Effects of Mulberry Leaves and Pennisetum Hybrid Mix-Silage on Fermentation Parameters and Bacterial Community
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silage Preparation
2.2. Chemical Composition and Fermentation Quality of Silage
2.3. Bacterial Community Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Pre-Ensiled Mulberry Leaves and Hybrid Pennisetum Material
3.2. Fermentation Quality of Mulberry Leaves and Hybrid Pennisetum Mix-Silage
3.2.1. The Chemical Composition of Mulberry Leaves and Hybrid Pennisetum Mix-Silage
3.2.2. The Protein Fraction of Mulberry Leaves and Hybrid Pennisetum Mix-Silage
3.2.3. Organic Acid Contents, pH of Mulberry Leaves and Hybrid Pennisetum Mixed Silage
3.3. Bacterial Community of Mulberry Leaves and Hybrid Pennisetum Silage
3.3.1. The Microbial Population of Mulberry Leaves and Hybrid Pennisetum
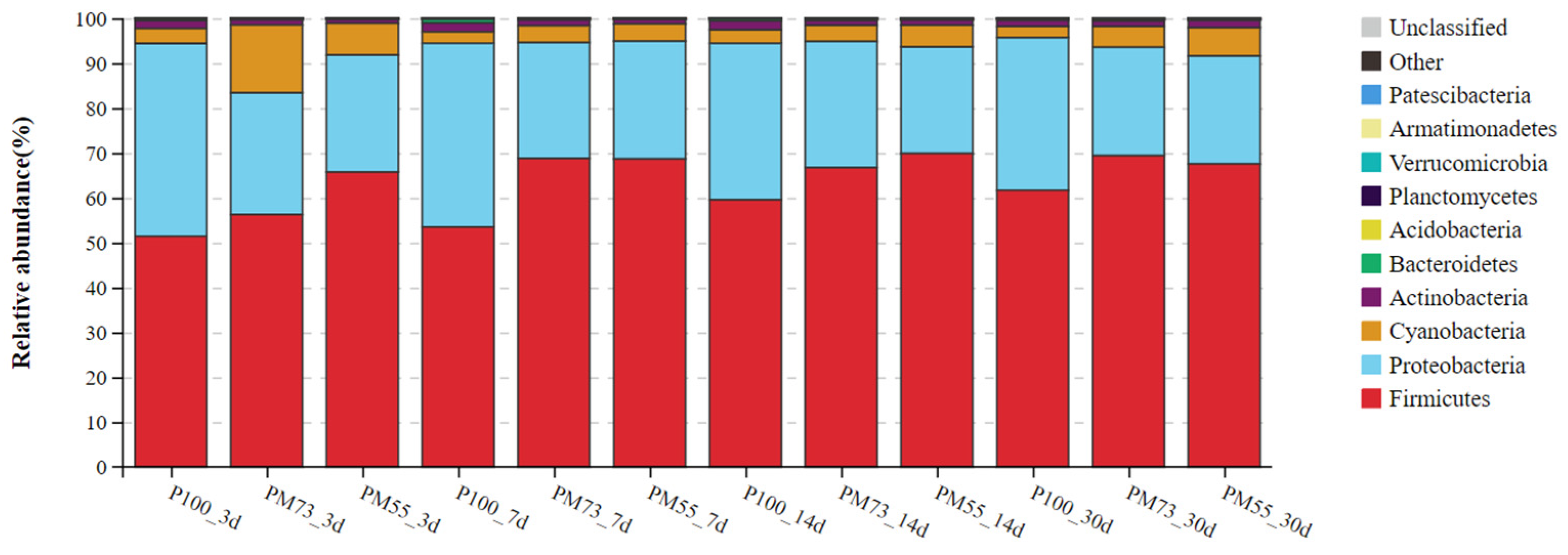
3.3.2. The Changes in the Dynamics of Relative Abundance among Bacterial Communities
3.3.3. Effect of Different Proportions of Hybrid Pennisetum and Mulberry Leaves Mixed Silage on Alpha Diversity of Bacteria
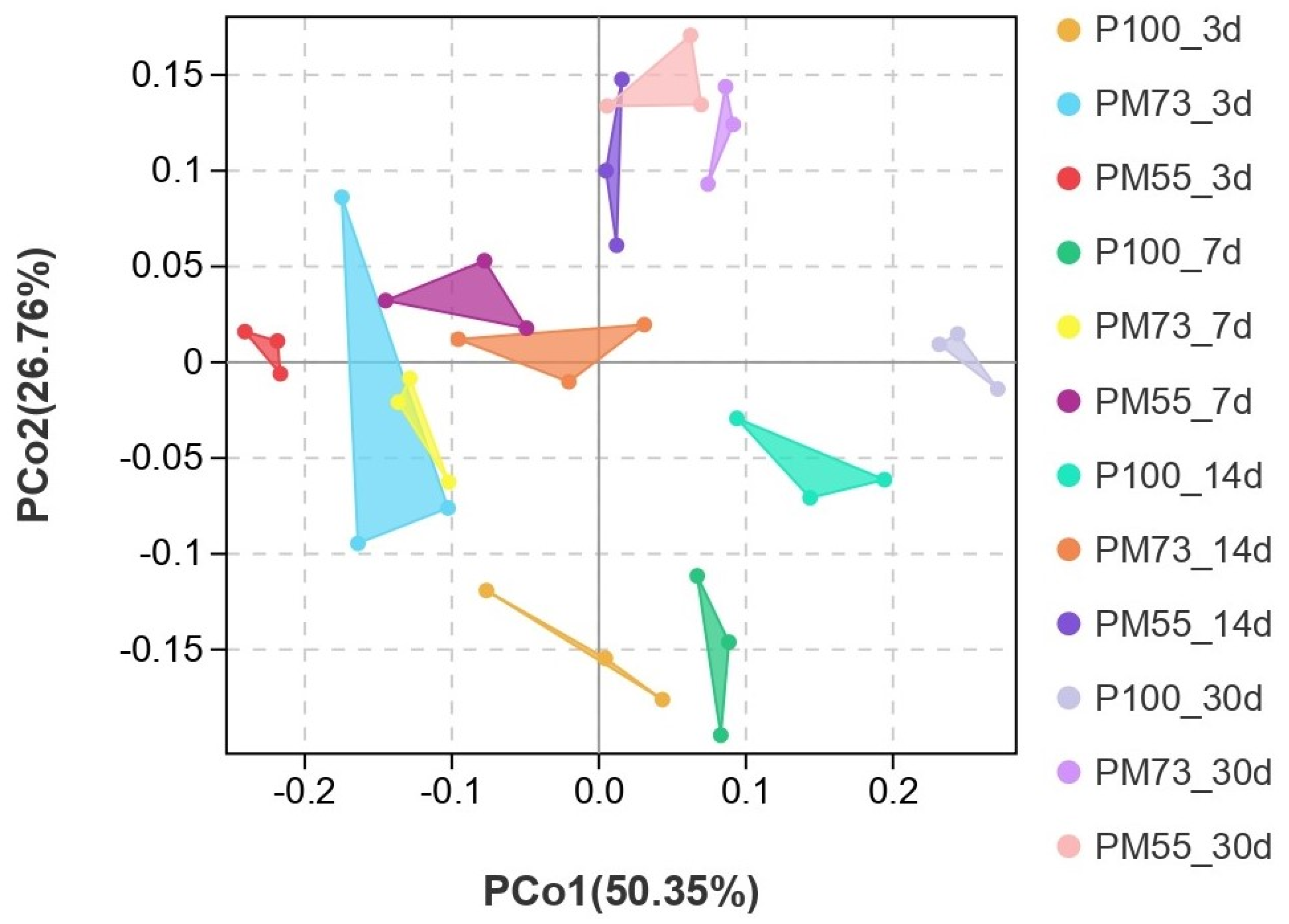
3.3.4. Effect of Different Proportions of Hybrid Pennisetum and Mulberry Leaves Mixed Silage on β-Diversity of Bacteria
3.3.5. 16S rDNA Gene-Predicted Functional Profiles
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yao, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, Z.; He, X.; Cao, R. Effects of feeding fermented Mulberry Leaf powder on growth performance, slaughter performance, and meat quality in chicken broilers. Animals 2021, 11, 3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Mei, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, H. Effects of Mulberry Branch and Leaves silage on microbial community, rumen fermentation characteristics, and milk yield in lactating dairy cows. Fermentation 2022, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, G.; Gao, W.; Chen, K. Efficient conversion of Hubrid Pennisetum to glucose by oxygen-aqueous alkaline ionic liquid media pretreatment under benign conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Lung, S.; Du, Z.; Chye, M. Engineering plants to tolerate abiotic stresses. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2014, 3, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Qian, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Khan, S.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Khan, I.; Zhong, X. Effects of natamycin and Lactobacillus plantarum on the chemical composition, microbial community, and aerobic stability of Hybrid Pennisetum at different temperatures. Rsc Adv. 2020, 10, 8692–8702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Luo, H. Effects of mulberry leaf silage on antioxidant and immunomodulatory activity and rumen bacterial community of lambs. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Qing, Z. Effect of cellulase and Lactobacillus casei on ensiling characteristics, chemical composition, antioxidant activity, and digestibility of mulberry leaf silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9919–9931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, L.; Luo, Q.; Ye, M.; Luo, G.; Kuang, Z. Effects of mulberry (Morus alba) leaf polysaccharides on growth performance, diarrhea, blood parameters, and gut microbiota of early-weanling pigs. Livest. Sci. 2015, 177, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Yao, J.; Yan, B.; Yu, J.Q.; Shi, Z.Q. Effects of mulberry leaves to replace rapeseed meal on performance of sheep feeding on ammoniated rice straw diet. Small Rumin. Res. 2001, 39, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana, P.; Cisneros, L.; Martínez, A.; Pascual, S. Conservation and chemical composition of Leucaena leucocephala plus fresh or wilted Pennisetum purpureum mixed silages. Revista MVZ Córdoba 2015, 20, 4895–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yy, A.; Xl, A.; Hao, G.; Lh, A.; Xiao, M.; Yan, P.; Zhou, L.; Gang, N.; Jz, A.; Wy, B. Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of Italian ryegrass silage prepared with corn stover and lactic acid bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josefa, M.; Antonio, M.; Fuensanta, H.; María, D. A comparative study on the determination of lactic acid in silage juice by colorimetric, high-performance liquid chromatography and enzymatic methods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1999, 79, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erwin, S.; Marco, G.; Emery, A.E. Volatile fatty acid analyses of blood and rumen fluid by gas chromatography. J. Dairy Sci. 1961, 44, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.; Ding, W.; Xu, D.; Ding, L.; Zhang, R.; Li, F.; Guo, X. Effects of addition of malic or citric acids on fermentation quality and chemical characteristics of alfalfa silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 8958–8966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helrick, K. Official Methods of Analysis, 15th ed.; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1990; p. 703. [Google Scholar]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.P. A method for the extraction of plant samples and the determination of total soluble carbohydrates. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 9, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Wu, F.; Hao, G.; Qi, Q.; Rong, L.; Li, N.; Wei, L.; Chai, T. Bacillus subtilis improves immunity and disease resistance in rabbits. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huan, H.; Gu, H.; Xu, N.; Shen, Q.; Ding, C. Dynamics of a microbial community during ensiling and upon aerobic exposure in lactic acid bacteria inoculation-treated and untreated barley silages. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Wu, S.; Zou, X.; Chen, X.; Ge, L.; Zhang, Q. Effects of gallic acid on fermentation parameters, protein fraction, and bacterial community of whole plant soybean silage. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 662966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojo, V.; Ogunsakin, A.; Dele, P.; Adelusi, O.; Olanite, J.; Adeoye, S.; Amole, T.; Onifade, O. Yield and chemical composition of Pennisetum hybrid fertilized with animal manures and harvested at different times. Mal. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 18, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Soest, P.; Mertens, D.; Deinum, B. Preharvest factors influencing quality of conserved forage. J. Anim. 1978, 47, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Z.; Yu, Z.; Yang, H.; Na, R. The effects of stage of growth and additives with or without cellulase on fermentation and invitro degradation characteristics of Leymus chinensis silage. Grass Forage Sci. 2016, 71, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Qing, Z.; Chen, X.; Yang, F. Fermentation dynamics and diversity of bacterial community in four typical woody forages. Ann. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyader, J.; Baron, V.; Beauchemin, K. Corn Forage Yield and quality for silage in short growing season areas of the canadian prairies. Agronomy 2018, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, S.; Cutrignelli, M.I.; Bovera, F.; Piccolo, G.; Infascelli, F. In vitro fermentation kinetics of carbohydrate fractions of fresh forage, silage and hay of Avena sativa. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 1838–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.; He, L.; Zhou, W.; Yang, F.; Qing, Z. The bacterial community and fermentation quality of mulberry (Morus alba) leaf silage with or without Lactobacillus casei and sucrose. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 293, 122059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yuan, X.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Shao, T. Effect of ensiling corn stover with legume herbages in different proportions on fermentation characteristics, nutritive quality and invitro digestibility on the Tibetan Plateau. Grassl. Sci. 2017, 63, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhou, W.; Guo, X.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, Q. Citric acid influences the dynamics of the fermentation quality, protease activity and microbial community of Mulberry Leaf Silage. Fermentation 2021, 7, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabi, E.B.; Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Shah, A.A.; Shao, T. Effect of glucose and lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation quality, chemical compositions and in vitro digestibility of Mulberry (Morns alba) Leaf Silage. Pak. J. Zool. 2017, 49, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, S.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Nishino, N. Effects of inoculation with lactic acid bacteria on the bacterial communities of Italian ryegrass, whole crop maize, guinea grass and rhodes grass silages. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2010, 160, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, Z.G.; Muck, R.E. New trends and opportunities in the development and use of inoculants for silage. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 19, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Ohmomo, S.; Kumai, S.; Nakase, T. Influence of Lactobacillus spp. from an inoculant and of Weissella and Leuconostoc spp. from forage crops on silage fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahlow, G.; Muck, R.E.; Driehuis, F.; Elferink, S.O.; Spoelstra, S.F. Microbiology of ensiling. Silage Sci. Technol. 2003, 42, 31–93. [Google Scholar]
