Microbiota Composition in Raw Drinking Milk from Vending Machines: A Case Study in Croatia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Milk Sampling
2.2. Flow Cytometry Method and Plate Count Method
2.3. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry
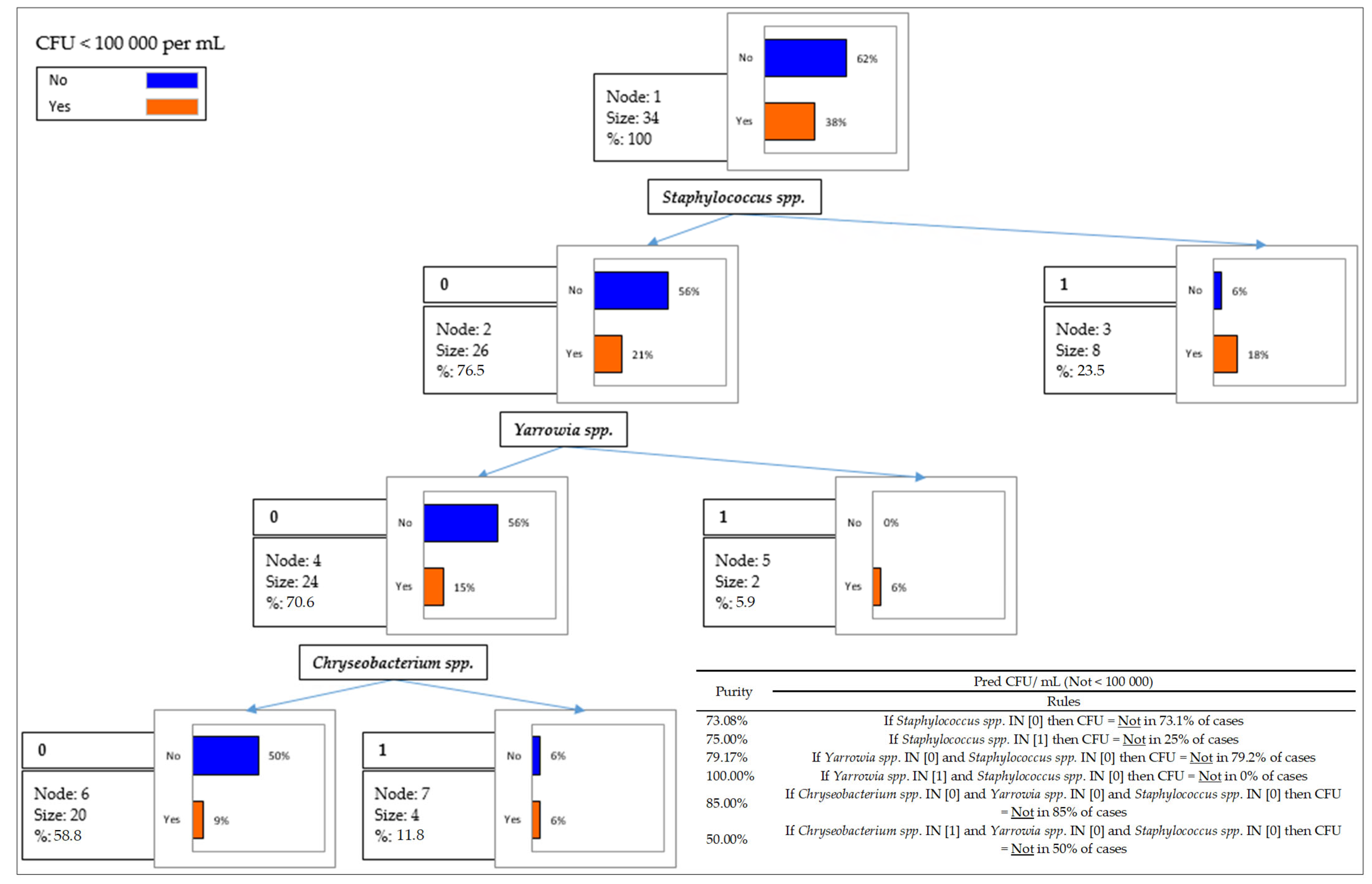
2.4. Data Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliver, S.P.; Boor, K.J.; Murphy, S.C.; Murinda, S.E. Food safety hazards associated with consumption of raw milk. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacometti, F.; Bonilauri, P.; Serraino, A.; Peli, A.; Amatiste, S.; Arrigoni, N.; Bianchi, M.; Bilei, S.; Cascone, G.; Comin, D.; et al. Four-year monitoring of foodborne pathogens in raw milk sold by vending machines in Italy. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1902–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croatian Agency for Agriculture and Food (HAPIH). O Javno Zdravstvenom Riziku Vezanom Za Konzumaciju Sirovog Mlijeka; Scientific Opinion; Croatian Food Agency: Osijek, Croatia, 2016. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Kunová, S.; Golian, J.; Zeleňáková, L.; Lopašovský, L.; Čuboň, J.; Haščik, P.; Kačániová, M. Microbiological quality of fresh and heat-treated cow’s milk during storage. Potravin. Slovak J. Food Sci. 2017, 11, 652–657. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA. Scientific opinion on the public health risks related to the consumption of raw drinking milk. EFSA—European Food Saftey Authority. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 3940–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaržija, D. Mljekarska Mikrobiologija; Hrvatska mljekarska udruga (HMU): Zagreb, Croatia, 2021. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Jay, J.M.; Loessner, M.J.; Golden, D.A. Modern Food Microbiology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation (EC) No. 853/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 29 April 2004 Laying down Specific Hygiene Rules for Food of Animal Origin. OJEU L 139/55. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2004/853/oj/eng (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Ministarstvo Poljoprivrede Republike Hrvatske. Pravilnik o Registraciji Subjekata te Registraciji i Odobravanju Objekata u Poslovanju s Hranom (OG 84/15). Available online: https://narodne-novine.nn.hr/clanci/sluzbeni/2015_07_84_1641 (accessed on 18 July 2024). (In Croatian).
- Ministarstvo Poljoprivrede Republike Hrvatske. Pravilnik o Pregledu Sirovog Mlijeka Namijenjenog Javnoj Potrošnji. (OG 84/16). Available online: https://narodne-novine.nn.hr/clanci/sluzbeni/2016_09_84_1853.html (accessed on 18 July 2024). (In Croatian).
