Evaluation of the Impact of Fermentation Conditions, Scale Up and Stirring on Physicochemical Parameters, Antioxidant Capacity and Volatile Compounds of Green Tea Kombucha
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Green Tea Infusion and Kombucha Fermentation
2.2. Evaluation of Scale-Up and Effect of Stirring on Green Tea Kombucha Fermentation
2.3. Physicochemical Parameters Determination
2.4. Total Phenolic Content
2.5. Antioxidant Capacity and Total Phenolic Content of Kombucha Fermented Tea
2.6. Identification of Volatile Compounds
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of the Influence of Fermentation Conditions on Kombucha Production from Green Tea from Camellia Sinensis
3.1.1. Effects on pH, Total Titratable Acidity and Total Soluble Solids
3.1.2. Total Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity
3.2. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of Green Tea Kombucha Fermentation Process
3.3. Scale-Up of and Evaluation of Stirring Influence on Green Tea Kombucha Fermentation
3.4. Volatile Compounds of Green Tea Kombucha Produced in Static and Stirred Processes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Perspectives Futures
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VOCs | Volatile organic compounds |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| TTA | Total titratable acidity |
| TSS | Total soluble solids |
| SCOBY | Symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast |
References
- Batista, P.; Penas, M.R.; Pintado, M.; Oliveira-Silva, P. Review Kombucha: Perceptions and Future Prospects. Foods 2022, 11, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakubczyk, K.J.; Piotrowska, G.; Janda, K. Characteristics and Biochemical Composition of Kombucha—Fermented Tea. Med. Ogólna i Nauk. o Zdrowiu 2020, 26, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsch, P.; Etter, D.; Fischer, P. Transient: In Situ Measurement of Kombucha Biofilm Growth and Mechanical Properties. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4015–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarasinghe, H.; Weerakkody, N.S.; Waisundara, V.Y. Evaluation of Physicochemical Properties and Antioxidant Activities of Kombucha “Tea Fungus” during Extended Periods of Fermentation. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, J.M.; Suárez, L.V.; Jayabalan, R.; Oros, J.H.; Escalante-Aburto, A. A Review on Health Benefits of Kombucha Nutritional Compounds and Metabolites. CYTA-J. Food 2018, 16, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laavanya, D.; Shirkole, S.; Balasubramanian, P. Current Challenges, Applications and Future Perspectives of SCOBY Cellulose of Kombucha Fermentation. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayisoglu, S.; Coskun, F. Determination of Physical and Chemical Properties of Kombucha Teas Prepared with Different Herbal Teas. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 41, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emiljanowicz, K.E.; Malinowska-Pańczyk, E. Kombucha from Alternative Raw Materials–The Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 60, 3185–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanwal, N.; Gupta, A.; Bareen, M.A.; Sharma, N.; Sahu, J.K. Kombucha Fermentation: Recent Trends in Process Dynamics, Functional Bioactivities, Toxicity Management, and Potential Applications. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvetković, D.; Markov, S.; Djurić, M.; Savić, D.; Velićanski, A. Specific Interfacial Area as a Key Variable in Scaling-up Kombucha Fermentation. J. Food Eng. 2008, 85, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Soto, S.A.; Beaufort, S.; Bouajila, J.; Souchard, J.P.; Renard, T.; Rollan, S.; Taillandier, P. Impact of Fermentation Conditions on the Production of Bioactive Compounds with Anticancer, Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties in Kombucha Tea Extracts. Process Biochem. 2019, 83, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolomedi, B.M.; Paglarini, C.S.; Brod, F.C.A. Bioactive Compounds in Kombucha: A Review of Substrate Effect and Fermentation Conditions. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.; Grandvalet, C.; Verdier, F.; Martin, A.; Alexandre, H.; Tourdot-Maréchal, R. Microbiological and Technological Parameters Impacting the Chemical Composition and Sensory Quality of Kombucha. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2050–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.O.; Monteiro, A.L.B.; da Silva, C.M.; da Silva, T.M.S.; de Oliveira, R.L.; Porto, C.S.; Porto, T.S. Investigation of the Influence of Different Camellia Sinensis Teas on Kombucha Fermentation and Development of Flavored Kombucha with Brazilian Fruits. Beverages 2025, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitwetcharoen, H.; Phung, L.T.; Klanrit, P.; Thanonkeo, S.; Tippayawat, P.; Yamada, M.; Thanonkeo, P. Kombucha Healthy Drink—Recent Advances in Production, Chemical Composition and Health Benefits. Fermentation 2023, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, D.; Bhattacharya, S.; Patra, M.M.; Chakravorty, S.; Sarkar, S.; Chakraborty, W.; Koley, H.; Gachhui, R. Antibacterial Activity of Polyphenolic Fraction of Kombucha Against Enteric Bacterial Pathogens. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 73, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of Dinitrosalicylic Acid Reagent for Determination of Reducing Sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. [14] Analysis of Total Phenols and Other Oxidation Substrates and Antioxidants by Means of Folin-Ciocalteu Reagent. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a Free Radical Method to Evaluate Antioxidant Activity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuta, A.G.; De Menezes, J.L.; Dutra, T.V.; Ferreira, V.; Castro, J.C.; Antonia, C.; Jorge, E.; Junior, M.M.; Alves, B.; Filho, D.A. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity of Green Tea Kombucha at Two Fermentation Time Points against Alicyclobacillus spp. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 130, 109641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Den Dool, H.; Kratz, P.D. A Generalization of the Retention Index System Including Linear Temperature Programmed Gas—Liquid Partition Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1963, 11, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparkman, O.D. Identification of Essential Oil Components by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectroscopy Robert P. Adams. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1997, 8, 671–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Van Mullem, J.; Dias, D.R.; Schwan, R.F. The Chemistry and Sensory Characteristics of New Herbal Tea-Based Kombuchas. J. Food Sci. 2021, 86, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, L.; Ben Abid, S.; Hamdi, M. Development of a Beverage from Red Grape Juice Fermented with the Kombucha Consortium. Ann. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, R.F.; Hikal, M.S.; Abou-Taleb, K.A. Biological, Chemical and Antioxidant Activities of Different Types Kombucha. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2020, 65, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravorty, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chatzinotas, A.; Chakraborty, W.; Bhattacharya, D.; Gachhui, R. Kombucha Tea Fermentation: Microbial and Biochemical Dynamics. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 220, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, R.O.; Dias, F.O.; Shenoy, C.K. Kombucha for Healthy Living: Evaluation of Antioxidant Potential and Bioactive Compounds. Int. Food Res. J. 2017, 24, 541–546. [Google Scholar]
