Abstract
The fermentation processes of algicidal bacteria offer an eco-friendly and promising approach for controlling harmful algae blooms (HABs). The strain Ba3, previously isolated and identified as Bacillus sp., displays robust algicidal activity against HABs dinoflagellate in particular. Microbial fermentation products have also been found to provide metabolites with multiple bioactivities, which has been shown to reduce harmful algae species’ vegetative cells and thus reduce red tide outbreaks. In this study, the microbial fermentation of algicidal bacterium Ba3 was analyzed for its potential ability of algicidal compounds. A treatment time increased the algicidal efficiency of the fermentation products against Prorocentrum donghaiense (91%) and Alexandrium tamarense (82%). Among the treatment groups, the changing trend for the 2% treatment group was faster than that for the other treatments, showing that the inhibition rate could reach 99.1% in two days. Active components were separated by organic solvent extraction and macroporous resin, and the molecular weight of the active components was analyzed by LC-MS. The result shows that the microbial fermentation products offer a potential, not practical use for controlling the outbreaks of dinoflagellate blooms. As a result of its potential application for inhibiting HABs, these findings provide an encouraging basis for promoting large-scale fermentation production and the controlling the outbreaks of red tide.
1. Introduction
Harmful algal blooms (HABs) have become a primary global concern because they endanger public health, the environment, and a variety of commercial interests. Over the last few decades, the frequency, magnitude, and duration of HABs have increased in marine and freshwater ecosystems worldwide [1]. In general, intensive and semi-intensive aquaculture ponds are considered high-risk waters for HAB occurrence because of their higher loads of organic matter and nutrients [2,3]. Furthermore, a single bloom may have significant economic and environmental consequences due to deterioration of the aquatic ecosystem and the heightened mortality of aquatic animals [4,5]. During the last decade, algicidal bacteria capable of algal cell lysis or growth inhibition have been isolated from the aquatic ecosystem and offer a promising and eco-friendly biological approach for controlling HABs [6,7]. In recent years, algicidal bacteria have also attracted increased attention as a possible measure to control HABs in aquaculture ponds [8]. Screening for bacteria in naturally occurring waters for their algicidal abilities to control HAB, which offers a practical strategy since algicidal bacteria occur in natural aquatic environments and inhibit algal growth and proliferation [8]. There has also been considerable success in screening and analyzing certain characteristics of algicidal bacteria [9,10]. However, these bacteria have not yet been developed for commercial applications in eradicating HABs [11].
Most algicidal bacteria indirectly attack the target algae by discharging active algicidal compounds (agarase, amino-peptidase, lipase, proteins, alkaline phosphatase, and various other enzymes) into the surrounding medium [12]. These active compounds are synthesized primarily as a result of bacterial metabolism processes. Fermentation is one essential process to consider in the large-scale production of microbial cultures suitable for the development of microbial algicides. Studies have shown that the productivity of secondary metabolites of microorganisms can be enhanced during repeated fermentations [13,14]. Nevertheless, there are critical technological challenges in fermenting algicidal strains which, derived from naturally occurring waters, are sensitive to many environmental stresses such as fermentation vessel pressure, ventilation, and temperature [15,16]. Thus, it is necessary to identify and verify the presence of active algicidal ingredients in fermentation products.
The algicidal bacterium Bacillus strain Ba3 used in this study was isolated from the Fujian coastal area in China and was confirmed to have indirect algicidal activity against Gymnodinium catenatum. In our previous study, Ba3 displayed solid algicidal activity against dinoflagellates [17]. The Ba3 strain was fermented using different fermentation methods in our study, and then the algicidal properties of Ba3 fermentation products were further examined against harmful dinoflagellate species, Prorocentrum donghaiense and Alexandrium tamarense. Though the bacteria themselves could not lyse algal cells, the cell-free supernatants of the fermentation broth were able to do so. Our results show that the use of large-scale fermentation and application of the algicidal bacterium Ba3 could be utilized as a potential microbial algicide to control red tide.
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Cultivation of the Dinoflagellate Species
Prorocentrumdonghaiense and Alexandrium tamarense were obtained from Shanghai Guangyu Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. We maintained the axenic algal culture at 20 ± 2 °C in a sterile F/2 medium, which was prepared with natural seawater filtered to 0.45 µm and maintained under a 12:12 h light/dark cycle. We also counted cell numbers under a microscope. The algal culture was then transferred once a week to a fresh, sterilized medium, ensuring that experiments were always conducted with new cultures during the exponential growth phase.
2.2. Microbial Culture and Fermentation Broth Preparation
The surface morphological characteristics of strain Ba3 on beef extract peptone solid medium, as shown in Supplementary Figure S1a. Strain Ba3 was cultured on beef extract peptone solid plate for 48 h, and formed pale yellow colonies with diameters of 1–2 mm. The colonies were round, with smooth, moist and protruding surfaces. Bacteria can be divided into two categories after being stained by the Gram staining method; one is stained red, called Gram-negative bacteria. Through microscope observation, the staining results are shown in Supplementary Figure S1b; the strain Ba3 is stained light purple, which belongs to Gram-positive bacteria. Scanning electron microscope images are shown in Supplementary Figure S1c; Ba3 cells are cylindrical, about 3.1–4.1 μm long and 0.8–1.2 μm wide. The 16S rRNA gene of Ba3 was amplified and sequenced. The phylogenic tree produced by the neighbor-joining analysis revealed that Ba3 belongs to Bacillus Supplementary Figure S1d. Based on the morphologic characteristics and molecular analysis above, we identified it as Bacillus sp. Ba3 and NCBI accession number: OK103791.1. Microbial slopes were prepared as fresh YPD using a beef extract peptone slope. After culturing for 1 d at 30 °C, a full ring of microbial lichen was selected and inoculated into a 50 mL conical flask containing 20 mL liquid medium, then cultured for 1 d in a constant temperature oscillation incubator at 30 °C and 180r/min. The prepared seed suspension was inoculated at 1% into a 100 mL conical flask containing 50 mL liquid medium, and the fermentation supernatant was collected at a constant temperature of 180 r/min for 1 d, 2 d, and 3 d, then centrifuged at 10,000 rpm/min for 15 min. Microbial fermentation broth with different fermentation times was obtained by using a 0.22 μm aseptic filtration membrane.
2.3. Inhibition Experiment of Fermentation Liquid
The microbial fermentation liquid was added to 40 mL of liquid containing P. donghaiense and A. tamarense at volume ratios of 0.3%, 0.7%, 1.0%, and 2.0%. The untreated control group was shaken by hand twice a day, placed in a light incubator for 10 days and counted every 2 days under a microscope. Each group analyzed consisted of three replicates.
2.4. Calculation Method of Algae Removal Rate
The algae removal rate was monitored by estimating cell numbers by utilizing a microscope to calculate according to the following equation:
where RE is the removal rate of algal cells; N0: vegetative cell density before adding an algae inhibitor; Nt is the vegetative cell density after adding the algae inhibitor.
RE (%) = (1 − Nt/N0) × 100%
2.5. Crude Extraction of Algal Inhibitory Substances in Fermentation Liquid
An amount of 20 mL fermentation liquid of Ba3 strain and 60 mL anhydrous ethanol was decanted into a 250 mL beaker. The beaker was placed on a magnetic stirrer for 30 min and placed overnight in a refrigerator at 4 °C. The next day, fermentation liquid was centrifuged at 6000 r/min for 10 min, after which ethanol extract and ethyl extract were collected. The alcohol precipitated phase was then removed by vacuum rotary evaporation at 45 °C. Sterile distilled water was used to compare the constant volume with the original volume, and the algae inhibition experiment was carried out by adding 20 mL petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol into the Ba3 strain fermentation broth three times. The broth was left standing for 45 min each time to collect the organic and aqueous phases of the three solvents. The organic solvent was then removed by vacuum rotary evaporation at 45 °C, and sterile distilled water was used to keep the volume similar to the original volume for the algae inhibition experiment.
2.6. Analysis of Molecular Weight of Algicidal Substances in Dialysis Bags
Through vacuum rotating evaporation at 45 °C, 100 mL of Ba3 fermentation liquid was concentrated to 10 mL and then deposited into a dialysis bag. The fermentation liquid’s molecular weight ranged from 8000 to 14,000. At room temperature, sterile distilled water was used for dialysis for 48 h. Sterile distilled water was replaced every 12 h, and dialysate inside and outside the bag was collected. A 0.22 μm filter membrane was used for sterilization, and the concentration was reduced to 10 mL by vacuum rotary evaporation at 45 °C.
