Abstract
The synergistic application of magnetic fields and iron oxide nanorod particles (IONPs) presents a novel therapeutic approach for inducing lysosome-dependent cell death (LDCL) via magneto-mechanical force (MMF). This study demonstrates the efficacy of decaying oscillating pulsed magnetic fields (DOPMFs) to propel IONPs to induce rapid tumor regression via lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP). The systematic evaluation of dose-dependent parameters revealed that DOPMF intensity and pulse number critically determine A375 melanoma cell viability reduction. Mechanistic investigations identified two hallmark biomarkers of LMP: increased cytosolic cathepsin B activity and downregulated LAMP-2 expression. Crucially, in vivo experiments using A375 melanoma-bearing mouse models corroborated the therapeutic potential of this approach, showing significant tumor growth inhibition without systemic toxicity or invasive procedures. Collectively, our findings demonstrate that MMF by IONPs under DOPMF stimulation exhibits significant efficacy in suppressing melanoma proliferation, offering a non-invasive, targeted approach for oncological intervention.
1. Introduction
Cutaneous melanoma accounts for 73% of skin cancer-related mortality, with over 325,000 new cases diagnosed annually worldwide [1]. Despite advancements in molecular-targeted therapies (e.g., BRAF/MEK inhibitors) and immunotherapies (anti-PD-1/CTLA-4 antibodies) [2,3,4], the emergence of drug resistance and systemic toxicity persist as substantial clinical challenges [3,4,5,6]. These therapeutic limitations underscore the imperative for developing intervention strategies with novel mechanisms of action.
Lysosomes, as the central regulators of intracellular homeostasis, have been demonstrated to exhibit dual functionality in stress responses: executing macromolecular degradation while mediating programmed cell death through the “suicide bag” mechanism [7,8]. Specifically, lysosomal membrane permeabilization (LMP) induces cytoplasmic leakage of cathepsins, subsequently triggering lysosome-dependent cell death (LDCD) [9]. Emerging evidence reveals that ion dysregulation via lysosomal leakage disrupts cellular homeostasis, thereby initiating LDCD cascades [9,10,11,12]. These findings position LMP modulation as a promising therapeutic paradigm in oncology.
The biological effects of magnetic fields on living systems have garnered increasing attention, with alternating magnetic fields (AMFs) demonstrating modulatory effects on cellular signaling pathways, inflammatory responses, and tissue regeneration processes, as evidenced by recent comprehensive reviews [13]. Among various physical stimuli, magneto-mechanical force (MMF) generated by magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) under applied magnetic fields offers distinct advantages including painless application, deep tissue penetration, and spatiotemporally precise remote control [14,15]. Recent advances have validated the capability of MNP-mediated magnetic actuation to induce controlled LMP [16,17,18,19]. Capitalizing on both passive and active tumor-targeting mechanisms, MNPs demonstrate efficient lysosomal accumulation in malignant cells. Subsequent magnetic field application enables the precise induction of LDCD through targeted mechanical disruption, an approach that has shown therapeutic efficacy across multiple cancer models [16,17,19,20,21]. This synergistic strategy combining tumor-specific MNPs localization with remotely regulated magnetic stimulation presents a novel intervention framework for melanoma treatment via LDCD.
However, the current magneto-mechanical tumor therapeutic strategies exhibit notable limitations. While AMF induces the rotational oscillation of MNPs to generate magneto-torque effects—disrupting phospholipid bilayers or activating mechanosensitive ion channels via periodic directional shifts [22,23,24,25]—while their clinical implementation is constrained by high power consumption, bulky cooling systems, and limited field intensity (~1–100 mT) [26,27,28,29]. Notably, emerging applications of pulsed magnetic fields (PMFs) in osteoarthritis management and antineuropathic pain therapy have highlighted their superior tissue penetrability and neuromodulatory potential [30], suggesting broader biomedical applicability beyond oncology. PMFs demonstrate significant advantages in magneto-mechanical therapy (MMT), including high-intensity upper limits for reduced treatment duration [31], parameter tunability [32], and enhanced cellular permeability with improved MNP internalization efficiency through high transient dB/dt rates [33,34], positioning them as a promising modality in oncotherapy [35].
Nevertheless, technical limitations persist: the inherent narrow pulse width of PMFs curtail the mechanical action of MNPs per cycle, diminishing cytotoxic efficacy. Furthermore, the application of magneto-mechanical therapy (MMT) in vivo experiments is mainly a rotating magnetic field, alternating magnetic field, and static magnetic field [36,37,38,39], while MMT using a pulsed magnetic field is only verified at the level of a 3D multi-cell model [31,32,35]. In contrast to dynamic magnetic fields, static magnetic fields (SMFs) exhibit inherent limitations in MMT due to their lack of oscillatory mechanical forces. The therapeutic mechanism of SMF predominantly depends on the gradual accumulation of MMF, which results in substantially lower cytotoxicity compared to pulsed magnetic field approaches. Achieving measurable cellular effects typically requires prolonged exposure durations ranging from several hours to multiple days. This temporal constraint fundamentally restricts their clinical applicability in tumor ablation strategies that demand precise spatiotemporal control of MMF [40,41].
Therefore, to address these challenges, this study proposes a novel methodology utilizing a high-intensity decaying oscillating magnetic field (DOPMF) to drive IONPs in generating MMF, thereby inducing LDCD in melanoma. This technique facilitates periodic oscillations of IONPs, offering a more straightforward implementation compared to conventional AMF systems while retaining the inherent advantages of PMF, including high transient dB/dt rates and high flux densities. The optimized system achieves an average magnetic field intensity of up to 3 T, which, when combined with multiple pulses, enables the efficient elimination of A375 melanoma cells within shortened treatment durations. Furthermore, the therapeutic efficacy of this MMT has been validated through systematic in vivo murine tumor model experiments, demonstrating significant tumor growth inhibition.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Magnetic System
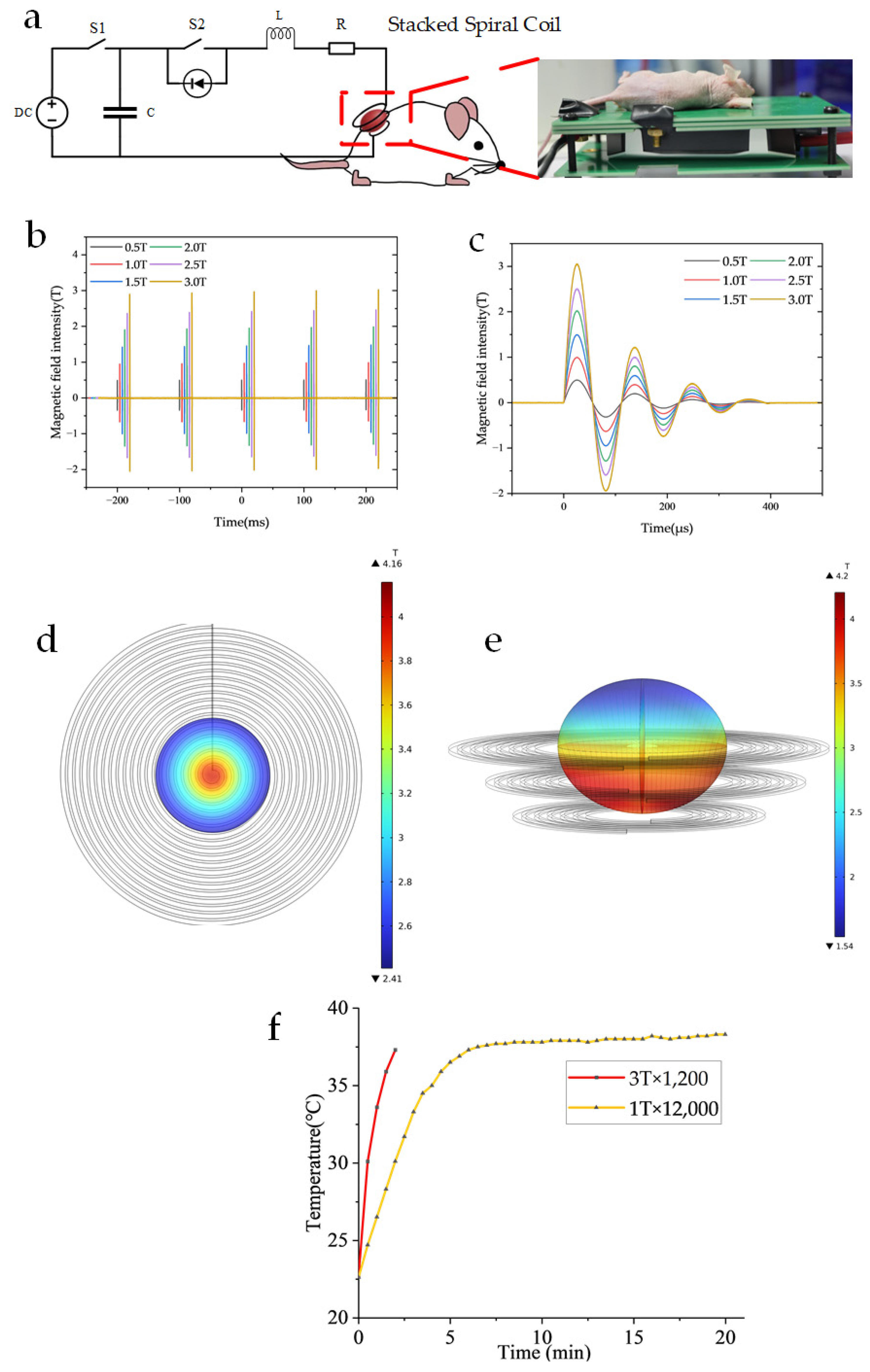
Figure 1 illustrates the magnetic field generator system for MMT in murine melanoma models.
