Abstract
Several ultrasonic cleaning tanks (UCTs) had a problem: a manufacturer complained that there were damages to cleaning objects, they were unclarified, and it needed to be abruptly solved. To investigate and solve the problem, a small UCT filled with 3.92 L of water, with a frequency of 28 kHz, two horn transducers, and a total power of 100 W was built for simulation and experiment. A built tank body material of UCT can be adjustable to acrylic, glass, and stainless steel. Since the cavitation causing the cleaning relates to acoustic pressure, harmonic response analysis (HRA) in ANSYS software was employed to calculate the acoustic pressure inside the UCT for different designs such as mentioned materials, power, thickness, volume, and frequency. The HRA results revealed uneven acoustic pressure depending on the tank designs, consistent with foil corrosion and power concentration experiments. Furthermore, using the tank body material with acrylic, glass, and stainless steel provided the highest, moderate, and lowest acoustic pressure levels, respectively. The uneven acoustic pressure resulted from the differences in material transmission coefficients. In addition, the damage occurred because of improper tank design, resulting in excessive acoustic pressure. Therefore, the tank design is indispensable in designing high-efficiency UCTs to reduce damage and meet customer requirements.
1. Introduction
Thailand is one of the technology leaders in manufacturing ultrasonic cleaners in Southeast Asia. Many manufacturers are capable of producing ultrasonic cleaners ranging from simple functioning devices for household usage to large machines with complex systems for industrial usage. The advantages of domestic manufacturers are that they can design and produce ultrasonic cleaners and components that match customers’ requirements at a low price. In addition, they can quickly solve any usage problems complained by the customers and suggest ways to improve the cleaning performance. Behind the success of leadership is using finite element analysis (FEA). Research on the development of ultrasonic cleaning based on FEA was divided into two groups: cleaners and processes.
First, since the cleaners consist of three essential components, i.e., transducer, tank body, and controller (generator), most research has focused on developing the first two rather than the last because transducer and tank body developments can lead to high-efficiency, rapid cleaning, meet the requirements of a wide range of users, and are worth the investment. Meanwhile, the controller development is relatively slow because the existing technology can be practical on an industrial scale. FEA to develop the transducer and tank body impacting the industries can be exemplified as follows. The structural analysis [1,2], modal analysis [3,4,5,6], and harmonic response analysis (HRA) [6] were employed to investigate stress, deformation, and related results for optimizing the design of front masses for transducers to suit usages. Furthermore, since the transducer consists of front mass, piezoelectric (PZT) material, and back mass, the PZT is also studied and developed for many purposes [7]. As a result, HRA confirmed that PZT4 provided more intense acoustic pressure than PZT8 [8,9].
Second, for the cleaning process development, the structural analysis helped to find a suitable fouling removal method [10,11]. In addition, the HRA determined suitable positions of cleaning objects [12] and optimized transducer placements [13,14,15] to achieve higher ultrasonic cleaning efficiency.
Because ultrasonic cleaning efficiency depends on many factors such as cleaning fluid, temperature, standing waves, power, and frequency [16,17], optimized design concerning these factors ensures optimum efficiency. Therefore, from the literature review mentioned above and the authors’ experience, it can be concluded that the HRA is more suitable than the structural analysis and modal analysis to achieve higher ultrasonic cleaning efficiency. For example, the HRA can display more accurate acoustic pressure, leading to fluid cavitation, when adjusting the related factors than the other analyses. In addition, the structural and modal analyses require boundary conditions of external sources with specific frequencies. Still, the HRA can report the results at all frequencies, does not require boundary conditions from external sources, and is easy to use. Therefore, most of the recent research prefers to use the HRA to help design and develop ultrasonic cleaning technology [8,9,12,13,14,15].
The origin of this research came from customers complaining to manufacturers. They informed us that the cleaning objects were damaged and not clean in some ultrasonic cleaning tanks (UCTs). In fact, repositioning the transducers to the proper position, as suggested in previous research [13,14], is already a potential solution. However, the mentioned method cannot identify the cause of this problem; therefore, finding the root cause, alternative solution, and ways to improve efficiency should be urgently addressed and were aims of this research. Preliminary investigation revealed that a material typically used to invent the tank body could cause the problem.
An actual UCT in a laboratory was built to help solve the problem. The tank body material could be adjusted to typical material used in the cleaning process, such as acrylic, glass, and stainless steel. Using water as a cleaning fluid and three mentioned materials as variables, the HRA was employed to determine the acoustic pressure inside the UCT. The HRA simulation results were compared with the experimental results obtained from foil corrosion and power concentration experiments to confirm reliability and methodology. Next, the HRA was applied to calculate acoustic pressure by varying tank designs such as tank body material, thickness, power, volume, and frequency. All simulation results were analyzed to find the root cause and a solution to achieve high-efficiency UCT. The highlight is that boundary conditions and settings in this research are based on actual cleaning processes in the factory. In addition, the built UCT was exclusively designed for this research. Finally, the research methodology was explained step by step.
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Harmonic Response Analysis (HRA) and Ultrasonic Cleaning
The HRA is a linear dynamic analysis employed to determine the reaction of materials responding to sinusoidal wave loads in the steady state. Recently, it has been widely applied in developing the UCTs [8,9,12,13,14,15] and is briefly described in this section.
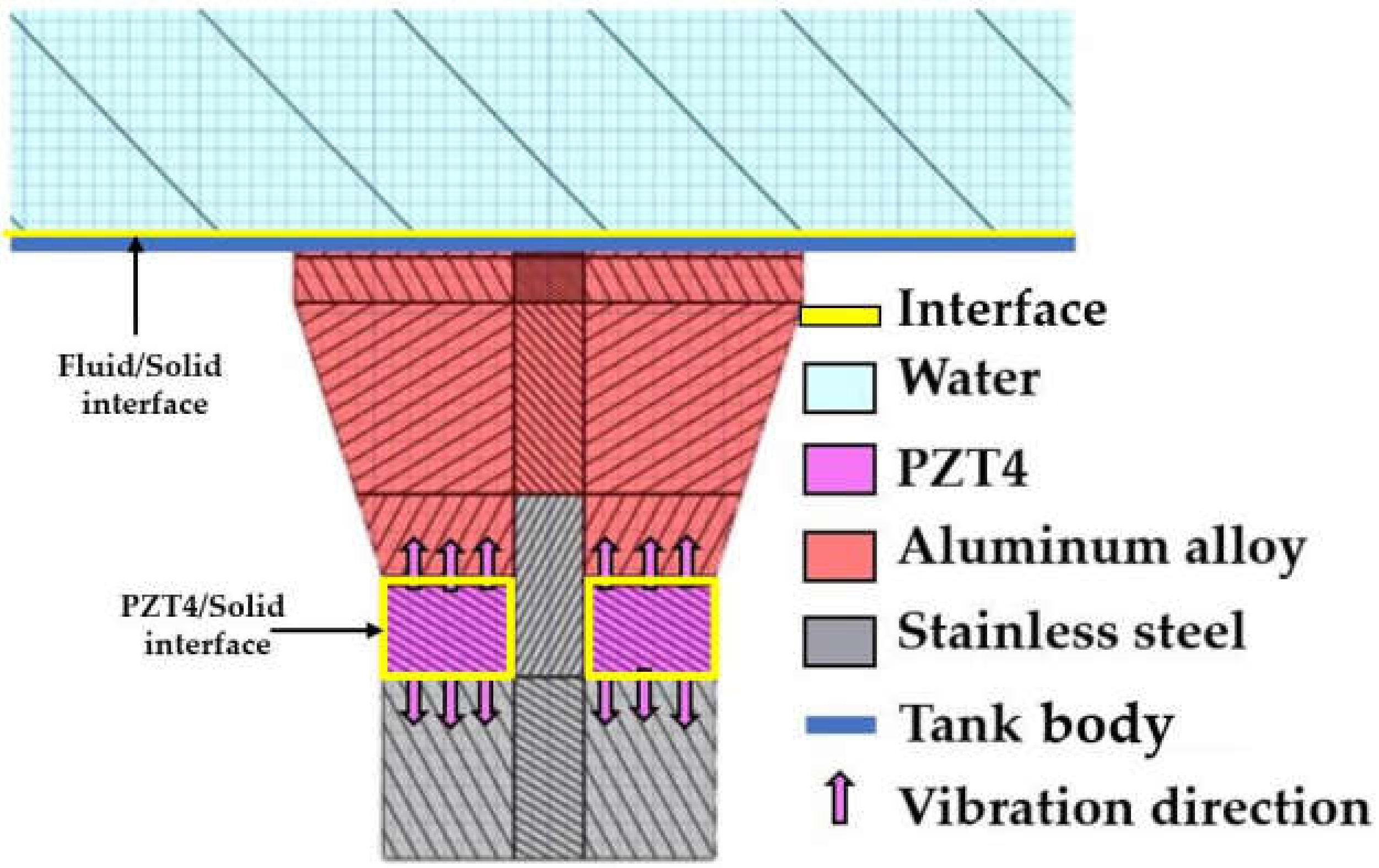
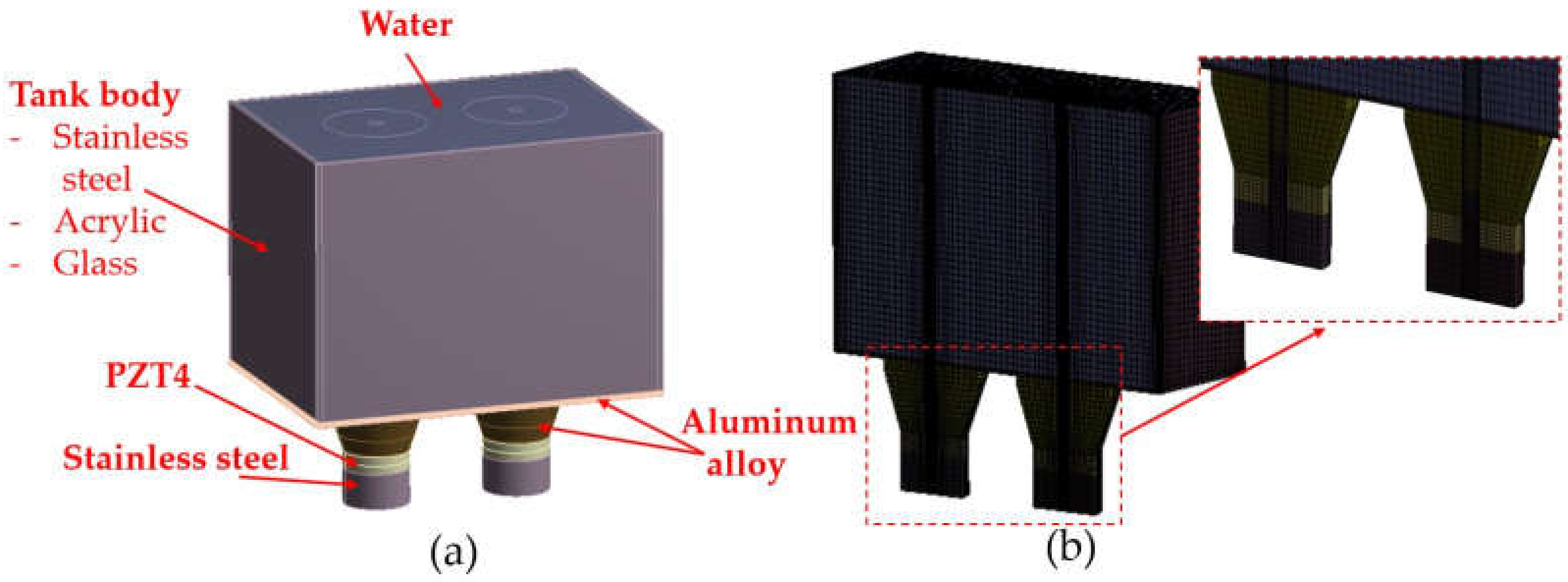
The HRA can be calculated in ANSYS software by dividing domains of the UCT materials into interfaces, water, PZT4, aluminum alloy, stainless steel, and tank body [9,14,15], as shown in Figure 1. However, the division is that equations governing the domains are different.
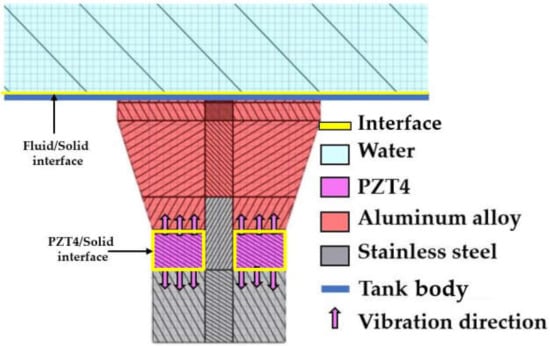
Figure 1.
