Insight into the Substrate Specificity of Lactobacillus paracasei Aspartate Ammonia-Lyase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Construction of the Expression Vectors
2.3. E. coli Strains and Protein Expression Conditions
2.4. Preparations of LpAAL and MBP-LpAAL Enzymes
2.5. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
2.6. AAL-F Activity Assay
2.7. AAL-R Activity Assay
2.8. PAL Activity Assay
2.9. TAL Activity Assay
2.10. Enzyme Biochemical Properties and Kinetics
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the LpAAL Gene
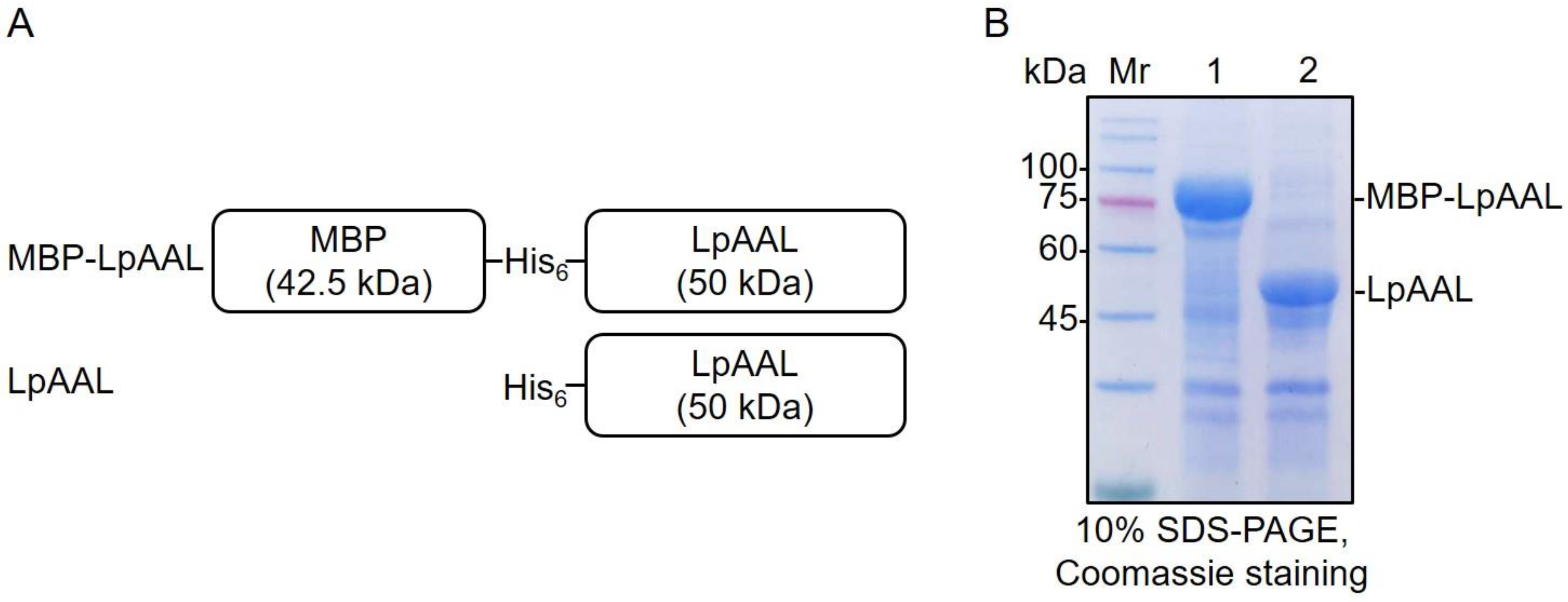
3.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant LpAAL and MBP-LpAAL Proteins in Escherichia coli
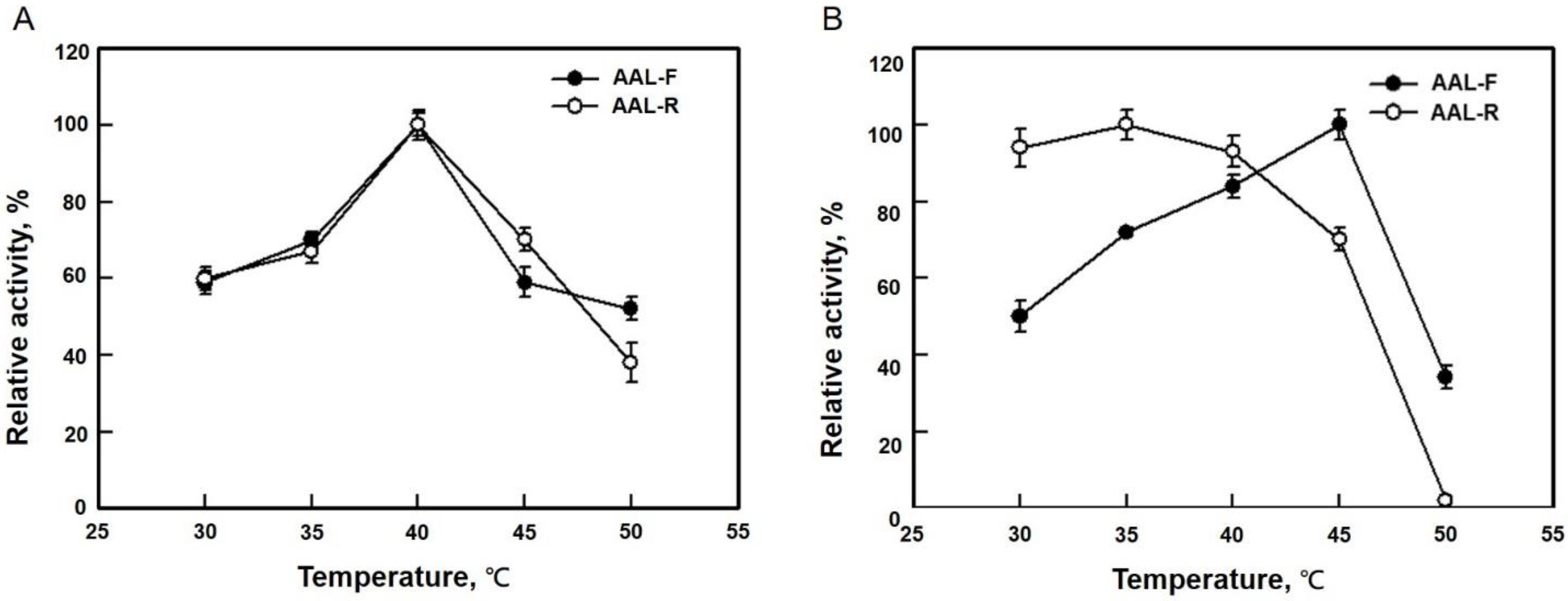
3.3. Optimum Temperature of AAL and AAL-R Activities of LpAAL and MBP-LpAAL Proteins
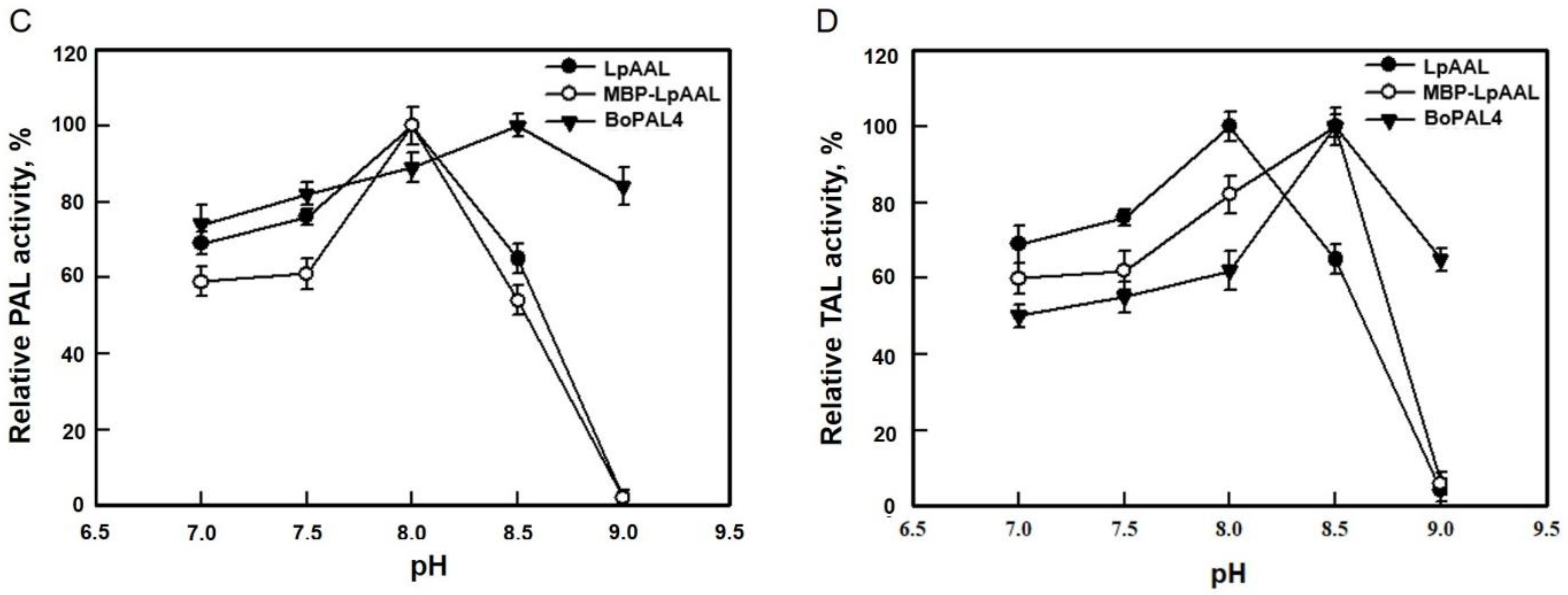
3.4. Optimum pH for AAL-F and AAL-R Activities of LpAAL and MBP-LpAAL Proteins
3.5. Kinetic Parameters for AAL-F and AAL-R Activities of LpAAL and MBP-LpAAL Proteins
3.6. Optimum Temperature and pH between PAL and TAL for LpAAL and MBP-LpAAL
3.7. Kinetics Parameters for LpAAL and MBP-LpAAL with L-Phenylalanine and L-Tyrosine as Substrates
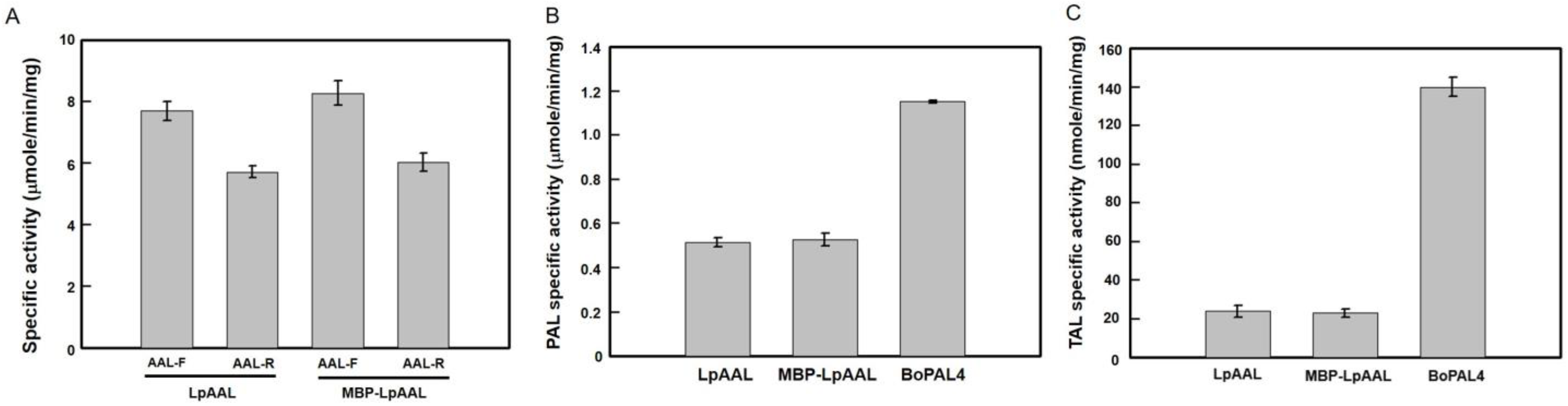
3.8. Comparison of Specific Activities in LpAAL, MBP-LpAAL, and BoPAL4 Proteins
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAL | aspartate ammonia-lyase |
| AAL-F | aspartate ammonia-lyase forward reaction |
| AAL-R | aspartate ammonia-lyase reverse reaction |
| bAAL | B: Bacillus sp. YM55-1 aspartate ammonia-lyase |
| BoPAL4 | Bambusa oldhamii phenylalanine ammonia-lyase 4 |
| eAAL | e: E. coli aspartate ammonia-lyase |
| IPTG | isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside |
| LB | Luria-Bertani |
| LpAAL | Lp: Lactobacillus paracasei aspartate ammonia-lyase |
| MBP | maltose-binding protein |
| pAAL | p: Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 aspartate ammonia-lyase |
| PAL | phenylalanine ammonia-lyase |
| pfAAL | pf: Pseudomonas fluorescens R124 aspartate ammonia-lyase |
| PTAL | phenylalanine-tyrosine ammonia-lyase |
