Abstract
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant global health threat, largely driven by the overuse and misuse of antibiotics. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), a multidrug-resistant pathogen, remains a critical target for novel antibiotic development. This study explores the rhizosphere of the wild apple tree (Malus trilobata) in Lebanon as a potential source of antibacterial compounds. A bacterial strain, MR7S4, identified as Streptomyces anulatus, was isolated and characterized. Its crude extracts exhibited potent activity against Gram-positive pathogens, with minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) values of 2 µg/mL against S. aureus ATCC 29213, S. aureus Newman, and S. aureus N315 (MRSA), and of 1 µg/mL against Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 19433. Bio-guided fractionation and structural analysis identified a novel antibacterial pyrazinone derivative, MR7S4-F3. This compound demonstrated MIC values of 4–16 µg/mL against Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633, multiple S. aureus strains, E. faecalis ATCC 19433, E. faecium DSM 17050 (VRE), and E. faecium DSM 20478, while exhibiting no activity against Gram-negative bacteria. Whole-genome sequencing of MR7S4 revealed 35 biosynthetic gene clusters, underscoring its potential for natural product discovery. These findings highlight the untapped microbial diversity of the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region as a valuable reservoir for antibiotic discovery. MR7S4-F3 emerges as a promising bioactive scaffold, addressing the urgent need for new therapeutic options to combat AMR.
1. Introduction
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has been a growing risk to the effective management of a wide spectrum of diseases caused by bacteria, parasites, viruses, and fungi for several decades. AMR causes the efficacy of antimicrobial medicine to decrease, making patient treatment challenging, expensive, or sometimes even impossible [1]. While AMR is a natural evolutionary adaptation in microorganisms, its rapid escalation is primarily driven by the selective pressure from widespread antimicrobial drug use, compounded by overuse and misuse in both human and animal health [2]. The rise and dissemination of multidrug-resistant pathogens pose a complex global health crisis. With existing antimicrobials losing efficacy and new antibiotic development lagging, many experts are worried about a return to a “pre-antibiotic” era [1]. Without immediate and effective interventions to curb drug resistance, projections indicate that by 2050, 10 million lives per year and a cumulative USD 100 trillion of economic output will be at risk due to the rise of drug-resistant infections [3].
One of the most significant bacteria human pathogens is Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), a Gram-positive bacterium that can coexist with the normal flora on the skin and in the nose. However, it can cause severe infections at the level of the skin, soft tissues, bones, and bloodstream (Lee et al., 2018) [4].
In 1960, methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) emerged around the world due to AMR and became a major cause of bacterial infections in both healthcare facilities and the general public [5].
Given the challenges faced by the pharmaceutical industry in developing new antimicrobial agents, interventions are crucial to limit the spread of resistant pathogens and mitigate their impact on public health. Over the decades, natural products (NPs) also known as secondary metabolites (SMs), produced by microorganisms have served as a rich source for the discovery of new antimicrobial agents. In fact, NPs, their derivatives, or their mimics represented almost 50% of all antimicrobials discovered in the last four decades [6]. Namely, the genus Streptomyces has significantly advanced medicine with the production of antimicrobial and anticancer compounds during the past 80 years.
Based on our previous review of the antimicrobial natural products derived from microorganisms inhabiting the MENA region, we highlighted the region’s significant potential as a source of novel natural products [7]. Given the region’s distinct ecological features, we decided to investigate its unexplored microbial resources. In the hope of discovering novel antimicrobial agents, we decided to exploit the microbiome of the Lebanese wild apple, Malus trilobata [8]. The root microbiota largely originates from the diverse array of microorganisms present in the soil environment, including Acidobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Planctomycetes, and Actinobacteria [9]. The rhizosphere, a thin layer of soil directly influenced by plant roots, is thought to be a hub of microbial activity and one of the most intricate ecosystems that play a crucial role in the production of SMs. Soil bacteria, including those in the rhizosphere, secrete these SMs to protect themselves from other microbes, serving important ecological roles [10,11]. These SMs have been a prolific source and an inspiration for numerous clinically utilized drugs with widely divergent chemical structures and biological activities, including antimicrobial, immunosuppressive, anticancer, and anti-inflammatory activities [6].
In this study, we report the isolation and structural elucidation of novel antimicrobial compounds, exhibiting potent anti-MRSA activity, from the crude extracts of a previously isolated Streptomyces strain [8]. Our results show that Lebanese environmental bacteria are a valuable source of novel and potent antimicrobials that require further investigation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Metabolite Production and Extraction
By adding 35 μL of the bacterial stock to 5 mL of International Streptomyces Project Medium 3 (ISP3) (20 g of oats and 2.5 mL of ISP3 trace elements in 1 L of distilled water, pH = 7.8), a starter culture known as the first seed was initiated and incubated at 28 °C and 130 rpm for 48 h. Under the same conditions, a second seed was incubated. This culture consisted of 1 mL of the first seed in 10 mL of the ISP3 broth. To induce the production of SMs, 1 mL of the second seed was used to inoculate 50 mL of each of the 14 different media, as described by Awada et al. [12]. The cultures were then incubated for 7 days in the same conditions. Then, 1 mL of Amberlite XAD 16N resin was added to each culture and left for 4 h to adsorb the SMs. The resins and cell pellets were precipitated by centrifugation and the SMs were consequently extracted with a mixture of 10 mL methanol and 30 mL acetone. The organic layer was then dried by evaporation before the crude extract was resuspended in concentrated dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO 99.99%). The crude extracts were then named, with the name of the bacterium preceding the name of the media. For example, MR7S4 NL2 is the crude synthesized by the bacterium MR7S4 in medium NL2.
2.2. Antibacterial Activity Testing
The following panel of human ESKAPE pathogenic bacteria was subjected to the antibacterial activity screening process: Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) ATCC 29213, S. aureus Newman, S. aureus N315 MRSA, Enterococcus faecalis (E. faecalis) ATCC 19433, Enterococcus faecium (E. faecium) DSM 17050 VRE, E. faecium DSM 20478, Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis) ATCC 6633, Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) DSM, K. pneumoniae ATCC 13883, Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii) DSM 30008, Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) ATCC 27853, P. aeruginosa ATCC 10145 P. aeruginosa MexAB, Escherichia coli (E. coli) ATCC 25922, E. coli ATCC 3521, E. coli J53, and Mycobacterium smegmatis (M. smegmatis) 89.
The antibacterial activity of the crude extracts and the pure compounds were tested using the conventional broth microdilution test (BMD) in 96-well plates following CLSI guidelines. The BMD assay utilizes two-fold serial dilutions of crudes or compounds, already dissolved in DMSO, in the appropriate medium, namely cation-adjusted Mueller–Hinton broth (MHCAB) (BD PhoenixTM). The dilutions took place between columns 1 and 11 with a final volume of 90 µL. Similarly, a two-fold serial dilution of the vehicle DMSO was prepared for each biological replicate, where the starting DMSO volume was equivalent to the volume of the crude extract or compound introduced. The wells of column 12 only contained 90 µL of MHCAB, and these served as either positive or negative controls. Some of the negative control wells also received DMSO. Each well, except the negative controls, was inoculated with 10 μL of a bacterial suspension with a 5 × 106 CFU/mL density. After 24 h of incubation at 37 °C, bacterial growth was measured by the turbidity of the media, allowing visual determination of the MIC values. The MIC was determined as the lowest value where inhibition of bacterial growth is observed. For each BMD assay, crude extracts or compounds were tested in duplicates. These assays were repeated in three independent biological replicates (n = 3).
2.3. Bioguided Purification
As the crude extract MR7S4 NL2 yielded a prominent inhibition against S. aureus N315, a large-scale fermentation of MR7S4 in medium NL2 (2.5 g of yeast extract, 10 g of calcium carbonate, 20 g of molasses, and 15 g of soy flour in 1 L of distilled water, pH = 7.8) was prepared. However, the cultures were incubated for 14 days at 150 rpm and 28 °C in a shaker incubator. The secondary metabolites were extracted using an acetone/methanol procedure similar to that used in small-scale SM production. Following liquid–liquid extraction, the obtained crude extracts were separated into four different fractions, namely hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, and water/methanol, which were tested for their antibacterial activity using the previously described BMD assay.
