Abstract
In semiarid regions of Brazil, water and/or soil salinity is one of the limiting factors for sour passion fruit production. Low rainfall rates combined with edaphic conditions (high concentrations of soluble salts) intensify deleterious effects on plants. Thus, strategies that minimize the effects of salt stress, e.g., grafting with tolerant species and soil mulching, are extremely important to ensure the expansion of irrigated fruit farming in this region. From this perspective, this study aimed to evaluate the effect of grafting and mulching on the quantum yield, ionic relations, and fruit production of sour passion fruit irrigated with moderately saline water. The experiment was conducted under field conditions in split plots, in a 2 × (2 × 2) factorial arrangement to evaluate the combination of low and moderate salinity water (main plot) with the propagation method (seeds and grafting on P. cincinnata) and without and with plastic mulching (subplots), with four replications and three plants per plot. The ionic relations in passion fruit leaves were increased with the use of rootstocks and plastic mulching under irrigation with moderately saline water. The use of mulching increased the yield of photosystem II in sour passion fruit. The passion fruit plants propagated by seeds had 187.52% more fruits than those grafted onto P. cincinnata. The use of rootstocks with P. cincinnata in sour passion fruit restricted the uptake of Na and Cl but reduced fruit production.
1. Introduction
In the last few years, arid and semiarid regions worldwide have been affected by rainfall shortages and high temperatures in the spacetime scenario due to climate changes, which, allied to the inadequate use of water in agricultural systems, are becoming increasingly saline [1,2]. It is estimated that 7% of the total area of the planet is affected by some degree of salinity, and 25% of soils are degraded due to salt excess [3,4], thus reducing food production [5].
The production of sour passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) in Brazil is mainly concentrated in semiarid areas of the northeast region, responsible for almost 70% of the national production in 2021 [6]. Rainfall scarcity in the last few years led passion fruit producers in the region to adopt irrigation practices to supply the water requirements of the crop, which, in several cases, is performed using water with moderate electrical conductivity and different cation compositions [7], contributing to the formation of holomorphic soils, which severely affects physiological and nutritional plant processes due to the accumulation of Na+ and Cl- ions in plant tissues [8,9] combined with low contents of NO3−, H2PO4−, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, and SO42− [10,11].
Studies report that sodium chloride (NaCl) affects several physiological processes in plants, including chlorophyll fluorescence in several organs, tissues, and cells of plant species [12,13], including in sour passion fruit [7]. This variable provides valuable information about the transference of light energy during the photosynthetic process [14,15]. Furthermore, chlorophyll fluorescence has shown to be an important parameter to evaluate plant tolerance to salt stress and is commonly measured to indicate damage to the photosynthetic apparatus caused by ionic effects [16,17].
From this perspective, grafting is employed with cultivation under saline conditions, because some tolerant species, when used as rootstocks, can exclude Na+ and Cl− ions through mechanisms that regulate their uptake and transport within the plant [18,19,20]. This behavior is verified in several commercial species, e.g., mango–Mangifera indica L. [19]; citrus—Citrus macrophylla Wester, Citrus reticulata, and Punica granatum L. [21,22]; and tomato—Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. [10].
Plastic mulching (PM) has been reported as a way of minimizing salt accumulation in the soil [23,24] and, consequently, toxicity to plants caused by irrigation water [7,25]. The use of mulching in arid and semiarid regions has been increasingly employed in agriculture as it maintains soil moisture at high levels and reduces temperature [26,27,28], especially in places where the only water source available shows considerable concentrations of soluble salts [29]. According to [30] Aragüés et al. (2014), plastic mulching reduces the need for frequent irrigation as it prevents water loss through evaporation into the atmosphere. Furthermore, in cases where the water source is salinized, this practice reduces salt accumulation in the soil profile.
In this scenario, the grafting with Passiflora cincinnata, which, according to results obtained by [11], reduces the accumulation of Na+ and Cl− ions in sour passion fruit and, in association with plastic mulching, reduces salt accumulation in the soil [30], reducing the effects of salt stress on plants. From this perspective, this study aimed to evaluate the use of grafting with P. cincinnata and plastic mulching on the ionic relationships, quantum yield, and production of sour passion fruit irrigated with moderately saline water under semiarid conditions in northeastern Brazil.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of the Experimental Area
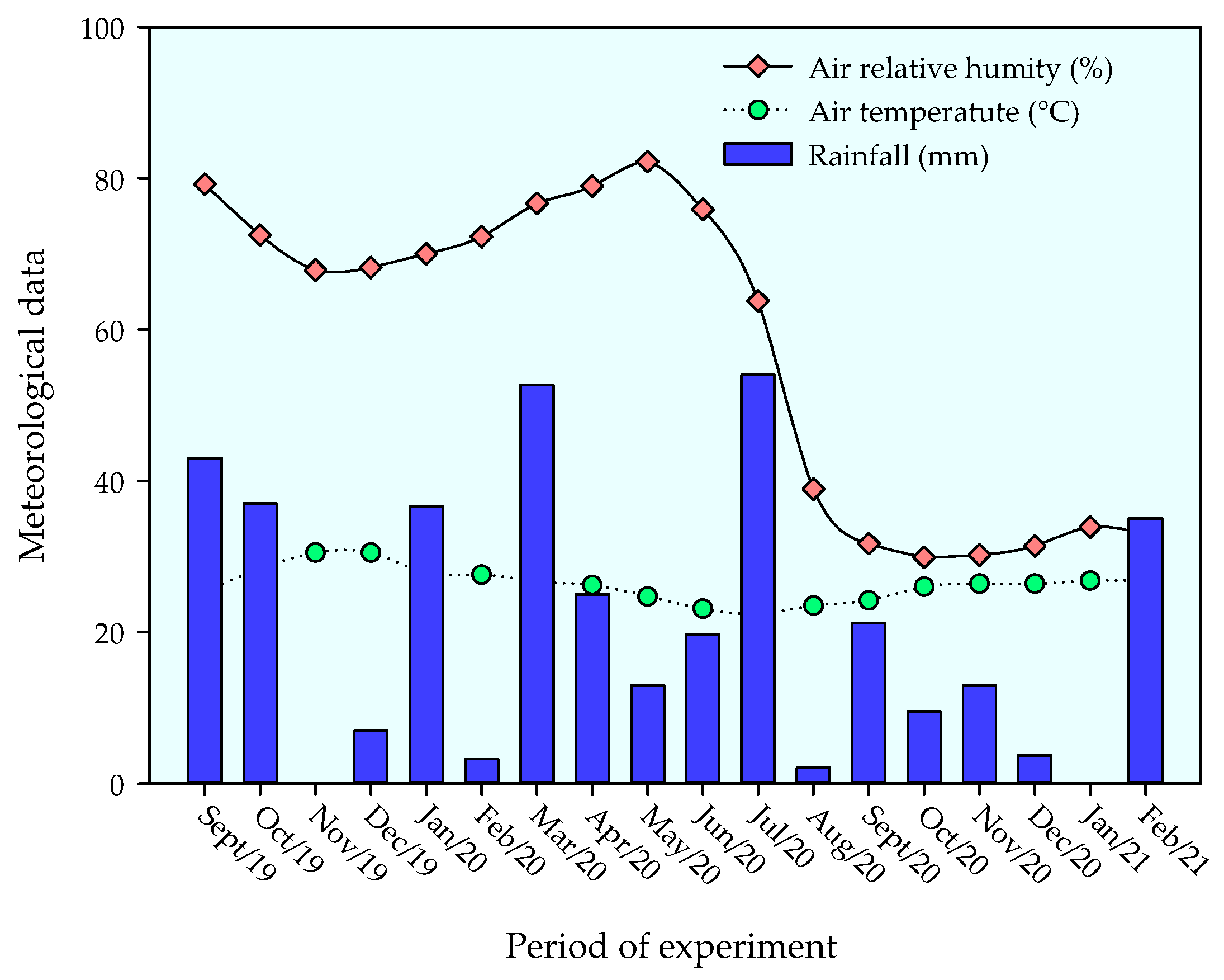
The experiment was conducted under field conditions from September 2019 to February 2021 in an experimental area located in the municipality of Remígio, State of Paraíba, Brazil. The location of the experiment is georeferenced by the coordinates 7°00′0.3″ S and 35°47′54″ W, at an elevation of 562 m above sea level. The climate of the region is classified as As’, i.e., tropical with dry summers and rainfall concentration in the winter and autumn seasons [31]. During the experimental period, daily data on temperature and relative air humidity were collected, showing the respective mean values of 27.5 °C and 68.5%. The cumulative rainfall during the period was 852.2 mm (Figure 1).
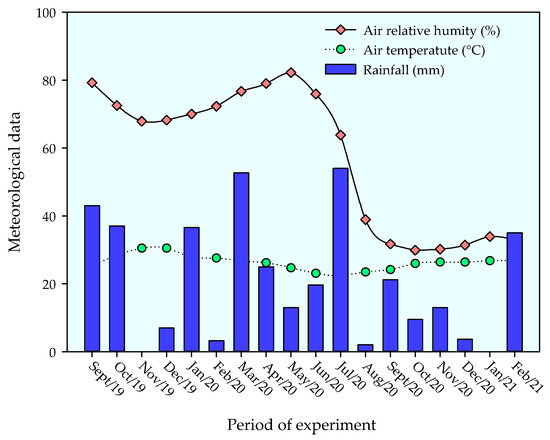
Figure 1.
Meteorological data collected in the area during the experiment.
