Metagenomic Analysis of Bacterial Diversity in Traditional Fermented Foods Reveals Food-Specific Dominance of Specific Bacterial Taxa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Food Samples
2.2. Proximate Compositional Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and Amplicon Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics and Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Proximate Compositional Analysis
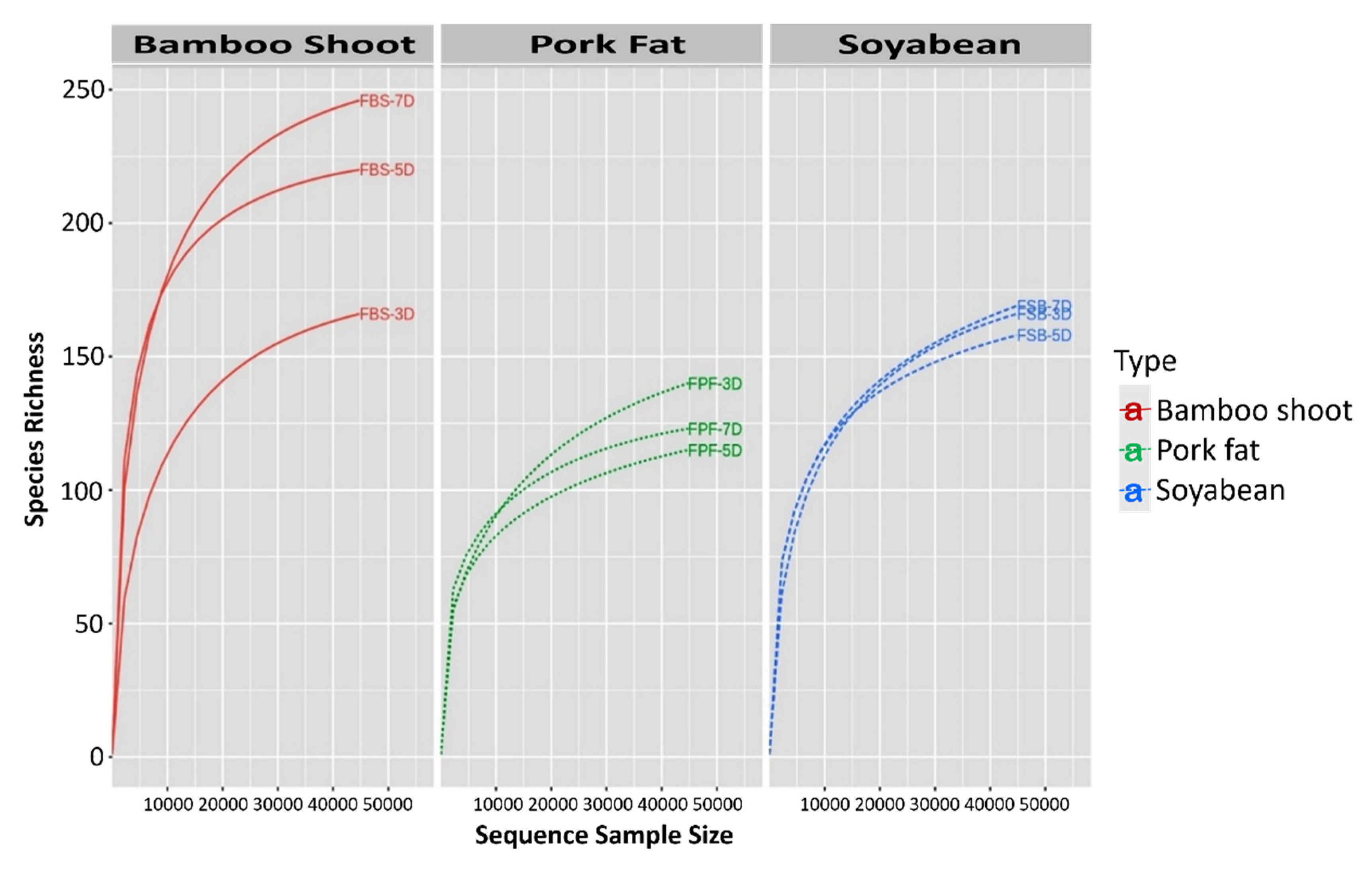
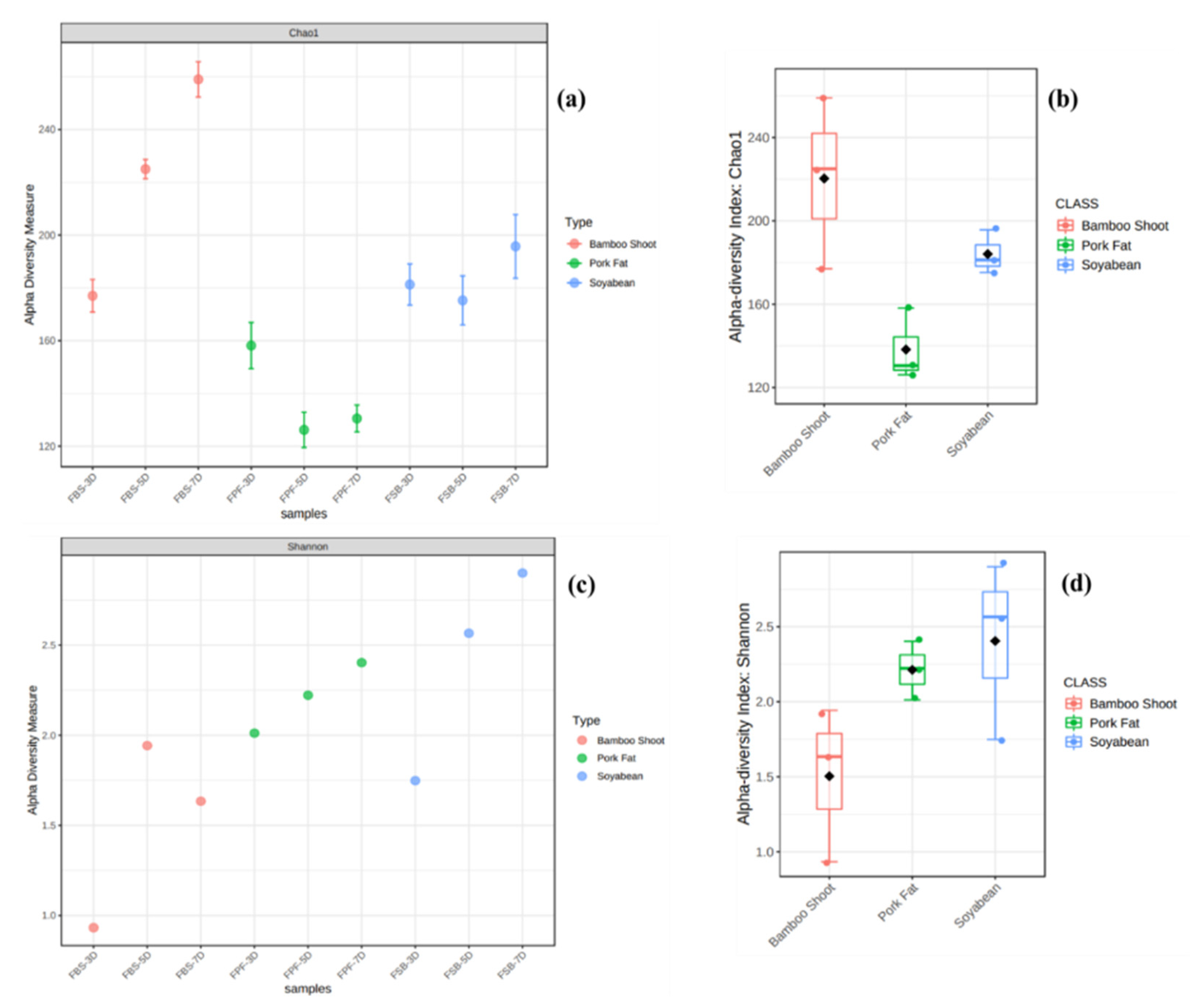
3.2. Bacterial Diversity
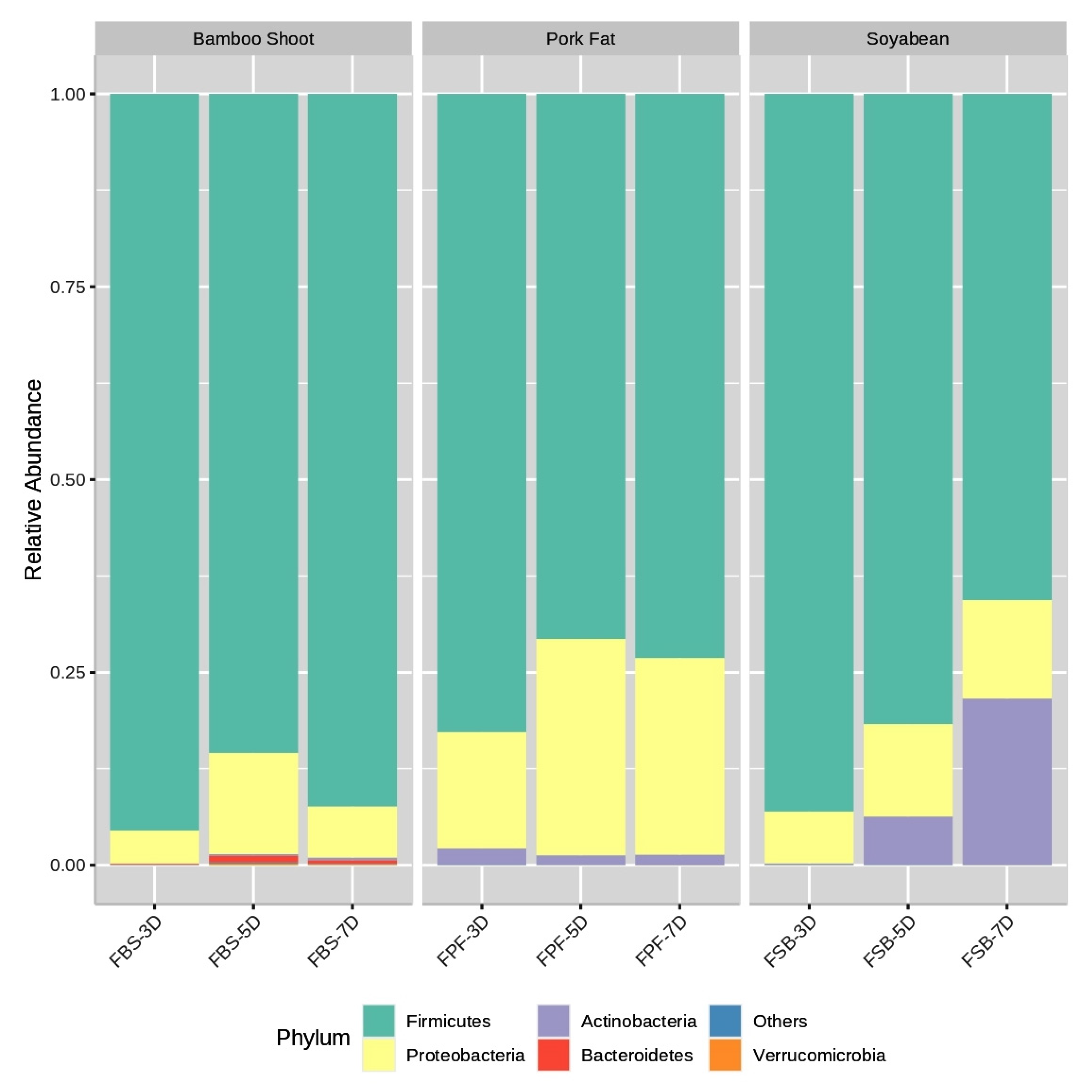
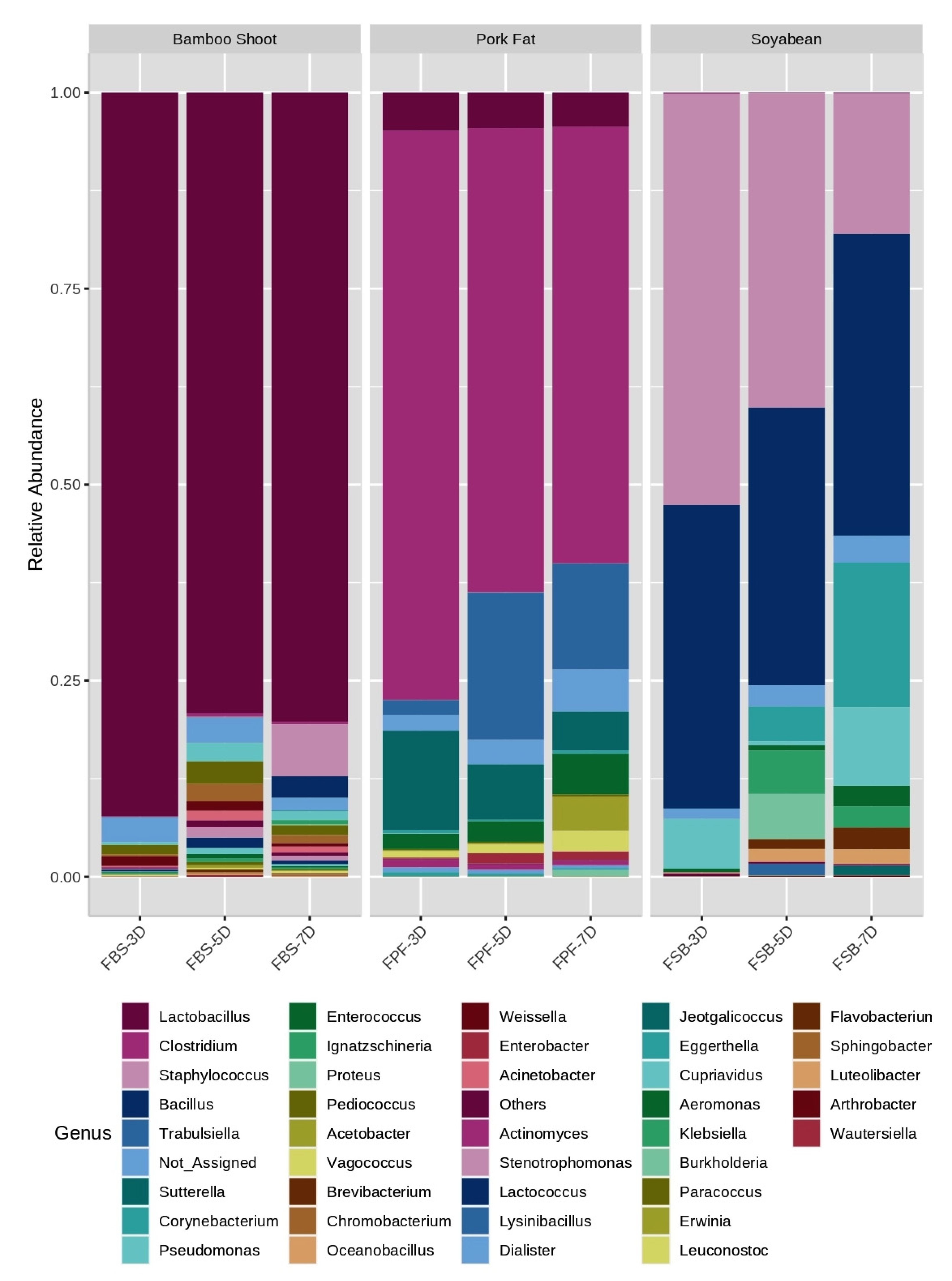
3.3. Bacterial Community Composition
3.4. Comparison of Bacterial Communities during the Fermentation Process
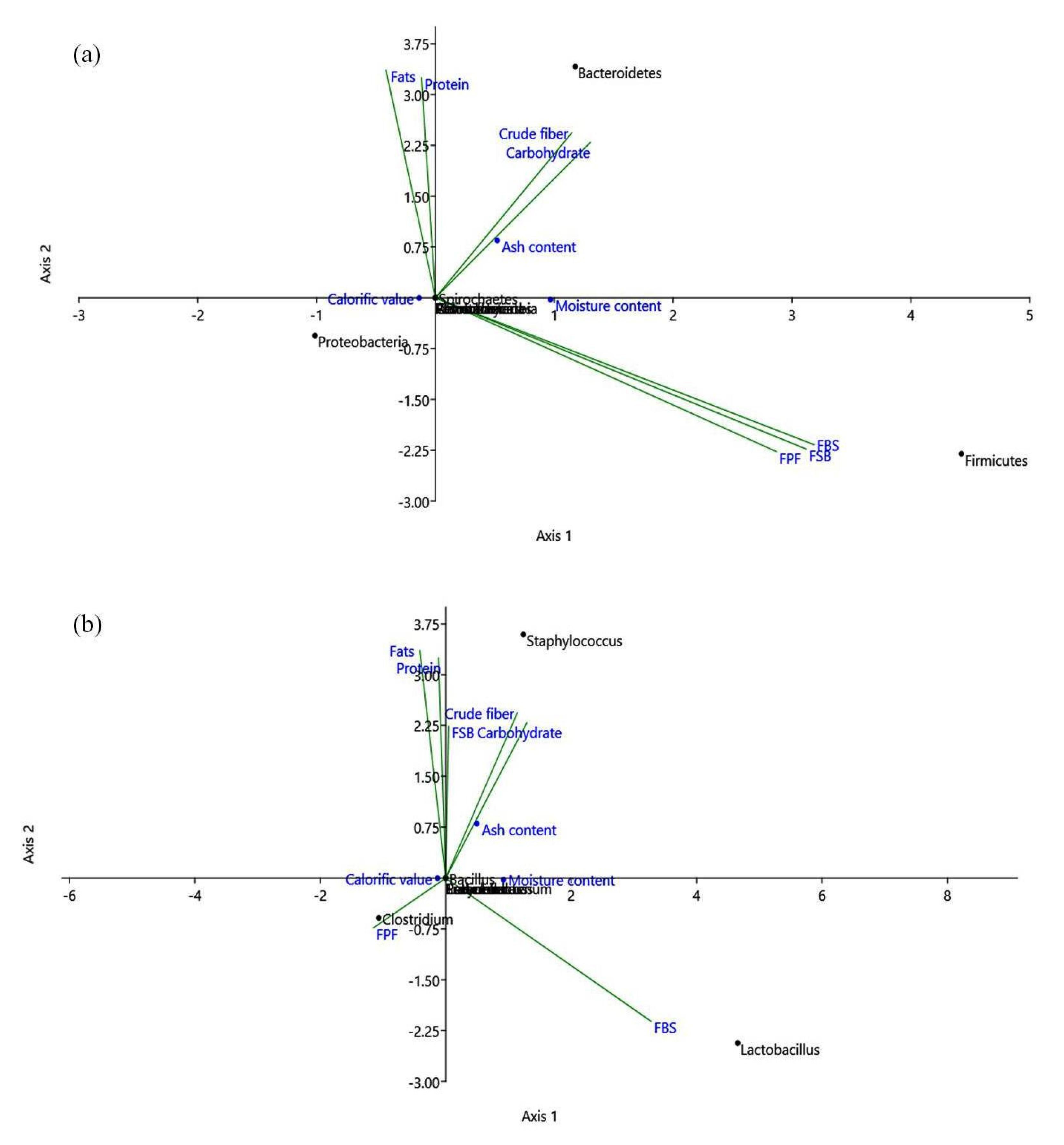
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Nutritional Parameters with Bacterial Diversity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsafrakidou, P.; Michaelidou, A.M.; Biliaderis, C.G. Fermented Cereal-based Products: Nutritional Aspects, Possible Impact on Gut Microbiota and Health Implications. Foods 2020, 9, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathara, J.M.; Schillinger, U.; Kutima, P.M.; Mbugua, S.K.; Holzapfel, W.H. Isolation, identification and characterization of the dominant microorganisms of kulenaoto: The Maasai traditional fermented milk in Kenya. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokoena, M.P.; Mutanda, T.; Olaniran, A.O. Perspectives on the probiotic potential of lactic acid bacteria from African traditional fermented foods and beverages. Food Nutr. Res. 2016, 60, 29630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplice, E.; Fitzgerald, G.F. Food fermentations: Role of microorganisms in food production and preservation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 50, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestri, G.; Santarelli, S.; Aquilanti, L.; Beccaceci, A.; Osimani, A.; Tonucci, F.; Clementi, F. Investigation of the microbial ecology of Ciauscolo, a traditional Italian salami, by culture-dependent techniques and PCR-DGGE. Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.E.; Park, M.H.; Chang, H.C.; Kim, H.Y. Analysis of microbial communities in doenjang, a Korean fermented soybean paste, using nested PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 131, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, N.; Tanaka, S.; Sonomoto, K.; Nakayama, J. 16S rRNApyrosequencing-based investigation of the bacterial community in nukadoko, a pickling bed of fermented rice bran. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 144, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehetre, G.T.; Paranjpe, A.S.; Dastager, S.G.; Dharne, M.S. Complete metagenome sequencing based bacterial diversity and functional insights from basaltic hot spring of Unkeshwar, Maharashtra, India. Genom. Data 2016, 7, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Fanning, S.; Proos, S.; Jordan, K.; Srikumar, S. A review on the applications of next generation sequencing technologies as applied to food-related microbiome studies. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.M.; Park, M.S.; Bae, J.W.; Hahn, Y.; Madsen, E.L.; Jeon, C.O. Metagenomic analysis of Kimchi, a traditional Korean fermented food. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2264–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalbantoglu, U.; Caker, A.; Dogan, H.; Abaci, N.; Ustek, D.; Sayood, K.; Can, H. Metagenomic analysis of the microbial community in kefir grains. Food Microbiol. 2014, 41, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, L. Metagenomic sequencing reveals the relationship between microbiota composition and quality of Chinese Rice Wine. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, J.P.; Tamanag, B.; Schillinger, U.; Guigas, C.; Holzapfel, W.H. Functional properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from ethnic fermented vegetables of the Himalayas. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2009, 135, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nongdam, P. Traditional fermented bamboo shoot foods of North-East India and their characteristics natural microbial flora. In Proceedings of the 10th World Bamboo Congress, Damyeng, Korea, 17–22 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lalthanpui, P.B.; Lalruatfela, B.; Zoramdinthara; Lalthanzara, H. Traditional food processing techniques of the Mizo people of Northeast India. Sci. Viss. 2015, 15, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Marco, M.L.; Heeney, D.; Binda, S.; Cifelli, C.J.; Cotter, P.D.; Foligné, B.; Gänzle, M.; Kort, R.; Pasin, G.; Pihlanto, A.; et al. Health benefits of fermented foods: Microbiota and beyond. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.J.; Deka, S.C. Fermented foods and beverages of the North-East India. Int. Food Res. J. 2012, 19, 377. [Google Scholar]
- Rawat, K.; Kumari, A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, R.; Gehlot, R. Traditional fermented products of India. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2018, 7, 1873–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, J.P.; Tamang, N.; Thapa, S.; Dewan, S.; Tamang, B.; Yonzan, H.; Rai, A.K.; Chettri, R.; Chakrabarty, J.; Kharel, N. Microorganisms and nutritional value of ethnic fermented foods and alcoholic beverages of North East India. Indian J. Trad. Know. 2012, 11, 7–25. [Google Scholar]
- Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC). Official Methods of Analysis, 20th ed.; AOAC International: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.K.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhariwal, A.; Chong, J.; Habib, S.; King, I.L.; Agellon, L.B.; Xia, J. Microbiome Analyst: A web-based tool for comprehensive statistical, visual and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2017, 45, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, D.H.; Tyson, G.W.; Hugenholtz, P.; Beiko, R.G. STAMP: Statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3123–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, O.; Harper, D.A.T.; Ryan, P. PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol. Electron. 2001, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters, R.F. Fermentation microorganisms and flavor changes in fermented foods. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, 2002–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Garg, P.; Kumar, P.; Bhatia, S.K.; Kulshrestha, S. Microbial fermentation and its role in quality improvement of fermented foods. Fermentation 2020, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anal, A.K. Quality ingredients and safety concerns for traditional fermented foods and beverages from Asia: A Review. Fermentation 2019, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Y.; Wang, H.; Kong, B.H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q. The succession and correlation of the bacterial community and flavour characteristics of Harbin dry sausages during fermentation. LWT 2021, 138, 110689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugula, J.K.; Narvhus, J.A.; Sørhaug, T. Use of starter cultures of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts in the preparation of togwa, a Tanzanian fermented food. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 83, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.D.; Singh, S.A.; Singh, N.R.; Singh, R. Biochemical composition of Soibum-A fermented bamboo shoot and its dynamics during fermentation in real time model. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Food Engineering and Biotechnology, Bangkok, Thailand, 28–29 May 2011; Volume 9, pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, W.; Tang, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhao, X.; Guo, Z.; Shan, C. Bacterial diversity and flavor profile of Zha-Chili, a traditional fermented food in China. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, X.; Ji, C.; Li, S.; Liang, H. Effects of different temperatures on bacterial diversity and volatile flavor compounds during the fermentation of suancai, a traditional fermented vegetable food from northeastern China. LWT 2020, 118, 108773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonar, N.R.; Halami, P.M. Phenotypic identification and technological attributes of native lactic acid bacteria present in fermented bamboo shoot products from North-East India. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 4143–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badwaik, L.S.; Borah, P.K.; Deka, S.C. Production and Purification of Anti-Bacterial Biometabolite from Wild-Type Lactobacillus, Isolated from Fermented Bamboo Shoot: Future Suggestions and a Proposed System for Secondary Metabolite Onsite Recovery during Continuous Fermentation. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiles, M.E.; Holzapfel, W.H. Lactic acid bacteria of foods and their current taxonomy. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1997, 36, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; von Wright, A.; Ouwehand, A. Lactic Acid Bacteria: Microbiological and Functional Aspects, 3rd ed.; CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar, R.K.; Gupta, S. Isolation, identification and characterization of Staphylococcus sp. from Indian ethnic fermented fish product. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 71, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, F.; Shah, A.A.; Javed, S.; Hameed, A. Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2006, 39, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, S.; Lee, J.H.; Jeong, D.W. Food-derived coagulase-negative Staphylococcus as starter cultures for fermented foods. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetsch, A.; Johler, S. Staphylococcus aureus as a foodborne pathogen. Curr. Clin. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 5, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, M.; Baldi, A. Selective identification and characterization of potential probiotic strains: A review on comprehensive polyphasic approach. Appl. Clin. Res. Clin. Trials Regul. Aff. 2017, 4, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keisam, S.; Tuikhar, N.; Ahmed, G.; Jeyaram, K. Toxigenic and pathogenic potential of enteric bacterial pathogens prevalent in the traditional fermented foods marketed in the Northeast region of India. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 296, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, J.; Xu, Y.; Xia, W.; Yu, D.; Gao, P.