Advances in Hemostatic Hydrogels That Can Adhere to Wet Surfaces
Abstract
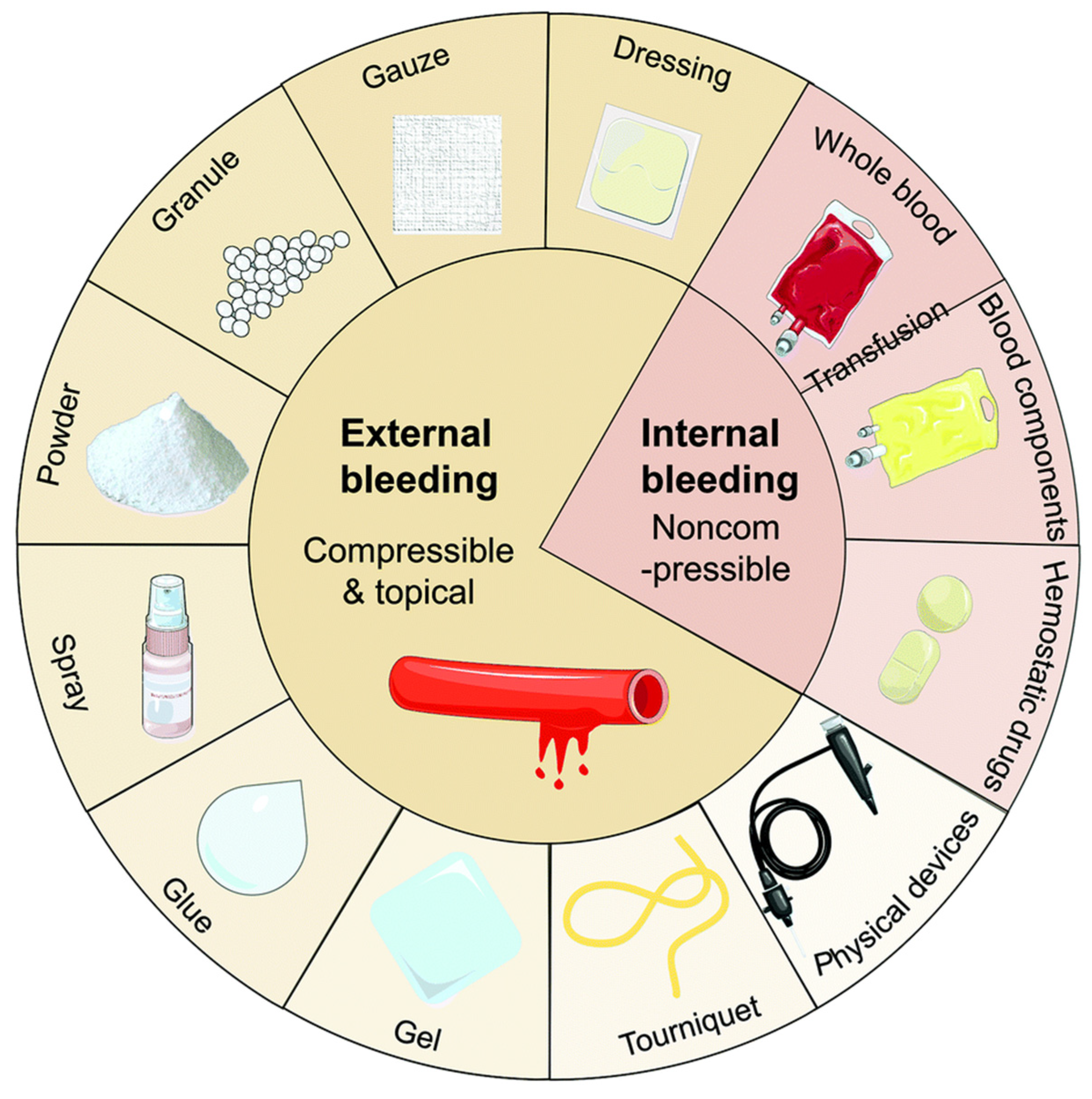
1. Introduction
2. Properties of Wet Adhesive Hemostatic Hydrogel
2.1. Hemostatic Properties
2.2. Adhesion Properties
2.2.1. Four Theories of Bio-Adhesion
2.2.2. Influence Factors of Wet Surface Adhesion
- (1)
- Typical Chemical Bond
- (2)
- Hydrogen Bond
- (3)
- Van der Waals Force
- (4)
- Electrostatic Interactions
- (5)
- Metal Coordination Bond and Ionic Bond
| Influence Factors | Hydrogels | Adhesion Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Permanent and dynamic covalent bonds | Hyaluronic acid and dopamine polymerized hydrogel [51] In situ photo-responsive chitosan (CS) hydrogel [52] | Dopamine catechol chemical adhesion After exposure to UV light, o-nitrobenzene is converted to o-nitrobenzaldehyde, which is further cross-linked with amino groups on the tissue surface. |
| Hydrogen bond | Konjac glucomannan, dopamine hydrochloride, L-cysteine hydrochloride, and epigallocatechuic acid ester pH-responsive hydrogels [55] Catechol-modified poly(lysine)/poly(acrylamide) hydrogels [56] Anthracene-based polyethyleneimine underwater adhesion hydrogel [63] | Hydrogen bonding and catechol chemical adhesion Strong adhesion of hydrogel due to large amount of hydrogen bonding The high water absorption of polyethyleneimine promotes the absorption of interfacial water molecules, allowing the hydrogel to adhere firmly to other substances |
| Van der Waals force | Polyethylene glycol hydrogel [65] | Water absorption properties, capillary and van der Waals forces |
| Electrostatic interactions | 2-Acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid, gelatin, CS, ethyl 2-methoxyacrylate, and acrylic acid bonded hydrogels [69] Catechol-modified CS and polyvinyl alcohol were used as raw materials to prepare physical hydrogels [70] | Synergistic hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions Dynamic hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interactions |
| Metal coordination bond and ionic bond | Acrylamide, sodium alginate, and acrylic acid super tough hydrogel [75] | Strong ionic and weak hydrogen bonding interactions |
- (6)
- Biomimemtic Strategies

3. Application of Wet Adhesion Hemostatic Hydrogels
3.1. Skin
3.2. Heart
3.3. Liver
3.4. Other Applications
4. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Li, P.; Hao, X.; Yang, X.; Xi, G.; Liu, W.; Feng, Y.; He, H.; Shi, C. Polysaccharide based hemostatic strategy for ultrarapid hemostasis. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, 1900370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushimoto, S.; Kudo, D.; Kawazoe, Y. Acute traumatic coagulopathy and trauma-induced coagulopathy: An overview. J. Intensive Care 2017, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, A.; Shukla, A.; Brown, A.C. Biomaterials for hemostasis. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 24, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tummalapalli, M.; Anjum, S.; Kumari, S.; Gupta, B. Antimicrobial surgical sutures: Recent developments and strategies. Polym. Rev. 2016, 56, 607–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Campos, R.; Navarro-Barrios, Á.; Martínez-Caceres, C.; Revilla-Nuin, B.; Brusadin, R.; López-López, V.; López-Conesa, A.; Caballero-Planes, A.; de la Peña-Moral, J.; Parrilla-Paricio, P. The contribution of the deportalized lobe to liver regeneration in tourniquet-ALPPS. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, E94–E96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, R.B.; Reynolds, B.Z.; Shiver, S.A.; Lerner, E.B.; Greenfield, E.M.; Solis, R.A.; Kimpel, N.A.; Coule, P.L.; Singletary, J.G.M.; Woods, W. Comparison of two packable hemostatic gauze dressings in a porcine hemorrhage model. Prehosp. Emerg. Care 2011, 15, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafalu, P.; Tamayol, A.; Rahimi, R.; Ochoa, M.; Khalilpour, A.; Kiaee, G.; Yazdi, I.K.; Bagherifard, S.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Ziaie, B.; et al. Smart bandages: Smart bandage for monitoring and treatment of chronic wounds. Small 2018, 14, 1870150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hu, E.; Yu, K.; Xie, R.; Lu, F.; Lu, B.; Bao, R.; Li, Q.; Dai, F.; Lan, G. Recent advances in materials for hemostatic management. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 7343–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, L.; Wang, S. Enhanced photothermal and chemotherapy of pancreatic tumors by degrading the extracellular matrix. Colloids Surf. B 2023, 221, 113010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Ye, C.; Wang, S.; An, X. Development of PVA-based microsphere as a potential embolization agent. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2022, 135, 112677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; You, X.; Dai, C.; Tong, T.; Wu, J. Hemostatic nanotechnologies for external and internal hemorrhage management. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 4396–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Zhou, J. Recent advances on synthetic and polysaccharide adhesives for biological hemostatic applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyednejad, H.; Imani, M.; Jamieson, T.; Seifalian, A.M. Topical haemostatic agents. Br. J. Surg. 2008, 95, 1197–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiara, O.; Cimbanassi, S.; Bellanova, G.; Chiarugi, M.; Mingoli, A.; Olivero, G.; Ribaldi, S.; Tugnoli, G.; Basilicò, S.; Bindi, F.; et al. A systematic review on the use of topical hemostats in trauma and emergency surgery. BMC Surg. 2018, 18, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spotnitz, W.D. Hemostats, sealants, and adhesives: A practical guide for the surgeon. Am. Surg. 2012, 78, 1305–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yao, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S. Injectable wound dressing based on carboxymethyl chitosan triple-network hydrogel for effective wound antibacterial and hemostasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Zeng, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J. Multifunctional carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized dextran/sodium alginate hydrogels as dressing for hemostasis and closure of infected wounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 1337–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S. Multifunctional hydrogels based on chitosan, hyaluronic acid and other biological macromol-eculesfor the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 227, 505–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Fan, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S. Sodium alginate hydrogel containing platelet-rich plasma for wound healing. Colloids Surf. B 2023, 221, 113010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ding, J. Injectable hydrogels as unique biomedical materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Chuah, Y.J.; Wang, D.A. Bioadhesives for internal medical applications: A review. Acta Biomater. 2018, 74, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokhande, G.; Carrow, J.K.; Thakur, T.; Xavier, J.R.; Parani, M.; Bayless, K.J.; Gaharwar, A.K. Nanoengineered injectable hydrogels for wound healing application. Acta Biomater. 2018, 70, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Celiz, A.D.; Yang, J.; Yang, Q.; Wamala, I.; Whyte, W.; Seo, B.R.; Vasilyev, N.V.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z.; et al. Tough adhesives for diverse wet surfaces. Science 2017, 357, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, B.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, W.; Xie, X.; Lai, H.; Xue, J.; Rai, A.; Li, Z.; et al. Adhesive Hemostatic Hydrogel with Ultrafast Gelation Arrests Acute Upper Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage in Pigs. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 32, 2109332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Hu, E.; Yu, K.; Xie, R.; Lu, F.; Lu, B.; Bao, R.; Zhao, T.; Dai, F.; Lan, G. Self-propelling Janus particles for hemostasis in perforating and irregular wounds with massive hemorrhage. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Yan, F.; Zhao, X.; Chu, X.; Xu, W.; Sun, C. A review of the properties and applications of bioadhesive hydrogels. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 3721–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuyttens, B.P.; Thijs, T.; Deckmyn, H.; Broos, K. Platelet adhesion to collagen. Thromb. Res. 2011, 127, S26–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broos, K.; Feys, H.B.; de Meyer, S.F.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Deckmyn, H. Platelets at work in primary hemostasis. Blood Rev. 2011, 25, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Rana, V. Techniques for the assessment of mucoadhesion in drug delivery systems: An overview. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 2251–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, C.; Ji, J.; Liu, J. Mechanisms underlying the biological wet adhesion: Coupled effects of interstitial liquid and contact geometry. J. Bionic Eng. 2020, 17, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xie, J.; Dai, Q.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. Effect of wetting case and softness on adhesion of bioinspired micropatterned surfaces. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 78, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandyra, D.; Walheim, S.; Gorb, S.; Barthlott, W.; Schimmel, T. The capillary adhesion technique: A versatile method for determining the liquid adhesion force and sample stiffness. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Li, M.; Dai, Q.; Huang, W.; Wang, X. Key parameters of biomimetic patterned surface for wet adhesion. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2018, 82, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.; Ho, V.A. Wet adhesion of soft curved interfaces with micro pattern. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 4273–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.C.; Bruschi, M.L.; Evangelista, R.C.; Gremião, M.P.D. Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 46, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Wang, S.; Zuo, A.; Guo, J. Bioadhesion design of hydrogels: Adhesion strategies and evaluation methods for biological interfaces. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2022, 36, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Leeden, M.C.; Frens, G. Surface properties of plastic materials in relation to their adhering performance. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2002, 4, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, M.; Yang, J. Design strategies and applications of tissue bioadhesives. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, E.; Fujisawa, A.; Lee, H. Diatom silica/polysaccharide elastomeric hydrogels: Adhesion and interlocking synergy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 21703–21713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, H.; Ren, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Hu, B.; Gu, N. Dual-network hydrogel based on ionic nano-reservoir for gastric perforation sealing. Sci. China Mater. 2021, 65, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, S.; Guo, Y.; Li, M.; You, R. Mechanically robust and flexible silk protein/polysaccharide composite sponges for wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 216, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorwald, C.E.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, T.; Joshee, S.; Sikorski, P.; Leach, J.K. Tunable fibrin-alginate interpenetrating network hydrogels to support cell spreading and network formation. Acta Biomater. 2020, 108, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.H.; Pan, B.B.H.; Xin, Z. Underwater and wet adhesion strategies for hydrogels in biomedical applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 431, 133372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvarenko, S.; Voronov, A.; Samaryk, V.; Tarnavchyk, I.; Nosova, N.; Kohut, A.; Voronov, S. Covalent grafting of polyacrylamide-based hydrogels to a polypropylene surface activated with functional polyperoxide. React. Funct. Polym. 2010, 70, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yan, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, H. Mussel foot protein inspired tough tissue-selective underwater adhesive hydrogel. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 8, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Meng, X.; Xu, W.; Zhang, S.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Y.; Ma, S.; Xue, Z.; et al. Single network double cross-linker (SNDCL) hydrogels with excellent stretchability, self-recovery, adhesion strength, and conductivity for human motion monitoring. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 7323–7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, H. Mechanisms and applications of bioinspired underwater/wet adhesives. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 59, 2911–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, S. Oxidation triggered formation of polydopamine-modified carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel for anti-recurrence of tumor. Colloids Surf. B 2021, 207, 112025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiz-Poseu, J.; Mancebo-Aracil, J.; Nador, F.; Busqué, F.; Ruiz-Molina, D. The chemistry behind catechol-based adhesion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019, 58, 696–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zeng, H.; Yu, J. Recent progress in synthesis and application of mussel-inspired adhesives. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 1307–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, S.; Pei, M.; Yang, H.; Gu, S.; Tao, Y.; Ye, D.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, W.; Xiao, P. Dopamine-modified hyaluronic acid hydrogel adhesives with fast-forming and high tissue adhesion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18225–18234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yao, J.; Liu, Q.; Han, T.; Zhao, J.; Ma, X.; Tong, Y.; Jin, G.; Qu, K.; Li, B.; et al. Liquid bandage harvests robust adhesive, hemostatic, and antibacterial performances as a first-aid tissue adhesive. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2001820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Bai, R.; Suo, Z. Topological adhesion of wet materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, e1800671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, F.; Li, Z.; Lin, S.; Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y. Hydrogel cross-linked with dynamic covalent bonding and micellization for promoting burn wound healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 25194–25202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Lin, L.; Mu, R.; Pang, J. Novel synthesis of mussel inspired and Fe3+ induced pH-sensitive hydrogels: Adhesion, injectable, shapeable, temperature properties, release behavior and rheological characterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 116045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Z.; Sidi, L.; Xubo, Y.; Jin, Z.; Xin, H. An in situ catechol functionalized ε-polylysine/polyacrylamide hydrogel formed by hydrogen bonding recombination with high mechanical property for hemostasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Ge, X.; Dai, J.; Ren, P.; Wei, D.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Q.; He, C.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, T. High-strength hydrogel adhesive formed via multiple interactions for persistent adhesion under saline. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 5016–5025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Shen, Q.; Kong, L.; Huang, G.; Wu, J. Tough underwater super-tape composed of semi-interpenetrating polymer networks with a water-repelling liquid surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Wu, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, T.; Wu, M.; Yang, D.; Peng, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, H. Coacervate-based instant and repeatable underwater adhesive with anticancer and antibacterial properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48239–48251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Fan, C.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, M.; Wu, T.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, B.; Xu, Z.; Qu, B.; et al. Water-triggered hyperbranched polymer universal adhesives: From strong underwater adhesion to rapid sealing hemostasis. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1905761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Ye, S.; Wang, R.; She, W.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, W. Hydrogel networks as underwater contact adhesives for different surfaces. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, S.; Zhang, B.; Sun, J.; Kai, J.-j.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z. Instant and strong underwater adhesion by coupling hygroscopicity and in situ photocuring. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 8822–8830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, L.; Xiao, H.; Cong, H.; Wang, S. A reversible underwater glue based on photo- and thermo-responsive dynamic covalent bonds. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 7, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autumn, K.; Sitti, M.; Liang, Y.A.; Peattie, A.M.; Hansen, W.R.; Sponberg, S.; Kenny, T.W.; Fearing, R.