| TAL | tyrosine ammonia-lyase |
References
- Kazuoka, T.; Masuda, Y.; Oikawa, T.; Soda, K. Thermostable aspartase from a marine psychrophile, Cytophaga sp. KUC-1: Molecular characterization and primary structure. J. Biochem. 2003, 133, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fibriansah, G.; Veetil, V.P.; Poelarends, G.J.; Thunnissen, A.M.W. Structural basis for the catalytic mechanism of aspartate ammonia lyase. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 6053–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsten, W.E.; Hunsley, J.R.; Viola, R.E. Purification of aspartase and aspartokinase-homoserine dehydrogenase I from Escherichia coli by dye-ligand chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 147, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, Y.; Tamura, K.; Yano, S.; Mizobata, T.; Nagai, J.; Esaki, N.; Soda, K.; Tokushige, M.; Yumoto, N. Purification and characterization of thermostable aspartase from Bacillus sp. YM55-1. Arch. Biochem. Biophy. 1999, 366, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuiry, I.I.; Hermes, J.D.; Weiss, P.M.; Chen, C.Y.; Cook, P.F. Kinetic mechanism and location of rate-determining steps for aspartase from Hafnia alvei. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 5168–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Studies on the properties of mutants of aspartase from Escherichia coli Wa. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 864, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.S.; Yadav, M. Single-step purification and characterization of recombinant aspartase of Aeromonas media NFB-5. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2012, 167, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Villiers, M.; Veetil, V.P.; Raj, H.; de Villiers, J.; Poelarends, G.J. Catalytic mechanisms and biocatalytic applications of aspartate and methylaspartate ammonia lyases. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veetil, V.P.; Raj, H.; Quax, W.J.; Janssen, D.B.; Poelarends, G.J. Site-directed mutagenesis, kinetic and inhibition studies of aspartate ammonia lyase from Bacillus sp. YM55-1. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 2994–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmeggiani, F.; Weise, N.J.; Ahmed, S.T.; Turner, N.J. Synthetic and therapeutic applications of ammonia-lyases and aminomutases. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 73–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.T.; Akhani, R.C.; Patel, M.J.; Dedania, S.R.; Patel, D.H. Bioproduction of L-aspartic acid and cinnamic acid by L-aspartate ammonia lyase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 182, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, P.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Lim, G.C.W.; Chen, Y.P.; Hsiao, C.J.; Chen, L.H.; Ciou, J.Y.; Hsieh, L.S. Production of trans-cinnamic acid by immobilization of the Bambusa oldhamii BoPAL1 and BoPAL2 phenylalanine ammonia-lyases on electrospun nanofibers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Yeh, H.H.; Hong, P.Y.; Hsiao, C.J.; Hsieh, L.S. Phenylalanine, tyrosine, and DOPA are bona fide substrates for Bambusa oldhamii BoPAL4. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Qu, X. Genetic mechanisms of prebiotic carbohydrate metabolism in lactic acid bacteria: Emphasis on Lacticaseibacillus casei and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei as flexible, diverse and outstanding prebiotic carbohydrate starters. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 115, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, M.; Mohsin, M.; Ijaz, H.; Tulain, U.R.; Ashraf, M.A.; Fayyaz, A.; Kamran, Q. Lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented Asian foods. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 30, 1803–1804. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.; Sugrue, I.; Tobin, C.; Hill, C.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. The Lactobacillus casei group: History and health related applications. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rollan, G.C.; Manca de Nadra, M.C.; Pesce de Ruiz Holgado, A.A.; Oliver, G. Aspartate metabolism in Lactibacillus murinus CNRS 313. I. Aspartase. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 1985, 31, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, M.; Zúñiga, M. Amino acid catabolic pathways of lactic acid bacteria. Crit. Rev. Microbio1. 2006, 32, 155–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.J.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Hsieh, L.S. Cloning and characterization of the Bambusa oldhamii BoMDH-encoded malate dehydrogenase. Protein Expr. Purif. 2020, 174, 105665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.H.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, P.R.; Hsieh, L.S. NLIP and HAD-like domains of Pah1 and Lipin 1 phosphatidate phosphatases are essential for their catalytic activities. Molecules 2021, 26, 5470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csuka, P.; Molnár, Z.; Tóth, V.; Imarah, A.O.; Balogh-Weiser, D.; Vértessy, B.G.; Poppe, L. Immobilization of the aspartate ammonia-lyase from Pseudomonas fluorescens R124 on magnetic nanoparticles: Characterization and kinetics. ChemBioChem 2022, 23, e202100708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ida, N.; Tokushige, M. L-Aspartate-induced activation of aspartase. J. Biochem. 1985, 98, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. A QM/MM study of the catalytic mechanism of aspartate ammonia lyase. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2014, 51, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eze, S.O.O.; Ghulam, J.; Husain, A.; Nozaki, T. Molecular cloning and characterization of aspartate ammonia-lyase from Entamoeba histolytica. Nigerian J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 24, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.J.; Kong, X.D.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, X.P.; Zhang, J. Enhancement of the activity of L-aspartase from Escherichia coli W by directed evolution. Biochem. Biophy. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cárdenas-Fernández, M.; López, C.; Alvaro, G.; López-Santín, J. Immobilized L-aspartate ammonia-lyase from Bacillus sp. YM55-1 as biocatalyst for highly concentrated L-aspartate synthesis. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 35, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrowietz, U.; Christophers, E.; Altmeyer, P. Treatment of psoriasis with fumaric acid esters: Results of a prospective multicentre study. Br. J. Dermatol. 1998, 138, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa Engel, C.A.; Straathof, A.J.; Zijlmans, T.W.; van Gulik, W.M.; van der Wielen, L.A. Fumaric acid production by fermentation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 78, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werpy, T.; Petersen, G. Top Value Added Chemicals from Biomass: Volume I-Results of Screening for Potential Candidates from Sugars and Synthesis Gas (No. DOE/GO-102004-1992); National Renewable Energy Lab.: Golden, CO, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prorok, T.; Jana, M.; Patel, D.; Pahan, K. Cinnamic acid protects the nigrostriatum in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorα. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 751–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, S. Protective effects of cinnamic acid and cinnamic aldehyde on isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial ischemia in rats. J. Eethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, W.; Xu, W. Production of trans-cinnamic and p-coumaric acids in engineered E. coli. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Plasmids | Relevant Characteristics | Source/Reference |
|---|---|---|
| pET28a | E. coli expression vector with N-terminal His6-tag fusion | Invitrogen |
| pET28a-LpAAL | LpAAL coding sequence inserted into pET28b | This study |
| pMAL-c2x | E. coli expression vector with N-terminal MBP fusion | New England Biolab |
| pMAL-LpAAL | LpAAL coding sequence inserted into pMAL-c2x | This study |
| pTrcHis-BoPAL4 | BoPAL4 coding sequence inserted into pTrcHisA | [13] |
| Enzyme | Substrate | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Optimum pH | Optimum Temp (°C) | Vmax (nmole/min) | kcat (s−1) | Km (mM) | kcat / Km (s−1 mM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LpAAL | L-Asp | 7.7 × 107 | 8.0 | 40 | 93 | 6.7 | 5.70 | 1.18 | This study |