- Ministarstvo Poljoprivrede, Ribarstva i Ruralnog Razvoja Republike Hrvatske. Vodič za Mikrobiološke Kriterije za Hranu, 3rd ed.; Ministarstvo Poljoprivrede, Ribarstva i Ruralnog Razvoja: Zagreb, Croatia, March, 2011. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Zdolec, N.; Jankuloski, D.; Kiš, M.; Hengl, B.; Mikulec, N. Detection and Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis Typing of Listeria monocytogenes Isolates from Milk Vending Machines in Croatia. Beverages 2019, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulec, N.; Špoljarić, J.; Zamberlin, S.; Krga, M.; Radeljević, B.; Plavljanić, D.; Kesić, I.H.; Zdolec, N.; Dobranić, V.; Antunac, N. The investigation of suitability of raw milk consumption from vending machines in Croatia. J. Cent. Eur. Agric. 2019, 20, 1076–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayarao, B.; Pillai, S.; Sawant, A.; Wolfgang, D.; Hegde, N. Guidelines for monitoring bulk tank milk somatic cell and bacterial counts. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 3561–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, N.H.; Trmčić, A.; Hsieh, T.-H.; Boor, K.J.; Wiedmann, M. The evolving role of coliforms as indicators of unhygienic processing conditions in dairy foods. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benić, M.; Maćešić, N.; Cvetnić, L.; Habrun, B.; Cvetnić, Z.; Turk, R.; Đuričić, D.; Lojkić, M.; Dobranić, V.; Valpotić, H.; et al. Bovine mastitis: A persistent and evolving problem requiring novel approaches for its control—A review. Vet. Arh. 2018, 88, 535–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lean, I.J.; Edmondson, A.J.; Smith, G.; Villanueva, M. Corynebacterium pyogenes mastitis outbreak in inbred heifers in a California dairy. Cornell Vet. 1987, 77, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gelgie, A.E.; Desai, S.E.; Gelalcha, B.D.; Dego, O.K. Mycoplasma bovis mastitis in dairy cattle. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1322267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begić, B.B.; Džafić, N.; Barać, K.N.; Andreanszky, T.; Sablić, M. Detection of Listeria monocytogenes in cheese and in cow mastitis—A case report. Vet. Stanica 2025, 56, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Islam, A.; Rahman, M.; Islam, K.; Islam, M.; Kamal, M.; Islam, N. Presence of Brucella spp. in milk and dairy products: A comprehensive review and its perspectives. J. Food Qual. 2023, 2023, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pexara, A.; Solomakos, N.; Govaris, A. Q fever and prevalence of Coxiella burnetii in milk. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 71, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, B.; Bhunia, A. Fundamental Food Microbiology, 5th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Perin, L.M.; Pereira, J.G.; Bersot, L.S.; Nero, L.A. Chapter 3—The Microbiology of Raw Milk. In Raw Milk: Balance Between Hazards and Benefits; Nero, L.A., de Carvalho, A.F., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 4833-1:2013; Microbiology of the Food Chain—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Microorganisms—Part 1: Colony Count at 30 °C by the Pour Plate Technique. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013.