3. Isolation of Macroporous Resin from Algicidal Substances of Strain Ba3
3.1. Crude Extract of Algicidal Substance in Fermentation Broth of Strain Ba3
The activated suspension of Ba3 strain was inoculated into a 500 mL conical flask containing 200 mL of a liquid beef extract peptone medium of 1%. The bacterial fermentation broth was obtained through a constant temperature oscillation culture at 30 °C and 180 r-min for 2 days. The Ba3 fermentation supernatant was collected in batches through centrifugation at 10,000 rpm/min for 15 min. A 0.22 μm sterile filter membrane was used for filtration and sterilization, and 10 L of sterile fermentation liquid was finally obtained.
The collected fermentation liquid of 10 L Ba3 strain was concentrated through three methods: vacuum rotary evaporation at 45 °C, warm air blowing at 30 °C, and freeze-drying at −65 °C. The fermentation liquid of the Ba3 strain was transferred to a 200 mm Petri dish. The liquid form was then placed in a −20 °C refrigerator to solidify, in a −80 °C ultra-low temperature refrigerator to freeze overnight, then transferred into a freeze dryer. After 52h, the solidified fermentation liquid of the Ba3 strain was dried into a powder. The aqueous phase of the 200 mL concentrated solution was extracted with ethyl acetate, and the ethyl acetate was removed by vacuum rotary evaporation at 45 °C. Then, the extract was extracted by ethanol, which was then removed by vacuum rotary evaporation at 45 °C to obtain the crude extract of the anti-alga active substance from the Ba3 strain.
3.2. Selection of Macroporous Resin
An appropriate amount of HZ803 and HZ830 macroporous resin was soaked overnight in three times the strength of 95% ethanol and then eluted continuously until the eluent and water lacked white turbidity. The resin was then eluted with distilled water until there was no alcohol taste and the water was clear. Amounts of 5 g of HZ803 and HZ830 resins were weighed and placed in a 50 mL centrifuge tube, and 20 mL of Ba3 strain fermentation broth at the same concentration was added. In this experiment, the adsorption was accomplished by shaking for 2 h at 120 rpm at room temperature. After adsorption, the supernatant was collected and desorbed with anhydrous ethanol at different concentrations. The eluent was collected, and the ethanol was removed by vacuum rotary evaporation at 45 °C. Sterile distilled water was used to bring the constant volume to 10 mL to conduct the algal inhibition experiments.
3.3. Separation of Macroporous Lipid, an Algicidal Substance
Macroporous lipids, considered algal inhibitors, were separated, and a certain amount of pre-treated HZ-830 resin was wet-packed into a glass column (13 × 400 mm). The fermentation broth of the Ba3 strain with certain concentrations coursed through the macroporous resin column at a flow rate of 1 mL/min. After the adsorption, 10 ethanol gradient elution components of 150 mL were collected using distilled water and a 10–100% ethanol gradient elution. For the algal inhibition experiments, ethanol was removed by vacuum rotary evaporation at 45 °C, and sterile distilled water was added at a constant volume of 10 mL.
3.4. LC-MS Analysis of Algal Inhibition Substances
Macroporous resin fractions were analyzed using ThermoFisherU3000 high-performance liquid chromatography Shanghai, China on a Thermo Hypersil GOLD C18 (150 mm × 2.1 mm, 3 mm. The sample volume was 10 μL, with the flow rate set at 1 mL/min. The mobile phase employed gradient elution using water plus 1% formic acid (A) and methanol plus 1% formic acid (B). The elution procedure was as follows: 0–5 min, 5% B, 5–35 min, 10% B, and 35–45 min, 95% B. The ionization mode used electrospray (ESI) in the positive ion mode. The mass detector was a four-level mass analyzer, and the detection range was 100–700 Da.
4. Results
4.1. Effects of Ba3 Strain Fermentation Broth on the Growth of Two Kinds Red Tide Algae
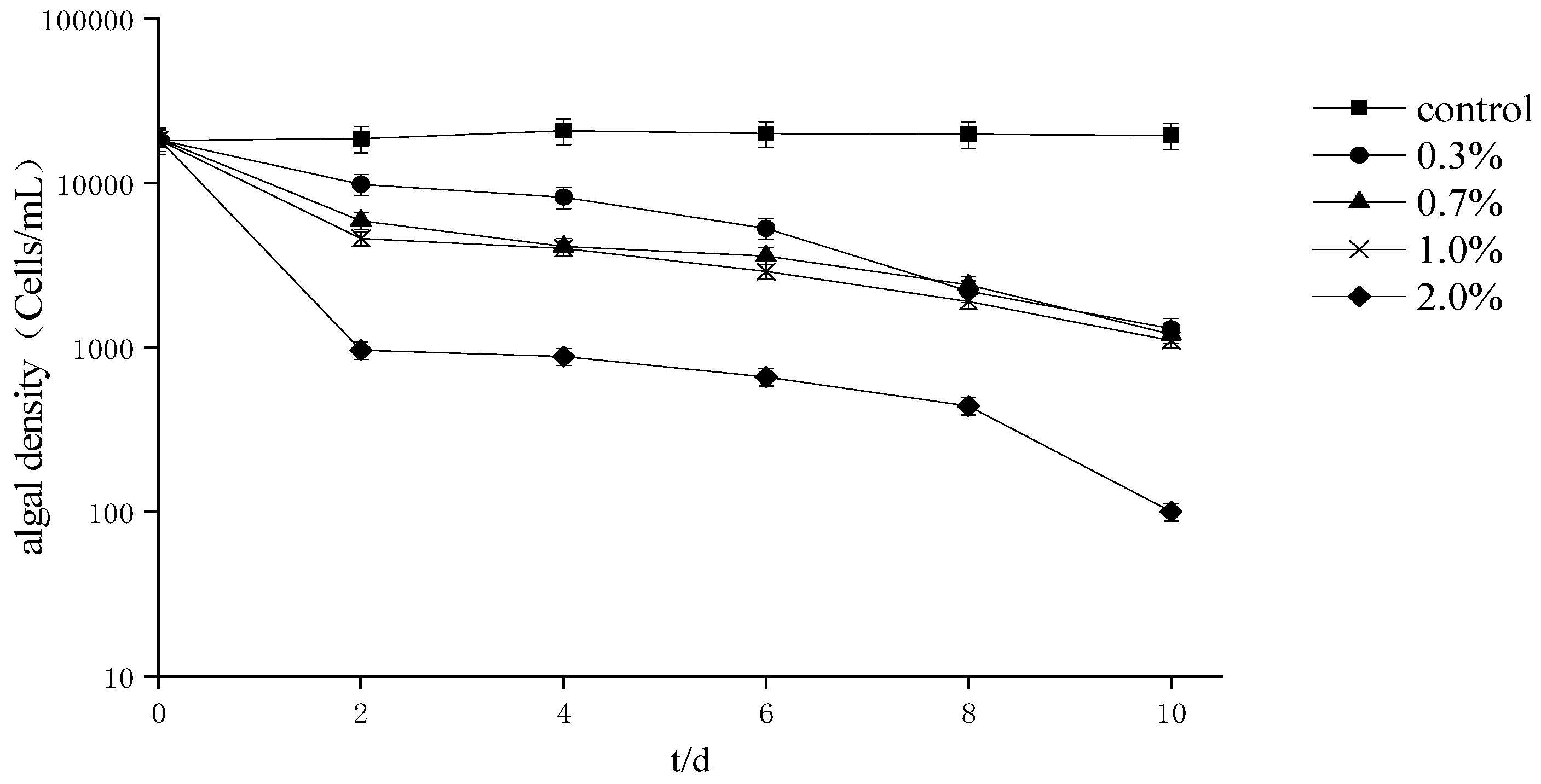
The effect of different fermentation broth amounts on the growth of A. tamarense (Figure 1) indicates that the cell density decreased with the extension of the treatment period and that the 0.3% treatment group variability trend was relatively gentle compared to that of the other treatment groups. In addition, after 10 days of culture, the inhibition rate of each treatment group was greater than 98%.
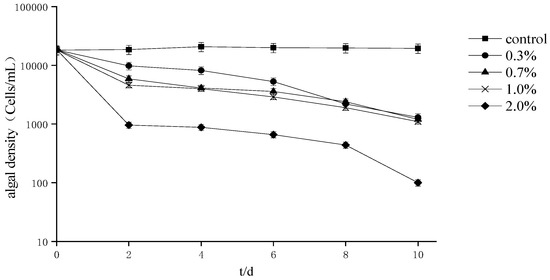
Figure 1.
Effects of different proportions of fermentation broth on the growth of Alexandrium tamarense.