Thin liquid chromatography (TLC) was performed to identify a mixture of components. On aluminum supports, pre-coated silica gel 60 F254 plates (20 × 20 cm; layer thickness, 0.20 mm; Merck, Burlington, MA, USA) were used. Samples were spotted on TLC plates. The mobile phase for the chromatography was 90% dichloromethane and 10% methanol + 1% formic acid (FA). For the complete removal of the solvents, developed plates were left to dry before being analyzed.
The fraction that showed the highest antibacterial activity was subjected to further purification by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). HPLC was performed using a Phenomenex Luna® 5 μm C18 column (Phenomenex, Torrance, DE, USA) 100 Å 250 × 10 mm for reverse-phase chromatography with a mobile phase of acetonitrile and water with 0.1% FA. A gradient elution mode with a flow rate of 4 mL/min was used, and the injection volume was 100 µL. The total analysis time was 50 min, and the elution was monitored at 220 and 280 nm.
2.4. Analytical Techniques for the Structural Elucidation of the Bioactive Compound
2.4.1. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
Measurements were performed using an AB Sciex X500R QTOF ESI mass spectrometer (SCIEX, Framingham, MA, USA). The liquid chromatography flow was split to 500 nL/min before entering the ion source. Mass spectra were acquired in centroid mode ranging from 150 to 1000 m/z, with resolution R = 30,000. A Luna Omega C18 (Phenomenex, Torrance, DE, USA), 150 × 2.1 mm, 1.6 µm column was used, with an injection volume = 1 µL. A gradient of (A) H2O + 0.1% FA and (B) acetonitrile + 0.1% FA at a flow rate of 0.55 mL/min was used to achieve separation. Gradient conditions started at 5% B, increased to 10% B in 1 min, increased to 35% B from min 1→15, increased to 50% B from min 15→22, and finally increased to 80% B from min 22→25. After a 1 min hold at 80% B, the system was re-equilibrated for 5 min with the initial conditions. Ultraviolet radiation data were acquired using a photodiode array detector (PDA) (SCIEX, Framingham, MA, USA) (wavelength 200–800 nm ± 8 nm), while mass spectrometry detection was performed simultaneously.
2.4.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy
All 1D (1H and 13C) and 2D (COSY, HSQC-DEPT, and HMBC) NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker 500 MHz Avance HD spectrometer (Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) with a 5 mm BBFO Smart probe with a Z-gradient (1H at 500 MHz, 13C at 125.7 MHz). Two-dimensional experiments were recorded using standard pulse programs. The samples were dissolved in CDCl3 and the chemical shifts of the solvent signals at 7.24 ppm (δH) and 77.0 ppm (δC) were considered as the internal standard (reference signal). The observed chemical shift (δ) values are given in ppm and the coupling constants (J) are given in Hz.
2.5. Strain Identification and Characterization
MR7S4 was chosen for further purification because extracts produced by this isolate revealed the highest potency against S. aureus N315 (MRSA).
2.5.1. Morphological Characterization and Microscopic Visualization
To show the mycelium’s morphology and color, the isolate was streaked over the ISP3 agar and incubated for 10 days at 28 °C. A standardized Gram staining technique for bacteria was used during this study. Furthermore, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to visualize the detailed morphology of bacterial cells. To prepare the bacteria for SEM, overnight cultures were centrifuged at 5000× g for 2 min at 4 °C, the supernatant was discarded, and the pellet was washed with 1X phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and centrifuged at 6000× g for 2 min at 4 °C. The pellet was resuspended in 50 μL of 2% Formaldehyde. Then, 10 μL of the bacteria/formaldehyde mixture was transferred to the center of a carbon adhesive tab placed on an aluminum specimen mount. The samples were then incubated for 25 min at room temperature for primary fixation, washed with 10 μL of 1X PBS, and covered with 2.5% glutaraldehyde. After a 25 min incubation, the samples were washed with 20 μL of autoclaved distilled water. The fixed dried samples were coated with 5 nm of platinum before being observed by SEM.
2.5.2. Physiological and Biochemical Tests
Resistance Toward Sodium Chloride
A useful method for identifying various Actinobacteria species is their resistance to sodium chloride (NaCl). Thus, the isolate was tested for its resistance to NaCl through its growth on basal medium 5339 (10 g of casein peptone, 5 g of yeast extract, and 20 g of agar in 1 L of distilled water, pH = 7) with 0, 2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10% of NaCl [13]. The growth was checked after incubation for 10 days at 28 °C.
pH Tolerance
The isolate’s tolerance to different pH levels was tested by cultivating it on International Streptomyces Project 2 (ISP2) agar (10 g of malt extract, 4 g of yeast extract, 4 g of glucose, and 15 g of agar in 1 L of distilled water) with the pH levels of 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and 10 [13]. The growth was checked after incubation for 10 days at 28 °C.
Api 20 E
The Api 20 E is a micro-method that can be used to identify Actinobacteria by their physiological fingerprint. The kit was used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.5.3. Genomic Characterization: DNA Extraction, Sequencing, and Data Analysis
DNA Extraction
Following bacterial growth in TSB broth, the bacterial cultures were centrifuged at 4000 rpm and 4 °C for 5 min to pellet the cells, the supernatant was discarded, and the pellet was resuspended in 200 µL of PBS. DNA was extracted using the Zymo Research Quick-DNA Fungal/Bacterial Miniprep Kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA), following the manufacturer’s instructions. To achieve ultra-pure DNA, the eluate underwent purification using the Zymo DNA Clean & Concentrator®-5 kit (Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, USA). The purification was carried out in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions for genomic DNA (gDNA). Furthermore, the gDNA obtained from the extraction and purification processes was assessed for both purity and yield using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
Whole-Genome Sequencing
gDNA was used for library preparation whereas, for short-read sequencing, the Illumina DNA Prep kit (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) was used according to the manufacturer’s instructions with 500 ng of gDNA for library preparation, and the prepared libraries were then sequenced using the MiSeq Reagent Kit v2 (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) (500 cycles) on a MiSeq device over 36 h. For long-read sequencing, library preparation used the Rapid Barcoding Kit V14 from Oxford Nanopore Technologies (Oxford Nanopore Technologies plc, Oxford, UK), following the manufacturer’s instructions, with 50 ng of gDNA as input. Sequencing was performed on an MK1C device, with data acquisition and base-calling conducted in real time over 72 h.
Data Analysis
For assembly and annotation, the Fastq files, both short and long reads (which were concatenated into one file in advance), were processed through the nf-core/bacass pipeline version 2.1.0 [14] where the hybrid assembly step used Unicycler, specifying the assembly type as hybrid in the pipeline parameters. BUSCO was used to assess genome completeness. Taxonomic classification was performed using both Kraken2 [15] and Kmerfinder 3.2 [16], and a species-level phylogenetic tree was built using SaffronTree 0.1.2 [17] with the WGS files, with taxonomic classification matches used as references. Average nucleotide identity was assessed using pyANI 0.2.18 [18], and all strains belonging to the determined species were used for phylogenetic tree construction to examine strain-level relatedness. In addition, pangenome analysis was performed using Roary 3.11.2 pipeline to look for gene conservation between MR7S4 and its reference genome. Furthermore, secondary metabolites and clusters of orthologous groups of proteins (COGs) were identified using antiSMASH 7.0 [19] and a COG classifier [20], respectively. The genomic map was drawn using the DNAplotter function in Artemis 18.2.0 [21].
