Micro-Malting for the Quality Evaluation of Rye (Secale cereale) Genotypes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiment
2.1. Rye Samples
2.2. Rye Grain Quality Tests
2.3. Micro-Malting
2.4. Malt Quality Tests
2.5. Wort Quality Tests
2.6. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Statistical Interpretation
3.2. Rye Grain Quality
3.3. Rye Malt Quality Evaluation
3.3.1. Malting Loss
3.3.2. Malt Extract
3.3.3. Malt Amylolytic Enzymes
3.3.4. Wort Fermentable Sugars
3.3.5. Wort Soluble Protein Content, S/T and FAN
3.3.6. Wort Viscosity, AX and β-Glucan
3.3.7. Wort Phenolic Acids
3.4. Relationships between Rye Malt Quality Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stika, H.P. Early Iron Age and Late Mediaeval malt finds from Germany-attempts at reconstruction of early Celtic brewing and the taste of Celtic beer. Archaeol. Anthropol. Sci. 2011, 3, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, G.; Colicchio, T. The Oxford Companion to Beer; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011; ISBN 0195367138. [Google Scholar]
- Stambor, Z. Trend: Rye Beers. Available online: http://draftmag.com/rye-not/ (accessed on 28 June 2017).
- Brewers Association Presents 2017 Great American Beer Festival® Competition Style List. Descriptions and Specifications. 2017, 14–15. Available online: https://www.greatamericanbeerfestival.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/17_GABF_Beer_Style_Guidelines_Final.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2017).
- Asimov, E. All But Lost, Rye Is Revived as the Next Boutique Find. Available online: http://www.nytimes.com/2006/11/29/dining/29wine.html (accessed on 29 November 2006).
- Ralph, R. The production of American whiskies (Bourbon, Corn, Rye, Wheat and Tennessee). In The Alcohol Textbook; Jacques, K.A., Lyons, T.P., Kelsall, D.R., Eds.; Nottingham University: Nottingham, UK, 1999; p. 211. [Google Scholar]
- Bushuk, W. Rye production and uses worldwide. Cereal Foods World 2001, 46, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations Top 10 Country Production of Rye 2016. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#rankings/countries_by_commodity (accessed on 7 June 2018).
- USDA National Agricultural Statistics Service Crop Production Historical Track Records 2016, 240. Available online: http://usda.mannlib.cornell.edu/MannUsda/viewDocumentInfo.do?documentID=1593 (accessed on 7 June 2018).
- Darby, H.; Cubins, J.; Calderwood, L.; Cummings, E.; Gupta, A.; Post, J.; Ziegler, S. 2015 Cereal Rye Variety Trial; University of Vermont: Burlington, VT, USA, 2016; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel, R. Rye: Genetics, Breeding, and Cultivation; CRC Press Taylor & Fracis Group, LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; ISBN 9781466561434. [Google Scholar]
