Abstract
Water reuse is critical to national development, sustenance, and survival in this era of climate, demographic, and social changes. There is no systemic national approach to systematically addressing this challenge. This paper presents a framework and method to develop a national research strategy for water reuse. It presents an ontology of water reuse strategies that encapsulates the combinatorial complexity of the problem clearly, concisely, and comprehensively. Subsequently, it discusses the method to use the framework to develop a national strategy, adapt it through feedback and learning, and ultimately effect a revolutionary change in the strategy for water reuse.
1. Introduction
“In practice, all the water on the planet is eventually reused” [1] (p. 5). The long-term global transportation and transformation of water for use and reuse transcends geographical boundaries. However, to assure daily water security, public health security, and ecosystem resilience for stakeholders, this transportation and transformation must be managed and controlled internationally, nationally, regionally, and locally. For instance, the reuse of municipal water in the U.S. could potentially increase the nation’s available resources by approximately 6% of total water use [2], while water conservation could reduce household water use by more than 30% [3]. Hence, there is a need for a national research strategy for water reuse.
There is a rapidly growing body of literature on water reuse. As of 13 November 2023, there were 1846 papers with ‘water reuse’ in their title indexed in the Scopus database, covering many countries. This corpus excludes papers that address water reuse in their content. There is also a large, growing corpus on the subject not indexed in Scopus. Despite this large volume of research, there is no clear, concise, and comprehensive framework to guide the research to address the challenge. There is no ‘Google Map’ for research on water reuse.
Tzanakakis et al. [1] conducted an extensive review of the literature and listed the following knowledge gaps in water reuse research:
- Possible interactions of agricultural reuse with soils, plants, and crops;
- Fate of organic microcontaminants in receiving environmental media and targets;
- Epidemiological risk of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and/or resistance genes released in the environment with treated effluents;
- Issues concerning climate change and/or variability;
- Strategies to overcome barriers to water reuse;
- Links among reuse schemes, ecosystem services, and SDGs.
These are significant gaps, and there may be many more. We shall not know the missing gaps without a framework to map the corpus. There may be pathways for water reuse that have been effective and must be reinforced, those that have been ineffective and must be redirected, and those that have been untested/unknown and must be researched.
Almost all countries today are being compelled to address the challenge of water reuse by the changes in their demography, climate, economy, industry, sociology, and other similar factors. There is a need for a systemic framework to systematically guide countries’ national research strategies for water reuse. This framework must help systematize local research, localize global research, and globalize local research. We present an ontological framework for developing a national research strategy for water reuse.
An ontology is an organization of the terminologies, taxonomies, and narratives of a problem that can be conceptualized as a scientific theory of the problem [4,5,6,7]. As a scientific theory, it can be used to describe, explain, predict, and control [8] water reuse through feedback and learning [9,10] systemically as part of a broader ecosystem, and systematically by exploring the innumerable pathways within it. Ontological frameworks have been used to study river water sharing [11], national healthcare policies [12,13,14,15,16], design thinking [17], public health informatics [18], local climate change [19], and other domains. In the following paper, we (a) present an ontology of water reuse strategies based on the present definitions of water reuse, (b) discuss how it can be used as a comprehensive, national research design framework, and (c) delineate its implications for research on, policies for, and the practice of water reuse.
2. The Ontology of Water Reuse
Water reuse is a complex combinatorial problem. Its many definitions simplify the problem and address only parts of it and not the whole. A coordinated national research strategy for water reuse must address the combinatorial complexity systemically and systematically.
The Ontology of Water Reuse Strategies (Figure 1) will be used to do so. It incorporates the key terminologies and taxonomies of water reuse strategies from the Water Research Foundation (WRF) research projects (https://www.waterrf.org/research, accessed on 13 November 2023), the associated workshops, the 1846 global papers with ‘water reuse’ in the title indexed in Scopus (as of 13 November 2023), and other related literature. This ontology, after validation by stakeholders, can serve as the framework for developing a coordinated national strategy for water reuse. It is described below.