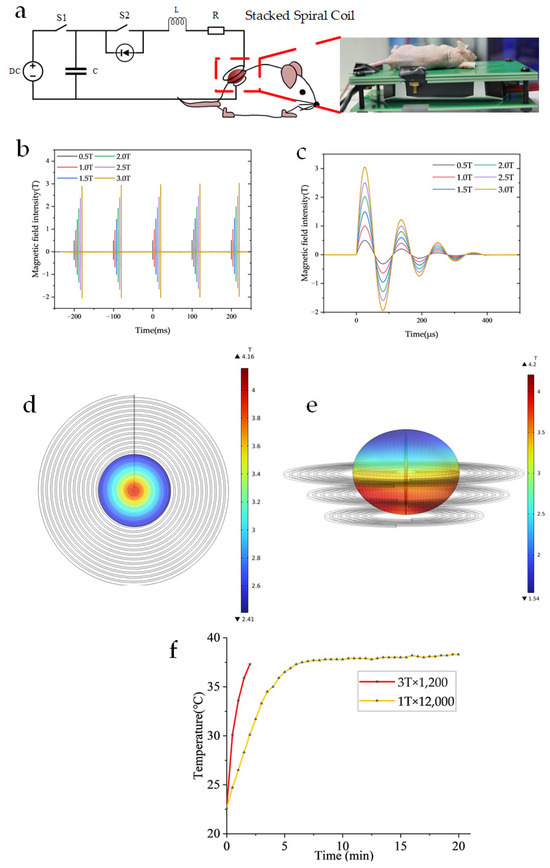
Figure 1.
Illustrates the magnetic field generator system for MMT in murine melanoma models (a) Electrical schematic diagram of the magnetic field setup for tumor treatment in A375 melanoma-bearing mice. (b) Operational parameters: pulse repetition frequency of 10 Hz. (c) Field intensity ranging from 0.5 T to 3 T, with a single pulse duration of approximately 400 μs. (d) Simulation of the magnetic field distribution for a 21-turn planar helical coil was conducted. The maximum magnetic flux density reached 4.16 T, while the average magnetic flux density was 3.01 T. The simulation was performed under a current of 2100 A, with the magnetic field region corresponding to a single well in a 48-well plate, located 1 mm away from the coil. (e) Simulation of the magnetic field distribution for a stacked spiral coil was conducted. The maximum magnetic induction intensity reached 4.2 T, while the average magnetic induction intensity was 3.05 T. The simulation was performed under a current of 2100 A, with the magnetic field covering an ellipsoidal tumor measuring 12 × 10 mm in size. (f) The temperature was measured at 1 T × 12,000 and 3 T × 1200 using a T-type thermocouple while the cooling device was in operation.
The magnetic field generator consists of a custom-designed pulse discharge system capable of producing DOPMF, as depicted in the electrical schematic diagram of the magnetic field device for animal experiments (Figure 1a). The fundamental principle of this magnetic field generator aligns with that of previous studies [32,34,42]. Building upon this foundation, the current study primarily modifies the capacitor, loop inductor, and diode to ensure that the magnetic field frequency of the three-layer spiral coil corresponds to the resonant frequency of the RLC circuit (9 kHz). Specifically, the capacitor used was 10 μF (MMJ4 KV-10 μF, Xi’an Farah, Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, China), the additional oscillation inductance was 20 μH, and the magnetic field coil had an inductance of 4.8 μH. The magnetic field generator produces a 400 μs pulse every 100 ms, achieving an average magnetic field amplitude of up to 3 T (Figure 1b,c). The magnetic field distribution is illustrated in Figure 1d,e through COMSOL Multiphysics 6.0 simulation results. Heat dissipation in the device is primarily managed via a high thermal conductivity AlN PCB board and a semiconductor heat sink located at its base. Temperature measurements were conducted using a T-type thermocouple temperature sensor, revealing no significant temperature increase during the application of the magnetic field pulses, which are consistently maintained near 37 °C (Figure 1f).
2.2. Cell Culture
This study utilized A375 human malignant melanoma cells (procured from Procell Life Technology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China). These cells were cultured in high-glucose Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM, BL301A, Biosharp, Hefei, AH, China) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, A5669701, Gibco, New York, NY, USA) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin (10,000 U/mL) (PS, 15140122, Gibco, New York, NY, USA). The cells were maintained in a humidified incubator at 37 °C with 5% CO₂. When the cells grew to about 80% in the culture flask, 0.25% trypsin-EDTA (25200056, Gibco, New York, NY, USA) was used for digestion and subculture or for subsequent experiments.
2.3. IONPs
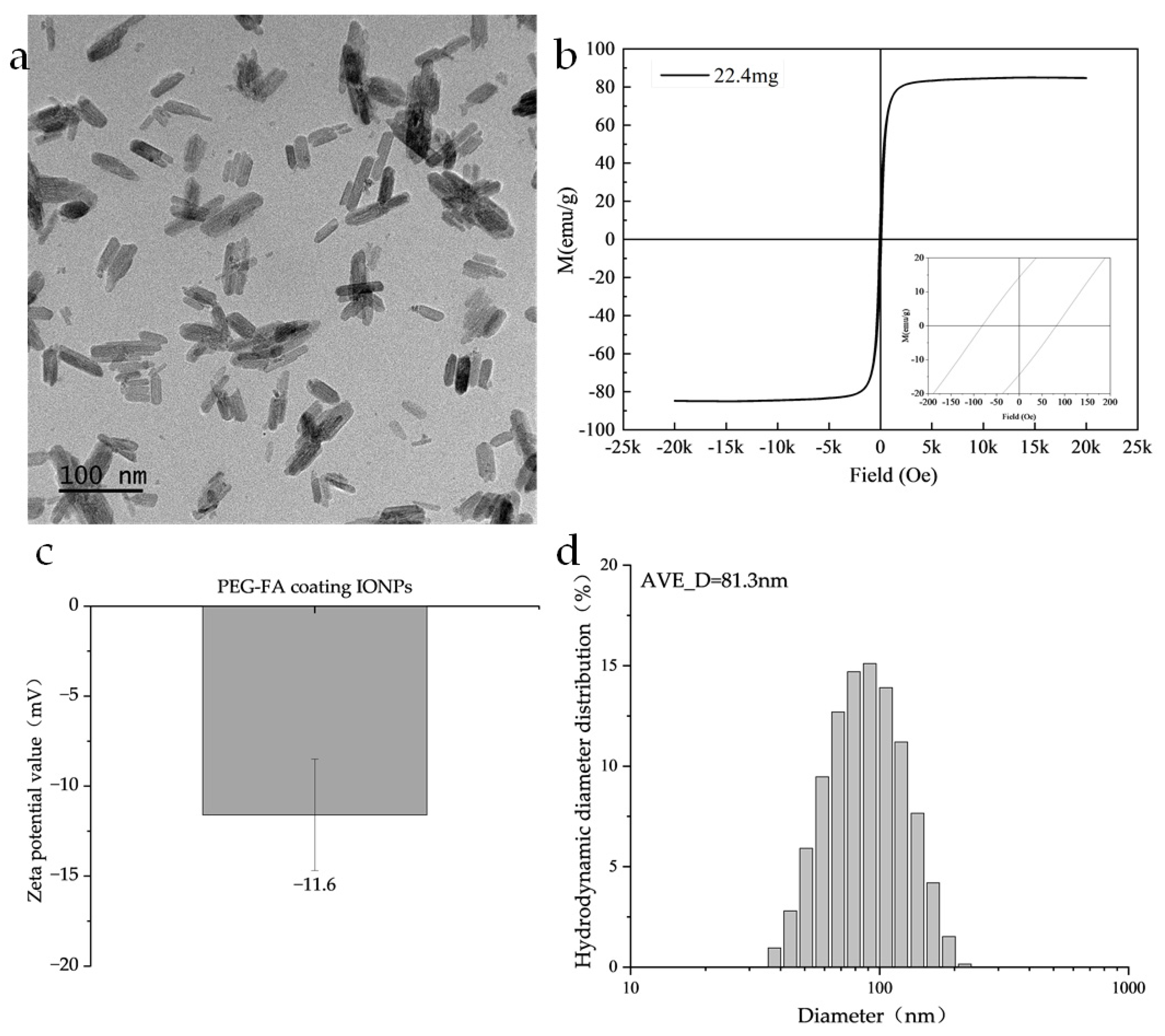
The nanoparticles used in this study were PEG-FA-coated IONPs, in which PEG provided the nanoparticles with good biocompatibility and dispersion, and folic acid (FA) provided good tumor targeting [32]. As shown in Figure 2a, TEM images show that the Fe3O4 nanoparticles are rod-like with a length of 60 nm and a diameter of 20 nm. Regarding the magnetic characterization, the magnetic properties of the samples were systematically evaluated in this study using a Lakeshore Model 7404 Vibrating Sample Magnetometer (VSM). The measurements were conducted at a constant temperature of 300 K and under an applied magnetic field of ± 2.17 T. As shown in Figure 2b, its saturation magnetization is 84 emu/g, the coercivity is 83.1 Oe, and the remanence is 14.2 emu/g. As seen in Figure 2c, its zeta potential is −11.6 ± 3.1 mV, which has good colloidal stability. In Figure 2d, its hydrodynamic diameter is distributed around 81.3 nm.