- Sorrells, M.E. 2017 Small Grains Performance Trials for New York; Cornell University: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, D. 2017 Winter Rye Field Crop Trials Results; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Bushuk, W. Rye: Production, Chemistry, and Technology, 2nd ed.; American Association Cereal Chemistry Inc.: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2001; ISBN 9780913250112. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, D. Malts and Malting; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1998; ISBN 978-0-412-29800-4. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, D.G.; Humphrey, P.M.; Boxall, J.; Smith, P.J. Brewing of Englihs-style ales with malted cereals, other than barley. Tech. Q. 1998, 35, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Pomeranz, Y.; Standridge, N.; Schreck, J.J.; Goplin, E.D. Rye in malting and brewing. Crop Sci. 1973, 13, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, F.; Schehl, B.D.; Gebruers, K.; Courtin, C.M.; Delcour, J.A.; Arendt, E.K. Influence of germination time and temperature on the properties of rye malt and rye malt based worts. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 52, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Society of Brewing Chemists. ASBC Methods of Analysis (Online), 14th Edition. Barley-2 Physical Tests (B. Bushelweight, C. Assortment, D. 1000-Kernel Weight, H. Injury by Sprout); Barley-3 Germination; Barley-5 Moisture; Malt-3 Moisture; Malt-4 Extract; Malt-6 Diastatic Power; Malt-7 Alpha-Amylas; American Society of Brewing Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-1-881696-21-6. [Google Scholar]
- Banasik, O.J.; Myhre, D.; Harris, R.H. A micro-malting method for nursery samples. I. Apparatus and development of the method. Brewer’s Dig. 1955, 31, 50–55. [Google Scholar]
- Karababa, E.; Schwarz, P.B.; Horsley, R.D. Effect of kiln schedule on micromalt quality parameters. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 1993, 51, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallett, J. Malt: A Practical Guide from Field to Brewhouse; Hertrich, J., Palmer, J., Eds.; Brewer Publication: Boulder, CO, USA, 2014; ISBN 1938469127. [Google Scholar]
- Carpita, N.; Shea, E. Linkage structure of carbohydrates by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) of partially methylated alditol acetates. In Analysis of Carbohydrates by GLC and MS; Biermann, C., McGinnis, G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Rton, FL, USA, 1989; pp. 157–216. [Google Scholar]