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, F. Dynamics and diversity of microbial community succession during fermentation of Suanyu, a Chinese traditional fermented fish, determined by high throughput sequencing. Food Res. Intern. 2018, 111, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adesulu-Dahunsi, A.T.; Sanni, A.I.; Jeyaram, K. Rapid differentiation among Lactobacillus, Pediococcus and Weissella species from some Nigerian indigenous fermented foods. LWT 2017, 77, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Adesulu-Dahunsi, A.T.; Sanni, A.I.; Jeyaram, K. Diversity and technological characterization of Pediococcuspentosaceus strains isolated from Nigerian traditional fermented foods. LWT 2021, 140, 110697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamang, J.P.; Watanabe, K.; Holzapfel, W.H. Diversity of microorganisms in global fermented foods and beverages. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.; Huang, J.; Wu, X.; Fan, J.; Xu, Y.; Wu, C.; Jin, Y.; Zhou, R. Effect of raw material and starters on the metabolite constituents and microbial community diversity of fermented soy sauce. J. Sci. Food Agri. 2019, 99, 5687–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, J.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Walsh, A.M.; Macori, G.; Walsh, C.J.; Barton, W.; Finnegan, L.; Crispie, F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Claesson, M.J.; et al. Fermented-Food Metagenomics Reveals Substrate-Associated Differences in Taxonomy and Health-Associated and Antibiotic Resistance Determinants. Msystems 2020, 5, e00522-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.Y.; Chai, L.J.; Zhong, X.Z.; Jiang, Y.J. Deciphering the succession patterns of bacterial community and their correlations with environmental factors and flavor compounds during the fermentation of Zhejiang rosy vinegar. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 341, 109070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, E.; Zotta, T.; Faust, K.; De Filippis, F.; Ercolini, D. Structure of association networks in food bacterial communities. Food Microbiol. 2018, 73, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Proximate Parameters (Weight in %) | Fermented Food Samples | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tuaither | Bekang | Sa-um | |||||||