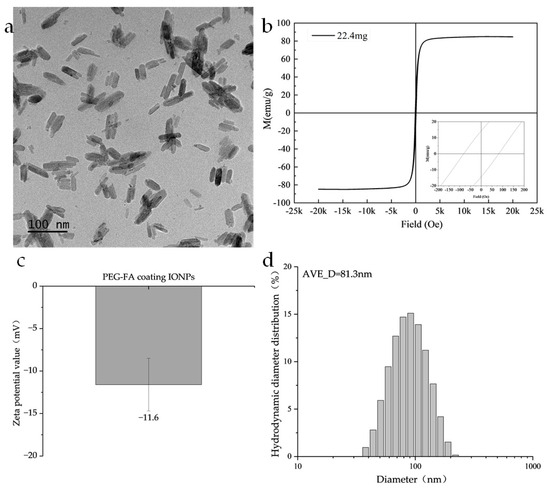
Figure 2.
Illustrates the particle parameters: (a) TEM image of the nanoparticles. (b) Magnetic hysteresis loop measured at X K and up to X T using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). (c) Zeta potential value. (d) The hydrodynamic diameter obtained by the DLS method.
2.4. Cell Activity Experiment and Evaluation
To analyze cell viability, we utilized the CCK-8 assay (Cell Counting Kit-8, Dojindo, Japan). The principle of this assay is based on the reduction in the WST-8 compound, a water-soluble tetrazolium salt, by intracellular dehydrogenases in mitochondria. Higher cell activity results in an increased reduction in WST-8 into an orange-yellow formazan product, leading to darker solution coloration. This allows the spectrophotometric quantification of metabolically active cells in culture. Cells (A375 human malignant melanoma cells) were seeded in 48-well plates at a density of 1.5 × 104 cells per well. After 24 h, the cells were divided into four experimental groups: Control group: 300 μL of A375 cells resuspended in complete medium were placed in 48-well plates and subsequently placed in the switched-off device for the same time as the experimental treatment group. IONPs group: A375 cells treated with 300 μL of magnetic nanoparticles (100 μg/mL, dimensions 20 × 60 nm) and subsequently placed in the switched-off device for the same time as the experimental treatment group. DOPMF group: A375 cells exposed to the decaying oscillating magnetic field (0.5–3 T, 10 Hz, n = 120–12,000). IONPs + DOPMF group: A375 cells treated with 100 μg/mL of nanoparticles (20 × 60 nm IONPs) and simultaneously exposed to DOPMF (0–3 T, 10 Hz, n = 120–12,000). At 12 h post-treatment, CCK-8 reagent was added to each well, followed by incubation at 37 °C for 2 h to allow formazan formation. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader (BioTek EPOCH2, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Cell viability and growth inhibition rates were calculated based on the optical density (OD) values of the blank control group and the experimental group, as defined in Equations (1) [32] and (2).
To more precisely evaluate cellular activity, YO-PRO-1 (YP1)/Propidium Iodide (PI) double staining was employed in this study. The cell survival was determined based on alterations in cell membrane permeability: YP1 selectively labeled early apoptotic cells with increased membrane permeability, while PI specifically stained necrotic cells exhibiting a loss of membrane integrity. Cells that were not labeled by either YP1 or PI were identified as cells surviving with intact membranes. Following experimental treatment, A375 cells were harvested and transferred to a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube. Subsequently, the cells were pelleted by centrifugation, resuspended in 500 μL of buffer, and stained with 0.5 μL of YP1 and PI. After incubation at 37 °C for 20 min, the samples were analyzed using flow cytometry (Novocyte Advanteon, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
2.5. TEM
A375 cells (2 × 105) were seeded into 60 mm culture dishes. After 24 h, the cells were incubated with culture medium containing IONPs (100 μg/mL) for 12 h. Subsequently, cells were harvested and fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde. Following dehydration, the samples were embedded in Epon Araldite resin. Ultrathin sections of 50 nm thickness were prepared and examined by transmission electron microscopy (TEM, JEM-2100F, JEOL, Tokyo, Japan).
2.6. Assessment of Lysosomal Membrane Integrity Using Lyso Tracker Red
Lyso Tracker Red (C1046, Beyotime, Shanghai, China) is a weakly alkaline red fluorescent probe that specifically labels lysosomes by accumulating in acidic intracellular compartments [43,44]. Cells were seeded into 48-well transparent-bottom plates at a density of 1.5 × 104 cells per well. After 24 h, the cells were incubated with culture medium containing IONPs (100 μg/mL) under standard conditions (37 °C, 5% CO2) for 12 h. Subsequently, the cells were exposed to intermittent DOPMF (3 T, 10 Hz, n = 4000, 2 min on/1 min off). Following magnetic field treatment, Lyso Tracker Red stock solution was diluted 1:15,000 in fresh culture medium to prepare the working solution. Cells were incubated with this staining solution at 37 °C for 25 min, after which the solution was replaced with PBS. Lysosomal morphology and fluorescence intensity were immediately analyzed using an inverted fluorescence microscope (DMi8, Leica, Wetzlar, Germany).
2.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
A375 melanoma cells were seeded in 48-well plates at a density of 1.5 × 104 cells/well, incubated with 100 μg/mL IONPs for 12 h, and then subjected to intermittent DOPMF (3 T, 10 Hz, 4000 pulses, 2 min on/1 min off) to induce changes in lysosomal membrane permeability. The specific operation is as follows: the medium was removed by rinsing with PBS 3 times (5 min each time), fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (0.2 mL) for 15 min, washed with PBS, and permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 for 5 min to increase the membrane permeability. Then, the cells were immersed in PBS 3 times (5 min each time). Cathepsin B (1:400, 122161-1-AP) and LAMP2 (1:400, 65566-1-MR) were added after blocking with 10% goat serum at room temperature for 2 h. The cells were incubated in a dark place at room temperature for 2 h and washed with PBS 3 times (5 min each time). Subsequently, the cells were incubated with fluorescent secondary antibodies at 37 °C in the dark for 1 h. After the last PBS wash, images were acquired using a Leica DMi8 microscope to assess lysosomal membrane integrity.