- Blakeney, A.B.; Harris, P.J.; Henry, R.J.; Stone, B.A. A simple and rapid preparation of alditol acetates for monosaccharide analysis. Carbohydr. Res. 1983, 113, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, M.; Ohm, J.-B.; Delcour, J.A.; Gebruers, K.; Meinhardt, S.; Simsek, S. Variability in arabinoxylan, xylanase activity, and xylanase inhibitor levels in hard spring wheat. Cereal Chem. 2013, 90, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcmurrough, I.; Roche, G.P.; Cleary, K.G. Phenolic acids in beers and worts. J. Inst. Brew. 1984, 90, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, P.B.; Li, Y.; Barr, J.; Horsley, R.D. Effect of operational parameters on the determination of laboratory extract and associated wort quality factors. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2007, 65, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerck, J.D. A Textbook of Brewing; Chapman & Hall Ltd.: London, UK, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, K.; Du, J. Effects of wheat protein content on endosperm composites and malt quality. J. Inst. Brew. 2008, 114, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadosky, P.; Schwarz, P.B.; Horsley, R.D. Effect of arabinoxylans, β-glucans, and dextrins on the viscosity and membrane filterability of a beer model solution. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2002, 60, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, P.B.; Han, J.-Y. Arabinoxylan Content of Commercial Beers. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 1995, 53, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coote, N.; Kirsop, B.H. A haze consisting largely of pentosan. J. Inst. Brew. 1976, 82, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamforth, C.W.; Russell, I.; Stewart, G. Handbook of Alcoholic Brebages—Beer: A Quality Perspective; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-12-669201-3. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhang, Z.; Speers, R.A. Enhancing the levels of 4-vinylguaiacol and 4-vinylphenol in pilot-scale top-fermented wheat beers by response surface methodology. J. Inst. Brew. 2015, 121, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]





| Rye Type | Samples/Cultivars (N) | Plump Kernels (%) | Thin Kernels (%) | 1000 Kernel Weight (g) | Protein (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Range | Mean | Range | Mean | Range | Mean | Range | ||
| Forage | 11/7 | 13.4 | 1.2–57.2 | 35.0 | 7.5–66.2 | 20.2 | 15.2–29.9 | 15.7 | 10.5–19.6 |
| Conventional Grain | 25/13 | 54.5 | 7.9–90.0 | 8.6 | 0.3–30.3 | 28.3 | 19.8–34.4 | 11.3 | 7.7–13.9 |
| Hybrid Grain | 12/12 | 70.5 | 58.3–79.0 | 2.4 | 1.4–8.5 | 30.9 | 27.1–37.7 | 8.6 | 7.6–11.3 |
| Selected for Malting | |||||||||
| Sample A | 63.1 | 8.6 1 | 28.5 | 10.9 | |||||
| Sample B | 42.1 | 4.1 1 | 28.3 | 12.7 | |||||
| Parameters | Malting Loss (%) | Extract (% Malt, db) | Diastatic Power (°ASBC) | α-Amylase (DU, db) | Wort Soluble Protein (% Malt, db) | S/T (%) | Wort FAN (mg/L) | Wort Viscosity (cP) | Wort AX (mg/L) | A/X Ratio (%) | Wort β-Glucans (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | |||||||||||