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Full, R.J. Evidence for van der Waals adhesion in gecko setae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12252–12256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Lee, S.H.; Seong, M.; Kwak, M.K.; Jeong, H.E. Bioinspired reversible hydrogel adhesives for wet and underwater surfaces. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 8064–8070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Aoyama, Y.; Yamanaka, J.; Toyotama, A.; Okuzono, T. Particle adsorption on hydrogel surfaces in aqueous media due to van der Waals attraction. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Gao, G.; Chen, J.; Yin, J.; Fu, J. Macroscopic assembly of oppositely charged polyelectrolyte hydrogels. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Tang, Z.; Peng, S.; Zhang, P.; Sun, T.; Wei, W.; Zeng, L.; Guo, H.; Guo, H.; Meng, G. Modification of hydrophobic hydrogels into a strongly adhesive and tough hydrogel by electrostatic interaction. Macromolecules 2021, 55, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, G.; Liu, Y.; Yu, M.; Liang, C.; Yang, D.; Huang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Electrostatic Interaction-based high tissue adhesive, stretchable microelectrode arrays for the electrophysiological interface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 4852–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Zhang, J.; Lu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Tao, Y.; Shao, C.; Wang, H. A mussel-inspired flexible chitosan-based bio-hydrogel as a tailored medical adhesive. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Q.; Niu, Y.; Zhao, D. Adhesion mechanism and application progress of hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 173, 111277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, X.; Ding, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ren, C.; Xu, W. Hydrogels for underwater adhesion: Adhesion mechanism, design strategies and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 11823–11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-H.; Kim, Y.-W.; Woo, J.; Park, H.; Hur, K.; Suo, Z.; Sun, J.-Y. Fast healing of ionic bonds in tough hydrogels under an acoustic excitation. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2019, 33, 100572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, J.; Liu, T.; Yan, Y.; Long, S.; Li, X. Strong tough polyampholyte hydrogels via the synergistic effect of ionic and metal–ligand bonds. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xue, J.; Du, B.; Nie, J. Ultrastiff, tough, and healable ionic–hydrogen bond cross-linked hydrogels and their uses as building blocks to construct complex hydrogel structures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5441–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Meng, J.; Gu, Z.; Wan, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, S. Bioinspired multiscale wet adhesive surfaces: Structures and controlled adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1905287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sareh, S.; Althoefer, K.; Li, M.; Noh, Y.; Tramacere, F.; Sareh, P.; Mazzolai, B.; Kovac, M. Anchoring like octopus: Biologically inspired soft artificial sucker. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Kim, M.K.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, S.W.; Kim, J. Adhesive hydrogel patch with enhanced strength and adhesiveness to skin for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2004407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.J.; Joo, K.I.; Kim, K.H.; Lim, G.; Cha, H.J. Bio-inspired swellable hydrogel-forming double-layered adhesive microneedle protein patch for regenerative internal/external surgical closure. Biomaterials 2019, 222, 119439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujioka, K.; Matsuo, Y.; Shimomura, M.; Hirai, Y. A new concept for an adhesive material inspired by clingfish sucker nanofilaments. Langmuir 2022, 38, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Nag, T.C. Fine structure of the organ of attachment of the teleost, Garra gotyla gotyla (Ham). Zoology 2006, 109, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Um, D.-S.; Lee, Y.; Lim, S.; Kim, H.