3. Results
3.1. Crude Extract from Soil-Isolated Bacteria Showed Activity Against MRSA
Our group had previously isolated a large number of bacterial strains from the microflora of the wild apple relative Malus trilobata [8]. Some of these isolates belonged to the genera Streptomyces and Microbacterium and were able to antagonize phytopathogens [8]. The ability of plant microbiota to inhibit the growth of their host’s pathogens is common. However, we wanted to explore them as a potential source of NPs with activity against human pathogens. Antimicrobial activity testing was performed on the crude extracts produced by 9 isolates in 14 different media. Most of the tested crudes showed a relatively low level of activity on a panel of ESKAPE pathogens. However, extracts originating from an isolate called MR7S4 inhabiting the rhizosphere of Malus trilobata from the Ehden reserve showcased noticeable inhibition of the growth of Gram-positive bacteria (Table S1). The extract synthesized by MR7S4 in NL2 medium was of particular interest as it strongly inhibited the growth of Gram-positive pathogens with MIC values of 2 µg/mL against S. aureus ATCC 29213, S. aureus Newman, S. aureus N315 (MRSA), and with an MIC value of 1 µg/mL against E. feacalis ATCC 19433. The DMSO solvent did not exhibit any antimicrobial activity.
3.2. Pure Compound Showed Antibacterial Activity Against MRSA
As a result of the screening process, a large-scale fermentation of the MR7S4 bacterium was prepared in medium NL2, as described above. A portion of the extracted SMs was preserved as crude while the rest were subjected to liquid-liquid partition. Among the 3 obtained fractions, the chloroform and ethyl acetate fractions totally inhibited the growth of MRSA with an MIC < 0.25 µg/mL, similar to the large-scaled crude extract. Before resuming the process of bio-guided fractionation of these fractions, we combined them due to their similar chemical composition, as seen by the TLC assay. This combined fraction was then used as a template for HPLC. Different peaks were visualized. In this study, we chose to analyze using the BMD assay the extended spectrum of activity of F3 due to its important antibacterial activity. As shown in Table 1, the MICs of this pure compound vary between 4, 8, and 16 µg/mL against, B. subtilis ATCC 6633, different S. aureus strains, E. feacalis ATCC 19433, E. faecium DSM 17050 VRE, and E. faecium DSM 20478, respectively. This compound is not effective against the tested Gram-negative bacteria with MIC values greater than or equal to 250 µg/mL.

Table 1.
MICs (μg/mL) of the obtained pure compound after HPLC against a panel of human pathogenic bacteria using the broth microdilution assay.
3.3. Structure Elucidation of the Bioactive Compound
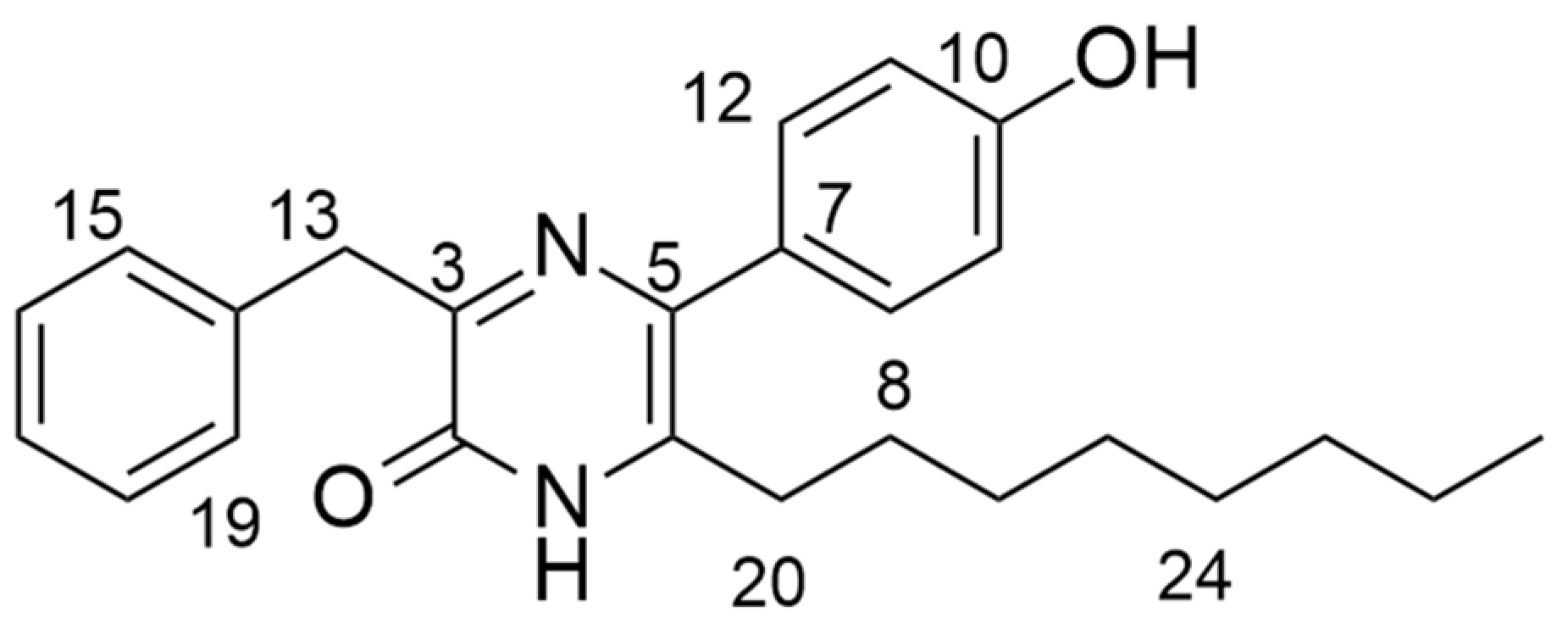
To elucidate the structure of the active fraction, MR7S4-F3 was run on HPLC-MS (high resolution, AB Sciex X500R QTOF) in ESI-positive mode. MR7S4-F3 gave a peak with m/z of 391.532 for [M + H]. The molecular formula generated from these peaks was C25H30N2O2, with nine double bonds. The possible structure of MR7S4-F3 was then investigated using a Bruker 500 MHz Ascend HD NMR. A detailed NMR analysis is shown in Table S2. The elucidation revealed a pyrazinone ring originating from two fused amino acids, namely phenylalanine and meta-hydroxyphenylglycine. The pyrazinone ring was further modified at the C-6 position with an octyl side chain, as shown in Figure 1.
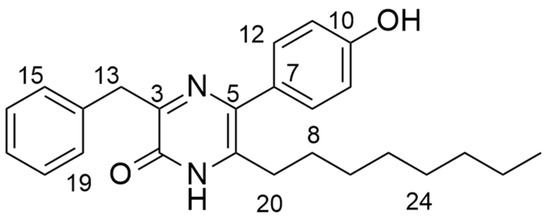
Figure 1.
Structure of MR7S4-F3.
The name of the molecule is 3-benzyl-5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6-octylpyrazin-2 (1H)-one.