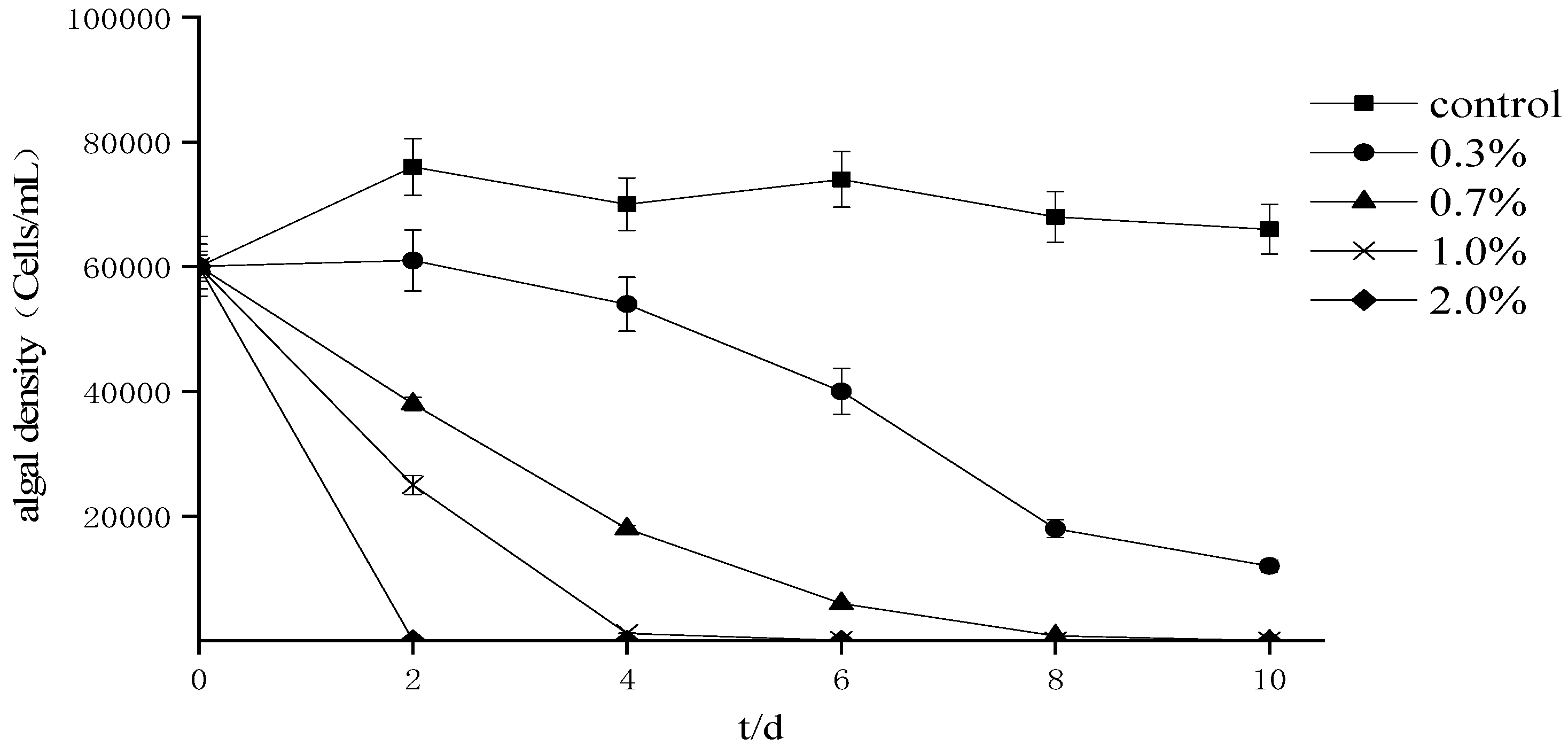
The effects of fermentation broth with different supplemental levels on the growth of P. donghaiense (Figure 2) indicate that the density of algae cells decreases with the prolongation of treatment time. Among the treatment groups, the changing trend for the 2% treatment group was faster than that for the other treatments, showing that the inhibition rate could reach 99.1% in two days. The results of the correlation analysis (Table 1) showed that treatment time and different supplemental levels had a significant correlation with the cell density of P. donghaiense (p < 0.01), while different supplemental levels had a significant correlation with A. tamarense algal cell density (p < 0.01).
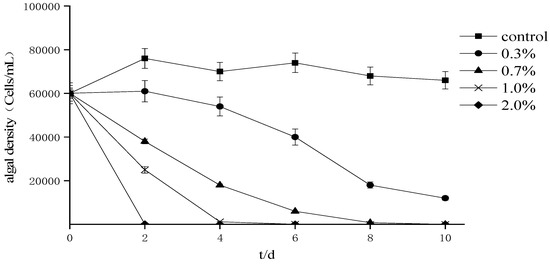
Figure 2.
Effects of different proportions of fermentation broth on the growth of Prorocentrum donghaiense.

Table 1.
Correlation analysis results show that the treatment time and the different cell densities of red tide algae.
Results showed that the inhibition effect of fermentation broths containing the Ba3 strain had a similar trend, i.e., the density of algae cells in each treatment group decreased, and the inhibitory effect of larger treatment doses gradually became apparent. Additionally, the inhibition rate of the two kinds of red tide algae cultured for 4 d–10 d in a fermentation broth containing 1% Ba3 reached 90%, indicating that the inhibition effect was stable.
4.2. Effects of Ethanol Crude Extract of Fermentation Broth on the Growth of Red Tide Algae
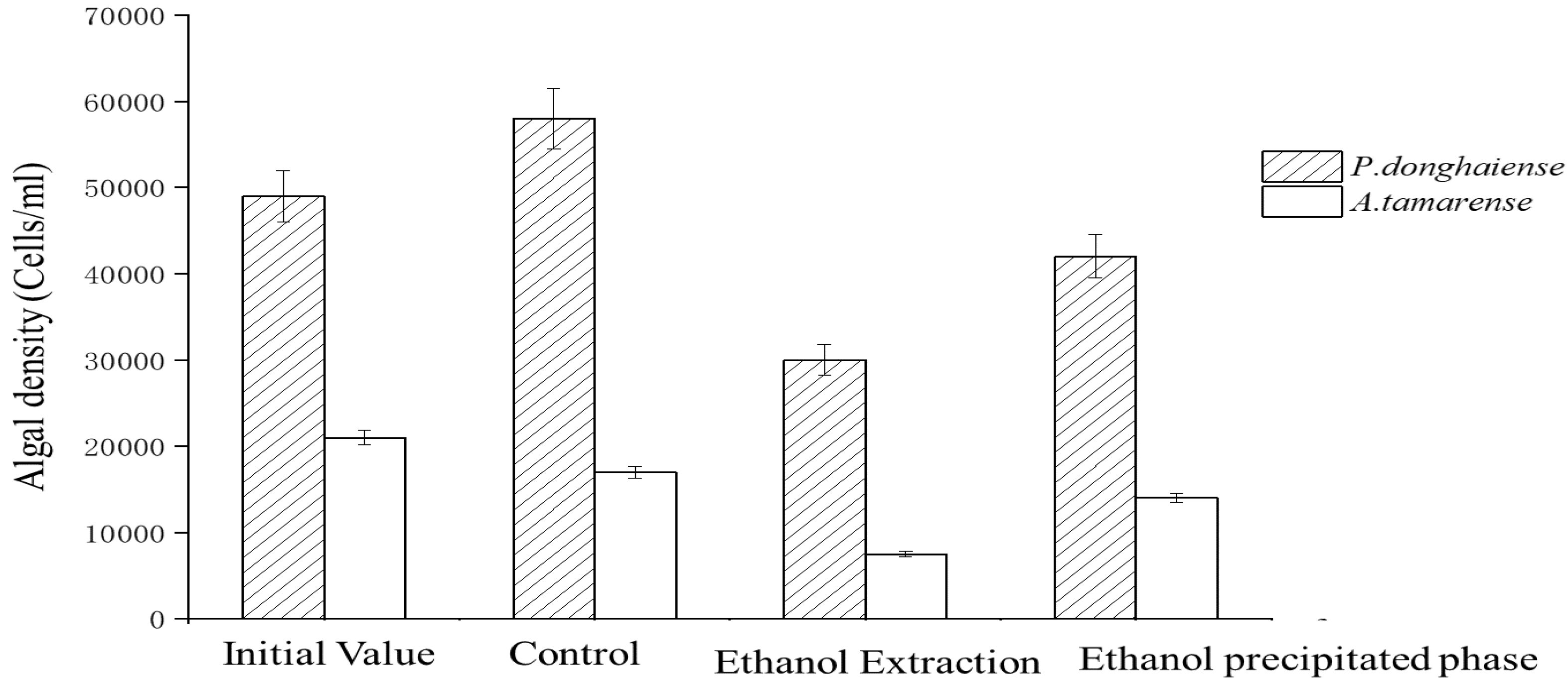
Figure 3 shows that the inhibition effect of the ethanol extraction phase proved more potent than that of the ethanol precipitation phase. After 6 days of culture, the ethanol leaching inhibition rates were 55.94% and 59.21%, while the inhibition rates of the ethanol precipitation phase were 17.49% and 10.53%. These results suggest that ethanol extract contained the most concentrated inhibitory substances.