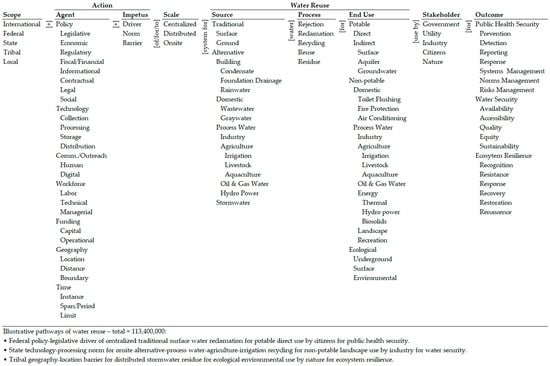
Figure 1.
Ontology of water reuse.
2.1. Water Reuse
‘Water Reuse’ at the center of the ontology is defined as a combination of the sources of water (Figure 1—Source), processes of reuse (Figure 1—Process), and end uses (Figure 1—End Use) of water, denoted by the taxonomies in the three columns. Each taxonomy is based on the current literature and its elements are reasonably mutually exclusive and sufficiently exhaustive. We shall discuss each in detail.
2.1.1. Sources of Water
A major part of the taxonomy of sources of water is based on the classification by Hayek et al. [20] (p. xii). They classify water sources as traditional and alternative sources. Further, they classify traditional sources as surface and groundwater. We have reorganized and extended their list of alternative water sources. We have grouped condensate, foundation drainage, and rainwater under buildings as a source. Similarly, we have grouped domestic wastewater and graywater as alternative domestic sources. Stormwater has been retained as a separate alternative source. We have refined the sources of processed water as follows: industry, agriculture, oil and gas, and hydro power [1,2,20,21,22,23]. Agriculture sources have been further classified as irrigation, livestock, and aquaculture [1,2,20,21,22,23].
The qualitative and quantitative properties of these sources of water are different. They are also likely to be different based on the geographical location, annual season, and other spatio-temporal factors. These sources must be separated, differentiated, integrated, and combined for effective water reuse.
2.1.2. Process of Water Reuse
The stages of the water reuse process are derived from the common body of knowledge and extended to include rejection and residue as the first and the last stages. Reclamation, recycling, and reuse are commonly used in many definitions [21,24,25,26,27]. Rejection [28] is not commonly used but is included in the taxonomy as a logical first stage. Similarly, residue is the logical last stage of the process—recognizing that some water may not be reused by a stakeholder. Procházková et al. [29] (p. 1) state the importance of managing the residue: “… water should be reused in a responsible and sustainable manner because if the liquid residue after water reuse has not been appropriately treated, it may pose a risk to both human health and the environment”.
The stages of the water reuse process are generally sequential. While ideally one may want to have both rejection and residue be zero, and maximize reclamation, recycling, and reuse, that is unlikely.
2.1.3. End Use of Water
The taxonomy of uses of water is based on the classification by Hayek et al. [20] (p. xii). We have retained their major potable and non-potable categories, but have reorganized the subcategories based on the literature [21,24,25,26,27,30]. In addition, we have added a third major category of end use—Ecological, with three subcategories of underground, surface, and environmental. The potable and non-potable water that is not reused will in a sense be ‘used’ by the ecology. The completion of this reuse sequence will be an important segment of the circular economy of water reuse [24,31,32,33,34]. While the time horizons of potable and non-potable reuses are short, that of ecological reuse is long. The desirable and undesirable effects of ecological reuse can emerge and be propagated over a long period of time and large distances.
2.1.4. Water Reuse Definition
This ontological definition of water reuse encapsulates 14 × 5 × 20 = 1400 potential combinations of source–process–end use. It includes, for example, the following: (a) traditional surface water reclamation for direct potable use, (b) alternative process water agriculture–irrigation recycling for non-potable landscape use, and (c) stormwater residue for ecological environmental use. It encapsulates and extends the present definitions of water reuse. Only a subset of the 1400 potential combinations may be instantiated at one place at a time; many may not be instantiable.
2.2. Stakeholders
There are many stakeholders in water reuse, each with their own perspectives, motivations, and interests [1,20,35,36]. We have broadly categorized them as belonging to the government, utilities, industry, citizenry, and nature (at large). They are listed in the corresponding column (Figure 1—Stakeholder). The list can be lengthened, shortened, aggregated, and disaggregated.