3.4. Characterization of the Producer Strain
3.4.1. Colony Morphology
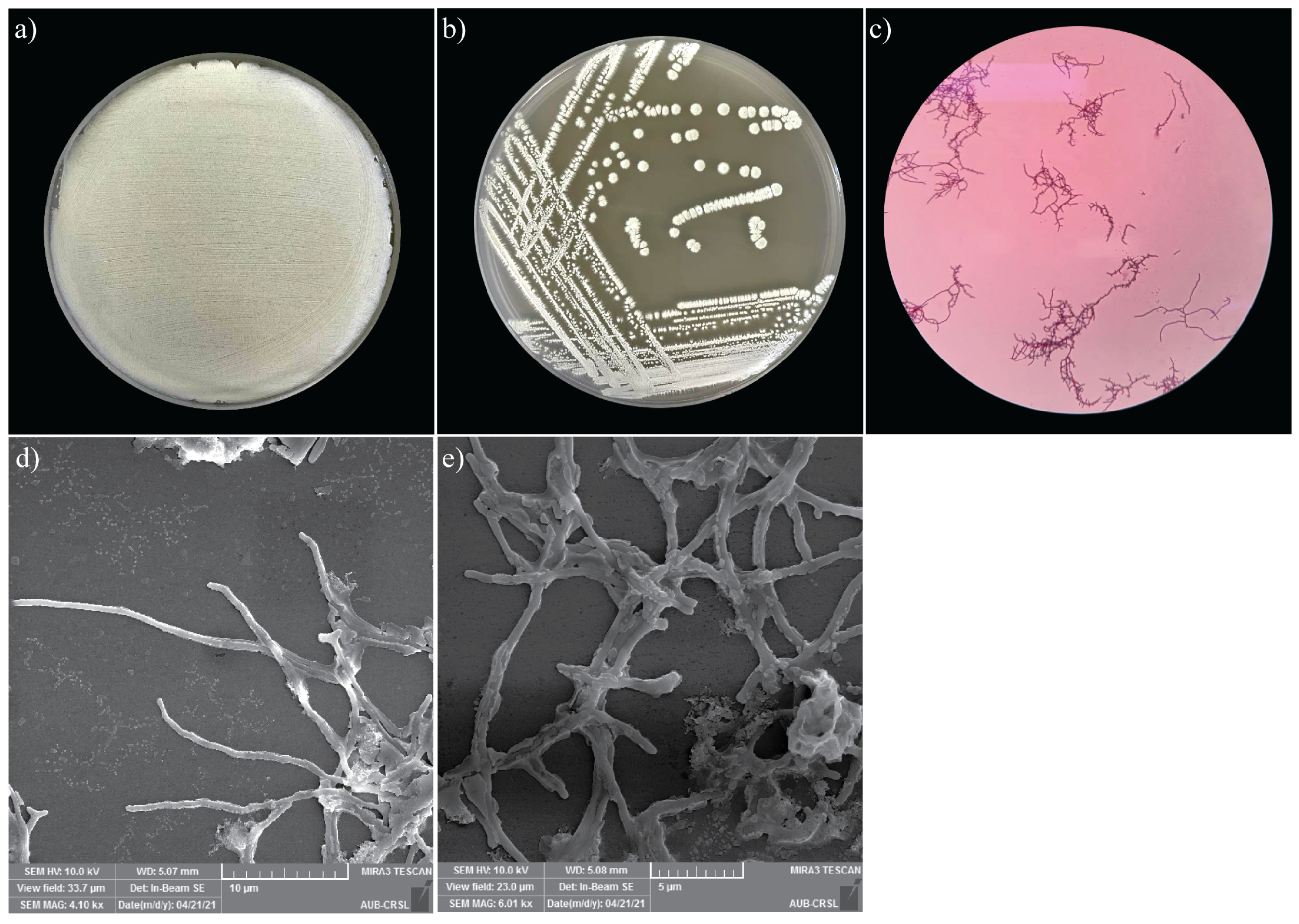
Morphological analysis of the MR7S4 isolate was observed on the standard ISP3 agar plates. The colony was powdery. Within 5 days of growth at 28 °C, white pigmentation and the presence of exudate drops on the colony surface were noticed. Furthermore, microscopic morphology was observed under SEM, and structures of Streptomyces development, including hyphae and spores, were noticed (Figure 2). Additionally, the colonies presented a positive Gram stain, characteristic of Streptomyces.
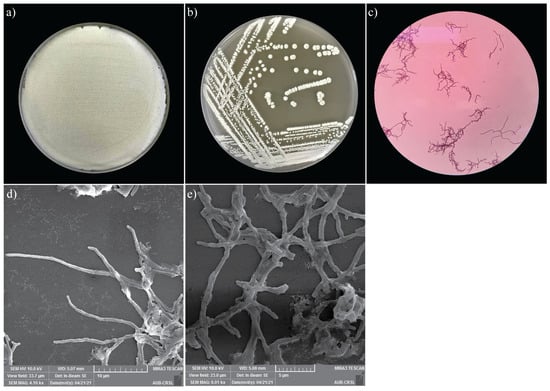
Figure 2.
(a) Heavy growth of MR7S4 colonies on ISP3 agar plate. (b) Single colony streaking of MR7S4 on ISP3 agar plate. (c) Gram-positive filamentous of MRS74 under the light microscope. (d) The zoomed-out view of the scanning electron microscopy shows the extensive network of hyphae of MR7S4 at ×4000. (e) The zoomed-in view of the scanning electron microscopy shows the hyphae and spores of MR7S4 characteristic at ×6000.
3.4.2. Growth Conditions and Biochemical Properties of MR7S4
On agar 5339, MR7S4 was able to grow normally when the NaCl level was less than or equal to 5%. However, no growth was seen when the NaCl content exceeded 7.5%. MR7S4 did not grow on ISP2 (International Streptomyces Project Medium 2) agar when the pH was equal to three or four, but it grew when the pH was more than or equal to five (Table S3). Finally, using the API 20E kit (bioMérieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France), MR7S4 was able to utilize the citrate as a carbon source (CIT-positive) and showed to have the gelatinase (GEL-positive) enzyme (Table S4).
3.4.3. Genomic Characterization
Characterization and Functional Analysis
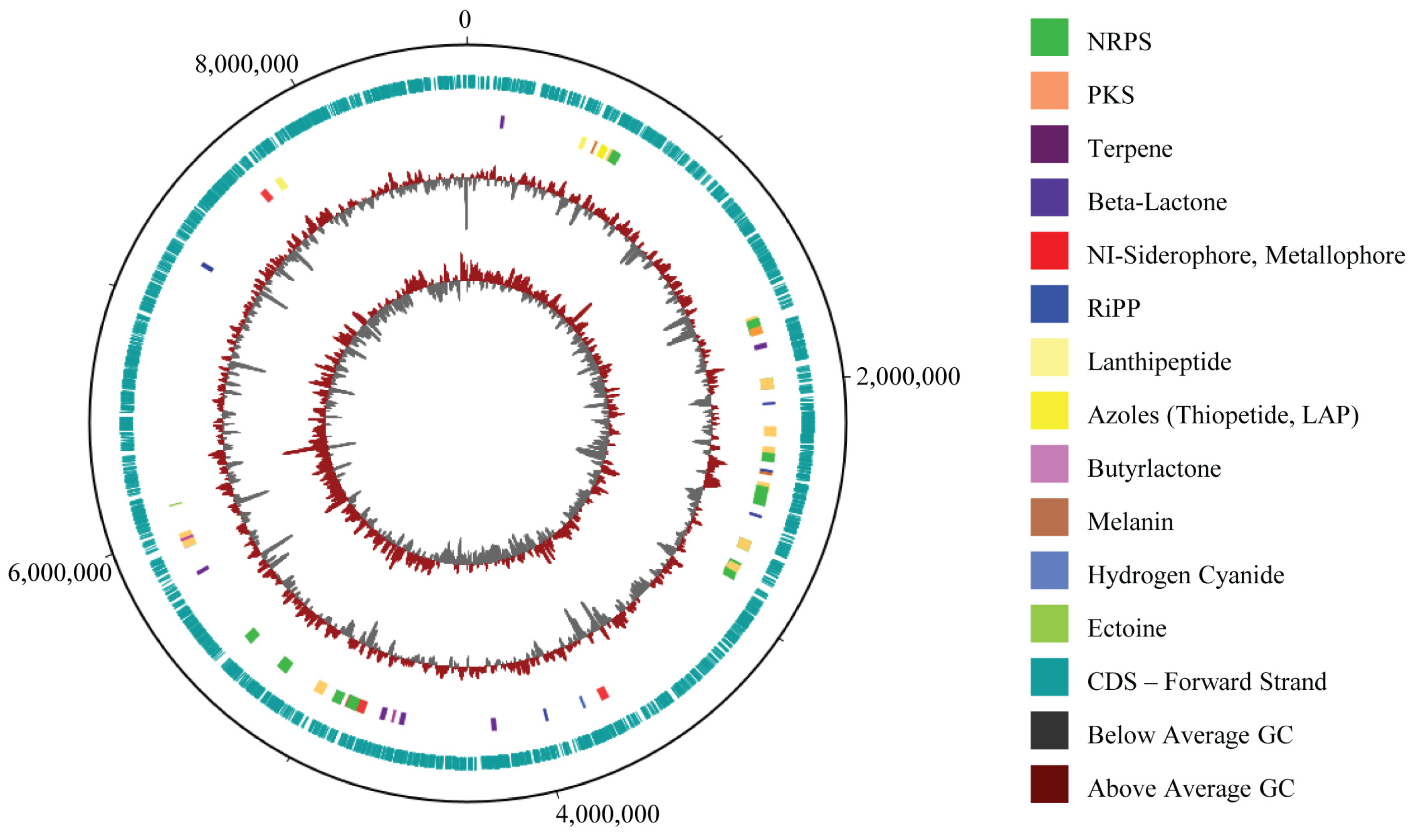
MR7S4 whole-genome sequencing followed by hybrid assembly of short and long reads yielded 14 contigs (Table S5), showing a completeness of 97.6% (Figure S6). The sample has a genome spanning 8,650,217 bp with a guanine–cytosin (GC) content of 71.63%, comprising 7534 coding sequences (CDS), 18 rRNA genes, 84 tRNA genes, and 1 tmRNA, totaling 7637 genes (Figure 3). The contig sequences associated with the genome have been submitted to GenBank and are available under accession number JBMGUW000000000.
