Impact of Media Heat Treatment on Cell Morphology and Stability of L. acidophilus, L. johnsonii and L. delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii during Fermentation and Processing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Culture Media
2.3. Culture Conditions
2.4. Sample Preparation for Freeze Drying and Storage Conditions
2.5. Determination of the Total Cell Concentration and Cell Volume Distribution
2.6. Determination of Cell Viability via Colony Forming Units
2.7. Determination of Cell Viability via Flow Cytometry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Media Heat Treatment on the Growth Characteristics of Three Sensitive Lactobacilli
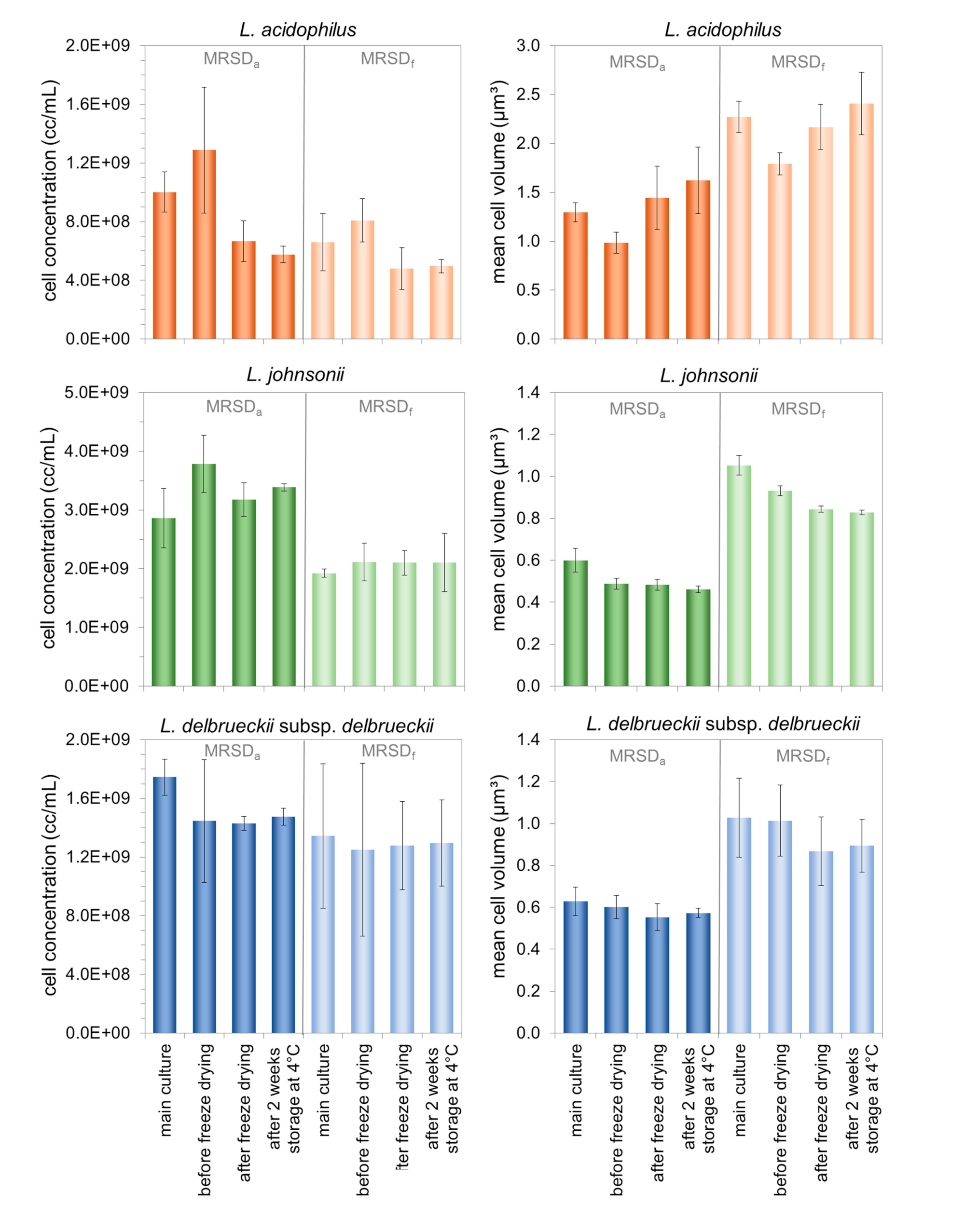
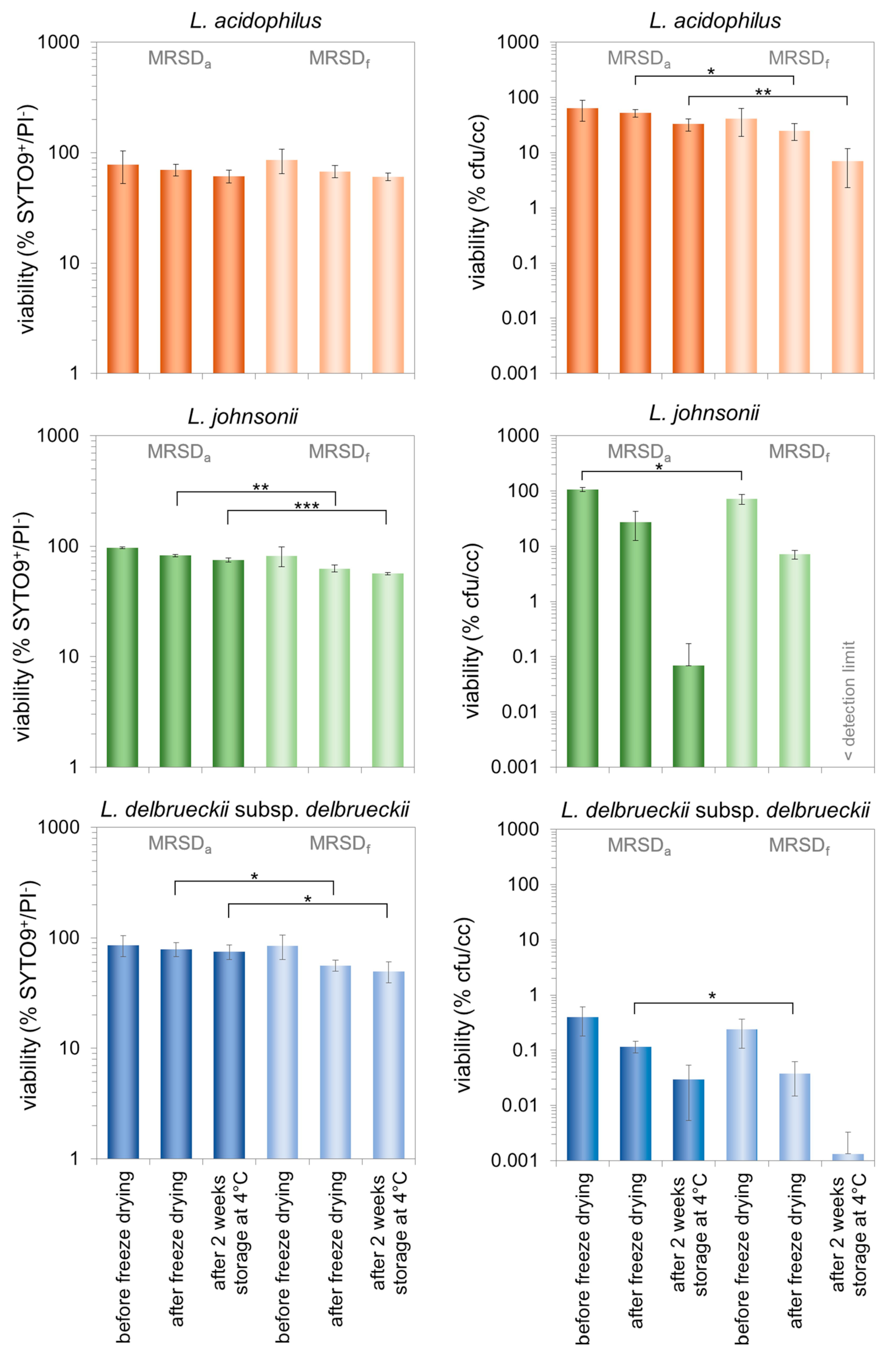
3.2. Characterization of Morphologically Different Populations of the Three Lactobacilli during the Production of Freeze-Dried Preparations and Subsequent Storage
4. Discussion
4.1. Relation between Media Preparation and Growth Characteristics of L. acidophilus, L. johnsonii and L. delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii
4.2. Effect of the Cell Properties Induced by the Growth Medium on the Stability Properties of the Three Investigated Lactobacilli
4.3. The Role of the Viability Assessment for the Process Evaluation
4.4. Practical Relevance of the Identified Relations between Growth Medium and Cell Properties
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Harris, H.M.B.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bintsis, T. Lactic acid bacteria: Their applications in foods. JBMOA 2018, 6, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanders, M.E.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Invited review: The scientific basis of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM functionality as a probiotic. J. Dairy Sci. 2001, 84, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, M.E.; Merenstein, D.J.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Rastall, R.A. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: From biology to the clinic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, M.; Plummer, S.; Marchesi, J.; Mahenthiralingam, E. The life history of Lactobacillus acidophilus as a probiotic: A tale of revisionary taxonomy, misidentification and commercial success. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2013, 349, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, P.; Fares, C.; Longo, A.; Spano, G.; Capozzi, V. Lactobacillus plantarum with broad antifungal activity as a protective starter culture for bread production. Foods 2017, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Man, J.C.; Rogosa, M.; Sharpe, M. A medium for the cultivation of lactobacilli. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1960, 23, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W.