The soil of the experimental area was classified as an Entisol Psamment, according to criteria for soil taxonomy of the US Soil Survey Staff [32]. Before the experiment was set up, soil samples were collected from the 0–0.40 m layer to characterize the chemical attributes with regard to fertility and salinity, in addition to the physical attributes [33], and the following values were presented: “Soil fertility”—pH = 6.00; P = 16.63 mg dm−3; K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, and Na+, respectively, 0.08, 1.09, 1.12, and 0.05 cmolc dm−3; sum of bases—SB = (K+ + Ca2+ + Mg2+ + Na+) = 2.34 cmolc dm−3; potential acidity (H+ + Al3+) = 1.24 cmolc dm−3; exchangeable acidity (Al3+) = 0; cation exchange capacity—CEC =(K+ + Ca2+ + Mg2+ + Na+ + [H+ + Al3+]) = 3.58 cmolc dm−3; bases saturation—V(%) ([SB/CEC] × 100) = 65.36%; organic matter = 13.58 g kg−1; “Soil salinity”—pHsp = 6.16; electrical conductivity in the 1:2 soil:water suspension = 0.22 dS m−1; cations—K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, and Na+, respectively, 0.89, 5.12, 15.25, and 5.70 mmolc L−1, and anions—SO42− and Cl−, respectively, 3.51 and 15.00 mmolc L−1; sodium adsorption rate (SAR) = 0.28 (mmol L−1)−0.5 and exchangeable sodium percentage (ESP) = 1.39%; classification = non-saline and non-sodic; “Soil physical”—sand, silt, and clay = 834.5, 100.0, and 65.5 g kg−1, respectively; flocculation degree = 1000 kg dm−3; soil and particle density = 1.53 and 2.61 kg dm−3; total porosity = 0.42 m3 m−3; soil moisture at field capacity (0.01 MPa) = 65.0 g kg−1; soil moisture at 80% of field capacity (0.03 MPa) = 49.0; soil moisture at the permanent wilting point (1.50 MPa) = 28.0 and textural class = loamy sand.
2.2. Plant Material and Experimental Design
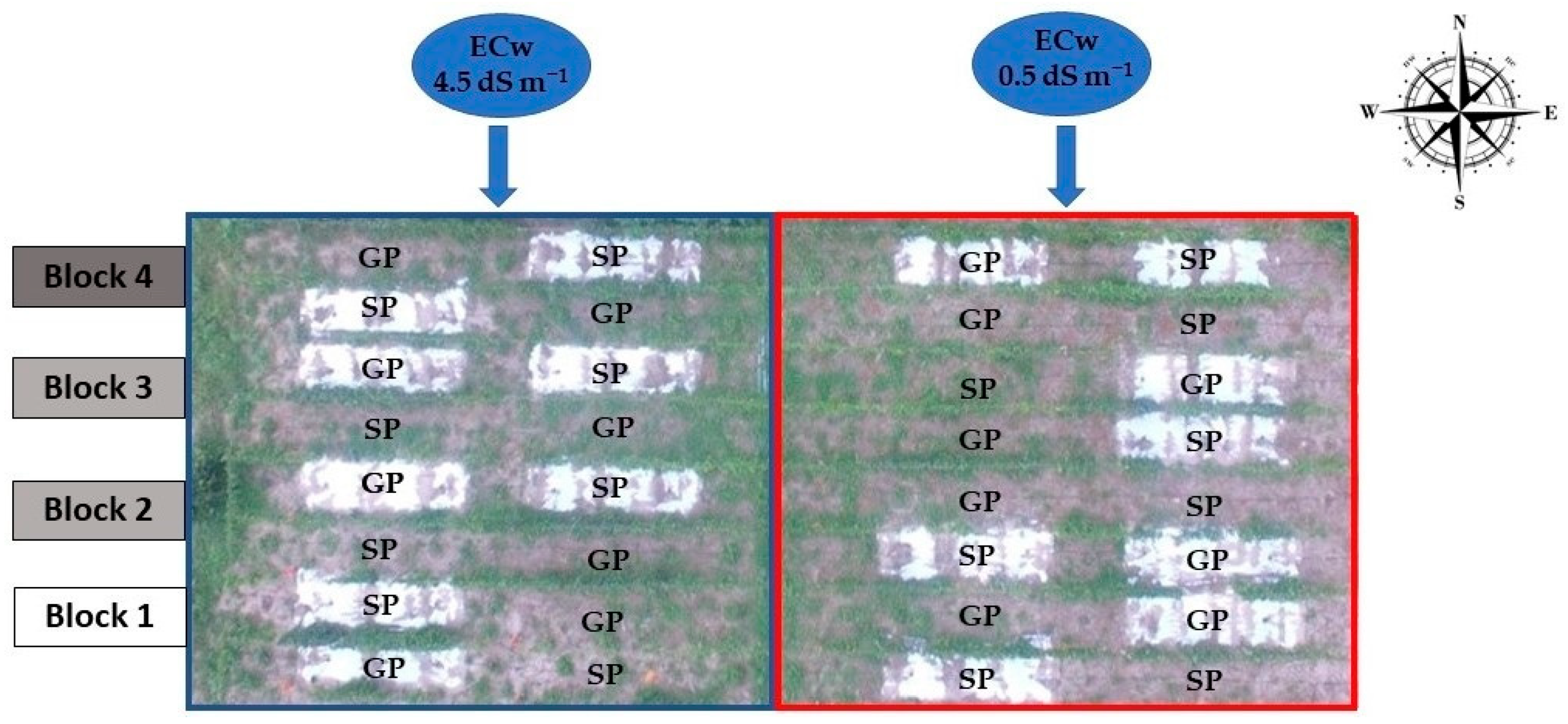
The sour passion fruit accession, “Guinezinho”, was used in this study (Passiflora edulis flavicarpa Deneger), a variety traditionally grown in northeastern Brazil, especially in the States of Paraíba and Rio Grande do Norte [34]. The experiment was distributed in a split-plot design (2 × (2 × 2)) in randomized blocks, with four replications and three plants by combining the subplots inside each plot. The main plot referred to the water of low (electrical conductivity—EC of 0.5 dS m−1) and moderate electrical conductivity (EC = 4.5 dS m−1), whereas the subplots referred to seed propagation (SP) and grafting (GP) using Passiflora cincinnata as a rootstock in the soil without (WOM) and with (WM) plastic mulching (Figure 2).
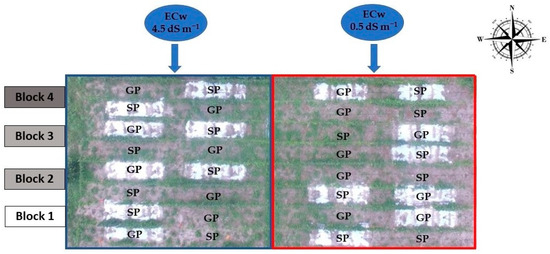
Figure 2.
Layout of the experiments in the area.
2.3. Conduction of the Experiment
The seeds of the sour passion fruit accession, “Guinezinho”, were collected in the experimental area from matrix plants with fruits at the stage of full physiological maturity (7°00′1.95″ S and 35°47′55″ W), i.e., when they had a predominant yellow color over the green surface of the peel [35]. The sour passion fruit scions were obtained from terminal sprouts in the tertiary vegetative branches of plants grown close to the experiment. The rootstock was produced with wild passion fruit seeds (P. cincinnata) collected in Cerro Corá, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil (6°2′44″ S and 36°20′52″ W). The cleft grafting technique was employed using the rootstocks 90 days after sowing (DAS).
The transplanting holes measuring 0.40 m × 0.40 m × 0.40 m (volume = 64 dm3) were opened by separating the soil portions of 0–0.20 m to 0.20–0.40 m. The 0–0.20 m portion received 20 L of cattle manure 120 g of dolomitic limestone (CaO = 47%, MgO = 3.4%, and RNV = 82%), and 50 g of FTE-BR12 (S = 3.9%; B = 1.8%; Cu = 0.85%; Mn = 2.0%, and Zn = 9.0%), which were mixed and poured back into the holes.
The planting system used was an espalier system using 2 m high pickets and smooth wire No. 12 fixed on top of the pickets, which were spaced at 3 m. At the ends of the espaliers, posts with a diameter of 0.20 m were installed to withstand the tension imposed by the weight of the plants. The seed-propagated and grafted seedlings were transplanted, respectively, 60 days after sowing and 30 days after grafting, when the plants had, on average, four pairs of definitive leaves and heights ranging from 0.25 to 0.30 m. The spacing employed was 3 × 2 m, representing a population density of 1667 plants ha−1.
The water of low electrical conductivity (EC = 0.5 dS m−1) came from a surface dam located close to the experimental area, whose chemical characteristics were obtained according to [36] and had the following values: Electrical conductivity at 25 °C = 0.5 dS m−1; pH = 6.10; K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, Cl−, and, SO42− = 6.10, 0.28, 0.65, 0.27, 1.88, and 0.51 mmolc L−1; SAR = 2.77 (mmol L−1)0.5; and C1S1 = low risk of soil salinization and sodification.
The moderately saline water (EC = 4.5 dS m−1) was obtained by dissolving sodium chloride (NaCl—94% purity and non-iodized in low-salinity water (EC = 0.5 dS m−1). The electrical conductivity was measured with an Instrutherm portable conductivity meter model CR-850. In order to determine the amount of NaCl to be dissolved in water to obtain the EC = 4.5 dS m−1, the relationship between the EC and the concentration of salts in the irrigation water was considered according to [36], using Equation (1):
where C = salt content to be dissolved (mmolc L−1) and EC = electrical conductivity of irrigation water (dS m−1).