Domains.
When alternating current is applied to PZT4 inside the transducer, the PZT4 vibrates with a natural frequency. Then, the vibration is transferred through different components of UCT until entering the water and resulting in acoustic pressure.
In the PZT4 domains and PZT4/solid interface, {u} can be calculated from a coupling between structural and electrical responses as
where [Muu] is a coupling mass matrix (kg), [Cuu] is a structural damping matrix (N s/m), [Cvv] is a dielectric dissipation matrix, [Kuu] is a structural stiffness matrix (N/m), [Kuv] is piezoelectric coupling element matrix, [Kvv] is dielectric permittivity matrix, F is mechanical load, Q is electrical load, {u} is a nodal displacement vector (m), {} is a nodal velocity vector (m/s), {ü} is a nodal acceleration vector (m/s2), {V} is a nodal voltage (V), and {} and {} are the first and second derivatives of nodal voltage, respectively.
In the stainless steel, aluminum alloy, and tank body domains, {u} is calculated by
where [M] is a mass matrix (kg), [C] is a damping matrix (N s/m), and [K] is a structural stiffness matrix (N/m).
In the solid/fluid interface. {u} is calculated using (3).
where [MS] is a solid mass matrix (N s2/m), {ρf} is a fluid density (kg/m3), [R]T is a acoustic fluid boundary matrix (m3), [MF] is a fluid mass matrix (N s2/Pa), [CS] is a damping matrix (N s/m), [CF] is a acoustic damping matrix (N s/Pa), [KS] is a structural stiffness matrix (N/m), [KF] is an acoustic fluid stiffness matrix (N/Pa), {fS} is a structural load (N), {fF} is an acoustic load (N), {p} is a nodal acoustic pressure vector (Pa), and {ṗ} and {} are the first and second derivatives of nodal acoustic pressure, respectively.
In the water domain, {p} is an acoustic pressure of wave propagating through a medium and has a time-harmonic relation as p = p0eiωt, which can be calculated in the HRA of ANSYS software based on the Navier-Stokes equations by
where ω is the angular frequency (driving frequency), [M] is the acoustic mass matrix, [C] is the acoustic damping matrix, [K] is the acoustic stiffness matrix, and {F} is the acoustic load vector. The subscript F denotes the fluid, which was water in this research.
The {p} is a crucial result representing the cavitation effect of the cleaning process. The larger the value of {p}, the greater the intensity of cavitation but does not imply the bubble size. The bubble size can be estimated from the ω. The higher the value of ω, the smaller the cavitating bubble size [9,18]. For the most efficient cleaning, the bubble size should be close to the size of the contaminant and dirt. Generally, factories will start the cleaning process at 28 kHz. This frequency gives a bubble size of approximately 14 μm, which can be used to clean many types of dirt, microorganisms, grease, and dust, etc. The mixing frequency produces bubbles of various sizes, which is a benefit and helps to clean more kinds of dirt [15]. Therefore, if accurate HRA simulation results are obtained, it will lead to high-efficiency UCTs matching customers’ requirements. The description above is a brief example of using the HRA to develop the cleaning process.
2.2. Reflection, Transmission, and Vibration, in the UCT
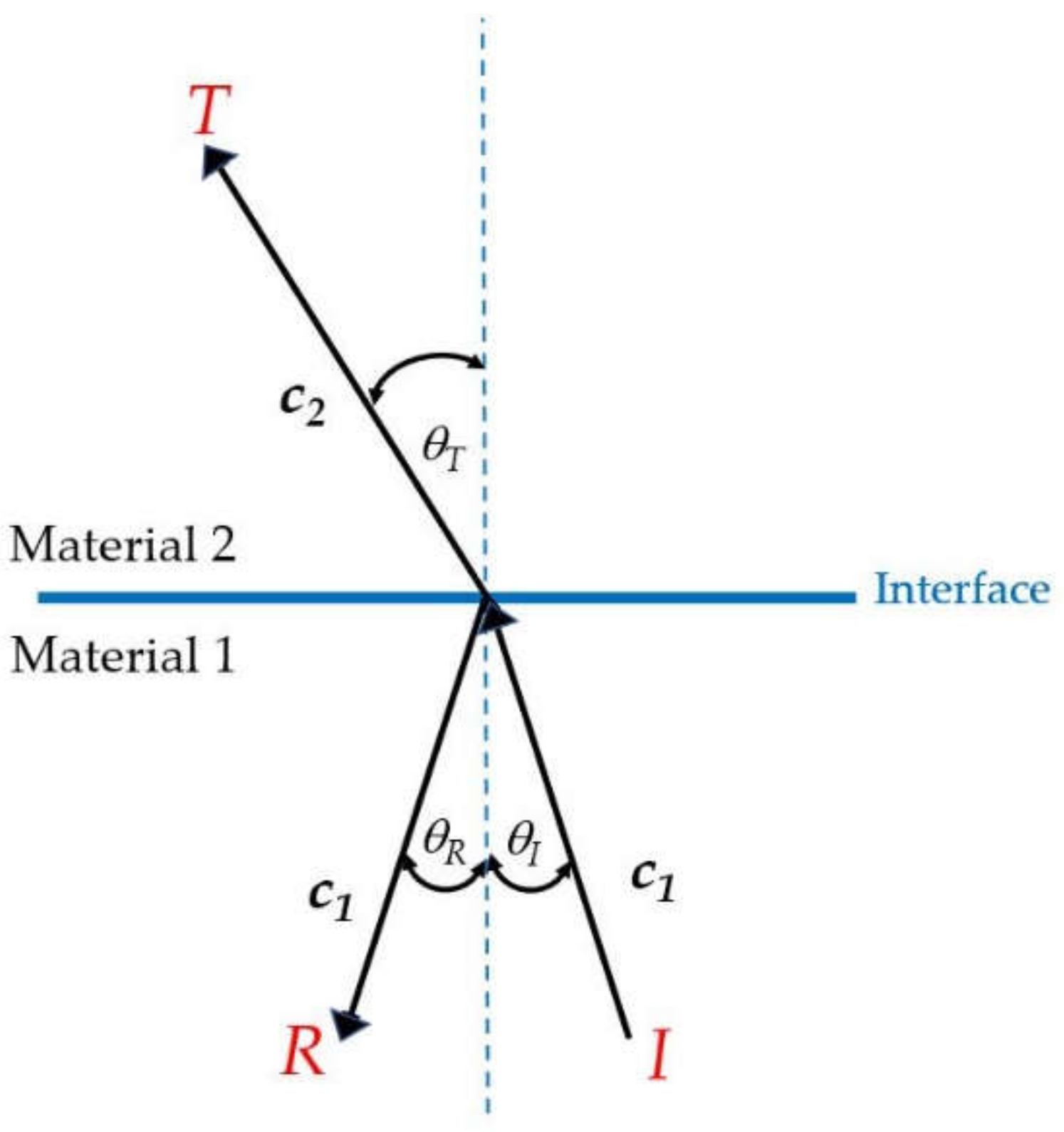
As mentioned in Section 1, the cause of the problem may be the material to make the tank body. In physics, cavitation caused by vibration, reflection, and transmission recurring inside the UCT can be explained in Figure 2.
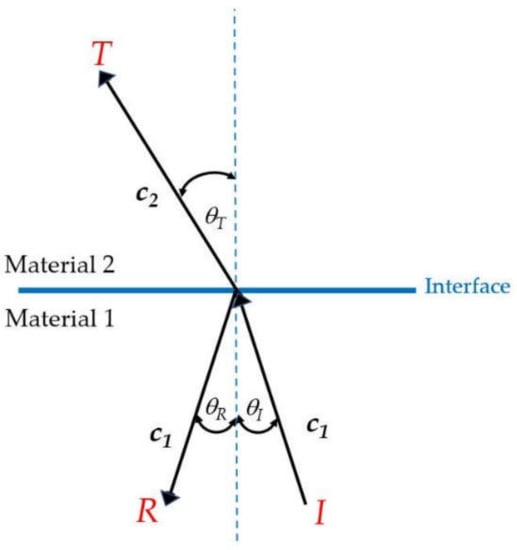
Figure 2.
Wave propagation through an interface.
Figure 2 shows wave propagation through an interface; when an incident wave (I) in material 1 passes to material 2, it generates reflected (R) and transmission (T) waves. The acoustic impedance (Z) is given by [19]
where ρ is the material density and c is the sound speed. The Z relates reflection (αR) and transmission (αT) coefficients as in Equations (6) and (7)
In order to link the physics in Figure 1 to the cavitation, the transducer in this figure consists of materials: PZT4 as a vibrator, aluminum alloy as a front mass, and stainless steel as a back mass. The tank body contains water and can be adjusted to materials such as stainless steel, acrylic, and glass, depending on usage purposes. Therefore, when the PZT4 vibrates, it causes ultrasonic waves to pass through the water, producing reflected and transmitted waves and cavitation. Generally, the front mass is designed with a less dense material to allow easy wave transmission to the front, while the back mass is designed with a dense material to reflect the waves from the back to the front, and the PZT is designed to match the vibration of the front mass shape. As a result, changing the tank designs such as tank body material, power, volume, and frequency alters the variables in Equations (1)–(7), resulting in different {p}. Therefore, the {p} is a key result to be calculated.
3. Methodology
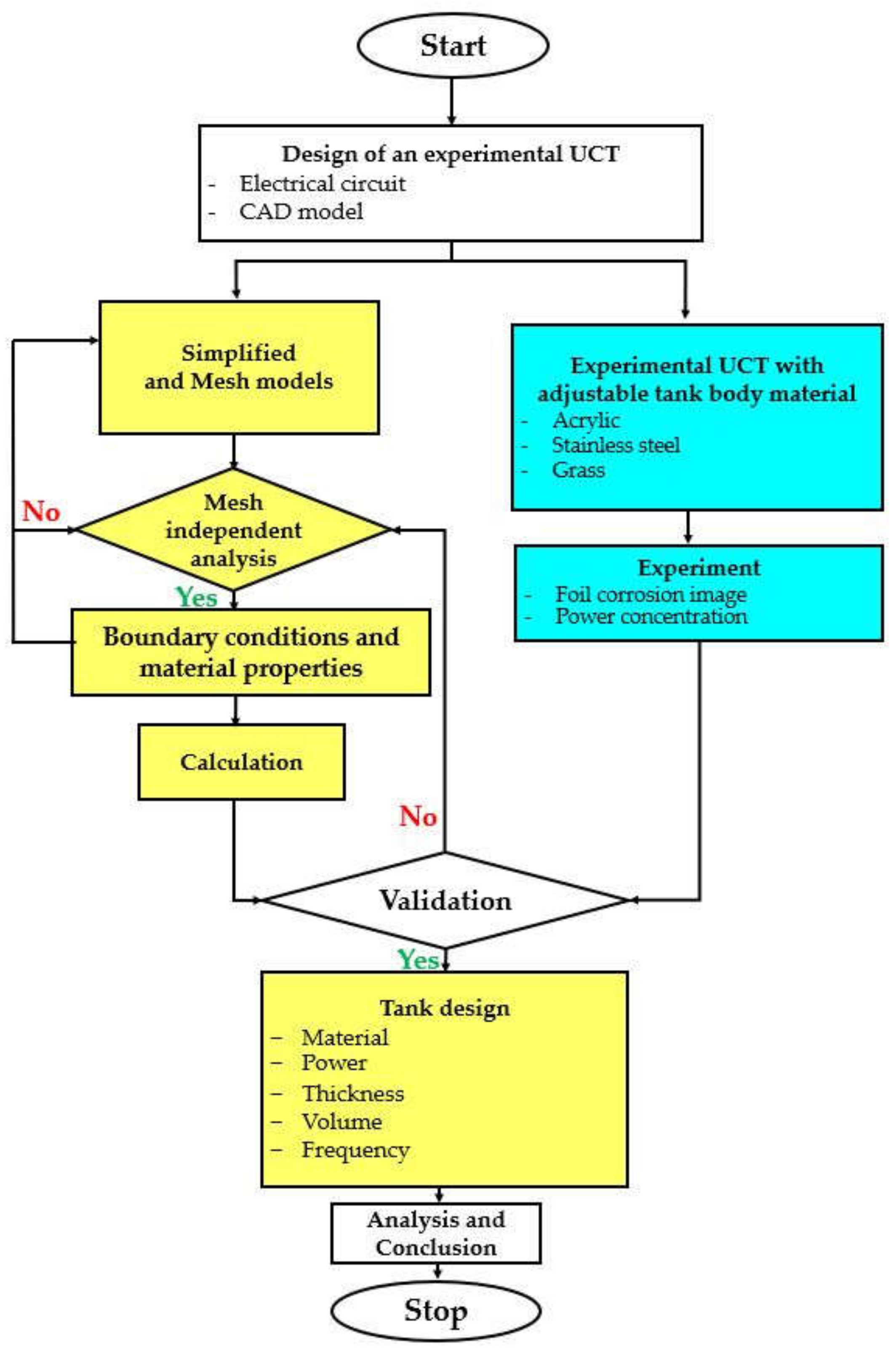
The research methodology is shown in Figure 3. The yellow and blue colors are for the HRA simulation and the experiment, respectively. It can be described as follows.
