.; Maleki, M.; Eghbaljoo-Gharehgheshlaghi, H.; Khezerlou, A.; Mohammadian, E.; Liu, Q.; Jafari, S.M. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles as multifunctional surface-active materials for smart/active nanocomposite packaging films. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 300, 102593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, M.; Papchenko, K.; Degli Esposti, M.; Tondi, G.; De Angelis, M.G.; Morselli, D.; Fabbri, P. Fully biobased polyhydroxyalkanoate/tannin films as multifunctional materials for smart food packaging applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 28594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh-Sani, M.; Tavassoli, M.; McClements, D.J.; Hamishehkar, H. Multifunctional halochromic packaging materials: Saffron petal anthocyanin loaded-chitosan nanofiber/methyl cellulose matrices. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavassoli, M.; Sani, M.A.; Khezerlou, A.; Ehsani, A.; McClements, D.J. Multifunctional nanocomposite active packaging materials: Immobilization of quercetin, lactoferrin, and chitosan nanofiber particles in gelatin films. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 118, 106747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balbinot-Alfaro, E.; Craveiro, D.V.; Lima, K.O.; Costa, H.L.G.; Lopes, D.R.; Prentice, C. Intelligent packaging with pH indicator potential. Food Eng. Rev. 2019, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, H.; Su, H.M.; Imani, S.M.; Alkhaldi, K.M.; Filipe, C.D.; Didar, T.F. Intelligent food packaging: A review of smart sensing technologies for monitoring food quality. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Yang, M.; Abdalkarim, S.Y.H.; Yu, H.Y. In situ growth of curcumin-loaded cellulose composite film for real-time monitoring of food freshness in smart packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 279, 135090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echegaray, N.; Guzel, N.; Kumar, M.; Guzel, M.; Hassoun, A.; Lorenzo, J.M. Recent advancements in natural colorants and their application as coloring in food and in intelligent food packaging. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, C.M.; Maciel, V.B.V.; Mendonça, M.E.D.; Franco, T.T. Chitosan biobased and intelligent films: Monitoring pH variations. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 55, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, H.; Xue, C.; Ji, D.; Wen, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Sustainably sourced, water-soluble biofilms based on keratin constructed through two crosslinking modes: Turning waste into useful materials. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jing, Y.; Li, J.; Zhan, H. An acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on ionic liquid functionalized graphene–gelatin-modified electrode for sensitive detection of pesticides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 210, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Wu, X. A Review of Modified Gelatin: Physicochemical Properties, Modification Methods, and Applications in the Food Field. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 20705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidau, C.; Râpă, M.; Ionita, G.; Stanculescu, I.R.; Zaharescu, T.; Constantinescu, R.R.; Lazea-Stoyanova, A.; Stanca, M. The Influence of Gamma Radiation on Different Gelatin Nanofibers and Gelatins. Gels 2024, 10, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Hossen, M.A.; Zeng, Y.; Dai, J.; Li, S.; Qin, W.; Liu, Y. Gelatin-based composite films and their application in food packaging: A review. J. Food Eng. 2022, 313, 110762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsuwat, S.; Zhang, P.; Ng, K.; Fang, Z. Fish gelatin as an alternative to mammalian gelatin for food industry: A meta-analysis. LWT 2021, 141, 110899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Zi, Y.; Peng, J.; Shi, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhong, J. Gelatin as a bioactive nanodelivery system for functional food applications. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziola, F.; Candido, T.M.; Oliveira, C.A.D.; Peres, D.D.A.; Issa, M.G.; Mota, J.; Rosado, C.; Consiglieri, V.O.; Kaneko, T.M.; Velasco, M.V.R.; et al. Gelatin-based microspheres crosslinked with glutaraldehyde and rutin oriented to cosmetics. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 52, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscaglia, M.; Guérard, F.; Roquefort, P.; Aubry, T.; Fauchon, M.; Toueix, Y.; Fauchon, M.; Toueix, Y.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Hellio, C.; et al. Mechanically enhanced salmo salar gelatin by enzymatic cross-linking: Premise of a bioinspired material for food packaging, cosmetics, and biomedical applications. Mar. Biotechnol. 2022, 24, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Wu, D. Design of gum Arabic/gelatin composite microcapsules and their cosmetic applications in encapsulating tea tree essential oil. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nimry, S.; Dayah, A.A.; Hasan, I.; Daghmash, R. Cosmetic, biomedical and pharmaceutical applications of fish gelatin/hydrolysates. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Qader, I.B.; Abbott, A.P. Controlled release of pharmaceutical agents using eutectic modified gelatin. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukiran, N.A.; Anuar, N.A.A.; Jamaludin, M.A. Gelatin in halal pharmaceutical products. Malays. J. Syariah Law 2023, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dille, M.J.; Hattrem, M.N.; Draget, K.I. Soft, chewable gelatin-based pharmaceutical oral formulations: A technical approach. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2018, 23, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girdhar, V.; Patil, S.; Dubey, S.K.; Singhvi, G. Pharmaceutical applications of gelatin. In Natural Polymers for Pharmaceutical Applications; Apple Academic Press: Florida, NJ, USA, 2019; p. 93. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, L.C.; Huang, Q.Y.; Ding, W.; Xiao, X.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xiong, L.X. Fish gelatin: The novel potential applications. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 63, 103581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.B.; Showva, N.N.; Hoque, M.E. Gelatin-based scaffolds: An intuitive support structure for regenerative therapy. Current Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2023, 26, 100452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, F.; Raza, Z.A.; Batool, S.R.; Zahid, M.; Onder, O.C.; Rafique, A.; Nazeer, M.A. Preparation, properties, and applications of gelatin-based hydrogels (GHs) in the environmental, technological, and biomedical sectors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 218, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanto, S.; Narayana, S.; Merai, K.P.; Kumar, J.A.; Bhunia, A.; Hani, U.; Fatease, A.A.; Gowda, B.H.J.; Nag, S.; Ahmed, M.G.; et al. Advancements in gelatin-based hydrogel systems for biomedical applications: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Seedi, H.R.; Said, N.S.; Yosri, N.; Hawash, H.B.; El-Sherif, D.M.; Abouzid, M.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Yaseen, M.; Omarl, H.; Shou, Q.; et al. Gelatin nanofibers: Recent insights in synthesis, bio-medical applications and limitations. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, Y.S.; Salgado, P.R.; Mauri, A.N. Gelatin based films capable of modifying its color against environmental pH changes. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duconseille, A.; Astruc, T.; Quintana, N.; Meersman, F.; Sante-Lhoutellier, V. Gelatin structure and composition linked to hard capsule dissolution: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 43, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.Z.; Sha, X.M.; Huang, T.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.Y.; Tu, Z.C. Microbial transglutaminase (MTGase) modified fish gelatin-γ-polyglutamic acid (γ-PGA): Rheological behavior, gelling properties, and structure. Food Chem. 2021, 348, 129093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedinia, A.; Nafchi, A.M.; Sharifi, M.; Ghalambor, P.; Oladzadabbasabadi, N.; Ariffin, F.; Huda, N. Poultry gelatin: Characteristics, developments, challenges, and future outlooks as a sustainable alternative for mammalian gelatin. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 104, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.Z.; Regenstein, J.M. Optimization of extraction conditions for pollock skin gelatin. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songchotikunpan, P.; Tattiyakul, J.; Supaphol, P. Extraction and electrospinning of gelatin from fish skin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.K.; Ham, Y.K.; Shin, D.M.; Kim, H.W.; Jang, H.W.; Kim, Y.B.; Choi, Y.S. Extraction of crude gelatin from duck skin: Effects of heating methods on gelatin yield. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, P.F.; Lannes, S.C.D.S. Extraction and physicochemical characterization of gelatin from chicken by-product. J. Food Process Eng. 2013, 36, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarbon, N.M.; Badii, F.; Howell, N.K. Preparation and characterisation of chicken skin gelatin as an alternative to mammalian gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 30, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foox, M.; Zilberman, M. Drug delivery from gelatin-based systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Tu, Z.C.; Shangguan, X.; Sha, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Bansal, N. Fish gelatin modifications: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedinia, A.; Ariffin, F.; Huda, N.; Nafchi, A.M. Preparation and characterization of a novel biocomposite based on duck feet gelatin as alternative to bovine gelatin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.B.; Huang, F.; Lu, Y.H.; Huang, J.M.; Ali, M.; Jia, X.Z.; Zeng, X.; Huang, Y.Y. Polysaccharide-based food packaging and intelligent packaging applications: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, T.; Yoshihara, R.; Danjo, S.; Fukuhara, Y.; Evans, C.; Tomimatsu, R.; Ohzuno, Y.; Yoshida, M. Hydrophobically-modified gelatin hydrogel as a carrier for charged hydrophilic drugs and hydrophobic drugs. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramwit, P.; Jaichawa, N.; Ratanavaraporn, J.; Srichana, T. A comparative study of type A and type B gelatin nanoparticles as the controlled release carriers for different model compounds. Mater. Express 2015, 5, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulidori, E.; Micalizzi, S.; Koutsomarkos, N.; Bramanti, E.; Tinè, M.R.; Vozzi, G.; De Maria, C.; Chatzinikolaidou, M.; Duce, C. Analysis of gelatin secondary structure in gelatin/keratin-based biomaterials. J. Mol. Struct. 2023, 1279, 134984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipal, J.; Pu’Ad, N.M.; Lee, T.C.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Sahari, N.; Basri, H.; Idris, M.; Abdullah, H.Z. A review of gelatin: Properties, sources, process, applications, and commercialisation. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, M.M. Strategies for surface modification of gelatin-based nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 183, 110407. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhailov, O.V. Gelatin as it is: History and modernity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, X.; Kang, Q.; Zhu, L.; Qin, G.; Chen, Q. Freezing-tolerant and robust gelatin-based supramolecular conductive hydrogels with double-network structure for wearable sensors. Polym. Test. 2021, 93, 106879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, T.; Raza, Z.A.; Nazeer, M.A.; Khan, A. Synthesis of aminolyzed gelatin-mediated chitosan as pH-responsive drug-carrying porous scaffolds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 256, 128525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suderman, N.; Isa, M.I.N.; Sarbon, N.M. The effect of plasticizers on the functional properties of biodegradable gelatin-based film: A review. Food Biosci. 2018, 24, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althawab, S.A.; Alsulami, T.; Alzahrani, H.; Alzahrani, A. Doped carbon dots reinforced flexible nanocomposite active polymer film for antibacterial and antioxidant activities. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 698, 134554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, T. Applications of gelatin in biosensors: Recent trends and progress. Biosensors 2022, 12, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, M.D.L.L.R.; da Rocha Pires, N.; da Cunha, P.L.R.; de Freitas Rosa, M.; de Souza, B.W.S.; de Andrade Feitosa, J.P.; de Souza, M.D.S.M. Effect of tannic acid as crosslinking agent on fish skin gelatin-silver nanocomposite film. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2019, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshizadeh, M.; Ayaseh, A.; Hamishehkar, H.; Kafil, H.S.; Moghaddam, T.N.; Haghi, P.B.; Tavassoli, M.; Amjadi, S.; Lorenzo, J.M. Multifunctional performance of packaging system based on gelatin/alove vera gel film containing of rosemary essential oil and common poppy anthocyanins. Food Control 2023, 154, 110017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.S.; Sarbon, N.M. Physical and mechanical characteristics of gelatin-based films as a potential food packaging material: A review. Membranes 2022, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.S.; Howell, N.K.; Sarbon, N.M. A review on potential use of gelatin-based film as active and smart biodegradable films for food packaging application. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, J.A.; Akhter, N.; Ashraf, Q.S.; Mir, S.A.; Makroo, H.A.; Majid, D.; Barba, F.J.; Khaneghah, A.M.; Dar, B.N. A comprehensive review on gelatin: Understanding impact of the sources, extraction methods, and modifications on potential packaging applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Ning, X.; Sun, J.; Chen, Q.; Ling, M. Reversible cross-linking of gelatin by a disulphide-containing bis-succinimide for tunable degradation and release. Food Chem. 2023, 18, 100699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, B.T.; Borges, L.L.R.; de Leon, N.M.E.P.; Arruda, T.R.; Ribeiro, A.R.C.; Marques, C.S.; Stringheta, P.C.; de Oliveira, T.V.; Soares, N.D.F.F. Gelatin/polyvinyl alcohol films incorporated with different blueberry extracts as potential colorimetric indicators to detect acidic and basic vapors. Food Control 2024, 165, 110648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.; Gogoi, J.; Dubey, S.; Chowdhury, D. Animal derived biopolymers for food packaging applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 255, 128197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaari, M.; Elhadef, K.; Akermi, S.; Ben Akacha, B.; Fourati, M.; Chakchouk Mtibaa, A.; Ennouri, M.; Sarkar, T.; Shariati, M.A.; Rebezov, M.; et al. Novel active food packaging films based on gelatin-sodium alginate containing beetroot peel extract. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, Y.S.; Salgado, P.R.; Maur, A.N. Smart gelatin films prepared using red cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) extracts as solvent. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibeogu, I.H.; Bako, H.K.; Yar, M.S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, M.; Ke, W.; Shan, K.; Zhou, G.; et al. Gelatin-serum plasma film incorporated with curcumin for improvement of antioxidant and antibacterial properties for fresh pork packaging application. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 149, 109617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.; Liu, J. Polysaccharide-catechin conjugates: Synthesis methods, structural characteristics, physicochemical properties, bioactivities and potential applications in food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 145, 104353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.W. Preparation of gelatin/carrageenan-based color-indicator film integrated with shikonin and propolis for smart food packaging applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 4, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jancikova, S.; Jamróz, E.; Kulawik, P.; Tkaczewska, J.; Dordevic, D. Furcellaran/gelatin hydrolysate/rosemary extract composite films as active and intelligent packaging materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadi, A.; Ferfera-Harrar, H. Cross-linked CMC/Gelatin bio-nanocomposite films with organoclay, red cabbage anthocyanins and pistacia leaves extract as active intelligent food packaging: Colorimetric pH indication, antimicrobial/antioxidant properties, and shrimp spoilage tests. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Liu, M.; Chen, H.; Farag, M.A.; Wu, W.; Fang, X.; Niu, B.; Gao, H. Preparation and characterization of a novel intelligent starch/gelatin binary film containing purple sweet potato anthocyanins for Flammulina velutipes mushroom freshness monitoring. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Zou, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Holmes, M.; et al. Natural biomaterial-based edible and pH-sensitive films combined with electrochemical writing for intelligent food packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, H.M.S.; Ahmed, S.; Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E.; Gierszewska, M.; Brzezinska, M.S.; Dembińska, K.; Kalwasińska, A. Carboxymethyl cellulose based films enriched with polysaccharides from mulberry leaves (Morus alba L.) as new biodegradable packaging material. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, S.; Xu, K.; Xia, J.; Wu, Q.; Lü, X.; Wang, L. Development and application of multifunctional films based on modified chitosan/gelatin polyelectrolyte complex for preservation and monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotouhi, M.; Nasihatkon, B.; Solouki, S.; Seidi, S. A card instead of a lab: A ligand embedded in a bio-composite of starch/gelatin intelligent film for milk quality test followed by colorimetric analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 228, 426. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Xie, F. Chitosan-gelatin films: Plasticizers/nanofillers affect chain interactions and material properties in different ways. Polymers 2022, 14, 3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.W.; Lee, H.; Park, S.; Lee, M.E.; Jin, H.J. Chemical and physical reinforcement of hydrophilic gelatin film with di-aldehyde nanocellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 146, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Lin, D. Bacterial cellulose nanofibers used as nanofillers improved the fresh-keeping performance of gelatin-based edible coating for fresh-cut apples. J. Food Sci. 2023, 88, 4131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Jaiswal, L.; Rhim, J.W. Gelatin-based nanocomposite films: Potential use in antimicrobial active packaging. In Antimicrobial Food Packaging; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; p. 339. [Google Scholar]
- Boughriba, S.; Souissi, N.; Jridi, M.; Li, S.; Nasri, M. Thermal, mechanical and microstructural characterization and antioxidant potential of Rhinobatos cemiculus gelatin films supplemented by titanium dioxide doped silver nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 103, 105695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Cao, S.; Shang, T.; Yan, H.; Lin, Q. Nano-SiO2 reinforced alginate-chitosan-gelatin nanocomposite hydrogels with improved physicochemical properties and biological activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 228, 113413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, S.; Khalid, U.; Azim, W.; Kanwal, M.; Hossain, N. Reinforcement of biodegradable SiO2NPs-modified cellulose-gelatin hydrogel films with antioxidant and antibacterial properties as potential food packaging composite. J. Clust. Sci. 2024, 35, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.W. Gelatin-based film integrated with copper sulfide nanoparticles for active packaging applications. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Roy, S.; Rhim, J.W. Gelatin/agar-based color-indicator film integrated with Clitoria ternatea flower anthocyanin and zinc oxide nanoparticles for monitoring freshness of shrimp. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Ganguly, S.; Ahmed, S.R.; Sherazee, M.; Margel, S.; Gedanken, A.; Srinivasan, S.; Rajabzadeh, A.R. Carbon dot biopolymer-based flexible functional films for antioxidant and food monitoring applications. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 9323. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.; Tang, P.; Li, G. Development of a pH-sensitive film based on collagen/chitosan/ZnO nanoparticles and mulberry extract for pork freshness monitoring. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yuan, C.; Wu, C.; Hu, Y. Intelligent gelatin/oxidized chitin nanocrystals nanocomposite films containing black rice bran anthocyanins for fish freshness monitorings. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, Z.; Khan, A.; Rhim, J.W.; Shin, G.H.; Kim, J.T. Gelatin/poly (vinyl alcohol)-based dual functional composite films integrated with metal-organic frameworks and anthocyanin for active and intelligent food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 249, 126040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabee, M.; Elmogy, S.A.; Morsy, M.; Lawandy, S.; Zahran, M.A.H.; Moustafa, H. Biosynthesis of MgO nanoparticles and their impact on the properties of the PVA/gelatin nanocomposites for smart food packaging applications. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- e Silva, N.D.S.; de Souza Farias, F.; dos Santos Freitas, M.M.; Hernández, E.J.G.P.; Dantas, V.V.; Oliveira, M.E.C.; Joele, M.R.S.P.; Lourenço, L.D.F.H. Artificial intelligence application for classification and selection of fish gelatin packaging film produced with incorporation of palm oil and plant essential oils. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2021, 27, 100611. [Google Scholar]
- Torabiardekani, N.; Karami, F.; Khorram, M.; Zare, A.; Kamkar, M.; Zomorodian, K.; Zareshahrabadi, Z. Encapsulation of Zataria multiflora essential oil in polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan/gelatin thermo-responsive hydrogel: Synthesis, physico-chemical properties, and biological investigations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 243, 125073. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Dong, M.; Li, L.; Zhangsun, H.; Wang, L. Dual-functional intelligent gelatin based packaging film for maintaining and monitoring the shrimp freshness. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107258. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Zhuang, D.; Feng, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, J. Novel “all-in-one” multifunctional gelatin-based film for beef freshness maintaining and monitoring. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 136003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bule, M.; Khan, F.; Nisar, M.F.; Niaz, K.; Nabavi, S.; Saeedi, M.; Sanches Silva, A. Tannins (hydrolysable tannins, condensed tannins, phlorotannins, flavono-ellagitannins). In Recent Advances in Natural Products Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, NL, USA, 2020; p. 132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Roy, S.; Ezati, P.; Yang, D.P.; Rhim, J.W. Tannic acid: A green crosslinker for biopolymer-based food packaging films. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 136, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhen, M.; Wu, Y.; Ma, M.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, Y. Effect of catechin and tannins on the structural and functional properties of sodium alginate/gelatin/poly (vinylalcohol) blend films. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamari, A.; Phillip, E. Chitosan, gelatin and methylcellulose films incorporated with tannic acid for food packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1119. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Tian, R.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X. Enhancing the properties of soy protein isolate and dialdehyde starch films for food packaging applications through tannic acid crosslinking. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 332, 121903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Feng, H.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, D.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, J. A double-layer film based on the strategy of tannic acid-anthocyanin co-pigmentation and tannic-crosslinked-gelatin/− reduced Ag nanoparticles for beef preservation and monitoring. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxabide, A.; Yang, Y.; Maté, J.I.; de la Caba, K.; Kilmartin, P.A. Developing active and intelligent films through the incorporation of grape skin and seed tannin extracts into gelatin. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; An, H.; Alam, S.; Kalsoom, S.; Chen, S.H.; Begeno, T.A.; Du, Z. Smart colorimetric indicator films prepared from chitosan and polyvinyl alcohol with high mechanical strength and hydrophobic properties for monitoring shrimp freshness. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Yang, L.; Ma, R.; Xiang, Y.; Dai, Y.; Ren, J.; Xu, B.B.; El-Bahy, Z.M.; Thabet, H.K.; Huang, Z.; et al. Amoxicillin-laded sodium alginate/cellulose nanocrystals/polyvinyl alcohol composite nanonetwork sponges with enhanced wound healing and antibacterial performance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 280, 135701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.; Ahmad, M.; Minhas, M.U.; Rehmani, S. Alginate-polyvinyl alcohol based interpenetrating polymer network for prolonged drug therapy, optimization and in-vitro characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 166, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, N.; Liao, L. A novel approach in biomedical engineering: The use of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel encapsulating human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for enhanced osteogenic differentiation and angiogenesis in bone regeneration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorkhani, E.; Faryabi, A.; Noorafkan, Y.; Heirani, A.; Behboudi, B.; Fazeli, M.S.; Kazemeini, A.; Keramati, M.R.; Keshvari, A.; Tafti, S.M.A. Biomedical properties and hemostatic efficacy of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) based hydrogel in experimental rat liver injury model. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2023, 21, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Gou, Q.; Song, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Li, S. Smart carrageenan/carboxymethyl cellulose films combined with zein/gellan gum microcapsules encapsulated by composite anthocyanins for chilled beef freshness monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 153, 110059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oun, A.A.; Shin, G.H.; Rhim, J.W.; Kim, J.T. Recent advances in polyvinyl alcohol-based composite films and their applications in food packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 34, 100991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, H.; Gullo, M.; La China, S.; Pfeifer, F.; Siesler, H.W.; Licciardello, F.; Pulvirenti, A. Characterization of bio-nanocomposite films based on gelatin/polyvinyl alcohol blend reinforced with bacterial cellulose nanowhiskers for food packaging applications. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Khan, A.; Ezati, P.; Priyadarshi, R.; Sani, M.A.; Rathod, N.B.; Goksen, G.; Rhim, J.W. Advances in sustainable food packaging applications of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol blend films. Food Chem. 2024, 443, 138506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Ahmed, S. Eco-friendly natural extract loaded antioxidative chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol based active films for food packaging. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06550. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Li, W.; Hu, S.; Akhmedov, N.G.; Reed, D.; Li, X.; Liu, X. Polyvinyl alcohol coating induced preferred crystallographic orientation in aqueous zinc battery anodes. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Gonzales, R.R.; Abdel-Wahab, A.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K. Hydrophilic polyvinyl alcohol coating on hydrophobic electrospun nanofiber membrane for high performance thin film composite forward osmosis membrane. Desalination 2018, 426, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakarkar, S.; Muthukumaran, S.; Jegatheesan, V. Evaluation of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) loading in the PVA/titanium dioxide (TiO2) thin film coating on polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane for the removal of textile dyes. Chemosphere 2020, 257, 127144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Wang, P.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.; Zhang, T. Constructing anti-scaling and anti-wetting polyvinyl alcohol layers through spray-coating with improved water permeability in membrane distillation. Desalination 2023, 545, 116161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatt, S.R. Development of active/intelligent food packaging film containing Amaranthus leaf extract for shelf life extension of chicken/fish during chilled storage. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 24, 100506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpaslan, D.; Dudu, T.E.; Şahiner, N.; Aktas, N. Synthesis and preparation of responsive poly (Dimethyl acrylamide/gelatin and pomegranate extract) as a novel food packaging material. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 108, 110339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxabide, A.; Maté, J.I.; Kilmartin, P.A. Effect of curcumin, betanin and anthocyanin containing colourants addition on gelatin films properties for intelligent films development. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, I.M.; Haskaraca, G.; Ayhan, Z.; Gültekin, E. Development of real time-pH sensitive intelligent indicators for monitoring chicken breast freshness/spoilage using real packaging practices. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalitangkoon, J.; Monvisade, P. Synthesis of chitosan-based polymeric dyes as colorimetric pH-sensing materials: Potential for food and biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 260, 117836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjanzadeh, H.; Park, B.D. Covalent immobilization of bromocresol purple on cellulose nanocrystals for use in pH-responsive indicator films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatehi, F.; Khalili Sadrabad, E.; Feilizadeh, M.; Derakhshan, Z.; Kochaki, S.H.; Hekmatimoghaddam, S.; Jebali, A.; Mohajeri, F.A. Designing the pH-sensitive indicator based on starch nanoparticle with bromocresol green for monitoring meat spoilage. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2024, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhou, S.; Yang, X.; Lin, D. Applications of natural polysaccharide-based pH-sensitive films in food packaging: Current research and future trends. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 82, 103200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, F.W.; Fanta, S.W.; Tsige, A.A.; Delele, M.A. Current Status and Challenges of Colorimetric Intelligent Packaging for Fruit and Vegetables: A Review. J. Food Qual. 2025, 1, 6669828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Luan, M.; Zhang, Q. Preparation and characterization of pH-sensitive intelligent packaging films based on cassava starch/polyvinyl alcohol matrices containing Aronia melanocarpa anthocyanins. LWT 2024, 194, 115818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, V.A.; Vijayakumar, R.; Leena, M.M.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Co-electrospun-electrosprayed ethyl cellulose-gelatin nanocomposite pH-sensitive membrane for food quality applications. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Xie, C.; Wang, C.; Zhong, Y.; Fan, K. Recent advances in pH-sensitive indicator films based on natural colorants for smart monitoring of food freshness: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 64, 12800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.; Bist, Y.; Thakur, D.; Nagar, M.; Saxena, D.C. A review on the role of pH-sensitive natural pigments in biopolymers based intelligent food packaging films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 133869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Wang, Y.; Jia, H.; Hao, R.; Jan, M.; Li, S.; Pu, Y.; Dong, X.; Pan, J. The properties of pH-responsive gelatin-based intelligent film as affected by ultrasound power and purple cabbage anthocyanin dose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 230, 123156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Liu, L.; Yu, J.; Shao, P. Novel trends and applications of natural pH-responsive indicator film in food packaging for improved quality monitoring. Food Control 2022, 134, 108769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, D.; He, Y.; Zhu, H.; Hui, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, D.; Liu, J. Smart packaging films based on locust bean gum, polyvinyl alcohol, the crude extract of Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum petals and its purified fractions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 205, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Wu, R.; Huang, X.; Shi, J.; Zou, X. Anthocyanin loaded composite gelatin films crosslinked with oxidized alginate for monitoring spoilage of flesh foods. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2024, 42, 101255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Filho, J.G.; Bertolo, M.R.V.; Fernandes, S.S.; Lemes, A.C.; da Cruz Silva, G.; Junior, S.B.; de Azeredo, H.M.C.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Egea, M.B. Intelligent and active biodegradable biopolymeric films containing carotenoids. Food Chem. 2023, 434, 137454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halloub, A.; Raji, M.; Essabir, H.; Nekhlaoui, S.; Bensalah, M.O.; Bouhfid, R.; el kacem Qaiss, A. Stable smart packaging betalain-based from red prickly pear covalently linked into cellulose/alginate blend films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Tan, S.; Tan, G.; Zhang, H.; Xia, N.; Jiang, L.; Ren, H.; Rayan, A.M. Intelligent colorimetric soy protein isolate-based films incorporated with curcumin through an organic solvent-free pH-driven method: Properties, molecular interactions, and application. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 133, 107904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Jaramillo, C.; Ochoa-Yepes, O.; Bernal, C.; Famá, L. Active and smart biodegradable packaging based on starch and natural extracts. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh-Sani, M.; Mohammadian, E.; Rhim, J.W.; Jafari, S.M. pH-sensitive (halochromic) smart packaging films based on natural food colorants for the monitoring of food quality and safety. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, N.; Peng, H.; Yang, X.; Lin, D. The development of highly pH-sensitive bacterial cellulose nanofibers/gelatin-based intelligent films loaded with anthocyanin/curcumin for the fresh-keeping and freshness detection of fresh pork. Foods 2023, 12, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, M.; Qin, Y.; Chen, H. Effects of anthocyanin-rich Kadsura coccinea extract on the physical, antioxidant, and pH-sensitive properties of biodegradable film. Food Biophys. 2022, 17, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szadkowski, B.; Marzec, A. Chitosan vs chitin: Comparative study of functional pH bioindicators synthesized from natural red dyes and biopolymers as potential packaging additives. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 150, 109670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hossen, M.A.; Sameen, D.E.; Dai, J.; Li, S.; Qin, W. Fabrication and characterization of pH-responsive intelligent films based on carboxymethyl cellulose and gelatin/curcumin/chitosan hybrid microcapsules for pork quality monitoring. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Chen, G.; Xu, T.; Kong, L.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Ge, L. Gelatin-based active edible film with pH-sensing for maintaining and monitoring fish freshness. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 3, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, S.; Emaminia, S.; Davudian, S.H.; Pourmohammad, S.; Hamishehkar, H.; Roufegarinejad, L. Preparation and characterization of gelatin-based nanocomposite containing chitosan nanofiber and ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, U.; Khan, M.K.I.; Maan, A.A.; Nazir, A.; Riaz, S.; Khan, M.U.; Sultan, M.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Lorenzo, J.M. Biodegradable active, intelligent, and smart packaging materials for food applications. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanani, Z.N.; Roos, Y.H.; Kerry, J.P. Use and application of gelatin as potential biodegradable packaging materials for food products. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 71, 94. [Google Scholar]


| Sources of Gelatin | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Pig skin | 40% |
| Pig Cartilage | 6% |
| Bovine hides | 29.4% |
| Beef bones | 23.1% |
| Other sources (poultry, fish, vertebrates, and so on) | 1.5% |
| Active Carriers | pH-Sensitive Dye | Food Samples | Storage | Color Change | pH | Sensitivity | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time | Temp. (°C) | Initial (Fresh) | Final (Spoiled) | ΔE Value | |||||
| Gelatin, Chitosan, ZnO-nanoparticles | Mulberry extract (ME) | Pork | 8 d | 4 °C | red to blue/green | 5.7 | 6.5 | 30.55 | [94] |
| Gelatin, Oxidized chitin nanocrystals(O-ChNCs) | Black rice bran anthocyanins | Shrimp, Hairtail | 1 d | 25 °C | rose-carmine to yellow-green | 7.5 | 8.2 | 7.27–10.47 | [95] |
| Gelatin, Dialdehyde starch (DS) | Rosmarinic acid (RosA), Blueberry anthocyanins extract (BAE) | Fish | 24 h | 25 °C | red to brown to dark brown | 7.0 | 8.2 | 10.23 | [149] |
| Gelatin, Carrageenan | Shikonin extracted from the gromwell (Lithospermum erythrorhizon) root | Milk | - | 25 °C | bright red to blue | 6.6 | 4.5 | 55.7 | [76] |
| Gelatin, Starch | Red cabbage extracts | Milk | - | 25 °C | red to green/yellow | 6.8 | 4.0 | - | [83] |
| gelatin, Polyvinyl alcohol (pva) | Amaranthus leaf extract | Chicken | 12 d | 2–4 °C | pink to yellow | 5.5 | 8.6 | 22.13 | [123] |
| Gelatin, Bacterial cellulose nanofibers | Curcumin/Anthocyanin (Cur/ATH) | Pork | 4 d | 4 °C | yellow to red | 5.7 | 6.7 | 55.83 | [145] |
| Gelatin hydrolysate (GELH), Furcellaran (FUR), | Rosemary extract from dry leaves (DRE)) | Carp (Cyprinus carpio) | 14 d | 4 °C | green to red | 5.8 | 7.0 | 56.67 | [77] |
| Gelatin, Lavender essential oil | Alizarin (ALI) | Shrimp | 3 d | 25 °C | yellow to brown-red | 7.5 | 8.2 | 55 | [100] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R. From Lab to Shelf: Gelatin-Based pH Sensors Revolutionizing Food Packaging. Gels 2025, 11, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050327
Wang R. From Lab to Shelf: Gelatin-Based pH Sensors Revolutionizing Food Packaging. Gels. 2025; 11(5):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050327
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ruirui. 2025. "From Lab to Shelf: Gelatin-Based pH Sensors Revolutionizing Food Packaging" Gels 11, no. 5: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050327
APA StyleWang, R. (2025). From Lab to Shelf: Gelatin-Based pH Sensors Revolutionizing Food Packaging. Gels, 11(5), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050327







