Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Bacillus subtilis and Aspergillus niger in Black Soldier Fly Co-Fermentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Larval Rearing Conditions
2.2. Strains and Kits
2.3. Orthogonal Design of Co-Fermentation
2.4. Protein Extraction
2.5. Mass Spectrometry and Data Analysis
2.6. Product Detection
- W—fatty acid amount, (mg/kg):
- C—concentration of fatty acid methyl ester in the sample, mg/L:
- V—volume, mL:
- k—conversion ratio from fatty acid methyl ester to fatty acid
- N—dilution ratio:
- m—sample weight, (g)
2.7. True Protein Detection
- X—true protein concentration, g/100 g
- V1—standard HCl volume, mL
- V2—control group standard HCl volume, mL
- V3—volume of digestive fluid, mL
- c—concentration of standard HCl, mol/L
- m—sample weight, g
- F—conversion factor between N and protein.
3. Results and Discussion
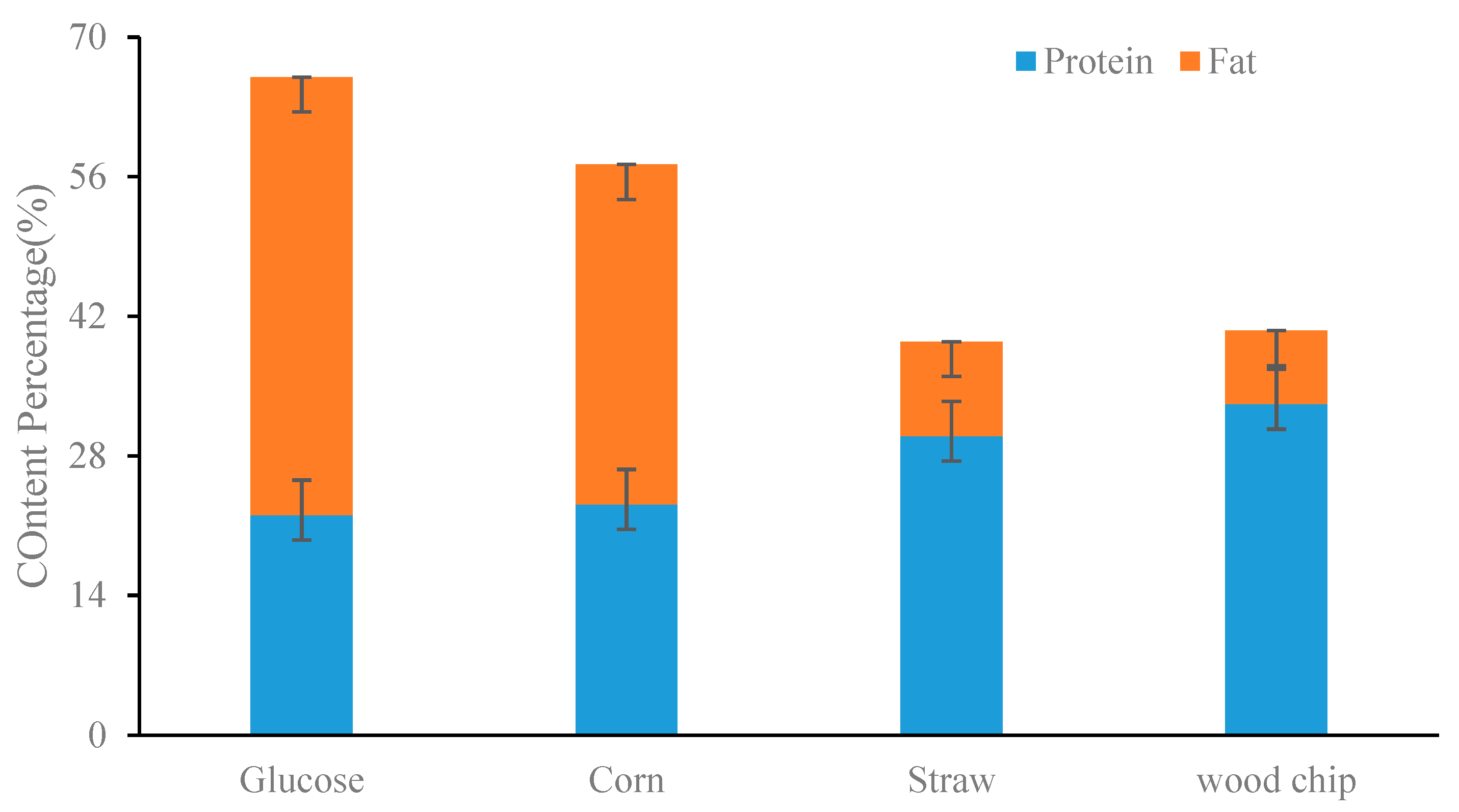
3.1. Growth Performance of BFL in Different Cultures
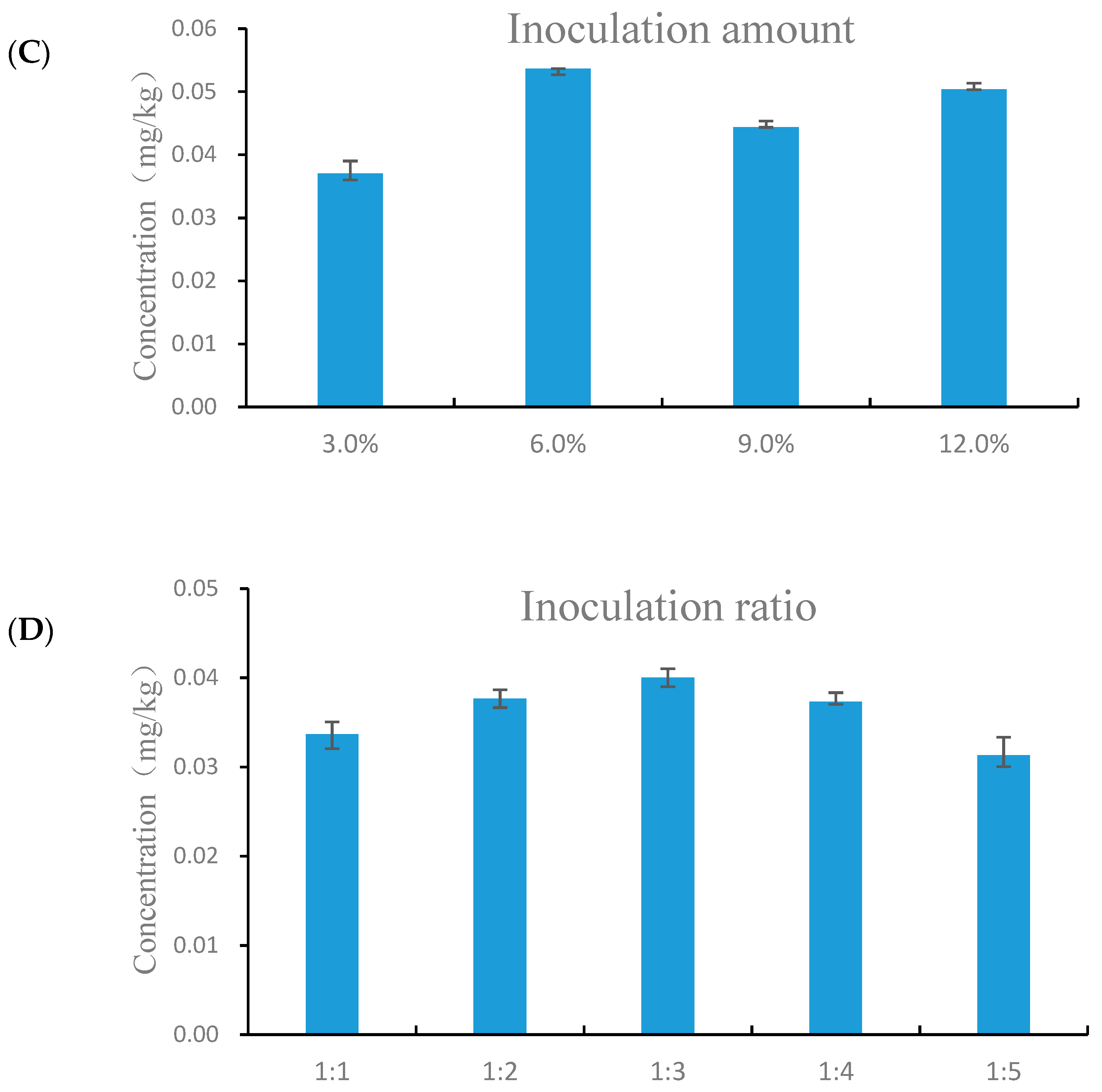
3.2. Optimum Co-Fermentation Conditions of B. subtilis and A. niger
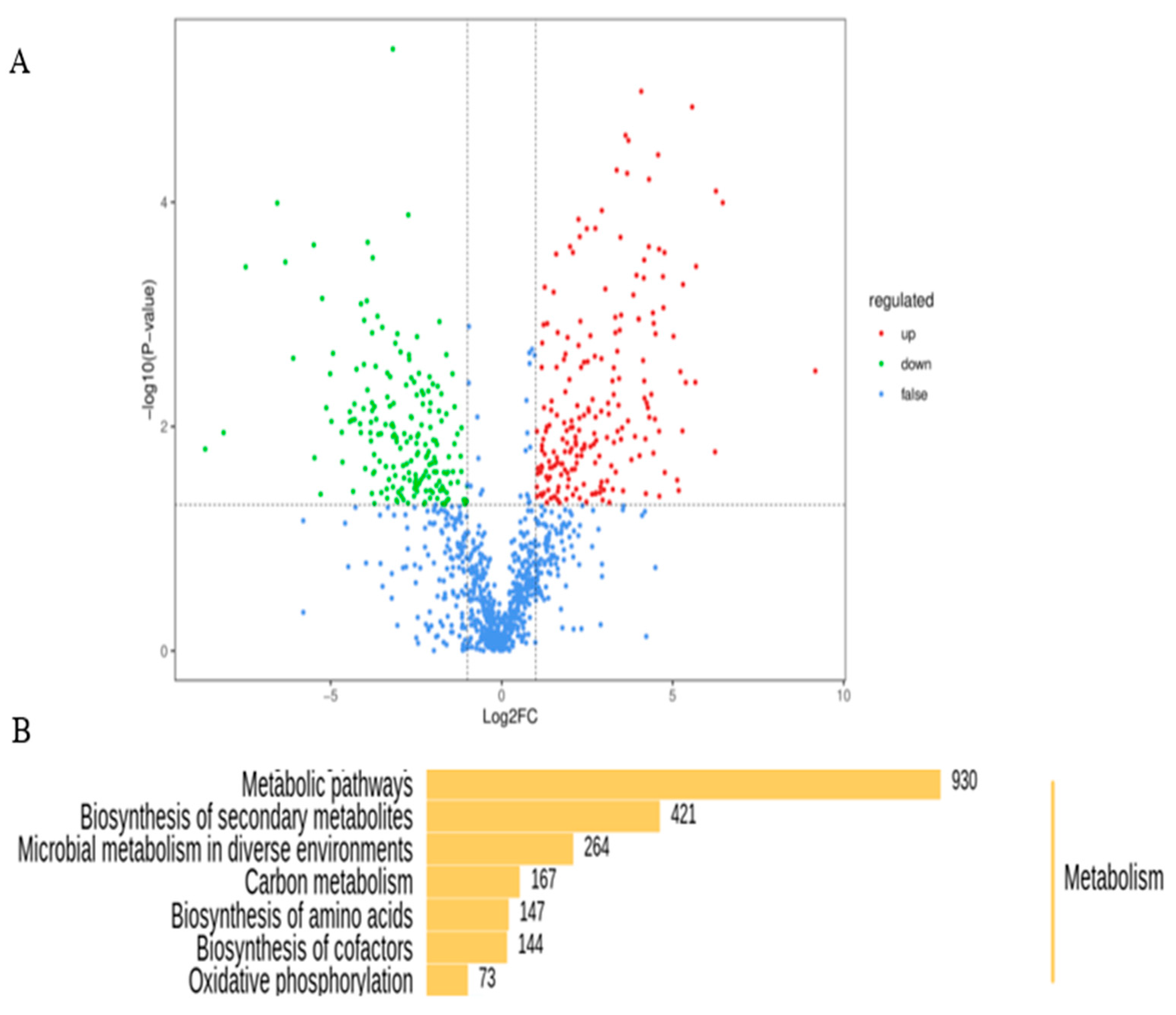
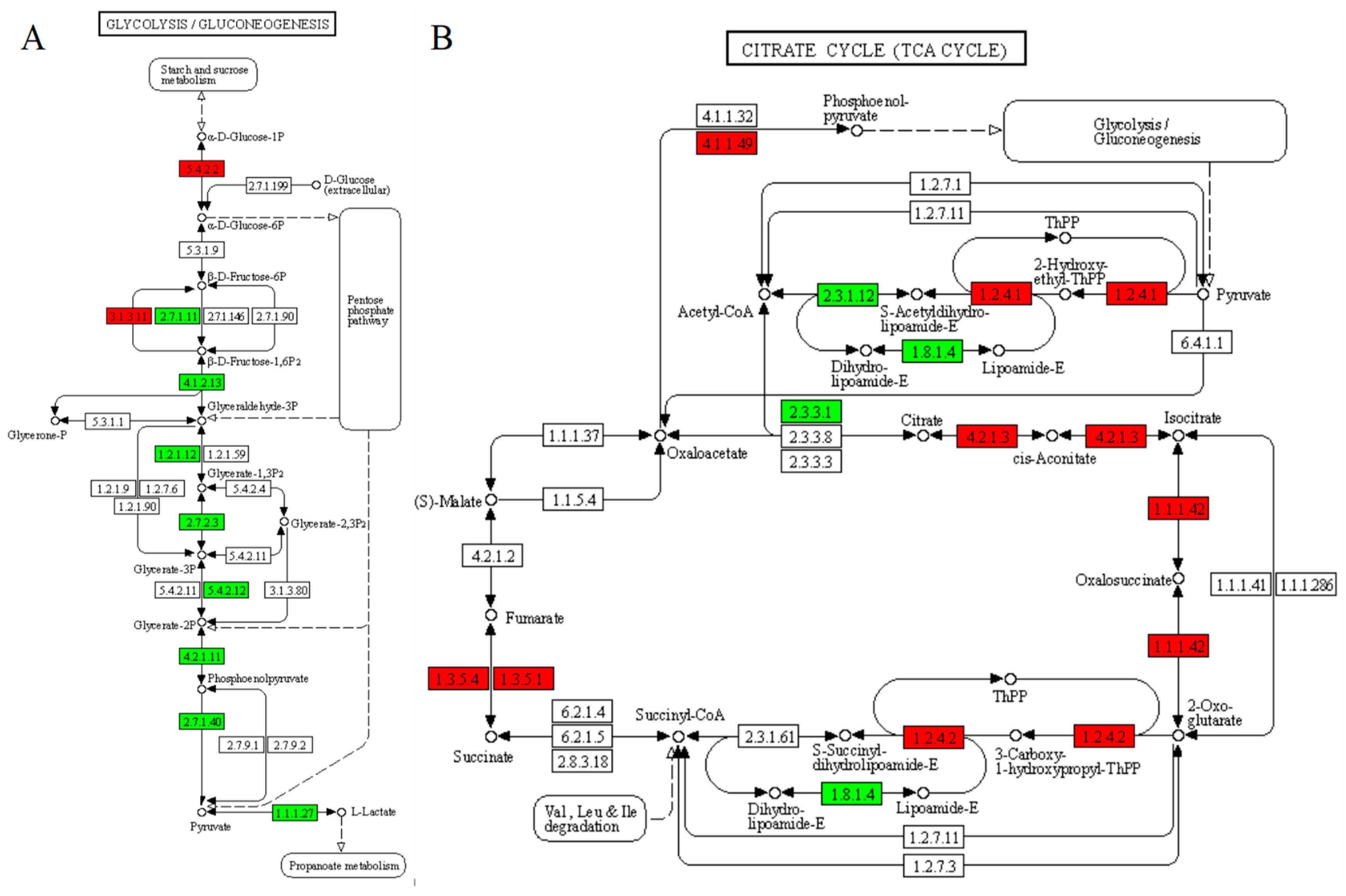
3.3. Proteomic Analysis of B.subtilis and A.niger after Co-Fermentation
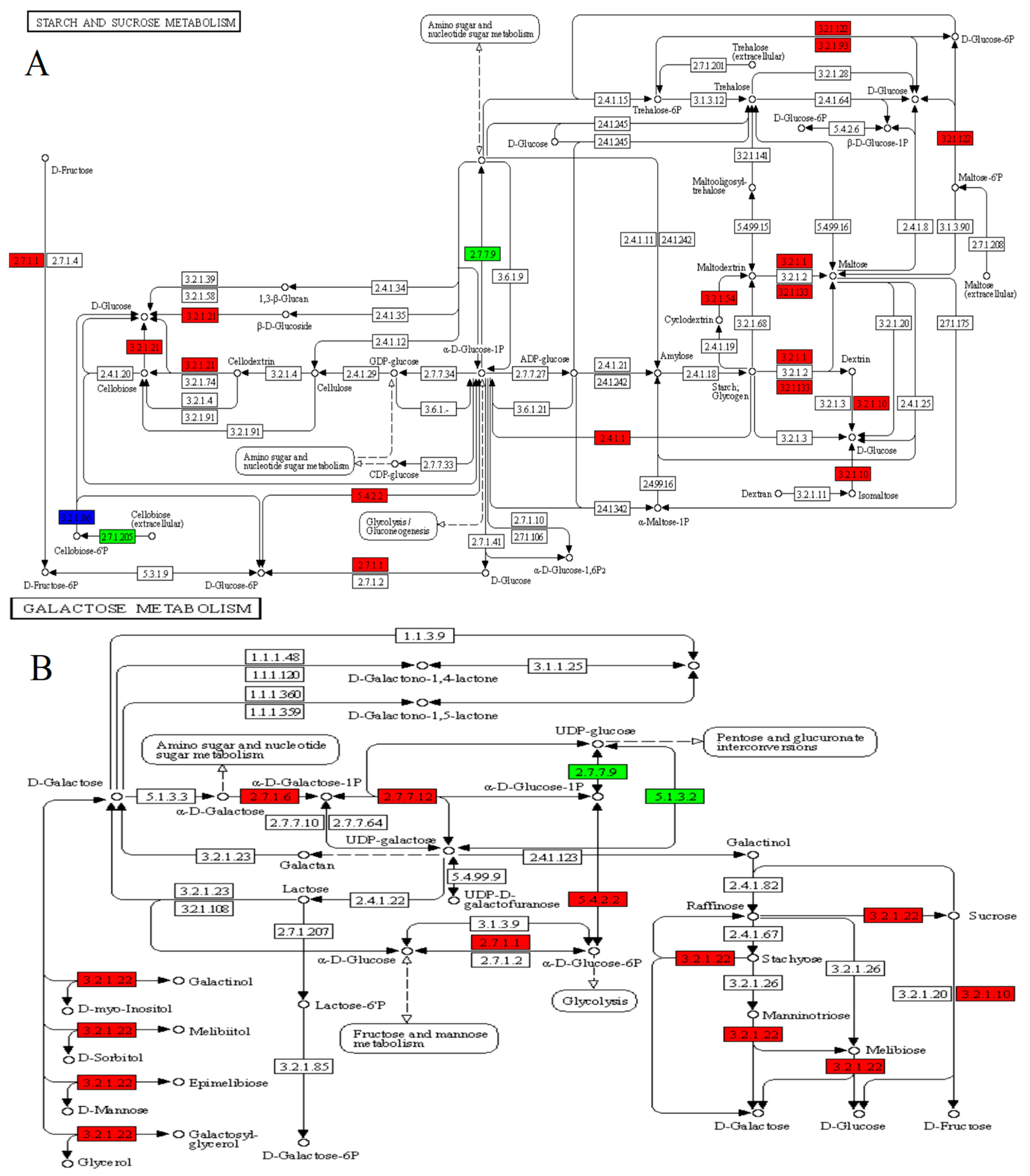
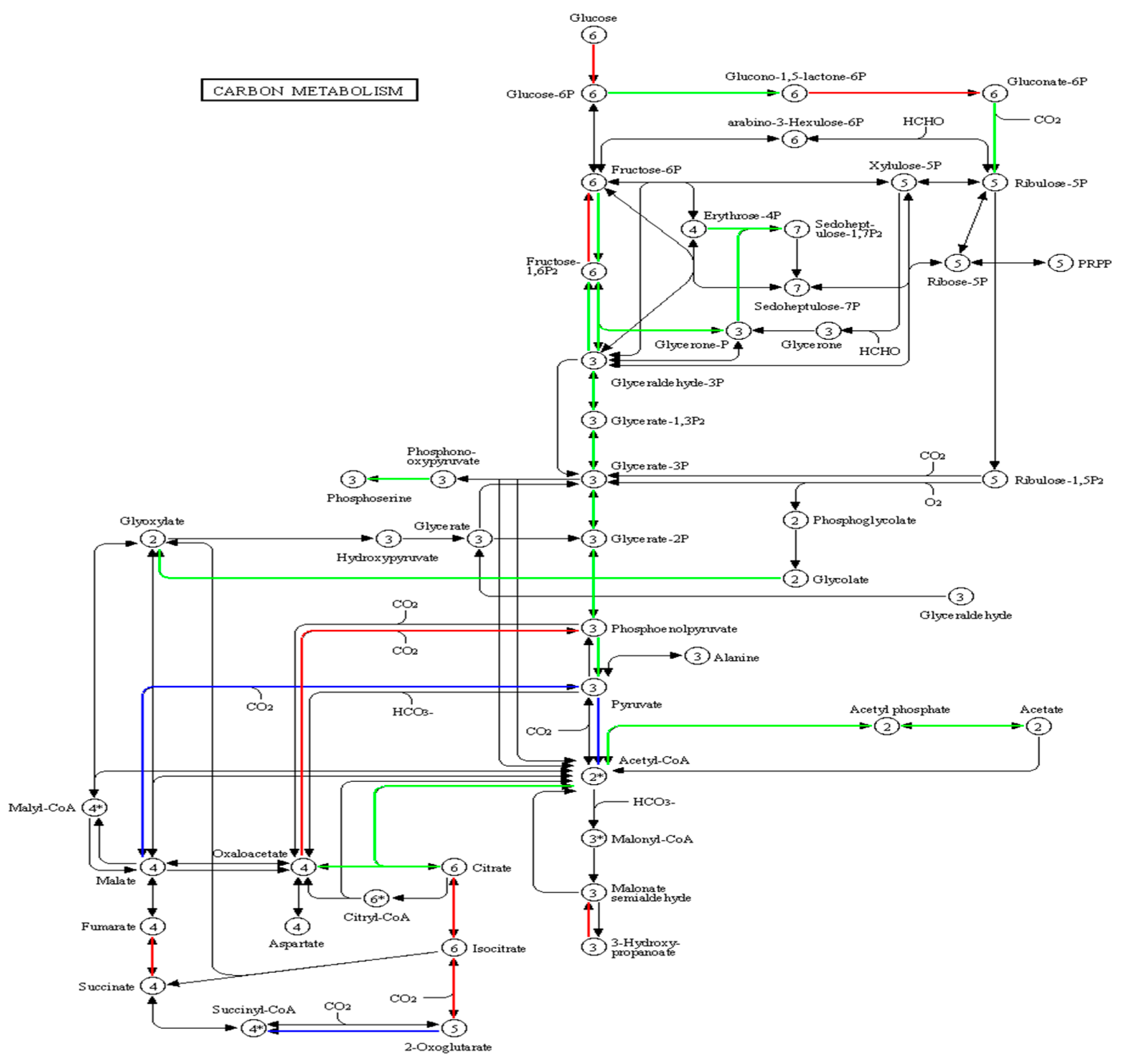
3.4. Carbon Metabolism
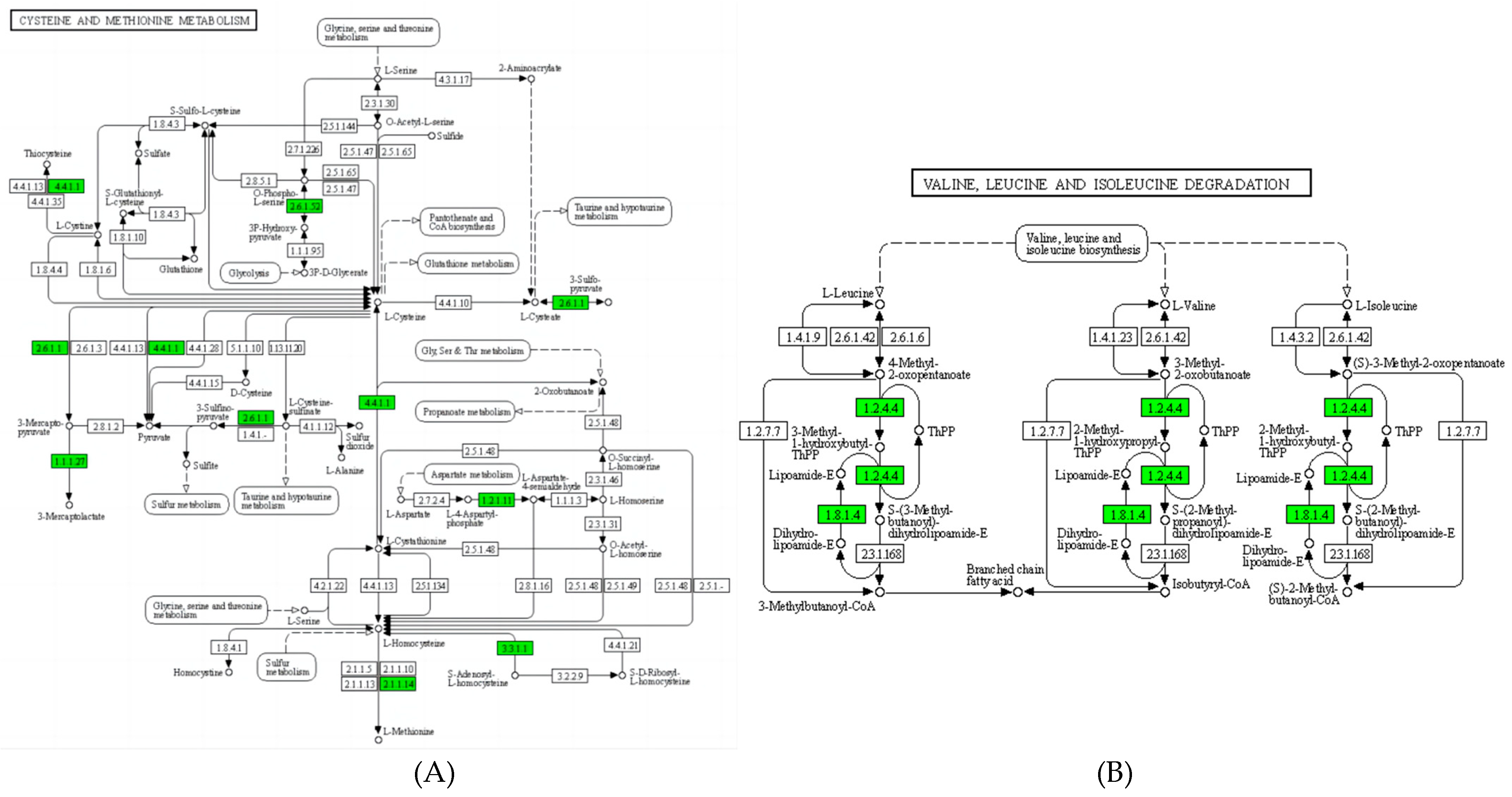
3.5. Amino Acid Metabolism
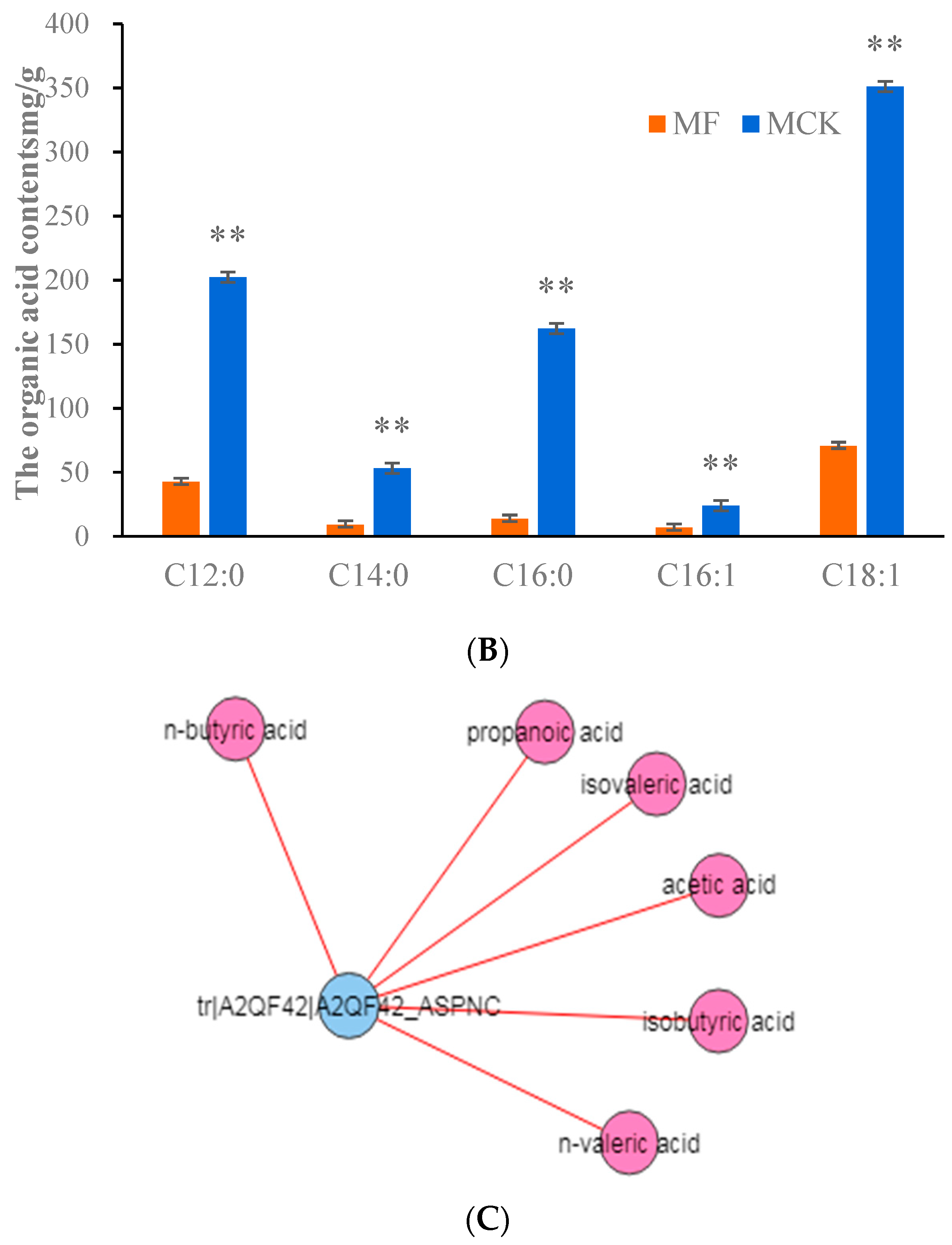
3.6. Fatty Acid Metabolism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rehman, K.U.; Hollah, C.; Wiesotzki, K.; Rehman, R.; Rehman, A.U.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, L.; Nienaber, T.; Heinz, V.; Aganovic, K. Black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens as a potential innovative and environmentally friendly tool for organic waste management: A mini-review. Waste Manag. Res. 2022, 22, 734242X221105441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proc, K.; Bulak, P.; Wiącek, D.; Bieganowski, A. Hermetia illucens exhibits bioaccumulative potential for 15 different elements—Implications for feed and food production. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raksasat, R.; Lim, J.W.; Kiatkittipong, W.; Kiatkittipong, K.; Ho, Y.C.; Lam, M.K.; Font-Palma, C.; Zaid, H.F.M.; Cheng, C.K. A review of organic waste enrichment for inducing palatability of black soldier fly larvae: Wastes to valuable resources. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 267, 115488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasco, L.; Biasato, I.; Dabbou, S.; Schiavone, A.; Gai, F. Animals Fed Insect-Based Diets: State-of-the-Art on Digestibility, Performance and Product Quality. Animals 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetto, A.; Oliva, S.; Riolo, K.; Savastano, D.; Parrino, V.; Cappello, T.; Maisano, M.; Fasulo, S.; Mauceri, A. Waste Valorization via Hermetia Illucens to Produce Protein-Rich Biomass for Feed: Insight into the Critical Nutrient Taurine. Animals 2020, 10, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-S.; Yun, E.-Y.; Goo, T.-W. Optimization of Feed Components to Improve Hermetia illucens Growth and Development of Oil Extractor to Produce Biodiesel. Animals 2021, 11, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, S.; Hu, Q.; Yi, L.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Cai, M.; Yu, C. Characteristics and nutrient function of intestinal bacterial communities in black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larvae in livestock manure conversion. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 886–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, Y.-K.; Kim, S.-W.; Song, D.-H.; Kim, H.-W.; Kim, I.-S. Nutritional Composition of White-Spotted Flower Chafer (Protaetia brevitarsis) Larvae Produced from Commercial Insect Farms in Korea. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2021, 41, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Lei, J.; Yao, Y.; Qu, X.; Chen, J.; Xie, K.; Wang, X.; Yi, Q.; Xiao, B.; Guo, S.; et al. Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal Modulates Intestinal Morphology and Microbiota in Xuefeng Black-Bone Chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 706424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawska, D.; Daszkiewicz, T.; Sobotka, W.; Gesek, M.; Witkowska, D.; Matusevičius, P.; Bakuła, T. Partial and Total Replacement of Soybean Meal with Full fat Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens L.) Larvae Meal in Broiler Chicken Diets: Impact on growth Performance, Carcass Quality and Meat Quality. Animals 2021, 11, 2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendra, K.; Tomberlin, J.K.; van Huis, A.; Cammack, J.A.; Heckmann, L.-H.L.; Khanal, S.K. Rethinking organic wastes bioconversion: Evaluating the potential of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens (L.)) (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) (BSF). Waste Manag. 2020, 117, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tippayadara, N.; Dawood, M.A.O.; Krutmuang, P.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Doan, H.V.; Paolucci, M. Replacement of Fish Meal by Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal: Effects on growth, Haematology, and Skin Mucus Immunity of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Animals 2021, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Li, C.; Xu, Z.; Peng, P.; Xue, C.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Hu, W.; Cao, Y. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens L.) larval diet improves CD8+ lymphocytes proliferation to eliminate chicken coronavirus at an early infection stage. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 260, 109151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Latif, H.M.; Abdel-Tawwab, M.; Khalil, R.H.; Metwally, A.A.; Shakweer, M.S.; Ghetas, H.A.; Khallaf, M.A. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal in diets of European seabass: Effects on antioxidative capacity, non-specific immunity, transcriptomic responses, and resistance to the challenge with Vibrio alginolyticus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 111, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaklader, R.; Howieson, J.; Fotedar, R.; Siddik, M.A.B. Supplementation of Hermetia illucens Larvae in Poultry By-Product Meal-Based Barramundi, Lates calcarifer Diets Improves Adipocyte Cell Size, Skin Barrier Functions, and Immune Responses. Front. Nutr. 2021, 7, 613158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, Y.-M.; Park, Y.-K.; Yang, Y.-C.; Jung, B.-G.; Lee, B.-J. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae enhances immune activities and increases survivability of broiler chicks against experimental infection of Salmonella Gallinarum. J. Veter. Med. Sci. 2018, 80, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipema, A.F.; Bokkers, E.A.M.; Gerrits, W.J.J.; Kemp, B.; Bolhuis, J.E. Providing live black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) improves welfare while maintaining performance of piglets post-weaning. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Yuan, B.; Liu, M.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; Xie, G.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Lv, Y.; et al. Dietary Hermetia illucens Larvae Replacement Alleviates Diarrhea and Improves Intestinal Barrier Function in Weaned Piglets Challenged with Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88. Front. Veter-Sci. 2021, 8, 746224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaemba, C.N.; Kidoido, M.M.; Owuor, G.; Tanga, C.M. Consumers’ perception towards eggs from laying hens fed commercial black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae meal-based feeds. Poult. Sci. 2021, 101, 101645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, M.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Rong, T.