-j.; Ko, H. Octopus-Inspired Smart Adhesive Pads for Transfer Printing of Semiconducting Nanomembranes. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7457–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autumn, K.; Peattie, A.M. Mechanisms of adhesion in geckos. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2002, 42, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Z.; Li, Z.; Cui, Z.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, C. A novel bionic topography with miR-21 coating for improving bone-implant integration through regulating cell adhesion and angiogenesis. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 7716–7721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Tan, D.; Xue, L.; Barnes, W.J.P. Tree frog adhesion biomimetics: Opportunities for the development of new, smart adhesives that adhere under wet conditions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2019, 377, 31177956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowska, A.K.; Spano, F.; Derler, S.; Adlhart, C.; Spencer, N.D.; Rossi, R.M. The relationship between skin function, barrier properties, and body-dependent factors. Skin Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Pei, M.; Wan, T.; Yang, H.; Gu, S.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, W.; Xiao, P. Self-healing hyaluronic acid hydrogels based on dynamic Schiff base linkages as biomaterials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 250, 116922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Xu, T.; Yun, S.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Sato, T.; Chi, B.; Xu, H. A biomimetic mussel-inspired ε-poly-l-lysine hydrogel with robust tissue-anchor and anti-infection capacity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Lu, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, K.; Fang, L.; Weng, L.-T.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Ren, F.; Zhao, C.; et al. Mussel-inspired adhesive and tough hydrogel based on nanoclay confined dopamine polymerization. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2561–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Yan, L.; Wang, K.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Weng, L.-T.; Xu, J.; Weng, J.; et al. Tough, self-healable and tissue-adhesive hydrogel with tunable multifunctionality. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, D.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, R.; Yu, B.; Ma, G.; Li, Y.; Hao, D.; Xu, F.-J. Engineering platelet-rich plasma based dual-network hydrogel as a bioactive wound dressing with potential clinical translational value. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Tsai, C.W.; Tsai, N.Y.; Chiang, C.Y.; Lin, R.S.; Pereira, R.F.; Li, Y.E. An injectable, dual crosslinkable hybrid pectin methacrylate (PECMA)/gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogel for skin hemostasis applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchami, P.; Prachi, T. Hydrogels differentiated by length scales: A review of biopolymer-based hydrogel preparation methods, characterization techniques, and targeted applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 163, 110935. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Duan, X.; Guo, B. Mussel-inspired adhesive antioxidant antibacterial hemostatic composite hydrogel wound dressing via photo-polymerization for infected skin wound healing. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 8, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Liu, X.; Qi, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Qin, J. Poly(aspartic acid) based self-healing hydrogel with blood coagulation characteristic for rapid hemostasis and wound healing applications. Colloids Surf. B 2022, 214, 112430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.; Lv, X.; He, S.; Bai, S.; Liu, X.; Hou, L.; He, J.; Tong, D.; Ruan, R.; Zhang, J.; et al. A mussel-inspired supramolecular hydrogel with robust tissue anchor for rapid hemostasis of arterial and visceral bleedings. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2829–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Wei, D.; Yao, Z.; Ren, P.; Dai, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q. Hydrogel adhesive formed via multiple chemical interactions: From persistent wet adhesion to rapid hemostasis. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 1486–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Zhou, F.