Low-Cost Methods to Assess Beer Quality Using Artificial Intelligence Involving Robotics, an Electronic Nose, and Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Description
2.2. Electronic Nose (E-Nose)
2.3. Sensory: Consumer Acceptance Test
2.4. Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
2.5. Physical Parameters
2.6. Statistical Analysis and Machine-Learning Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Multivariate Data Analysis
3.2. Machine-Learning Modeling
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationships between E-Nose and Physicochemical Analysis
4.2. Artificial Intelligence Applied to Beer Quality Assessment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gasiński, A.; Kawa-Rygielska, J.; Szumny, A.; Czubaszek, A.; Gąsior, J.; Pietrzak, W. Volatile Compounds Content, Physicochemical Parameters, and Antioxidant Activity of Beers with Addition of Mango Fruit (Mangifera Indica). Molecules 2020, 25, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasiński, A.; Kawa-Rygielska, J.; Szumny, A.; Gąsior, J.; Głowacki, A. Assessment of Volatiles and Polyphenol Content, Physicochemical Parameters and Antioxidant Activity in Beers with Dotted Hawthorn (Crataegus punctata). Foods 2020, 9, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawa-Rygielska, J.; Adamenko, K.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Prorok, P.; Piórecki, N. Physicochemical and antioxidative properties of Cornelian cherry beer. Food Chem. 2019, 281, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Bi, H.; Yin, H.; Yu, J.; Dong, J.; Yang, M.; Ma, Y. Influence of ultrasound assisted thermal processing on the physicochemical and sensorial properties of beer. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, I.M.C.; Neto, J.D.M.; Figueiredo, R.W.; Carvalho, J.D.G.; Figueiredo, E.A.T.D.; Menezes, N.V.S.D.; Gaban, S.V.F. Physicochemical characterization, antioxidant activity, and sensory analysis of beers brewed with cashew peduncle (Anacardium occidentale) and orange peel (Citrus sinensis). Food Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prestes, D.N.; Spessato, A.; Talhamento, A.; Gularte, M.A.; Schirmer, M.A.; Vanier, N.L.; Rombaldi, C.V. The addition of defatted rice bran to malted rice improves the quality of rice beer. LWT 2019, 112, 108262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Vegara, S.; Martí, N.; Valero, M.; Saura, D. Physicochemical characterization of special persimmon fruit beers using bohemian pilsner malt as a base. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humia, B.V.; Santos, K.S.; Schneider, J.K.; Leal, I.L.; de Abreu Barreto, G.; Batista, T.; Machado, B.A.S.; Druzian, J.I.; Krause, L.C.; da Costa Mendonça, M. Physicochemical and sensory profile of Beauregard sweet potato beer. Food Chem. 2020, 312, 126087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, S.-A.; Lee, S.-J. Physicochemical and sensory characteristics of commercial top-fermented beers. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 49, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viejo, C.G.; Fuentes, S.; Howell, K.; Torrico, D.; Dunshea, F. Integration of non-invasive biometrics with sensory analysis techniques to assess acceptability of beer by consumers. Physiol. Behav. 2019, 200, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H.; Bleibaum, R.; Thomas, H.A. Sensory Evaluation Practices; Elsevier/Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kemp, S.; Hollowood, T.; Hort, J. Sensory Evaluation: A Practical Handbook; Wiley: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Viejo, C.G.; Fuentes, S.; Li, G.; Collmann, R.; Condé, B.; Torrico, D. Development of a robotic pourer constructed with ubiquitous materials, open hardware and sensors to assess beer foam quality using computer vision and pattern recognition algorithms: RoboBEER. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condé, B.C.; Fuentes, S.; Caron, M.; Xiao, D.; Collmann, R.; Howell, K.S. Development of a robotic and computer vision method to assess foam quality in sparkling wines. Food Control 2017, 71, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vann, L.; Layfield, J.B.; Sheppard, J.D. The application of near-infrared spectroscopy in beer fermentation for online monitoring of critical process parameters and their integration into a novel feedforward control strategy. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viejo, C.G.; Caboche, C.H.; Kerr, E.D.; Pegg, C.L.; Schulz, B.L.; Howell, K.; Fuentes, S. Development of a Rapid Method to Assess Beer Foamability Based on Relative Protein Content Using RoboBEER and Machine Learning Modeling. Beverages 2020, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viejo, C.G.; Fuentes, S.; Torrico, D.; Howell, K.; Dunshea, F.R. Assessment of beer quality based on foamability and chemical composition using computer vision algorithms, near infrared spectroscopy and machine learning algorithms. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viejo, C.G.; Fuentes, S. A Digital Approach to Model Quality and Sensory Traits of Beers Fermented under Sonication Based on Chemical Fingerprinting. Fermentation 2020, 6, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Torrico, D.D.; Dunshea, F.R.; Fuentes, S. Emerging Technologies Based on Artificial Intelligence to Assess the Quality and Consumer Preference of Beverages. Beverages 2019, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viejo, C.G.; Fuentes, S.; Godbole, A.; Widdicombe, B.; Unnithan, R.R. Development of a low-cost e-nose to assess aroma profiles: An artificial intelligence application to assess beer quality. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 127688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viejo, C.G.; Fuentes, S. Beer Aroma and Quality Traits Assessment Using Artificial Intelligence. Fermentation 2020, 6, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thazin, Y.; Pobkrut, T.; Kerdcharoen, T. Prediction of acidity levels of fresh roasted coffees using e-nose and artificial neural network. In Proceedings of the 2018 10th International Conference on Knowledge and Smart Technology (KST), Chiangmai, Thailand, 31 January–3 February 2018; pp. 210–215. [Google Scholar]
- Romani, S.; Cevoli, C.; Fabbri, A.; Alessandrini, L.; Rosa, M.D. Evaluation of coffee roasting degree by using electronic nose and artificial neural network for off-line quality control. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, C960–C965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Gao, L.; Wang, J. Classification and regression of ELM, LVQ and SVM for E-nose data of strawberry juice. J. Food Eng. 2015, 144, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Z.; Lin, H.; Zhao, D.-A. Discrimination of green tea quality using the electronic nose technique and the human panel test, comparison of linear and nonlinear classification tools. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 159, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.; Hines, E.; Gardner, J.; Kashwan, K.; Bhuyan, M. Tea quality prediction using a tin oxide-based electronic nose: An artificial intelligence approach. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 94, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, S.; Summerson, V.; Viejo, C.G.; Tongson, E.; Lipovetzky, N.; Wilkinson, K.L.; Szeto, C.; Unnithan, R.R. Assessment of Smoke Contamination in Grapevine Berries and Taint in Wines Due to Bushfires Using a Low-Cost E-Nose and an Artificial Intelligence Approach. Sensors 2020, 20, 5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías, M.; Agudo, J.; Manso, A.; Orellana, C.; Velasco, H.; Caballero, R. A compact and low cost electronic nose for aroma detection. Sensors 2013, 13, 5528–5541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Shi, Y.; Fu, S.; Jiao, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, J. Mining Feature of Data Fusion in the Classification of Beer Flavor Information Using E-Tongue and E-Nose. Sensors 2017, 17, 1656. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi-Varnamkhasti, M.; Mohtasebi, S.S.; Siadat, M.; Lozano, J.; Ahmadi, H.; Razavi, S.H.; Dicko, A. Aging fingerprint characterization of beer using electronic nose. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 159, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornpanomchai, C.; Suthamsmai, N. Beer classification by electronic nose. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Wavelet Analysis and Pattern Recognition, Hong Kong, China, 30–31 August 2008; pp. 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Wojnowski, W.; Majchrzak, T.; Dymerski, T.; Gębicki, J.; Namieśnik, J. Electronic noses: Powerful tools in meat quality assessment. Meat Sci. 2017, 131, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnowski, W.; Majchrzak, T.; Dymerski, T.; Gębicki, J.; Namieśnik, J. Portable electronic nose based on electrochemical sensors for food quality assessment. Sensors 2017, 17, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deisingh, A.K.; Stone, D.C.; Thompson, M. Applications of electronic noses and tongues in food analysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutfi, A.; Coradeschi, S.; Mani, G.K.; Shankar, P.; Rayappan, J.B.B. Electronic noses for food quality: A review. J. Food Eng. 2015, 144, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, J. Use of electronic nose technology for identifying rice infestation by Nilaparvata lugens. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 160, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yu, J.; Pei, F.; Mariga, A.M.; Ma, N.; Fang, Y.; Hu, Q. Effect of hot air drying on volatile compounds of Flammulina velutipes detected by HS-SPME–GC–MS and electronic nose. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rosa, A.R.; Leone, F.; Cheli, F.; Chiofalo, V. Fusion of electronic nose, electronic tongue and computer vision for animal source food authentication and quality assessment—A review. J. Food Eng. 2017, 210, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiger, K. zNose Series. Available online: https://www.cbrnetechindex.com/Print/4362/electronic-sensor-technology-inc/znose-series (accessed on 26 October 2020).
