A New Specific and Sensitive RT-qPCR Method Based on Splinted 5? Ligation for the Quantitative Detection of RNA Species Shorter than microRNAs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
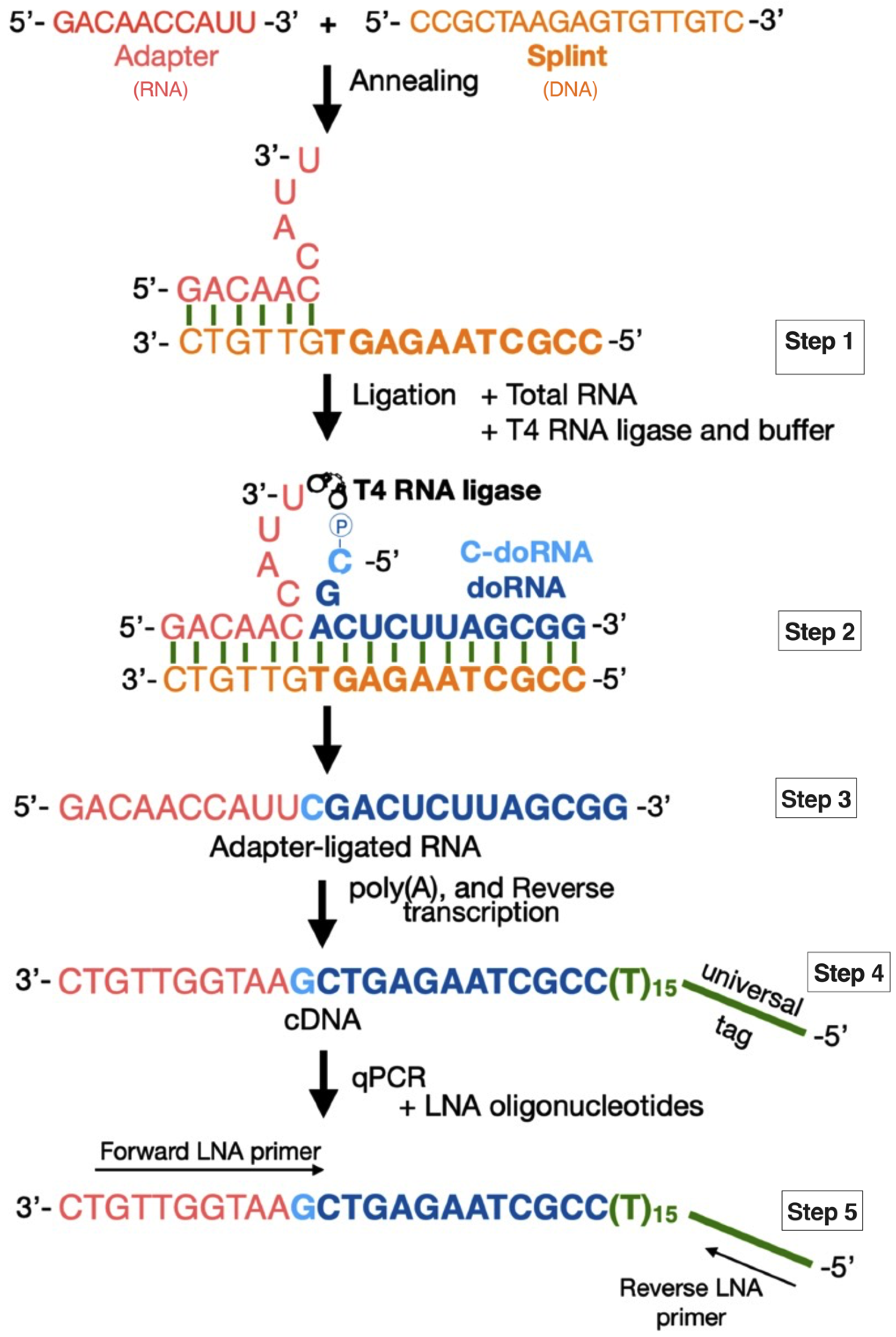
2.1. Detection of doRNAs by a New Splinted 5′ Ligation RT-qPCR Method
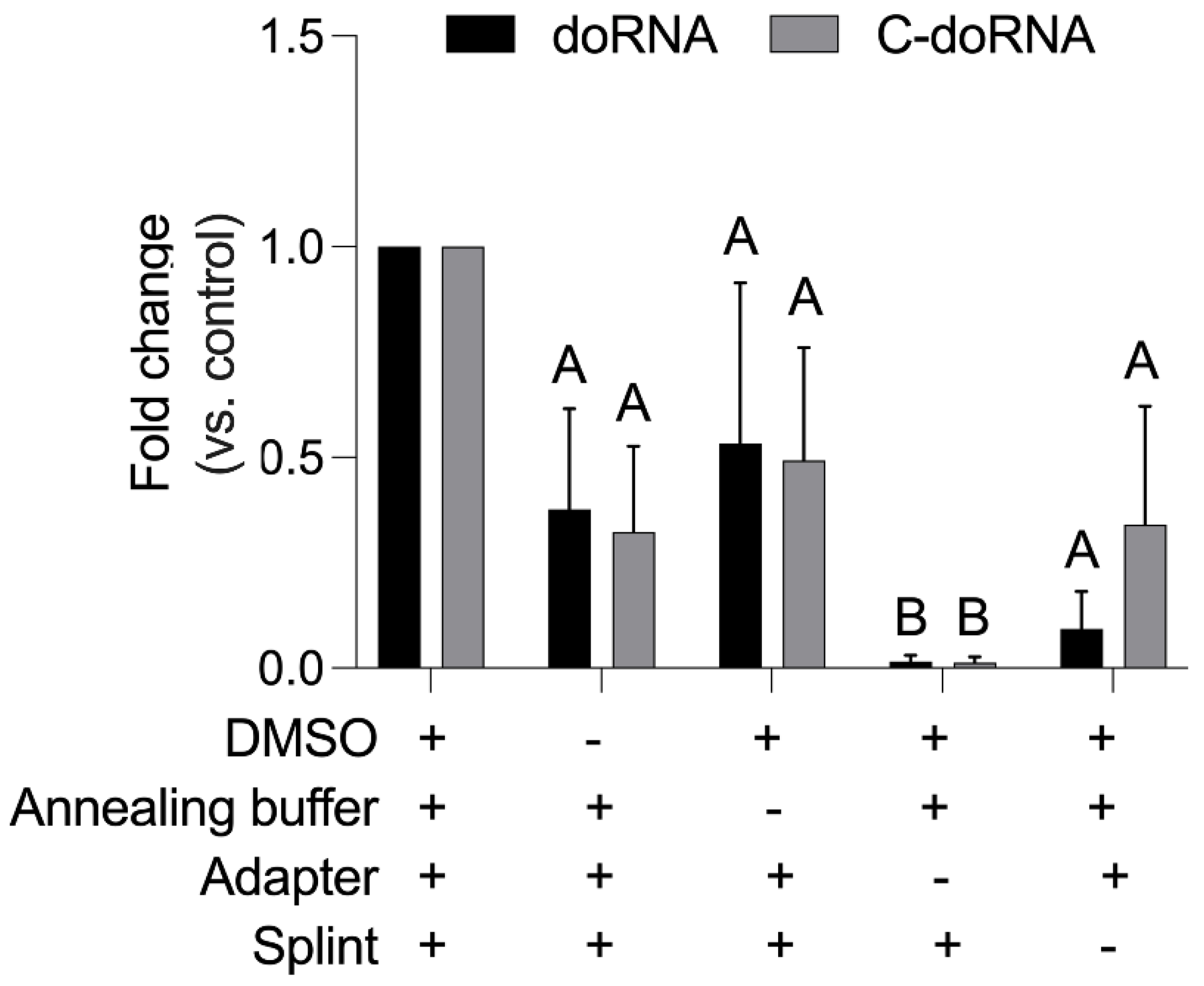
2.2. Optimization of the Ligation Reaction
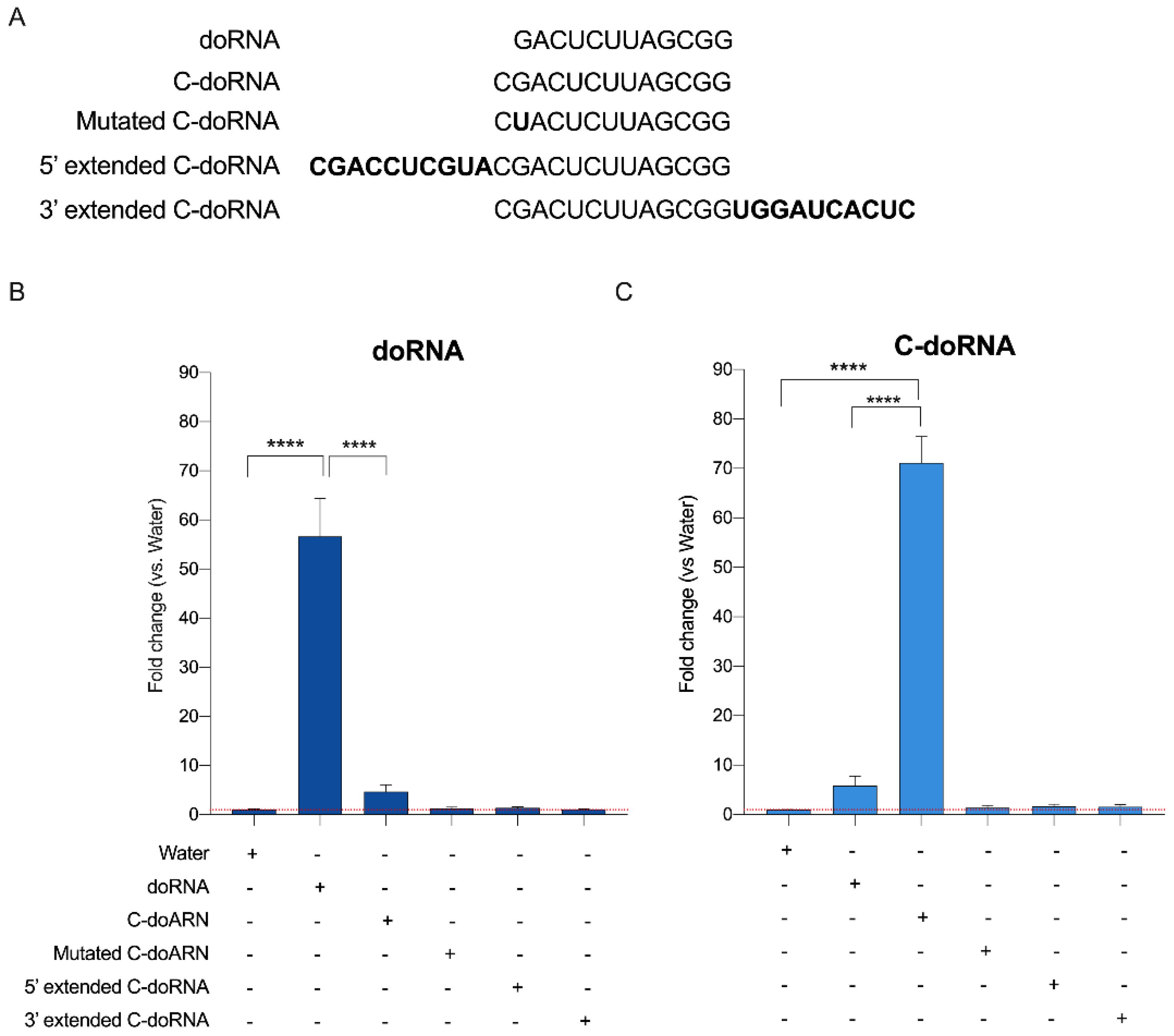
2.3. Splinted 5′ Ligation RT-qPCR Specifically Amplify doRNA and C-doRNA
2.4. Splinted 5′ Ligation RT-qPCR May Discriminate between doRNA, C-doRNA and Precursor Sequences
2.5. doRNA and C-doRNA Detection by Splinted 5′ Adapter RT-qPCR Is Linear over a Range of 7 Logs
2.6. Splinted 5′ Ligation RT-qPCR Validation of Small RNA-Seq Data
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. RNA and DNA Oligonucleotides
4.2. Splinted 5′ Ligation RT-qPCR Method
4.2.1. Adapter Sequence
4.2.2. Splint Sequences
4.2.3. Adapter–Splint Annealing
4.2.4. Splinted 5′ Ligation RT-qPCR
4.2.5. Standard Curve
4.3. doRNA and C-doRNA Product Cloning and Sequencing
4.4. Validation of the Splinted 5′ Ligation RT-qPCR Detection Method
4.5. Primary and Cultured Human and Mouse Cells and Tissue
4.5.1. Polymorphonuclear (PMN) Leukocyte Isolation
4.5.2. Platelet Isolation
4.5.3. Cell Lines
4.5.4. Mouse Tissue
4.6. Total RNA Isolation
4.7. Validation of Small RNA-Sequencing (RNA-Seq) Data
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lui, L.; Lowe, T. Small nucleolar RNAs and RNA-guided post-transcriptional modification. Essays Biochem. 2013, 54, 53–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.-W.; Huang, K.; Yang, C.; Kang, C.-S. Non-coding RNAs as regulators in epigenetics (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hombach, S.; Kretz, M. Non-coding RNAs: Classification, Biology and Functioning. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 937, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, M.; Shergill, I.S.; Williamson, M.; Gommersall, L.; Arya, N.; Patel, H.R.H. Basic principles of real-time quantitative PCR. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2005, 5, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, E.; Serrano-Heras, G.; Castano, M.J.; Solera, J. Real-time PCR detection chemistry. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2015, 439, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajadini, M.; Panjehpour, M.; Javanmard, S.H. Comparison of SYBR Green and TaqMan methods in quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction analysis of four adenosine receptor subtypes. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2014, 3, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeka, F.; Mestdagh, P.; Vandesompele, J. RT-qPCR-based quantification of small non-coding RNAs. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1296, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iempridee, T.; Wiwithaphon, S.; Piboonprai, K.; Pratedrat, P.; Khumkhrong, P.; Japrung, D.; Temisak, S.; Laiwejpithaya, S.; Chaopotong, P.; Dharakul, T. Identification of reference genes for circulating long noncoding RNA analysis in serum of cervical cancer patients. FEBS Open Bio 2018, 8, 1844–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevaert, A.B.; Witvrouwen, I.; Vrints, C.J.; Heidbuchel, H.; Van Craenenbroeck, E.M.; Van Laere, S.J.; Van Craenenbroeck, A.H. MicroRNA profiling in plasma samples using qPCR arrays: Recommendations for correct analysis and interpretation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, P.; Anaya, J.; Mudunuri, S.B.; Dutta, A. Meta-analysis of tRNA derived RNA fragments reveals that they are evolutionarily conserved and associate with AGO proteins to recognize specific RNA targets. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, M.; Benmoussa, A.; Provost, P. Small Non-Coding RNAs Derived from Eukaryotic Ribosomal RNA. Non-Coding RNA 2019, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asha, S.; Soniya, E. V The sRNAome mining revealed existence of unique signature small RNAs derived from 5.8SrRNA from Piper nigrum and other plant lineages. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.; Fraser, W.D.; Dalmay, T. Transfer RNA-derived small RNAs in the cancer transcriptome. Pflugers Arch. 2016, 468, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, E.J.; Kim, T.