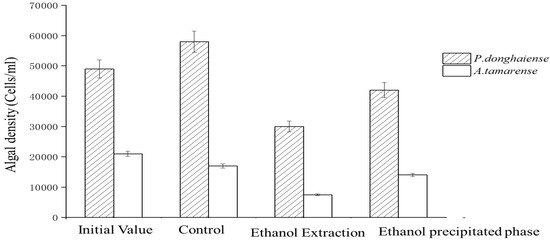
Figure 3.
Inhibitory effect of the ethanol extraction phase and precipitation phase on algae growth.
4.3. Effects of Different Organic Solvents Extracted from Fermentation Broth on the Growth of Red Tide Algae
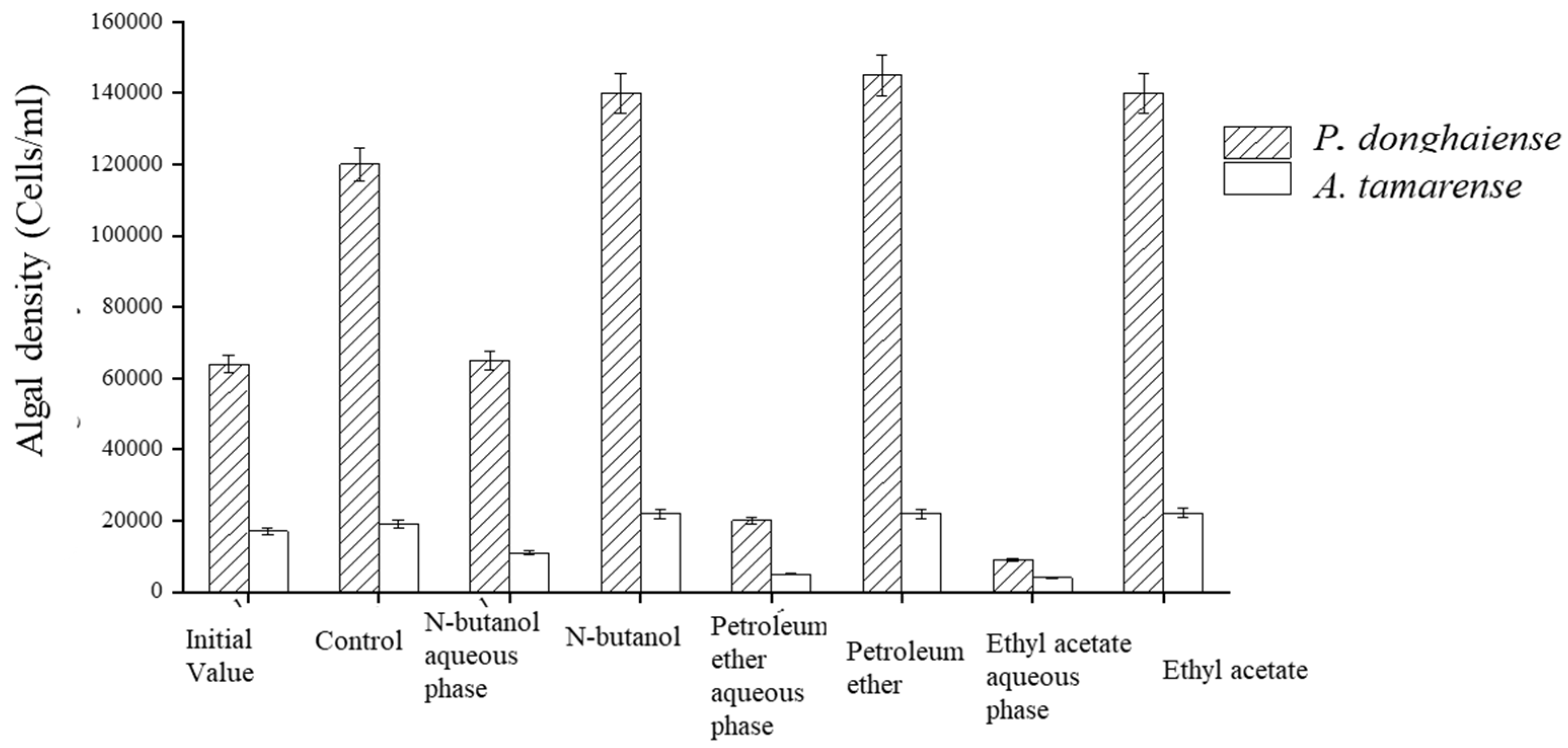
The fermentation broth of the Ba3 strain displayed the full range of polarity when extracted with petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol. The organic phase of all three solvents had virtually no inhibition effect on the algae, while the water phase after extraction had a potent inhibitory effect. The P. donghaiense growth inhibition rates of petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol were 85%, 93%, and 44%, respectively, and 84%, 86%, and 30%, respectively, for the growth of A. tamarense. These results indicate that the extracellular exudates of the Ba3 strain contained highly polar active substances operating against algae (Figure 4).
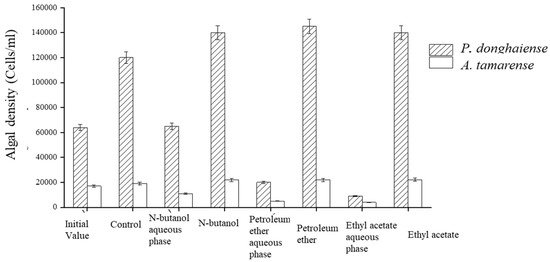
Figure 4.
Inhibitory effect of different organic solvent extraction phases on algae growth.
4.4. Molecular Weight Analysis of Dialysis Bags for Algal Inhibition Substances
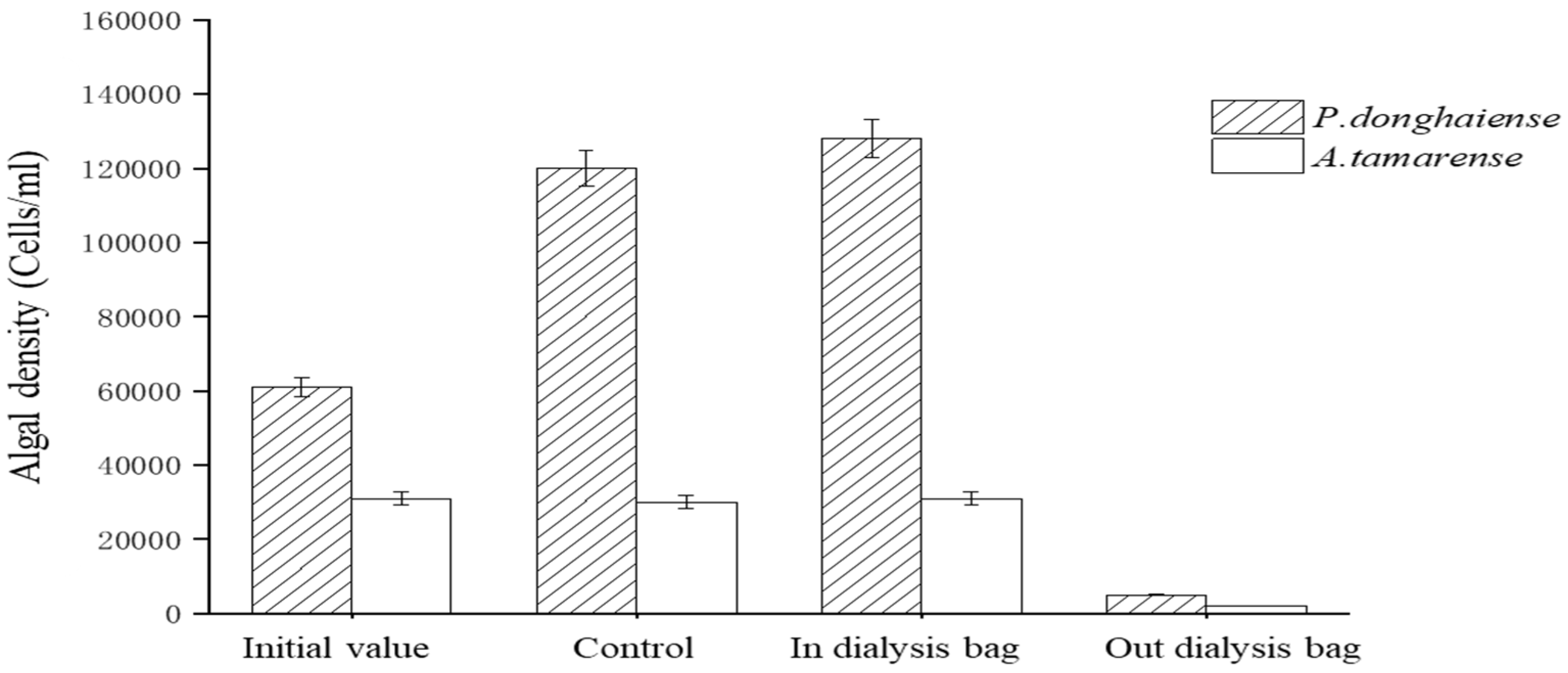
The fermentation broth of the Ba3 strain at a cut-off range of 8–14 kD was dialyzed with a dialysis bag. Substances with a molecular weight greater than 8000 were retained in the dialysis bag, while substances with less than 8000 filtered through the dialysis bag. The inhibitory effect of the solution inside and outside the dialysis bag (Figure 5) showed that the solution inside the bag had almost no inhibiting effect on the growth of P. donghaiense or A. tamarense. By contrast, the inhibition factors of the solution outside the bag were 97% and 92% for P. donghaiense or A. tamarense, respectively. Therefore, it was preliminarily determined that the molecular weight of the active substances against algae in the Ba3 strain fermentation broth was less than 8000.