2.8. In Vivo Experiments
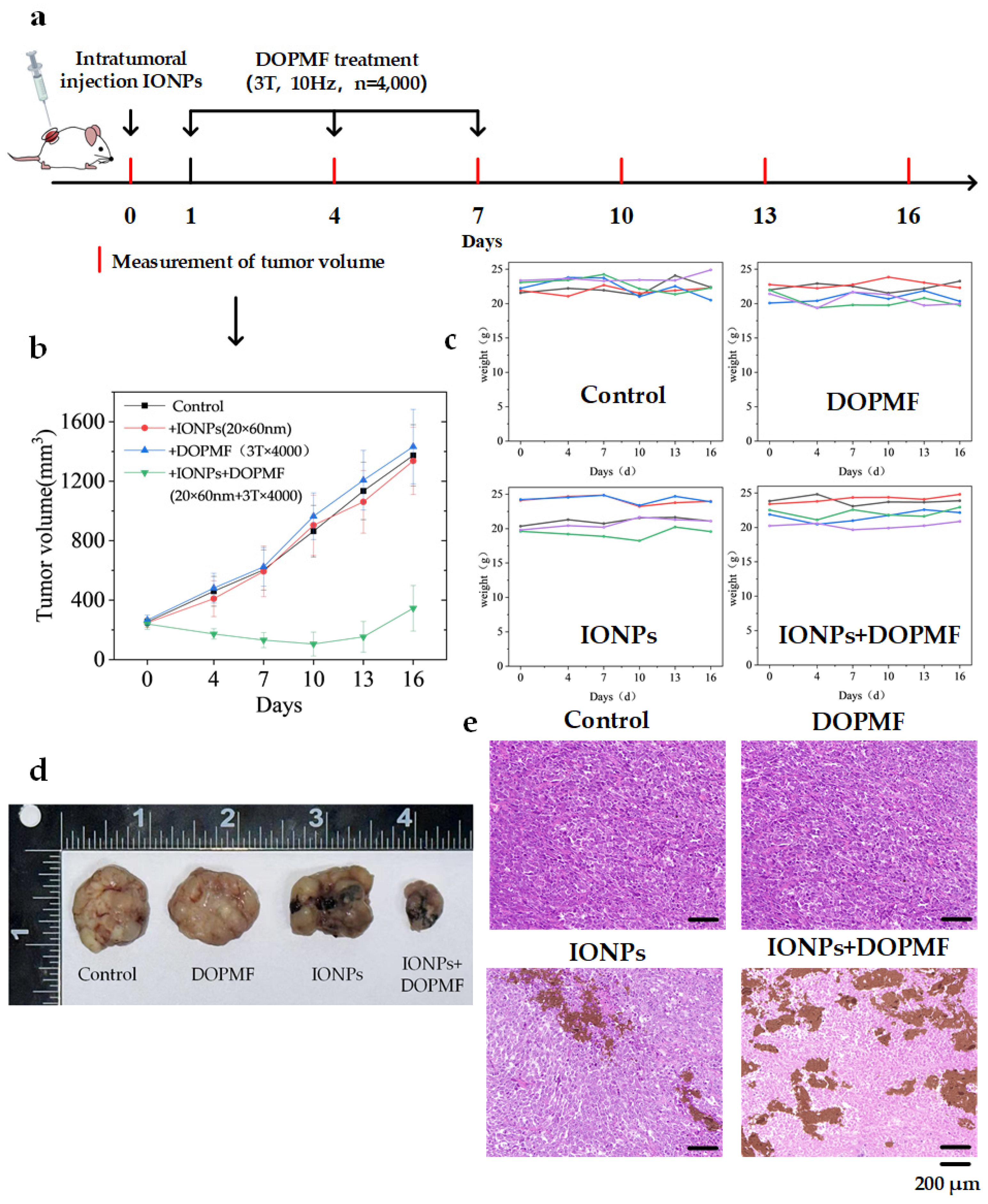
A total of 24 male BALB/c mice (4 weeks old, 20 ± 1.8 g) were obtained from Vital River Laboratory Animal Technology Co., Ltd. (Beijing City, China). All experimental protocols were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (Approval No. TOP-IACUC-2024-0238) and conducted in strict accordance with guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals. The mice were bred in an SPF barrier environment. A375 melanoma cells (2 × 106 cells suspended in PBS) were subcutaneously inoculated into the lateral dorsum of 4–6-week-old mice. Tumors were allowed to establish and grow until reaching a volume of approximately~250 mm3 before treatment initiation. To evaluate the efficacy of DOPMF-mediated MMT on tumor-bearing mice, the animals were randomly divided into four groups (6 per group): control group (PBS injection), IONPs group (Fe3O4 nanoparticle injection), DOPMF group (PBS injection + DOPMF exposure), and IONPs + DOPMF group (Fe3O4 nanoparticle injection + DOPMF exposure). The intratumoral injection of IONPs (30 mg/mL) was administered 24 h prior to treatment, with the injection volume equivalent to half of the tumor volume. MMT was applied every 3 days using intermittent DOPMF (3 T, 10 Hz, n = 4000, 2 min on/1 min off). The tumor dimensions and weight of the mice were measured every 3 days post-treatment using digital calipers. The tumor volume (mm3) was calculated using the formula, V = 1/2 × L × W2, where L represents tumor length and W denotes width. After 9 days of treatment, one mouse from each group was randomly selected, euthanized, and its tumor tissue was dissected and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. Subsequently, the tumor tissue underwent hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining for pathological examination.
2.9. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
All entailed data were statistically analyzed using Origin 2025, and the data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD) and statistically evaluated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). A threshold of p > 0.05 indicates no statistically significant differences between groups, * p < 0.05 denotes statistical significance, ** p < 0.01 represents highly significant differences, and *** p < 0.001 signifies extremely significant differences.
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Magneto-Mechanical Force Induced by Decaying Oscillating Pulsed Magnetic Fields on the Viability of A375 Melanoma Cells
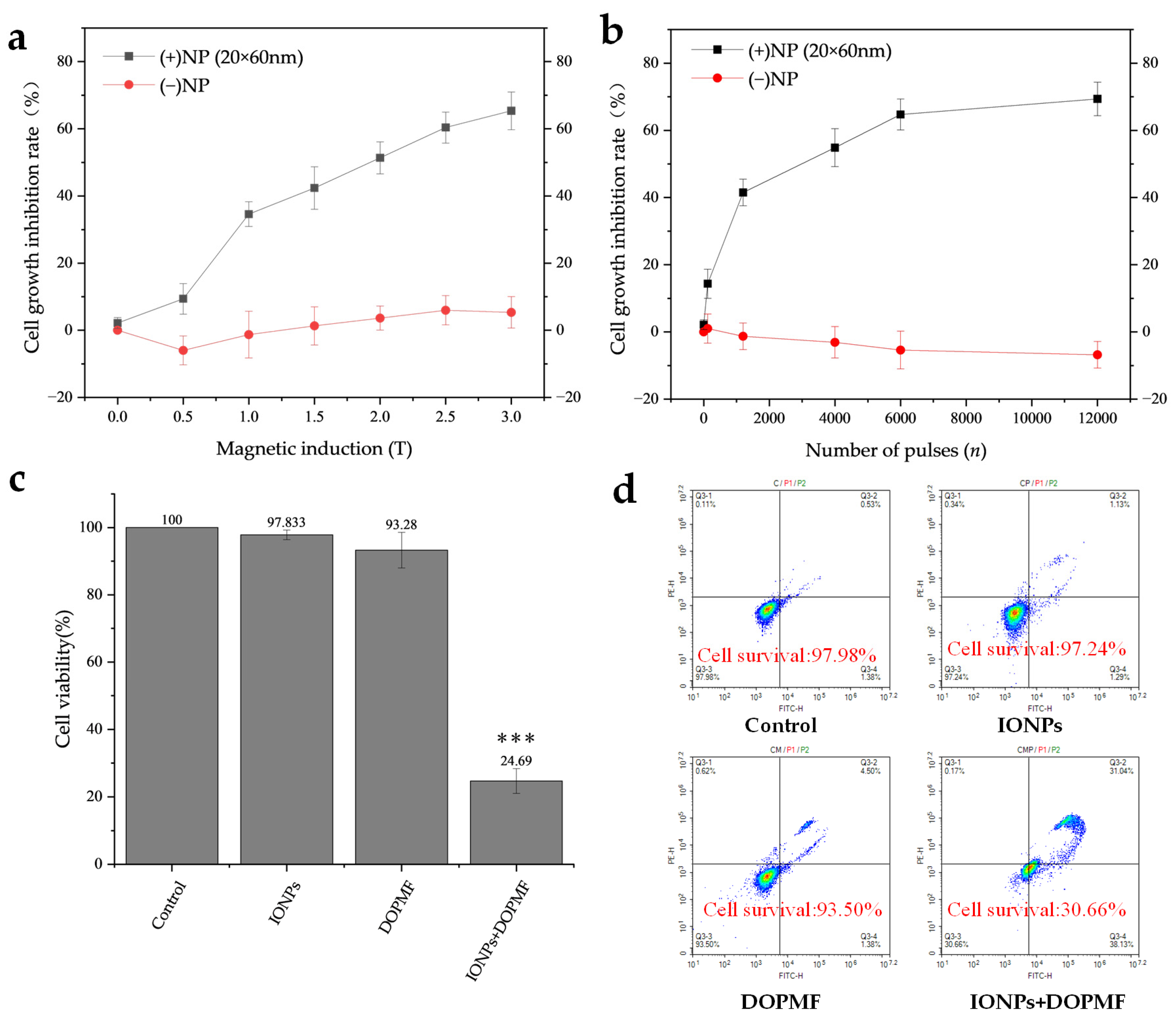
In this study, we employed DOPMF in conjunction with IONPs to induce MMT in A375 melanoma cells. The combined treatment of IONPs + DOPMF demonstrated the anticipated dose-dependent response: the rate of cell growth inhibition increased proportionally with the magnetic field intensity (Figure 3a) and the number of pulses (Figure 3b). When the magnetic field intensity was altered (Figure 3a), the cell growth inhibition rate in the DOPMF alone group remained largely unchanged; even at 0.5 T, there was a slight promoting effect on the viability of A375 cells under low magnetic field intensity. In contrast, the cell growth inhibition rate in the IONPs + DOPMF combined treatment group exhibited a stepwise increase with the rise in magnetic field intensity. Specifically, cell viability sharply increased from 9.4% at 0.5 T to 34.6% at 1 T, and finally reached 65.4% at 3 T. When the number of pulses was varied (Figure 3b), the DOPMF alone group showed a mild promoting effect on cell viability, which became more pronounced as the number of pulses increased. The cell growth inhibition rate in the IONPs + DOPMF group rose from 14.4% at 120 pulses to 69.4% at 12,000 pulses. However, between 6000 and 12,000 pulses, the inhibition rate approached saturation.
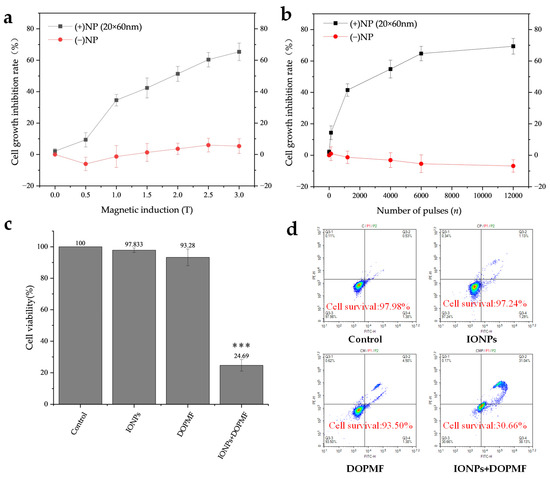
Figure 3.