-H. Fine-Tuning of Gene Expression by tRNA-Derived Fragments during Abiotic Stress Signal Transduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Locati, M.D.; Pagano, J.F.B.; Abdullah, F.; Ensink, W.A.; van Olst, M.; van Leeuwen, S.; Nehrdich, U.; Spaink, H.P.; Rauwerda, H.; Jonker, M.J.; et al. Identifying small RNAs derived from maternal- and somatic-type rRNAs in zebrafish development. Genome 2018, 61, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plante, I.; Plé, H.; Landry, P.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Provost, P. Modulation of microRNA Activity by Semi-microRNAs. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambert, M.; Benmoussa, A.; Diallo, I.; Ouellet-Boutin, K.; Dorval, V.; Majeau, N.; Joly-Beauparlant, C.; Droit, A.; Bergeron, A.; Têtu, B.; et al. Identification of Abundant and Functional dodecaRNAs (doRNAs) Derived from Ribosomal RNA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astakhova, I.K.; Wengel, J. Scaffolding along nucleic acid duplexes using 2’-amino-locked nucleic acids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1768–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorra, D.; Arar, K.; Hurley, J.M. Design considerations and effects of LNA in PCR primers. Mol. Cell. Probes 2003, 17, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New England Biolabs Site: NEB.ca. Available online: https://international.neb.com/tools-and-resources (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Stark, M.R.; Pleiss, J.A.; Deras, M.; Scaringe, S.A.; Rader, S.D. An RNA ligase-mediated method for the efficient creation of large, synthetic RNAs. RNA 2006, 12, 2014–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munafó, D.B.; Robb, G.B. Optimization of enzymatic reaction conditions for generating representative pools of cDNA from small RNA. RNA 2010, 16, 2537–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alexander, R.C.; Johnson, A.K.; Thorpe, J.A.; Gevedon, T.; Testa, S.M. Canonical nucleosides can be utilized by T4 DNA ligase as universal template bases at ligation junctions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3208–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Vogt, C.E.; McBrairty, M.; Al-Hashimi, H.M. Influence of dimethylsulfoxide on RNA structure and ligand binding. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9692–9698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harrison, B.; Zimmerman, S.B. Polymer-stimulated ligation: Enhanced ligation of oligo- and polynucleotides by T4 RNA ligase in polymer solutions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 8235–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Xi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Shen, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Alexeev, A.; Peters, B.A.; Albert, A.; et al. 3′ Branch ligation: A novel method to ligate non-complementary DNA to recessed or internal 3′OH ends in DNA or RNA. DNA Res. 2019, 26, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dard-Dascot, C.; Naquin, D.; d’Aubenton-Carafa, Y.; Alix, K.; Thermes, C.; van Dijk, E. Systematic comparison of small RNA library preparation protocols for next-generation sequencing. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, G.; Yin, X.; Luo, H.; Xu, X.; Bolund, L.; Zhang, X.; Gan, S.-Q.; Li, N. Sequencing bias: Comparison of different protocols of microRNA library construction. BMC Biotechnol. 2010, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maguire, S.; Lohman, G.J.S.; Guan, S. A low-bias and sensitive small RNA library preparation method using randomized splint ligation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diallo, I.; Provost, P. RNA-Sequencing Analyses of Small Bacterial RNAs and their Emergence as Virulence Factors in Host-Pathogen Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duchez, A.-C.; Boudreau, L.H.; Naika, G.S.; Bollinger, J.; Belleannee, C.; Cloutier, N.; Laffont, B.; Mendoza-Villarroel, R.E.; Levesque, T.; Rollet-Labelle, E.; et al. Platelet microparticles are internalized in neutrophils via the concerted activity of 12-lipoxygenase and secreted phospholipase A2-IIA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3564–E3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laffont, B.; Corduan, A.; Rousseau, M.; Duchez, A.-C.; Lee, C.H.C.; Boilard, E.; Provost, P. Platelet microparticles reprogram macrophage gene expression and function. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Name | Sequence * |
