Biogas Production and Energy Balance in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Thermophilic versus Mesophilic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Analysis
2.2. Fruit and Vegetable Waste
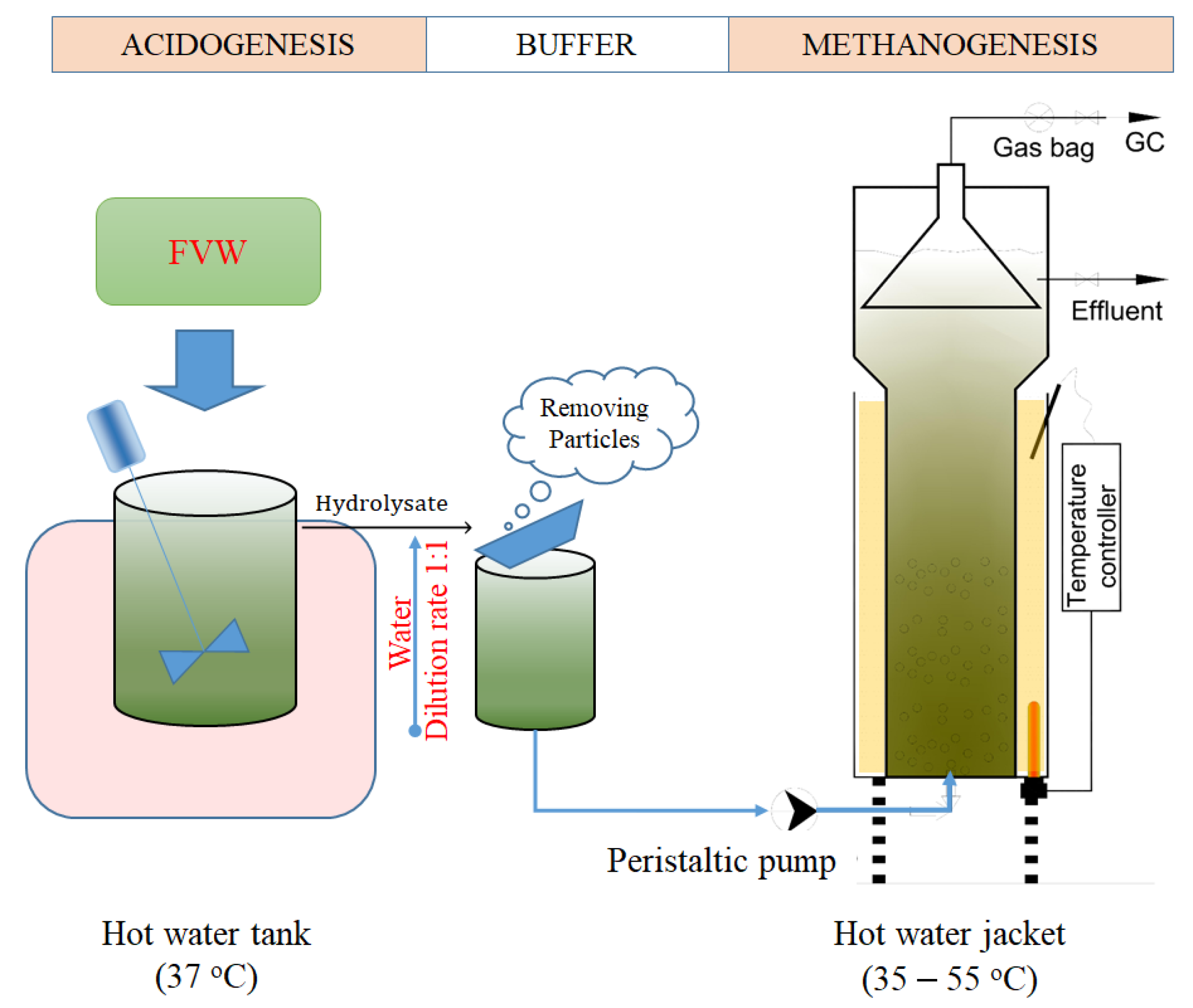
2.3. Experimental Model and Operation
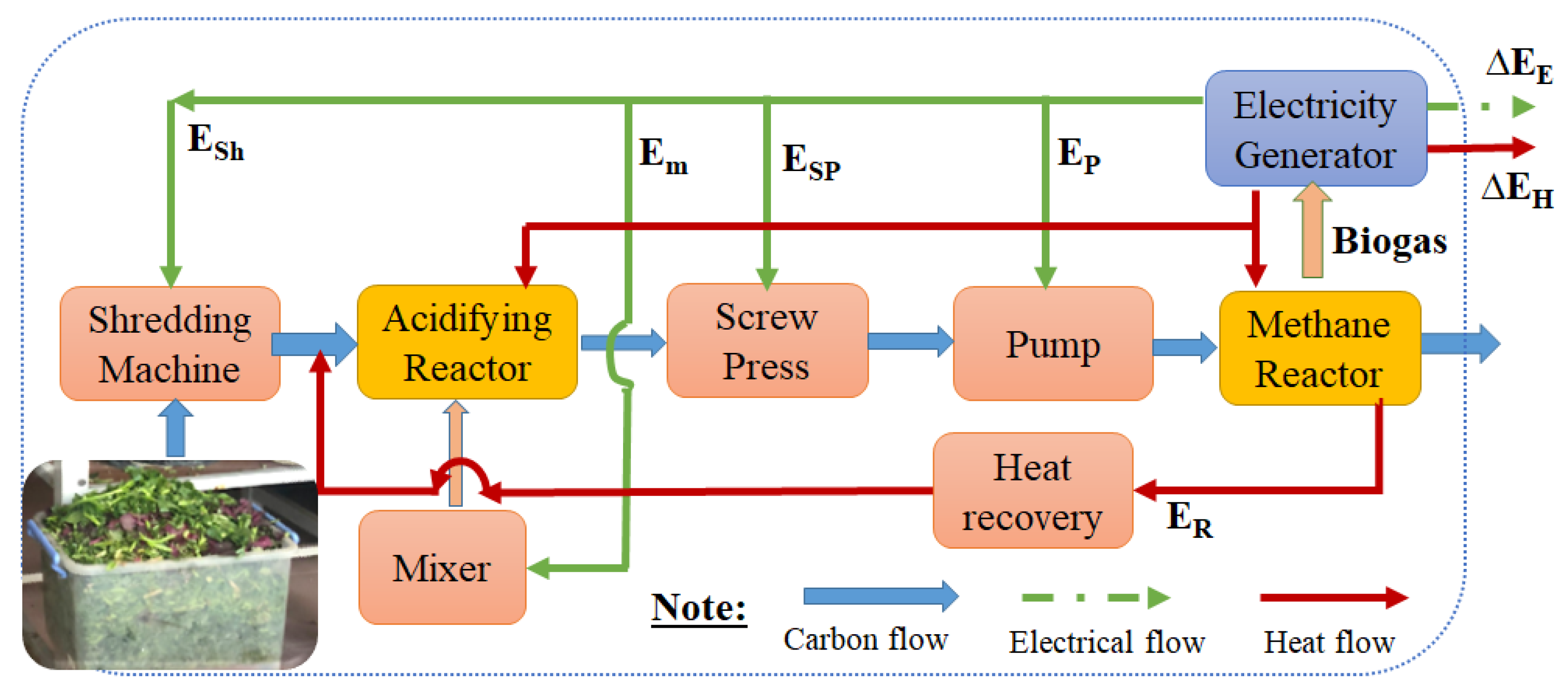
2.4. Energy Balance Modeling
3. Results and Discussions
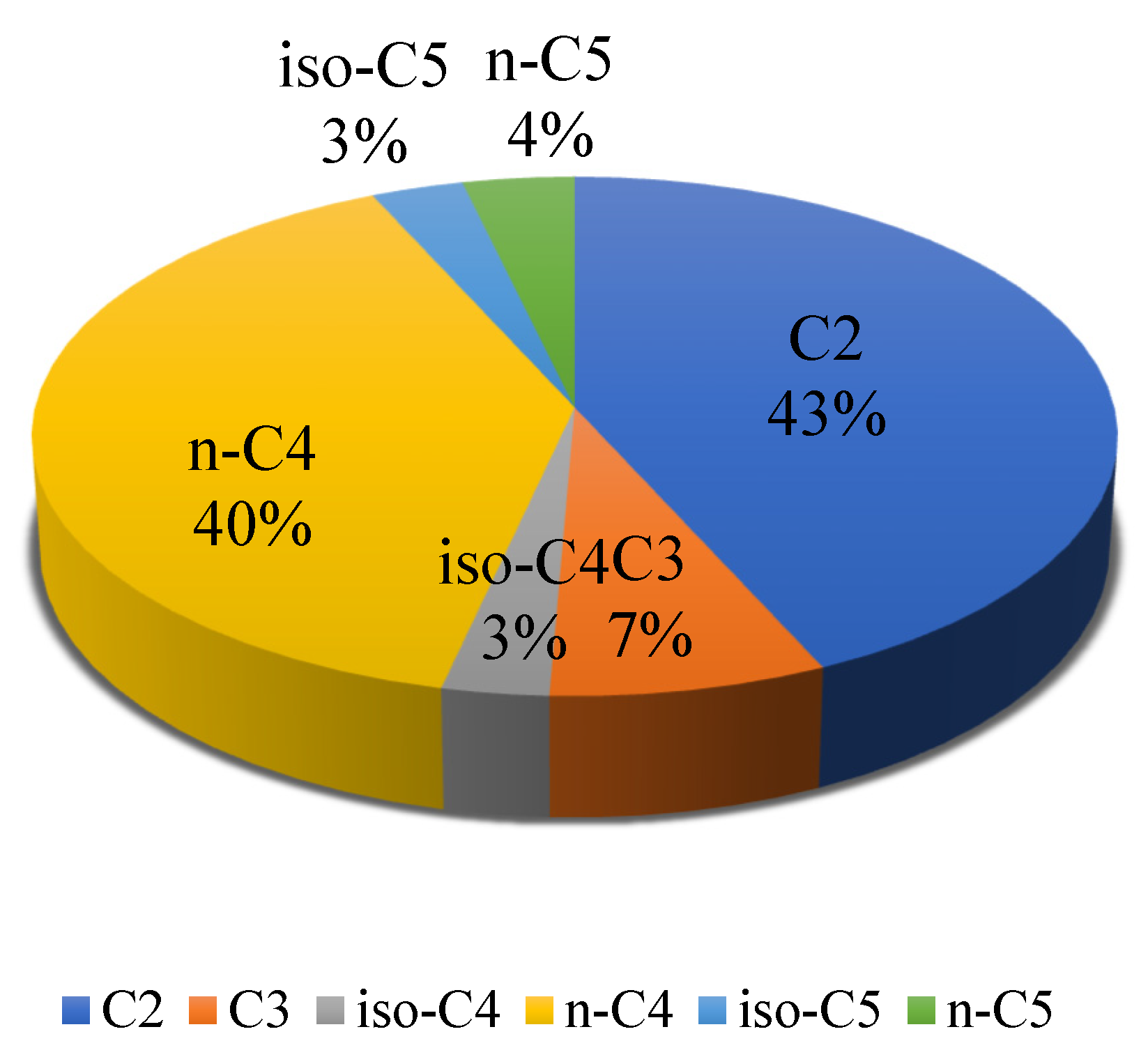
3.1. Acidogenesis
3.2. Methanogenesis
3.3. Energy Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, C.; Kong, C.-X.; Mei, Z.-L.; Li, J. A review of the anaerobic digestion of fruit and vegetable waste. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 183, 906–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monserrat, M.G.M.; Esteban, V.C.S.; Josefina, P.V.; Gabriela, Z.J.; Alejandra, V.P.; Kikey, C.S.C. Two-stage anaerobic digestion of fruit and vegetable wastes. J. Biotechnol. Res. 2019, 10, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Dinh, P.V.; Fujiwara, T.; Giang, H.M.; Phu, S.P. The fate of carbon in two-stage anaerobic digestion of vegetable waste. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 307, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinh, P.V.; Fujiwara, T.; Tho, B.L.; Toan, P.P.S.; Minh, G.H. A review of anaerobic digestion systems for biodegradable waste: Configurations, operating parameters, and current trends. Environ. Eng. Res. 2020, 25, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinh, P.V.; Takeshi, F.; Minh, G.H.; Phu, S.T.P. Comparison between single and two-stage anaerobic digestion of vegetable waste: Kinetics of methanogenesis and carbon flow. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 6095–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Kuila, A.; Adak, S.; Bishai, M.; Banerjee, R. Utilization of vegetable wastes for bioenergy generation. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerardi, M.H. The Microbiology of Anaerobic Digesters; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; p. 188. [Google Scholar]
- Babæe, A.; Shayegan, J. Effect of organic loading rates (OLR) on production of methane from anaerobic digestion of vegetables waste. In Proceedings of the World Renewable Energy Congress-Sweden, Linköping, Sweden, 8–13 May 2011; pp. 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Shen, F.; Yuan, H.; Zou, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Li, X. Anaerobic co-digestion of kitchen waste and fruit/vegetable waste: Lab-scale and pilot-scale studies. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 2627–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yun, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Han, F.; Jia, B.; Chen, J.; Li, B. Improving performance and phosphorus content of anaerobic co-digestion of dairy manure with aloe peel waste using vermiculite. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Almquist, C.B. The anaerobic co-digestion of fruit and vegetable waste and horse manure mixtures in a bench-scale, two-phase anaerobic digestion system. Environ. Technol. 2014, 35, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Yuan, H.; Pang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhu, B.; Zou, D.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Yu, L.; Li, X. Performances of anaerobic co-digestion of fruit & vegetable waste (FVW) and food waste (FW): Single-phase vs. two-phase. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, S.; Trabold, T.A. Anaerobic digestion of food waste with unconventional co-substrates for stable biogas production at high organic loading rates. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravi, P.P.; Lindner, J.; Oechsner, H.; Lemmer, A. Effects of target pH-value on organic acids and methane production in two-stage anaerobic digestion of vegetable waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasinski, S. Mesophilic and Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Organic Fraction Separated during Mechanical Heat Treatment of Municipal Waste. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schievano, A.; Tenca, A.; Scaglia, B.; Merlino, G.; Rizzi, A.; Daffonchio, D.; Oberti, R.; Adani, F. Two-stage vs single-stage thermophilic anaerobic digestion: Comparison of energy production and biodegradation efficiencies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8502–8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Qin, Y.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Yu, P.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.-Y. Comparison of single-stage and two-stage thermophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste: Performance, energy balance and reaction process. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 156, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Total, Fixed, and Volatile Solids in Water, Solids and Biosolids. In Method 1684; EPA-821-R-01-015; USEPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- DIN ISO 10694:1995; Soil Quality–Determination of Organic and Total Carbon after Dry Combustion (Elementary Analysis). International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- Zhang, C.; Yun, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Du, T. Low-cost composited accelerants for anaerobic digestion of dairy manure: Focusing on methane yield, digestate utilization and energy evaluation. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yun, S.; Zhu, J.; Du, T.; Zhang, C.; Li, X. Mesophilic anaerobic co-digestion of aloe peel waste with dairy manure in the batch digester: Focusing on mixing ratios and digestate stability. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xiao, G.; Peng, L.; Su, H.; Tan, T. The anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.-S.; Han, S.; Song, Y.; Lee, C. Performance of UASB reactor treating leachate from acidogenic fermenter in the two-phase anaerobic digestion of food waste. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3441–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, D.; Suto, P.; Peck, C. Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste: Funding Opportunity; EPA-R9-WST-06-004; US Environmental Protection Agency Region 9: Hawthorne, CA, USA, 2008.