- Darrer, M. Identifikacija Aerobno Mezofilnih Bakterija MALDI-TOF Tehnikom u Mlijeku iz Mljekomata. Master’s Thesis, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2023. Available online: https://urn.nsk.hr/urn:nbn:hr:204:936561 (accessed on 18 July 2024). (In Croatian).
- ISO 21187:2021; Milk—Quantitative Determination of Microbiological Quality—Guidance for Establishing and Verifying a Conversion Relationship Between Results of an Alternative Method and Anchor Method Results. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 17025:2017; General Requirements for the Competence of Testing and Calibration Laboratories. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017.
- Sauer, S.; Freiwald, A.; Maier, T.; Kube, M.; Reinhardt, R.; Kostrzewa, M.; Geider, K. Classification and identification of bacteria by mass spectrometry and computational analysis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croatian Agency for Agriculture and Food, Center for Quality Control of Livestock Products (HAPIH), Annual Report for 2023. Available online: https://www.hapih.hr/ckksp/publikacije/ (accessed on 29 October 2024). (In Croatian).
- Imre, K.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Herman, V.; Sallam, K.I.; Cristina, R.T.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Morar, D.; Popa, S.A.; Imre, M.; Morar, A. Occurrence, Pathogenic Potential and Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli Isolated from Raw Milk Cheese Commercialized in Banat Region, Romania. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghiante, F.; dos Santos, E.A.; Martins, O.A. Yersinia enterocolitica in milk and dairy products: A review. Rev. Bras. Hig. E Sanidade Anim. RBHSA 2018, 12, 420–427. [Google Scholar]
- Mikulec, N.; Špoljarić, J.; Plavljanić, D.; Lovrić, N.; Oštarić, F.; Kljusurić, J.G.; Sarim, K.M.; Zdolec, N.; Kazazić, S. MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry-Based Identification of Aerobic Mesophilic Bacteria in Raw Unpreserved and Preserved Milk. Processes 2024, 12, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukančíková, L.; Lipničanová, S.; Kačániová, M.; Chmelová, D.; Ondrejovič, M. Natural microflora of raw cow milk and their enzymatic spoilage potential. Nova Biotechnol. Chim. 2016, 15, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, S.; Cunningham, C.; Ingenhoff, L.; Norris, J.; Zadoks, R.N. Low prevalence of antimicrobial resistant organisms (methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, extended beta-lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae, and vancomycin resistant enterococci) in bulk tank milk in New South Wales, Australia. Aust. Vet. J. 2023, 101, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, M.R.H.; O’callaghan, M.; Glare, T.R.; Jackson, T.A. Serratia spp. bacteria evolved in Aotearoa-New Zealand for infection of endemic scarab beetles. N. Z. J. Zool. 2023, 52, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, L.; O’Sullivan, O.; Stanton, C.; Beresford, T.P.; Ross, R.P.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Cotter, P.D. The complex microbiota of raw milk. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 664–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Xu, J.; Meng, X.; Wu, Z.; Hou, X.; He, Z.; Shang, R.; Zhang, H.; Pu, W. Molecular epidemiology and characterization of antimicrobial-resistant Staphylococcus haemolyticus strains isolated from dairy cattle milk in Northwest, China. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1183390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morar, A.; Ban-Cucerzan, A.; Herman, V.; Tîrziu, E.; Sallam, K.I.; Abd-Elghany, S.M.; Imre, K. Multidrug Resistant Coagulase-Positive Staphylococcus aureus and Their Enterotoxins Detection in Traditional Cheeses Marketed in Banat Region, Romania. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwin, G.; Breen, J. Streptococcus uberis-associated mastitis in dairy herds: Dealing with outbreaks and improving control. Clin. Pract. 2022, 44, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitkälä, A.; Koort, J.; Björkroth, J. Identification and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus uberis and Streptococcus parauberis isolated from bovine milk samples. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 4075–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merin, U.; Fleminger, G.; Komanovsky, J.; Silanikove, N.; Bernstein, S.; Leitner, G. Subclinical udder infection with Streptococcus dysgalactiae impairs milk coagulation properties: The emerging role of proteose peptones. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2008, 88, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, D.; Santos, J.S.; Escher, G.B.; Ferreira, B.L.; Maggio, R.M. Use of principal component analysis (PCA) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) for multivariate association between bioactive compounds and functional properties in foods: A critical perspective. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 72, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.S.; Bezerra, M.A.; Cerqueira, U.M.F.M.; Rodrigues, C.J.O.; Santos, B.C.; Novaes, C.G.; Almeida, E.R.V. An introductory review on the application of principal component analysis in the data exploration of the chemical analysis of food samples. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 1323–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Yuan, Y.; Nag, A.; Feng, S.; Afsarimanesh, N.; Han, T.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Organ, D.R. A Review on the Use of Impedimetric Sensors for the Inspection of Food Quality. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 5220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, Z. Principal Component Analysis for Big Data. In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online; Balakrishnan, N., Colton, T., Everitt, B., Piegorsch, W., Ruggeri, F., Teugels, J.