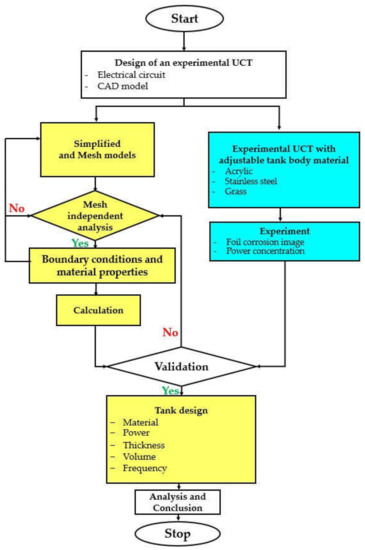
Figure 3.
A flowchart methodology.
3.1. An Experimental UCT
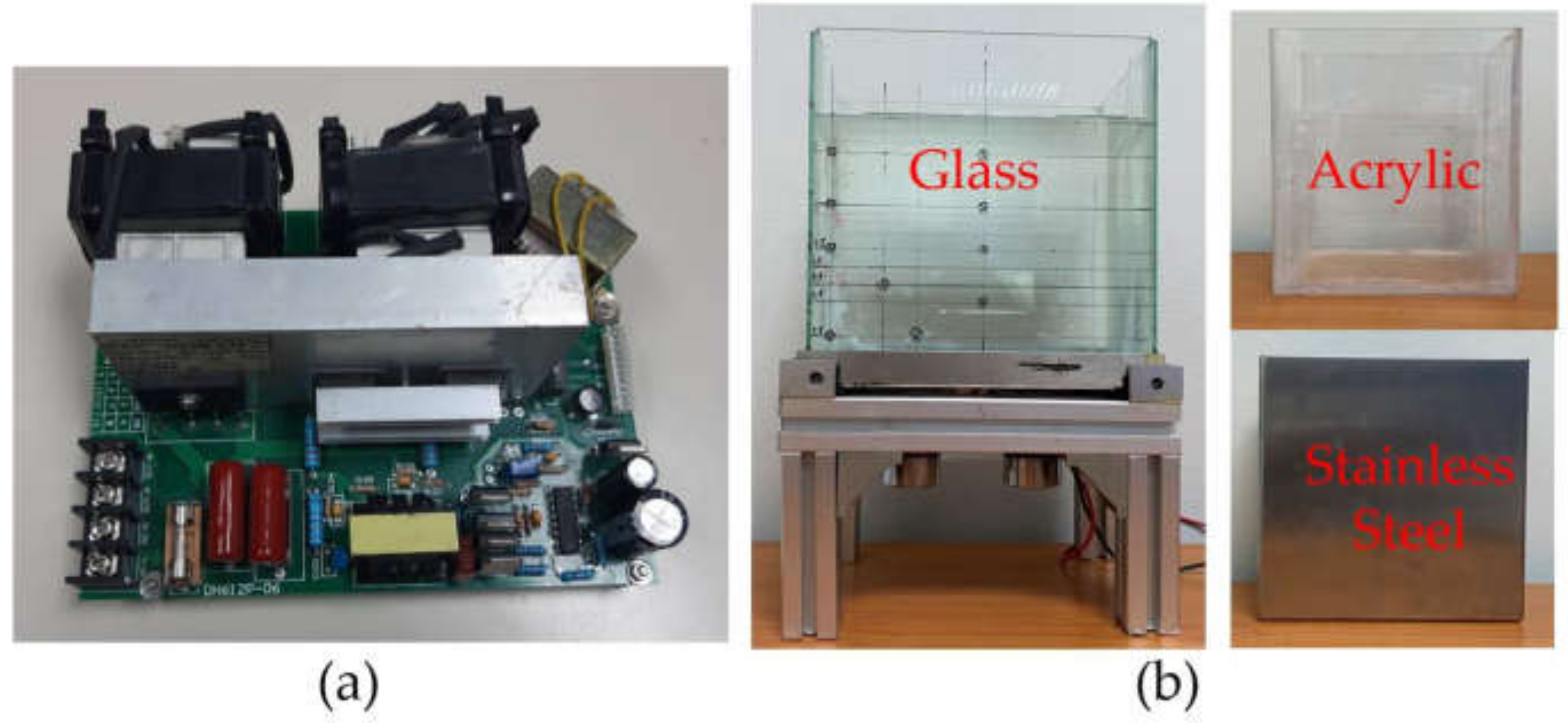
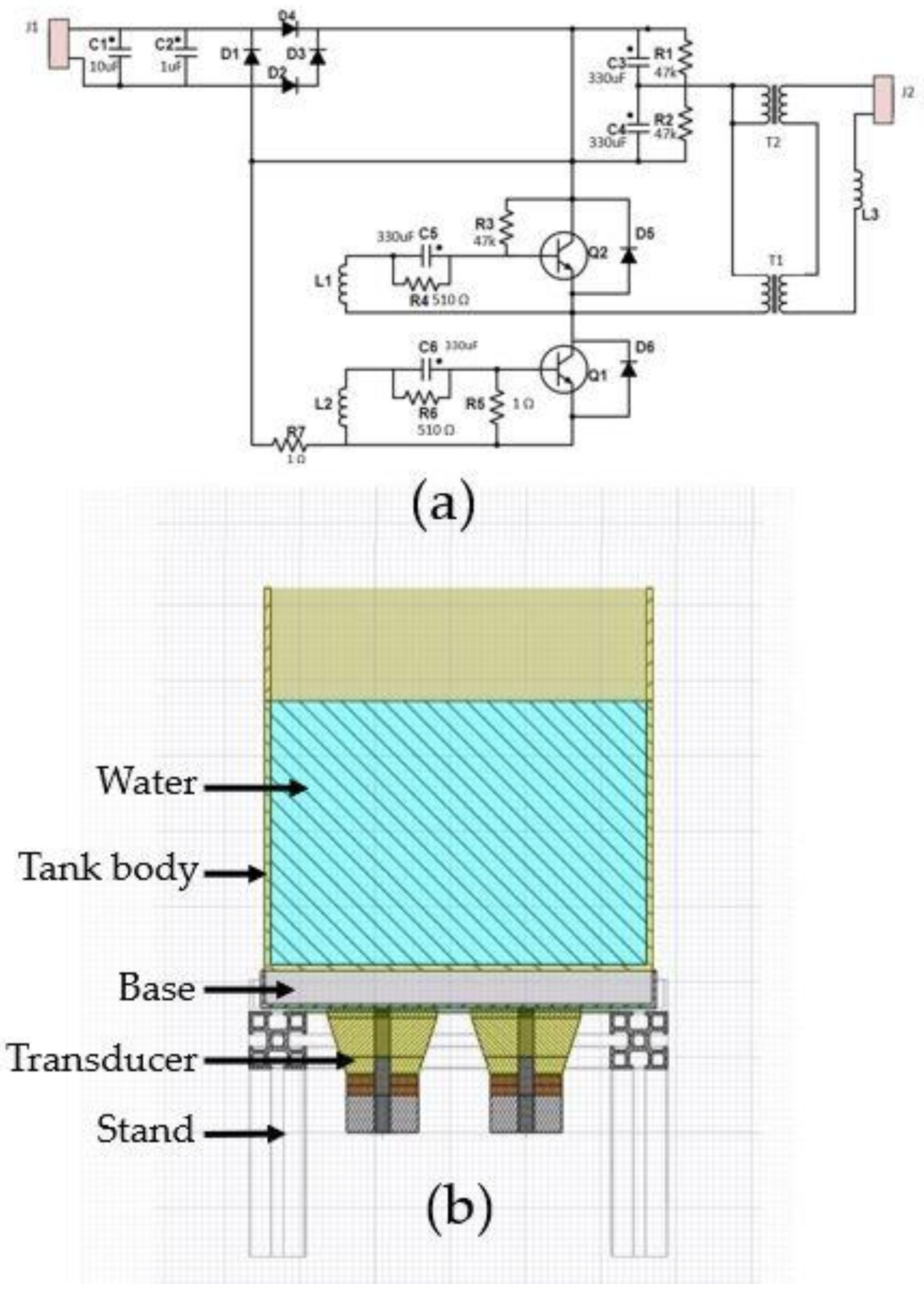
Since there are no UCTs from the manufacturers whose properties correspond to the aims of this research, a prototype UCT in a laboratory was designed and built. To understand the functioning of built UCT, two parts needed to be mentioned: an electric circuit and a tank body. Figure 4 reveals (a) diagrams of an electric circuit and (b) a CAD model of UCT, specifically modified and built, respectively, supporting this research. The functions can be summarized as follows.
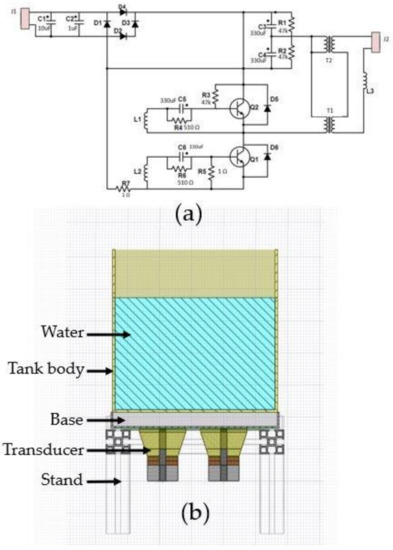
Figure 4.
Diagrams of (a) an electric circuit and (b) a CAD model of UCT.
Firstly, an electric circuit for 40–60 kHz designed for an ultrasonic generator presented in [20] was employed as a prototype and adjusted to suit 28 kHz, as shown in Figure 4a. The 28 kHz is a natural frequency of the horn transducer generating a vibration with longitudinal amplitude shown in the direction of Figure 1, enhancing the cleaning efficiency. On the contrary, other natural frequencies produce a vibration with less amplitude in the direction obstructing the cleaning efficiency.
Secondly, the two transducers were attached to a rectangular stainless steel base placed a supporting structure. The transducer details are in Figure 1, connecting to the electric circuit of Figure 4a. For the supporting structures, stands and beams were aluminum alloys welded to the base and transducers to allow vibration as much as possible, as shown in Figure 4b. Moreover, a tank body with a thickness of 2.0 mm did not weld to the supporting structures but could be adjusted to stainless steel, acrylic, and glass, materials generally used by UCT manufacturers.