- Men, H.; Shi, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Gong, F.; Liu, J. Electronic nose sensors data feature mining: A synergetic strategy for the classification of beer. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 2016–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Gong, F.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Men, H. A deep feature mining method of electronic nose sensor data for identifying beer olfactory information. J. Food Eng. 2019, 263, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimsuk, N. Improvement of accuracy in beer classification using transient features for electronic nose technology. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, M.; Adebiyi, A.; Fasoli, A.; Mannari, A.; Labby, R.; Bozano, L. Model Comparison of Beer data classification using an electronic nose. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual Conference, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 26 April–1 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Quarto, A.; Soldo, D.; Di Lecce, F.; Giove, A.; Di Lecce, V.; Castronovo, A. Electronic nose for evaluating water use in beer production. In Proceedings of the 2017 ISOCS/IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose (ISOEN), Montreal, QC, Canada, 28–31 May 2017; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Sànchez, C.; Lozano, J.; PedroSantos, J.; Azabal, A.; Ruiz-Valdepeñas, S. Discrimination of aromas in beer with electronic nose. In Proceedings of the 2018 Spanish Conference on Electron Devices (CDE), Salamanca, Spain, 14–16 November 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Voss, H.G.J.; Mendes Júnior, J.J.A.; Farinelli, M.E.; Stevan, S.L. A Prototype to Detect the Alcohol Content of Beers Based on an Electronic Nose. Sensors 2019, 19, 2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, S.; Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Torrico, D.; Dunshea, F. Development of a biosensory computer application to assess physiological and emotional responses from sensory panelists. Sensors 2018, 18, 2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, K.; Jain, M.; Salhi, S. Logistics, Supply