C = 10 × EC
During the first 30 days after transplanting (DAT), the plants were irrigated with low-salinity water to allow the formation of their root systems. After this period, sour passion fruit was irrigated with low (0.5 dS m−1) and moderately saline water (EC = 4.5 dS m−1) by providing a water volume according to the crop evapotranspiration requirements (ETc). Irrigation was performed daily by considering the crop evapotranspiration (ETo) and the crop coefficient (Kcs) according to the plant development phase. The Kcs used were 0.69 in the vegetative phase, 0.82 in the flowering phase, and 1.09 in the fruit setting phase, according to [37]. The irrigation method used was localized irrigation with drippers below the plastic cover (mulching). Each plant received four self-compensating drippers operating at a flow rate of 4 L h−1 and a pressure of 0.20 MPa—two facing east and two facing west—distanced, respectively, 0.20 m and 0.40 m from the stem of the plants.
The mulch used was a plastic film with a white surface and a thickness of 320 µ, which was used to protect the soil surface of three plants per plot in the treatments with soil protection. In the plots, the plastic mulch was installed with dimensions of 2.0 m in width between rows and 12 m in length, covering an area of 24 m2. In the area where the seedlings were transplanted, holes measuring 0.40 m were opened and, soon after transplanting, the unprotected area was covered with plastic to prevent water loss through evaporation.
Topdressing fertilization was performed with nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), according to the crop requirements, through fertigation using a Venturi injector [38]. N and K were provided in a proportion of 1N:1K every 15 days as urea (45% N) and potassium sulfate (50% K2O and 45% S), whereas P was provided monthly as monoammonium phosphate—MAP (50% P2O5 and 11% N). The levels of N and K were, respectively, 1.5 g of each nutrient at 30 and 60 DAT, 3 g and 5 g, at 60 and 90 DAT, 10 g at 120, 150, and 180 DAT, and 15 g from 210 to the end of the production cycle, provided by diluting these components in irrigation water to provide the necessary dosage [38]. Fertigation with MAP occurred at the levels of 5, 10, 10, 10, 10, 15, 15, and 15 g of P2O5 at 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, 210, and 300 DAT, respectively [38]. The supply of micronutrients throughout the passion fruit crop cycle was performed monthly, by foliar spraying using Ajifol Gold (B = 0.3%; Cu = 0.5% Mn = 5.0%; Mo = 0.2%, and Zn = 1.0%) at the dose of 1.5 L ha−1, Niphokam 585 (B = 0.5%; Cu = 0.2%, Mn =0.5%, and Zn = 1.0%) at the dose of 1.0 L ha−1, and Ferro EDTA iron chelates (Fe = 12%) at the dose of 150 g 100L−1.
2.4. Determination of the Ionic Relations
The foliar contents of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), sulfur (S), sodium (Na), and chlorine (Cl) were determined during the full flowering stage of passion fruit by collecting the third pair of leaves from the branches counting from the tip of the apical meristem [11]. Nitrogen was determined by the Kjeldahl method (dry digestion), whereas phosphorus was determined by spectrometry with molybdenum blue; potassium and sodium were determined by flame spectrometry; calcium, magnesium, and sulfur were determined using atomic absorption spectrophotometer at the respective wavelengths of 422.7, 285.2, and 400.0; and chloride (Cl−) was determined by Mohr’s volumetric method. These determinations were used to determine the relationship between K, Ca, and Mg cations with Na (K/Na, Ca/Na, and Mg/Na) and between N, P, and S anions with Cl (N/Cl, P/Cl, and S/Cl).
2.5. Fluorescence Analysis of Chlorophyll a
During the full flowering phase (120 DAT), the third pair of leaves counting from the tip of the apical meristem was selected to evaluate the fluorescence of chlorophyll “a” using a PEA (plant efficiency analyzer) II Modulated Fluorometer (Opti-Sciences, Hudson, NH, USA). The readings were performed on two leaves per plant in each treatment, one on the east side and one on the west side, from 8:00 to 11:00 a.m. by adapting the leaves to the dark for 30 min using the fluorometer clamps [7]. The variables analyzed were the initial (Fo), maximum (Fm), and variable fluorescence (Fv) and the quantum yield of photosystem II (EFM = Fv/Fm), according to [39].
2.6. Mean Weight and Number of Fruits
The sour passion fruits harvested referred to consecutive crop seasons, from February to August 2020 (first crop season) and from April to July 2021 (second crop season), when the number of fruits (NF) and mean fruit weight (MF) were determined. Fruit harvest occurred 60 days after flower anthesis when they showed physiological maturity and the maximum juice yield [35].
2.7. Data Analysis
The data were tested for normality (Shapiro–Wilk) and homogeneity. Soon after, the data were subjected to analysis of variance by the F-test (p ≤ 0.05). The means referring to the sources of variation and the interaction were compared by Tukey’s test (p ≤ 0.05) using R Studio statistical software [40] (R Team 2020). The principal component and clustering analyses were performed using the R Studio analysis packages [40] (R Team 2020).
3. Results
3.1. Ionic Relations
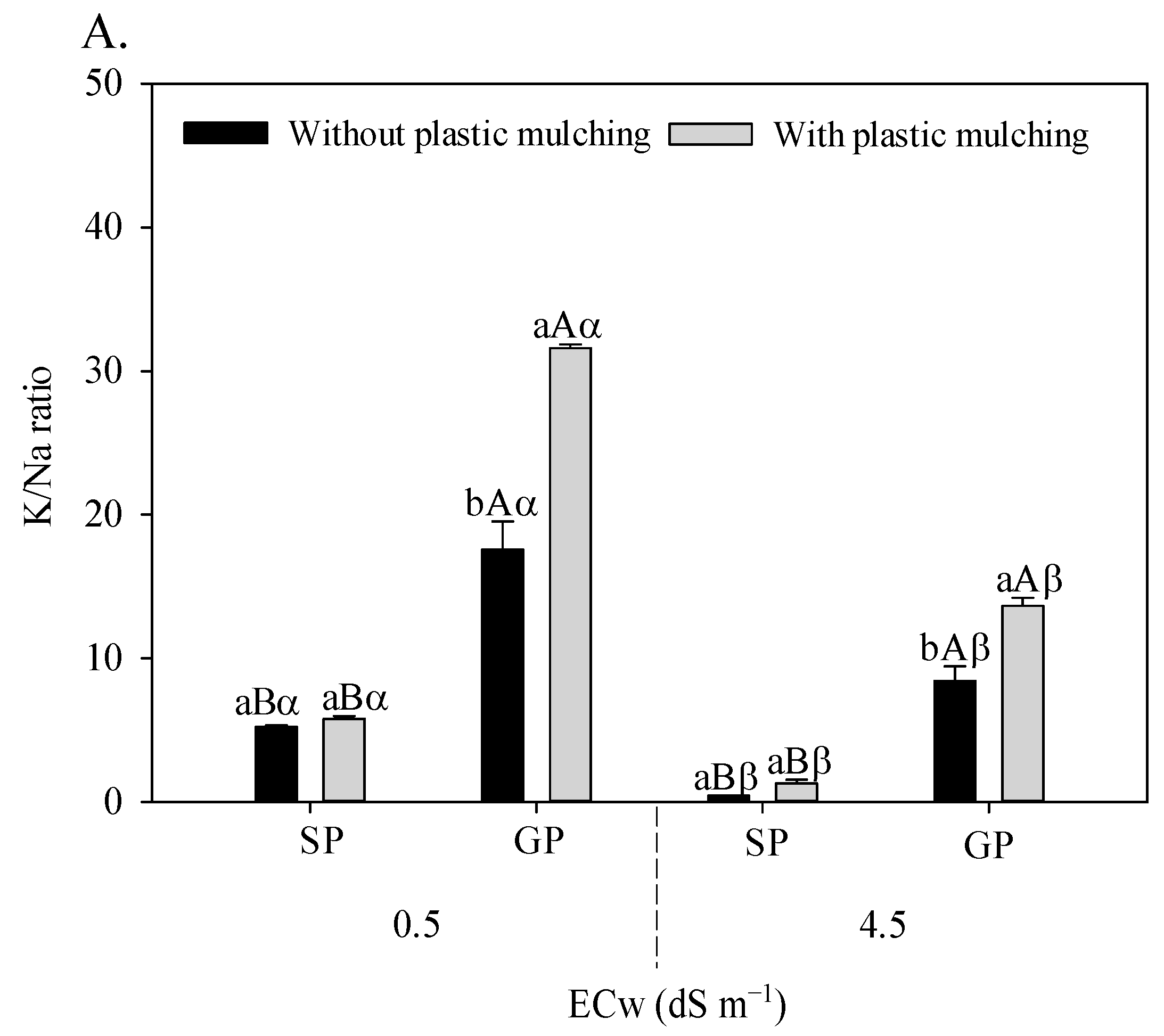
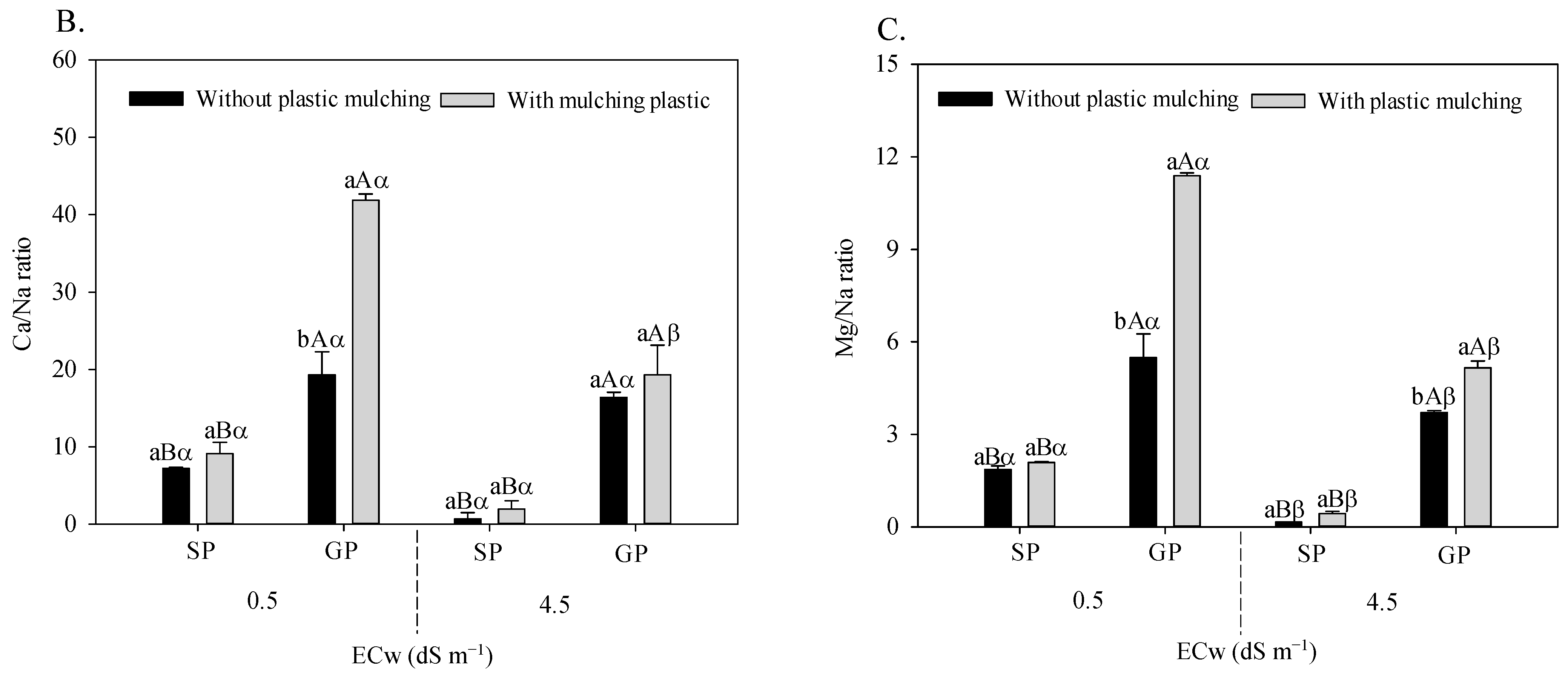
The irrigation water salinity × plastic mulching × propagation methods interaction influenced the foliar relations of K/Na (F = 21.533; p = 0.006 **), Ca/Na (F = 15.493; p = 0.0020 **), and Mg/Na (F = 41.683; 0.00001 **) in sour passion fruit (Figure 3A–C).