| fumaric acid | 6.09 | 8.0 | 40 | 257 | 0.45 | 8.50 | 0.05 | ||
| MBP-LpAAL | L-Asp | 8.3 × 107 | 8.5 | 45 | 97 | 13.1 | 5.20 | 5.20 | This study |
| fumaric acid | 5.73 | 8.0 | 35 | 267 | 37.64 | 8.50 | 8.5 | ||
| pAAL 1 | L-Asp | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- | 4.91 | 3 × 10−4 | ---- | [11] |
| BAAL 2 | L-Asp | ---- | ---- | ---- | 287 (mM/h) | ---- | 213 | ---- | [26] |
| pfAAL 3 | L-Asp | ---- | 8.8 | ---- | ---- | 130 | 5.1 | 25 | [21] |
| Proteins | Substrate | Optimum pH | Optimum Temp (°C) | kcat (s−1) | Km (mM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LpAAL | L-Phe | 8.0 | 40 | 0.45 | 4.43 | This study |
| L-Tyr | 8.0 | 40 | 0.02 | 1.17 | ||
| MBP-LpAAL | L-Phe | 8.0 | 40 | 0.84 | 4.07 | This study |
| L-Tyr | 8.5 | 40 | 0.04 | 1.10 | ||
| BoPAL4 | L-Phe | 9.0 | 50 | 1.14 | 2.10 | [13] |
| L-Tyr | 8.5 | 60 | 0.18 | 0.10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.-H.; You, W.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Ciou, J.-Y.; Hsieh, L.-S. Insight into the Substrate Specificity of Lactobacillus paracasei Aspartate Ammonia-Lyase. Fermentation 2023, 9, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010049
Huang Y-H, You W-C, Chen Y-J, Ciou J-Y, Hsieh L-S. Insight into the Substrate Specificity of Lactobacillus paracasei Aspartate Ammonia-Lyase. Fermentation. 2023; 9(1):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010049
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yi-Hao, Weir-Chiang You, Yung-Ju Chen, Jhih-Ying Ciou, and Lu-Sheng Hsieh. 2023. "Insight into the Substrate Specificity of Lactobacillus paracasei Aspartate Ammonia-Lyase" Fermentation 9, no. 1: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010049
APA StyleHuang, Y.-H., You, W.-C., Chen, Y.-J., Ciou, J.-Y., & Hsieh, L.-S. (2023). Insight into the Substrate Specificity of Lactobacillus paracasei Aspartate Ammonia-Lyase. Fermentation, 9(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9010049








