Challenges in Expression and Purification of Functional Fab Fragments in E. coli: Current Strategies and Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Major Developments in Upstream Processing of Fab Fragments in E. coli
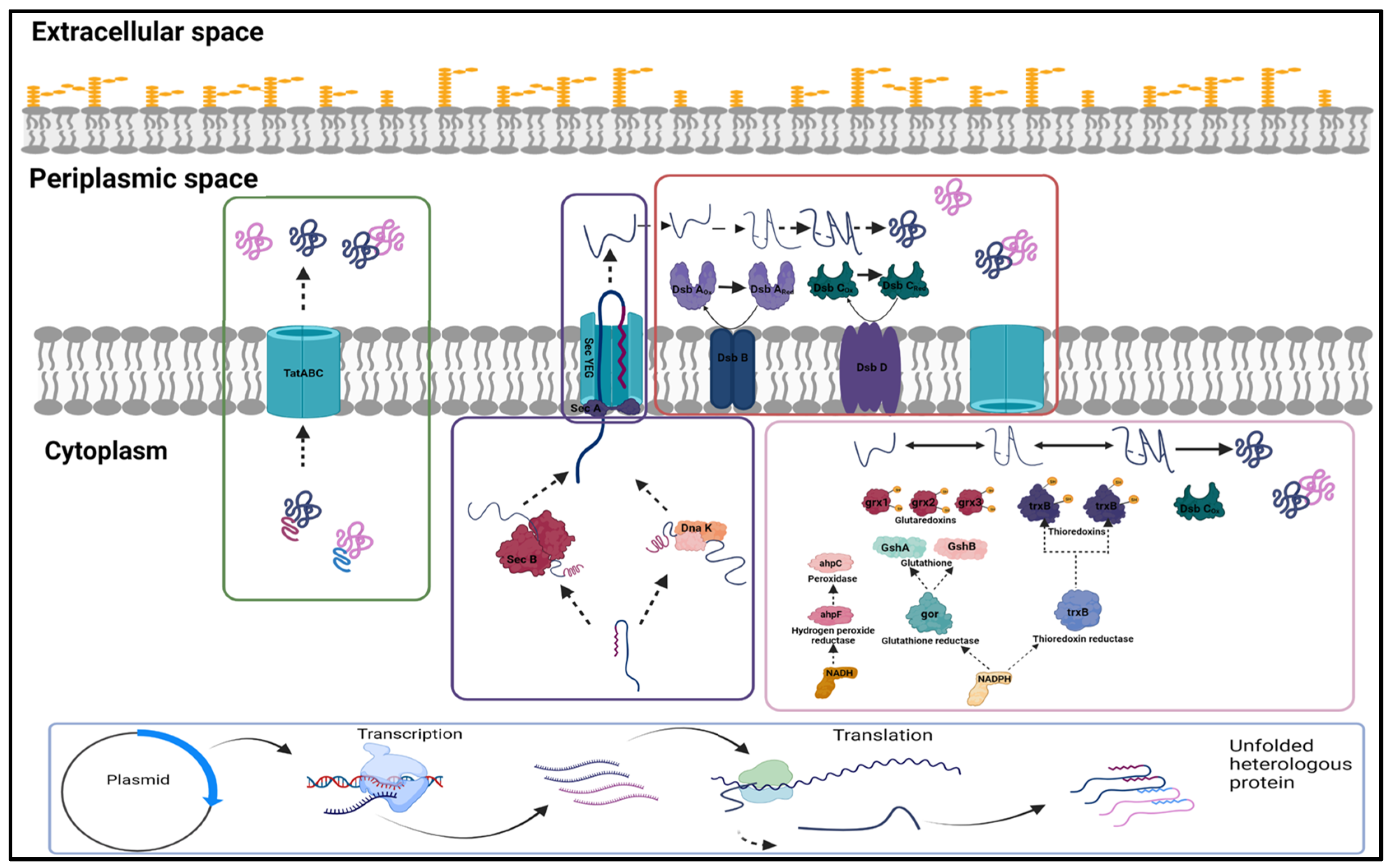
2.1. Expression and Localisation of Fab Fragment
2.2. Co-Expression of Soluble Expression Partners
2.3. Strain Development and Protein Expression
2.4. Fermentation Process and Media Development
3. Major Developments in Downstream Processing of Fab Fragments in E. coli
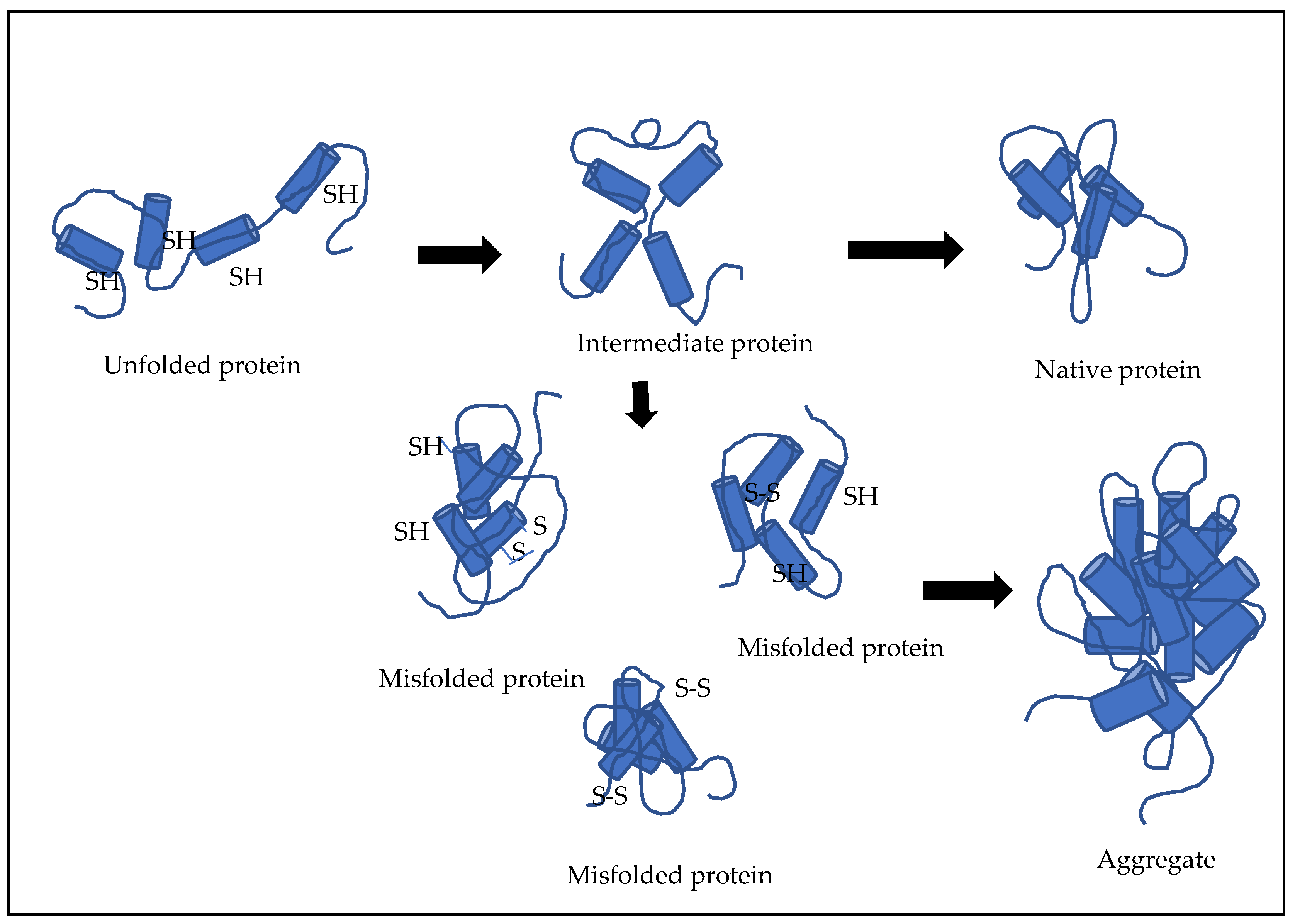
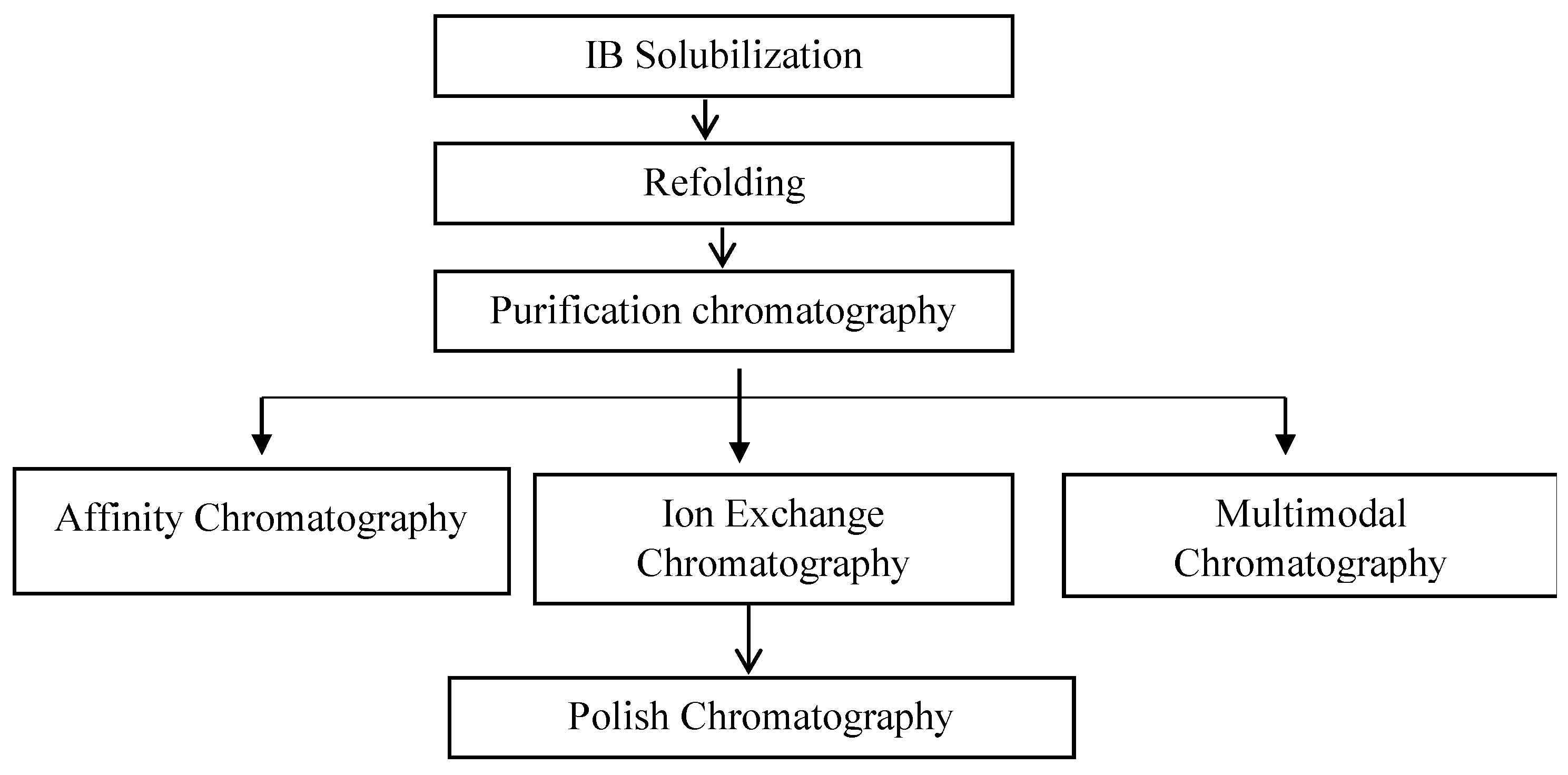
3.1. Refolding
3.2. Purification of Fab Molecules
4. Remaining Challenges in Production of Fab Fragments in E. coli
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rezaie, F.; Davami, F.; Mansouri, K.; Amiri, S.A.; Fazel, R.; Mahdian, R.; Davoudi, N.; Enayati, S.; Azizi, M.; Khalaj, V. Cytosolic expression of functional Fab fragments in Escherichia coli using a novel combination of dual SUMO expression cassette and EnBase® cultivation mode. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, A.; Power, C.A. David vs. Goliath: The Structure, Function, and Clinical Prospects of Antibody Fragments. Antibodies 2019, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sandomenico, A.; Sivaccumar, J.P.; Ruvo, M. Evolution of Escherichia coli Expression System in Producing Antibody Recombinant Fragments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.J.; Jeong, K.J. Challenges to production of antibodies in bacteria and yeast. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 120, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakruddin, M.; Mazumdar, R.M.; Mannan, K.S.; Chowdhury, A.; Hossain, M.N. Critical Factors Affecting the Success of Cloning, Expression, and Mass Production of Enzymes by Recombinant E. coli. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 590587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Levy, R.; Weiss, R.; Chen, G.; Iverson, B.L.; Georgiou, G. Production of correctly folded Fab antibody fragment in the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli trxB gor mutants via the coexpression of molecular chaperones. Protein Expr. Purif. 2001, 23, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeshen, M.N.; Al-Hejin, A.M.; Bora, R.S.; Ahmed, M.M.M.; Ramadan, H.A.I.; Saini, K.S.; Baeshen, N.A.; Redwan, E.M. Production of Biopharmaceuticals in E. coli: Current Scenario and Future Perspectives. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farajnia, S.; Ghorbanzadeh, V.; Dariushnejad, H. Effect of Molecular Chaperone on the Soluble Expression of Recombinant Fab Fragment in E. coli. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2020, 26, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, G.L.; Ceccarelli, E.A. Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.C.; Thomas, O.R.; Overton, T.W. Periplasmic expression in and release of Fab fragments from Escherichia coli using stress minimization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimek, C.; Kubek, M.; Scheich, D.; Fink, M.; Brocard, C.; Striedner, G.; Cserjan-Puschmann, M.; Hahn, R. Three-dimensional chromatography for purification and characterization of antibody fragments and related impurities from Escherichia coli crude extracts. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1638, 461702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gani, K.; Bhambure, R.; Deulgaonkar, P.; Mehta, D.; Kamble, M. Understanding unfolding and refolding of the antibody fragment (Fab). I. In-vitro study. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 164, 107764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmala, A.; Huovinen, T.; Lamminmäki, U. Improvement of Fab expression by screening combinatorial synonymous signal sequence libraries. Microb. Cell Factories 2019, 18, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schofield, D.M.; Sirka, E.; Keshavarz-Moore, E.; Ward, J.; Nesbeth, D.N. Improving Fab’ fragment retention in an autonucleolytic Escherichia coli strain by swapping periplasmic nuclease translocation signal from OmpA to DsbA. Biotechnol. Lett. 2017, 39, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fink, M.; Vazulka, S.; Egger, E.; Jarmer, J.; Grabherr, R.; Cserjan-Puschmann, M.; Striedner, G. Microbioreactor Cultivations of Fab-Producing Escherichia coli Reveal Genome-Integrated Systems as Suitable for Prospective Studies on Direct Fab Expression Effects. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 14, e1800637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, M.; Zhao, M.; Cagliero, C.; Jiang, H.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, Y.; et al. A general platform for efficient extracellular expression and purification of Fab from Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 3341–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dariushnejad, H.; Farajnia, S.; Zarghami, N.; Aria, M.; Tanomand, A. Effect of DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE and DsbC Chaperons on Periplasmic Expression of Fab Antibody by E. coli SEC Pathway. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 25, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.; Patel, P.; Edon, M.; Ramage, W.; Dickinson, R.; Humphreys, D.P. Development of a high yielding E. coli periplasmic expression system for the production of humanized Fab’fragments. Biotechnol. Prog. 2017, 33, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaciarz, A.; Veijola, J.; Uchida, Y.; Saaranen, M.J.; Wang, C.; Hörkkö, S.; Ruddock, L.W. Systematic screening of soluble expression of antibody fragments in the cytoplasm of E. coli. Microb. Cell Factories 2016, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schofield, D.M.; Templar, A.; Newton, J.; Nesbeth, D.N. Promoter engineering to optimize recombinant periplasmic Fab′ fragment production in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Prog. 2016, 32, 840–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojima-Kato, T.; Fukui, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Hashimura, D.; Miyake, S.; Hirakawa, Y.; Yamasaki, T.; Kojima, T.; Nakano, H. ‘Zipbody’leucine zipper-fused Fab in E. coli in vitro and in vivo expression systems. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2016, 29, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Azarian, B.; Azimi, A.; Sepehri, M.; Fam, V.S.; Rezaie, F.; Talebkhan, Y.; Khalaj, V.; Davami, F. Proteomics investigation of molecular mechanisms affected by EnBase culture system in anti-VEGF fab fragment producing E. coli BL21 (DE3). Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 49, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Ha, G.S.; Lee, G.; Lim, S.I.; Lee, C.M.; Yang, Y.H.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.E.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, Y.; et al. Enhanced expression of soluble antibody fragments by low-temperature and overdosing with a nitrogen source. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2018, 115, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corisdeo, S.; Wang, B. Functional expression and display of an antibody Fab fragment in Escherichia coli: Study of vector designs and culture conditions. Protein Expr. Purif. 2004, 34, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venturi, M.; Seifert, C.; Hunte, C. High level production of functional antibody fab fragments in an oxidizing bacterial cytoplasm. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 315, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiefhaber, T.; Rudolph, R.; Kohler, H.-H.; Buchner, J. Protein Aggregation in vitro and in vivo: A Quantitative Model of the Kinetic Competition between Folding and Aggregation. Nat. Biotechnol. 1991, 9, 825–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarthi, S.; Jessop, C.E.; Bulleid, N.J. The role of glutathione in disulphide bond formation and endoplasmic-reticulum-generated oxidative stress. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, S.M.; Panda, A.K. Solubilization and refolding of bacterial inclusion body proteins. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 99, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasuda, M.; Murakami, Y.; Sowa, A.; Ogino, H.; Ishikawa, H. Effect of Additives on Refolding of a Denatured Protein. Biotechnol. Prog. 1998, 14, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, S.; Schmitt, J.; Schmid, R. High-yield expression of the recombinant, atrazine-specific Fab fragment K411B by the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. J. Immunol. Methods 2001, 255, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furuta, T.; Ogawa, T.; Katsuda, T.; Fujii, I.; Yamaji, H. Efficient production of an antibody Fab fragment using the baculovirus–insect cell system. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Hamada, H.; Ogawa, T.; Ohmuro-Matsuyama, Y.; Katsuda, T.; Yamaji, H. Efficient production of antibody Fab fragment by transient gene expression in insect cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2017, 124, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Somani, S.; Pandey, A.; Mishra, A.; Mody, R.S. Refolding Process for Antibody’s Fragments. US20180230206A1, 22 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ban, B.; Sharma, M.; Shetty, J. Optimization of Methods for the Production and Refolding of Biologically Active Disulfide Bond-Rich Antibody Fragments in Microbial Hosts. Antibodies 2020, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, T.H.; Ahn, S.J.; Lee, E.K. Refolding of protein inclusion bodies directly from E. coli homogenate using expanded bed adsorption chromatography. Bioseparation 2001, 10, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, T.; Ohkuri, T.; Onodera, R.; Ueda, T. Stable Supply of Large Amounts of Human Fab from the Inclusion Bodies in E. coli. J. Biochem. 2007, 141, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-H.; Kwak, J.-W. Expression and functional reconstitution of a recombinant antibody (Fab’) specific for human apolipoprotein B-100. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 101, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphreys, D.P.; Carrington, B.; Bowering, L.C.; Ganesh, R.; Sehdev, M.; Smith, B.J.; King, L.M.; Reeks, D.G.; Lawson, A.; Popplewell, A.G. A plasmid system for optimization of Fab’ production in Escherichia coli: Importance of balance of heavy chain and light chain synthesis. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 26, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalalirad, R. Efficient Chromatographic Processes for Elevated Purification of Antibody Fragment (Fab D1.3) from Crude Escherichia coli Culture. Biotechnology 2013, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, A.; Pinto, I.F.; Chu, V.; Aires-Barros, M.R.; Conde, J.P.; Azevedo, A.M. Studies on the purification of antibody fragments. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 195, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo, G.; Gruvegård, M.; Van Alstine, J.M. Antibody Fragments and Their Purification by Protein L Affinity Chromatography. Antibodies 2015, 4, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roque, A.C.A.; Lowe, C.R. Rationally Designed Ligands for Use in Affinity Chromatography. In Affinity Chromatography; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundaram, B.; Chhatre, S.; Arora, D.; Titchener-Hooker, N.J.; Bracewell, D.G. Study of the conditions for multi-modal chromatographic capture of Fab′ from dual-salt precipitated E. coli homogenate. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundaram, B.; Sachdeva, S.; Bracewell, D.G. Dual salt precipitation for the recovery of a recombinant protein from Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 27, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhambure, R.S.; Gani, K.M. A Process for the Purification of Recombinant Antibody Fragments. US20200095277A1, 26 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Eifler, N.; Medaglia, G.; Anderka, O.; Laurin, L.; Hermans, P. Development of a novel affinity chromatography resin for platform purification of lambda fabs. Biotechnol. Prog. 2014, 30, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patil, R.S.; Anupa, A.; Gupta, J.A.; Rathore, A.S. Challenges in Expression and Purification of Functional Fab Fragments in E. coli: Current Strategies and Perspectives. Fermentation 2022, 8, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040175
Patil RS, Anupa A, Gupta JA, Rathore AS. Challenges in Expression and Purification of Functional Fab Fragments in E. coli: Current Strategies and Perspectives. Fermentation. 2022; 8(4):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040175
Chicago/Turabian StylePatil, Rucha S., Anupa Anupa, Jaya A. Gupta, and Anurag S. Rathore. 2022. "Challenges in Expression and Purification of Functional Fab Fragments in E. coli: Current Strategies and Perspectives" Fermentation 8, no. 4: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040175
APA StylePatil, R. S., Anupa, A., Gupta, J. A., & Rathore, A. S. (2022). Challenges in Expression and Purification of Functional Fab Fragments in E. coli: Current Strategies and Perspectives. Fermentation, 8(4), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8040175