-R. Melanoidins produced by the Maillard reaction: Structure and biological activity. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helou, C.; Marier, D.; Jacolot, P.; Abdennebi-Najar, L.; Niquet-Léridon, C.; Tessier, F.J.; Gadonna-Widehem, P. Microorganisms and Maillard reaction products: A review of the literature and recent findings. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, D.; Peterson, R. Influence of the amino acid-dextrose reaction on growth of lactic acid bacteria. Can. J. Res. 1949, 27, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Matsuo, H.; Deguchi, T.; Shiga, A.; Samejima, H. Growth-promoting factors for Lactobacillus bifidus var. pennsylvanicus produced by the Amino-Carbonyl Reaction of l -Lysine and d -Glucose. Agric. Biol. Chem. 2014, 32, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senz, M.; van Lengerich, B.; Bader, J.; Stahl, U. Control of cell morphology of probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus for enhanced cell stability during industrial processing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 192, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senz, M.; Keil, C.; Schmacht, M.; Palinski, S.; Cämmerer, B.; Hageböck, M. Influence of media heat sterilization process on growth performance of representative strains of the genus Lactobacillus. Fermentation 2019, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Einarsson, H.; Eklund, T.; Nes, I. Inhibitory mechanisms of Maillard reaction products. Microbios 1988, 53, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ames, J.M.; Wynne, A.; Hofmann, A.; Plos, S.; Gibson, G.R. The effect of a model melanoidin mixture on faecal bacterial populations in vitro. Brit. J. Nutr. 1999, 82, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rurián-Henares, J.A.; Morales, F.J. Antimicrobial activity of melanoidins against Escherichia coli is mediated by a membrane-damage mechanism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2357–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hauser, C.; Müller, U.; Sauer, T.; Augner, K.; Pischetsrieder, M. Maillard reaction products as antimicrobial components for packaging films. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deibel, R.H.; Downing, M.; Niven, C.F., Jr.; Schweigert, B.S. Filament formation by Lactobacillus leichmannii when desoxyribosides replace vitamin B12 in the growth medium. J. Bacteriol. 1956, 71, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beck, W.S.; Hook, S.; Barnett, B.H. The metabolic functions of vitamin B12: Distinctive modes of unbalanced growth behavior in Lactobacillus leichmannii. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1962, 55, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, I.; Kitahara, K. Effect of several vitamins on the cell division and the growth of Lactobacillus delbrueckii. J. Vitaminol. 