Effects of MMT via the combination of DOPMF and IONPs on A375 melanoma cell viability. (a) Magnetic field intensity-dependent effects on cell viability; A375 cells were treated with MNPs and exposed to DOPMF (10 Hz, n = 1200); the cell growth inhibition rate increased as the magnetic field intensity escalated (0.5 T, 1 T, 1.5 T, 2 T, 2.5 T, and 3 T). (b) Pulse number-dependent effects on cell viability; A375 cells were treated with MNPs and exposed to DOPMF (1 T, 10 Hz); the cell growth inhibition rate increased as the pulse number escalated (n = 120, 1200, 4000, 6000, and 12,000). (c) Efficacy of MMT; control group: without any treatment; IONPs group: A375 cells treated with 300 μL of MNPs (100 μg/mL; 20 × 60 nm Fe3O4 nanorods); DOPMF group: A375 cells exposed to DOPMF (intensity: 3 T; frequency: 10 Hz; pulse number: n = 4000; intermittent treatment: 2 min on/1 min off); IONPs + DOPMF group: A375 cells co-treated with IONPs and exposed to intermittent DOPMF. The data are represented by mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD); *** extremely significant difference (p < 0.001) by Tukey’s multiple comparisons; N = 5. (d) Results of YP1/PI dual staining assessed by flow cytometry. Control group: without any treatment; IONPs group: A375 cells treated with 300 μL of MNPs (100 μg/mL; 20 × 60 nm Fe3O4 nanorods); DOPMF group: A375 cells exposed to DOPMF (intensity: 3 T; frequency: 10 Hz; pulse number: n = 4000; intermittent treatment: 2 min on/1 min off); IONPs + DOPMF group: A375 cells co-treated with MNPs and exposed to intermittent DOPMF.
Notably, under an intermittent DOPMF exposure of 3 T and 4000 pulses (2 min on/1 min off), the IONPs + DOPMF group achieved an approximately 75.31% tumor cell death (Figure 3c). In contrast, neither IONPs alone nor DOPMF alone significantly affected cell viability. To further examine the cell survival under these conditions, we conducted YP1/PI double staining. The results are presented in Figure 3d. Cells in the Q3 region (no YP1/no PI) indicated survival, while the survival rate of the IONPs + DOPMF group decreased to 30.66%, aligning closely with the activity measured by CCK-8. These findings suggest that the combination of DOPMF and IONPs exerts a significant impact on cell viability.
3.2. Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization in A375 Cells Induced by MMF via Decaying Oscillating Pulsed Magnetic
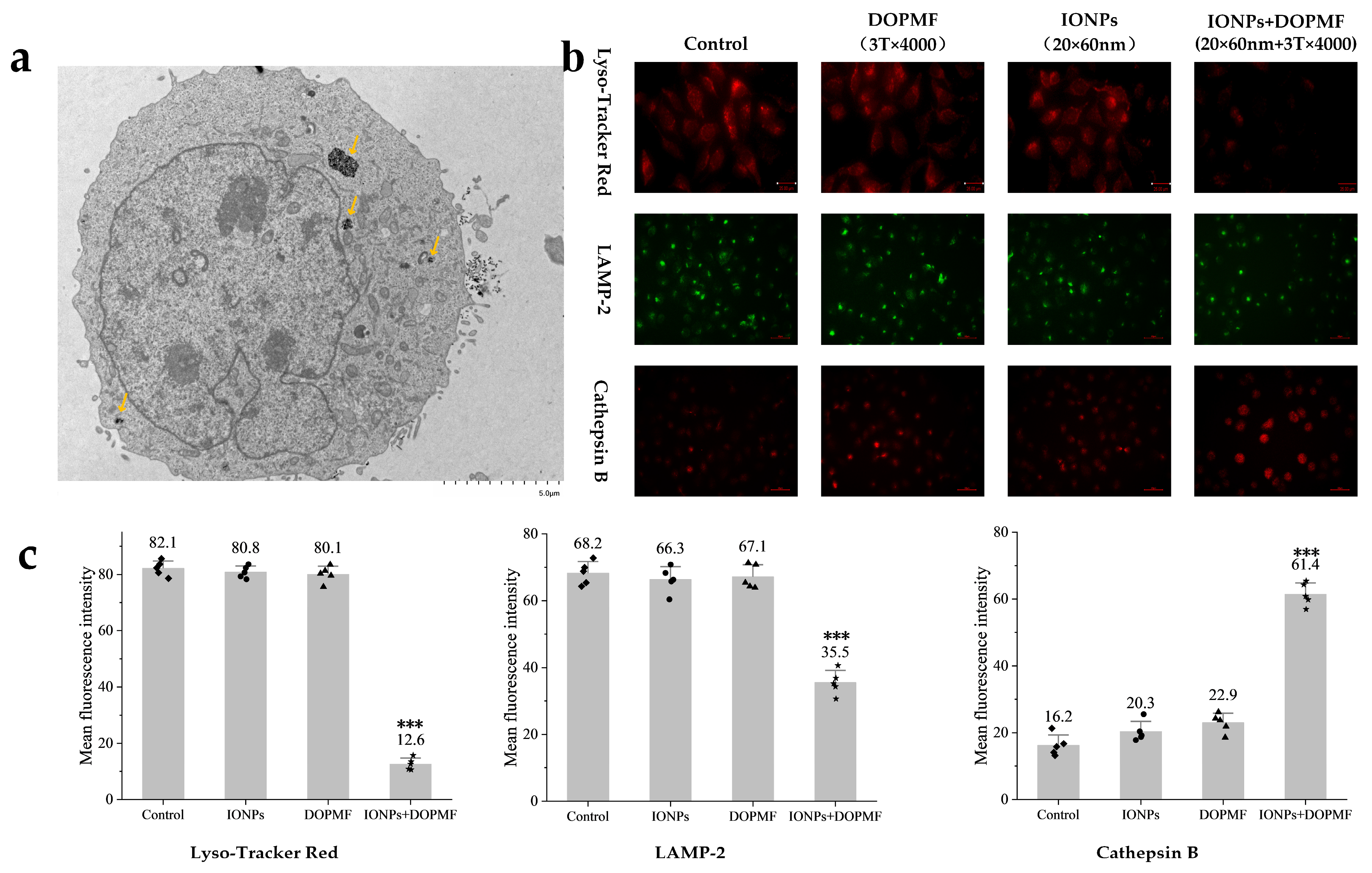
As shown in the TEM images (Figure 4a), a significant proportion of internalized IONPs were localized within lysosomal compartments. Based on this observation, we hypothesized that lysosomes loaded with IONPs would undergo MMF following DOPMF treatment, leading to lysosomal leakage and subsequent LDCD.
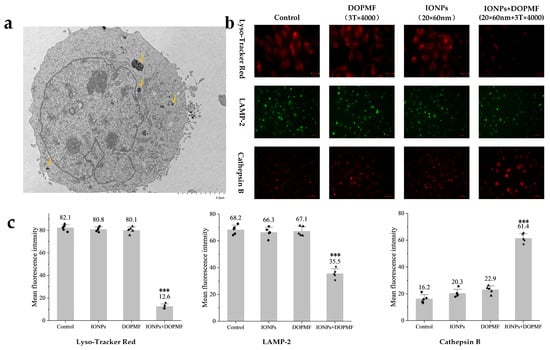
Figure 4.
Effects of MMT with DOPMF on lysosomes in A375 cells. (a) Bio-TEM image showing the predominant localization of IONPs within lysosomes, and the yellow arrows indicate internalized MNPs in lysosomes (scale bar: 5 μm). (b) Impact of MMT (IONPs: 100 μg/mL, 20 × 60 nm Fe3O4 nanorods; DOPMF: 3 T, 10 Hz, n = 4000 pulses, intermittent treatment: 2 min on/1 min off) on lysosomal integrity. Lyso Tracker Red staining (red fluorescence, scale bar: 25 μm) and immunofluorescence staining for LAMP-2 (green fluorescence, scale bar: 60 μm) and cathepsin B (red fluorescence, scale bar: 60 μm) were performed to evaluate lysosomal membrane permeability and enzyme leakage. (c) Mean fluorescence intensity of Lyso Tracker Red, LAMP-2, and cathepsin B. Five randomly selected fields were counted using Imagej. The data are represented by mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD), *** extremely significant difference (p < 0.001) by Tukey’s multiple comparisons.
To experimentally validate lysosomal damage, we employed Lyso Tracker Red staining: a mature methodology for detecting lysosomal integrity through pH-dependent fluorescence accumulation [43,44]. This fluorophore exhibits intense red fluorescence in acidic lysosomal environments, with signal attenuation indicating a loss of lysosomal membrane integrity. Quantitative analysis revealed a significant reduction in red fluorescence intensity in the IONPs + DOPMF group compared to other groups, the mean fluorescence intensity decreased to 12.6 (*** p < 0.001, significant difference compared with the other three groups), and neither IONPs nor DOPMF alone demonstrated significant effects (Figure 4b,c).