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Ma, X. Use of Hermetia illucens larvae as a dietary protein source: Effects on growth performance, carcass traits, and meat quality in finishing pigs. Meat Sci. 2019, 158, 107837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osimani, A.; Milanović, V.; Roncolini, A.; Riolo, P.; Ruschioni, S.; Isidoro, N.; Loreto, N.; Franciosi, E.; Tuohy, K.; Olivotto, I.; et al. Hermetia illucens in diets for zebrafish (Danio rerio): A study of bacterial diversity by using PCR-DGGE and metagenomic sequencing. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimoldi, S.; Gini, E.; Iannini, F.; Gasco, L.; Terova, G. The Effects of Dietary Insect Meal from Hermetia illucens Prepupae on Autochthonous Gut Microbiota of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Animals 2019, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenberg, O.K.; Holen, E.; Piemontese, L.; Liland, N.S.; Lock, E.-J.; Espe, M.; Belghit, I. Effect of dietary replacement of fish meal with insect meal on in vitro bacterial and viral induced gene response in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) head kidney leukocytes. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 91, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.; Lim, C.-H.; Lee, S.H.; Goo, T.-W.; Yun, E.-Y. Effect of Feed Containing Hermetia illucens Larvae Immunized by Lactobacillus plantarum Injection on the Growth and Immunity of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Insects 2021, 12, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, K.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hori, A.; Kawasaki, T.; Hirayasu, H.; Iwase, S.-I.; Hashizume, A.; Ido, A.; Miura, C.; Miura, T.; et al. Evaluation of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae and Pre-Pupae Raised on Household Organic Waste, as Potential Ingredients for Poultry Feed. Animals 2019, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weththasinghe, P.; Lagos, L.; Cortés, M.; Hansen, J.; Øverland, M. Dietary Inclusion of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Larvae Meal and Paste Improved Gut Health but Had Minor Effects on Skin Mucus Proteome and Immune Response in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar). Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 599530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longvah, T.; Mangthya, K.; Ramulu, P. Nutrient composition and protein quality evaluation of eri silkworm (Samia ricinii) prepupae and pupae. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Ding, Z.; Ke, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, M.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Guo, X. Different lactic acid bacteria and their combinations regulated the fermentation process of ensiled alfalfa: Ensiling characteristics, dynamics of bacterial community and their functional shifts. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, R.Y.; Ham, J.R.; Ryu, H.S.; Lee, S.S.; Miguel, M.A.; Paik, M.J.; Ji, M.; Park, K.W.; Kang, K.Y.; Lee, H.I.; et al. Defatted Tenebrio molitor Larva Fermentation Extract Modifies Steatosis, Inflammation and Intestinal Microflora in Chronic Alcohol fed Rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, J.R.; Choi, R.Y.; Lee, Y.; Lee, M.K. Effects of Edible Insect Tenebrio molitor Larva Fermentation Extract as a Substitute Protein on Hepatosteatogenesis and Proteomic Changes in Obese Mice Induced by High fat Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Gao, D.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Wen, J. Metabolomic and proteomic analysis of d-lactate-producing Lactobacillus delbrueckii under various fermentation conditions. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 45, 681–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.M.; Nogueira, F.C.; Brasil, A.A.; Carvalho, P.C.; Leprevost, F.V.; Domont, G.B.; Eleutherio, E.C. Quantitative proteomic analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae industrial strains CAT-1 and PE-2. J. Proteom. 2017, 151, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, W.M.; Sousa, C.S.; Oliveira, L.C.; Soares, S.C.; Souza, G.F.M.H.; Tavares, G.C.; Resende, C.P.; Folador, E.L.; Pereira, F.L.; Figueiredo, H.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of four biotechnological strains Lactococcus lactis through label free quantitative proteomics. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Qi, Q.; Sadiq, F.A.; Wang, W.; He, X.; Wang, W. Proteomic Analysis Explores Interactions between Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae during Sourdough Fermentation. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, Z.; Latty, T.; Abbas, A. Understanding dietary carbohydrates in black soldier fly larvae treatment of organic waste in the circular economy. Waste Manag. 2021, 137, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soetemans, L.; Uyttebroek, M.; Bastiaens, L. Characteristics of chitin extracted from black soldier fly in different life stages. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 3206–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Moll, L.; De Smet, J.; Paas, A.; Tegtmeier, D.; Vilcinskas, A.; Cos, P.; Van Campenhout, L. In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Peptides from the Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) against a Selection of Human Pathogens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0166421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.J.; White, S.W.; Rock, C.O. Lipid biosynthesis as a target for antibacterial agents. Prog. Lipid Res. 2001, 40, 467–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Glucose(CK) | Straw | Wood Chip | Corn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chicken manure(g) | 1405 | 1180 | 1528 | 560 |
| Glucose(g) | 281 | / | / | / |
| Straw(g) | / | 332 | / | / |
| Wood chip(g) | / | / | 253 | / |
| Corn(g) | / | / | / | 547 |
| Water(ml) | 320 | 490 | 220 | 900 |
| C/N | 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 |
| Moisture(%) | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 |
| Subject | Inoculation Proportion | Inoculation Amount (v/w) | Inoculation Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1:1 | 4% | 2d |
| 2 | 1:1 | 8% | 3d |
| 3 | 1:1 | 12% | 4d |
| 4 | 1:2 | 4% | 4d |
| 5 | 1:2 | 8% | 2d |
| 6 | 1:2 | 12% | 3d |