3.2. Experiment
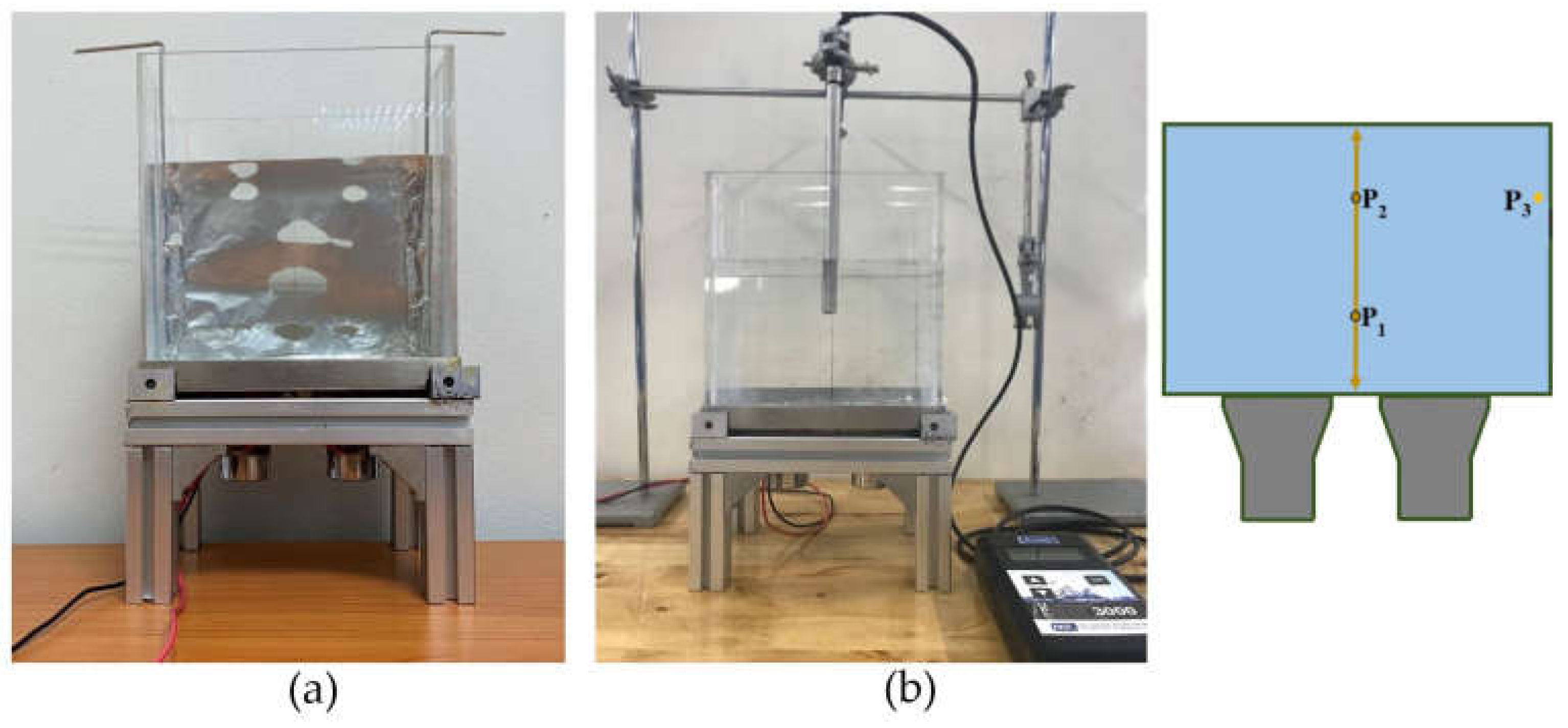
This paragraph explains the equipment and its setup. For convenience, we did not rebuild a circuit board entirely but modified it from a commercial product of the manufacturer using our design presented in Figure 4a. The modified circuit board was connected to the supporting structures and two transducers functioning as the ultrasonic generator applying ultrasonic waves of 28 kHz, which was tested for safety and precision before being employed in the actual experiment. For the tank body, three rectangular tanks made of glass, acrylic, and stainless steel with a dimension of 14 × 20 × 18 cm3 (W × L × H) 5.04 L, were built. Figure 5 shows the equipment, which are outcomes of Figure 4: (a) a modified circuit board and (b) a built UCT with an adjustable tank body to glass, acrylic, and stainless steel.

Figure 5.
The equipment for experiment: (a) a modified circuit board and (b) a built UCT.
In the experiment, water as a cleaning fluid of 14 × 20 × 14 cm3, 3.92 L was filled into the tank body placed on the supporting structures shown in Figure 5b. When the power of the ultrasonic generator was turned on, cavitation occurred in the water, according to the physics principles with the theoretical background described in Section 2. The experiment changed the tank body material to determine the effect on the ultrasonic cleaning. The experiment was divided into foil corrosion and power concentration experiments.
3.2.1. Foil Corrosion Experiment
This experiment was conducted to test the suitable location of the ultrasonic cleaning in the fluid. The same technique used previously in [12,13,14] was applied again. The foil sheet was stretched with wires; it was then submerged to the water inside the tank body with a sonication time of 3 min. Cavitation caused corrosion of the foil sheet, which can be employed for acoustic pressure and tank design analyses. Figure 6a reveals an example of foil corrosion after the experiment using the tank body made of acrylic, which can be changed to glass and stainless steel later.
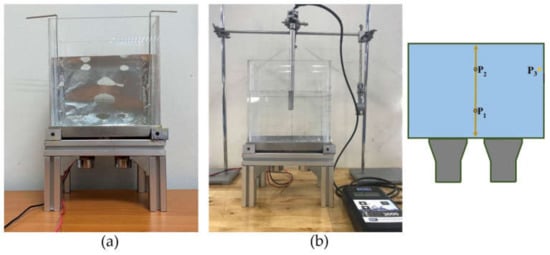
Figure 6.
The example of experiment setup: (a) a foil corrosion and (b) a power concentration and sampling points.
3.2.2. Power Concentration Experiment
This experiment was conducted to determine the cavitation intensity. Again, the same technique employed previously in [9,13] was used. The NGL measurer (Model UPC 30000) measured the power concentration in three sampling points: P1, P2, and P3. P1 and P2 were in a middle plane of the UCT located near and far away from transducers, respectively. P3 is near the tank body at an aside. Each sampling point was repeated five times to calculate an average value and a standard deviation. The NGL measurer with a resolution of ±0.1% W/L is a popular tool among manufacturers to determine cavitation intensity of the UCTs of frequency below 68 kHz. At a frequency higher than 68 kHz, the NGL measurer is not appropriate because the measurement sensitivity does not match the cavitation intensity. The higher the measured power concentration, the greater the cavitation intensity. In academics, the cavitation intensity can be significantly presented in terms of acoustic pressure [9,13]. Figure 6b shows an example of the power concentration experiment using the tank body made of acrylic and sampling points.
3.3. HRA Simulation
3.3.1. Simplified and Mesh Models
The designed CAD model in Figure 4b was simplified by ignoring components that did not affect the simulation results, leading to a simplified CAD model shown in Figure 7a. It consists of water, the tank body, PZT4, stainless steel, and aluminum alloy domains.
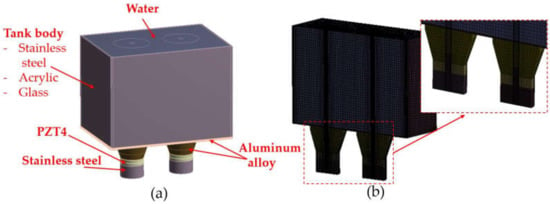
Figure 7.
Models: (a) a simplified CAD model and (b) a mesh model.
The simplified model in Figure 7a was employed as a prototype to create a mesh model, as shown in Figure 7b. Because of symmetry, a half-mesh model was therefore created to calculate faster. According to the mesh criteria, at least six mesh elements are required in one wavelength [9,15,21]. Since the transducer frequency was 28 kHz and the sound velocity in water was 1507 m/s, the wavelength was 53.8 mm. Therefore, the largest mesh size that produced accurate results enough was approximately 9 mm. In this research, the mesh size was 3.5 mm, smaller than the mesh criteria. As a result, this mesh size can be applied to simulate up to 68 kHz with high accuracy. In this research, the maximum frequency to be investigated was 40 kHz, so the created mesh size was smaller than the criteria, ensuring accuracy. In the mesh model, elements over 96% were hexahedrons, while 4% were wedges and pyramids. A picture on the right shows an enlarged of the elements in fine detail. After using the mesh independent analysis to find suitable mesh models, models which provided accurate results proper to computational resource usage, we found the mesh models with 88,531–150,523 elements, 368,529–47,3736 nodes, 0.58–0.70 skewness was the suitable mesh model. The number of elements and nodes varies slightly depending on the changing variables.
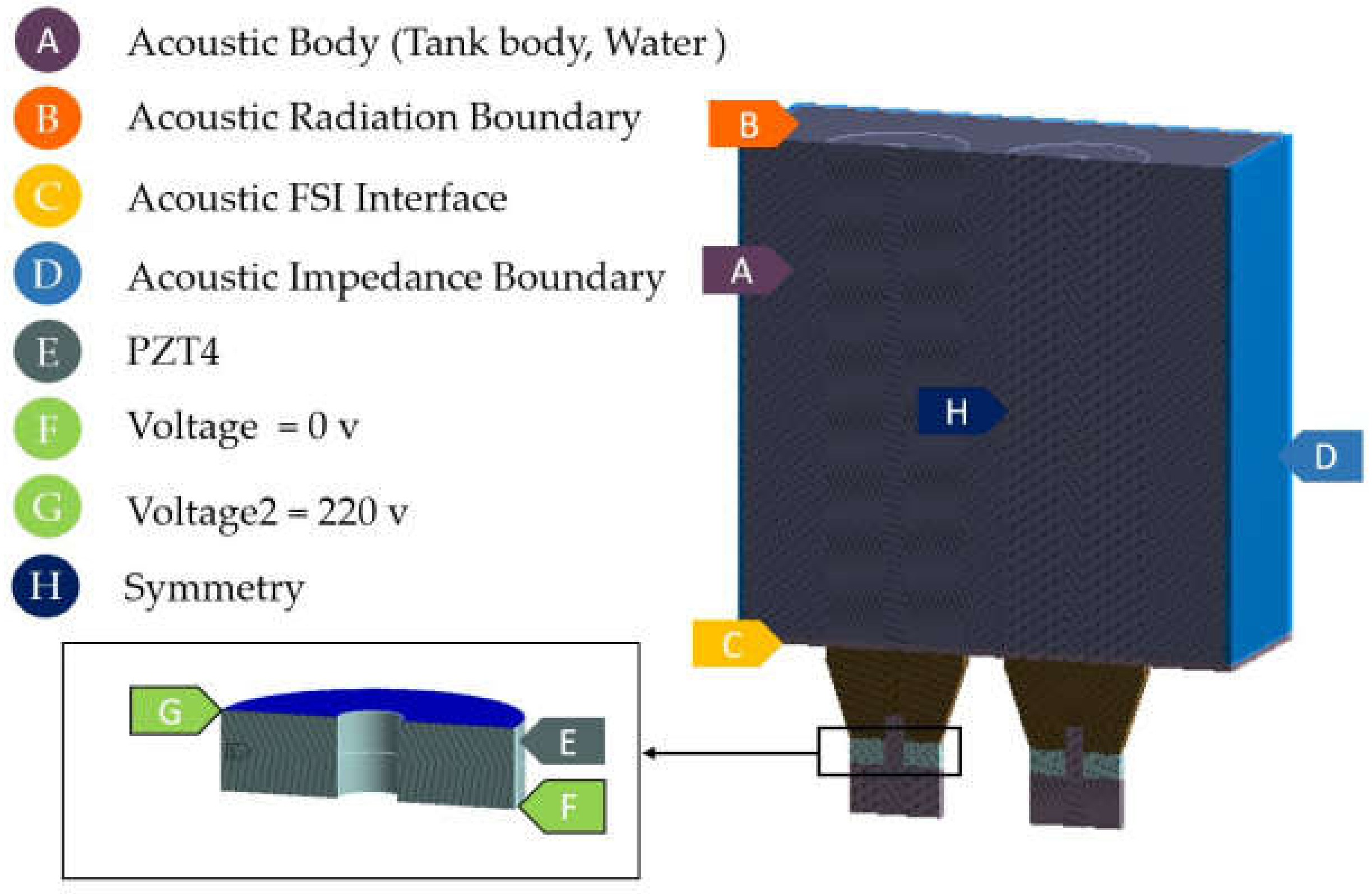
3.3.2. Boundary Conditions and Material Properties
Figure 8 shows boundary conditions defined in the HRA labeled as A-H. A small picture reveals boundary conditions for transducers in detail. Since the UCT is approximately 3.92 L, which is a small volume compared with the UCTs in [13,14,15] with a capacity of 10–20 L, the critical settings, therefore different from [13,14,15], are an acoustic radiation boundary (B) assigned to the topwater surface and an acoustic impedance boundary (D) assigned to the tank body. The assignments of B and D were made to mimic the reflection, transmission, and radiation of the ultrasonic waves and achieve high accurate simulation results consistent within the aims of this research. The UCTs in [13,14,15] had higher water volume, so without setting of both B and D did not affect the results and conclusion. In addition, the symmetry condition enabled rapid calculation. As a result, the simulation results across the symmetrical plane were identical.
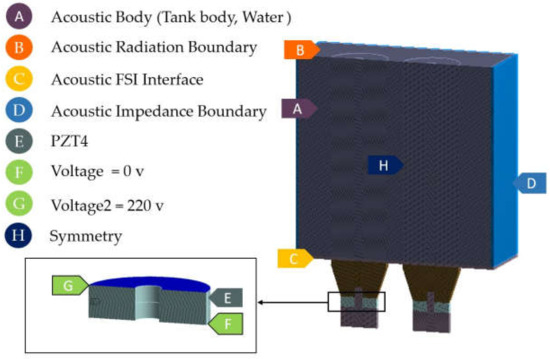
Figure 8.
Boundary conditions.
Mechanical properties of materials such as acrylic, glass, stainless steel, aluminum alloy, PZT4, and water were defined according to Table 1. When the boundary conditions and material properties were defined entirely, the calculation displayed the acoustic pressure in shade color for easy analysis.

Table 1.
Material properties for the HRA simulation (data from Refs. [13,14,15]).