The further investigation of LMP-specific biomarkers (LAMP-2 membrane protein and cathepsin B protease) provided mechanistic confirmation. LAMP-2, a lysosomal membrane structural component, demonstrates decreased membrane association upon lysosomal rupture, while cathepsin B, normally confined within lysosomes, becomes detectable in the cytosol following membrane permeabilization [45,46,47,48,49]. Immunofluorescence analysis demonstrated two hallmark features of LMP in DOPMF-treated cells: dispersal and partial degradation of LAMP-2 membrane proteins, evidenced by diminished green fluorescence intensity, so the mean fluorescence intensity decreased to 35.5 (*** p < 0.001, significant difference compared with the other three groups) (Figure 4b,c); the cytosolic redistribution of cathepsin B manifested as an enhanced red fluorescence signal compared to control groups, so the mean fluorescence intensity decreased to 61.4 (*** p < 0.001, significant difference compared with the other three groups) (Figure 4b,c); neither IONPs alone nor the DOPMF alone group showed significant fluorescence changes.
3.3. MMT with Decaying Oscillating Pulsed Magnetic Field Inhibits Tumor Growth in A375 Melanoma-Bearing Mice
Building on the success of in vitro cell experiments with DOPMF, we established a BALB/c NUDE mouse model bearing A375 melanoma tumors to further validate the efficacy of this LDCD strategy. When tumor volumes reached ~250 mm3, 24 A375 tumor-bearing mice were randomly divided into four groups: control, IONPs, DOPMF, and IONPs + DOPMF. One day prior to treatment, the control and DOPMF groups received intratumoral injections of PBS (volume equivalent to half the tumor volume), while the IONPs and IONPs + DOPMF groups were injected with IONPs (20 × 60 nm nanorods, 30 mg/mL concentration); these two groups were subjected to three sessions of MMT (3 T, 10 Hz, n = 4000 pulses, intermittent treatment: 2 min on/1 min off) at 2-day intervals. Tumor volumes and weights were measured every 3 days during the treatment period. The schematic diagram of the treatment process is shown in Figure 5a.
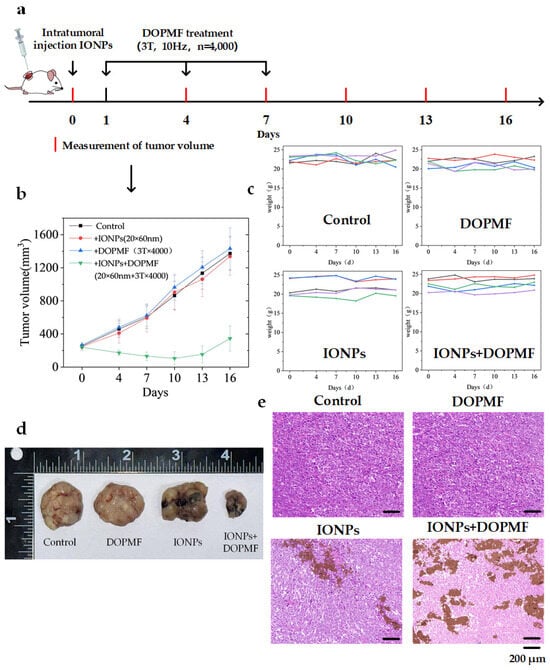
Figure 5.
Anti-tumor effects of MMT with DOPMF in A375 tumor-bearing mice. (a) Schematic diagram of the treatment procedure for mice bearing A375 melanoma cells. (b) Tumor growth curves across four experimental groups; the data are represented by mean ± standard deviation (mean ± SD) (N = 5). (c) Changes in the weights of the 5 mice in the four groups. (d) After 9 days of treatment, one mouse from each group was randomly selected for euthanasia, followed by the collection and documentation of dissected tumor images. (e) H&E-stained images of tumor tissues from the four groups (scale bar: 200 μm).
Tumor growth in the IONPs + DOPMF group was significantly attenuated compared to the other three groups, thereby validating the synergistic anti-tumor efficacy of the combined IONPs and DOPMF therapy. In contrast, neither IONPs nor DOPMF administered individually demonstrated significant tumor suppression (Figure 5b). To further assess the inhibitory effects of MMT on A375 melanoma, one mouse from each group was randomly selected after 9 days of treatment, euthanized, and the tumors were excised for analysis (Figure 5d). The tumor volume following MMT with IONPs + DOPMF was markedly reduced compared to the other three groups. Subsequently, the resected tumors were subjected to HE staining. The IONPs + DOPMF group exhibited extensive damage to tumor tissue, whereas minimal structural disruption was observed in the control, IONPs, and DOPMF groups (Figure 5e). Furthermore, no overt signs of distress or adverse effects were noted in the mice during the treatment period, and their weights remained stable throughout the observation period (Figure 5c).
4. Discussion
The lysosomal membrane permeabilization triggered by external magnetic fields in magnetic nanoparticle-loaded cells has demonstrated applicability across various cancer models [11,26,50,51,52]. The concept that magnetic nanoparticles under magnetic fields can deliver sufficient MMF to destabilize lysosomal membranes has been extensively validated [31,50,53,54,55]. However, current MMT predominantly relies on alternating magnetic fields (AMFs), which require high-power generation systems with bulky cooling equipment and exhibit limited magnetic field intensity [26,27,28,29]. In contrast, pulsed magnetic fields (PMFs) offer many advantages, such as higher peak intensity which reduces treatment duration [31] and flexible parameter modulation [32]. Here, we propose for the first time the application of a high-intensity DOPMF to drive magneto-mechanical force from magnetic nanomaterials, inducing lysosome-dependent cell death in melanoma. Our data revealed a clear dose-dependent inhibitory effect: the cell growth inhibition rate increased with both magnetic field intensity (Figure 3a) and pulse number (Figure 3b), though saturation occurred at 12,000 pulses. Consequently, subsequent experiments employed optimized parameters (magnetic field intensity: 3 T, pulse number: 4000 pulses, intermittent treatment: 2 min on/1 min off) combined with IONPs, achieving an approximately 75.31% A375 melanoma cell death in less than 10 min of treatment time (Figure 3c). To more accurately assess cell viability, following the experimental treatment conducted under the optimal parameter conditions, flow cytometry analysis with YP1/PI double staining revealed that the cell viability in the INOPs + DOPMF group decreased to 30.6% (Figure 3d). This result was largely consistent with the activity previously measured using the CCK-8 assay. The IONPs alone or DOPMF alone groups had no effect on cell activity, which was also similar to previous studies [19,31,32]. The formula was used to calculate the rotational moment of the particle under DOPMF: L = MVB sinθ (where M is the particle saturation magnetization, V is the particle volume, B is the magnetic field density, and θ is the angle between the particle’s long axis and field direction) [32]. We estimated a maximum magneto-mechanical force of ~750 pN, sufficient to induce subcellular organelle damage and subsequent cell death [22,31]. However, a subset of cells remained unaffected, suggesting a reduced cellular uptake of magnetic nanoparticles, which is consistent with the previously published study: cell activity also depends on the concentration of magnetic nanoparticle-treated cells [31]. Therefore, in the future, this treatment method can be considered to achieve improved particle modification for enhanced targeting and dispersion, so as to ensure that particles can accurately target more tumor cells.