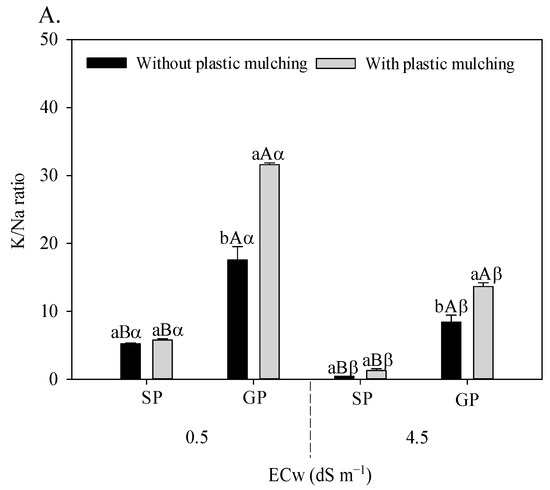
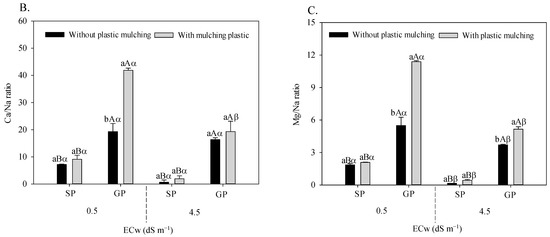
Figure 3.
K/Na (A), Ca/Na (B), and Mg/Na (C) foliar ratio in sour passion fruit propagated by seeds (SP) and grafting (GP) and irrigated with saline water in soil with and without plastic mulching. The vertical bar represents the standard error of the mean (n = 4). For the same treatment, means with the same lowercase letters do not indicate a significant difference (p > 0.05) for soil without and with mulching, and means with the same uppercase letter indicate no significant difference (p > 0.05) for seed propagation via seeds and grafting, while equal Greek letters indicate no differences between plants irrigation with water of low and high salinity.
Grafted sour passion fruit plants grown in soil with plastic mulching showed higher K/Na (Figure 3A), Ca/Na (Figure 3B), and Mg/Na (Figure 3C) relations regardless of the electrical conductivity of irrigation water. Under irrigated conditions with 4.5 dS m−1, the grafted plants grown in soil with plastic mulching increased the K/Na, Ca/Na, and Mg/Na foliar relations by 3072.09%, 453.62%, and 3.3340%, respectively, compared to plants propagated by seeds and without plastic mulching.
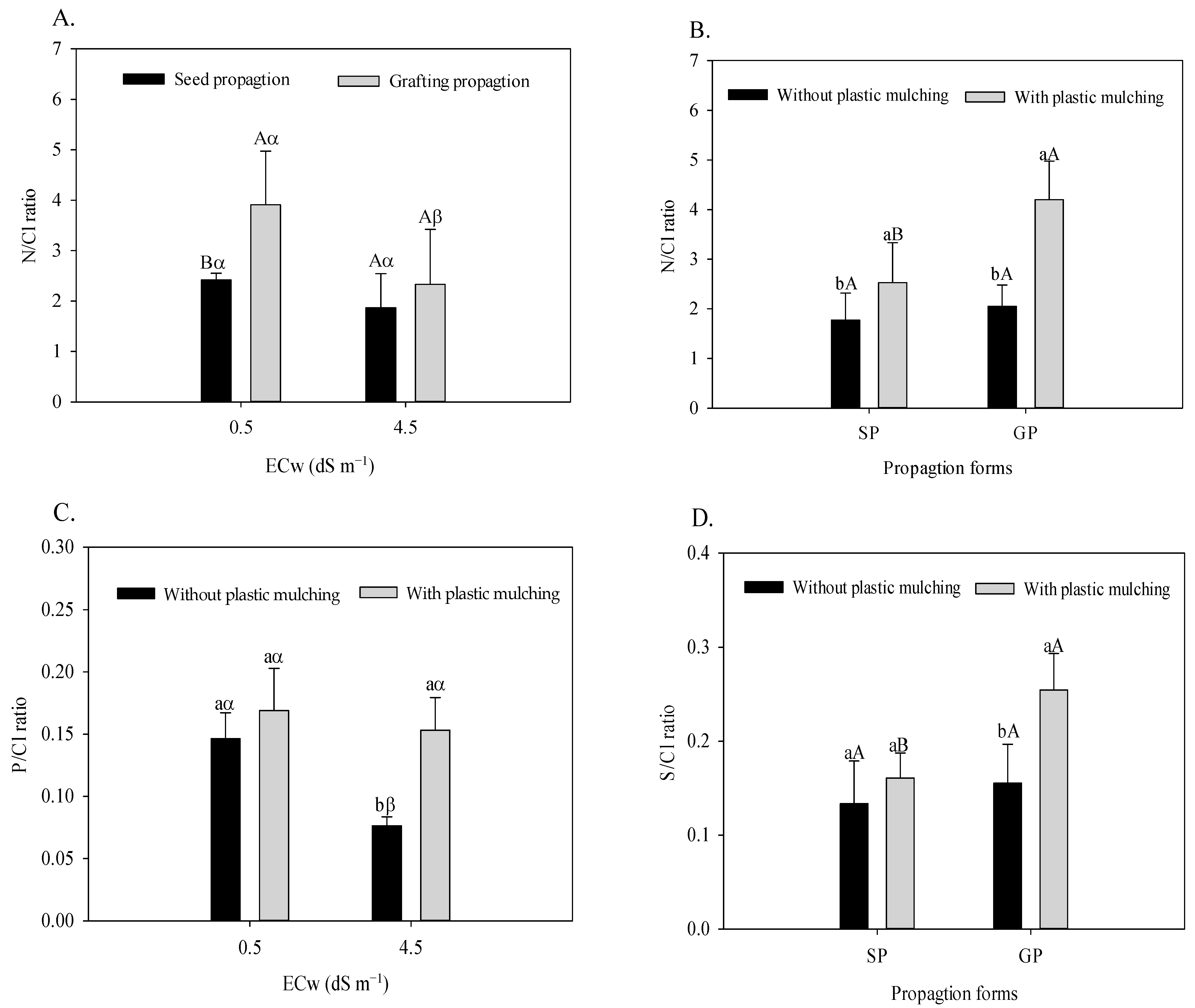
According to Figure 4A,B, the N/Cl relation responded to the interactions referring to the propagation method × irrigation water salinity (F = 5.32; p = 0.039 *) and propagation method × plastic mulching (F = 9.31; p = 0.0092 **). The plastic mulching × irrigation water salinity interaction interfered with the foliar relation of P/Cl (F = 7.37; p = 0.0187 *), and the S/Cl relation was also significantly affected by the plastic mulching × propagation method interaction (F = 7.67; p = 0.0170 *), as observed in Figure 4C,D.
