MuscleMap: An Open-Source, Community-Supported Consortium for Whole-Body Quantitative MRI of Muscle
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Develop a standardized acquisition protocol for whole-body quantitative MRI of muscle for the most common MR manufacturers (General Electric, Siemens, and Philips).
- (2)
- Generate a large (n ≥ 1000) open-source annotated multi-site, multi-racial, and multi-ethnic heterogenous whole-body muscle MRI dataset across the lifespan using MuscleMap’s standardized acquisition protocol.
- (3)
- Create an open-source toolbox for the analysis of whole-body muscle morphometry and composition using the MuscleMap whole-body muscle MRI dataset.
- (4)
- Develop normative models for whole-body human skeletal muscle morphometry and composition with respect to age, sex, gender, site, race, ethnicity, and body habitus using the MuscleMap database.
- (5)
- Identify and quantify changes in skeletal muscle morphometry and composition associated with diseases and disorders, compared to MuscleMap normative models.
- (6)
- Establish the necessary regulatory and data informatics infrastructure for the implementation of the MuscleMap toolbox and normative models into clinical workflows.
2. Why Is MuscleMap Needed?
3. Regional Anatomy and Musculature
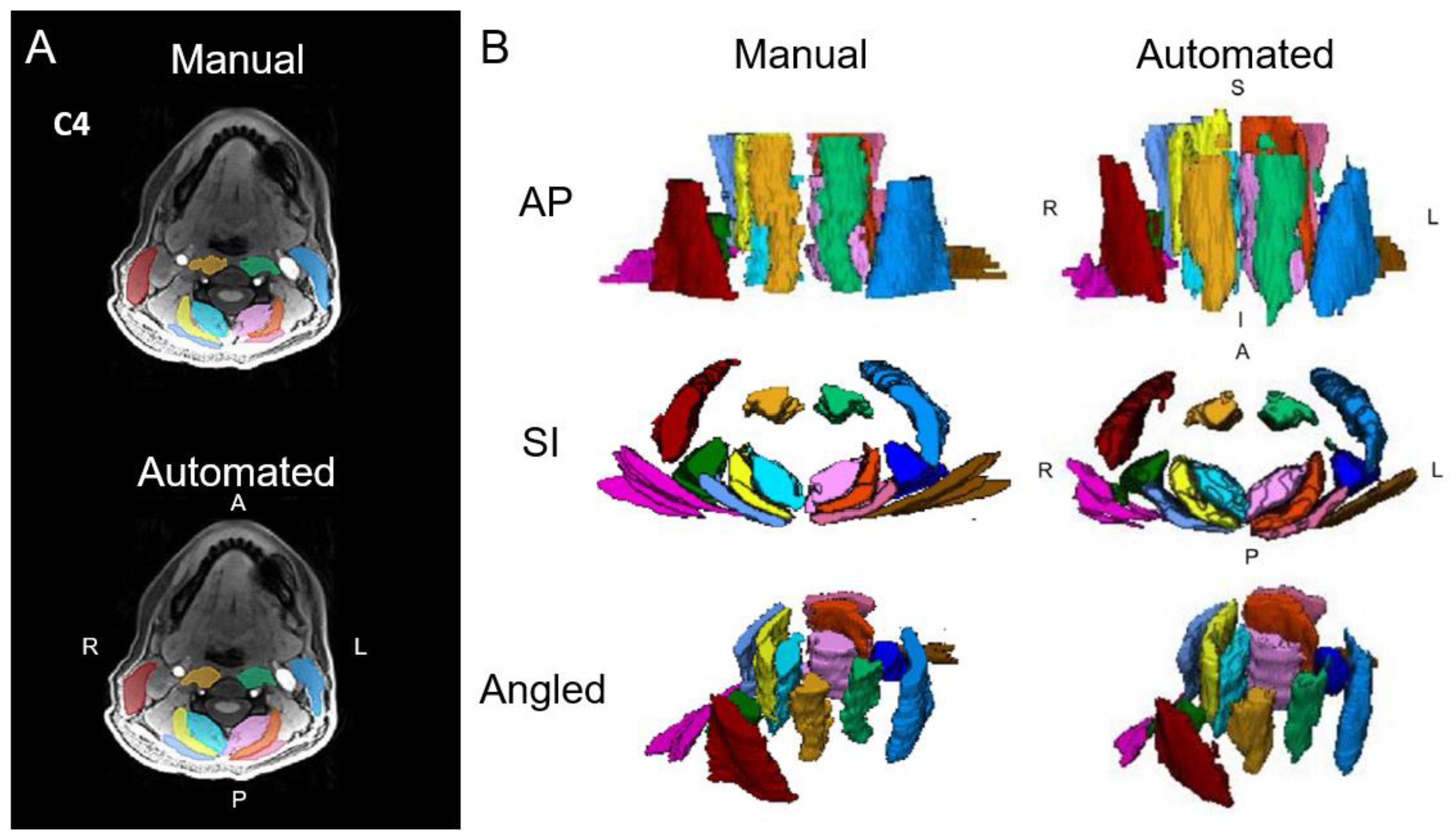
3.1. Cervical Spine
3.2. Muscles Involved in Deglutition
3.3. Shoulder
3.4. Lumbar Spine
3.5. Pelvic Floor
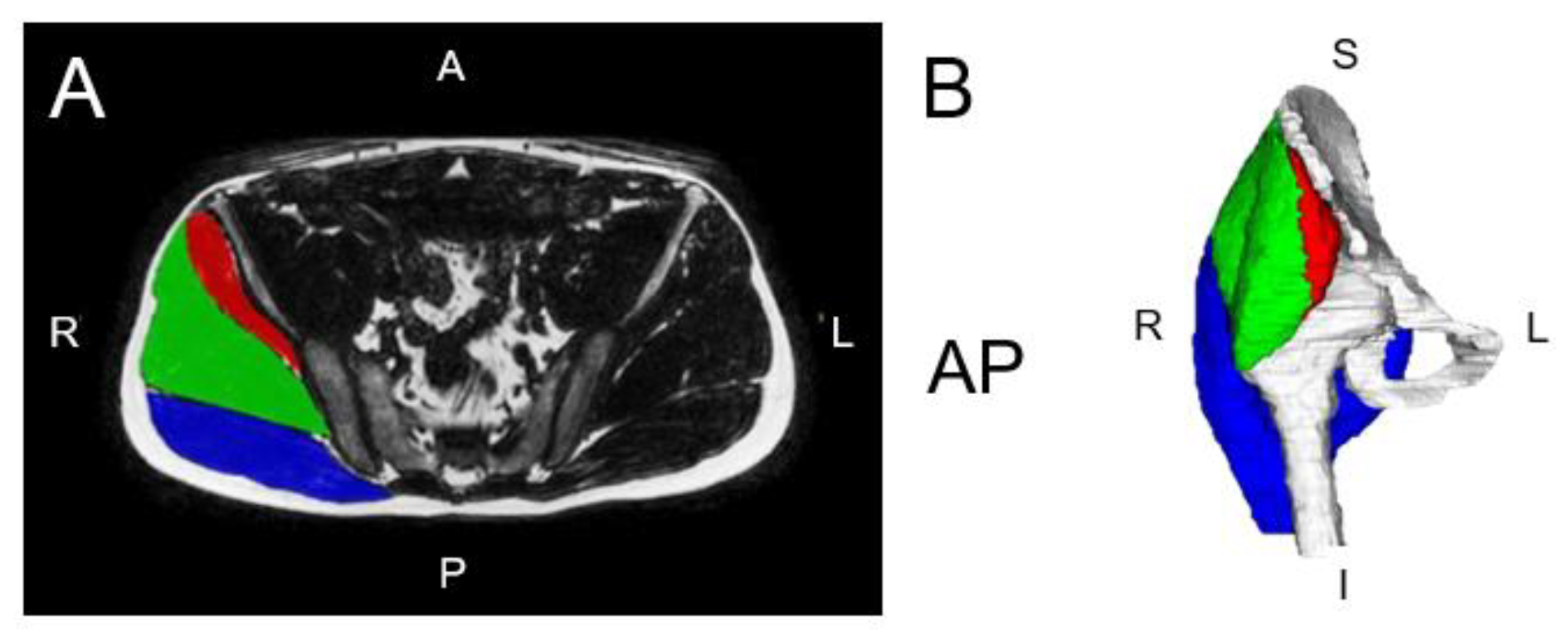
3.6. Gluteal Muscles
3.7. Thigh and Leg Musculature
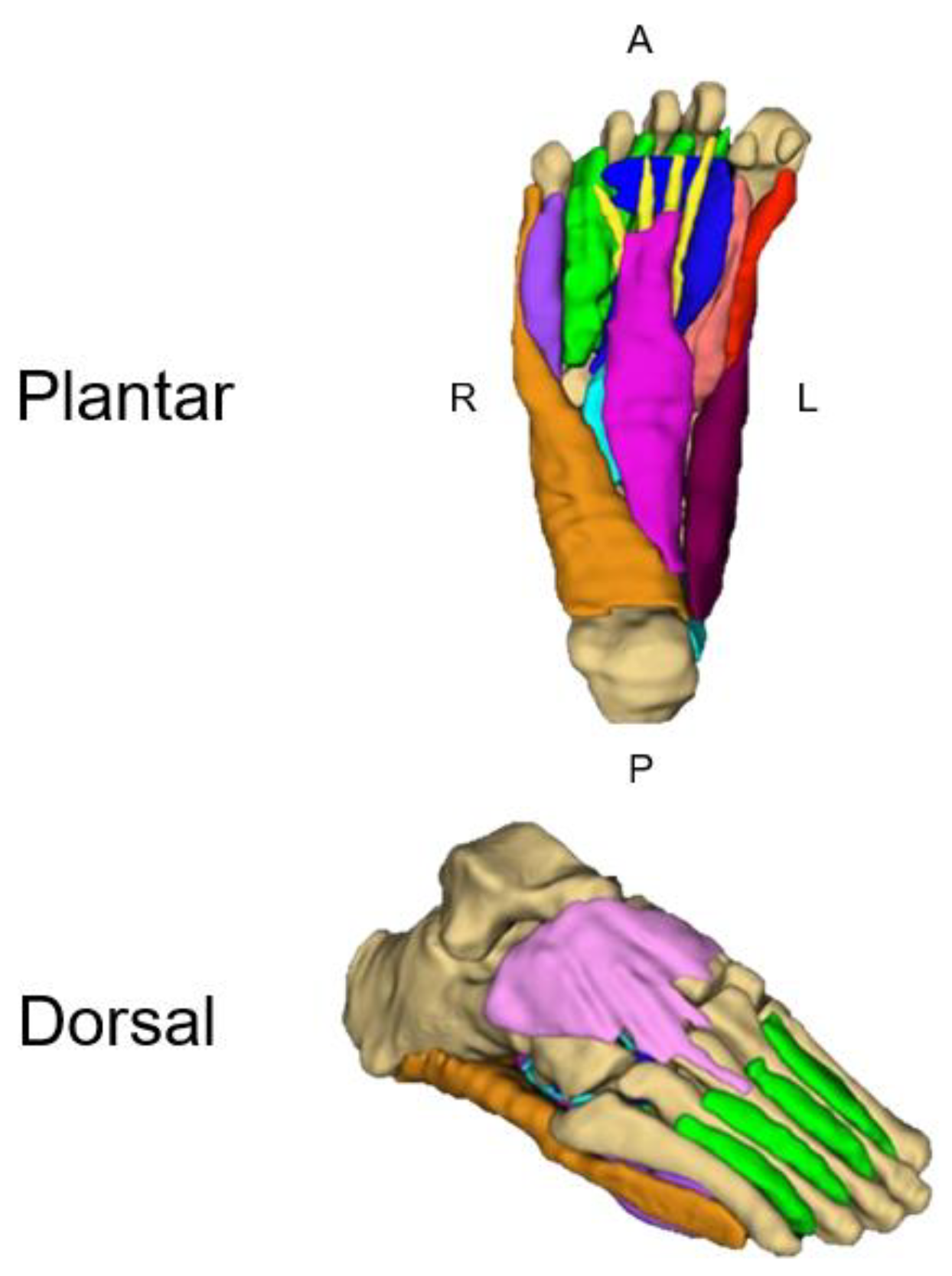
3.8. Foot and Ankle
4. Conditions and Disorders
4.1. Spinal Cord Injury
4.2. Sarcopenia and Frailty
Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy
4.3. Osteoarthritis
4.4. Diabetes
4.5. Cancer
4.6. Incontinence
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lube, J.; Cotofana, S.; Bechmann, I.; Milani, T.L.; Ozkurtul, O.; Sakai, T.; Stenke, H.; Hammer, N. Reference data on muscle volumes of healthy human pelvis and lower extremity muscles: An in vivo magnetic resonance imaging feasibility study. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2016, 38, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcon, M.; Berger, N.; Manoliu, A.; Fischer, M.A.; Nanz, D.; Andreisek, G.; Ulbrich, E.J. Normative values for volume and fat content of the hip abductor muscles and their dependence on side, age and gender in a healthy population. Skelet. Radiol. 2016, 45, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulbrich, E.J.; Nanz, D.; Leinhard, O.D.; Marcon, M.; Fischer, M.A. Whole-body adipose tissue and lean muscle volumes and their distribution across gender and age: MR-derived normative values in a normal-weight Swiss population. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentin, S.; Licka, T.; Elliott, J. Age and side-related morphometric MRI evaluation of trunk muscles in people without back pain. Man. Ther. 2015, 20, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, K.A.; Abbott, R.; Bojilov, V.; Smith, A.C.; Wasielewski, M.; Hastie, T.J.; Parrish, T.B.; Mackey, S.; Elliott, J.M. Multi-muscle deep learning segmentation to automate the quantification of muscle fat infiltration in cervical spine conditions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselink, E.; Elliott, J.; Coppieters, M.; Hancock, M.; Cronin, B.; Pool-Goudzwaard, A.; Weber, K.A. Convolutional neural networks for the automatic segmentation of lumbar paraspinal muscles in people with low back pain. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelke, K.; Chaudry, O.; Gast, L.; Eldib, M.A.; Wang, L.; Laredo, J.D.; Schett, G.; Nagel, A.M. Magnetic resonance imaging techniques for the quantitative analysis of skeletal muscle: State of the art. J. Orthop. Transl. 2023, 42, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-J.; He, J.; Zhao, F.-D.; Fang, X.-Q.; Zhou, L.-N.; Fan, S.-W. An assessment of the intra-and inter-reliability of the lumbar paraspinal muscle parameters using CT scan and magnetic resonance imaging. Spine 2011, 36, E868–E874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.M.; Sinclair, C.D.; Fischmann, A.; Machado, P.M.; Reilly, M.M.; Yousry, T.A.; Habil, M.; Thornton, J.S.; Hanna, M.G. MRI biomarker assessment of neuromuscular disease progression: A prospective observational cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 15, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, A.M.; Willcocks, R.J.; Triplett, W.T.; Forbes, S.C.; Daniels, M.J.; Chakraborty, S.; Lott, D.J.; Senesca, C.R.; Finanger, E.L.; Harrington, A.T.; et al. MR biomarkers predict clinical function in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology 2020, 94, e897–e909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, J.M.; Sinclair, C.D.; Fischmann, A.; Reilly, M.M.; Hanna, M.G.; Yousry, T.A.; Thornton, J.S. Reproducibility, and age, body-weight and gender dependency of candidate skeletal muscle MRI outcome measures in healthy volunteers. Eur. Radiol. 2014, 24, 1610–1620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Crawford, R.J.; Filli, L.; Elliott, J.; Nanz, D.; Fischer, M.; Marcon, M.; Ulbrich, E.J. Age-and level-dependence of fatty infiltration in lumbar paravertebral muscles of healthy volunteers. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornett, K.M.; Wojciechowski, E.; Sman, A.D.; Walker, T.; Menezes, M.P.; Bray, P.; Halaki, M.; Burns, J. MRI of the anterior compartment of the lower leg is a biomarker for weakness, disability and impaired gait in childhood Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Muscle Nerve 2019, 59, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselink, E.; Elliott, J.; Pool-Goudzwaard, A.; Coppieters, M.; Pevenage, P.; Di Ieva, A.; Weber, K.A. Quantifying lumbar paraspinal intramuscular fat: Accuracy and reliability of automated thresholding models. N. Am. Spine Soc. J. 2024, 17, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselink, E.O.; Pool-Goudzwaard, A.; De Leener, B.; Law, C.S.W.; Fenyo, M.B.; Ello, G.M.; Coppieters, M.W.; Elliott, J.W.; Mackey, S.; Weber, K.A. Investigating the associations between lumbar paraspinal muscle health and age, BMI, sex, physical activity and back pain using an automated computer-vision model: A UK biobank study. Spine J. 2024, 24, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Adad Alonso-Ortiz, E.; Abramovic, M.; Arneitz, C.; Atcheson, N.; Barlow, L.; Barry, R.L.; Barth, M.; Battiston, M.; Buchel, C. Generic acquisition protocol for quantitative MRI of the spinal cord. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 4611–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, M.; Reinke, A.; Bakas, S.; Farahani, K.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Landman, B.A.; Litjens, G.; Menze, B.; Ronneberger, O.; Summers, R.M.; et al. The medical segmentation decathlon. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Bai, H.; Ge, C.; Yang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Zhanng, L.; Ma, W.; Wan, X.; et al. Amos: A large-scale abdominal multi-organ benchmark for versatile medical image segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 36722–36732. [Google Scholar]
- Kavur, A.E.; Gezer, N.S.; Barış, M.; Aslan, S.; Conze, P.-H.; Groza, V.; Pham, D.D.; Chatterjee, S.; Ernst, P.; Özkan, S.; et al. CHAOS challenge-combined (CT-MR) healthy abdominal organ segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 69, 101950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, C.; Gallacher, J.; Allen, N.; Beral, V.; Burton, P.; Danesh, J.; Downey, P.; Elliott, P.; Green, J.; Landray, M.; et al. UK biobank: An open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, A.; Littlejohns, T.J.; Sudlow, C.; Doherty, N.; Adamska, L.; Sprosen, T.; Collins, R.; Allen, N.E. Comparison of sociodemographic and health-related characteristics of UK Biobank participants with those of the general population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 186, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozek, J.; Griffanti, L.; Lau, S.; Jenkinson, M. Normative models for neuroimaging markers: Impact of model selection, sample size and evaluation criteria. NeuroImage 2023, 268, 119864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutherford, S.; Barkema, P.; Tso, I.F.; Sripada, C.; Beckmann, C.F.; Ruhe, H.G.; Marquand, A.F. Evidence for embracing normative modeling. Elife 2023, 12, e85082. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, J.M.; Cornwall, J.; Kennedy, E.; Abbott, R.; Crawford, R.J. Towards defining muscular regions of interest from axial magnetic resonance imaging with anatomical cross-reference: Part II-cervical spine musculature. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2018, 19, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, J.M.; Smith, A.C.; Hoggarth, M.A.; Albin, S.R.; Weber, K.A.; Haager, M.; Fundaun, J.; Wasielewski, D.; Courtney, D.M.; Parrish, T.B. Muscle fat infiltration following whiplash: A computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging comparison. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, R.J.; Cornwall, J.; Abbott, R.; Elliott, J.M. Manually defining regions of interest when quantifying paravertebral muscles fatty infiltration from axial magnetic resonance imaging: A proposed method for the lumbar spine with anatomical cross-reference. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2017, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloney, M.; Smith, A.C.; Coffey, T.; Paliwal, M.; Dhaher, Y.; Parrish, T.; Elliott, J.; Smith, Z.A. Fatty infiltration of the cervical multifidus musculature and their clinical correlates in spondylotic myelopathy. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 57, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.C.; Parrish, T.B.; Hoggarth, M.A.; McPherson, J.G.; Tysseling, V.M.; Wasielewski, M.; Kim, T.E.; Hornby, T.G.; Elliott, J.M. Potential associations between chronic whiplash and incomplete spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord Ser. Cases 2015, 1, 15024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snodgrass, S.J.; Stanwell, P.; Weber, K.A.; Shepherd, S.; Kennedy, O.; Thompson, H.J.; Elliott, J.M. Greater muscle volume and muscle fat infiltrate in the deep cervical spine extensor muscles (multifidus with semispinalis cervicis) in individuals with chronic idiopathic neck pain compared to age and sex-matched asymptomatic controls: A cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 973. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.C.; Albin, S.R.; Abbott, R.; Crawford, R.J.; Hoggarth, M.A.; Wasielewski, M.; Elliott, J.M. Confirming the geography of fatty infiltration in the deep cervical extensor muscles in whiplash recovery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11471. [Google Scholar]