- Malbaša, R.V.; Lončar, E.S.; Vitas, J.S.; Čanadanović-Brunet, J.M. Influence of Starter Cultures on the Antioxidant Activity of Kombucha Beverage. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1727–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabalan, R.; Subathradevi, P.; Marimuthu, S.; Sathishkumar, M.; Swaminathan, K. Changes in Free-Radical Scavenging Ability of Kombucha Tea during Fermentation. Food Chem. 2008, 109, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Li, R.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, F.; Gao, Y.; Fu, Y.Q.; Xu, Y.Q.; Yin, J.F. Zijuan Tea- Based Kombucha: Physicochemical, Sensorial, and Antioxidant Profile. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayabalan, R.; Malbaša, R.V.; Lončar, E.S.; Vitas, J.S.; Sathishkumar, M. A Review on Kombucha Tea-Microbiology, Composition, Fermentation, Beneficial Effects, Toxicity, and Tea Fungus. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal, S.A.; Beaufort, S.; Bouajila, J.; Souchard, J.; Taillandier, P. Understanding Kombucha Tea Fermentation: A Review. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 580–588. [Google Scholar]
- Lonǎr, E.; Djurić, M.; Malbaša, R.; Kolarov, L.J.; Klašnja, M. Influence of Working Conditions upon Kombucha Conducted Fermentation of Black Tea. Food Bioprod. Process. 2006, 84, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, A.J.; O’Sullivan, O.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Sequence-Based Analysis of the Bacterial and Fungal Compositions of Multiple Kombucha (Tea Fungus) Samples. Food Microbiol. 2014, 38, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cvetkovic, D.; Markov, S. Preparation of Kombucha from Winter Savory (Satureja montana L.) in the Laboratory Bioreactor. Acta Period. Technol. 2005, 266, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbaša, R.; Lončar, E.; Djurić, M.; Došenović, I. Effect of Sucrose Concentration on the Products of Kombucha Fermentation on Molasses. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, R.M.D.; de Almeida, A.L.; do Amaral, R.Q.G.; da Mota, R.N.; Sousa, P.H.M.d. Kombucha: Review. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2020, 22, 100272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antolak, H.; Piechota, D.; Kucharska, A. Kombucha Tea—A Double Power of Bioactive Compounds from Tea and Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeasts (SCOBY). Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zailani, N.S.; Adnan, A. Substrates and metabolic pathways in symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) fermentation: A mini review. J. Teknol. 2022, 84, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suffys, S.; Richard, G.; Burgeon, C.; Werrie, P.Y.; Haubruge, E.; Fauconnier, M.L.; Goffin, D. Characterization of Aroma Active Compound Production during Kombucha Fermentation: Towards the Control of Sensory Profiles. Foods 2023, 12, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ahmad, W.; Zhu, A.; Geng, W.; Kang, W.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Q. Identification of Volatile Compounds and Metabolic Pathway during Ultrasound-Assisted Kombucha Fermentation by HS-SPME-GC/MS Combined with Metabolomic Analysis. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 94, 106339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, X. Microbial Interactions and Dynamic Changes of Volatile Flavor Compounds during the Fermentation of Traditional Kombucha. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 137060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, M.; Yu, C.; Liu, Q.; He, Z.; Song, S.; Feng, T.; Yao, L. Flavor and Sensory Profile of Kombucha Fermented with Raw Pu-Erh Tea and Evaluation of the Antioxidant Properties. LWT 2024, 200, 116220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

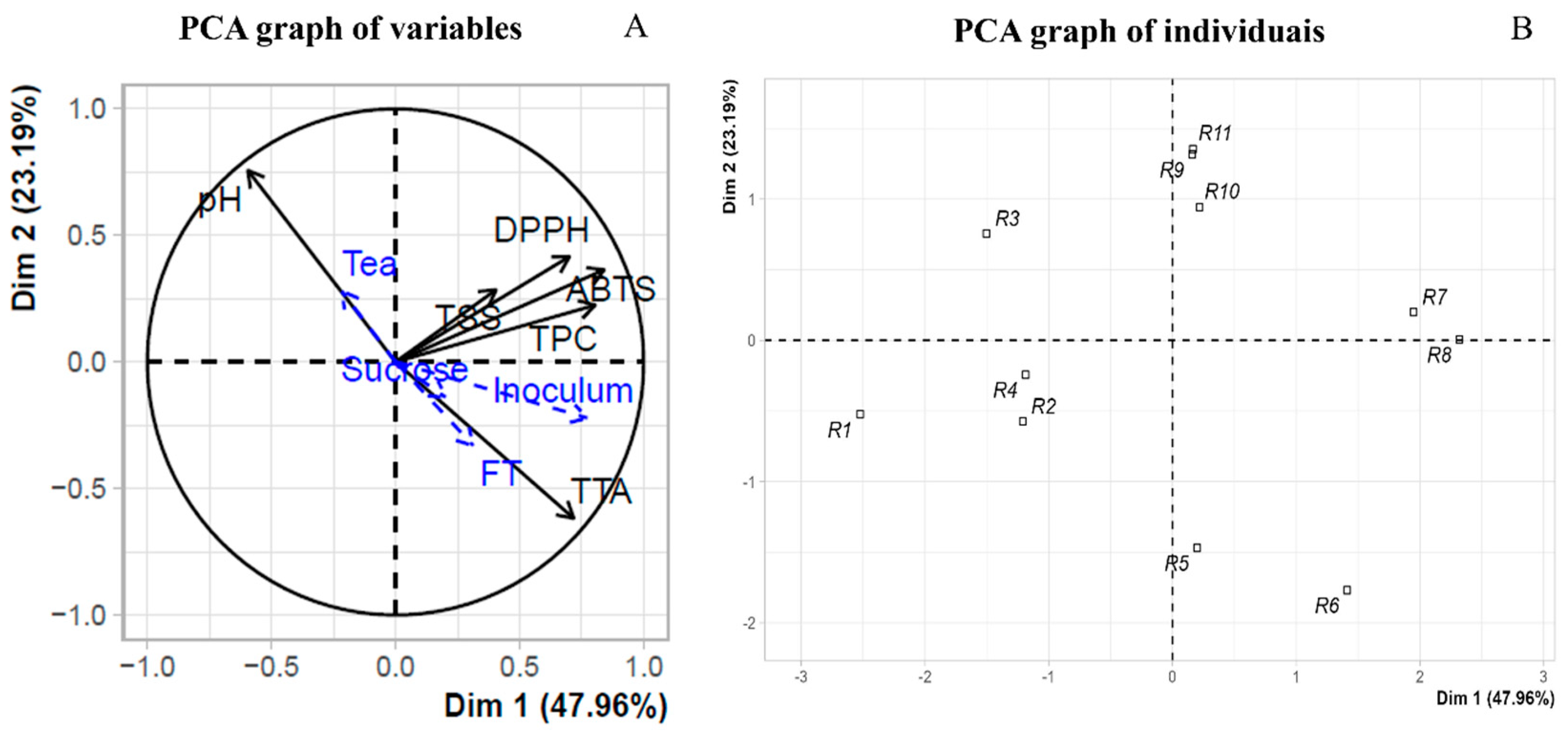
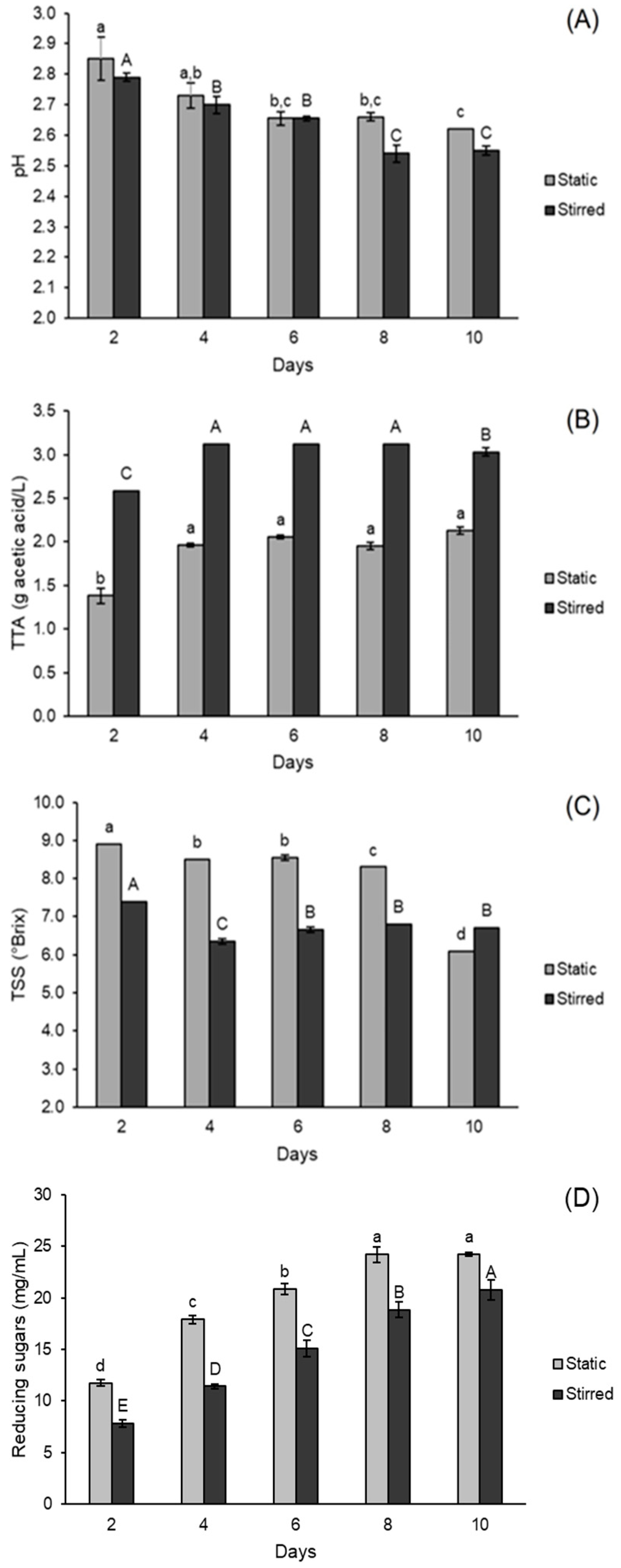
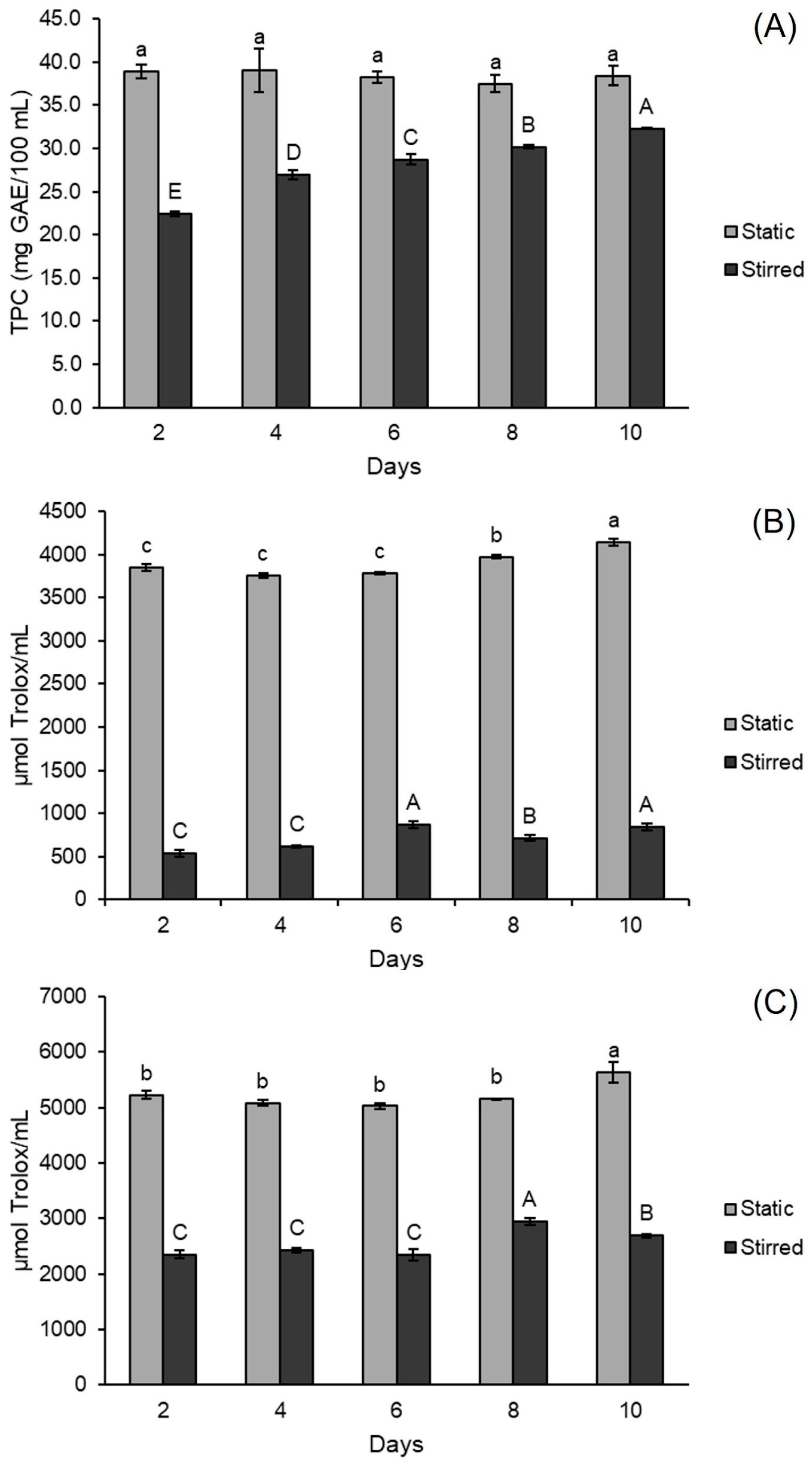
| Run | Independent Variables | Dependent Variables | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sucrose (g/L) | Green Tea (g/L) | Inoculum (%) | pH | TTA a (g/L) | TSS b (°Brix) | TPC c (mg GAE/100 mL) | DPPH d (µmol/mL) | ABTS e (µmol/mL) | |
| 1 | 40 | 4 | 10 | 3.20 | 1.70 ± 0.02 c | 3.60 ± 0.05 g | 37.87 ± 0.44 h | 2590.00 ± 41.48 b | 4661.42 ± 80.81 e |
| 2 | 80 | 4 | 10 | 3.06 | 1.83 ± 0.03 b,c | 6.80 ± 0.10 b,c | 49.93 ± 0.08 f | 3031.67 ± 188.56 b | 5654.28 ± 20.30 d,e |
| 3 | 40 | 8 | 10 | 3.41 | 1.34 ± 0.05 d,e | 3.20 ± 0.05 h | 79.01 ± 0.84 c | 2681.67 ± 205.61 b | 8540.00 ± 232.33 a,b |