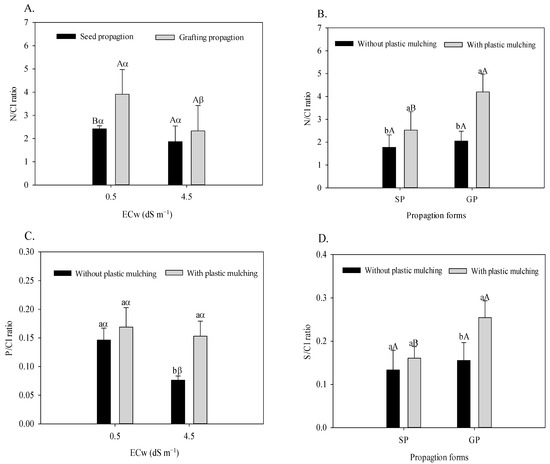
Figure 4.
Foliar N/Cl ratio in sour passion fruit propagated by seeds (SP) and grafting (GP) irrigated with saline water (A), with and without plastic mulching (B); foliar P/Cl ratio in passion fruit irrigated with saline water in soil with and without plastic mulching (C); foliar S/Cl ratio in passion fruit propagated by seeds (SP) and grafting (GP) in soil with plastic mulching (D). The vertical bar represents the standard error of the mean (n = 4). For the same treatment, means with the same lowercase letter indicate no significant difference (p > 0.05) for soil without and with mulching, and means with the same uppercase letter indicate no significant difference (p > 0.05) for seed propagation and grafting, whereas equal Greek letters indicate no difference for irrigation with water of low and high salinity.
Plants grafted onto P. cincinnata showed a reduction of 40.4% in the leaf N/Cl ratio when irrigated with moderately saline water (Figure 4A). However, the N/Cl ratio of grafted sour passion fruit was higher than that of seed-propagated plants. This behavior is evidenced by the higher increments in irrigation conditions with low salinity (61.57%) compared to moderately saline (24.95%) water. According to Figure 4B, plastic mulching increased the leaf N/Cl ratio in seed-propagated (26.26%) and grafted plants (109.75%).
Moderately saline water reduced the leaf P/Cl ratio by 47.94% in the soil without plastic mulching (Figure 4C). Under irrigation with water of 4.5 dS m−1, plastic mulching increases the uptake of P in relation to Cl in sour passion fruit, increasing the P/Cl ratio by 101.31%. The association of plastic mulching with grafting increases the leaf S/Cl ratio (Figure 4D). With regard to the control (SP and without mulching), the S/Cl ratio was increased from 0.133 to 0.254, which represents a 90.97% increase.
3.2. Quantum Yield
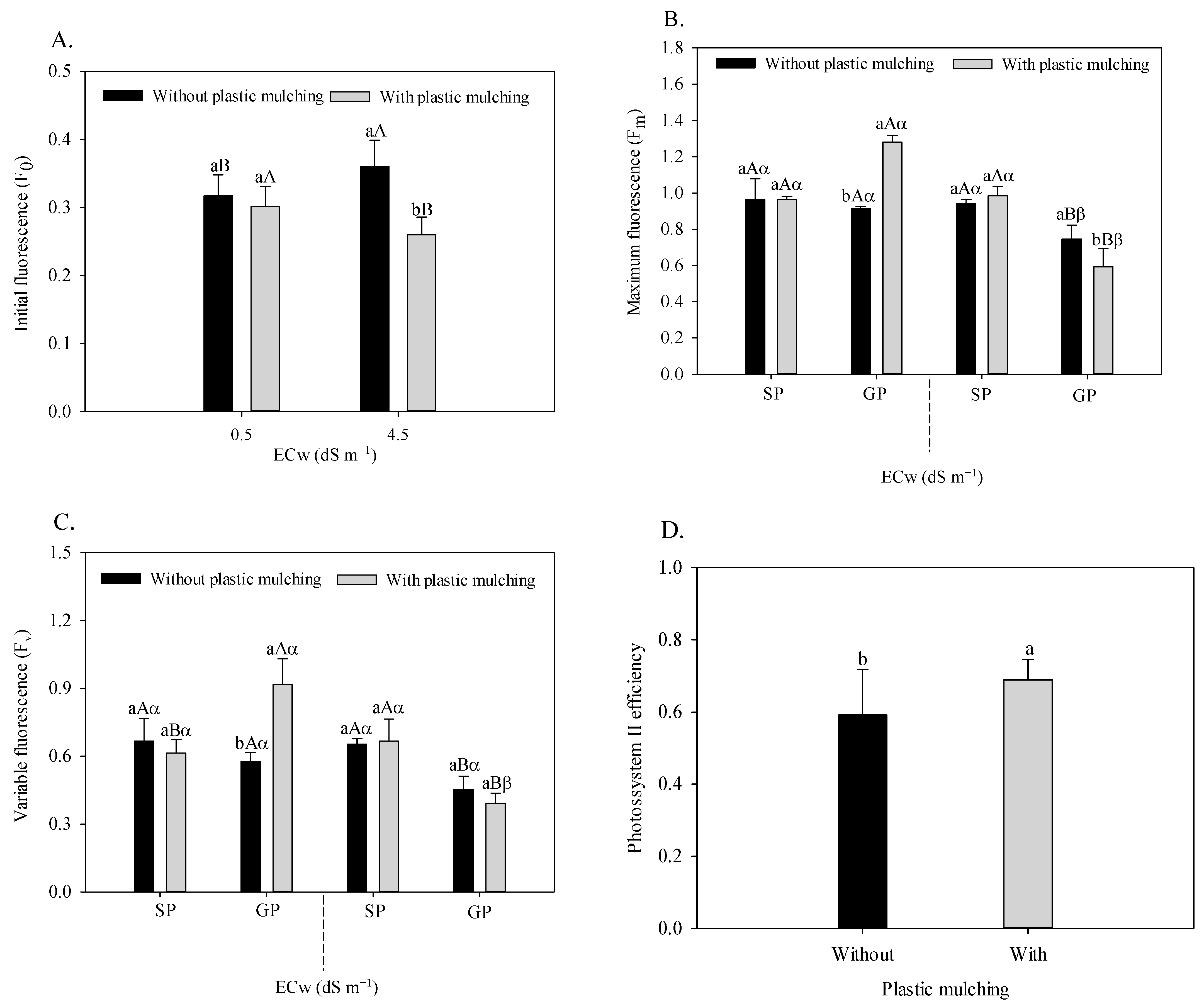
The initial fluorescence of sour passion fruit (Figure 5A) was significantly influenced by the plastic mulching × irrigation water salinity interaction (F = 10.254; p = 0.0042 **). The use of plastic mulching in the soil irrigated with low salinity water did not interfere with the Fo, however, it was reduced by 27.7% when irrigated with moderately saline water (4.5 dS m−1). In the soil without plastic mulching, irrigation with water of 4.5 dS m−1 increased the initial fluorescence of passion fruit plants but reduced this variable in the absence of mulching.
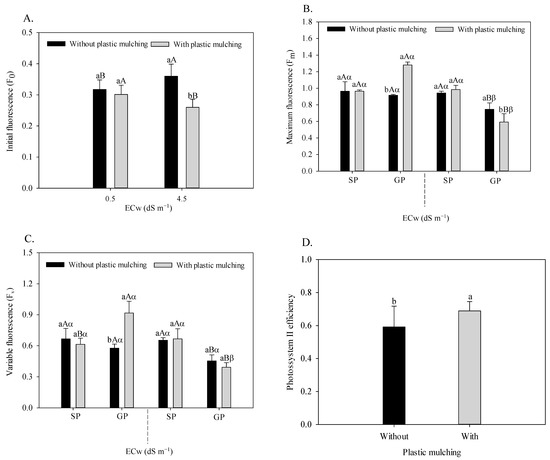
Figure 5.
Initial fluorescence of sour passion fruit irrigated with saline water and plastic mulching (A), maximum and variable fluorescence of sour passion fruit irrigated with saline water, plastic mulching, and propagation methods (B,C), and efficiency of photosystem II of sour passion fruit in soil with plastic mulching (D). The vertical bar represents the standard error of the mean (n = 4). For the same treatment, means with the same lowercase letter indicate no significant difference (p > 0.05) for soil without and with mulching; means with the same uppercase letter indicate no significant difference (p > 0.05) for seed propagation and grafting; and means with the same Greek letter indicate no significant difference for irrigation with water of low and high salinity.
The water salinity × plastic mulching × propagation methods interaction influenced the maximum (F = 0.165; p = 0.00001 **) and variable (F = 0.106; p = 0.0012 **) fluorescence, as shown in Figure 5B, C, respectively. The highest Fm and Fv values were found in grafted passion fruit irrigated with 0.5 dS m−1 water with plastic mulching. Under irrigation with 4.5 dS m−1, the highest Fm and Fv values occurred in the passion fruit plants propagated by seeds regardless of mulching. Under salt stress, the absence of plastic mulching increased the maximum fluorescence of passion fruit by 25.78%.
Plastic mulching had a significant effect (F = 6.989; p = 0.0165 *) on the quantum yield of photosystem II of sour passion fruit, with increases amounting to 15.2% compared to plants with the absence of soil protection (Figure 5D).
