Improved Fermentation Yield of Doramectin from Streptomyces avermitilis N72 by Strain Selection and Glucose Supplementation Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbial Strains, Culture Media and Culture Conditions
2.2. Assessment of Strain CHC Tolerance and Mutagenic Lethality
2.2.1. CHC Tolerance Assessment
2.2.2. Mutagenic Lethality
2.3. Screening and Genetic Stability of High-Yielding Strains
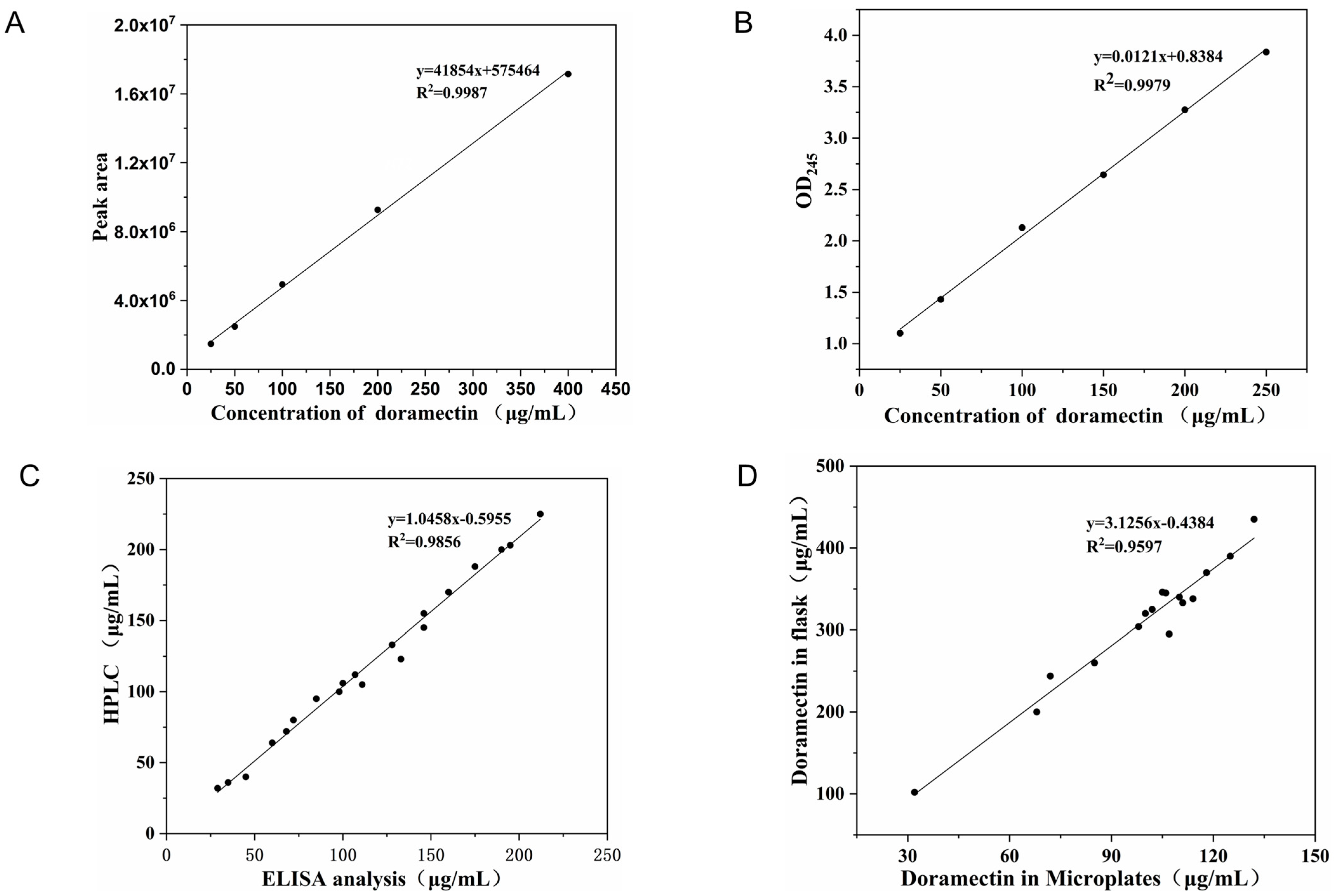
2.3.1. Testing of the Analytical Method for Doramectin Content
2.3.2. 96-Well Plate Surface Culture Primary Sieve
2.3.3. Shake Flask Fermentation Rescreening
2.3.4. Assessing the Genetic Stability of High-Yielding Strains
2.4. Comparison of the Differences in Growth and Fermentation Characteristics between S. avermitilis N72 and the High-Yielding Strain XY-62
2.4.1. Growth Characteristics of the Strains in Seed Shake Flasks
2.4.2. Metabolic Characteristics of the Strains in Fermentation Shake Flasks
2.5. Supplementary Fermentation of High-Yielding Strain XY-62 with a 50 L Fermenter Scale-Up Culture
2.5.1. Shake Flask Fermentation with Glucose Supplementation
2.5.2. Scaled-Up Culture in 50 L Fermenters
2.6. Analysis Methods
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
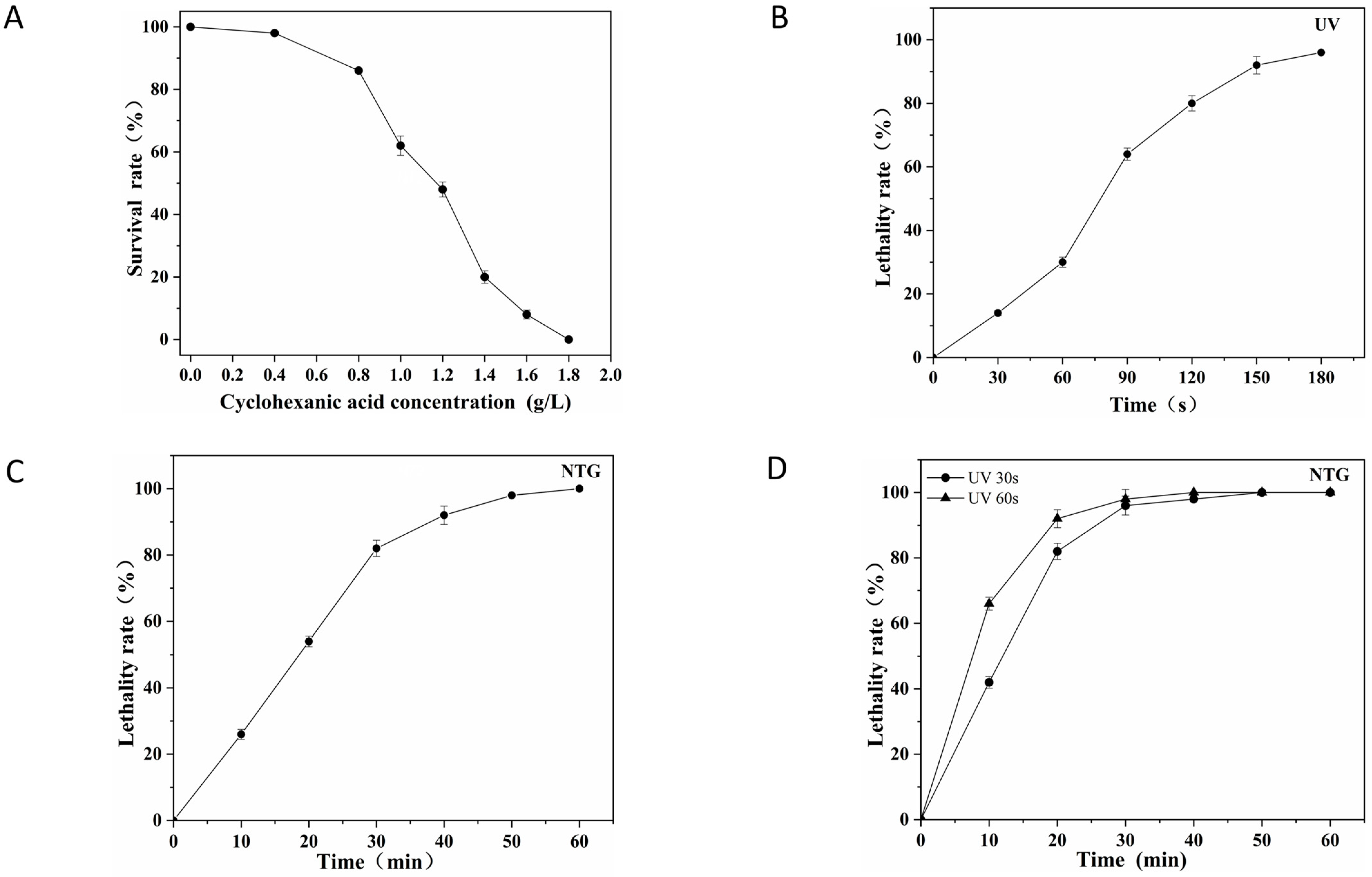
3.1. Assessment of Strain CHC Tolerance and Mutagenic Conditions
3.1.1. Effect of CHC Concentration on the Viability of S. avermitilis N72 Cells
3.1.2. Effect of UV Light and NTG on the Viability of S. avermitilis N72 Cells
3.2. Selection and Breeding of High-Yielding Strains and Their Genetic Stability
3.2.1. Analysis of Doramectin Content and Feasibility of Fermentation Methods
3.2.2. 96-Well Plate Primary Sieve for Surface Culture
3.2.3. Shake Flask Fermentation Rescreening and Genetic Stability of High-Yielding Strains
3.3. Comparison of the Differences in Growth and Fermentation Characteristics between the High-Yield Strains XY-62 and S. avermitilis N72
3.3.1. Growth Characteristics of the Strain
3.3.2. Metabolic Characteristics of the Strains
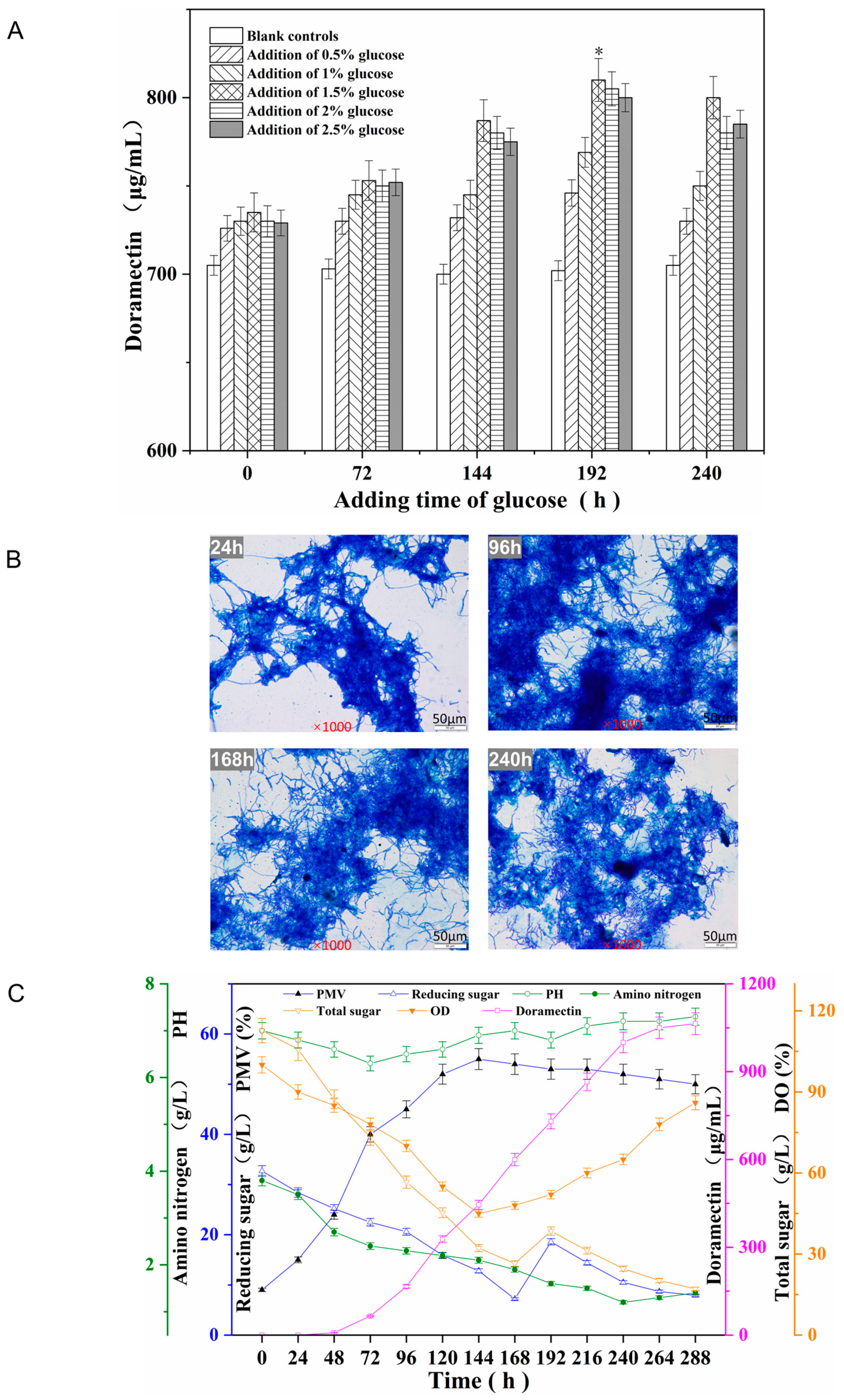