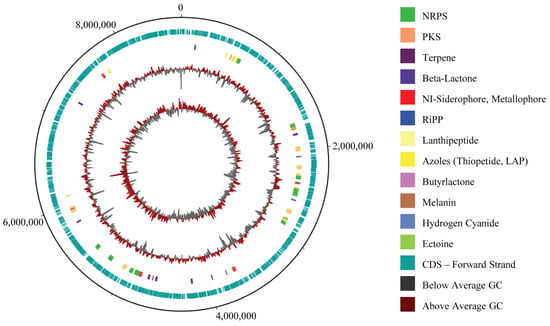
Figure 3.
MR7S4 genomic map. From outer to inner circle: map backbone (Unicycler 0.5.1 FASTA file), CDS annotation (PROKKA GBK file), antiSMASH 7.0 annotation protoclusters, GC% plot, and GC skew. MR7S4 genome spans 8,650,217 bp with a GC content of 71.63%, 7534 coding sequences (CDS), 18 rRNA genes, 84 tRNA genes, and 1 tmRNA, totaling 7637 genes. A total of 36 biosynthetic gene clusters were identified.
The antiSMASH 7.0 analysis revealed 36 biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs), with 12 exhibiting 75% or more similarity to known compounds. Notably, two consecutive BGCs of a similar type were initially observed at the edge of a contig (Table S6), constituting the same BGC that is extending across 2 adjacent contigs; consequently, the total count of BGCs is 35. COG analysis revealed that the genome holds 5759 COG-classified genes, including 255 genes specifically involved in secondary metabolite biosynthesis, transport, and catabolism (Figure S7).
Strain Identification
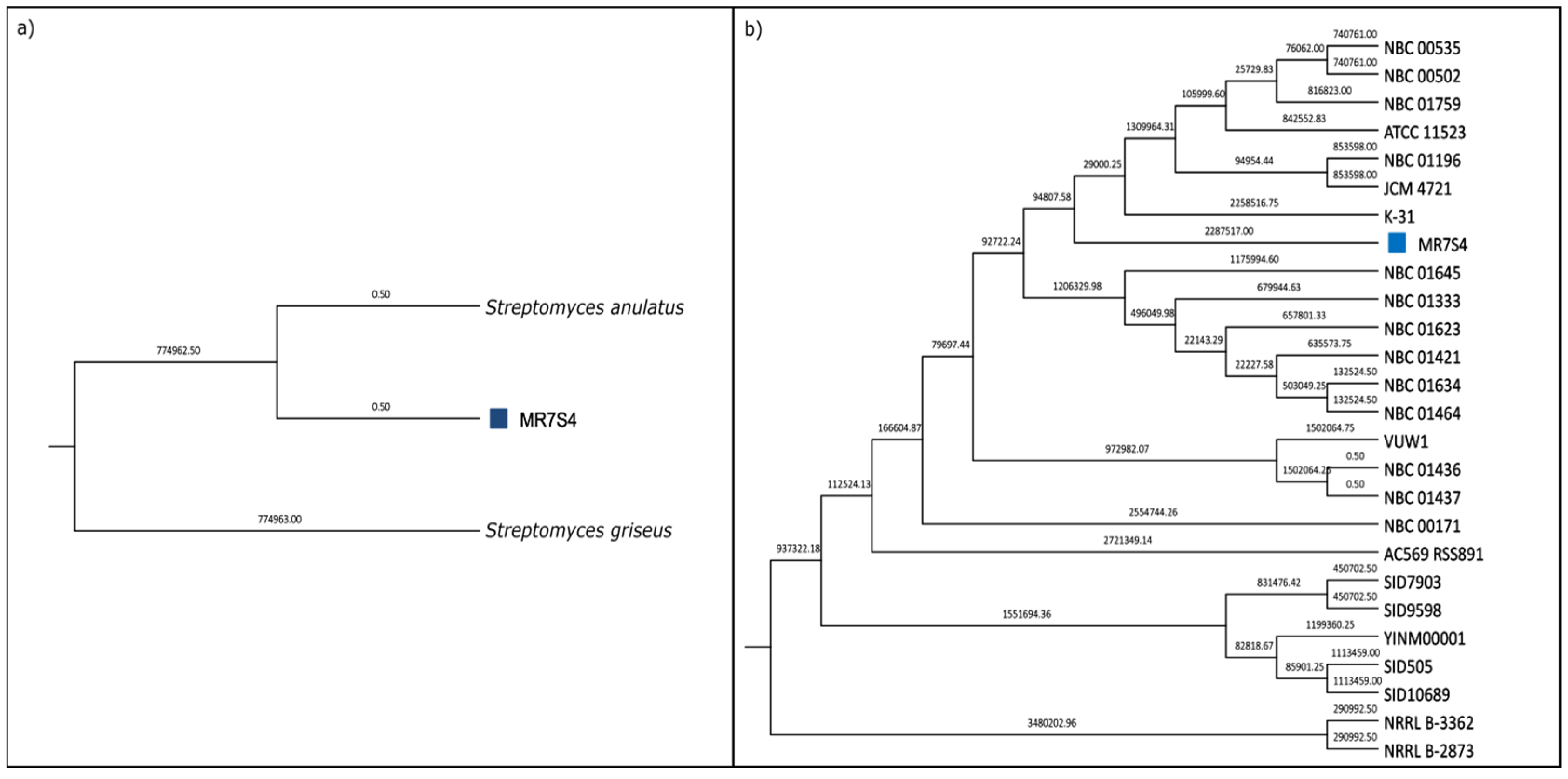
Phylogenetic analysis identified MR7S4 as Streptomyces anulatus, supported by maximum likelihood tree construction using whole-genome sequencing data (Figure 4a) and an average nucleotide identity (ANI) value exceeding 95% [22] when compared to the Streptomyces anulatus reference genome (Figure S8). Further comparison of MR7S4’s genome with all NCBI strains of Streptomyces anulatus revealed its closest relation to strain K-31 (Figure 4b).
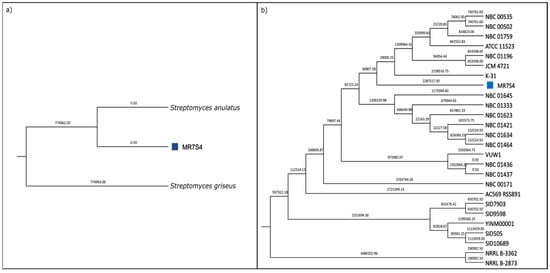
Figure 4.
(a) MR7S4 species-level phylogenetic tree. A maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree was generated using SaffronTree 0.1.2 and visualized with MEGA 11.0.13 software. It represents species-level relatedness using reference genomes for Streptomyces anulatus and Streptomyces griseus. Branch lengths are displayed with a precision of 2 decimal places, indicating the number of substitutions per site. The scale bar corresponds to 0.05 substitutions per site. (b) MR7S4 strain-level phylogenetic tree. A maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree was generated using SaffronTree 0.1.2 and visualized with MEGA 11.0.13 software. It illustrates strain-level relatedness among all strains of Streptomyces anulatus. Branch lengths are depicted with a precision of 2 decimal places, indicating the number of substitutions per site. The scale bar represents 0.05 substitutions per site. The sample of interest is marked with a blue square.