3.3. Mean Weight and Number of Fruits
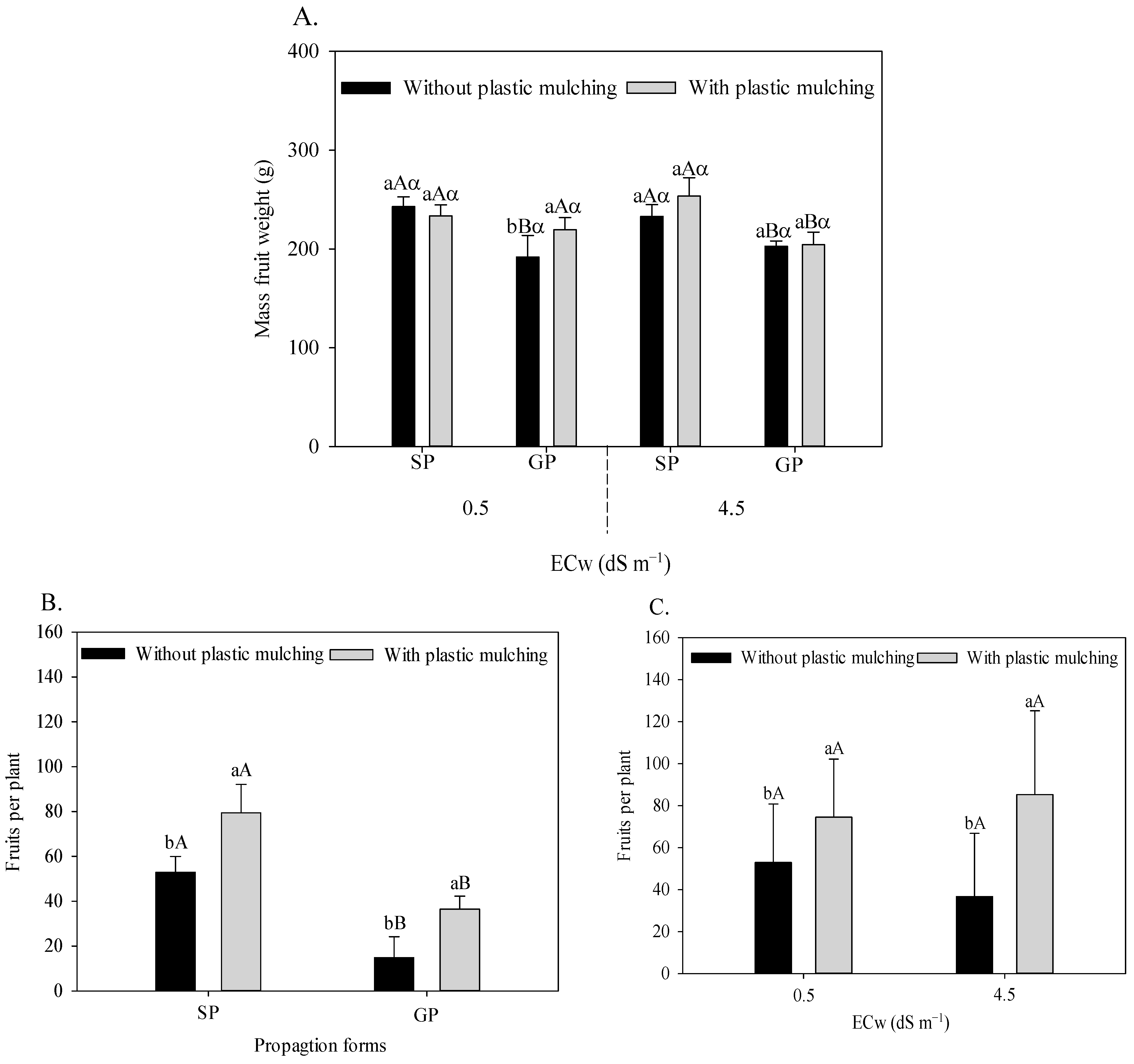
Under irrigation with water of 0.5 dS m−1, plastic mulching increased the mean fruit weight by 14.34% of sour passion fruit grafted onto P. cincinnata (Figure 6A). When irrigated with 4.5 dS m−1, the passion fruit plants propagated by seeds showed a higher fruit weight in comparison to grafted plants, with a superiority of 14.89% and 24.14% in soil without (233.05 to 202.84 g) and with (253.57 to 204.26 g) plastic mulching, respectively.
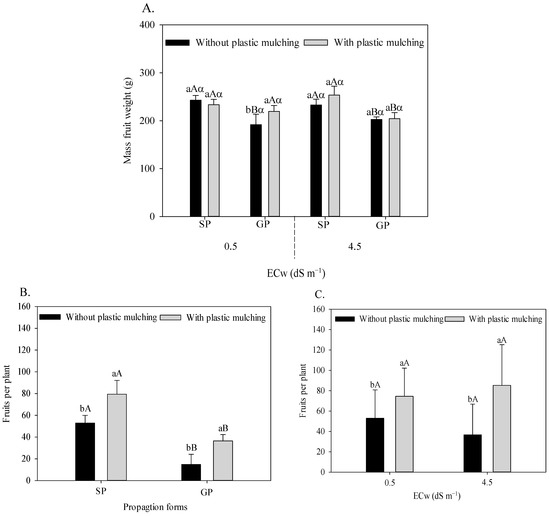
Figure 6.
Mean fruit weight of sour passion fruit (A) propagated by seeds (SP) and grafting (GP), irrigated with saline water in soil with and without plastic mulching; number of sour passion fruits in plants propagated by seeds (SP) and grafting (GP) in soil with and without mulching (B); and irrigated with low- and high-salinity water in soil with plastic mulching (C). The vertical bar represents the standard error of the mean (n = 4). For the same treatment, means with the same lowercase letter indicate no significant (p > 0.05) for soil without and with mulching, means with the same uppercase letter indicate no significant difference (p > 0.05) for seed propagation and grafting, and means with the same Greek letter indicate no difference (p > 0.05) for irrigation with water of low and high salinity.
Plastic mulching increased the number of sour passion fruits, with increments of 50.04% in seed-propagated plants and 146.38% in P. cincinnata grafts (Figure 6B). In addition, the plants propagated by seeds showed an increase of 187.52% in the number of fruits compared to the grafted ones. Plastic mulching promoted an increased number of fruits under irrigation with low (40.72%) and mainly high salinity water (132.62%), as seen in Figure 6C.
3.4. Principal Component Analysis
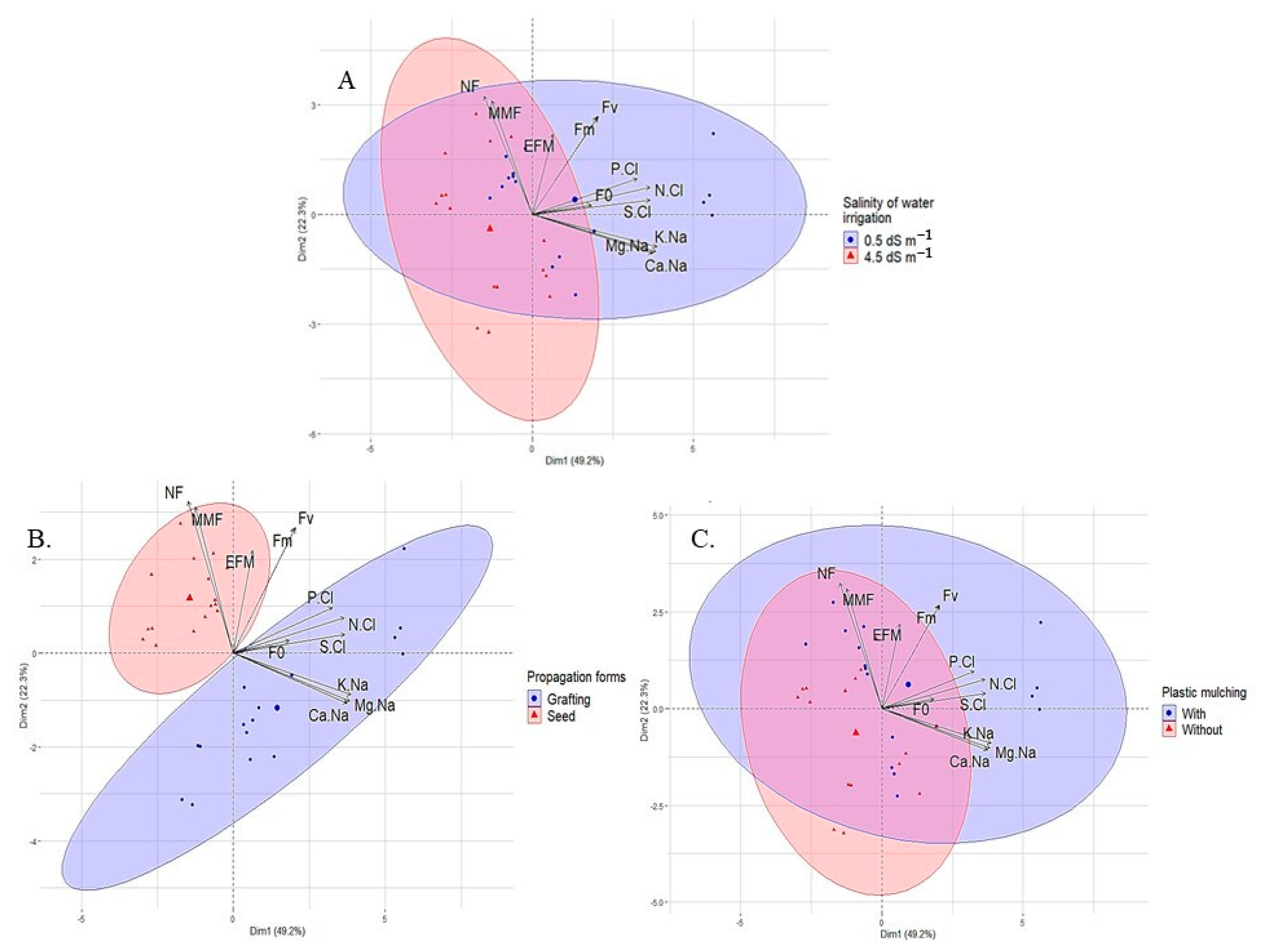
According to Figure 7, components 1 and 2 explained 71.6% of the total variance when considering 12 parameters. Component 1 is responsible for 49.3% of the total variance of the variables of sour passion fruit subjected to the treatments (water salinity, propagation method, and plastic mulching), and component 2 is responsible for 22.3%. Among the parameters studied, the number of fruits, followed by the mean fruit weight and the cation ratios (K/Na, Ca/Na, and Mg/Na), showed greater sensitivity to the application of treatments, unlike the initial fluorescence (Fo), which showed low influence.