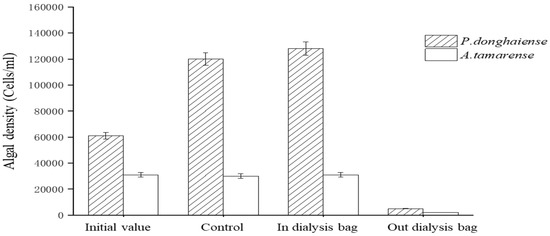
Figure 5.
Antialgae effect of the dialysis bag internal and external liquid.
4.5. Selection of Macroporous Resin
HZ830 and HZ807 have a specific adsorption capacity for the active substances against algae in the fermentation broth of the Ba3 strain, but the macroporous resin HZ830 provides a larger adsorption capacity than HZ807 and can concentrate the active substances more effectively. Therefore, the macroporous resin H2830 was selected as the experimental material for the subsequent separation steps.
4.6. Inhibition Effect of Ethanol Elution of HZ830 Macroporous Resin
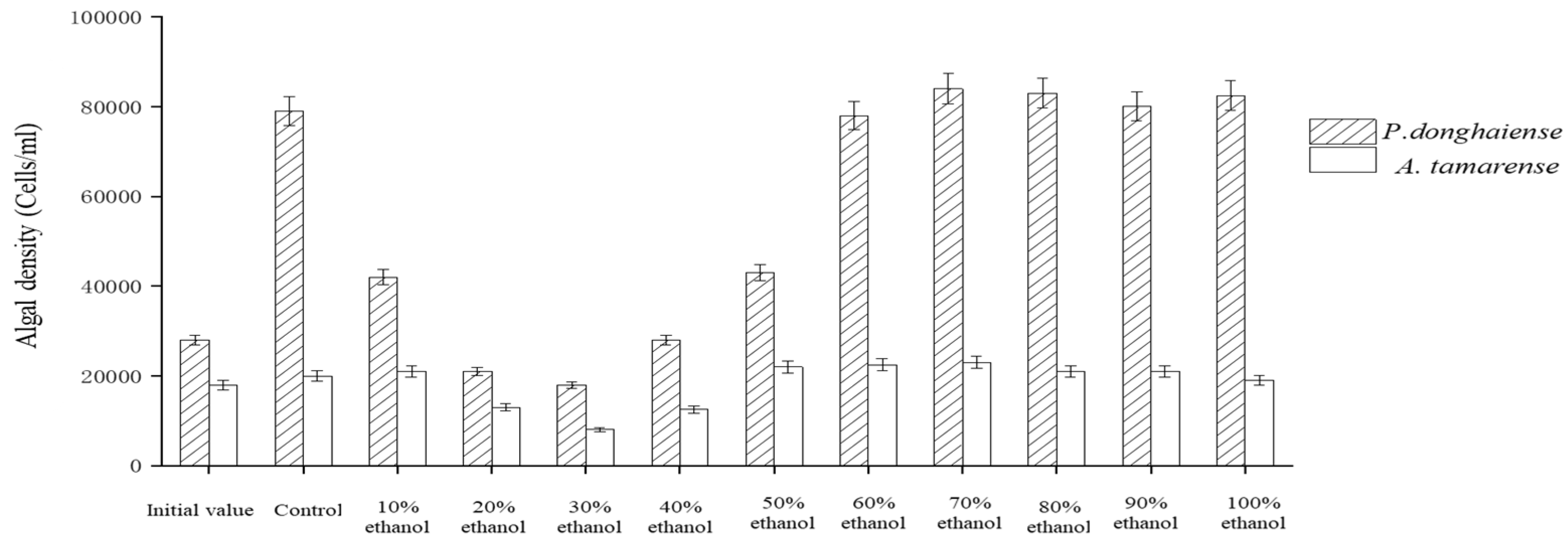
The Ba3 strain fermentation broth was eluted by HZ830 macroporous resin at different ethanol concentrations to obtain each component. The effects of each component on the growth of P. donghaiense and A. tamarense are shown in Figure 6. These results showed that the inhibition effect of each eluting component on the growth of the two red tide algae, from strong to weak, was as follows: 30% ethanol eluting component and GT; 20% ethanol elution component and GT; 40% ethanol elution component and GT; 10% ethanol elution component and GT; and 50% ethanol elution fraction. Among these effects, the inhibition rate of 30% ethanol eluting fraction on the growth of P. donghaiense was 79%, and the inhibition rate on the growth of A. tamarense was 63%. The 60% and 100% ethanol elution fractions had no perceptible inhibitory effect on algae.
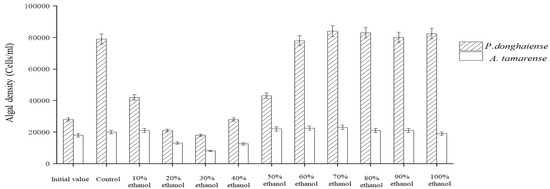
Figure 6.
Algae inhibition by gradient elution of macroporous resin with ethanol.