| 7 | 1:3 | 4% | 3d |
| 8 | 1:3 | 8% | 4d |
| 9 | 1:3 | 12% | 2d |
| Subject | Inoculation Proportion | Inoculation Amount | Inoculation Time | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.92 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1.02 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1.21 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 0.92 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1.54 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0.87 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 0.97 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1.06 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0.98 |
| K1 | 1.050 | 0.937 | 0.095 | |
| K2 | 1.110 | 1.207 | 0.973 | |
| K3 | 1.003 | 1.020 | 1.240 | |
| R | 0.107 | 0.270 | 0.290 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Mai, L.; Lin, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Li, Q. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Bacillus subtilis and Aspergillus niger in Black Soldier Fly Co-Fermentation. Fermentation 2022, 8, 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110593
Liu H, Yang X, Mai L, Lin J, Zhang L, Wang D, Li Q. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Bacillus subtilis and Aspergillus niger in Black Soldier Fly Co-Fermentation. Fermentation. 2022; 8(11):593. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110593
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, He, Xia Yang, Liwen Mai, Jiacong Lin, Liang Zhang, Dingmei Wang, and Qinfen Li. 2022. "Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Bacillus subtilis and Aspergillus niger in Black Soldier Fly Co-Fermentation" Fermentation 8, no. 11: 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110593
APA StyleLiu, H., Yang, X., Mai, L., Lin, J., Zhang, L., Wang, D., & Li, Q. (2022). Comparative Proteomic Analysis of Bacillus subtilis and Aspergillus niger in Black Soldier Fly Co-Fermentation. Fermentation, 8(11), 593. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110593