Thus, the three types of water reuse illustrated earlier may be combined with the types of stakeholders as follows: (a) traditional surface water reclamation for direct potable use by citizens, (b) alternative process water agriculture–irrigation recycling for non-potable landscape use by industry, and (c) stormwater residue for ecological environmental use by nature. In combination with the five types of stakeholders, there are 1400 × 5 = 7000 pathways.
2.3. Outcome
The desired outcomes of water reuse are listed in the last column (Figure 1—Outcome). They are public health security, water security, and ecosystem resilience.
Globally, all water is essentially reused water [1], and water is essential for the health and wellbeing of the public. All reuses of water must assure the public’s health security. This includes prevention, detection, reporting, responding, managing systems, managing norms, and managing risks of factors that may affect public health security [37,38,39].
Changes in global climate, demographics, agriculture, and industry are increasing the role of water reuse in assuring water security. An outcome of water reuse is to improve the availability, accessibility, quality, equity, and sustainability of water locally, regionally, nationally, and globally [40,41,42].
The ecosystem is an essential part of all water reuse—it is the ultimate source and sink of water. The resilience of the ecosystem is critical to the sustainability of water reuse. The ecosystem is the end user of water rejected for reuse and water that is the residue of reuse. The ecosystem must be resilient to changes due to water reuse for the latter to be sustainable. Ecosystem resilience denotes the capability to recognize changes, resist dysfunctional ones, respond to them, recover from them, restore the ecosystem, and potentially revive the same [43,44].
Combining the outcomes with the three illustrative pathways, we have the following: (a) traditional surface water reclamation for direct potable use by citizens for public health security risk management, (b) alternative process water agriculture–irrigation recycling for non-potable landscape use by industry for water security equity, and (c) stormwater residue for ecological environmental use by nature for ecosystem resilience restoration. In combination with the 18 outcomes, there are 1400 × 5 × 18 = 126,000 pathways.
2.4. Scale
The scale of water reuse may be one or a combination of three: centralized, distributed, and onsite (Figure 1—Scale) [20]. Generally, centralized systems cover a large geographical area, have multiple sources, cater to many end users, and handle large volumes of water for reuse. Distributed systems cover a smaller geographical area, cater to a few sources and end users, and handle moderate volumes of water for reuse. Onsite systems are designed for individual sources and users and handle a small volume for reuse. The complexity of the reuse process will likely be proportional to its scale; the number of stakeholders will also be similarly proportional.
Thus, the three illustrative pathways can be (a) centralized traditional surface water reclamation for direct potable use by citizens for public health security, (b) onsite alternative process water agriculture–irrigation recycling for non-potable landscape use by industry for water security, and (c) distributed stormwater residue for ecological environmental use by nature for ecosystem resilience. In combination with the three scales of operation, there are 1400 × 5 × 18 × 3 = 378,000 pathways.
2.5. Action
The actions for water reuse (Figure 1—Action) will be determined by the agents (Figure 1—Agent) and the impetus (Figure 1—Impetus) they provide. Many agents may provide the impetus; and these agents may drive it, normalize it, or be barriers to it. We shall describe the two in slightly greater detail next.
2.5.1. Agent
Many categories of agents, each with multiple subcategories, may provide the impetus for water reuse. The ontology lists policies, technology, communication/outreach, workforce, funding, geography, and time. These categories and subcategories are simply a reorganization and relabeling of the terminology in the vast body of literature on water reuse. The policy subcategories are based on Lascoumes et al. [45], the technology subcategories are derived from the literature and correspond to the stages of processing water for reuse, the communication/outreach subcategories denote the two broad methods practiced today, the workforce and funding subcategories are derived from the literature and correspond to the divisions in practice, and the geography and time categories are logical parameters that affect water reuse.
2.5.2. Impetus
The agents may drive water reuse, normalize it, or be barriers to it. The categories of drivers and barriers are widely used in the literature [46], that of norms is not. Yet, norms are implicit in the research and are essential for effective water reuse. In a sense, the ultimate objective is to normalize water reuse. Norms are also necessary, as reference levels, to manage the drivers and barriers through feedback and learning [10].