4.7. Liquid Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Algal Inhibition Substances
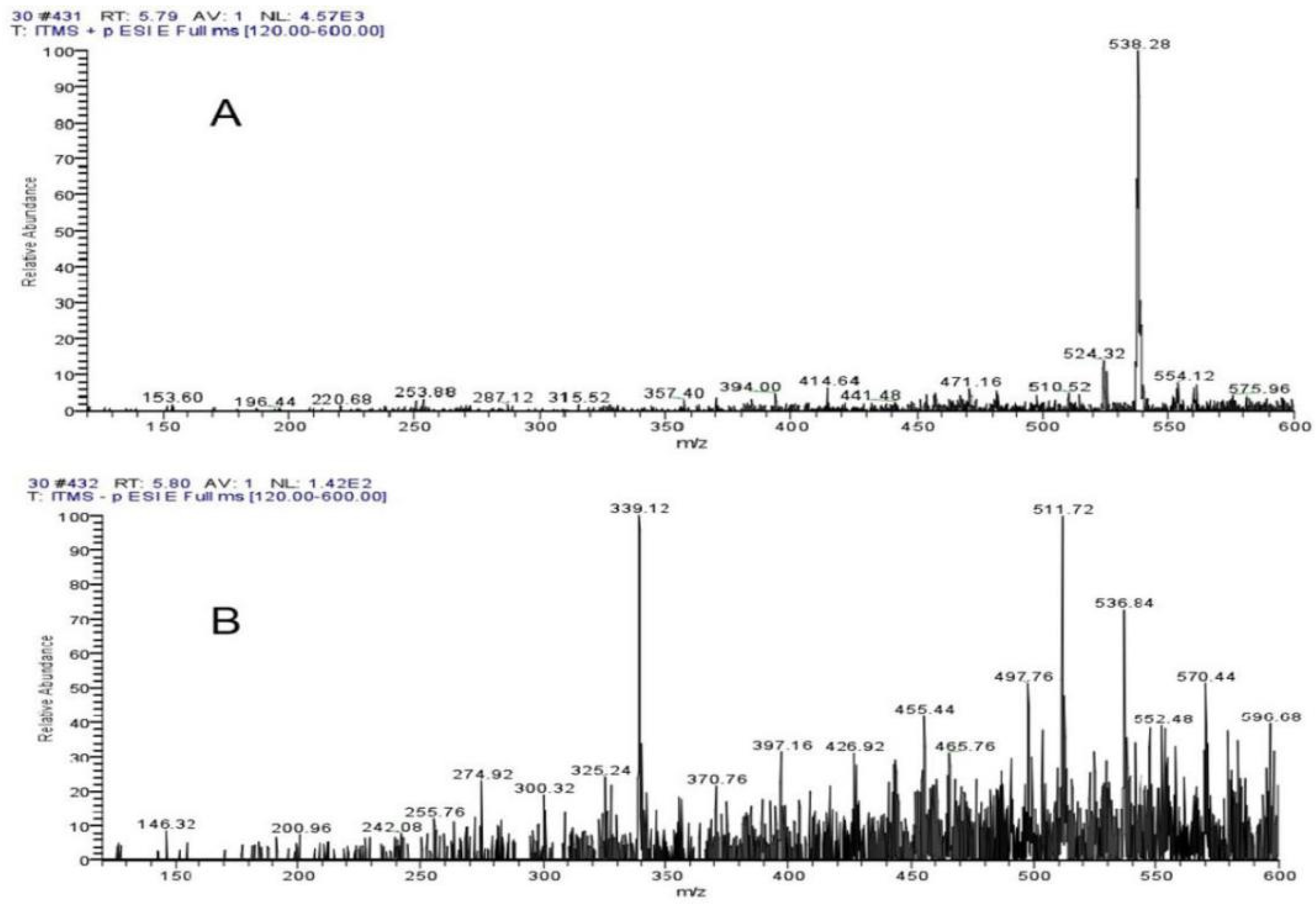
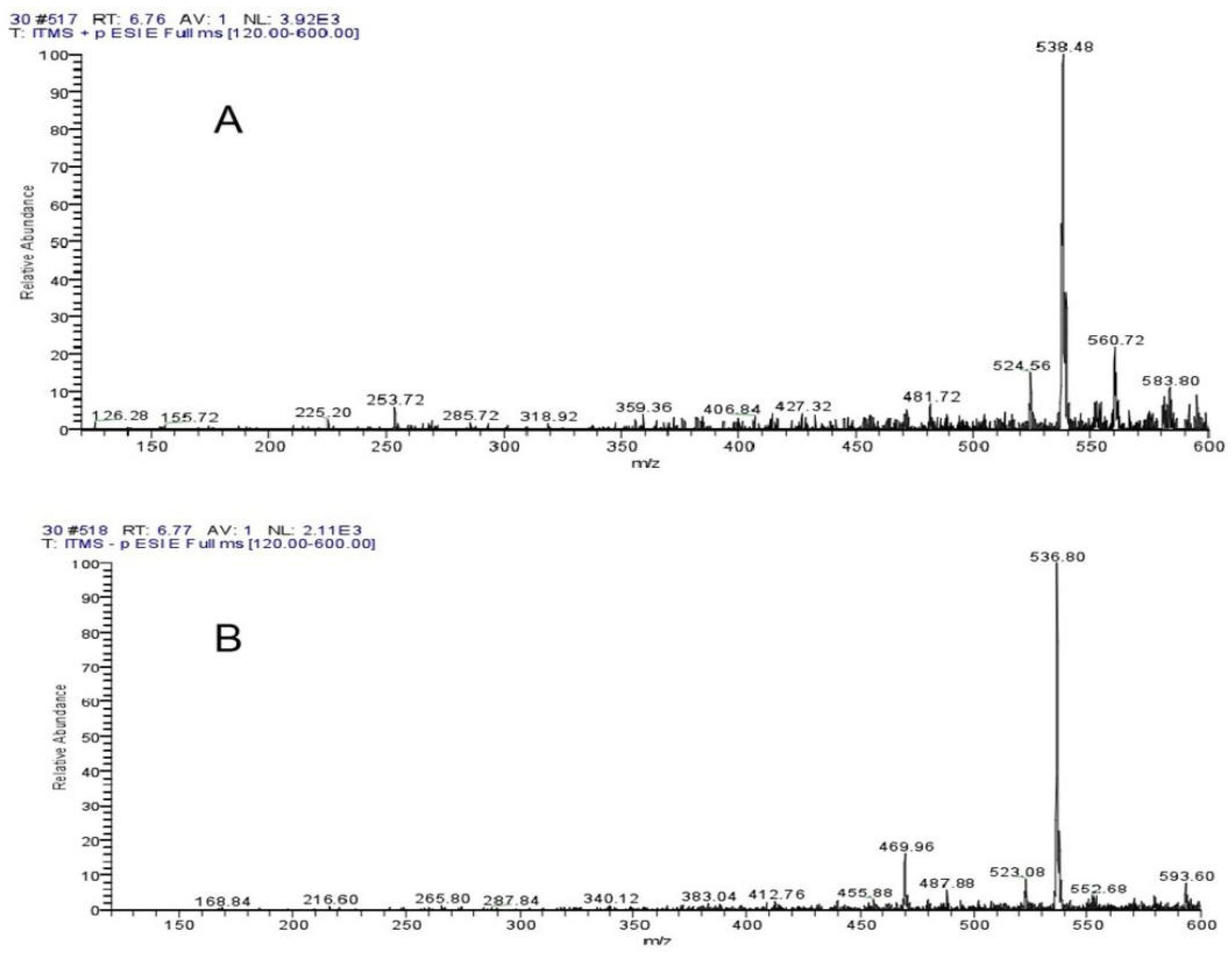
The ThermoFisherU3000 high-performance liquid chromatography was used for LC-MS detection of 10–50% ethanol elution components (Supplementary Figures S2–S6). The significant inhibitory effect of 30% ethanol elution components reached two peaks at 5.39 min and 6.20 min. Supplementary Figure S7 shows the UV absorption peak of 5.39 min, with the wavelength of PDA at 228 mm and 261 nm. Supplementary Figure S8 shows a UV absorption peak of 6.20 min, and the wavelength of PDA is 241 nm and 265 nm. As seen from Mass Spectrogram analysis, Figure 7A,B showed 538.28 positive ions and 536.84 negative ions at 5.39 min. As can be seen from Figure 8A,B, at 6.20 min, the molecular weight of the two compounds was 538.48 positive ions and 536.80 negative ions. Both compounds exhibited the same ionic binding form [M+H]+ and had a molecular weight of 537, suggesting that the two compounds are isomers.
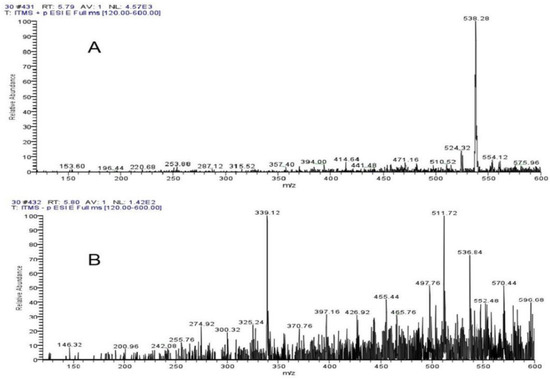
Figure 7.
Mass Spectrogram analysis showed (A) 538.28 positive ions and (B) 536.84 negative ions at 5.39 min.
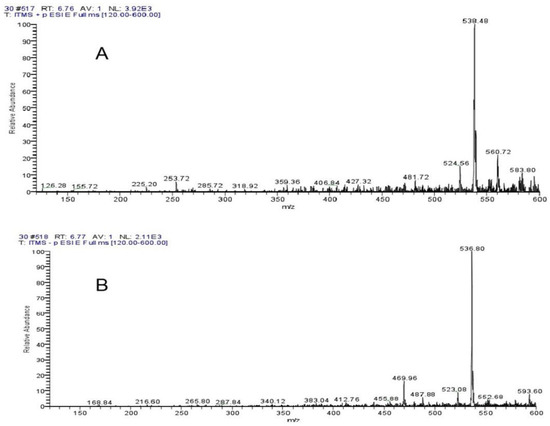
Figure 8.
Mass Spectrogram analysis showed (A) 538.48 positive ions and (B) 536.80 negative ions at 6.20 min.