4. Results and Discussion
This section divides the HRA simulation results of acoustic pressure into two parts: validation and tank design effect. First, the acoustic pressure distribution patterns were compared with the foil corrosion and the power concentration experiments to validate the results and methodology of this research. Second, the acoustic pressures at the sampling points obtained by varying variables such as tank body material, thickness, volume, and frequency were reported and analyzed to investigate the tank design effect on the ultrasonic cleaning process.
4.1. Validation
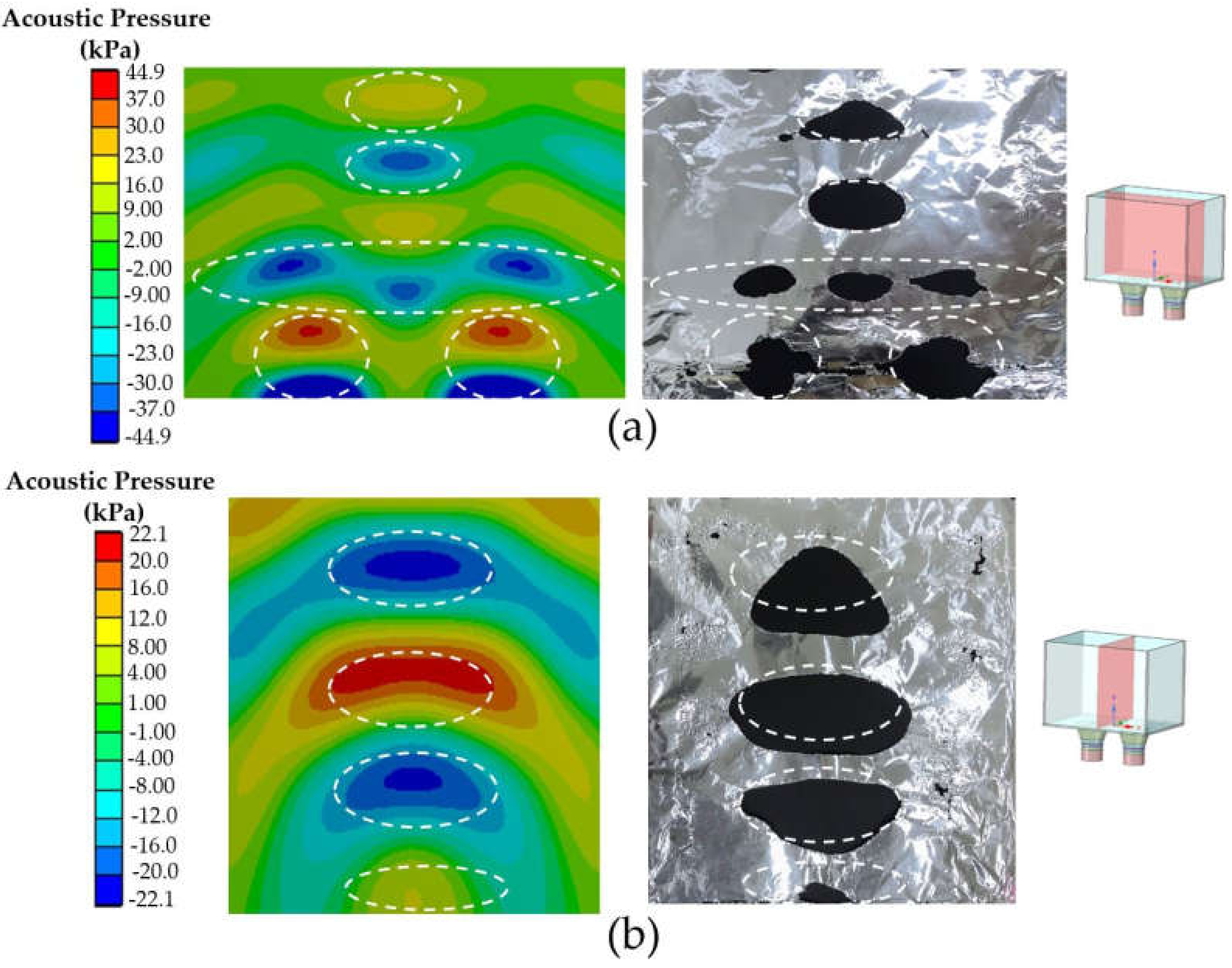
Figure 9 shows a comparison between the acoustic pressure distribution patterns on the left and foil corrosion on the right for (a) the xz and (b) the yz planes using acrylic as a tank body. Both planes were located in the middle position of the UCT, as shown in small pictures on the right. The red and blue colors present the maximum and minimum acoustic pressures, respectively. The comparison results revealed the consistency of both results in marked areas and indicated that the center position of UCT was suitable for the ultrasonic cleaning process, as expected. In addition, the acoustic pressure distribution depended on transducer positioning, consistent with the reports in [8,9,12,13,14,15]. Moreover, the comparison results of stainless steel and glass tank bodies remained the same but differed only in acoustic pressure and corrosion intensities.
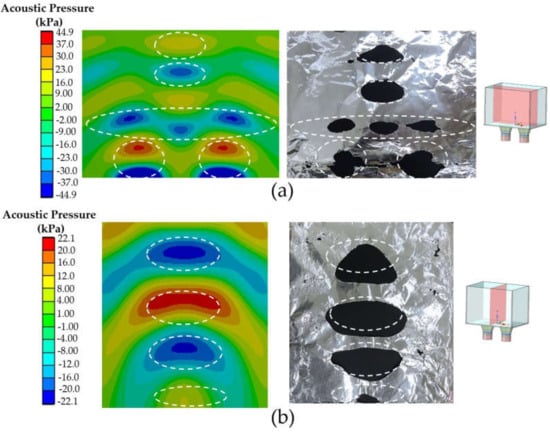
Figure 9.
Comparison between the acoustic pressure distribution pattern (left) and foil corrosion (right) for (a) the xz plane and (b) the yz plane using acrylic as a tank body.
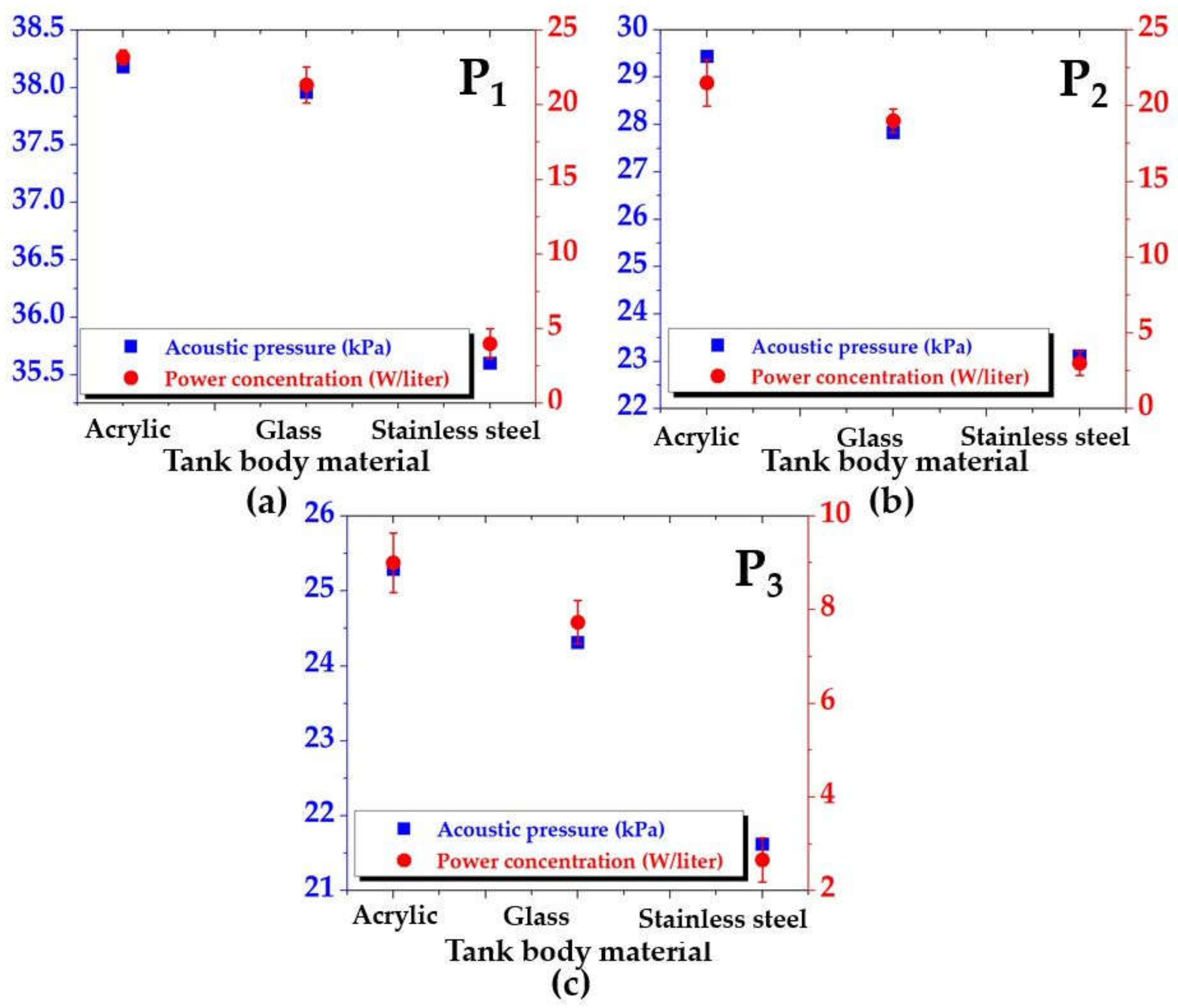
Figure 10 presents a comparison between the acoustic pressure and power concentration for tank bodies made of acrylic, glass, and stainless steel at the sampling points (a) P1, (b) P2, and (c) P3, in the same plane as Figure 9a. The blue is for the acoustic pressure, and the red is for the power concentration. Again, consistency of both results was found for all sampling points. Both results depended on the measured points. The error bar was calculated from the standard deviation of measurements. The difference in acoustic pressure at each sampling point, the effect of the tank body on acoustic pressure, and an explanation in physics are discussed at the end of this section.
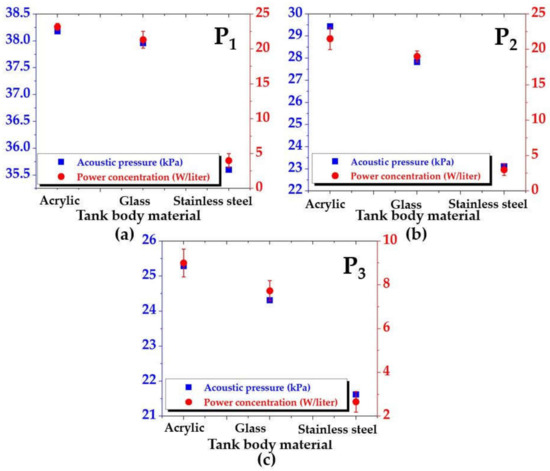
Figure 10.
Comparison between the acoustic pressure and power concentration for tank bodies made of acrylic, glass, and stainless steel at positions (a) P1, (b) P2, and (c) P3.
4.2. Tank Design Effect
This section reports the effect of the tank design on the acoustic pressure by varying variables such as material, power, thickness, volume, and frequency. Similar boundary conditions and settings were assigned to all UCT models but different only mentioned variables. All results were collected from the plane in Figure 9a.