2.5.3. Summary of Action
The ontology encapsulates 25 × 3 = 75 Agent–Impetus combinations. They include, for example, the following: (a) policy—legislative driver, (b) technology—processing norm, and (c) geography—location barrier. Thus, extending the earlier illustrations, one may have (a) policy—legislative driver of centralized traditional surface water reclamation for direct potable use by citizens for public health security, (b) technology—processing norm for onsite alternative process water agriculture–irrigation recycling for non-potable landscape use by industry for water security, and (c) geography—location barrier for distributed stormwater residue for ecological environmental use by nature for ecosystem resilience. In combination with the action combinations, there are 1400 × 5 × 18 × 3 × 75 = 28,350,000 pathways.
2.6. Scope
Last, the scope of the water reuse problem may vary (Figure 1—Scope). It ranges from the international to the local, and includes federal, state, tribal, and local. Scope defines the boundary of a water reuse project; yet, given the property of water to freely move across geographical boundaries, the definition of scope becomes fuzzy. A state water reuse project may have to necessarily consider federal, state, and local policies in implementation.
Thus, in combination with the scope one may envision the following (Figure 1): (a) federal policy—legislative driver of centralized traditional surface water reclamation for direct potable use by citizens for public health security, (b) state technology—processing norm for onsite alternative process water agriculture–irrigation recycling for non-potable landscape use by industry for water security, and (c) tribal geography—location barrier for distributed stormwater residue for ecological environmental use by nature for ecosystem resilience. In combination with scope, there are 1400 × 5 × 18 × 3 × 75 × 4 = 113,400,000 pathways for water reuse encapsulated in the ontology.
2.7. Summary of Ontology of Strategy for Water Reuse
The ontology of water reuse is a theory of a complex problem [10]. It is a clear, concise, and comprehensive organization of 122 key terms (words/phrases, excluding the column labels and connectors) and their taxonomies that define water reuse. It encapsulates the key terminology and taxonomies [4] of the domain grounded in the global research literature on the subject. It organizes a very large number of all possible nine-word/phrase combinations (122C9 = (122!/113! × 9! = 1.22 × 1013) corresponding to the nine columns and sub-columns of the ontology) into 113,400,000 semantically and practically meaningful pathways of water reuse. It visualizes the complexity of the problem in structured, natural English. While, at first glance, it may appear to be abstract and impractical, it is in fact concrete and practical—an illustration of the aphorism that there is nothing as practical as a good theory [47]. It can be used to describe the many pathways of water reuse in a context, explain their antecedents and consequences, predict the outcomes based on past research and practice, and control the trajectory through feedback and learning.
The ontology, by necessity, is complex—it is an isomorphic representation of a complex problem. It is also modular. Elements and pathways applicable to a context may be extracted and used without diminishing the effectiveness, thus reducing the complexity, yet addressing the problem systemically and systematically. Thus, although the scope of the present ontology is global, it can be reduced and simplified to apply locally without a loss of perspective and reducing the unintended consequences of a narrow perspective. The ontology can effectively capture wide-ranging water reuse initiatives at the international or regional levels as well as the local or municipal levels. For example, the unified water reuse strategy by the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries [48] involves both regional and municipal considerations of water reuse, which can be succinctly captured by the ontology. Similarly, the ontology can capture water reuse policies or initiatives by various countries around the world [49,50,51,52,53,54,55].
We have used the metaphor of Google Map to characterize the ontology. Like a Google Map when studied closely, the ontology presents a very large number of pathways to reuse water. One must select the preferred pathways based on the stakeholders’ desired criteria—such selection is automated in Google Maps to reduce the complexity of choice. Thus, it will help locate one’s state of water reuse on the map, define the desired state, determine the gap, and design pathways to bridge the gap.
A coordinated national research strategy for water reuse must help discover the following pathways for all stakeholders:
- Effective pathways across the ontology and how to reinforce them;
- Ineffective pathways across the ontology and how to redirect them;
- Innovative pathways across the ontology and experiment with them;
- Infeasible pathways across the ontology to avoid them.
In the following discussion, we describe a process of developing a national research strategy for water reuse using the ontology.