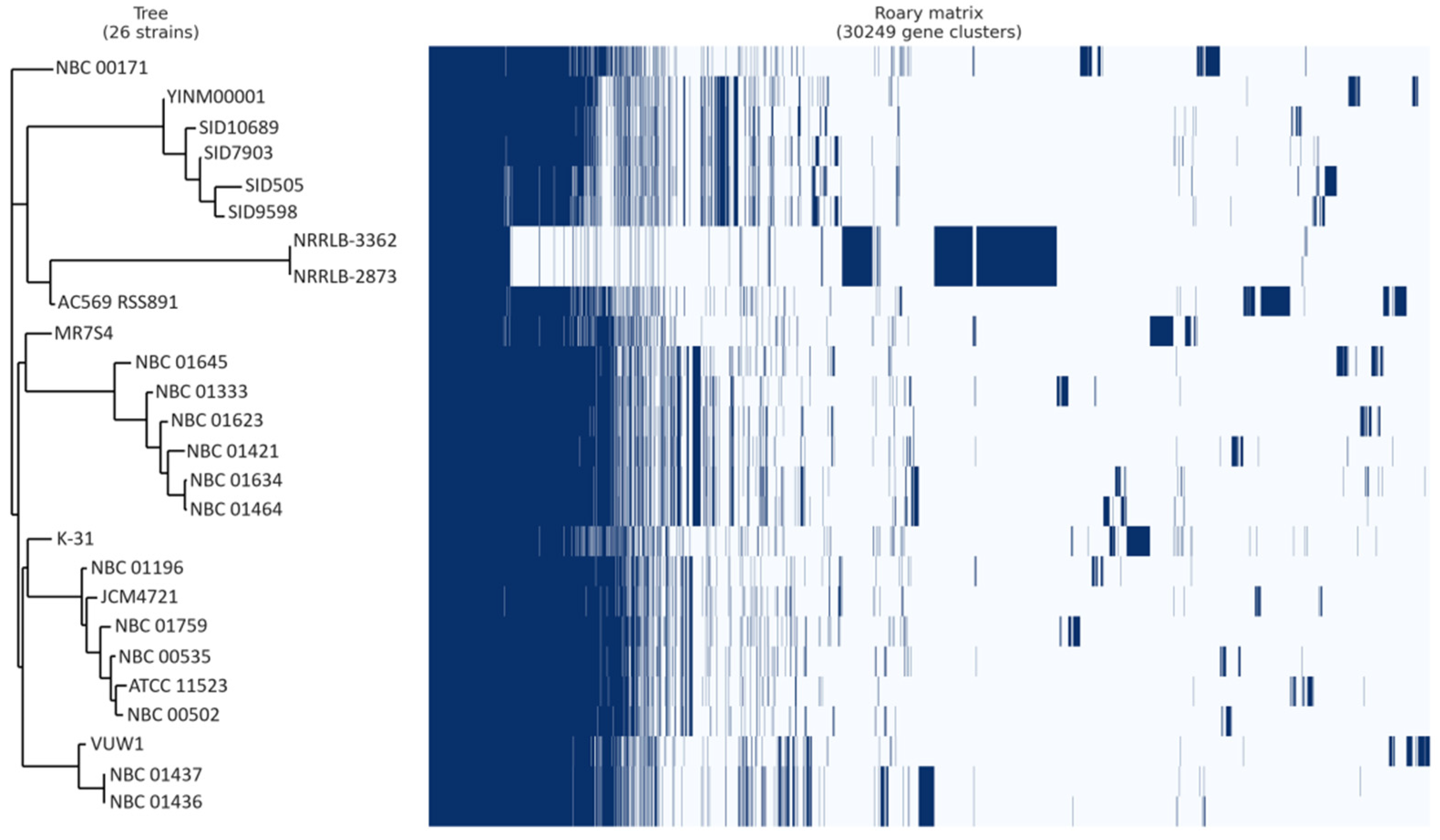
Pangenome analysis indicated that out of 30,249 genes analyzed, MR7S4 possesses 7530 genes, with 6598 genes shared with at least 1 other strain, leaving 932 genes unique to MR7S4 (Figure 5). Furthermore, pangenome analysis categorized these genes into 2265 core genes, 189 soft core genes, 7777 shell genes, and 20,018 cloud genes.
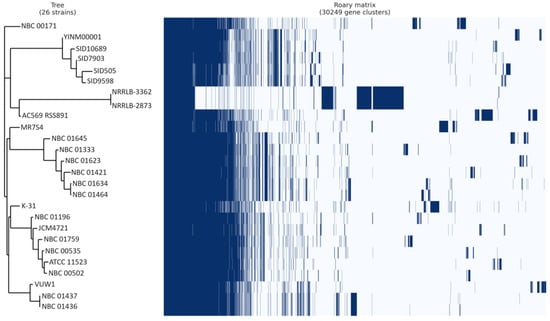
Figure 5.
Streptomyces anulatus pangenome gene matrix. Juxtaposition of a phylogenetic tree constructed based on binary presence and absence of accessory genes, with the matrix showing the absence and presence of genes in all Streptomyces anulatus strains. In the matrix, blue cells represent the presence of a gene, while white cells indicate its absence.
4. Discussion
AMR is considered one of the top 10 global public health threats by the World Health Organization (WHO), as it threatens the effectiveness of treatments for resistant infections [23]. The misuse and overuse of antibiotics have contributed to the global rise in AMR. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), AMR was responsible for 1.27 million deaths and nearly 5 million associated casualties in 2019 [24].
S. aureus, a major resistant pathogen, was initially treatable with penicillin. However, penicillin resistance started in the 1940s, and methicillin, developed in 1959, soon faced a similar issue, leading to the emergence of MRSA. The WHO continues to prioritize MRSA as a pathogen against which research and the development of new antibiotics are needed due to its global health threat [25].
In order to fight the increase in antibiotic-resistant-associated infections, new therapeutic approaches and antibacterial drugs must be developed immediately. Plants and microorganisms are rich sources for the discovery of structurally diverse NPs that inhibit microbial virulence via various modes of action. NPs derived from plants, fungi, and more importantly, bacteria, have shown activity against S. aureus standard strains and clinical isolates [26].
The genus Streptomyces is a diverse genus of Actinobacteria, which consists of more than 850 studied species, and it is a major component of soil microbiota [27]. This genus is known for its significant contribution to the discovery of bioactive NPs [28]. Such examples can be observed globally and more specifically in the MENA region [7]. For instance, a Streptomyces species called TN82 originating from Tunisian Saharan soil produced 2 compounds with activity against S. aureus. Among them, the novel 3-Phenylpyrazin-2(1H)-one inhibits the growth of S. aureus ATCC 6538 with an MIC of 4 µg/mL [29]. Thus, our findings are complementary to those from the literature and showcase the validity of MENA-derived Streptomyces sp. as generators of molecules that can combat S. aureus. Streptomyces sp. produce a wide range of SMs, with each species typically containing 20–50 BGCs [30], making them a key resource for drug discovery, and responsible for approximately 80% of all known natural antibiotics [31].
In our research, we focused on Streptomyces MR7S4, isolated from the rhizosphere of the Lebanese wild apple tree Malus trilobata [8], since the natural microflora associated with a wild relative of a major crop species are a valuable source of microbes with antimicrobial activities. Genomic analysis confirmed MR7S4 as Streptomyces anulatus, revealing unique genes and evolutionary features specific to its environment. Additionally, more than 30 BGCs were identified, some of which exhibited strain-specific diversity. As is widely recognized, Streptomyces serve as beneficial microorganisms in natural environments, as they act as beneficial partners, promoting plant growth and defending against harmful microbes [32]. Streptomyces anulatus, residing in the Malus trilobata rhizosphere, likely contributes to the tree’s adaptability through targeted antimicrobial activity, as evidenced by its anti-MRSA compound. Its diverse BGCs suggest potential roles in enhancing nutrient uptake specific to Malus trilobata needs and possibly in inducing systemic resistance against local pathogens that threaten this wild apple species.