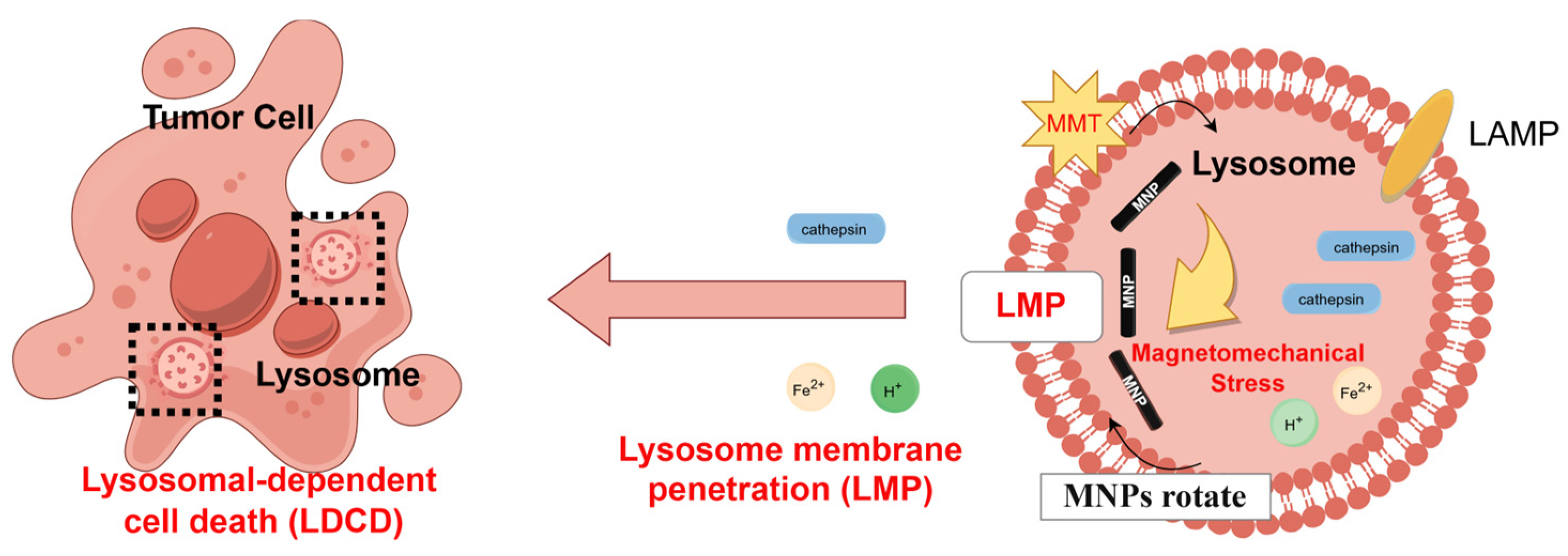
Previous studies have reported that the lysosomal membranes of cancer cells exhibit greater fragility compared to those of non-cancerous cells [56,57], rendering them more susceptible to magneto-mechanical stimulation. Consequently, upon observing the predominant localization of IONPs within lysosomal compartments (Figure 4a), we focused on investigating whether the magneto-mechanical forces exerted by internalized IONPs could compromise lysosomal membrane integrity, thereby inducing LDCD. To evaluate lysosomal integrity, Lyso Tracker Red staining revealed a significant reduction in red fluorescence intensity in the IONPs + DOPMF group compared to other groups, indicating the destabilization of lysosomal membranes and subsequent pH alteration: a phenomenon corroborated by other prior studies [19]. Furthermore, to confirm that cell death under intermittent DOPMF treatment was mediated by LMP, we analyzed the specific markers of lysosomal damage: the membrane protein LAMP-2 and cathepsin B. We found that the lysosomal membrane protein LAMP-2 was dispersed into the cytoplasm after magneto-mechanical treatment, and even part of the membrane protein LAMP-2 was decomposed, resulting in a weaker fluorescence. As shown in Figure 4b,c, the green fluorescence of LAMP-2 in the IONPs + DOPMF group was weaker than that in the other groups, while the mature lysosome was subjected to MMT; the cathepsin B released into the cytoplasm became detectable, and the red fluorescence of cathepsin B in the IONPs + DOPMF group was stronger than that in the other group; similarly, neither the IONPs nor DOPMF group alone showed significant fluorescence changes (Figure 4b,c). Therefore, it was demonstrated that after 12 h of incubation with IONPs and A375 cells, the PEG-FA modified IONPs were passively endocytosed into lysosomes by the cells due to their ability to target tumor cells. With the application of DOPMF, IONPs rotationally shear inside the lysosome to the lysosomal membrane, causing the lysosomal membrane to be destroyed, its internal cathepsin to leak, and inducing cell death; the mechanism of action is shown in Figure 6.
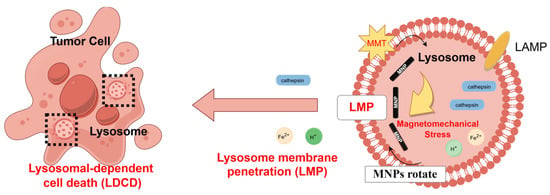
Figure 6.
Schematic diagram illustrating LDCD induced by MMT.
In addition, A375 melanoma-bearing mice were subjected to magneto-mechanical stimulation generated by DOPMF. The results revealed a significant inhibitory effect on melanoma growth (Figure 5b), which was further supported by the excised tumor images (Figure 5d). Histopathological analysis using HE staining demonstrated extensive necrosis of tumor tissue following MMT. The therapeutic efficacy of DOPMF-based MMT was successfully validated at the animal level. Notably, no apparent adverse effects or signs of discomfort were observed in the mice during the entire treatment period, and their weights remained stable (Figure 5c). Collectively, these findings suggest that this approach has considerable potential for selectively eliminating cancer cells and overcoming chemotherapy resistance in tumors.
5. Conclusions
This study first proposes a magneto-mechanical therapeutic strategy utilizing high-intensity DOPMF in combination with internalized IONPs for targeting A375 melanoma, with a comprehensive investigation into its biological mechanisms. Notably, the internalized IONPs were observed to specifically accumulate within lysosomes, and lysosomal structural integrity was significantly compromised upon exposure to DOPMF. In vivo experiments further validated the therapeutic efficacy of this approach in tumor-bearing mice. Our findings clearly demonstrate that the DOPMF-driven MMT in conjunction with IONPs induces rapid and non-invasive LMP, offering a promising modality for selective cancer cell destruction and overcoming chemoresistance in deep-seated tumors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.M., Resources Y.M., Software, S.T., C.M., W.Z. and J.C., Formal analysis, J.W., Writing—original draft, J.W., Writing—review & editing, J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52077022); Project supported by graduate research and innovation foundation of Chongqing, China (Grant No. CYB240025).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (Approval No. TOP-IACUC-2024-0238, 20 September 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| DOPMF | decaying oscillating pulsed magnetic fields |
| IONPs | iron oxide nanorod particles |
| LMP | lysosomal membrane permeabilization |
| LDCD | lysosome-dependent cell death |
| MNPs | magnetic nanoparticles |
| MMF | magneto-mechanical force |
| MMT | magneto-mechanical therapy |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| LAMP-2 | lysosomal-associated membrane protein 2 |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Eroglu, Z.; Infante, J.; Patel, S.; Daud, A.; Johnson, D.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Kefford, R.; Hamid, O.; Schuchter, L.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with BRAF V600-Mutant Metastatic Melanoma Who Received Dabrafenib Combined with Trametinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schadendorf, D.; Long, G.V.; Stroiakovski, D.; Karaszewska, B.; Hauschild, A.; Levchenko, E.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Schachter, J.; Garbe, C.; Dutriaux, C.; et al. Three-Year Pooled Analysis of Factors Associated with Clinical Outcomes across Dabrafenib and Trametinib Combination Therapy Phase 3 Randomised Trials. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 2017, 82, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dummer, R.; Ascierto, P.A.; Gogas, H.J.; Arance, A.; Mandala, M.; Liszkay, G.; Garbe, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Krajsova, I.; Gutzmer, R.; et al. Overall Survival in Patients with BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Receiving Encorafenib plus Binimetinib versus Vemurafenib or Encorafenib (COLUMBUS): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassel, J.C. 5-Year Results for Pembrolizumab Treatment of Advanced Melanoma. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1187–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, F.S.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.-J.; Rutkowski, P.; Cowey, C.L.; Lao, C.D.; Schadendorf, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Dummer, R.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone versus Ipilimumab Alone in Advanced Melanoma (CheckMate 067): 4-Year Outcomes of a Multicentre, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1480–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabio, A.; Bonifacino, J.S. Lysosomes as Dynamic Regulators of Cell and Organismal Homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, L.K.K.; Nielsen, I.Ø.; Maeda, K.; Jäättelä, M. SnapShot: Lysosomal Functions. Cell 2020, 181, 748–748.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Duve, C.; de Barsy, T.; Poole, B.; Trouet, A.; Tulkens, P.; Van Hoof, F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic Agents. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1974, 23, 2495–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagur, R.; Hajnóczky, G. Intracellular Ca2+ Sensing: Its Role in Calcium Homeostasis and Signaling. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Gu, M.; Hu, M.; Pinchi, P.; Chen, W.; Ryan, M.; Nold, T.; Bannaga, A.; Xu, H. Lysosomal Zn2+ Release Triggers Rapid, Mitochondria-Mediated, Non-Apoptotic Cell Death in Metastatic Melanoma. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzollo, F.; More, S.; Vangheluwe, P.; Agostinis, P. The Lysosome as a Master Regulator of Iron Metabolism. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2021, 46, 960–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarimov, R.M.; Serov, D.A.; Gudkov, S.V. Biological Effects of Magnetic Storms and ELF Magnetic Fields. Biology 2023, 12, 1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Hong, H.; Won, M.; Rha, H.; Ding, Q.; Kang, N.; Kang, H.; Kim, J.S. Mechanical Stimuli-Driven Cancer Therapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Leent, M.M.T.; Priem, B.; Schrijver, D.P.; de Dreu, A.; Hofstraat, S.R.J.; Zwolsman, R.; Beldman, T.J.; Netea, M.G.; Mulder, W.J.M. Regulating Trained Immunity with Nanomedicine. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, A.W.; Helmke, B.P.; Blackman, B.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Mechanisms of Mechanotransduction. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Kircher, M.F.; Koch, M.; Eliasson, L.; Goldberg, S.N.; Renström, E. Dynamic Magnetic Fields Remote-Control Apoptosis via Nanoparticle Rotation. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3192–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavassori, P.; Pancaldi, M.; Perez-Roldan, M.J.; Chuvilin, A.; Berger, A. Remote Magnetomechanical Nanoactuation. Small 2016, 12, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyridopoulou, K.; Aindelis, G.; Sarafidis, C.; Kalogirou, O.; Chlichlia, K. Magnetomechanical Stress-Induced Colon Cancer Cell Growth Inhibition. J. Nanotheranostics 2022, 3, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lv, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Cheng, Y. Magnetic Modulation of Lysosomes for Cancer Therapy. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 16, e1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Gao, R.; Ning, P.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Chen, E.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.; et al. A Lysosome-Targeted Magnetic Nanotorquer Mechanically Triggers Ferroptosis for Breast Cancer Treatment. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2302093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovin, Y.I.; Gribanovsky, S.L.; Golovin, D.Y.; Klyachko, N.L.; Majouga, A.G.; Master, A.M.; Sokolsky, M.; Kabanov, A.V. Towards Nanomedicines of the Future: Remote Magneto-Mechanical Actuation of Nanomedicines by Alternating Magnetic Fields. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2015, 219, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Kim, S.-J.; Cheresh, P.; Yun, J.; Lee, B.; Kamp, D.W.; Kim, D.-H. Magneto Mitochondrial Dysfunction Mediated Cancer Cell Death Using Intracellular Magnetic Nano-Transducers. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 5497–5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golovin, Y.I.; Gribanovsky, S.L.; Golovin, D.Y.; Zhigachev, A.O.; Klyachko, N.L.; Majouga, A.G.; Sokolsky, M.; Kabanov, A.V. The Dynamics of Magnetic Nanoparticles Exposed to Non-Heating Alternating Magnetic Field in Biochemical Applications: Theoretical Study. J. Nanopart. Res. 2017, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semina, P.N.; Isaev, I.L.; Komogortsev, S.V.; Klyuchantsev, A.B.; Kostyukov, A.S.; Blagodatova, A.V.; Khrennikov, D.E.; Kichkailo, A.S.; Zamay, T.N.; Lapin, I.N.; et al. Towards Understanding the Triggering of the Malignant Cell Death in High-Efficiency Magneto-Mechanical Anticancer Therapy. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2023, 56, 065401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.-H.; Rozhkova, E.A.; Ulasov, I.V.; Bader, S.D.; Rajh, T.; Lesniak, M.S.; Novosad, V. Biofunctionalized Magnetic-Vortex Microdiscs for Targeted Cancer-Cell Destruction. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domenech, M.; Marrero-Berrios, I.; Torres-Lugo, M.; Rinaldi, C. Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization by Targeted Magnetic Nanoparticles in Alternating Magnetic Fields. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5091–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Master, A.M.; Williams, P.N.; Pothayee, N.; Pothayee, N.; Zhang, R.; Vishwasrao, H.M.; Golovin, Y.I.; Riffle, J.S.; Sokolsky, M.; Kabanov, A.V. Remote Actuation of Magnetic Nanoparticles For Cancer Cell Selective Treatment Through Cytoskeletal Disruption. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Yan, L.; Xue, J.; Zhang, K.; Xu, F.-J. Degradable One-Dimensional Dextran-Iron Oxide Nanohybrids for MRI-Guided Synergistic Gene/Photothermal/Magnetolytic Therapy. Nano Today 2021, 38, 101118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tota, M.; Jonderko, L.; Witek, J.; Novickij, V.; Kulbacka, J. Cellular and Molecular Effects of Magnetic Fields. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunov, O.; Uzhytchak, M.; Smolková, B.; Lunova, M.; Jirsa, M.; Dempsey, N.M.; Dias, A.L.; Bonfim, M.; Hof, M.; Jurkiewicz, P.; et al. Remote Actuation of Apoptosis in Liver Cancer Cells via Magneto-Mechanical Modulation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Cancers 2019, 11, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, Y.; Zhang, M.-N.; Ma, C.; Zheng, W.; Teng, F. Feature Matching of Microsecond-Pulsed Magnetic Fields Combined with Fe3O4 Particles for Killing A375 Melanoma Cells. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novickij, V.; Girkontaitė, I.; Zinkevičienė, A.; Švedienė, J.; Lastauskienė, E.; Paškevičius, A.; Markovskaja, S.; Novickij, J. Reversible Permeabilization of Cancer Cells by High Sub-Microsecond Magnetic Field. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 2001904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Mi, Y. Pulsed Magnetic Field Generator for Enhancing Cell Membrane Permeability In Vitro. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2023, 51, 3647–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.; Gan, W.L.; Liu, N.; Lew, W.S. Magneto-Actuated Cell Apoptosis by Biaxial Pulsed Magnetic Field. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vegerhof, A.; Barnoy, E.; Motiei, M.; Malka, D.; Danan, Y.; Zalevsky, Z.; Popovtzer, R. Targeted Magnetic Nanoparticles for Mechanical Lysis of Tumor Cells by Low-Amplitude Alternating Magnetic Field. Materials 2016, 9, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brossel, R.; Yahi, A.; David, S.; Moreno Velasquez, L.; Guinebretière, J.-M. Mechanical Signals Inhibit Growth of a Grafted Tumor In Vivo: Proof of Concept. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamay, T.N.; Zamay, G.S.; Belyanina, I.V.; Zamay, S.S.; Denisenko, V.V.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Ivanchenko, T.I.; Grigorieva, V.L.; Garanzha, I.V.; Veprintsev, D.V.; et al. Noninvasive Microsurgery Using Aptamer-Functionalized Magnetic Microdisks for Tumor Cell Eradication. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Muroski, M.E.; Petit, D.C.M.C.; Mansell, R.; Vemulkar, T.; Morshed, R.A.; Han, Y.; Balyasnikova, I.V.; Horbinski, C.M.; Huang, X.; et al. Rotating Magnetic Field Induced Oscillation of Magnetic Particles for in Vivo Mechanical Destruction of Malignant Glioma. J. Control. Release 2016, 223, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Shin, T.-H.; Yoo, D.; Cheon, J. Magnetic Tandem Apoptosis for Overcoming Multidrug-Resistant Cancer. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 7455–7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Lin, S.; Dong, L.; Cheng, K.; Weng, W. Magnetically Actuated Mechanical Stimuli on Fe3O4/Mineralized Collagen Coatings to Enhance Osteogenic Differentiation of the MC3T3-E1 Cells. Acta Biomater. 2018, 71, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Mi, Y. High-Frequency Nanosecond Pulsed Magnetic Field Generator Utilizing Stacked Spiral Coil for Subcutaneous Tumor Ablation in Vivo. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2024, 52, 1406–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; He, C.; Li, X.; Huang, L.; Cheng, B.; Dong, S. Glucuronidase-Instructed Glycopeptide Self-Assembly for Selective Killing of Cancer Cells through Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization. Angew. Chem. Int. Engl. 2025, 64, e202420596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Bai, J.; Ji, X.; Zhao, W.; Dong, X. A Series of Meso Amide BODIPY Based Lysosome-Targeting Fluorescent Probe with High Photostability and Sensitivity. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1205, 339771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, I.; Joosten, M.; Roberg, K.; Öllinger, K. The Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Trichostatin A Reduces Lysosomal pH and Enhances Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.A.F.; Ivanova, L.; Solhaug, A.; Fæste, C.K. Enniatin B1-Induced Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization in Mouse Embryonic Fibroblasts. Mycotoxin Res. 2020, 36, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, T.; du Roure, P.D.; Mallavialle, A.; Laurent-Matha, V.; Roger, P.; Guiu, S.; Chardès, T.; Liaudet-Coopman, E. Cathepsins: Novel Opportunities for Antibody Therapeutics in Cancer. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2025, 182, 1671–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Xu, D.; Chen, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Yin, S. Cathepsin B Activatable Fluorescent Probe for Antitumor Efficiency Feedback: Attempt To Detect Certain Apoptotic Cells. Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 2932–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, C.J.; Markovina, S.; Good, M.; Wight, I.E.; Thomas, B.J.; Linneman, J.M.; Lanik, W.E.; Koroleva, O.; Coffman, M.R.; Miedel, M.T.; et al. Lysoptosis Is an Evolutionarily Conserved Cell Death Pathway Moderated by Intracellular Serpins. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.W.; Gan, W.L.; Teo, Y.K.; Lew, W.S. Interplay of Cell Death Signaling Pathways Mediated by Alternating Magnetic Field Gradient. Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leulmi, S.; Chauchet, X.; Morcrette, M.; Ortiz, G.; Joisten, H.; Sabon, P.; Livache, T.; Hou, Y.; Carrière, M.; Lequien, S.; et al. Triggering the Apoptosis of Targeted Human Renal Cancer Cells by the Vibration of Anisotropic Magnetic Particles Attached to the Cell Membrane. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 15904–15914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Ning, P.; Gao, R.; Feng, Q.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Qin, Y.; Plaza, G.R.; et al. Programmable ROS-Mediated Cancer Therapy via Magneto-Inductions. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, S.; Hallali, N.; Lalatonne, Y.; Hillion, A.; Antunes, J.C.; Serhan, N.; Clerc, P.; Fourmy, D.; Motte, L.; Carrey, J.; et al. Magneto-Mechanical Destruction of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Using Ultra-Small Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Low Frequency Rotating Magnetic Fields. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Bomba, H.N.; Zhu, Y.; Gu, Z. Mechanical Force-Triggered Drug Delivery. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12536–12563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorobets, O.; Gorobets, S.; Sharai, I.; Polyakova, T.; Zablotskii, V. Interaction of Magnetic Fields with Biogenic Magnetic Nanoparticles on Cell Membranes: Physiological Consequences for Organisms in Health and Disease. Bioelectrochemistry 2023, 151, 108390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Amaravadi, R.K. Targeting the Lysosome in Cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1371, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Puebla, A.; Boya, P. Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization as a Cell Death Mechanism in Cancer Cells. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2018, 46, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).