- Avila, C.; Carvalho, B.; Pinto, J.; Duarte, W.; Schwan, R. The use of Lactobacillus species as starter cultures for enhancing the quality of sugar cane silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2014, 97, 940–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omidiran, M.; Baiyewu, R.; Ademola, I.; Fakorede, O.; Adekunle, E. Phytochemical analysis, nutritional composition and antimicrobial activities of White Mulberry (Morus alba). Pak. J. Nutr. 2012, 11, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Deng, M.; Liu, G.; Sun, B. Effects of malic acid and sucrose on the fermentation parameters, CNCPS nitrogen fractions, and bacterial community of Moringa oleifera Leaves Silage. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberline, J.A. Cyanobacteria: Omics and manipulation. Environ. Prog. Sustain. 2017, 36, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Bao, J.; Luo, Y.; Yu, Z. Additives affect the distribution of metabolic profile, microbial communities and antibiotic resistance genes in high-moisture sweet corn kernel silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 315, 123821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, K.; Ulrich, A.; Idler, C.; Klocke, M. Bacterial community dynamics during ensiling of perennial ryegrass at two compaction levels monitored by terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 1479–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, B.; Su, R.; Pan, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, G.; Yong, T.; Liu, X.; Zhong, J. Assessing the fermentation quality and microbial community of the mixed silage of forage soybean with crop corn or sorghum. Bioresource Technol. 2018, 265, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellaglio, F.; Torriani, S. DNA-DNA homology, physiological characteristics and distribution of lactic acid bacteria isolated from maize silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1986, 60, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.M.; Liu, Q.H.; Xin, G.R.; Zhang, J.G. Characteristics of lactic acid bacteria isolates and their inoculating effects on the silage fermentation at high temperature. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 56, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohno, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Nomura, M.; Uegaki, R.; Cai, Y. Identification and characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from mixed pasture of timothy and orchardgrass, and its badly preserved silage. Anim. Sci. J. 2011, 3, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, L.; Zhen, Y.; Yong, S.; Xiao, K.; Peng, D.; Jia, Z. A reused method for molasses-processed wastewater: Effect on silage quality and anaerobic digestion performance of Pennisetum Purpereum. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polley, H.W.; Derner, W. Dominant species constrain effects of species diversity on temporal variability in biomass production of Tallgrass Prairie. Oikos 2007, 116, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; Mcdonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Thurber, R.V.; Knight, R. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Items | DM (%) | WSC (% DM) | NDF (% DM) | ADF (% DM) | CP (% DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mulberry leaves (± SEM) | 32.95 ± 1.54 | 7.34 ± 0.52 | 33.93 ± 1.27 | 22.03 ± 1.05 | 13.92 ± 0.05 |