| 3rd D | 5th D | 7th D | 3rd D | 5th D | 7th D | 3rd D | 5th D | 7th D | |
| Moisture content | 86.8 | 86.4 | 87.6 | 58.3 | 57.1 | 56.4 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 2.5 |
| Total ash content | 1.1 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 2.7 | 2.5 | 1.1 | - | - | - |
| Fat | 1.1 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 4.6 | 5.3 | 5.4 | 90.6 | 94.6 | 95.6 |
| Protein | 2.7 | 3.0 | 2.8 | 19.7 | 19.9 | 18.5 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.5 |
| Crude fiber | 3.1 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 10.6 | 2.4 | 2.5 | - | - | - |
| Carbohydrate | 5.2 | 6.5 | 7.9 | 4.1 | 12.8 | 16.2 | 4.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Calorific value (K cals/100 gm) | 3.97 | 4.19 | 3.98 | 7.20 | 8.36 | 8.23 | 5.89 | 3.99 | 4.04 |
| Fermented Bamboo Shoot (FBS) | |||
| Genus | FBS-3D | FBS-5D | FBS-7D |
| Lactobacillus sp. | 91.64 | 77.16 | 78.88 |
| Weissella sp. | 1.27 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Pediococcus sp. | 1.17 | 2.80 | 0.0 |
| Pseudomonas sp. | 0.36 | 2.24 | 1.25 |
| Chromobacterium sp. | 0.27 | 2.29 | 0.0 |
| Acinetobacter sp. | 0.0 | 1.35 | 1.14 |
| Corynebacterium sp. | 0.0 | 0.0 | 6.58 |
| Sphingobacterium sp. | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.74 |
| Unclassified | 3.13 | 2.28 | 2.27 |
| Others | 1.86 | 11.58 | 7.11 |
| Fermented Pork Fats (FPF) | |||
| Genus | FPF-3D | FPF-5D | FPF-7D |
| Clostridium sp. | 72.48 | 59.48 | 55.40 |
| Sutterella sp. | 12.54 | 7.01 | 4.85 |
| Lactobacillus sp. | 4.81 | 4.44 | 4.41 |
| Enterococcus sp. | 1.92 | 2.67 | 5.28 |
| Trabulsiella sp. | 1.81 | 18.45 | 13.36 |
| Unclassified sp. | 2.07 | 3.26 | 5.24 |
| Others | 3.17 | 4.67 | 11.43 |
| Fermented Soybean (FSB) | |||
| Genus | FSB-3D | FSB-5D | FSB-7D |