3. Discussion—National Research Strategy for Water Reuse
Stakeholders, by definition, have a stake in defining and addressing the problem of water reuse locally, tribally, regionally, nationally, and globally. Stakeholders may be government bureaucrats, water utility managers, industry users, citizen activists and users, and nature, which provides, sustains, and consumes water. Stakeholders are also likely (and understandably so) to be guided by their self-interest and thus to take a narrow, segmented approach to the problem. There is an inherent incentive to replay the story of the blind men and the elephant. Without a ‘Google Map’ of the problem, the stakeholders are likely to continue to talk past each other, become entrenched in their positions, reinforce past biases, not see the ‘big picture’, and see alternative win–win pathways. The ontology can make the ‘elephant’ visible. Studies on national healthcare policies [12,13,14,15,16], higher education policies [56], transboundary sharing of river water [11], and clean air policies [57] using ontologies provide evidence of the siloed, selective, sparse, segmented, and non-systemic. They are siloed in that the emphases on the columns are severely unbalanced, selective in their choice of elements addressed, sparse in the overall coverage of elements and the attendant pathways, segmented attention to pathways, and because of all the above, inattentive to addressing the problem systemically.
The federal government or a designated national research body of a country must play a central role in developing a national research strategy for water reuse, translating research into policies, translating policies into practice, and modifying the research strategy based on the feedback from the implementation of the policies and practices. Given the complexity of the challenge, an ad hoc strategy, like those that have been pursued to date, will be inadequate. These recommendations are based on the policy briefs developed for the G20 Summit in India in 2023 [58,59].
At present, there does not appear to be any national framework or concerted effort to address the challenge of water reuse and provide a roadmap. Each national body’s agenda must inform and be informed by the constituent state/province, tribal, and local agendas, those of other countries (especially the neighbors), and those of the United Nations (UN) and its agencies, the World Health Organization (WHO), and similar bodies.
The ontology of the strategy for water reuse or a similar one must be adopted as a framework for every country and its constituent entities. Within the framework, each entity must choose its pathways based on its local requirements, priorities, and resources. The adoption of a common framework will help formalize and transfer knowledge about and feedback and learnings from the implementation within a country and to other countries. Such an approach will help move the cycle of generating and applying knowledge on the challenge from a selective, segmented, and siloed effort to a synoptic, systemic, and systematic one.
The framework must be used to periodically map the state-of-the-art, state-of-the-need, and state-of-the-practice of water reuse. Analyzing the gaps between the three states must guide the translation of research into policy into practice and then back into research for feedback and learning to achieve the sustainable development goals’ vision. As such, national committees must help the member countries collaborate, coordinate their policies, and communicate their learning.
Each national body must form a national committee and encourage the creation of regional and local groups for water reuse. These committees must adapt and adopt the ontology as a common framework and pursue a systemic approach that harnesses the resources and unleashes the forces necessary for water reuse. These committees must be responsible and accountable for the outcomes.
A recommended agenda for national bodies is as follows:
- Finalize the ontology in consultation with stakeholders and researchers through extensive meetings;
- Finalize the corpus of the national and global research literature on water reuse;
- Map the documents onto the ontology to determine the following:
- Elements of the ontology that have been heavily addressed (bright spots), less addressed (light spots), and not addressed (blind/blank spots) in the corpus;
- The primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary, and quinary themes in the corpus;
- These maps will highlight the gaps within the corpus.
- Solicit feedback from stakeholders and researchers based on the ontology and the maps derived from the corpuses;
- The feedback should help prioritize the pathways to be reinforced, redirected, experimented, and avoided;
- The priority of pathways to be reinforced, redirected, experimented, and avoided shall form the basis of project ideas and research roadmaps;
- Develop a final roadmap anchored on the ontology, the mapping of the corpus, and the feedback from the stakeholders and researchers;
- Like a Google Map, the roadmap shall highlight the key pathways and their priorities;
- The roadmap shall be disseminated via the document, presentations, webinars, and roundtables;
- The ontology and the associated maps will be the basis for scientifically (a) describing the pathways to water reuse, (b) explaining their logic, (c) predicting the outcomes of choosing different pathways, and (d) controlling the outcomes through continuous feedback and learning.