4.2.1. Materials
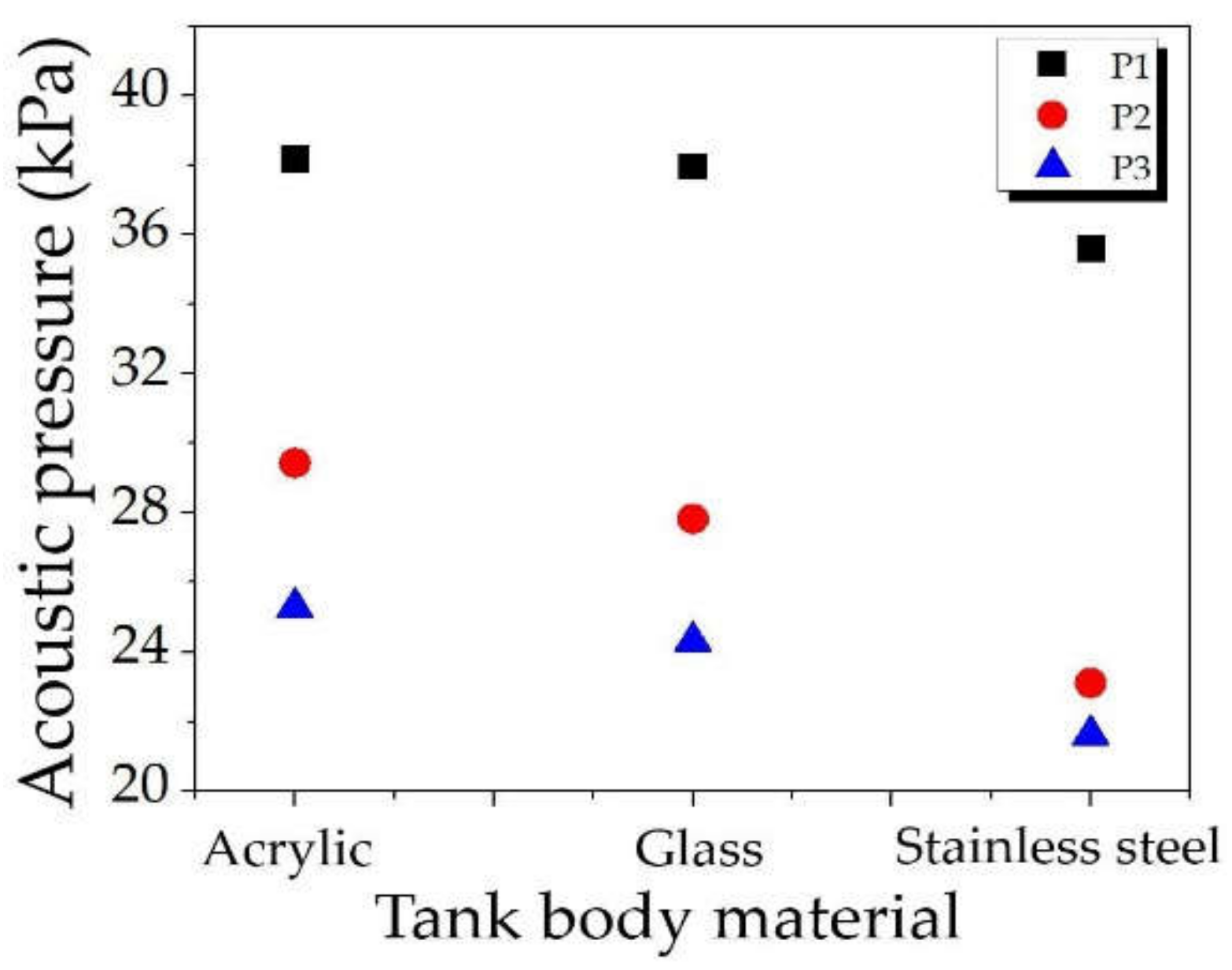
The acoustic pressures were plotted against the tank body materials at sampling points P1, P2, and P3, as shown in Figure 11. As expected, the acoustic pressure depended on the measured position with the same distribution pattern as displayed in Figure 9. By comparing the measured points, the acoustic pressures were the highest at P1, moderate at P2, and the lowest at P3, for all sampling points. In-depth, acoustic pressure inequality can be explained as P1 closest to transducers, P2 inferior, and P3 farthest. P1 and P2 provided greater acoustic pressure than P3, so they had more cavitation; therefore, they were proper for the ultrasonic cleaning process. In addition, P3 was not a proper position for the cleaning since it had less cavitation.
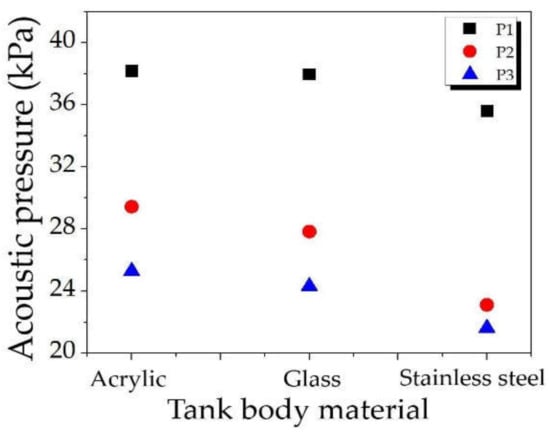
Figure 11.
The acoustic pressures for varying positions and tank body materials.
4.2.2. Power
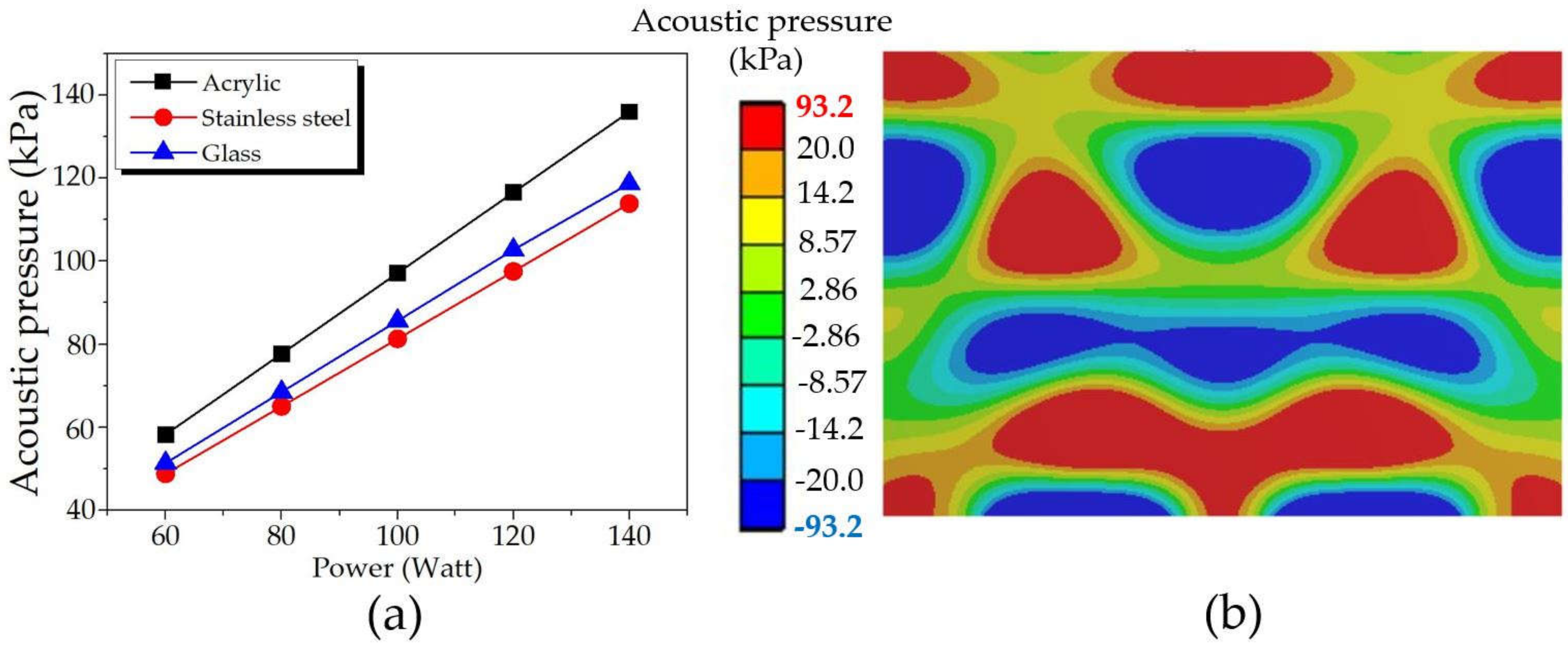
Figure 12 shows the maximum acoustic pressures: (a) comparison results for varying power of transducers at 60-140 W and (b) a sample of the distribution pattern of acrylic with the power of 100 W. As expected, the maximum acoustic power increased with increasing the power, consistent with [12,15]. However, changing the power and tank body material did not affect the acoustic pressure distribution pattern. Instead, it remained the same as in Figure 12b but only differed in the maximum acoustic pressure. Likewise, acrylic provided the highest acoustic pressure, followed by glass and stainless steel accordingly.
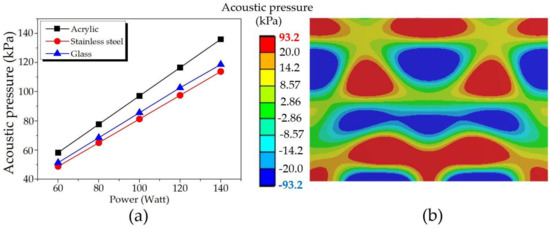
Figure 12.
The maximum acoustic pressures: (a) comparison results for varying power and tank body materials, and (b) a sample of the distribution pattern of acrylic with a power of 100 W.
4.2.3. Thickness
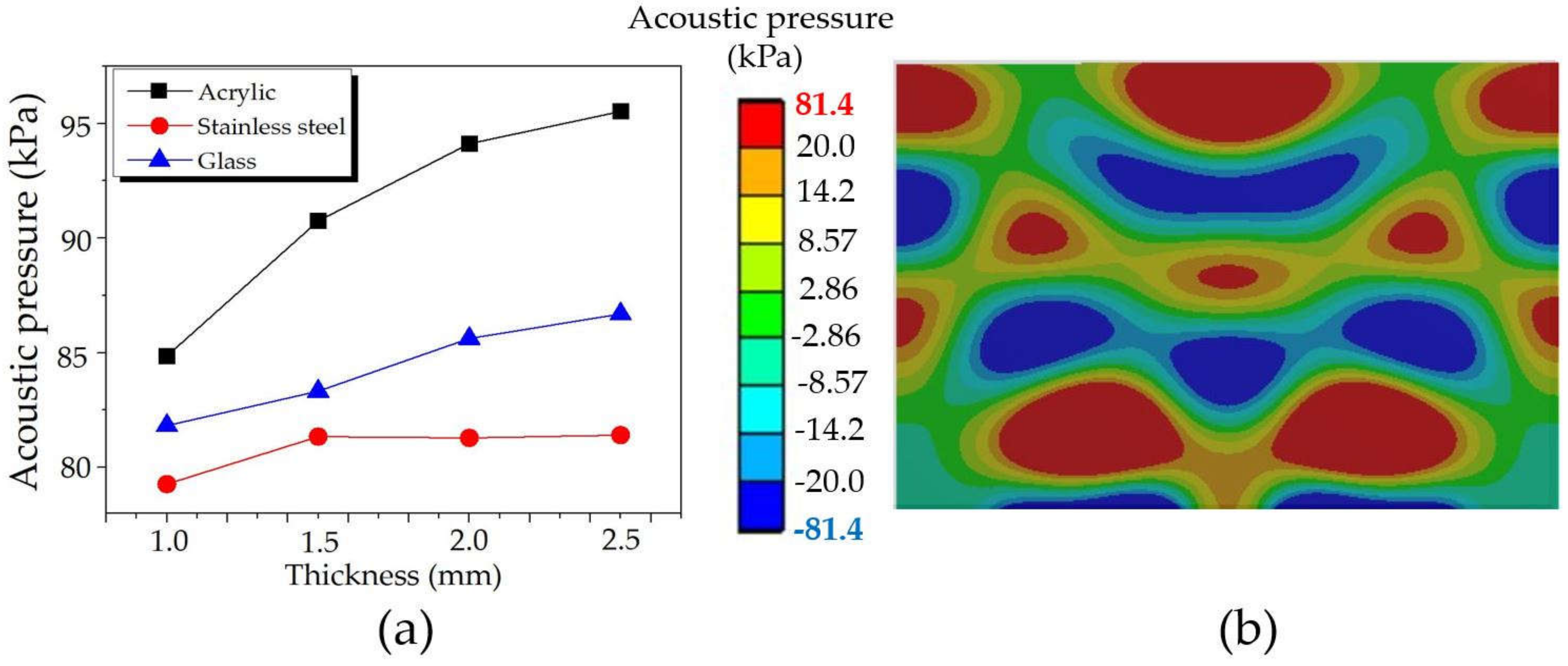
Similarly, Figure 13 presents the maximum acoustic pressure: (a) comparison results for varying materials of the tank body and thicknesses at 1.0–2.5 mm and (b) a sample of the distribution pattern of stainless steel with a thickness of 2.5 mm. The original tank body thickness is 2.0 mm. The maximum acoustic pressure increased with increasing the thickness. As expected, the increasing thickness did not affect the acoustic pressure distribution pattern since it depends on the frequency and transducer placement [7,8,9,12,13,14,15]. Again, the highest, moderate, and lowest acoustic pressures were found in acrylic, glass, and stainless steel tank bodies, respectively. It is worth noting that the maximum acoustic pressure was almost unchanged for stainless steel. According to the density of materials in Table 1, it might be because stainless steel has a density of 7550 kg/m3, 7 times higher than acrylic, and 3.5 times greater than glass, approximately. Therefore, it can be said that the UCT made with the tank body’s lower density provides higher acoustic pressure than the one with higher density. More in-depth supporting reasons are discussed at the end of this section. However, the tank body with lower density may have a lower durability not suitable for such applications requiring frequent relocating or long-continued usage.