Chain and Financial Predictive Analytics: Theory and Practices; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Delcour, J.A.; Hoseney, R.C. Principles of Cereal Science and Technology; AACC International: Eagan, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Viejo, C.G.; Fuentes, S.; Torrico, D.; Howell, K.; Dunshea, F. Assessment of Beer Quality Based on a Robotic Pourer, Computer Vision, and Machine Learning Algorithms Using Commercial Beers. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viejo, C.G.; Fuentes, S.; Howell, K.; Torrico, D.; Dunshea, F.R. Robotics and computer vision techniques combined with non-invasive consumer biometrics to assess quality traits from beer foamability using machine learning: A potential for artificial intelligence applications. Food Control 2018, 92, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perozzi, C.; Beaune, H. The Naked Brewer: Fearless Homebrewing Tips, Tricks & Rule-breaking Recipes; Penguin Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Perozzi, C.; Beaune, H. The Naked Pint: An Unadulterated Guide to Craft Beer; Penguin Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- De Keukeleire, D. Fundamentals of beer and hop chemistry. Quim. Nova 2000, 23, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.; Howard, G. The production of hydrogen sulphide by yeast and by Zymomonas anaerobia. J. Inst. Brew. 1974, 80, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Bamforth, C.W. The microbiology of malting and brewing. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, G.G. The production of secondary metabolites with flavour potential during brewing and distilling wort fermentations. Fermentation 2017, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeytilakarathna, P.; Fonseka, R.; Eswara, J.; Wijethunga, K. Relationship between total solid content and red, green and blue colour intensity of strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch.) fruits. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 8, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badui, S. Química de los Alimentos; Pearson Education: Naucalpan de Juarez, México, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Yao, C.