Technology, both modern and traditional, should be a key focus of the national research strategy for water reuse. Water use and reuse must be managed minute by minute, mile by mile, through deluge and drought. Modern information technology like sensors, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), internet of things (IoT), robots, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS) provide powerful tools to micro-manage water reuse spatially and temporally. They can provide the data, information, interpretation, and knowledge in real time to manage water reuse through feedback, control, adaptation, learning, and redirection. They must be deployed extensively as part of the national research strategy for water reuse.
At the same time, nature is one of the biggest stakeholders in water reuse. Many traditional, historical nature-based technologies for water reuse are being rediscovered and redeployed [60,61,62]. These technologies rely less on modern discoveries and more on harnessing the natural properties of the land, flora, and fauna. They are dependent on biochemical and physical feedback and control mechanisms. Many incorporate learning and adaptation over many past generations. These technologies too should be an integral part of the national strategy for water reuse.
4. Conclusions
The complex challenge of a national water reuse strategy cannot be simply the sum of many local, incremental, and ad hoc strategies. A synoptic view of the problem, as provided by the ontology, is necessary to address it systematically and systemically. The fragmentation of the formulations and segmentation of the solutions can diminish the intended, functional consequences, and enhance the unintended, dysfunctional consequences. They can lead to biases and blind spots in addressing the problem. A way to optimize the effort for water reuse is as follows: (a) have a roadmap like the ontology of water reuse strategies that has been proposed; (b) institute a process for continuous feedback and learning with stakeholders; (c) institute a process for continuous feedback and learning between research, policies, and practices; and (d) adapt the roadmap as new knowledge is generated. One could, using this approach, bring about a revolutionary change in the strategic management [9] of water reuse.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.R. and T.S.; methodology, A.R. and T.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.R. and T.S.; writing—review and editing, A.R. and T.S.; visualization, A.R. and T.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Tzanakakis, V.A.; Capodaglio, A.G.; Angelakis, A.N. Insights into Global Water Reuse Opportunities. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council of the National Academies. Water Reuse: Potential for Expanding the Nation’s Water Supply through Reuse of Municipal Wastewater; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; ISBN 0-309-22462-4. [Google Scholar]
- Asano, T.; Burton, F.L.; Leverenz, H.L.; Tsuchihashi, R.; Tchobanoglous, G. (Eds.) Water Reuse: Issues, Technologies, and Applications, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-07-145927-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, T.R.; Liu, L.; Ozsu, M.T. Encyclopedia of Database Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Quine, W.V.O. From a Logical Point of View: 9 Logico-Philosophical Essays; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980; ISBN 978-0-674-32351-3. [Google Scholar]
- Cimino, J.J. In Defense of the Desiderata. J. Biomed. Inform. 2006, 39, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, B.; Josephson, J.R.; Benjamins, V.R. What Are Ontologies, and Why Do We Need Them? IEEE Intell. Syst. Their Appl. 1999, 14, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coon, D.; Mitterer, J.O. Psychology: A Journey; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-285-68733-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaprasad, A. Revolutionary Change and Strategic Management. Behav. Sci. 1982, 27, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaprasad, A. On the Definition of Feedback. Behav. Sci. 1983, 28, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, V.; Halanaik, B.; Ramaprasad, A.; Swamy, T.R.K.; Singai, C.B.; Syn, T. Transboundary Sharing of River Water: Informating the Policies. River Res. Appl. 2020, 36, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Deng, F.; Ramaprasad, A.; Syn, T. China’s National Health Policies: An Ontological Analysis. Online J. Public Health Inform. 2016, 8, e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, A.; Ramaprasad, A.; Syn, T. National Healthcare Policies in Chile: An Ontological Meta-Analysis. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2015, 2015, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, N.K.B.; Madhumitha, M.; Ramaprasad, A.; Syn, T. National Healthcare Programs and Policies in India: An Ontological Analysis. Int. J. Community Med. Public Health 2017, 4, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ramaprasad, A.; Win, K.T.; Syn, T.; Beydoun, G.; Dawson, L. Australia’s National Health Programs: An Ontological Mapping. Australas. J. Inf. Syst. 2016, 20, 6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Sreeganga, S.D.; Rath, N.; Ramaprasad, A. Healthcare Policies to Eliminate Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs) in India: A Roadmap. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2023, 20, 6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaprasad, A.; Syn, T. Design Thinking and Evaluation Using an Ontology. In Design Science: Perspectives from Europe; Helfert, M., Donnellan, B., Kenneally, J., Eds.; Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer International Publishing: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 447, pp. 63–74. ISBN 978-3-319-13935-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaprasad, A.; Syn, T. Ontological Meta-Analysis and Synthesis. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2015, 37, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, C.A.; Ramaprasad, A.; Syn, T. Information Systems to Manage Local Climate Change Effects: A Unified Framework. In Proceedings of the PACIS 2018 Proceedings, Yokohama, Japan, 26–30 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hayek, C.; Lall, U.; Becker, W.; Knowles, P.; Faber, L. Implementing Onsite and Distributed Water Reuse Systems in the United States: Literature Review; The Water Research Foundation: Denver, CO, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Angelakis, A.N.; Tzanakakis, V.A.; Capodaglio, A.G.; Dercas, N. A Critical Review of Water Reuse: Lessons from Prehistoric Greece for Present and Future Challenges. Water 2023, 15, 2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortajada, C.; Nambiar, S. Communications on Technological Innovations: Potable Water Reuse. Water 2019, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.W. Integrated Concepts in Water Reuse: Managing Global Water Needs. Desalination 2006, 187, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.; Cunha Marques, R. Review of Water Reuse from a Circular Economy Perspective. Water 2023, 15, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoushtarian, F.; Negahban-Azar, M. Worldwide Regulations and Guidelines for Agricultural Water Reuse: A Critical Review. Water 2020, 12, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. A Critical Review on Sustainability Assessment of Recycled Water Schemes. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 426, 13–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.W. Water Reclamation and Reuse. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1980, 52, 1242–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Cordeiro, S.; Ferrario, F.; Pereira, H.X.; Ferreira, F.; Matos, J.S. Water Reuse, a Sustainable Alternative in the Context of Water Scarcity and Climate Change in the Lisbon Metropolitan Area. Sustainability 2023, 15, 12578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procházková, M.; Touš, M.; Horňák, D.; Miklas, V.; Vondra, M.; Máša, V. Industrial Wastewater in the Context of European Union Water Reuse Legislation and Goals. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-Y.; Singh, V.P. A Review on Monthly Water Balance Models for Water Resources Investigations. Water Resour. Manag. 1998, 12, 20–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellver-Domingo, Á.; Hernández-Sancho, F. Circular Economy and Payment for Ecosystem Services: A Framework Proposal Based on Water Reuse. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortoli, M.; Hollas, C.E.; Cunha, A.; Steinmetz, R.L.R.; Coldebella, A.; de Prá, M.C.; Soares, H.M.; Kunz, A. Water Reuse as a Strategy for Mitigating Atmospheric Emissions and Protecting Water Resources for the Circularity of the Swine Production Chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 345, 131127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Wang, S.-W.; Kim, H.; Pan, S.-Y.; Fan, C.; Lin, Y.J. Non-Conventional Water Reuse in Agriculture: A Circular Water Economy. Water Res. 2021, 199, 117193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulvoulis, N. Water Reuse from a Circular Economy Perspective and Potential Risks from an Unregulated Approach. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 2, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupiper, A.M.; Loge, F.J. Identifying and Overcoming Barriers to Onsite Non-Potable Water Reuse in California from Local Stakeholder Perspectives. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. X 2019, 4, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, T.R.; Nelson, K.L.; Binz, C.; Hacker, M.E. Actor Roles and Networks in Implementing Urban Water Innovation: A Study of Onsite Water Reuse in the San Francisco Bay Area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 6205–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuclear Threat Initiative; Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. Global Health Security Index; Hohns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sapkota, A.R. Water Reuse, Food Production and Public Health: Adopting Transdisciplinary, Systems-Based Approaches to Achieve Water and Food Security in a Changing Climate. Environ. Res. 2019, 171, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Health Systems for Health Security; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Asian Development Bank. Asian Water Development Outlook 2020: Advancing Water Security across Asia and the Pacific; Asian Development Bank: Mandaluyong, Philippines, 2020; ISBN 978-92-9262-616-7. [Google Scholar]