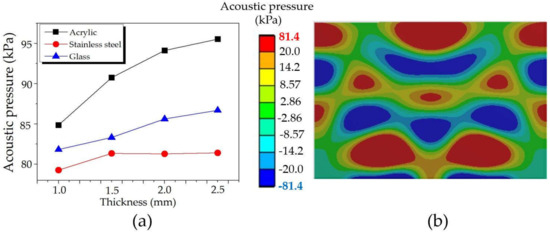
Figure 13.
The maximum acoustic pressures: (a) comparison results for varying thickness and tank body materials, and (b) a sample of the distribution pattern of stainless steel with thickness of 2.5 mm.
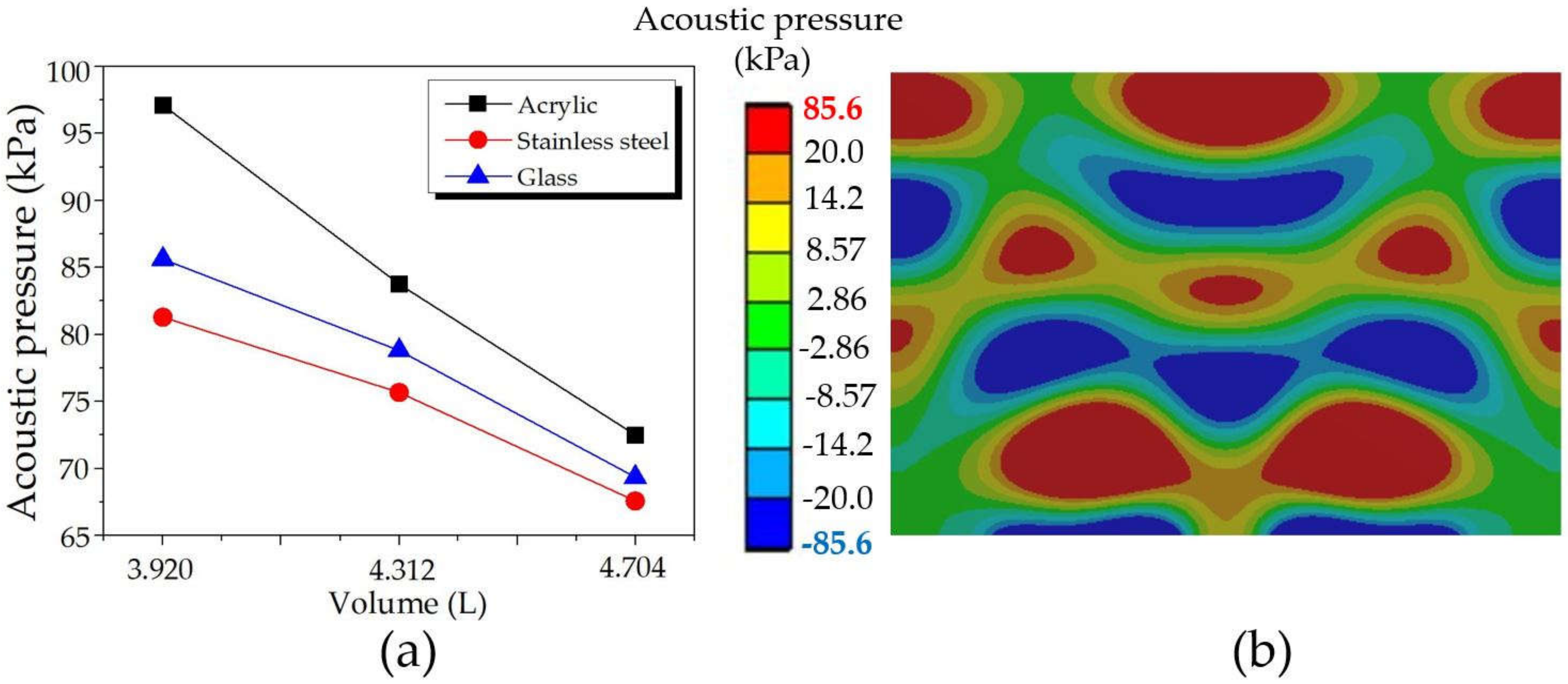
4.2.4. Volume
The water in the original UCT has a dimension of 14 × 20 × 14 cm3 (W × L × H) with a volume of 3.920 L; therefore, the HRA simulation was performed by extending the length from 20 mm to 22 mm and 24 mm. The extending changed the water volume to 4.312 L and 4.704 L, respectively. Figure 14 presents the maximum acoustic pressure: (a) comparison results for varying volume and tank body materials and (b) a sample of the distribution pattern of glass with a water volume of 3.920 L. The maximum acoustic pressure decreased with increasing volume. This result is consistent with the manufacturer’s report that for the same UCT model and specification, the tank body with a larger volume had lower cleaning efficiency than the smaller one. The larger the volume, the lower the efficiency of cleaning. Therefore, if the customers require a larger UCT, the manufacturers must increase the number of transducers to achieve a proper acoustic pressure level with the highest cleaning efficiency and meet customers’ requirements. Moreover, comparing Figure 14b to Figure 13b and Figure 12b, the distribution patterns still remained the same, so extending the length of the tank body in this range did not affect the distribution pattern. Additionally, acrylic, glass, and stainless steel provided superb, medium, and the least acoustic pressures, respectively.
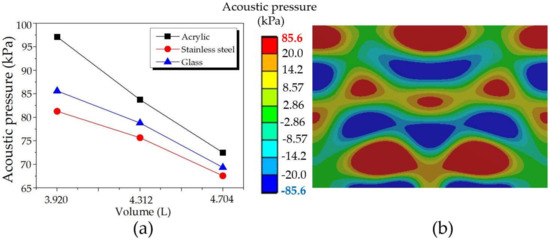
Figure 14.
The maximum acoustic pressures: (a) comparison results for varying volume and tank body materials, and (b) a sample of the distribution pattern of glass with a volume of 3.920 L.
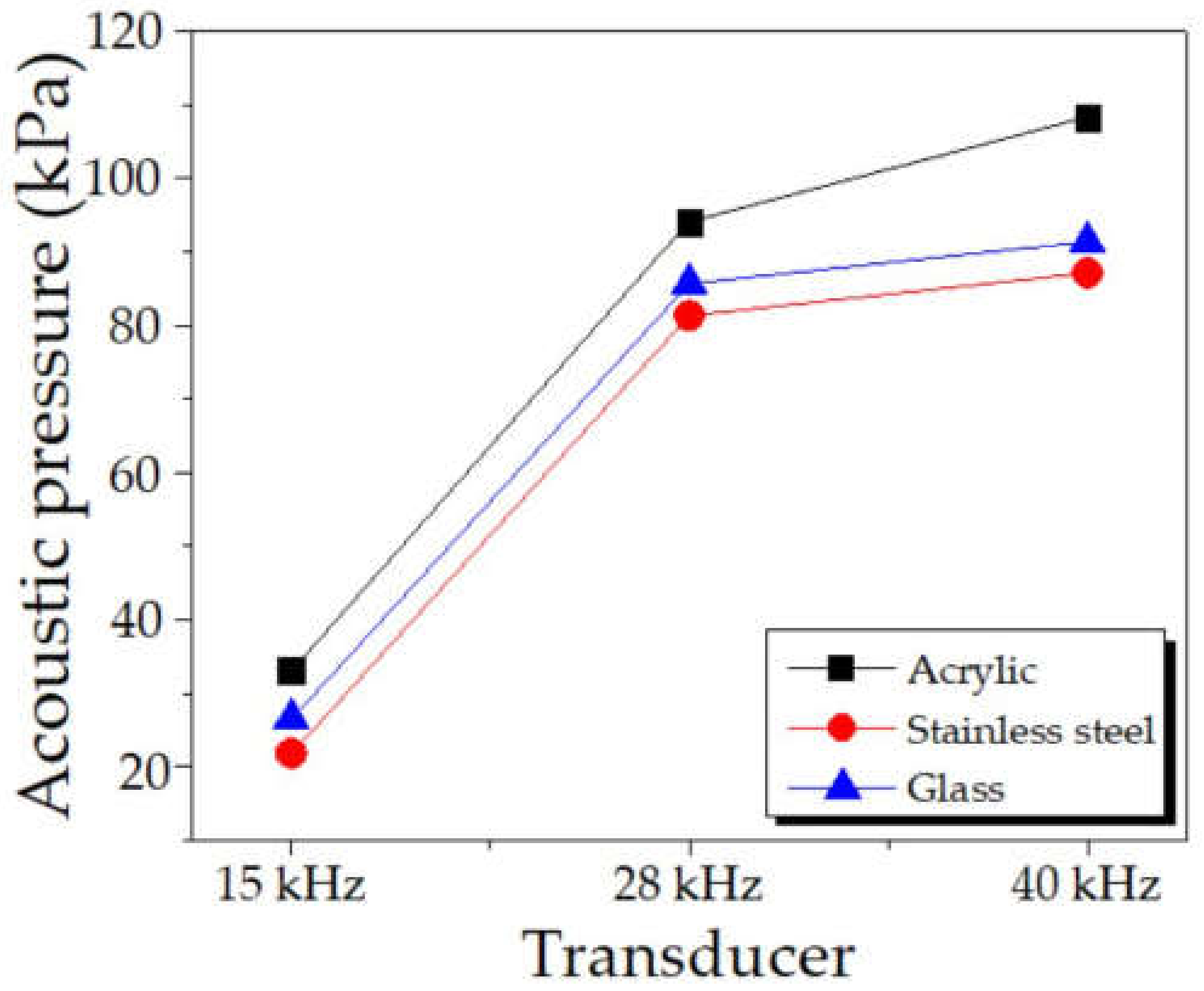
4.2.5. Frequency
The transducers were changed to 15 kHz and 40 kHz using exact specifications provided by the manufacturer to investigate the frequency effect on the acoustic pressure. Figure 15 compares the maximum acoustic pressure at 15 kHz, 28 kHz, and 40 kHz by varying tank body materials. As expected, the maximum acoustic pressure increased with increasing frequency, consistent with [12,15]. The higher the frequency, the greater the maximum acoustic pressure. Moreover, varying tank body materials also affected the acoustic pressure. A similar trend remained the same, from the highest to the lowest: acrylic, glass, and stainless steel, accordingly.
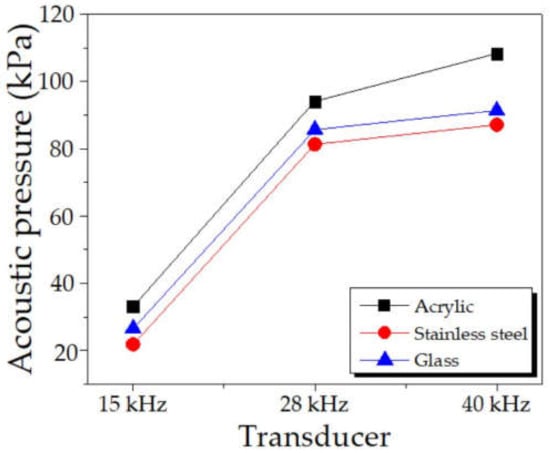
Figure 15.
Comparison of the maximum acoustic pressure for varying frequency of transducers.