- López, I.; Borzacconi, L. Anaerobic digestion for agro-industrial wastes: A Latin American perspective. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2017, 4, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Ludington, D. Calculating the Heating Value of Biogas; DLtech, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald, G.C.; Themelis, N.J. Technical and economic impacts of pre-shredding the MSW feed to moving grate WTE boilers. In Proceedings of the North American Waste-to-Energy Conference, Chantilly, VA, USA, 18–20 May 2009; pp. 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karunanithi, A. System Analysis of De-Watering Process for Treating Biogas Digestate; Linköping University: Linköping, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Xuan, L.T.T.; Egondi, T.; Ngoan, L.T.; Toan, D.T.T.; Huong, L.T. Seasonality in mortality and its relationship to temperature among the older population in Hanoi, Vietnam. Glob. Health Action 2014, 7, 23115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Ma, H.; Wu, J.; Zuo, J.; Wang, K. A new method of two-phase anaerobic digestion for fruit and vegetable waste treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, R.; Torrijos, M.; Sousbie, P.; Lugardon, A.; Steyer, J.P.; Delgenes, J.P. Single-phase and two-phase anaerobic digestion of fruit and vegetable waste: Comparison of start-up, reactor stability and process performance. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przemieniecki, S.W.; Kosewska, A.; Kosewska, O.; Purwin, C.; Lipiński, K.; Ciesielski, S. Polyethylene, polystyrene and lignocellulose wastes as mealworm (Tenebrio molitor L.) diets and their impact on the breeding condition, biometric parameters, metabolism, and digestive microbiome. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 154758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Yun, S.; Xing, T.; Li, B.; Abbas, Y.; Liu, X. Binary and ternary trace elements to enhance anaerobic digestion of cattle manure: Focusing on kinetic models for biogas production and digestate utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 323, 124571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Mu, H.; Hua, D.; Jin, F.; Meng, G. Acidogenic properties of carbohydrate-rich wasted potato and microbial community analysis: Effect of pH. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 128, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungerfeld, E.M. Metabolic hydrogen flows in rumen fermentation: Principles and possibilities of interventions. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raynal, J.; Delgenès, J.-P.; Moletta, R. Two-phase anaerobic digestion of solid wastes by a multiple liquefaction reactors process. Bioresour. Technol. 1998, 65, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisakti, B.; Irvan, M.; Turmuzi, M. Effect of temperature on methanogenesis stage of two-stage anaerobic digestion of palm oil mill effluent (POME) into biogas. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 206, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verrier, D.; Roy, F.; Albagnac, G. Two-phase methanization of solid vegetable wastes. Biol. Wastes 1987, 22, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, I.; Björnsson, L.; Mattiasson, B. The energy balance in farm scale anaerobic digestion of crop residues at 11–37 °C. Process Biochem. 2007, 42, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parawira, W.; Read, J.S.; Mattiasson, B.; Björnsson, L. Energy production from agricultural residues: High methane yields in pilot-scale two-stage anaerobic digestion. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Average |
|---|---|
| TS (%) | 8.33 ± 0.58 |
| VS (%TS) | 91.87 ± 1.12 |
| C (%TS) | 44.81 ± 0.53 |
| N (%TS) | 2.54 ± 0.01 |
| C/N | 17.64 ± 0.19 |
| Characteristics | Average |
|---|---|
| TS (%) | 31.36 |
| VS (%TS) | 78.42 ± 0.22 |
| C (%TS) | 41.03 ± 0.49 |
| N (%TS) | 1.76 ± 0.01 |
| C/N | 23.27 ± 0.27 |
| No. | Item | AR | M-MR | T-MR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ESH (kJ/g-VS) | 0.270 | ||
| 2 | Em (kJ/g-VS) | 0.018 | ||
| 3 | ESP (kJ/g-VS) | 0.048 | ||
| 4 | EP (kJ/g-VS) | 0.022 | ||
| 5 | Eh (kJ/g-VS) Ehl (kJ/g-VS) ER (kJ/g-VS) | −0.418 −0.149 | −0.000 −0.655 +0.251 | −0.907 −0.332 +0.795 |
| 6 | Eo (kJ/g-VS) | 0.000 | 9.446 | 11.196 |
| 7 | ∆Eelectricity (kJ/g-VS) | 3.104 | 3.561 | |
| 8 | ∆Eheat (kJ/g-VS) | 5.456 | 6.266 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dinh, P.V.; Fujiwara, T. Biogas Production and Energy Balance in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Thermophilic versus Mesophilic. Fermentation 2023, 9, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9070601
Dinh PV, Fujiwara T. Biogas Production and Energy Balance in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Thermophilic versus Mesophilic. Fermentation. 2023; 9(7):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9070601
Chicago/Turabian StyleDinh, Pham Van, and Takeshi Fujiwara. 2023. "Biogas Production and Energy Balance in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Thermophilic versus Mesophilic" Fermentation 9, no. 7: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9070601
APA StyleDinh, P. V., & Fujiwara, T. (2023). Biogas Production and Energy Balance in a Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion of Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Thermophilic versus Mesophilic. Fermentation, 9(7), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation9070601