| Hybrid Pennisetum (±SEM) | 35.35 ± 0.38 | 10.27 ± 0.44 | 72.60 ± 1.76 | 38.32 ± 0.15 | 6.40 ± 0.01 |
| Item | Treatment | Ensiling Days | SEM | p Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7 | 14 | 30 | D | T | D × T | |||
| DM (%) | P100 | 34.73 b | 35.09 b | 34.52 b | 35.10 b | 0.046 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.001 |
| PM73 | 35.33 aB | 36.62 aA | 36.53 aA | 36.64 aA | |||||
| PM55 | 34.36 bB | 35.33 bA | 35.73 aA | 36.03 bA | |||||
| WSC (% DM) | P100 | 6.44 A | 4.56 bB | 3.02 bC | 2.41 bC | 0.042 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| PM73 | 6.18 A | 5.54 aB | 4.71 aC | 4.35 aD | |||||
| PM55 | 5.93 A | 5.25 aB | 4.88 aB | 4.41 aC | |||||
| NDF (% DM) | P100 | 70.53 aA | 69.01 aA | 68.41 aA | 67.30 aB | 0.17 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.81 |
| PM73 | 60.58 bA | 58.54 bA | 58.76 bA | 57.70 bB | |||||
| PM55 | 50.48 cA | 49.89 cA | 48.65 cB | 47.26 cC | |||||
| ADF (% DM) | P100 | 36.93 aA | 35.37 aB | 34.31 aC | 33.85 aD | 0.078 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.26 |
| PM73 | 32.73 bA | 31.96 bA | 31.48 bA | 30.32 bB | |||||
| PM55 | 27.59 cA | 27.01 cA | 26.10 cA | 25.38 cB | |||||
| Item | Treatment | Ensiling Days | SEM | p Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7 | 14 | 30 | D | T | D × T | |||
| CP (% DM) | P100 | 5.32 cA | 5.04 cB | 4.96 cB | 4.97 cB | 0.016 | 0.001 | <0.01 | 0.01 |
| PM73 | 8.31 bA | 8.18 bAB | 8.07 bB | 8.27 bA | |||||
| PM55 | 10.76 aA | 10.65 aB | 10.69 aA | 10.84 aA | |||||
| TP (% DM) | P100 | 3.96 cA | 3.76 cB | 3.86 cAB | 3.91 cA | 0.014 | 0.023 | <0.01 | 0.009 |
| PM73 | 6.18 bAB | 6.21 bAB | 6.32 bA | 6.13 bB | |||||
| PM55 | 8.76 aA | 8.74 aA | 8.71 aA | 8.52 aB | |||||
| TP/CP | P100 | 0.750 bA | 0.760 bA | 0.779 bAB | 0.787 aAB | 0.003 | 0.031 | <0.01 | 0.017 |
| PM73 | 0.749 bB | 0.761 bAB | 0.783 bA | 0.741 bAB | |||||
| PM55 | 0.814 aA | 0.821 aA | 0.815 aA | 0.785 aB | |||||
| NH3-N | P100 | 0.25 cC | 0.30 cB | 0.37 cA | 0.39 cA | 0.003 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| (g/kg DM) | PM73 | 0.34 bC | 0.41 bB | 0.42 bB | 0.44 bA | ||||
| PM55 | 0.40 aD | 0.48 aC | 0.52 aB | 0.65 aA | |||||
| Item | Treatment | Ensiling Days | SEM | p Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7 | 14 | 30 | D | T | D × T | |||
| Lactic acid (g/kg DM) | P100 | 31.56 bB | 36.37 bA | 36.54 cA | 40.71 cA | 0.52 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| PM73 | 55.62 aB | 59.18 aB | 68.02 bA | 72.16 bA | |||||
| PM55 | 57.88 aC | 58.42 aC | 74.37 aB | 80.81 aA | |||||
| Acetic acid (g/kg DM) | P100 | 4.44 bD | 6.00 cC | 9.01 cB | 10.99 cA | 0.14 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| PM73 | 6.76 aC | 21.78 aB | 22.15 bB | 24.72 bA | |||||
| PM55 | 7.96 aC | 18.84 bB | 33.80 aA | 31.84 aA | |||||
| Propanoic acid (g/kg DM) | P100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | – | – | – | – |
| PM73 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| PM55 | 1.96 | 0.75 | 1.31 | 0 | |||||
| Butyric acid (g/kg DM) | P100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | – | – | – | – |
| PM73 | 2.38 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| PM55 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| P100 | 4.06 bA | 4.01 bB | 3.95 cC | 3.77 cD | 0.006 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| pH | PM73 | 4.40 aA | 4.20 aB | 4.23 aB | 3.99 bC | ||||
| PM55 | 4.46 aA | 4.24 aB | 4.18 bC | 4.06 aD | |||||
| Item | Treatment | Ensiling Days | SEM | p Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 7 | 14 | 30 | D | T | D × T | |||
| Lactic acid bacteria (log10 cfu/g FM) | P100 | 7.94 cC | 8.70 bA | 8.61 cA | 8.46 B | 0.02 | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.01 |
| PM73 | 8.31 aD | 9.21 aA | 9.05 aB | 8.49 C | |||||
| PM55 | 8.22 bC | 9.24 aA | 9.00 bA | 8.51 B | |||||
| Yeasts (log10 cfu/g FM) | P100 | 5.46 aC | 5.65 aB | 5.69 aA | 4.78 aD | 0.013 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| PM73 | 5.02 bA | 4.70 bB | 4.69 bB | 4.77 aB | |||||
| PM55 | 4.95 cA | 4.60 cB | 4.26 cC | 2.39 bD | |||||
| Molds (log10 cfu/g FM) | P100 | <2.00 | <2.00 | <2.00 | <2.00 | -- | - | - | - |
| PM73 | <2.00 | <2.00 | <2.00 | <2.00 | |||||
| PM55 | <2.00 | <2.00 | <2.00 | <2.00 | |||||
| Group | Sobs | Shannon | Simpson | Chao | Ace | Goods_Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P100_3d | 311.00 | 3.62 | 0.85 | 381.94 | 390.62 | 0.9992 |
| PM73_3d | 270.00 | 3.21 | 0.79 | 347.86 | 353.47 | 0.9991 |
| PM55_3d | 251.00 | 3.23 | 0.79 | 318.48 | 314.61 | 0.9993 |
| P100_7d | 340.67 | 3.84 | 0.88 | 398.86 | 395.82 | 0.9992 |
| PM73_7d | 281.67 | 3.34 | 0.81 | 349.45 | 351.21 | 0.9992 |
| PM55_7d | 247.67 | 3.37 | 0.83 | 319.03 | 315.84 | 0.9992 |
| P100_14d | 282.33 | 3.64 | 0.87 | 336.38 | 342.68 | 0.9993 |
| PM73_14d | 262.00 | 3.44 | 0.84 | 311.24 | 314.29 | 0.9994 |
| PM55_14d | 274.00 | 3.47 | 0.85 | 317.89 | 322.27 | 0.9993 |
| P100_30d | 272.33 | 3.51 | 0.85 | 311.91 | 306.31 | 0.9995 |
| PM73_30d | 322.00 | 3.48 | 0.83 | 358.63 | 363.33 | 0.9994 |
| PM55_30d | 263.33 | 3.51 | 0.85 | 298.34 | 298.25 | 0.9995 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, Z.; Deng, M.; Tian, H.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Sun, B.; Guo, Y. Effects of Mulberry Leaves and Pennisetum Hybrid Mix-Silage on Fermentation Parameters and Bacterial Community. Fermentation 2022, 8, 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8050197
Chi Z, Deng M, Tian H, Liu D, Li Y, Liu G, Sun B, Guo Y. Effects of Mulberry Leaves and Pennisetum Hybrid Mix-Silage on Fermentation Parameters and Bacterial Community. Fermentation. 2022; 8(5):197. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8050197
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Zhou, Ming Deng, Hanchen Tian, Dewu Liu, Yaokun Li, Guangbin Liu, Baoli Sun, and Yongqing Guo. 2022. "Effects of Mulberry Leaves and Pennisetum Hybrid Mix-Silage on Fermentation Parameters and Bacterial Community" Fermentation 8, no. 5: 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8050197
APA StyleChi, Z., Deng, M., Tian, H., Liu, D., Li, Y., Liu, G., Sun, B., & Guo, Y. (2022). Effects of Mulberry Leaves and Pennisetum Hybrid Mix-Silage on Fermentation Parameters and Bacterial Community. Fermentation, 8(5), 197. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8050197