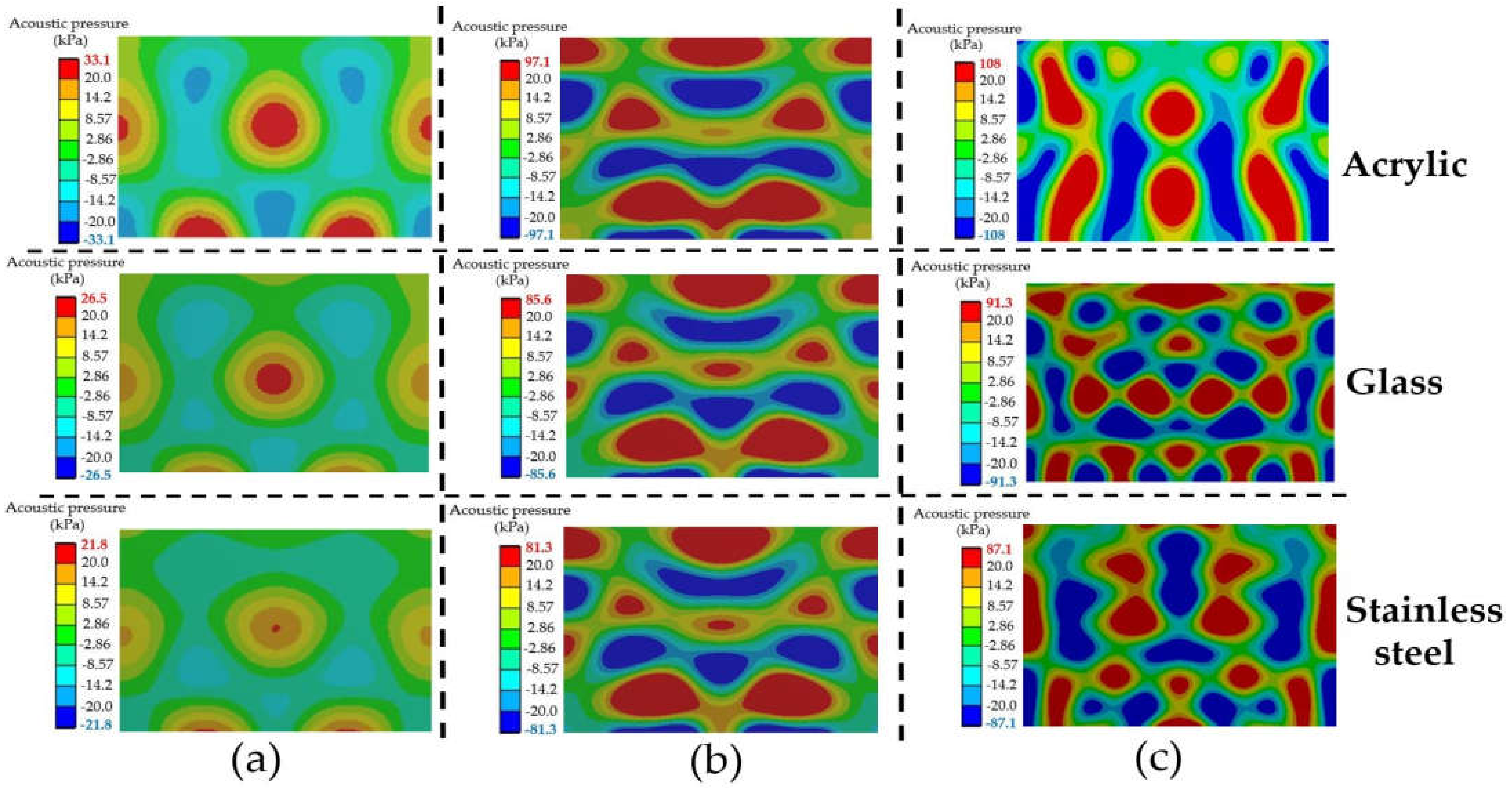
Figure 16, related to Figure 15, reports the acoustic pressure distribution pattern for varying tank body materials at the frequency of (a) 15 kHz, (b) 28 kHz, and (c) 40 kHz. The top, middle, and bottom rows display the HRA simulation results of acrylic, glass, and stainless steel, respectively. Again, increasing the frequency affected the distribution pattern. Higher acoustic pressure with smaller areas and more distribution throughout the UCT were observed. When increasing the frequency, the HRA simulations revealed higher acoustic pressure with the smaller area and more dispersed throughout the UCT, caused by increasing the number of wave superpositions. The higher the frequency, the greater the number of wave superpositions. The distribution patterns in this figure were consistent with the reported in [12,15]. Therefore, increasing the frequency increases the cavitation intensity and reduces the size of bubbles, which are dispersed more throughout the UCT.
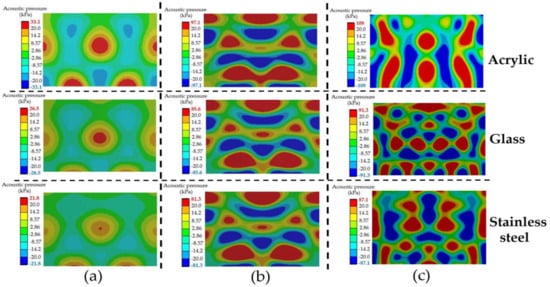
Figure 16.
The acoustic pressure distribution pattern for varying tank body materials with transducers of (a) 15 kHz, (b) 28 kHz, and (c) 40 kHz.
The section after this part discusses the maximum acoustic pressure inequality provided by acrylic, glass, and stainless steel, including the cause of the problem. By comparing all materials in Section 4.2.1, Section 4.2.2, Section 4.2.3, Section 4.2.4 and Section 4.2.5, acrylic was shown to yield the highest acoustic pressure, followed by glass and stainless steel, respectively. Therefore, the acoustic pressure depends on the tank body material. In factories, each tank body material is implemented in a different situation. For example, the tank body made of stainless steel is suitable for general cleaning objects. However, it is not suitable for acidic or base cleaning fluids. In contrast, glass is specially employed for acidic or base cleaning fluid. Furthermore, acrylic is often used in processes requiring timely inspection of cleanliness in a factory or an academic laboratory.
We determine the reason in physics why acrylic produced the highest acoustic pressure, and glass and stainless steel decreased, respectively. The reflection (αR) and transmission (αT) coefficients were calculated using Equations (6) and (7) and acoustic impedances in Table 1. The calculation results are reported in Table 2. Clearly, the acoustic pressure directly relates to the transmission coefficient. The tank body material with high αT yielded more significant acoustic pressure than the one with less. The higher the αT, the greater the acoustic pressure. Therefore, if the cleaning process requires intense cavitation, the UCT should have a tank body material with high αT.

Table 2.
The reflection (αR) and transmission (αT) coefficient of materials.
The HRA simulation results also indicated that the tank designs, such as power, body material, thickness, volume, and frequency, affected the acoustic pressure. Therefore, the complaint problem would be concluded that came from the tank designs that were not suitable for washing the products. As a result, the cavitation effect generated by the problematic UCTs might be too high to cause damage or too low to make unclean on the products. Indeed, choosing suitable tank designs and the HRA simulation not only solves the complaint problem but also ensures high cleaning efficiency. All research findings have already been applied as essential information for developing a new generation of high-efficiency UCTs by the manufacturers.
5. Conclusions and Further Study
This article aimed to investigate the cause of ultrasonic washing damage problems reported by the customers whose factories applied the UCTs in the cleaning process and find ways to achieve high cleaning efficiency. First, an electric circuit and a CAD model of the UCT were designed and then actually built in a laboratory for experiment and a computer for the simulation. For the experiment, the built UCT had a tank body of UCT that could be adjusted to acrylic, glass, and stainless steel materials. For the HRA simulation, the tank designs such as body material, power, thickness, volume, and frequency could be modified. Next, the foil corrosion and power concentration were applied to the experiments, and the HRA was employed in the simulation. Since acoustic pressure relates to cavitation and ultrasonic cleaning, it was analyzed to reach the aims. The HRA results revealed that the acoustic pressure was comparable to the foil corrosion and power concentration experiments, confirming the validity of simulation results and the research methodology. Then, by varying the tank designs, the HRA results revealed that the acoustic pressure increased with increasing the power, thickness, and frequency, but decreased with increasing volume. The tank body made of acrylic provided the highest acoustic pressure, moderate for glass, and the lowest for stainless steel, accordingly. In addition, changing frequency affected the acoustic pressure distribution pattern while varying the material, power, thickness, and volume did not alter the one, as expected. The acoustic pressure difference relates to the transmission coefficient of the material. The higher the transmission coefficient, the greater the acoustic pressure. Finally, all analysis results indicated that the complaint problem was caused by the tank design that was unsuitable for usage. Therefore, the HRA simulation, together with a proper tank design, will lead to a high-efficiency ultrasonic cleaning process in accordance with the customers’ requirements. The findings from this research are how to apply the HRA in developing the UCT and tank design effect on cavitation for interested persons to apply in their work.
Water is not a usage cleaning fluid in an actual ultrasonic cleaning process. Instead, most factories prefer to use deionized (DI) water. The DI water is mixed with surfactants and cleaning chemicals to activate the cavitation effect quickly. The mixing ratio depends on the type of dirt, sonication time, and cleaning objects to be washed, which is a secret of each factory and chemical vendor. With a proper mixing ratio, cavitation occurs rapidly and violently compared with regular water to avoid recontamination [14] and reduce sonication time. However, the proper mixing ratio comes from the test repeatedly, which consumes workload and budget. Unfortunately, the HRA simulation cannot accurately predict the acoustic pressure after the mixing. From the authors’ experience, adding the chemicals to aid in the ultrasonic cleaning process relates to fluid dynamics coupled with chemical reactions, which the HRA does not cover. Therefore, in further study, finding computer simulations and mathematical models that eliminate weakness and help support the HRA will surely enhance the cleaning efficiency and promote the domestic manufacturers to always be the leader in this field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P. and J.T.; methodology, S.P., K.K. and J.T.; software, S.P. and K.K.; validation, S.P., K.K. and J.T.; formal analysis, J.T.; investigation, J.T.; resources, J.T.; data curation, J.T.; writing—original draft preparation, S.P., K.K. and J.T.; writing—review and editing, J.T.; visualization, S.P.; project administration, J.T.; funding acquisition, J.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was sponsored by Fundamental Fund 2565 under a grant number RE-KRIS/FF65/21.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the College of Advanced Manufacturing Innovation, King Mongkut’s Institute of Technology Ladkrabang, and Pasuda Supplies and Services Co., Ltd.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest for this article.
References
- Chhabra, A.D.; Kumar, R.V.; Vundavilli, P.R.; Surekha, B. Design and Analysis of Higher Order Exponential Horn Profiles for Ultrasonic Machining. J. Manuf. Sci. Prod. 2016, 16, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunst, P.; Hemsel, T.; Bornmann, P.; Littmann, W.; Sextro, W. Optimization of Ultrasonic Acoustic Standing Wave Systems. Actuators 2020, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Huanhuan, R. Design and Finite Element Simulation of an Ultrasonic Transducer of Two Piezoelectric Discs. J. Meas. Eng. 2017, 5, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Ji, S.; Zhao, J.; He, Q. Theoretical Analysis and Finite Element Calculation of Ultrasonic Horn. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 612, 032032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addellpari, S.N. Modal Analysis of Horns used in Ultrasonic Vibration Assisted Drilling. Int. J. Innov. Eng. Technol. 2016, 7, 294–298. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, Y.; Wand, A.; Zhang, N. Design and Simulation Technology of Piezoelectric UST with Sandwich Composite Horn. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 470, 012043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K. Ultrasonic Transducers: Material and Design for Sensors, Actuators, and Medical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tangsopa, W.; Keawklan, T.; Kesngam, K.; Ngaochai, S.; Thongsri, J. Improved Design of Ultrasonic Cleaning Tank Using Harmonic Response Analysis in ANSYS. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 159, 012042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srathonghuam, K.; Wonganu, B.; Busayaporn, B.; Thongsri, J. Vibration Analysis and Development of a Submersible Ultrasonic Transducer for an Application in the Inhibitory Activity of Pathogenic Bacteria. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 142362–142373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lais, H.; Lowe, P.S.; Kanfoud, J.; Gan, T.H. Advancements in Fouling Removal using High Power Ultrasonics for Industrial Applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS), Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, 15–16 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lais, H.; Lowe, P.S.; Gan, T.H.; Wrobel, L.C. Numerical Modelling of Acoustic Pressure Fields to Optimize the Ultrasonic Cleaning Technique for Cylinders. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangsopha, W.; Thongsri, J. Simulation of Ultrasonic Cleaning and Ways to Improve the Efficiency. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON), Pattaya, Thailand, 8–10 March 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tangsopa, W.; Thongsri, J. Development of an Industrial Ultrasonic Cleaning Tank Based on Harmonic Response Analysis. Ultrasonics 2019, 91, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangsopa, W.; Thongsri, J. A Novel Ultrasonic Cleaning Tank Developed by Harmonic Response Analysis and Computational Fluid Dynamics. Metals 2020, 10, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tangsopa, W.; Thongsri, J. A Dual Frequency Ultrasonic Cleaning Tank Developed by Transient Dynamic Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, T.J. Ultrasonic cleaning: An Historical Perspective. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2016, 29, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, F.J. Ultrasonic Cleaning and Washing of Surfaces. In Power Ultrasonics; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 577–609. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, J. Ultrasonics—Number and Size of Cavitation Bubbles. Available online: https://techblog.ctgclean.com/2011/12/ultrsonics-number-and-size-of-cavitation-bubbles/ (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Kinsler, L.E.; Frey, A.R.; Coppens, A.B.; Sanders, J.V. Fundamentals of Acoustics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Sulistiya, A.; Surtono, A.; Supriyanto, A. A Frequency Generator of 40–60 kHz Based on Arduino for Ultrasonic Cleaner Applications. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1572, 012014. [Google Scholar]
- Ansys. Harmonic Analysis; Ansys: Southpoint, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).