Within the bioactive compounds isolated from MR7S4, fraction MR7S4 F3 exhibited potent anti-MRSA activity. Structural analysis revealed that it belongs to the pyrazinone family, a class of heterocyclic compounds biosynthesized through non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) pathways. The pyrazinone core is often biosynthesized from the condensation of two amino acids through an NRPS assembly line. This process entails a reduction in the ultimate step that produces dipeptide aldehyde, followed by the cyclization of imine functionality encouraged by the nucleophilic attack of the aldehyde by the α-amine of a single amino acid [33]. The pyrazinone ring is a non-aromatic heterocyclic ring with two nitrogens that are situated in parallel to each other. Unlike the aromatic pyrazine ring, which undergoes double oxidation to form the diketopiperazine ring found in many drugs, pyrazinones result from the single oxidation of one carbon atom, leading to their distinct non-aromatic heterocyclic structure. Furthermore, multiple acyclic components can be used as essential building blocks for assembling the 2(1H)-pyrazinone scaffold [34].
Pyrazinone derivatives have been widely reported in microbial secondary metabolism, exhibiting diverse bioactivities, including antibacterial, antifungal, and anticancer properties [34]. The 2(1H)-pyrazinone scaffold has been described as a crucial building block of great utility for numerous synthetic applications in drug design. Examples include favipiravir, an approved drug to target viral infections of influenza A and B [35] and Sorazinone B, produced by Sorangium cellulosum, which showed some activity against Gram-positive bacteria, particularly Nocardia sp. [36]. Moreover, Streptomyces sp. KIB-H1992 yielded two new 2(1H)-pyrazinone derivatives, 3,6-diisopropyl-5-methylpyrazin-2(1H)-one and 5(hydroxymethyl)-3,6-diisopropylpyrazin-2(1H)-one [37]. Additionally, Streptomyces sp. Did-27 isolate produced three new 2(1H)-pyrazinone derivatives, namely (S)-6-(sec-butyl)-3-isopropylpyrazin-2(1H)-one, (S)-3-(sec-butyl)-6-isopropylpyrazin- 2(1H)-one and (S)-6-(sec-butyl)-3-isobutylpyrazin-2(1H)-one, with variable cytotoxic activities against HCT-116 cancer cell lines [38]. Also, two 3,5,6-trisubstituted 2(1H)-pyrazinones, namely JBIR-56 and JBIR-57, were isolated from a culture of marine sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. SpD081030SC-03 [39]. Thus, the mode of action of a pyrazinone can vary depending on its structure and on the organism in which they are produced.
The observed potent antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive pathogens suggests that the novel compound holds promise for therapeutic applications. MRSA resists methicillin through the production of the penicillin-binding protein 2a (PBP2a), altering the structure its cell wall [5]. Despite not being beta-lactams, pyrazinones may be effective against MRSA strains due to other mechanisms. Pyrazinones may be more effective against MRSA via other mechanisms, as these compounds have a variety of biological properties, such as protease and kinase inhibition and quorum sensing activity [34]. They are implicated in the pathological mechanisms of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli, influence the production of biofilms in Vibrio cholerae, and regulate the virulence of Staphylococcus aureus [40]. Thus, in future studies, we aim to explore the mechanism of action of MR754-F3 on MRSA at its molecular endpoints. This process might rely on including resistance to this compound in MRSA followed by WGS to detect mutations in target genes.
Further development of this candidate into a drug also necessitates evaluating the compound’s stability under physiological conditions, including variations in pH, temperature, and enzymatic environments, to assess its suitability for systemic administration. Furthermore, thorough cytotoxicity assays on relevant mammalian cell lines will be performed to establish its safety profile. Finally, in vivo studies utilizing appropriate animal models are required to determine its efficacy and potential toxicity, providing crucial insights into pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. These comprehensive studies are vital for validating the therapeutic potential of this compound and ensuring its safe and effective application as a novel anti-MRSA agent.
5. Conclusions
We have successfully isolated a new anti-MRSA compound from a Streptomyces species inhabiting the rhizosphere of the Lebanese wild apple tree, Malus trilobata. Therefore, our new compound serves as a promising lead for further structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies leading to the development of novel antimicrobial agents with therapeutic potential. The Middle East and North Africa are largely unexplored regions for the development of antimicrobial drugs. Thus, more studies are required to investigate unexploited niches and the microorganisms that live in them to find novel antimicrobials.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation11040222/s1, Figure S1: 1H NMR spectrum of MR7S4-F3 in CDCl3 on a Bruker 500 MHz Ascend HD NMR. Figure S2: 13C NMR spectrum of MR7S4-F3 in CDCl3 on a Bruker 500 MHz Ascend HD NMR. Figure S3: COSY spectrum of MR7S4-F3 in CDCl3 on a Bruker 500 MHz Ascend HD NMR. Figure S4: HSQC spectrum of MR7S4-F3 in CDCl3 on a Bruker 500 MHz Ascend HD NMR. Figure S5: HMBC spectrum of MR7S4-F3 in CDCl3 on a Bruker 500 MHz Ascend HD NMR. Figure S6: MR7S4 genome completeness assessment by Busco. Figure S7: MR7S4 COG classification. Figure S8: MR7S4 ANI with Streptomyces anulatus and Streptomyces griseus reference genomes. Table S1: MICs (μg/mL) of crude extracts from MR7S4 against a panel of human pathogenic bacteria using the broth microdilution assay. Table S2: Chemical shifts for MR7S4-F3. Table S3: Physiological characteristics of MR7S4. Table S4: Biochemical characteristics of MR7S4 obtained by API 20E kit. Table S5: MR7S4 assembly statistics. Table S6: MR7S4 antiSMASH output.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.F. and M.K.A.; methodology D.A.C., B.A., G.D. and A.H.; software, D.A.C., B.A., G.D. and A.H.; validation, A.A.F. and M.K.A.; formal analysis, D.A.C., B.A. and G.D.; investigation, D.A.C., B.A. and G.D.; resources, D.A.C., B.A., G.D., A.A.F. and M.K.A.; data curation, D.A.C., B.A., G.D., A.A.F. and M.K.A.; writing—original draft preparation, D.A.C., B.A. and A.H.; writing—review and editing, G.D., A.A.F. and M.K.A.; visualization, G.D., A.A.F. and M.K.A.; supervision, A.A.F. and M.K.A.; project administration, A.A.F. and M.K.A.; funding acquisition, A.A.F. and M.K.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Council for Scientific Research of Lebanon (CNRS-L), the RESEARCH COUNCIL of Université Saint- Joseph de Beyrouth grant number FS164, and the Medical Practice Plan (MPP) at AUB/AUBMC.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable for this study.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The contig sequences associated with the genome have been deposited in GenBank and are publicly accessible under the accession number JBMGUW000000000.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the National Council for Scientific Research of Lebanon (CNRS-L) and the RESEARCH COUNCIL of Saint-Joseph University for awarding a doctoral scholarship to Dany Abi Chahine. SEM and NMR analyses were performed using equipment and facilities in the Kamal A. Shair Central Research Science Laboratory, Faculty of Arts and Sciences at the American University of Beirut.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| °C | Degree Celsius |
| A. baumannii | Acinetobacter baumannii |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| ANI | Average nucleotide identity |
| B. subtilis | Bacillus subtilis |
| BGCs | Biosynthetic gene clusters |
| BMD | Broth microdilution test |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| CFU | Colony forming unit |
| COGs | Clusters of orthologous genes |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli |
| E. faecalis | Enterococcus faecalis |
| E. faecium | Enterococcus faecium |
| FA | Formic acid |
| GC | Guanine–cytosine content |
| gDNA | Genomic DNA |
| H2O | Eau |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| ISP2 | International Streptomyces Project Medium 2 |
| ISP3 | International Streptomyces Project Medium 3 |
| K. pneumoniae | Klebsiella pneumoniae |
| M. smegmatis | Mycobacterium smegmatis |
| MENA | Middle East and North Africa |
| MHCAB | Adjusted Mueller–Hinton broth |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| mRNA | Messenger ribonucleic acid |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| NaCl | Sodium chloride |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| NPs | Natural products |
| NRPS | Non-ribosomal peptides synthetase |
| P. aeruginosa | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| PBP2a | Penicillin-binding protein 2a |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PDA | Photodiode array detector |
| pH | Potential of hydrogen |