| 4 | 80 | 8 | 10 | 3.09 | 2.09 ± 0.06 a,b | 6.80 ± 0.05 b,c | 47.13 ± 0.52 g | 3190.00 ± 129.64 b | 5368.57 ± 30.30 d,e |
| 5 | 40 | 4 | 30 | 3.03 | 1.64 ± 0.08 c,d | 5.80 ± 0.03 e | 84.73 ± 0.36 b | 4590.00 ± 388.91 a,b | 8068.57 ± 338.60 b,c |
| 6 | 80 | 4 | 30 | 2.94 | 1.88 ± 0.01 b,c | 6.50 ± 0.05 d | 64.96 ± 1.09 d | 4690.00 ± 35.35 a,b | 5911.42 ± 10.10 d |
| 7 | 40 | 8 | 30 | 3.13 | 1.19 ± 0.06 e | 4.10 ± 0.02 f | 78.44 ± 1.17 c | 6156.67 ± 11.78 a | 7618.57 ± 363.65 b,c |
| 8 | 80 | 8 | 30 | 3.12 | 2.27 ± 0.09 a | 7.80 ± 0.01 a | 98.61 ± 0.24 a | 6640.00 ± 341.77 a | 9647.14 ± 40.41 a |
| 9 | 60 | 6 | 20 | 3.32 | 1.83 ± 0.10 b,c | 7.00 ± 0.05 b | 58.68 ± 0.52 e | 3305.00 ± 188.56 b | 7525.71 ± 313.14 c |
| 10 | 60 | 6 | 20 | 3.34 | 1.91 ± 0.08 b,c | 6.90 ± 0.02 b,c | 58.51 ± 0.32 e | 3380.00 ± 129.64 b | 8018.57 ± 303.04 b,c |
| 11 | 60 | 6 | 20 | 3.27 | 1.79 ± 0.09 b,c | 6.70 ± 0.04 c,d | 58.51 ± 1.41 e | 3305.80 ± 153.21 b | 8332.85 ± 101.01 b,c |
| Variable or Interaction | pH | TTA a | TSS b | TPC c | DPPH d | ABTS e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) Sucrose concentration | −5.491 * | 13.594 * | 25.922 * | −14.540 * | 12.519 * | −2.004 |
| (2) Tea concentration | 5.099 * | −1.102 | −1.851 | 48.8887 * | 30.754 * | 5.977 * |
| (3) Inoculum | −5.295 * | −1.102 | 8.795 * | 83.935 * | 86.412 * | 6.101 * |
| 1 × 2 | −0.980 | 9.675 * | 7.869 * | −2.976 | 3.674 | 0.186 |
| 1 × 3 | 3.530 | 2.327 | −5.554 * | 15.045 * | −2.993 | 1.781 |
| 2 × 3 | 0.392 | −0.122 | 0.001 | −8.170 * | 26.672 * | −0.266 |
| 1 × 2 × 3 | 2.549 | 1.347 | 6.017 * | 62.415 * | 2.585 | 7.256 * |
| RT (Min) | Compounds | Class | Static System (Days) | Stirred System (Days) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | |||
| 7.408 | Cyclopentyl 4-ethylbenzoate | Ester | 2.53 | 2.45 | 3.55 | 1.85 | 2.31 | 17.78 | 2.45 | 3.55 | 1.85 | 2.31 |
| 10.766 | 2-ethyl-1-Hexanol | Alcohol | 11.84 | 6.83 | 10.86 | 9.96 | 7.62 | 5.73 | 6.83 | 10.86 | 9.96 | 7.62 |
| 12.833 | α-Terpinolene | Terpenes | nd | 0.99 | 2.01 | 1.29 | nd | 7.08 | 0.99 | 2.01 | 1.29 | nd |
| 15.490 | Octanoic acid | Carboxylic acids | 8.60 | 5.45 | 3.01 | 4.14 | 3.87 | 10.70 | 5.45 | 3.01 | 4.14 | 3.87 |
| 16.996 | 1,3-Di-tert-butylbenzene | Hydrocarbon | 2.67 | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| 17.714 | Ionone | Ketone | 9.86 | 8.59 | 7.99 | 8.03 | 8.97 | nd | 8.59 | 7.99 | 8.03 | 8.97 |