- Paliwal, M.; Weber, K.A.; Smith, A.C.; Elliott, J.M.; Muhammad, F.; Dahdaleh, N.S.; Bodurka, J.; Dhaher, Y.; Parrish, T.B.; Mackey, S.; et al. Fatty infiltration in cervical flexors and extensors in patients with degenerative cervical myelopathy using a multi-muscle segmentation model. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253863. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, K.A.; Smith, A.C.; Wasielewski, M.; Eghtesad, K.; Upadhyayula, P.A.; Wintermark, M.; Hastie, T.J.; Parrish, T.B.; Mackey, S.; Elliott, J.M. Deep learning convolutional neural networks for the automatic quantification of muscle fat infiltration following whiplash injury. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peolsson, A.; Karlsson, A.; Peterson, G.; Borén, H.; Zsigmond, P.; Elliott, J.M.; Leinhard, O.D. Morphology and composition of the ventral neck muscles in individuals with chronic whiplash related disorders compared to matched healthy controls: A cross-sectional case–control study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, N.; Dahlqvist Leinhard, O.; Elliott, J.M.; Peterson, G.; Borga, M.; Zsigmond, P.; Elliott, J.M.; Leinhard, O.D. Fatty infiltrate and neck muscle volume in individuals with chronic whiplash associated disorders compared to healthy controls—A cross sectional case–control study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, Y.; Uchiyama, Y.; Honda, K.; Yamashita, T.; Saito, S.; Domen, K. Age-related composition changes in swallowing-related muscles: A Dixon MRI study. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 33, 3205–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meheissen, M.A.; Mohamed, A.S.; Kamal, M.; Hernandez, M.; Volpe, S.; Elhalawani, H.; Barrow, M.P.; Ding, Y.; Wang, J.; Davuluri, R. A prospective longitudinal assessment of MRI signal intensity kinetics of non-target muscles in patients with advanced stage oropharyngeal cancer in relationship to radiotherapy dose and post-treatment radiation-associated dysphagia: Preliminary findings from a randomized trial. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 130, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wishart, L.R.; Ward, E.C.; Galloway, G. Advances in and applications of imaging and radiomics in head and neck cancer survivorship. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2023, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, D.; Ward, E.; Bogaardt, H.; Heard, R.; Martin-Harris, B.; Smith, A.; Elliott, J. Self-reported dysphagia and pharyngeal volume following whiplash injury. Dysphagia 2021, 36, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hutchison, A.; Nund, R.L.; Brown, B.; Ward, E.C.; Wishart, L. Using dosimetric information to guide dysphagia management in patients with head and neck cancer: Clinicians’ knowledge and experiences. Int. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2022, 24, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.; Thor, M.; Onochie, I.; Hesse, J.; Zakeri, K.; LoCastro, E.; Jiang, J.; Veeraraghavan, H.; Elguindi, S.; Lee, N.Y. Prospectively validated deep learning model for segmenting swallowing and chewing structures in CT. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 024001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsley, H.; Ganderton, C.; Arden, N.K.; Carr, A.J. Prevalence of rotator cuff tendon tears and symptoms in a Chingford general population cohort, and the resultant impact on UK health services: A cross-sectional observational study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e059175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, D.; Busija, L.; Page, R.S.; de Steiger, R.; Lorimer, M.; Ackerman, I.N. Lifetime Risk of Primary Shoulder Arthroplasty from 2008 to 2017: A Population-Level Analysis Using National Registry Data. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvin, A.C.; Egorova, N.; Harrison, A.K.; Moskowitz, A.; Flatow, E.L. National trends in rotator cuff repair. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2012, 94, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, A.; Hurworth, M.; O’Sullivan, P.; Mitchell, T.; Smith, A. Rising trends in surgery for rotator cuff disease in Western Australia. ANZ J. Surg. 2016, 86, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuye, I.O.; Jain, N.B.; Warner, L.; Herndon, J.H.; Warner, J.J. Economic evaluations in shoulder pathologies: A systematic review of the literature. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2012, 21, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Judge, A.; Murphy, R.; Maxwell, R.; Arden, N.; Carr, A. Temporal trends and geographical variation in the use of subacromial decompression and rotator cuff repair of the shoulder in England. Bone Jt. J. 2014, 96, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, J.; Walton, D.; MacDermid, J.C.; Athwal, G.S. Predictors of outcomes after rotator cuff repair—A meta-analysis. J. Hand Ther. 2017, 30, 276–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapner, P.L.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, T.; Athwal, G.S. Rotator cuff fatty infiltration and atrophy are associated with functional outcomes in anatomic shoulder arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.A.; Walch, G.; Pape, G.; Gohlke, F.; Favard, L. Secondary rotator cuff dysfunction following total shoulder arthroplasty for primary glenohumeral osteoarthritis: Results of a multicenter study with more than five years of follow-up. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2012, 94, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kälin, P.S.; Crawford, R.J.; Marcon, M.; Manoliu, A.; Bouaicha, S.; Fischer, M.A.; Ulbrich, E.J. Shoulder muscle volume and fat content in healthy adult volunteers: Quantification with DIXON MRI to determine the influence of demographics and handedness. Skelet. Radiol. 