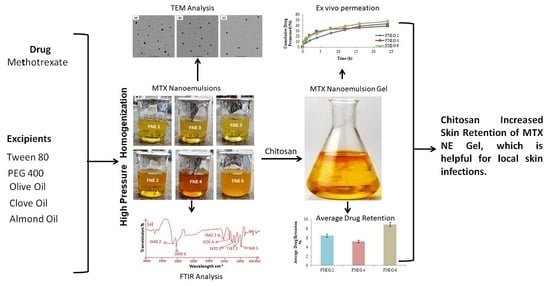
Formulation Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoemulsion Gel Formulations for Enhanced Topical Delivery
Abstract
Share and Cite
Latif, M.S.; Nawaz, A.; Asmari, M.; Uddin, J.; Ullah, H.; Ahmad, S. Formulation Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoemulsion Gel Formulations for Enhanced Topical Delivery. Gels 2023, 9, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010003
Latif MS, Nawaz A, Asmari M, Uddin J, Ullah H, Ahmad S. Formulation Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoemulsion Gel Formulations for Enhanced Topical Delivery. Gels. 2023; 9(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatif, Muhammad Shahid, Asif Nawaz, Mufarreh Asmari, Jalal Uddin, Hidayat Ullah, and Saeed Ahmad. 2023. "Formulation Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoemulsion Gel Formulations for Enhanced Topical Delivery" Gels 9, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010003
APA StyleLatif, M. S., Nawaz, A., Asmari, M., Uddin, J., Ullah, H., & Ahmad, S. (2023). Formulation Development and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Methotrexate-Loaded Nanoemulsion Gel Formulations for Enhanced Topical Delivery. Gels, 9(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels9010003