1962, 8, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeener, H.; Jeener, R. Cytological study of Thermobacterium acidophilus R 26 cultured in absence of deoxyribonucleosides or uracil. Exp. Cell Res. 1952, 3, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, W.S.; Levin, M. Purification, kinetics, and repression control of bacterial trans-N-deoxyribosylase. J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ives, D.H.; Ikeda, S. Life on the salvage path: Deoxynucleoside kinases of Lactobacillus acidophilus R-26. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1997, 59, 205–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, S.; Schmacht, M.; Malchow, S.; Wolff, L.; Senz, M. Preparation of freeze dried and vacuum dried yeast starter cultures: Evaluation of relevant viability detection analyses. Brew. Sci. 2020, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt-Jovin, D.J.; Jovin, T.M. Fluorescence Labeling and Microscopy of DNA. In Fluorescence Microscopy of Living Cells in Culture Part B. Quantitative Fluorescence Microscopy—Imaging and Spectroscopy; Taylor, D.L., Wang, Y.-L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 417–448. ISBN 9780080859286. [Google Scholar]
- Bringel, F.; Hubert, J.-C. Extent of genetic lesions of the arginine and pyrimidine biosynthetic pathways in Lactobacillus plantarum, L. paraplantarum, L. pentosus, and L. casei: Prevalence of CO(2)-dependent auxotrophs and characterization of deficient arg genes in L. plantarum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 2674–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siedler, A.J.; Nayder, F.A.; Schweigert, B.S. Studies on improvements in the medium for Lactobacillus acidophilus in the assay for deoxyribonucleic acid. J. Bacteriol. 1957, 73, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reich, J.; Soska, J. Thymineless death in Lactobacillus acidophilus R-26. II. Factors determining the rate of the reproductive inactivation. Folia Microbiol. 1973, 18, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, A.-C.; Hill, N.S.; Levin, P.A. Cell size control in bacteria. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R340–R349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parlindungan, E.; Dekiwadia, C.; Tran Khanh, T.M.; Jones, O.A.H.; May, B.K. Morphological and ultrastructural changes in Lactobacillus plantarum B21 as an indicator of nutrient stress. LWT 2018, 92, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, A.; Boran, B.; Bekers, K.M. Ohly White Paper, Impact of Nucleotides on L. bulgaricus Growth, Viability and Performance; Ohly GmbH: Hamburg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Aschenbrenner, M.; Först, P.; Kulozik, U. Freeze-Drying of Probiotics. In Advances in Probiotic Technology, 1st ed.; Foerst, P., Santivarangkna, C., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto-Shinohara, Y.; Nozawa, F.; Sukenobe, J.; Imaizumi, T. Survival of yeasts stored after freeze-drying or liquid-drying. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 56, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, A.S.; Silva, J.; Ho, P.; Teixeira, P.; Malcata, F.X.; Gibbs, P. Protective effect of sorbitol and monosodium glutamate during storage of freeze-dried lactic acid bacteria. Lait 2003, 83, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, F.; Béal, C.; Corrieu, G. Method of quantifying the loss of acidification activity of lactic acid starters during freezing and frozen storage. J. Dairy Res. 2000, 67, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur, P. The Role of Intracellular Freezing in the Death of Cells Cooled at Supraoptimal Rates. Cryobiology 1977, 14, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patapoff, T.W.; Overcashier, D.E. The importance of freezing on Lyophilization cycle development. BioPharm 2002, 15, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Santivarangkna, C.; Higl, B.; Foerst, P. Protection mechanisms of sugars during different stages of preparation process of dried lactic acid starter cultures. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.C.; Stanton, C.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Daly, C.; Ross, R.P. Anhydrobiotics: The challenges of drying probiotic cultures. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 1406–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santivarangkna, C.; Kulozik, U.; Foerst, P. Storing Lactic Acid Bacteria: Current Methodologies and Physiological Implications. In Stress Response in Lactic Acid Bacteria; Tsakalidou, E., Papadimitriou, K., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA; London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, M.G. Flow cytometry as a potential method of measuring bacterial viability in probiotic products: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 78, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, H.M. Life, death, and in-between: Meanings and methods in microbiology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5571–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Deng, Y.; Soteyome, T.; Li, Y.; Su, J.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Shirtliff, M.E.; Xu, Z.; Peters, B.M. Induction and recovery of the viable but nonculturable state of hop-resistance Lactobacillus brevis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshkova, D.M.; Simova, E.D.; Frengova, G.I.; Simov, Z.; Spasov, Z.N. Effect of oxygen on batch yogurt cultures. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 18, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, G.I.; Minahk, C.J.; Font de Valdez, G.; Morero, R. Effects of protective agents on membrane fluidity of freeze-dried Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneghel, J.; Passot, S.; Dupont, S.; Fonseca, F. Biophysical characterization of the Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus membrane during cold and osmotic stress and its relevance for cryopreservation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, M.C.; Espeche, M.C.; Nader-Macías, M.E. Optimization of the freeze-drying media and survival throughout storage of freeze-dried Lactobacillus gasseri and Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii for veterinarian probiotic applications. Proc. Biochem. 2007, 42, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajab, S.; Tabandeh, F.; Shahraky, M.K.; Alahyaribeik, S. The effect of lactobacillus cell size on its probiotic characteristics. Anaerobe 2020, 62, 102103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ummadi, M.S.; Bawden-Curic, M. Use of Protein Hydrolysates in Industrial Starter Culture Fermentations. In Protein Hydrolysates in Biotechnology; Pasupuleti, V.K., Demain, A.L., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; London, UK, 2010; pp. 91–114. [Google Scholar]
- Proust, L.; Sourabié, A.; Pedersen, M.; Besançon, I.; Haudebourg, E.; Monnet, V.; Juillard, V. Insights into the complexity of yeast extract peptides and their utilization by Streptococcus thermophilus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ludszuweit, M.; Schmacht, M.; Keil, C.; Haase, H.; Senz, M. Impact of Media Heat Treatment on Cell Morphology and Stability of L. acidophilus, L. johnsonii and L. delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii during Fermentation and Processing. Fermentation 2020, 6, 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6040094
Ludszuweit M, Schmacht M, Keil C, Haase H, Senz M. Impact of Media Heat Treatment on Cell Morphology and Stability of L. acidophilus, L. johnsonii and L. delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii during Fermentation and Processing. Fermentation. 2020; 6(4):94. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6040094
Chicago/Turabian StyleLudszuweit, Marie, Maximilian Schmacht, Claudia Keil, Hajo Haase, and Martin Senz. 2020. "Impact of Media Heat Treatment on Cell Morphology and Stability of L. acidophilus, L. johnsonii and L. delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii during Fermentation and Processing" Fermentation 6, no. 4: 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6040094
APA StyleLudszuweit, M., Schmacht, M., Keil, C., Haase, H., & Senz, M. (2020). Impact of Media Heat Treatment on Cell Morphology and Stability of L. acidophilus, L. johnsonii and L. delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii during Fermentation and Processing. Fermentation, 6(4), 94. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation6040094