3.4. Supplementary Fermentation of High-Yielding Strain XY-62 and Scale-Up Culture in 50 L Fermenters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dutton, C.; Gibson, S.; Kinns, M.; Swanson, A.; Bordner, J. Structure of doramectin. J. Chem. Soc. Peak T2 1995, 2, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cropp, T.; Wilson, A.; Reynolds, K. Identification of a cyclohexylcarbonyl CoA biosynthetic gene cluster and application in the production of doramectin. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuan, N.; Pandey, R.; Sohng, J. Recent advances in biochemistry and biotechnological synthesis of avermectins and their derivatives. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2014, 98, 7747–7759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, R.; Cristina, P.; Lgnacio, C.; Luis, R.; Margarita, A. The influence of gastrointestinal parasitism on fecal elimination of doramectin, in lambs. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 2017–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, A.; Quek, S.; Mueller, R. Doramectin in the treatment of generalized demodicosis. Vet. Dermatol. 2018, 29, 104-e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lye, G.; Jacob, A.; Pomroy, W.; Stafford, K.; Singh, P. Pharmacokinetics of subcutaneously administered doramectin in alpacas. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 43, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, M.; Howard, K.; Kawalek, J. Pharmacokinetic comparison of six anthelmintics in sheep, goats, and cattle. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 44, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, S.; Syed, Q.; Adnan, A.; Qureshi, F. Isolation, Characterization and Selection of Avermectin-Producing Streptomyces avermitilis Strains From Soil Samples. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2014, 7, e10366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, M.; Abbas, R.; Mehmood, K.; Hussain, R.; Shah, S.; Faheem, M.; Zaheer, T.; Abbas, A.; Morales, B.; Aneva, I.; et al. Assessment of Avermectins-Induced Toxicity in Animals. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, A.; Omura, S. Ivermectin, ‘Wonder drug’ from Japan: The human use perspective. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2011, 87, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Singh, K. Ivermectin: A Promising Therapeutic for Fighting Malaria. Current Status and Perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 9711–9731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, G.; Soloneski, S.; Larramendy, M. New Ventures in the Genotoxic and Cytotoxic Effects of Macrocyclic Lactones, Abamectin and Ivermectin. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2010, 128, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saber Batiha, G.; Alqahtani, A.; Ilesanmi, O.; Saati, A.; El-Mleeh, A.; Hetta, H.; Magdy Beshbishy, A. Avermectin Derivatives, Pharmacokinetics, Therapeutic and Toxic Dosages, Mechanism of Action, and Their Biological Effects. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liang, H.; Qin, R.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Du, S.; Chen, Z.; Meng, X.; Lv, Z.; Wang, Q.; et al. Doramectin inhibits glioblastoma cell survival via regulation of autophagy in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 60, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Omura, S. Avermectin Biosynthesis. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 2591–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Ishikawa, J.; Hanamoto, A.; Shinose, M.; Kikuchi, H.; Shiba, T.; Sakaki, Y.; Hattori, M.; Ōmura, S. Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, M.; Qin, H.; An, X.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y. Deciphering the Biosynthesis of TDP-beta-L-oleandrose in Avermectin. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3199–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, N.; Hwang, S.; Kim, W.; Cho, S.; Palsson, B.; Cho, B. Genome-scale analysis of genetic regulatory elements in Streptomyces avermitilis MA-4680 using transcript boundary information. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, C.; Gibson, S.; Goudie, A.; Holdom, K.; Pacey, M.; Ruddock, J.; Bulock, J.; Richards, M. Novel avermectins produced by mutational biosynthesis. J. Antibiot. 1991, 44, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutzman-Engwall, K.; Conlon, S.; Fedechko, R.; McArthur, H.; Pekrun, K.; Chen, Y.; Jenne, S.; La, C.; Trinh, N.; Kim, S.; et al. Semi-synthetic DNA shuffling of aveC leads to improved industrial scale production of doramectin by Streptomyces avermitilis. Metab. Eng. 2005, 7, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Pan, H.; Tang, G. Production of doramectin by rational engineering of the avermectin biosynthetic pathway. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 3320–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Tan, G.; Xia, X.; Zhang, L. Learn from microbial intelligence for avermectins overproduction. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 48, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chu, J.; Zhuang, Y. Mutation breeding of high avermectin B-1a-producing strain by the combination of high energy carbon heavy ion irradiation and sodium nitrite mutagenesis based on high throughput screening. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2017, 22, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Fan, K.; Tan, G.; Ai, G.; Lam, S.; Shui, G.; Yang, Z.; et al. Harnessing the intracellular triacylglycerols for titer improvement of polyketides in Streptomyces. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; You, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Wen, Y. Avermectin B1a production in Streptomyces avermitilis is enhanced by engineering aveC and precursor supply genes. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2022, 106, 2191–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Diao, J.; He, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, W. Streptomycin resistance-aided genome shuffling to improve doramectin productivity of Streptomyces avermitilis NEAU1069. J. Microbiol. Biot. 2013, 40, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Luo, Z.; Zeng, W.; Xu, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, J. Enhanced avermectin production by Streptomyces avermitilis ATCC 31267 using high-throughput screening aided by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2018, 102, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhang, M.; Sun, J.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; et al. Improved Neomycin Sulfate Potency in Streptomyces fradiae Using Atmospheric and Room Temperature Plasma (ARTP) Mutagenesis and Fermentation Medium Optimization. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Xiang, W. Improvement of milbemycin-producing Streptomyces bingchenggensis by rational screening of ultraviolet- and chemically induced mutants. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 25, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Shen, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, S.; Ju, D.; Chen, S. Enhancement of ascomycin production via a combination of atmospheric and room temperature plasma mutagenesis in Streptomyces hygroscopicus and medium optimization. AMB Express 2019, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Xiao, H.; Zhong, J. Combination of traditional mutation and metabolic engineering to enhance ansamitocin P-3 production in Actinosynnema pretiosum. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 2794–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, H.; Yang, J.; Hong, S.; Park, S.; Lee, M. Changes in quality properties of kimchi based on the nitrogen content of fermented anchovy sauce, Myeolchi Aekjeot, during fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Peng, H.; Cao, J.; Liao, A.; Long, P.; Huang, J.; Hui, M. Avilamycin production enhancement by mutagenesis and fermentation optimization in Streptomyces viridochromogenes. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, G.; Chen, Q.; Huang, D. Induced mutation breeding of Brevibacillus brevis FJAT-0809-GLX for improving ethylparaben production and its application in the biocontrol of Lasiodiplodia theobromae. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2018, 146, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhao, C.; Yang, X.; Song, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Xia, X.; et al. Application of a dissolved oxygen control strategy to increase the expression of Streptococcus suis glutamate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Chu, X.; Xiong, Z.; Chu, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, S. Oxygen uptake rate regulation during cell growth phase for improving avermectin B1a batch fermentation on a pilot scale (2 m3). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 2639–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, X.; Cai, J. Improved Fermentation Yield of Doramectin from Streptomyces avermitilis N72 by Strain Selection and Glucose Supplementation Strategies. Fermentation 2023, 9, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020121
Pan X, Cai J. Improved Fermentation Yield of Doramectin from Streptomyces avermitilis N72 by Strain Selection and Glucose Supplementation Strategies. Fermentation. 2023; 9(2):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020121
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Xiaojun, and Jun Cai. 2023. "Improved Fermentation Yield of Doramectin from Streptomyces avermitilis N72 by Strain Selection and Glucose Supplementation Strategies" Fermentation 9, no. 2: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020121
APA StylePan, X., & Cai, J. (2023). Improved Fermentation Yield of Doramectin from Streptomyces avermitilis N72 by Strain Selection and Glucose Supplementation Strategies. Fermentation, 9(2), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9020121




