CdTe Quantum Dot Fluorescence Modulation by Spin Crossover
Abstract
:1. Introduction
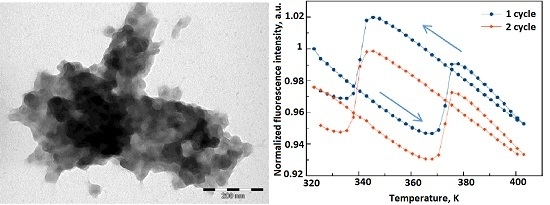
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Details
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bousseksou, A.; Molnar, G.; Salmon, L.; Nicolazzi, W. Molecular spin crossover phenomenon: Resent achievements and prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3313–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, J.; Quintero, C.M.; Molnar, G.; Salmon, L.; Bousseksou, A. Spin-Crossover Materials; Halcrow, M.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2013; pp. 347–373. [Google Scholar]
- Piguet, C.; Rivara-Minten, E.; Hopfgartner, G.; Bünzli, J.-C.G. Molecular magnetism and iron(II) spin-state equilibrium as structural probes in heterodinuclear d–f complxes. Helv. Chim. Acta 1995, 78, 1651–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piguet, C.; Rivara-Minten, E.; Bernardinelli, G.; Bünzli, J.-C.G.; Hopfgartner, G. Non-covalent lanthanide podates with predetermined physicochemical properties: Iron(II) spin-state equilibria in self-assembled heterodinuclear d–f supramolecular complexes. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1997, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeser, M.; Fabbrizzi, L.; Licchelli, M.; Sacchi, D. A fluorescent molecular thermometer based on the nickel(II) high-spin/low-spin interconversion. Chem. Commun. 1999, 1191–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edder, C.; Piguet, C.; Bünzli, J.-G.; Hopfgartner, G. High-spin iron(ii) as a semitransparent partner for tuning europium(iii) luminescence in heterodimetallic d–f complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 3014–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Renz, F.; Hara, T.; Kikuchi, Y.; Fukuda, Y.; Okubo, J.; Hoshi, T.; Linert, W. Fluorescence spectra of Fe(II) spin crossover complexes with 2,6-bis(benzimidazole-2′-yl)pyridine. Chem. Phys. 2002, 277, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Isozaki, H.; Tajima, H. Electroluminescence quenching caused by a spin-crossover transition. Chem. Lett. 2008, 374–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Isozaki, H.; Tajima, H. Reproducible on-off switching of the light emission from the electroluminescent device containing a spin crossover complex. Thin Solid Films 2008, 517, 1465–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukizono, H.; Kuroiwa, K.; Kimizuka, N. Self-assembly-directed spin conversion of iron(II) 1,2,4-triazole complexes in solution and their effect on photorelaxation processes of fluorescent counter ions. Chem. Lett. 2008, 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovee, C.A.; Kilner, C.A.; Thomas, J.A.; Halcrow, M.A. Co-crystallising two functional complex molecules in a terpyridine embrace lattice. Cryst. Eng. Commun. 2009, 11, 2069–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, L.; Molna’r, G.; Zitouni, D.; Quintero, C.; Bergaud, C.; Micheau, J.-C.; Bousseksou, A. A novel approach for fluorescent thermometry and thermal imaging purposes using spin crossover nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5499–5503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titos-Padilla, S.; Herrera, J.M.; Chen, X.-W.; Delgado, J.J.; Colacio, E. Bifunctional hybrid SiO2 nanoparticles showing synergy between core spin crossover and shell luminescence properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3290–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, Y.; Robert, F.; Naik, A.D.; Zhou, G.; Tinant, B.; Robeyns, K.; Michotte, S.; Piraux, L. Spin transition charted in a fluorophore-tagged thermochromic dinuclear iron(II) complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15850–15853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Prieto, R.; Fleury, B.; Schramm, F.; Zoppellaro, G.; Chandrasekar, R.; Fuhr, O.; Lebedkin, S.; Kappes, M.; Ruben, M. Tuning the spin-transition properties of pyrene-decorated 2,6-bispyrazolylpyridine based Fe(II) complexes. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 7564–7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero, C.M.; Gural’skiy, I.A.; Salmon, L.; Molnar, G.; Bergaud, C.; Bousseksou, A. Soft lithographic patterning of spin crossover complexes. Part 1: Fluorescent detection of the spin transition in single nano-objects. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 3745–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gural’skiy, I.A.; Quintero, C.M.; Abdul-Kader, K.; Lopes, M.; Bartual-Murgui, C.; Salmon, L.; Zhao, P.; Molnar, G.; Astruc, D.; Bousseksou, A. Detection of molecular spin-state changes in ultrathin films by photonic methods. J. Nanophotonics 2012, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Kiyoshima, K.; Uchida, R.; Kinoshita, N.; Tajima, H. Characteristics of organic light-emitting devices consisting of dye-doped spin crossover complex films. Thin Solid Films 2013, 531, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, V.; Halász, K.; Gural’skiy, I.A.; Tricard, S.; Carayon, M.-T.; Molnár, G.; Bousseksou, A.; Salmon, L.; Csóka, L. Cellulose fiber nanocomposites displaying spin-crossover properties. Colloids Surf. A 2014, 456, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, L.J.; Cook, R.K.; Kulmaczewski, S.A.; Barrett, O.; Halcrow, M.A. Iron(II) complexes of tridentate indazolylpyridine ligands: Enhanced Spin-crossover hysteresis and ligand-based fluorescence. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, J.M.; Titos-Padilla, S.; Pope, S.; Berlanga, I.; Zamora, F.; Delgado, J.J.; Kamenev, K.; Wang, X.; Prescimone, A.; Brechin, E.K.; et al. Studies on bifunctional Fe(II)-triazole spin crossover nanoparticles: Time-dependent luminescence, surface grafting and the effect of a silica shell and hydrostatic pressure on the magnetic properties. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7819–7829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimanov, I.; Kraieva, O.; Costa, J.S.; Fritsky, I.O.; Molnár, G.; Salmon, L.; Bousseksou, A. Electronic communication between fluorescent pyrene excimers and spin crossover complexes in nanocomposite particles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5026–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, V.; Suleimanov, I.; Molnár, G.; Salmon, L.; Bousseksou, A.; Csóka, L. Cellulose-spin crossover particle composite papers with reverse printing performance: A proof of concept. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7897–7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimanov, I.; Kraieva, O.; Molnár, G.; Salmon, L.; Bousseksou, A. Enhanced luminescence stability with a Tb-spin crossover nanocomposite for spin state monitoring. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15098–15101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-F.; Li, R.-F.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wei, R.-J.; Zheng, L.-S.; Tao, J. Synergetic spin crossover and fluorescence in one-dimensional hybrid complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 1574–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochenie, C.; Wagner, K.G.; Karg, M.; Weber, B. Modulation of the ligand-based fluorescence of 3D metal complexes upon spin state change. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 7925–7935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L.J.K.; Halcrow, M.A. Doping ruthenium complexes into a molecular spin-crossover material. Polyhedron 2015, 87, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Salitros, I.; Heinrich, B.; Fuhr, O.; Ruben, M. A charge neutral iron(II) complex with an above room temperature spin crossover (SCO) and hysteresis loop. J. Mat. Chem. C 2015, 3, 11635–11644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, H. Quantum size colloids: From size-dependent properties of discrete particles to self-organized superstructures. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 3, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science 1996, 271, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleimanov, I.; Costa, J.S.; Molnar, G.; Salmon, L.; Bousseksou, A. The photo-thermal plasmonic effect in spin crossover@silica—Gold nanocomposites. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13015–13018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tissot, A.; Enachescu, C.; Boillot, M.-L. Control of the thermal hysteresis of the prototypal spin-transition FeII(phen)2(NCS)2 compound via the microcrystallites environment: Experiments and mechanoelastic model. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 20451–20457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.W.; Sundar, V.C.; Rudzinski, C.M.; Wun, A.W.; Bawendi, M.G.; Nocera, D.G. Quantum-dot optical temperature probes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 3555–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Gu, P.; Chu, H.; Zhang, H.; Cui, T.; Wang, Y.; et al. Temperature-dependent photoluminescence of ZnCuInS/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 19288–19294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Westcott, S.; Chen, W. Nanoparticle Luminescence Thermometry. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 11203–11209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, E.; Ge, P.; Lee, S.H.; Jeyifous, O.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wilson, K.M.; Lim, S.J.; Baird, M.A.; Stone, J.E.; et al. Stable small quantum dots for synaptic receptor tracking on live neurons. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12484–12488. [Google Scholar]



© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kraieva, O.; Suleimanov, I.; Molnár, G.; Salmon, L.; Bousseksou, A. CdTe Quantum Dot Fluorescence Modulation by Spin Crossover. Magnetochemistry 2016, 2, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry2010011
Kraieva O, Suleimanov I, Molnár G, Salmon L, Bousseksou A. CdTe Quantum Dot Fluorescence Modulation by Spin Crossover. Magnetochemistry. 2016; 2(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry2010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleKraieva, Olena, Iurii Suleimanov, Gábor Molnár, Lionel Salmon, and Azzedine Bousseksou. 2016. "CdTe Quantum Dot Fluorescence Modulation by Spin Crossover" Magnetochemistry 2, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry2010011
APA StyleKraieva, O., Suleimanov, I., Molnár, G., Salmon, L., & Bousseksou, A. (2016). CdTe Quantum Dot Fluorescence Modulation by Spin Crossover. Magnetochemistry, 2(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/magnetochemistry2010011