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlino, V.M.; Renna, M.; Nery, J.; Muresu, A.; Ricci, A.; Maggiolino, A.; Celano, G.; De Ruggieri, B.; Tarantola, M. Are Local Dairy Products Better? Using Principal Component Analysis to Investigate Consumers’ Perception towards Quality, Sustainability, and Market Availability. Animals 2022, 12, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Chattopadhyay, P. Application of principal component analysis (PCA) as a sensory assessment tool for fermented food products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mafra, I.; Honrado, M.; Amaral, J.S. Animal Species Authentication in Dairy Products. Foods 2022, 11, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockburn, M. Review: Application and Prospective Discussion of Machine Learning for the Management of Dairy Farms. Animals 2020, 10, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punia, H.; Tokas, J.; Malik, A.; Sangwan, S.; Baloda, S.; Singh, N.; Singh, S.; Bhuker, A.; Singh, P.; Yashveer, S.; et al. Identification and Detection of Bioactive Peptides in Milk and Dairy Products: Remarks about Agro-Foods. Molecules 2020, 25, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltemur, D.; Robatscher, P.; Oberhuber, M.; Scampicchio, M.; Ceccon, A. Applications of Solution NMR Spectroscopy in Quality Assessment and Authentication of Bovine Milk. Foods 2023, 12, 3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizzarin, M.; Gormley, I.; Berry, D.; Murphy, T.; Casa, A.; Lynch, A.; McParland, S. Predicting cow milk quality traits from routinely available milk spectra using statistical machine learning methods. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7438–7447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’hara, C.; O’sullivan, A.; Gibney, E.R. A Clustering Approach to Meal-Based Analysis of Dietary Intakes Applied to Population and Individual Data. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 2297–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Shao, W.; Liu, Z.; Ma, X.; Chen, H.; Zheng, N.; Zhao, Y. Microbial diversity in camel milk from Xinjiang, China as revealed by metataxonomic analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1367116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, A. Enhancing supply chain coordination: A comparative analysis of clustering techniques for the Production Routing Problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 196, 110455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharbach, M.; Mansouri, M.A.; Taabouz, M.; Yu, H. Current Application of Advancing Spectroscopy Techniques in Food Analysis: Data Handling with Chemometric Approaches. Foods 2023, 12, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Castro, M.; Feller, J.-F. Review on Sensor Array-Based Analytical Technologies for Quality Control of Food and Beverages. Sensors 2023, 23, 4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Milk Vending Machines | CFU × 103/mL | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 February 2013 | 13 February 2023 | 20 February 2023 | 27 February 2023 | 6 March 2023 | 27 March 2023 | 3 April 2023 | |
| W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | S1 | S2 | S3 | |
| 1st | 53 ± 4 A,b | 969 ± 125 A,d | 82 ± 1 A,b,c | 292 ± 2 C,c | 7 ± 4 A,a | 54 ± 2 B,b | 170 ± 1 A,c |
| 2nd | 387 ± 16 C,b | 446 ± 55 A,b | 84 ± 4 A,a | 112 ± 6 A,a | 5270 ± 562 D,d | 457 ± 1 D,b | 3818 ± 39 C,c |
| 3rd | 169 ± 3 B,b | 12 ± 1 B,a | 248 ± 2 B,c | 98 ± 1 A,a,b | 82 ± 6 B,a,b | 188 ± 5 C,b | 307 ± 13 B,c |
| 4th | 48 ± 2 A,b | 15 ± 0 B,a | 685 ± 8 C,d | 208 ± 1 B,c | 242 ± 44 C,c | 26 ± 2 A,a | 246 ± 21 B,c |
| 5th | 60 ± 2 A,a | 15 ± 2 B,a | 305 ± 20 B,b | 196 ± 2 B,b | 5830 ± 0 D,d | 1753 ± 72 E,c | 167 ± 2 A,b |
| Gram-Negative Bacteria | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | S1 | S2 | S3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | |
| Acinetobacter albensis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acinetobacter guillouiae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acinetobacter johnsonii | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acinetobacter parvus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aeromonas bestiarum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aeromonas eucrenophila | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aeromonas salmonicida | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brevundimonas diminuta | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buttiauxella gaviniae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buttiauxella warmboldiae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chryseobacterium bovis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chryseobacterium indoltheticum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chryseobacterium piscium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chryseobacterium scophthalmum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chryseobacterium shigense | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chryseobacterium vrystaatense | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Citrobacter braakii | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comamonas terrigena | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Escherichia coli | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hafnia alvei | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Janthinobacterium lividum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Klebsiella oxytoca | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lactobacillus curvatus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Moraxella osloensis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pantoea agglomerans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Paracoccus yeei | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas azotoformans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas brenneri | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas extremorientalis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas gessardii | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas libanensis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas lundensis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas proteolytica | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas rhodesiae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas synxantha | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas tolaasii | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pseudomonas veronii | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rahnella inusitata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serratia marcescens | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serratia proteamaculans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sphingobacterium faecium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sphingobacterium multivorum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stenotrophomonas spp. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yersinia enterocolitica | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yersinia enterolitica | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gram-Positive Bacteria | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | S1 | S2 | S3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | |
| Bacillus licheniformis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Brochothrix thermosphacta | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carnobacterium maltaromaticum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corynebacterium callunae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corynebacterium frankenforstense | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corynebacterium provencense | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corynebacterium vitaeruminis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Corynebacterium xerosis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enterococcus faecalis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enterococcus hirae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kocuria uropygioeca | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kocuria varians | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lacticaseibacillus paracasei | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lactobacillus curvatus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lactobacillus spp | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lactococcus lactis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lactococcus plantarum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lactococcus raffinolactis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Leuconostoc carnosum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Leuconostoc citreum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Leuconostoc mesenteroides | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Luteococcus japonicus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Microbacterium aurum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Microbacterium lacticum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Microbacterium liquefaciens | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Microbacterium oxydans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Micrococcus luteus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rhodococcus baikonurensis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Staphylococcus aureus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Staphylococcus borealis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Staphylococcus chromogenes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Staphylococcus haemolyticus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Staphylococcus vitulinus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Staphylococcus warneri | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Streptococcus dysgalactiae | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Streptococcus parauberis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Streptococcus uberis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Streptomyces albidoflavus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yeasts and Molds | W1 | W2 | W3 | W4 | S1 | S2 | S3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | |
| Scopulariopsis brevicaulis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kluyveromyces lactis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kluyveromyces marxianus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnusiomyces capitatus | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pichia fermentans | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pichia kudriavzevii | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yarrowia lipolytica | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikulec, N.; Špoljarić, J.; Plavljanić, D.; Darrer, M.; Oštarić, F.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J.; Sarim, K.M.; Zdolec, N.; Kazazić, S. Microbiota Composition in Raw Drinking Milk from Vending Machines: A Case Study in Croatia. Fermentation 2025, 11, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020055
Mikulec N, Špoljarić J, Plavljanić D, Darrer M, Oštarić F, Gajdoš Kljusurić J, Sarim KM, Zdolec N, Kazazić S. Microbiota Composition in Raw Drinking Milk from Vending Machines: A Case Study in Croatia. Fermentation. 2025; 11(2):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020055
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikulec, Nataša, Jasminka Špoljarić, Dijana Plavljanić, Monica Darrer, Fabijan Oštarić, Jasenka Gajdoš Kljusurić, Khan Mohd. Sarim, Nevijo Zdolec, and Snježana Kazazić. 2025. "Microbiota Composition in Raw Drinking Milk from Vending Machines: A Case Study in Croatia" Fermentation 11, no. 2: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020055
APA StyleMikulec, N., Špoljarić, J., Plavljanić, D., Darrer, M., Oštarić, F., Gajdoš Kljusurić, J., Sarim, K. M., Zdolec, N., & Kazazić, S. (2025). Microbiota Composition in Raw Drinking Milk from Vending Machines: A Case Study in Croatia. Fermentation, 11(2), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020055