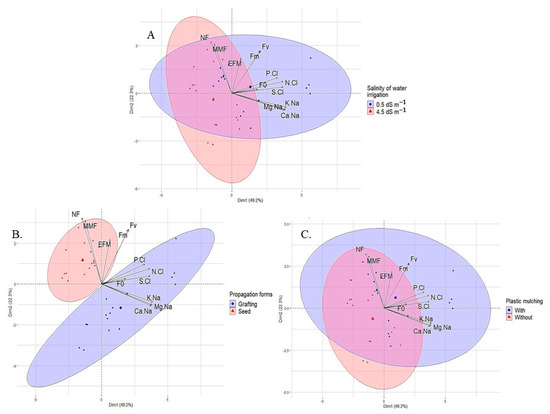
Figure 7.
Results of the principal component analysis and clustering analysis among the sour passion fruit variables analyzed and irrigation water salinity (A); propagation method (B); and plastic mulching (C).
According to the cluster analysis for each isolated factor, there were well-defined contributions (Figure 7A). Low-salinity water (0.5 dS m−1) strongly influenced all studied variables, whereas moderately saline water (4.5 dS m−1) interfered mainly with the production components (weight and number of fruits), initial fluorescence, and the efficiency of photosystem II of sour passion fruit (Figure 7A). Similar behavior was observed for plastic mulching, with the soil without this protection influencing all studied variables, whereas mulching contributed mainly to NF, MFF, and EFM (Figure 7C).
When analyzing the influence of the propagation method on the evaluated variables of sour passion fruit (Figure 7B), seed propagation strongly influenced the number and weight of fruits, in addition to the quantum yield of photosystem II. On the other hand, the passion fruit plants propagated by grafting strongly interfered with the initial fluorescence and ionic relations of the plants (K/Na, Ca/Na, Mg/Na, N/Cl, P/Cl, and S/Cl).
4. Discussion
Plant tolerance to salinity is associated with their ability to restrict the uptake and/or transport of toxic salts from roots to the shoot [21,22]. As shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4, the use of sour passion fruit seedlings grafted onto Passiflora cincinnata associated with plastic mulching on the soil resulted in greater plant tolerance to saline stress since, under these conditions, they showed higher values of foliar ionic relations, with higher foliar contents of N, P, K, Ca, Mg, and S to the detriment of the reduction in Na and Cl uptake and transport.
From this perspective, rootstocks with tolerant species can limit the passage of Na+ and Cl− ions from the xylem sap of the roots to the shoot parts of the plants (scion), as verified by [41] in ungrafted and grafted tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) irrigated with saline water. Karimi and Hassanpour [22] evaluated the effect of salinity on the nutrient uptake and transport of K, Ca, Mg, and toxic ions (Na and Cl) in pomegranate plants—Punica granatum L. (ungrafted and grafted), concluding that tolerant rootstocks reduce the presence of sodium and chloride and increase the transport of K and Mg in leaf tissues. The authors also highlighted that the response is associated with the selectivity of nutrient transport and mechanisms of limitation and accumulation of Na and Cl in the shoot as a way of preventing possible damage to photosynthetically active sites and newly-formed leaves [10,41].
Allied to this, in semiarid regions, plastic mulching is used to reduce the impact of irrigation with saline water on the increase in soil salinity [23,24] and plant-toxic ions [25]. Plastic mulching reduces water evaporation from the soil surface by up to 80%, keeping it wetter compared to bare soil [29]. Thus, the deposition of sodium chloride salts via irrigation with saline water is low, mainly due to the lower crop water requirements [30].
As observed in Figure 5, in general, irrigation with moderately saline water reduces the fluorescence of sour passion fruit (Fo, Fm, and Fv), mainly in grafted plants. Salt stress reduces chlorophyll fluorescence, compromising energy transfer to photosystem II reaction centers [12,14,17,42]. In sour passion fruit, moderately saline water (4.5 dS m−1) has been shown to reduce the quantum yield, negatively affecting the photosynthetic activity of the crop [7].
The increase in the uptake of essential elements and the reduction in Na+ and Cl− accumulation in the leaf tissues confers to sour passion fruit grafted onto P. cincinnata a greater energy capture efficiency or a larger number of active reaction centers of PSII, jointly contributing to a better photosynthetic performance [13]. In citrus, Simpson et al. (2015) [18] evaluated the effect of irrigation with saline water on chlorophyll fluorescence and found a marked reduction in fluorescence, mainly in non-grafted plants, and attributed it to the accumulation of toxic ions (Na+ and Cl−) in leaf tissues, which reduced electron transfer efficiency, intensifying the damage related to low water absorption.
Photoinhibition is denoted by the reduction of EFM values and can detect damage to PSII and photosynthetic efficiency of the leaf, which occurs due to the destruction of the oxygen evolution complex and the reaction center of photosystem II [7,13]. Furthermore, under osmotic stress conditions, there are disturbances in the Calvin–Benson cycle, which can induce the downregulation of PSII [43]. Therefore, plastic mulching, by keeping the soil cooler and moister [25,26,28], attenuated the effects of water/salt stress in sour passion fruit (Figure 4). Khayyat et al. [27] point out that the quantum yield of PSII is a very sensitive variable to oxidative stress, with a positive correlation with photosynthesis. The authors observed that the use of plastic mulching in the soil contributed to increasing the Fv/Fm in barberry (Berberris vulgaris L.) compared to uncovered soil.
The increase in the mean weight (Figure 6A) and in the number of fruits of grafted sour passion fruit (Figure 6B,C) observed in the plants under plastic mulching is due to the positive impact on soil properties, especially the maintenance of thermal amplitude (temperature) and moisture, which greatly influence the uptake of nutrients and water by the roots and the growth of the soil microbiota, consequently affecting the production components [26,44]. Similar behavior was verified by Wang et al. [45] in peach trees, when they concluded that plastic mulching significantly increases the soil water content, with effects of fruit expansion and contributing to increased production.
The higher mean fruit weight and number of fruits observed in sour passion fruit plants propagated by seeds compared to those grafted onto P. cincinnata (Figure 6A,B) reflects the reduced plant development in the field, e.g., smaller stem diameters and low emission of productive branches in grafted plants. This justification is confirmed by [46], who attributed the lower development of passion fruit grafted onto Passiflora gibertti (less biomass accumulation) to the reduction of production components (weight and number of fruits) in comparison to ungrafted plants. When evaluating the effect of form of propagation on the growth and physiology of sour passion fruit, Gomes et al. [47] observed that grafted plants had smaller roots and leaf systems compared to those propagated by seeds, thus reducing plant vigor.
Among the factors evaluated in the PC analysis (Figure 7), the formation of two very distinct groups stands out for the form of propagation under the influence of the studied variables. The sour passion fruit plants propagated by grafting had more influence on the ionic relations in the leaf tissue. However, there was a negative relationship between the mean fruit weight and the number of fruits, whereas seed-propagated plants had a high positive influence on the production components. In the literature, it is shown, for several crops, that the use of salinity-tolerant rootstocks limits the uptake and transport of toxic ions from the roots to the shoot in the graft union region and favors nutrient uptake [8,10,41]. However, specifically in passion fruit, despite reducing the presence of Na and Cl in leaf tissues, grafting caused loss of vigor in the shoot part as already reported in previous studies, through the reduction in growth and accumulation of plant biomass, which was strongly related to low crop yields [11,46,47].
5. Conclusions
Grafting and especially plastic mulching increase the quantum yield of photosystem II and the ionic relations of sour passion fruit under irrigation with moderately saline water. The use of P. cincinnata as a rootstock had a positive effect on the foliar ionic relations of sour passion fruit irrigated with moderately saline water, with foliar Na and Cl restriction and higher nutrient contents. However, this did not result in higher mean fruit weights and number of fruits. Concerning the fruit production capacity, plastic mulching favored sour passion fruit plants grown under salt stress, with higher values of fruit weight and number of fruits. Therefore, seed propagation can be indicated as a form of propagation for sour passion fruit.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G.d.L.S., L.F.C. and E.N.d.M.; methodology, A.G.d.L.S., L.F.C.; E.N.d.M. and Í.H.L.C.; software, F.d.O.M., L.d.S.S. and A.S.d.M.; validation Í.H.L.C., G.S.d.L., E.F.d.M. and H.R.G.; formal analysis, F.d.O.M., L.d.S.S. and B.d.S.; investigation, A.G.d.L.S., L.F.C., Í.H.L.C. and L.S.R.; resources, A.G.d.L.S., L.F.C., G.S.d.L. and H.R.G.; data collection, A.G.d.L.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.G.d.L.S., G.S.d.L., B.d.S. and H.R.G.; writing—review and editing, A.G.d.L.S., Í.H.L.C., E.F.d.M., A.S.d.M. and E.N.d.M.; supervision, L.F.C. and Í.H.L.C.; project administration, A.G.d.L.S., L.F.C. and Í.H.L.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
CNPq (National Council for Scientific and Technological Development) process No. 160146/2019-4, CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel), and UFPB (Federal University of Paraíba).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article. No supplemental data is provided.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Graduate Program in Agricultural Engineering of the Federal University of Campina Grande, the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), and the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) for the financial support in carrying out this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Etikalar, B.; Adimalla, N.; Madhav, S.; Somagouni, S.G.; Kumar, P.L.K.K. Salinity problems in groundwater and management strategies in arid and semi-arid regions. GWMR 2021, 1, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, N.; Hasnain, M.; Roessner, U.; Abideen, Z. Strategies in improving plant salinity resistance and use of salinity resistant plants for economic sustainability. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 55, 2150–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, M.M.; Singh, R.; Trivedi, M.; Tiwari, R.K. Sodic soil: Management and reclamation strategies. In Environmental Concerns and Sustainable Development; Shukla, V., Kumar, N., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanavelu, A.; Naganna, S.R.; Al-Ansari, N. Irrigation induced salinity and sodicity hazards on soil and groundwater: An overview of its causes, impacts and mitigation strategies. Agriculture 2021, 11, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Geilfus, C.M.; Dietz, K.J. Salinity and crop yield. Plant Biol. 2019, 21, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística [IBGE]. Brazilian Production of Passion Fruit; IBGE: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2021.