5. Discussion
Studies have shown that the productivity of secondary metabolites of microorganisms can be enhanced during repeated fermentations [16,18]. Thus, fermentation is essential for the large-scale production of the appropriate algicidal compounds. In this study, the culture parameters of the fermentation system were obtained in strict accordance with a flask optimization experiment, so the aeration volume and rotation speed related to dissolved oxygen were adjusted accordingly. Currently, algicidal strains have typically been selected and studied in small-scale cultures [19,20,21], eliminating the need for algicidal property analysis after fermentation processing to some extent. Repeated batch fermentation of immobilized bacteria has been widely applied to produce secondary metabolites [22,23]. Studies have shown that the productivity of secondary metabolites of microorganisms, such as penicillin [24], gibberellic acid [25], cyclosporin A [26], and lovastatin [27] can be enhanced during repeated fermentations. Despite limited research regarding the potential application of fermentation products for controlling HABs, it is possible that fermentation products of algicidal bacteria may be considered an effective biological agent for treating HABs. Therefore, strains applied as microbial algicides should exhibit high survival rates during fermentation and downstream processes, including centrifugation, drying, and storage [13]. In terms of their biological safety, metabolites are biodegradable. Moreover, when used to control blooms, they appear to be harmless to the environment [28]. Zhao et al. [29] isolated secondary metabolites from a fermentation broth of Bacillus B1 strain had a strong alga dissolving effect against Phaeocystis globosa. In our previous study, a Ba3 Bacillus strain of fermentation broth had the best removal effect on G. catenatum. These results strongly bolster the claim that Ba3 has potential applications in controlling dinoflagellate outbreaks [16]. All fermentation products from strain Ba3 showed algicidal activity against harmful dinoflagellates; however, their efficacies differed significantly. For all tested dinoflagellates, the vegetative bacteria cells in the group exhibited the best inhibitory and algicidal effects in only one day, whereas Bacillus spores in the group were the least effective in inhibiting dinoflagellate growth.
The ethanol precipitation method offers a fundamental method for material separation. In ethanol, the solubility of biological macromolecules such as protein, nucleic acid, and polysaccharides is significantly reduced. Therefore, different components in the microbial fermentation broth can be effectively separated by complete oscillation [30]. Many scholars have used the ethanol precipitation method to study the active components of algal inhibition. For example, Wang et al. [31] isolated a strain of bacteria H2 inhibiting Microcysts aeruginosa from Chaohu Lake. The inhibitory effect of extracellular secretions extracted by ethanol was more potent than that of ethanol precipitation, with an inhibition rate of 52.50%. In this study, ethanol crude extraction was used to determine the fermentation broth composition with significant algal inhibition effect in the Ba3 strain, indicating that the algal inhibition active compound may not be a protein, nucleic acid polysaccharide, or other biological macromolecules. Nevertheless, according to Yu’s study [32] of the inhibitory activity of actinomycete G-11 against red tide algae after ethanol precipitation, the constituent with the best inhibitory effect was detected in the ethanol precipitation phase.
According to the principle of “similar phase dissolution”, microbial fermentation broth can be extracted with organic solvents of different polarities. For example, Wang et al. [33] extracted the supernatant of Aureus S7 culture with cyclohexane, ethyl acetate, and chloroform and uncovered that the aqueous phase’s inhibitory effect of the three aqueous solvents was more significant than that of the organic phase. Chen [34] extracted bacillus B1 fermentation broth with ethyl acetate, petroleum ether, and n-butanol in three different polar organic solvents. The inhibition effect of the water phase of the three solvents was more significant than that of the organic phase. In this study, the results of petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, and n-butanol abstraction showed that the aqueous phase of the three solvents inhibited the growth of the two red tide algae that form blooms significantly more than the organic phase, indicating that the extracellular secretion of Ba3 strain contained more polar-active substances against algae.
The preliminary analysis of the molecular weight of the algicidal substances can also be performed by using a dialysis bag. For example, Li et al. [35] discovered through a dialysis bag experiment that the active substance of bacteria L7 inhibiting Anabaena sp. alga was less than 3.5 kD, while the active substance of bacteria 18 and L18 inhibiting alga was between 3.5 kD and 7 kD. Tang et al. [36] isolated substances with inhibitory effects on M. aeruginosa from the fermentation broth of actinomycin L74 and determined the molecular weight of the anti-alga substance was lower than 3 kD, also through using a dialysis bag. In this study, dialysis bags with a cut-off range of 8000–14,000 were used to determine that the molecular weight of active substances against algae in the fermentation broth of the Ba strain was less than 8000.
Macroporous resin has strong absorbability in water and is suitable for separating compounds from aqueous solutions; therefore, its separation effect is suitable for this purpose and has been widely used [37]. Through using a macroporous resin with a suitable mesh structure and high surface area, macroporous resin adsorption can separate crude extracts of different components, and then by applying the appropriate solvent gradient elution, collect a target component that has been separated from crude extracts of sugar, pigment, and others. Our study compared the separation effects of two kinds of macroporous resin. The crude extract of Ba3 strain was adsorbed by HZ830 macroporous resin and eluted by 10–100% ethanol gradient, and 10 components were obtained, among which the 30% ethanol eluted component had the most significant inhibitory effect.
The structures of the separated components could also be investigated by infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC-MS), high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS), and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR). Among these methods, the liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) combined technology is most suitable for treating samples with poor gasification and thermal stability, which plays an essential role in material separation research. For polar materials, an ESI power supply is generally used. Separation purification and identification are not yet well-developed; therefore, various technologies must be combined to achieve these goals. As of now, there are a limited number of substances that can be identified as effective in inhibiting algae, primarily proteins, peptides, antibiotics, pigments, amino acids, fatty acids, nitrogen compounds, and alkaloids. In this study, LC-MS detection was carried out on the elution fractions of 10–50% ethanol with the effect of detecting algae, and the eluting fractions of 30% ethanol had the best inhibitory activity peaking at 5.39 min and 6.20 min. The ionic binding form of the two compounds is [M+H]+, and the molecular weight is 537, suggesting that they are isomers, which suggests that the difficulty in separating similar active algal compounds from their precursors may be related to the adsorption of macroporous resin on the active algal compounds. The subsequent identification of the specific structure of compounds requires more advanced techniques such as nuclear magnetic resonance and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Further studies are needed to determine whether the nutrient changes caused by fermentation broth can be re-released from the algae matrix into the water, which may contribute to the formation of resting cysts [30]. Additionally, it should be noted that this research would have been more complete if it had been supplemented with data on the effects of Ba3 broth on algal cultures [16]. The purification and identification of the algicidal compounds, as well as the safety evaluation in marine environment and its impact on cultured organisms which requires further investigation [13,38].
In recent years, the frequent outbreak of red tide has brought a severe threat to coastal areas. As part of the ongoing fight against red tides, microbiological management has become an increasingly important research topic. China has made some of the most recent achievements in studying microbial red tide control, especially the “bacteria against algae” variety; however, microbial red tide control has also propounded a lengthy and complicated investigation pathway. Even though more and more microorganisms with algal inhibitory effects are being discovered, a systematic classification of the prevalence and specificity of inhibition effects of different microorganisms on different algal species remains insufficient [39]. Furthermore, the specific compounds of the active algicidal substances of the Ba3 strain have not been identified or purified. In subsequent studies, more advanced technologies such as nuclear magnetic resonance and high-resolution mass spectrometry could be applied to purify and identify the structure of the active algicidal substances present in the Ba3 strain. In this study, only the components with significant activity were separated and detected during the separation process, potentially overlooking some highly active but trace active algal substances.
6. Conclusions
In our study, the algicidal activity of the fermentation broth showed significant inhibitive effects on red tide algae. Through using crude extraction with an organic solvent, the active components of the Ba3 strain fermentation liquid were mainly found in the ethanol extraction phase and the aqueous phase of three organic solvents (petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butanol), with the molecular weight of the algicidal substance being less than 8000 in a dialysis bag. After adsorption by HZ830 macroporous resin, the crude extract of fermentation liquid of the Ba3 strain was eluted by 10–100% ethanol in gradient elution, obtaining an elution fraction of 10–50% ethanol which indicates promising algal inhibition activity. The elution fraction of 30% had the best algal inhibition effect overall. According to LC-MS detection, the fraction showed a peak at 5.39 min and 6.20 min. The effect of bacterial fermentation broth on killing algae is complete. The active substances in the fermentation broth act on the algae cells to lyse them. In practice, algal active substances do not act alone, and the results of the joint action of multiple substances also need to be considered. The combination of fermentation liquid and clay can improve the effect of control of dinoflagellates. To advance research on the relationship between bacteria and algae and to explore the mechanism of algal toxin production, it is necessary not only to obtain abundant information on species diversity in the algal community but also to isolate and culture key microorganisms from the algal community for further research. Our findings will integrate well into the future studies of controlling toxic dinoflagellate cysts in the marine environment.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation8040176/s1, Figure S1. Identification of Ba3 by the morphology, plate shape (a); under microscope (b); SEM image (c), and 16S rRNA gene, which was shown as the phylogenic tree (d); Figure S2. High performance liquid chromatography of elution component 10% ethanol; Figure S3. High performance liquid chromatography of elution component 20% ethanol; Figure S4. High performance liquid chromatography of elution component 30% ethanol; Figure S5. High performance liquid chromatography of elution component 40% ethanol; Figure S6. High performance liquid chromatography of elution component 50% ethanol; Figure S7. Ultraviolet absorption peak of 5.39min; Figure S8. Ultraviolet absorption peak of 6.20 min.