| Sample A | 11.9 a | 84.0 a | 131.8 a | 83.2 a | 8.2 a | 64.2 a | 223.0 a | 5.2 a | 3791.5 a | 85.2 a | 68.6 a |
| Sample B | 11.3 b | 87.1 b | 115.2 b | 88.6 b | 7.2 b | 65.9 b | 221.8 a | 4.5 b | 3849.2 a | 88.1 a | 59.4 b |
| Germination time | |||||||||||
| Three day | 8.6 a | 85.0 a | 117.8 a | 69.3 a | 7.5 a | 63.4 a | 217.1 a | 5.4 a | 3579.7 a | 88.9 a | 113.2 a |
| Four day | 10.4 b | 85.7 b | 121.5 ab | 80.6 b | 7.7 b | 65.2 b | 223.4 ab | 5.0 b | 4112.2 ab | 87.7 a | 66.9 b |
| Five day | 12.9 c | 85.7 b | 129.9 b | 93.5 c | 7.7 b | 65.1 c | 227.1 b | 4.6 c | 3860.1 b | 84.4 a | 43.1 c |
| Six day | 14.5 d | 85.9 b | 125.0 ab | 100.2 d | 7.9 b | 66.6 d | 222.1 ab | 4.5 c | 3729.3 b | 85.7 a | 32.9 d |
| Grain Size | |||||||||||
| Plump | 11.5 a | 85.9 a | 123.4 a | 83.2 a | 7.9 a | 67.2 a | 230.6 a | 4.8 a | 3823.3 a | 84.8 a | 63.7 a |
| Medium | 11.7 a | 85.2 b | 123.6 a | 88.6 b | 7.4 b | 62.9 b | 214.2 b | 4.9 a | 3817.4 a | 88.5 a | 64.4 a |
| Germination moisture | |||||||||||
| 40% | 5.6 a | 85.9 a | 108.2 a | 71.3 a | 7.6 a | 64.7 ab | 215.9 a | 5.4 a | 3907.2 a | 85.1 a | 136.1 a |
| 45% | 12.7 b | 84.8 a | 109.0 a | 82.8 b | 7.8 b | 66.1 b | 211.0 a | 4.8 b | 3834.2 a | 90.5 a | 40.2 b |
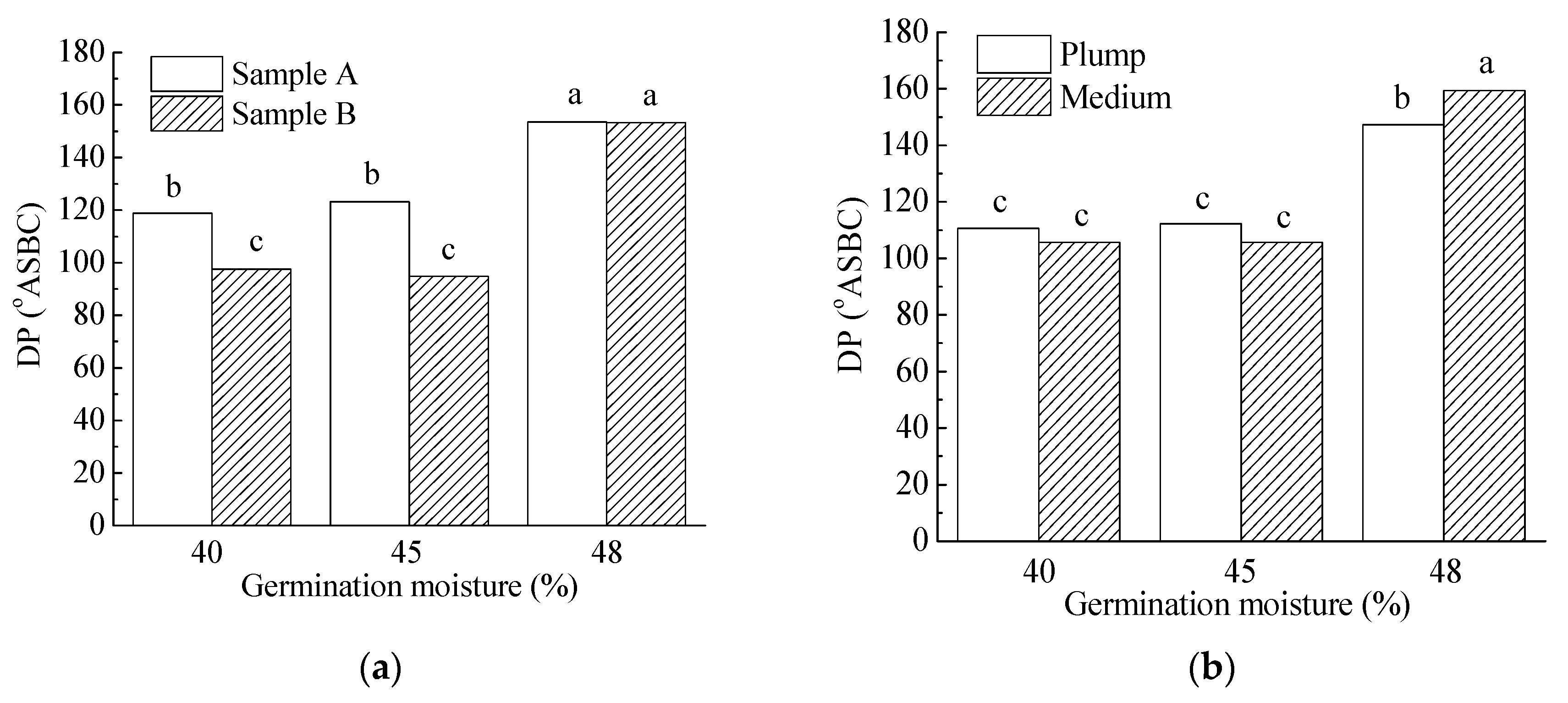
| 48% | 16.4 c | 86.1 b | 153.4 b | 103.6 c | 7.6 a | 64.3 a | 240.3 b | 4.4 c | 3719.7 a | 84.4 a | 15.7 c |
| Parameters | Fructose | Glucose | Maltose | Maltotriose | Total Fermentable Sugar |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | |||||
| Sample A | 0.1 a | 0.7 a | 3.7 a | 1.0 a | 5.5 a |
| Sample B | 0.2 b | 0.9 b | 3.8 b | 1.2 b | 6.0 b |
| Germination Time | |||||
| Three day | 0.1 a | 0.7 a | 3.8 a | 1.0 a | 5.5 a |
| Four day | 0.1 a | 0.8 b | 3.8 a | 1.1 b | 5.7 b |
| Five day | 0.1 b | 0.8 c | 3.7 ab | 1.1 c | 5.9 bc |
| Six day | 0.2 c | 0.9 d | 3.7 b | 1.2 c | 5.9 c |
| Grain Size | |||||
| Plump | 0.1 a | 0.8 a | 3.8 a | 1.1 a | 5.8 a |
| Medium | 0.1 a | 0.8 a | 3.7 b | 1.1 a | 5.7 a |
| Germination Moisture | |||||
| 40% | 0.1 a | 0.7 a | 3.8 a | 1.0 a | 5.5 a |
| 45% | 0.1 b | 0.8 b | 3.7 b | 1.1 b | 5.7 b |
| 48% | 0.2 c | 0.9 c | 3.8 a | 1.2 c | 6.1 c |
| Parameters | Caffeic Acid | Ferulic Acid | p-Coumaric Acid | Sinapinic Acid | Syringic Acid | Vanillic Acid | Gallic Acid | Catechin | Total Phenolic Acids |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | |||||||||
| Sample A | 11.0 a | 326.5 a | 10.3 a | 6.8 a | 6.5 a | 170.7 a | 22.7 a | 0.1 a | 554.9 a |
| Sample B | 17.0 b | 448.6 b | 22.1 b | 8.1 b | 7.9 b | 257.4 b | 10.3 b | 0.1 a | 770.5 b |
| Germination Time | |||||||||
| Three day | 11.5 a | 323.8 a | 12.2 a | 6.8 a | 6.6 a | 183.2 a | 23.3 a | 0.0 a | 567.3 a |