- Freire, J.L.O.; Dias, T.J.; Cavalcante, L.F.; Fernandes, P.D.; Lima Neto, A.J. Rendimento quântico e trocas gasosas em maracujazeiro amarelo sob salinidade hídrica, biofertilização e cobertura morta. Ciênc. Agron. 2014, 45, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gondek, M.; Weindorf, D.C.; Thiel, C.; Kleinheinz, G. Soluble salts in compost and their effects on soil and plants: A review. Compost Sci./Land Util. 2020, 28, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, Z.; Faizan, S.; Gulzar, B. Salt stress, its impacts on plants and the strategies plants are employing against it: A review. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanwal, S.K.; Mann, A.; Kumar, A.; Kesh, H.; Kaur, G.; Rai, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, P.C.; Kumar, A.; Bahadur, A.; et al. Salt tolerant eggplant rootstocks modulate sodium partitioning in tomato scion and improve performance under saline conditions. Agriculture 2022, 12, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, A.G.L.; Cavalcante, L.F.; Melo, E.N.; Cavalcante, Í.H.L.; Silva, R.Í.L.; Lima, G.S.; Gheyi, H.R.; Pereira, W.E.; Paiva Neto, V.B.; Oliveira, C.J.A.; et al. Salinity and mulching effects on nutrition and production of grafted sour passion fruit. Plants 2023, 12, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, C.C.; Siqueira, D.L.; Martinez, H.E.P.; Cecon, P.R. Salt stress change chlorophyll fluorescence in mango. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2012, 34, 1245–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allel, D.; Ben-Amar, A.; Abdelly, C. Leaf photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence and ion content of barley (Hordeum vulgare) in response to salinity. J. Plant Nutr. 2018, 41, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaji, H.M.; Schansker, G.; Brestic, M.; Bussotti, F.; Calatayud, A.; Ferroni, L.; Goltsev, V.; Guidi, L.; Jajoo, A.; Li, P.; et al. Frequently asked questions about chlorophyll fluorescence, the sequel. Photosynth. Res. 2016, 132, 13–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.S.; Noreen, S.; Mahmood, S.; Athar, H.R.; Ashraf, M.; Alsahli, A.A.; Ahmad, P. Influence of salinity stress on PSII in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) genotypes, probed by chlorophyll-a fluorescence. J. King Saud. Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Xu, Y.; Jia, Q.; Ma, X.; Ahmad, I.; Adnan, M.; Gerard, R.; Ren, X.; Zhang, O.; Cai, T.; et al. Interactive effects of plastic film mulching with supplemental irrigation on winter wheat photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence and yield under simulated precipitation conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 207, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.; Cabrera, R.I. Growth and physiological responses of landscape plants to saline water irrigation: A review. HortScience 2010, 45, 1605–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, C.R.; Nelson, S.D.; Melgar, J.C.; Jifon, J.; Schuster, G.; Volder, A. Effects of salinity on physiological parameters of grafted and ungrafted citrus trees. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 197, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Zuazo, V.H.; Martínez-Raya, A.; Ruiz, J.A. Salt tolerance of mango rootstocks (Magnifera indica L. cv. Osteen). Span. J. Agric. Res. 2003, 1, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleda, F.J.; Madrid, R.; García-Torres, A.L.; Gracía-Lidón, Á.; Porras, I. Chlorophyll fluorescence and mineral nutrition in citrus leaves under salinity stress. J. Plant Nutr. 2011, 34, 1579–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, Y.A.; Hani, M.B.; Ayad, J.Y.; Hilaire, R.S. Salinity level influenced morpho-physiology and nutrient uptake of young citrus rootstocks. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, H.R.; Hassanpour, N. Effects of salinity, rootstock and position of sampling on macro nutrient concentration of pomegranate cv. Gabri. J. Plant Nutr. 2017, 40, 2269–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danierhan, S.; Shalamu, A.; Tumaerbai, H.; Guan, D. Effects of emitter discharge rates on soil salinity distribution and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) yield under drip irrigation with plastic mulch in an arid region of Northwest China. J. Arid Land. 2013, 5, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedaghati, N.; Alizadeh, A.; Ansari, A.; Hosseinifard, S.J. Study of changes in soil moisture and salinity under plastic mulch and drip irrigation in pistachio trees. J. Nuts 2016, 7, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, L.; He, J.; Chau, H.W.; Zou, Y.; Feng, H. Impacts of ridge with plastic mulch-furrow irrigation on soil salinity, spring maize yield and water use efficiency in an arid saline area. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 201, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amare, G.; Desta, B. Coloured plastic mulches: Impact on soil properties and crop productivity. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyat, M.; Mazhari-Majd, A.; Samadzadeh, A. Alternate bearing, chlorophyll fluorescence performance, vegetative growth and fruit quality of seedless barberry under different mulching treatments. Erwerbs-Obstbau 2022, 65, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamal-Salgado, J.; Loor, B.; Hirzel, J.; López, M.D.; Undurraga, P.; Zapata, N.; Vergara-Retamalas, R.; Olivares-Soto, H. Chlorophyll fluorescence and fruit quality response of blueberry to different mulches. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Dong, B.; Qiao, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M. Effects of sub soil plastic film mulch on soil water and salt content and water utilization by winter wheat under different soil salinities. Field Crops Res. 2018, 225, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragüés, R.; Medina, E.T.; Clavéria, I. Effectiveness of inorganic and organic mulching for soil salinity and sodicity control in a grapevine orchard drip-irrigated with moderately saline waters. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2014, 12, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares, C.A.; Stape, J.L.; Sentelhas, P.C.; Gonçalves, J.L.M.; Sparovek, G. Köppen’s climate classification map for Brazil. Meteorol. Z. 2013, 22, 711–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy; United States Department of Agriculture and Natural Resources Conservation Service: Lincoln, NE, USA, 2014; 332p.
- Silva, F.C. Analysis Manual Soil Chemistry, Plants and Fertilizers, 2nd ed.; Embrapa: Brasília, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Aguiar, A.V.M.; Cavalcante, L.F.; Silva, R.M.; Dantas, T.A.G.; Santos, E.C. Effect of biofertilization on yellow passion fruit production and fruit quality. Rev. Caatinga 2017, 30, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vianna-Silva, T.; Lima, R.V.; Azevedo, I.G.; Rosa, R.C.C.; Souza, M.S.; Oliveira, J.G. Determinação da maturidade fisiológica de frutos de maracujazeiro-amarelo colhidos na Região Norte do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Rev. Bras Frutic. 2010, 32, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and Improvement of Saline Alkali Soils, Agriculture; Handbook 60; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Freire, J.L.O.; Cavalcante, L.F.; Rebequi, A.M.; Dias, T.J.; Souto, A.G.L. Necessidade hídrica do maracujazeiro amarelo cultivado sob estresse salino, biofertilização e cobertura do solo. Rev. Caatinga 2011, 24, 82–91. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, A.L.; Coelho, E.F. Fertigation in tropical fruit trees. In Portuguese with English Summary, 2nd ed.; Embrapa: Cruz das Almas, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell, K.; Johnson, G.N. Chlorophyll fluorescence—A practical guide. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-García, N.; Martínez, V.; Carvajal, M. Effect of salinity on growth, mineral composition, and water relations of grafted tomato plants. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2004, 167, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrinho Galvão, T.; Silva, A.A.R.; Lima, G.S.; Lima, V.L.A.; Borges, V.E.; Nunes, K.G.; Soares, L.A.A.; Saboya, L.M.F.; Gheyi, H.R.; Gomes, J.P.; et al. Foliar applications of salicylic acid on boosting salt stress tolerance in sour passion rruit in two cropping cycles. Plants 2023, 12, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianguo, M.; Zhenwen, Y.; Yu, S. Radiation interception, chlorophyll fluorescence and senescence of flag leave in winter wheat under supplemental irrigation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Miles, C.; Gerdeman, B.; LaHue, D.G.; DeVetter, L. Plastic mulch use in perennial fruit cropping systems–A review. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 281, 109975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, F. Mulching affects photosynthetic and chlorophyll a fluorescence characteristics during stage III of peach fruit growth on the rain-fed semiarid Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 194, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavichioli, J.C.; Corrêa, L.S.; Boliani, A.C.; Santos, P.C. Desenvolvimento e produtividade do maracujazeiro-amarelo enxertado em três porta-enxertos. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2011, 33, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gomes, M.M.A.; Ramos, M.J.M.; Netto, A.T.; Rosa, R.C.C.; Campostrini, E. Water relations, photosynthetic capacity, and growth in passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims f. flavicarpa Deg.): Seedlings and grafted plants. Rev. Ceres 2018, 65, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).