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y. Quality grade identification of green tea using E-nose by CA and ANN. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 41, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Violino, S.; Figorilli, S.; Costa, C.; Pallottino, F. Internet of Beer: A Review on Smart Technologies from Mash to Pint. Foods 2020, 9, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patelli, N.; Mandrioli, M. Blockchain technology and traceability in the agrifood industry. J. Food Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiloglu, S. Authenticity and traceability in beverages. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
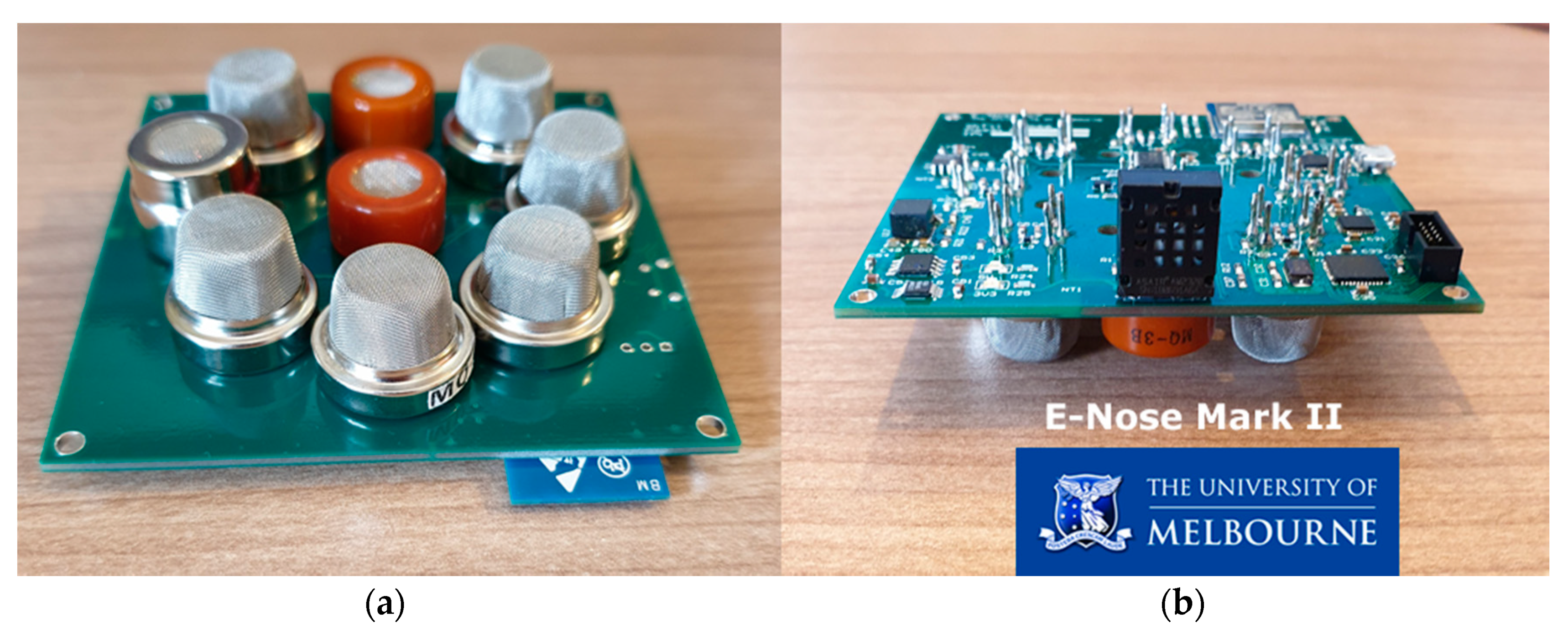




| Sensor (Gas) * | Label/Model | Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|
| Alcohol | MQ3 | 0.5–10 mg L−1 |
| Methane | MQ4 | 200–10,000 ppm |
| Carbon monoxide | MQ7 | 20–2000 ppm |
| Hydrogen | MQ8 | 100–10,000 ppm |
| Ammonia/Alcohol/Benzene | MQ135 | 10–300 ppm/10–300 ppm/10–1000 ppm |
| Hydrogen Sulfide | MQ136 | 1–100 ppm |
| Ammonia | MQ137 | 5–200 ppm |
| Benzene/Alcohol/Ammonia | MQ138 | 10–1000 ppm/10–1000 ppm/10–3000 ppm |
| Carbon dioxide | MG811 | 350–10,000 ppm |
| Attribute | Label | Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Carbonation Mouthfeel | Mcarb | 9-point hedonic |
| Bitterness | Tbitter | 9-point hedonic |
| Aroma | Aroma Liking | 9-point hedonic |
| Flavor | Flavor Liking | 9-point hedonic |
| Overall Liking | Overall Liking | 9-point hedonic |
| Parameter | Label |
|---|---|
| Maximum volume of foam | MaxVol |
| Total lifetime of foam | TLTF |
| Lifetime of foam | LTF |
| Foam drainage | FDrain |
| Color lab scale | L, a and b |
| Color RGB scale | R, G, and B |
| Small bubbles | SmBubb |
| Medium bubbles | MedBubb |
| Large bubbles | LgBubb |
| Stage | Samples | Accuracy | Error | Performance (MSE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | 36 | 100% | 0% | <0.01 |
| Validation | 12 | 92% | 8% | 0.10 |
| Testing | 12 | 92% | 8% | 0.10 |