| Staphylococcus sp. | 52.36 | 39.48 | 17.90 |
| Bacillus sp. | 38.47 | 35.56 | 37.87 |
| Pseudomonas sp. | 6.40 | 0.0 | 9.67 |
| Enterococcus sp. | 0.47 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Paenibacillus sp. | 0.19 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Proteus sp. | 0.0 | 5.89 | 0.0 |
| Ignatzschineria sp. | 0.0 | 5.49 | 0.0 |
| Corynebacterium sp. | 0.0 | 4.35 | 18.13 |
| Brevibacterium sp. | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.77 |
| Unclassified | 1.12 | 2.98 | 3.61 |
| Others | 0.95 | 6.23 | 10.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deka, P.; Mehetre, G.T.; Lalnunmawii, E.; Upadhyaya, K.; Singh, G.; Hashem, A.; Al-Arjani, A.-B.F.; Fathi Abd_Allah, E.; Singh, B.P. Metagenomic Analysis of Bacterial Diversity in Traditional Fermented Foods Reveals Food-Specific Dominance of Specific Bacterial Taxa. Fermentation 2021, 7, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030167
Deka P, Mehetre GT, Lalnunmawii E, Upadhyaya K, Singh G, Hashem A, Al-Arjani A-BF, Fathi Abd_Allah E, Singh BP. Metagenomic Analysis of Bacterial Diversity in Traditional Fermented Foods Reveals Food-Specific Dominance of Specific Bacterial Taxa. Fermentation. 2021; 7(3):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030167
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeka, Purbajyoti, Gajanan T. Mehetre, Esther Lalnunmawii, Kalidas Upadhyaya, Garima Singh, Abeer Hashem, Al-Bandari Fahad Al-Arjani, Elsayed Fathi Abd_Allah, and Bhim Pratap Singh. 2021. "Metagenomic Analysis of Bacterial Diversity in Traditional Fermented Foods Reveals Food-Specific Dominance of Specific Bacterial Taxa" Fermentation 7, no. 3: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030167
APA StyleDeka, P., Mehetre, G. T., Lalnunmawii, E., Upadhyaya, K., Singh, G., Hashem, A., Al-Arjani, A.-B. F., Fathi Abd_Allah, E., & Singh, B. P. (2021). Metagenomic Analysis of Bacterial Diversity in Traditional Fermented Foods Reveals Food-Specific Dominance of Specific Bacterial Taxa. Fermentation, 7(3), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030167