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ni, C.; Pan, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, D.; Yang, L.; Lin, Q.; et al. A strongly adhesive hemostatic hydrogel for the repair of arterial and heart bleeds. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formosa-Dague, C.; Feuillie, C.; Beaussart, A.; Derclaye, S.; Kucharíková, S.; Lasa, I.; van Dijck, P.; Dufrêne, Y.F. Sticky matrix: Adhesion mechanism of the staphylococcal polysaccharide intercellular adhesin. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 3443–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, S.; Xia, P.; Xu, P.; Li, G.; Zhang, K.; Yin, J. Thermoresponsive chitosan/DOPA-based hydrogel as an injectable therapy approach for tissue-adhesion and hemostasis. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 3619–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, H.; Zaldivar-Silva, D.; Agüero, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Qiu, B.; Zhao, J.; et al. An injectable anti-microbial and adhesive hydrogel for the effective noncompressible visceral hemostasis and wound repair. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 129, 112422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hu, T.; Han, Y.; Guo, B. Mussel-inspired, antibacterial, conductive, antioxidant, injectable composite hydrogel wound dressing to promote the regeneration of infected skin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, G.; Sun, F.; Liu, J.; Yang, F.; Tang, P.; Wu, D. Tetra-PEG based hydrogel sealants for in vivo visceral hemostasis. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1901580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shi, M.; Liang, Y.; Guo, B. Conductive adhesive self-healing nanocomposite hydrogel wound dressing for photothermal therapy of infected full-thickness skin wounds. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.X.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, B.Q.; Chen, T.Y.; Xu, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Cai, M.Y.; Zhou, P.H. A novel injectable thermo-sensitive binary hydrogels system for facilitating endoscopic submucosal dissection procedure. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2019, 7, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ren, F.; Li, J.; Zhu, S.; Ma, F.; Wu, R.; Lv, Y.; He, G.; et al. Injectable self-healing adhesive pH-responsive hydrogels accelerate gastric hemostasis and wound healing. Nanomicro Lett. 2021, 13, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Qing, R.; Hao, S.; Ding, Y.; Yin, H.; Zha, G.; Chen, X.; Ji, J.; Wang, B. Fabrication of ulcer-adhesive oral keratin hydrogel for gastric ulcer healing in a rat. Regener. Biomater. 2021, 8, rbab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Wu, T.; Gao, F.; Fan, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, B.; Liu, W. An autolytic high strength instant adhesive hydrogel for emergency self-rescue. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, K.M.; Schoenbaum, G. Dopamine. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, R817–R824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Shi, M.; Dong, C.; Liu, L.; Gao, C. Applications of tannic acid in membrane technologies: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 284, 102267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.; Booth, B.W. Biomedical applications of tannic acid. J. Biomater. Appl. 2022, 36, 1503–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, P.; Zhang, L.; Shen, H.; Wu, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, S.; Hu, L. Biodegradable MoSe2-polyvinylpyrrolidone nanoparticles with multi-enzyme activity for ameliorating acute pancreatitis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, W.; Wang, S. Advances in Hemostatic Hydrogels That Can Adhere to Wet Surfaces. Gels 2023, 9, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010002
Han W, Wang S. Advances in Hemostatic Hydrogels That Can Adhere to Wet Surfaces. Gels. 2023; 9(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Wenli, and Shige Wang. 2023. "Advances in Hemostatic Hydrogels That Can Adhere to Wet Surfaces" Gels 9, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010002
APA StyleHan, W., & Wang, S. (2023). Advances in Hemostatic Hydrogels That Can Adhere to Wet Surfaces. Gels, 9(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010002