- UN ESCAP. Water Security & the Global Water Agenda: A UN-Water Analytical Brief; United Nations University (UNU): Tokyo, Japan, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Van Beek, E.; Arriens, W.L. Water Security: Putting the Concept into Practice; TEC Background Papers; Global Water Partnership: Stockholm, Sweden, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Drechsel, P.; Qadir, M.; Baumann, J. Water Reuse to Free up Freshwater for Higher-Value Use and Increase Climate Resilience and Water Productivity. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 71, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotine, M.; Ramaprasad, A.; Syn, T. Managing a Smart City’s Resilience to Ebola: An Ontological Framework. In Proceedings of the 49th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Koloa, HI, USA, 5–8 January 2016; pp. 2935–2943. [Google Scholar]
- Lascoumes, P.; Galès, P.L.; Bezes, P.; Borraz, O.; Palier, B.; King, D.; Hood, C. Special Issue of Governance: Understanding Public Policy Through Its Instruments; CEE-Centre D’études Européennes et de Politique Comparée: Paris, France, 2006; p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.; Jepson, W. Drivers and Barriers to Urban Water Reuse: A Systematic Review. Water Secur. 2020, 11, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedeian, A.G. A Note on the Aphorism “There Is Nothing as Practical as a Good Theory”. J. Manag. Hist. 2016, 22, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zubari, W.; Al-Turbak, A.; Zahid, W.; Al-Ruwis, K.; Al-Tkhais, A.; Al-Muataz, I.; Abdelwahab, A.; Murad, A.; Al-Harbi, M.; Al-Sulaymani, Z. An Overview of the GCC Unified Water Strategy (2016–2035). Desalination Water Treat. 2017, 81, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, A.; Quadrado, M.; Franco, A.; Lacasta, N.; Machado, P. Water Reuse in Portugal: New Legislation Trends to Support the Definition of Water Quality Standards Based on Risk Characterization. Water Cycle 2020, 1, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, J. Policy Issues Confronting Australian Urban Water Reuse. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2016, 32, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, K.; Kumar, A. A Comprehensive View of Existing Policy Directives and Future Interventions for Water Reuse in India. Water Policy 2022, 24, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakhungu, M.J. An Ethnography of Policy: Water Reuse Policy in Kenya. Water Policy 2019, 21, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-Y.; Mendoza, J.A.M. Evaluation and Diagnosis for Policy of Water Reuse in the Republic of Korea. Water Cycle 2022, 3, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, K.; Exall, K.; Marsalek, J. Water Reuse and Recycling in Canada: A Status and Needs Assessment. Can. Water Resour. J. 2004, 29, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hares, H.; Aswed, M. Trends in Libyan Desalination and Water Reuse Policy. Desalination 1979, 30, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaprasad, A.; Singai, C.B.; Hasan, T.; Syn, T.; Thirumalai, M. India’s National Higher Education Policy Recommendations Since Independence. J. Educ. Plan. Adm. 2016, 30, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Anilkumar, M.; Kashyap, S.; Mitra, S.G.; Neogi, D.; Ramaprasad, A.; Sanjeev, A.; Singai, C.; Sreeganga, S.D.; Thodika, N.K. The Pathways to Manage Air Pollution: An Ontological Assessment of the National Clean Air Programme 2019, India. Curr. Sci. 2021, 120, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaprasad, A.; Martínez, V.; Nunez, A.; Sreeganga, S.D. Pathways to Universal Digital Access to Inclusive Healthcare in the G20. In T20 Policy Brief; G20/T20 India: New Delhi, India, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaprasad, A.; Mehta, V.K.; Gowrish, R. A Digitalisation Roadmap for Climate-Smart Agriculture in India. In T20 Policy Brief; G20/T20 India: New Delhi, India, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Vishwanath, S. Bangalore Water Crisis Explained: Karnataka Govt Failure? Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KNS1oL0miu0 (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Malligavad, A. Restoring the Lakes Glory. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FCGQzTG2_x8 (accessed on 6 March 2024).
- Capodaglio, A.G. Taking the Water Out of “Wastewater”: An Ineluctable Oxymoron for Urban Water Cycle Sustainability. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 2030–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).