Author Contributions
B.B.-P.: writing—original draft, methodology, writing—review, funding acquisition, data curation. Y.W.: methodology, data curation. Y.S.: funding acquisition, visualization, writing—review and editing. M.C.: methodology, data curation. And Y.Z.: funding acquisition, visualization. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by National Key Research & Development Plan “Strategic International Scientific and Technological Innovation Cooperation” (2016YFE0202100), Marine Red Tide Early Warning and Prevention in Pingtan coastal area (PT2021006). National Natural Science Foundation of China (41573075), Fujian Provincial Water Conservancy Technology Project (SC-292, DH-1558, 21NB000922, MSK202202).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors are also indebted to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions for the improvement of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Griffith, A.W.; Gobler, C.J. Harmful algal blooms: A climate change co-stressor in marine and freshwater ecosystems. Harmful Algae 2019, 91, 101590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glibert, P.M.; Al-Azri, A.; Icarus Allen, J.; Bouwman, A.F.; Beusen, A.H.W.; Burford, M.A.; Harrison, P.J.; Zhou, M. Key questions and recent research advances on harmful algal blooms in relation to nutrients and eutrophication. In Global Ecology and Oceanography of Harmful Algal Blooms; Glibert, P.M., Berdalet, E., Burford, M.A., Pitcher, G.C., Zhou, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 229–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, J. Historical Occurrence of Algal Blooms in the Northern Beibu Gulf of China and Implications for Future Trends. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCabe, R.M.; Hickey, B.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Lefebvre, K.A.; Adams, N.G.; Bill, B.D.; Gulland, F.M.; Thomson, R.E.; Cochlan, W.P.; Trainer, V.L. An unprecedented coast wide toxic algal bloom linked to anomalous ocean conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 10366–10376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, J.P.; Kudela, R.M.; Birch, J.M.; Blum, M.; Bowers, H.A.; Chavez, F.P.; Doucette, G.J.; Hayashi, K.; Marin, R.; Mikulski, C.M.; et al. Causality of an extreme harmful algal bloom in Monterey Bay, California, during the 2014–2016 northeast Pacific warm anomaly: Extreme HAB Causality in Monterey Bay. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 5571–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Chi, Y.X.; Wu, D.H.; Dai, X.Z.; Zhang, X.H.; Igarashi, Y.; Luo, F. Algicidal characterization and mechanism of Bacillus licheniformis Sp34 against Microcystis aeruginosa in Dianchi Lake. J. Basic. Microb. 2019, 59, 1112–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigalke, A.; Meyer, N.; Papanikolopoulou, L.A.; Wiltshire, K.H.; Pohnert, G. The algicidal bacterium Kordia algicida shapes a natural plankton community. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e02779-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, N.; Bigalke, A.; Kaulfuss, A.; Pohnert, G. Strategies and ecological roles of algicidal bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 880–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, K.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, H.; Lei, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Hong, Y.; Ma, X.; Zheng, W.; et al. The algicidal mechanism of prodigiosin from Hahella sp. KA22 against Microcystis aeruginosa. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, F.; Shao, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Yao, L.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, T.; et al. Flocculating properties and potential of Halobacillus sp. strain H9 for the mitigation of Microcystis aeruginosa blooms. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokrzywinski, K.L.; Tilney, C.L.; Warner, M.E.; Coyne, K.J. Cell cycle arrest and biochemical changes accompanying cell death in harmful dinoflagellates following exposure to bacterial algicide IRI-160AA. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, W.; Wang, D. Algal cell lysis by bacteria: A review and comparison to conventional methods. Algal Res. 2020, 46, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zaynab, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Li, S. Encapsulation and Algicidal Properties of Fermentation Products From Vibrio brasiliensis H115. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 676913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Gu, X.; Guo, Z.; Song, J.; Zhu, D. Stabilizing lactate production through repeated batch fermentation of food waste and waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 300, 122709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, F.; Nie, Y.; Liu, T. Effects of concentration variation on the physical properties of alginate-based substrates and cell behavior in culture. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Su, H.; Xu, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, S.; Huang, X. Algicidal properties of fermentation products from Bacillus cereus strain JZBC1 dissolving dominant dinoflagellate species Scrippsiella trochoidea, Prorocentrum micans, and Peridinium umbonatum. Biologia 2020, 75, 2015–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji Prasath, B.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Zheng, W.; Lin, H.; Yang, H. Coagulant Plus Bacillus nitratireducens Fermentation Broth Technique Provides a Rapid Algicidal Effect of Toxic Red Tide Dinoflagellate. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, B.; Xu, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, G.; Liu, X. A marine algicidal Thalassospira and its active substance against the harmful algal bloom species Karenia mikimotoi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 5131–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.-R.; Hu, C.-X.; Li, H.; Hu, Z.-L. Isolation and characterization of the marine algicidal bacterium Pseudoalteromonas S1 against the harmful alga Akashiwo sanguinea. Mar. Biol. 2016, 163, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cai, G.; Wang, H.; Li, D.; Yang, X.; An, X. Streptomyces alboflavus RPS and its novel and high algicidal activity against harmful algal bloom species Phaeocystis globosa. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.J.; Huang, L.P.; Su, J.Q.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, T.L. Algicidal effects of a novel marine actinomycete on the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Curr. Microbiol. 2011, 62, 1774–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.C.; Wen, G.L.; Li, Z.J.; Hu, X.J.; Xi, J.Y.; Li, S.S.; Huang, H.H. Bacillus Cereus Strain JZBC1 Dissolving Dominant Dinoflagellate of Pond-Scrippsiella Trochoidea and Its Application. China Patent ZL201610209371.X, 5 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, C.; Guo, X.; Cai, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, T. Novel algicidal evidence of a bacterium Bacillus sp. LP-10 killing Phaeocystis globosa, a harmful algal bloom causing species. Biol. Control 2014, 76, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.S.; Jetty, A.; Ramakrishna, S.V. Kinetic studies of penicillin production during batch and repeated batch in fluidized bed bioreactor with agar immobilized P. chrysogenum cells. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2004, 3, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Meleigy, S.A.; Khalaf, M.A. Biosynthesis of gibberellic acid from milk permeate in repeated batch operation by a mutant Fusarium moniliforme cells immobilized on loofa sponge. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvase, S.A.; Annapure, U.S.; Singhal, R.S. Gellan gum as an immobilization matrix for the production of cyclosporin A. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcel, E.M.R.; López, J.L.C.; Pérez, J.A.S.; Chisti, Y. Lovastatin production by Aspergillus terreus in a two-staged feeding operation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2008, 83, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perzborn, M.; Syldatk, C.; Rudat, J. Enzymatical and microbial degradation of cyclic dipeptides (diketopiperazines). AMB Express 2013, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, L.; Yin, P. Algicidal metabolites produced by Bacillus sp strain B1 against Phaeocystis globosa. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Sun, Y.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Activation of accumulated nitrite reduction by immobilized Pseudomonas stutzeri T13 during aerobic denitrification. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 187, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hong, G.; Zhang, J. Study on the algal-lysis mechanism of a Microcystis aeruginosa alginolytic bacteria. J. Anhui Univ. Archit. Technol. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2017, 25, 19–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, F. Isolation and Identification of Two High-Efficiency Actinomycetes of Heteroflexus Erythrolytica and Preliminary Research on Alginolytic Active Substances. Master’s Thesis, Central China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2011. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.X.; De, X.H.; Liu, J. Isolation and characterization of extracellular algic substances from algae-soluble bacteria. J. Inn. Mong. Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2014, 35, 67–71. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M. Isolation and Identification of Extracellular Active Substances from Algae-Soluble Bacteria Purified by Glucose Gel. Master’s Thesis, Jinan University, Jinan, China, 2013. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Pan, W.; Yang, L. Study on the separation characteristics of extracellular alginolytic active substances from three algicidal bacteria. Bull. Microbiol. 2008, 35, 7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, S.; Lin, W.; Li, J. Isolation of algae-lysing substances from Actinomyces L74 and their algae-lytic properties. Bull. Microbiol. 2011, 38, 6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zou, R.; Wu, F. HPLC–MS/MS Analysis and Study on the Adsorption/Desorption Characteristics of Ginsenosides on Anion-Exchange Macroporous Resins. Chromatographia 2021, 84, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Hu, G.; Huang, J.; Chen, L.; Yin, Y.; Cai, Y.; Shen, X.; Ji, N. Isolation and characterization of an algicidal bacterium against the bloom-forming algae raphidophyte Heterosigma akashiwo. Environ. Technol. 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.J.; Wen, G.L.; Xu, W.J.; Xu, Y.; Su, H.C.; Yang, K.; Xu, Y.N.; Li, Z.J.; Cao, Y.C. Effects of the algicidal bacterium CZBC1 on microalgal and bacterial communities in shrimp culture. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2019, 11, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).