| Overall | 60 | 97% | 3% | N/A |
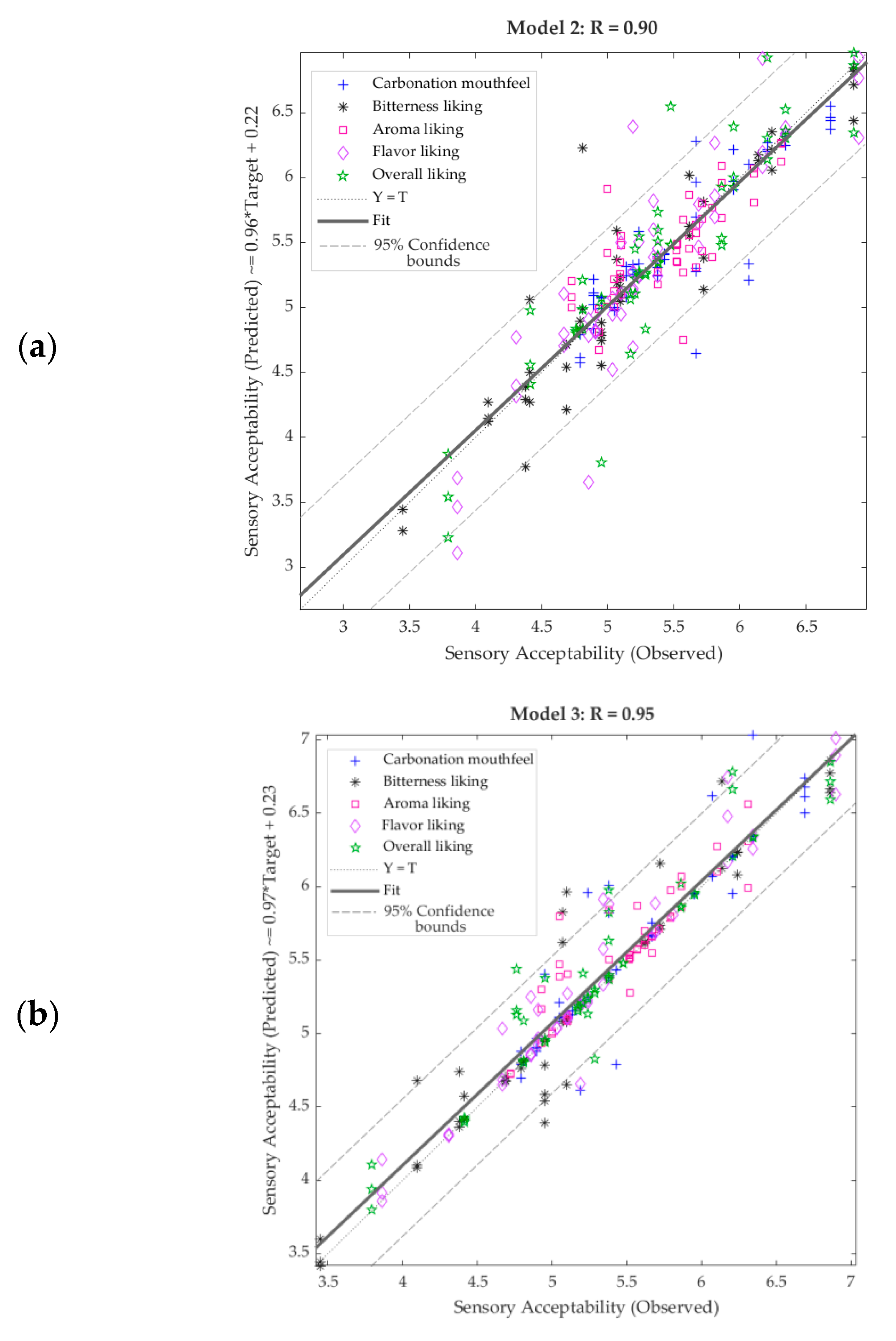
| Stage | Samples | Observations | R | Slope | Performance (MSE) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 2 (Near-infrared inputs/Sensory targets) | |||||
| Training | 36 | 180 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.02 |
| Validation | 12 | 60 | 0.87 | 0.85 | 0.12 |
| Testing | 12 | 60 | 0.80 | 1.00 | 0.30 |
| Overall | 60 | 300 | 0.90 | 0.96 | N/A |
| Model 3 (Electronic nose inputs/Sensory targets) | |||||
| Training | 36 | 180 | 0.99 | 1.00 | <0.01 |
| Validation | 12 | 60 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.15 |
| Testing | 12 | 60 | 0.85 | 0.94 | 0.13 |
| Overall | 60 | 300 | 0.95 | 0.97 | N/A |
| Model 3 (Electronic nose inputs/RoboBEER targets) | |||||
| Training | 36 | 468 | 0.98 | 0.93 | 0.02 |
| Validation | 12 | 156 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.10 |
| Testing | 12 | 156 | 0.82 | 0.87 | 0.20 |
| Overall | 60 | 780 | 0.93 | 0.89 | N/A |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonzalez Viejo, C.; Fuentes, S. Low-Cost Methods to Assess Beer Quality Using Artificial Intelligence Involving Robotics, an Electronic Nose, and Machine Learning. Fermentation 2020, 6, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6040104
Gonzalez Viejo C, Fuentes S. Low-Cost Methods to Assess Beer Quality Using Artificial Intelligence Involving Robotics, an Electronic Nose, and Machine Learning. Fermentation. 2020; 6(4):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6040104
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzalez Viejo, Claudia, and Sigfredo Fuentes. 2020. "Low-Cost Methods to Assess Beer Quality Using Artificial Intelligence Involving Robotics, an Electronic Nose, and Machine Learning" Fermentation 6, no. 4: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6040104
APA StyleGonzalez Viejo, C., & Fuentes, S. (2020). Low-Cost Methods to Assess Beer Quality Using Artificial Intelligence Involving Robotics, an Electronic Nose, and Machine Learning. Fermentation, 6(4), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6040104