| Four day | 12.3 a | 340.1 a | 13.4 a | 6.6 a | 7.0 ab | 190.2 a | 17.7 ab | 0.1 a | 587.4 a |
| Five day | 15.3 b | 426.1 b | 17.6 b | 7.0 a | 8.0 bc | 245.3 b | 17.0 ab | 0.1 a | 736.4 b |
| Six day | 16.8 b | 460.3 b | 21.7 b | 7.1 a | 8.3 c | 237.5 b | 8.1 b | 0.1 a | 759.8 b |
| Grain Size | |||||||||
| Plump | 13.6 a | 367.0 a | 13.4 a | 6.6 a | 7.5 a | 186.6 a | 21.1 a | 0.1 a | 615.8 a |
| Medium | 14.4 a | 408.2 b | 19.0 b | 7.1 b | 7.5 a | 241.6 b | 12.0 a | 0.1 a | 709.7 b |
| Moisture | |||||||||
| 40% | 13.4 a | 384.0 a | 12.8 a | 6.6 a | 7.6 a | 256.7 a | 24.0 a | 0.2 a | 704.8 a |
| 45% | 12.1 a | 328.6 b | 11.0 a | 6.5 a | 6.0 b | 183.2 b | 9.1 b | 0.0 b | 556.6 b |
| 48% | 16.4 b | 450.0 c | 24.9 b | 7.5 b | 8.9 c | 202.7 b | 16.4 ab | 0.1 b | 726.8 a |
| Factor | α-Amylase | Diastatic Power | Extract | Wort Viscosity | Wort Soluble Protein | S/T | Wort FAN | Wort β-Glucan | Wort AX | Wort A/X |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malting loss | 0.84 *** | 0.63 *** | 0.04 | −0.56 *** | 0.12 | 0.06 | 0.39 *** | −0.87 *** | −0.10 | −0.04 |
| α-Amylase | 1 | 0.60 *** | 0.23 * | −0.77 *** | −0.01 | 0.10 | 0.33 *** | −0.83 *** | −0.06 | 0.00 |
| Diastatic Power | 1 | −0.07 | −0.22 * | 0.06 | −0.25 * | 0.49 *** | −0.48 *** | −0.10 | −0.22 * | |
| Extract | 1 | −0.22 * | −0.07 | 0.44 *** | 0.42 *** | −0.11 | 0.16 | 0.00 | ||
| Wort Viscosity | 1 | 0.15 | −0.25 * | −0.18 | 0.76 *** | 0.02 | −0.01 | |||
| Wort Soluble Protein | 1 | 0.66 *** | 0.14 | −0.11 | −0.02 | 0.14 | ||||
| Kolbach Index | 1 | 0.13 | −0.18 | 0.02 | 0.25 * | |||||
| Wort FAN | 1 | −0.39 *** | 0.07 | −0.26 * | ||||||
| Wort β-Glucan | 1 | 0.03 | 0.01 | |||||||
| Wort AX | 1 | −0.43 *** | ||||||||
| A/X | 1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Jin, Z.; Barr, J.; Gillespie, J.; Simsek, S.; Horsley, R.D.; Schwarz, P.B. Micro-Malting for the Quality Evaluation of Rye (Secale cereale) Genotypes. Fermentation 2018, 4, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4030050
Wang Y, Jin Z, Barr J, Gillespie J, Simsek S, Horsley RD, Schwarz PB. Micro-Malting for the Quality Evaluation of Rye (Secale cereale) Genotypes. Fermentation. 2018; 4(3):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4030050
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yujuan, Zhao Jin, John Barr, James Gillespie, Senay Simsek, Richard D. Horsley, and Paul B. Schwarz. 2018. "Micro-Malting for the Quality Evaluation of Rye (Secale cereale) Genotypes" Fermentation 4, no. 3: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4030050
APA StyleWang, Y., Jin, Z., Barr, J., Gillespie, J., Simsek, S., Horsley, R. D., & Schwarz, P. B. (2018). Micro-Malting for the Quality Evaluation of Rye (Secale cereale) Genotypes. Fermentation, 4(3), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation4030050