| 20.341 | Decanoic acid | Carboxylic acids | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | 6.64 | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| 21.100 | β-Caryophyllene | Terpenes | 0.16 | 0.45 | 1.97 | 2.16 | 2.92 | 0.73 | 0.45 | 1.97 | 2.16 | 2.92 |
| 22.536 | Pentadecane | Carboxylic acids | 15.36 | 16.12 | 14.26 | 15.60 | 16.44 | nd | 16.12 | 14.26 | 15.60 | 16.44 |
| 22.977 | 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol | Phenols | 26.71 | 22.37 | 20.74 | 21.14 | 23.26 | 29.06 | 22.37 | 20.74 | 21.14 | 23.26 |
| 24.618 | Dodecanoic acid | carboxylic acids | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd | nd |
| Total (%) | 77.73 | 63.25 | 64.39 | 64.17 | 65.39 | 77.72 | 90.87 | 74.43 | 75.05 | 80.55 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves, R.O.; de Oliveira, R.L.; de Moraes, M.M.; Santos, W.W.V.; Gomes da Câmara, C.A.; da Silva, S.P.; Porto, C.S.; Porto, T.S. Evaluation of the Impact of Fermentation Conditions, Scale Up and Stirring on Physicochemical Parameters, Antioxidant Capacity and Volatile Compounds of Green Tea Kombucha. Fermentation 2025, 11, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040201
Alves RO, de Oliveira RL, de Moraes MM, Santos WWV, Gomes da Câmara CA, da Silva SP, Porto CS, Porto TS. Evaluation of the Impact of Fermentation Conditions, Scale Up and Stirring on Physicochemical Parameters, Antioxidant Capacity and Volatile Compounds of Green Tea Kombucha. Fermentation. 2025; 11(4):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040201
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves, Raniele Oliveira, Rodrigo Lira de Oliveira, Marcílio Martins de Moraes, Wallysson Wagner Vilela Santos, Cláudio Augusto Gomes da Câmara, Suzana Pedroza da Silva, Camila Souza Porto, and Tatiana Souza Porto. 2025. "Evaluation of the Impact of Fermentation Conditions, Scale Up and Stirring on Physicochemical Parameters, Antioxidant Capacity and Volatile Compounds of Green Tea Kombucha" Fermentation 11, no. 4: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040201
APA StyleAlves, R. O., de Oliveira, R. L., de Moraes, M. M., Santos, W. W. V., Gomes da Câmara, C. A., da Silva, S. P., Porto, C. S., & Porto, T. S. (2025). Evaluation of the Impact of Fermentation Conditions, Scale Up and Stirring on Physicochemical Parameters, Antioxidant Capacity and Volatile Compounds of Green Tea Kombucha. Fermentation, 11(4), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040201