| S. aureus | Staphylococcus aureus |
| SAR | Structure–activity relationship |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| SMs | Secondary metabolites |
| TLC | Thin liquid chromatography |
| tRNA | Transfer ribonucleic acid |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- World Health Organization. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/112642 (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Ma, F.; Xu, S.; Tang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L. Use of antimicrobials in food animals and impact of transmission of antimicrobial resistance on humans. Biosaf. Health 2021, 3, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations; Wellcome Trust: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.S.; De Lencastre, H.; Garau, J.; Kluytmans, J.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; Peschel, A.; Harbarth, S. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer. 2018, 4, 18033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhundi, S.; Zhang, K. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: Molecular Characterization, Evolution, and Epidemiology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00020-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, B.; Chahine, D.A.; Derbaj, G.; Khalek, P.A.; Awad, M.K.; Fayad, A.A. Antimicrobial Natural Products Derived from Microorganisms Inhabiting the MENA Region. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2023, 18, 1934578X2311549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, E.; Abou Fayad, A.; Karam Sarkis, D.; Fahs, H.; Gunsalus, K.C.; Kallassy Awad, M. The Microbiome of the Lebanese Wild Apple, Malus trilobata, is a Rich Source of Potential Biocontrol Agents for Fungal Post-Harvest Pathogens of Apples. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 1388–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T.R.; James, E.K.; Poole, P.S. The plant microbiome. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traxler, M.F.; Kolter, R. Natural products in soil microbe interactions and evolution. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 956–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demain, A.L.; Fang, A. The Natural Functions of Secondary Metabolites. In History of Modern Biotechnology I; Fiechter, A., Ed.; Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 69, pp. 1–39. ISBN 978-3-540-67793-2. [Google Scholar]
- Awada, B.; Hamie, M.; El Hajj, R.; Derbaj, G.; Najm, R.; Makhoul, P.; Ali, D.H.; Abou Fayad, A.G.; El Hajj, H. HAS 1: A natural product from soil-isolated Streptomyces species with potent activity against cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania tropica. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1023114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner-Mai, E.; Kroppenstedt, R.M.; Korn-Wendisch, F.; Kutzner, H.J. Morphological and biochemical characterization and emended descriptions of thermophilic actinomycetes species. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1987, 9, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.A.; Peltzer, A.; Fillinger, S.; Patel, H.; Alneberg, J.; Wilm, A.; Garcia, M.U.; Di Tommaso, P.; Nahnsen, S. The nf-core framework for community-curated bioinformatics pipelines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.E.; Lu, J.; Langmead, B. Improved metagenomic analysis with Kraken 2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasman, H.; Saputra, D.; Sicheritz-Ponten, T.; Lund, O.; Svendsen, C.A.; Frimodt-Møller, N.; Aarestrup, F.M. Rapid Whole-Genome Sequencing for Detection and Characterization of Microorganisms Directly from Clinical Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Hunt, M.; Seemann, T.; Keane, J.A. SaffronTree: Fast, reference-free pseudo-phylogenomic trees from reads or contigs. J. Open Source Softw. 2017, 2, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, L.; Glover, R.H.; Humphris, S.; Elphinstone, J.G.; Toth, I.K. Genomics and taxonomy in diagnostics for food security: Soft-rotting enterobacterial plant pathogens. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Augustijn, H.E.; Reitz, Z.L.; Biermann, F.; Alanjary, M.; Fetter, A.; Terlouw, B.R.; Metcalf, W.W.; Helfrich, E.J.N.; et al. antiSMASH 7.0: New and improved predictions for detection, regulation, chemical structures and visualisation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W46–W50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoyama, Y. COGclassifier: A Tool for Classifying Prokaryote Protein Sequences into COG Functional Category. March 2022. Available online: https://github.com/moshi4/COGclassifier (accessed on 3 July 2024).
- Carver, T.; Harris, S.R.; Berriman, M.; Parkhill, J.; McQuillan, J.A. Artemis: An integrated platform for visualization and analysis of high-throughput sequence-based experimental data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, C.; Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Phillippy, A.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T.; Aluru, S. High throughput ANI analysis of 90K prokaryotic genomes reveals clear species boundaries. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- amr-factsheet.pdf. Available online: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/antimicrobial-resistance/amr-factsheet.pdf?utm_source=chatgpt.com (accessed on 31 March 2025).
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Prioritization of Pathogens to Guide Discovery, Research and Development of New Antibiotics for Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections, Including Tuberculosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, S.-C.; Liu, F.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J.-Z. Natural Products That Target Virulence Factors in Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13195–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Mazumder, A.; Sikdar, S.; Zhao, Y.-M.; Hao, J.; Song, C.; Wang, Y.; Sarkar, R.; Islam, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Streptomyces: The biofactory of secondary metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 968053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, S.; Srinivas, V.; Prasanna, S.L. Chapter 5—Streptomyces. In Beneficial Microbes in Agro-Ecology; Amaresan, N., Senthil Kumar, M., Annapurna, K., Kumar, K., Sankaranarayanan, A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 55–71. ISBN 978-0-12-823414-3. [Google Scholar]
- El Euch, I.Z.; Frese, M.; Sewald, N.; Smaoui, S.; Shaaban, M.; Mellouli, L. Bioactive secondary metabolites from new terrestrial Streptomyces sp. TN82 strain: Isolation, structure elucidation and biological activity. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicault, M.; Zaiter, A.; Dumarcay, S.; Chaimbault, P.; Gelhaye, E.; Leblond, P.; Bontemps, C. Elicitation of Antimicrobial Active Compounds by Streptomyces-Fungus Co-Cultures. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demain, A.L. From natural products discovery to commercialization: A success story. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherdson, E.M.; Baglio, C.R.; Elliot, M.A. Streptomyces behavior and competition in the natural environment. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2023, 71, 102257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyeremeh, K.; Acquah, K.; Camas, M.; Tabudravu, J.; Houssen, W.; Deng, H.; Jaspars, M. Butrepyrazinone, a New Pyrazinone with an Unusual Methylation Pattern from a Ghanaian Verrucosispora sp. K51G. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5197–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesco-Llach, G.; Planas, M.; Feliu, L.; Joule, J.A. 2(1H)-Pyrazinones from acyclic building blocks: Methods of synthesis and further derivatizations. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 1162–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, J.; Reina, N. Favipiravir, a new concept of antiviral drug against influenza viruses. Rev. Esp. Quimioter. 2017, 30, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, R.; Sood, S.; Mohr, K.I.; Kunze, B.; Irschik, H.; Stadler, M.; Müller, R. Nannozinones and sorazinones, unprecedented pyrazinones from myxobacteria. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, S.-X. Two New 2(1H)-Pyrazinone Derivatives from the Plant Endophyte Streptomyces sp. KIB-H1992. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2020, 14, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.; Youssef, D.; Badr, J.; Harakeh, S. Bioactive 2(1H)-Pyrazinones and Diketopiperazine Alkaloids from a Tunicate-Derived Actinomycete Streptomyces sp. Molecules 2016, 21, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motohashi, K.; Inaba, K.; Fuse, S.; Doi, T.; Izumikawa, M.; Khan, S.T.; Takagi, M.; Takahashi, T.; Shin-ya, K. JBIR-56 and JBIR-57, 2(1H)-Pyrazinones from a Marine Sponge-Derived Streptomyces sp. SpD081030SC-03. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolf, J.D.; Loesgen, S. Pyrazinone Biosynthesis and Signaling─Myxo Style. ACS Cent. Sci. 2024, 10, 511–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).