|---|---|
| doRNA | /5Phos/rGrArCrUrCrUrUrArGrCrGrG |
| C-doRNA | /5Phos/rCrGrArCrUrCrUrUrArGrCrGrG |
| adapter-doRNA | /5Phos/rGrArCrArArCrCrArUrUrGrArCrUrCrUrUrArGrCrGrG |
| adapter-C-doRNA | /5Phos/rGrArCrArArCrCrArUrUrCrGrArCrUrCrUrUrArGrCrGrG |
| adapter | /5Phos/rGrArCrArArCrCrArUrU |
| splint 2:2 | CCGCTAAGAGTTGGTTGTC |
| splint 2:3 | CCGCTAAGAGTGGTTGTC |
| splint 2:4 | CCGCTAAGAGTGTTGTC |
| splint 2:5 | CCGCTAAGAGTTTGTC |
| mutated C-doRNA | /5Phos/rCrUrArCrUrCrUrUrArGrCrGrG |
| 5′ extended C-doRNA | /5Phos/rCrGrArCrCrUrCrGrUrArCrGrArCrUrCrUrUrArGrCrGrG |
| 3′ extended C-doRNA | /5Phos/rCrGrArCrUrCrUrUrArGrCrGrGrUrGrGrArUrCrArCrUrC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lambert, M.; Benmoussa, A.; Provost, P. A New Specific and Sensitive RT-qPCR Method Based on Splinted 5? Ligation for the Quantitative Detection of RNA Species Shorter than microRNAs. Non-Coding RNA 2021, 7, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7030059
Lambert M, Benmoussa A, Provost P. A New Specific and Sensitive RT-qPCR Method Based on Splinted 5? Ligation for the Quantitative Detection of RNA Species Shorter than microRNAs. Non-Coding RNA. 2021; 7(3):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7030059
Chicago/Turabian StyleLambert, Marine, Abderrahim Benmoussa, and Patrick Provost. 2021. "A New Specific and Sensitive RT-qPCR Method Based on Splinted 5? Ligation for the Quantitative Detection of RNA Species Shorter than microRNAs" Non-Coding RNA 7, no. 3: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7030059
APA StyleLambert, M., Benmoussa, A., & Provost, P. (2021). A New Specific and Sensitive RT-qPCR Method Based on Splinted 5? Ligation for the Quantitative Detection of RNA Species Shorter than microRNAs. Non-Coding RNA, 7(3), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7030059