2018, 47, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Freeman, T.H.; Kim, P.; Kuhn, J.E.; Garriga, G.A.; Khazzam, M.; Higgins, L.D.; Matzkin, E.; Baumgarten, K.M.; Bishop, J.Y. Obesity and sex influence fatty infiltration of the rotator cuff: The Rotator Cuff Outcomes Workgroup (ROW) and Multicenter Orthopaedic Outcomes Network (MOON) cohorts. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2022, 31, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, N.E.; Anema, J.R.; Cherkin, D.; Chou, R.; Cohen, S.P.; Gross, D.P.; Ferreira, P.H.; Fritz, J.M.; Koes, B.W.; Peul, W.; et al. Prevention and treatment of low back pain: Evidence, challenges, and promising directions. Lancet 2018, 391, 2368–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.L.; de Luca, K.; Haile, L.M.; Steinmetz, J.D.; Culbreth, G.T.; Cross, M.; Kopec, J.A.; Ferreira, P.H.; Blyth, F.M.; Buchbinder, R.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of low back pain, 1990–2020, its attributable risk factors, and projections to 2050: A systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Rheumatol. 2023, 5, e316–e329. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, C.; Underwood, M.; Buchbinder, R. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet 2017, 389, 736–747. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, R.J.; Fortin, M.; Weber, I.I.K.A.; Smith, A.; Elliott, J.M. Are magnetic resonance imaging technologies crucial to our understanding of spinal conditions? J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2019, 49, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemeyer, F.; Zanker, A.; Jonas, R.; Tao, Y.; Galbusera, F.; Wilke, H.-J. An externally validated deep learning model for the accurate segmentation of the lumbar paravertebral muscles. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 2156–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, P.W.; Bailey, J.F.; Fortin, M.; Battié, M.C. Paraspinal muscle imaging measurements for common spinal disorders: Review and consensus-based recommendations from the ISSLS degenerative spinal phenotypes group. Eur. Spine J. 2021, 30, 3428–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallaway, A.; Kite, C.; Griffen, C.; Duncan, M.; Tallis, J.; Renshaw, D.; Hattersley, J. Age-related degeneration of the lumbar paravertebral muscles: Systematic review and three-level meta-regression. Exp. Gerontol. 2020, 133, 110856. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fortin, M.; Videman, T.; Gibbons, L.E.; Battie, M.C. Paraspinal muscle morphology and composition: A 15-yr longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging study. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, E.; Hides, J.; Elliott, J.M.; Hoggarth, M.A.; Zange, J.; Lindsay, K.; Debuse, D.; Winnard, A.; Beard, D.; Cook, J.A.; et al. Intramuscular lipid concentration increased in localized regions of the lumbar muscles following 60 day bedrest. Spine J. 2022, 22, 616–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, R.J.; Elliott, J.M.; Volken, T. Change in fatty infiltration of lumbar multifidus, erector spinae, and psoas muscles in asymptomatic adults of Asian or Caucasian ethnicities. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 26, 3059–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, R.J.; Volken, T.; Valentin, S.; Melloh, M.; Elliott, J.M. Rate of lumbar paravertebral muscle fat infiltration versus spinal degeneration in asymptomatic populations: An age-aggregated cross-sectional simulation study. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 2016, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattab, K.; Dziesinski, L.K.; Crawford, R.; Ballatori, A.; Nyayapati, P.; Krug, R.; Fields, A.; O’Neill, C.W.; Lotz, J.C.; Bailey, J.F. Spatial distribution of fat infiltration within the paraspinal muscles: Implications for chronic low back pain. Eur. Spine J. 2022, 31, 2875–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.-M.; Dai, F.-F.; Yuan, M.-Q.; Yang, D.-Y.; Zheng, Y.-J.; Cheng, Y.-X. Advances in molecular mechanisms of pelvic organ prolapse. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1009. [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi, A.; Richardson, C.; Stanton, W.; Durbridge, G.; Donnelly, W.; Hides, J. The association between degenerative hip joint pathology and size of the gluteus medius, gluteus minimus and piriformis muscles. Man. Ther. 2009, 14, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrenson, P.; Crossley, K.; Vicenzino, B.; Hodges, P.; James, G.; Croft, K.; King, M.G.; Semciw, A.I. Muscle size and composition in people with articular hip pathology: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 181–195. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, V.; De Martino, E.; Hides, J.; Cable, G.; Elliott, J.M.; Hoggarth, M.; Zange, J.; Lindsay, K.; Debuse, D.; Winnard, A.; et al. Gluteal muscle atrophy and increased intramuscular lipid concentration are not mitigated by daily artificial gravity following 60-day head-down tilt bed rest. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perraton, Z.; Lawrenson, P.; Mosler, A.B.; Elliott, J.M.; Weber, K.A.; Flack, N.A.; Cornwall, J.; Crawford, R.J.; Stewart, C.; Semciw, A.I. Towards defining muscular regions of interest from axial magnetic resonance imaging with anatomical cross-reference: A scoping review of lateral hip musculature. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2022, 23, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perraton, Z.; Mosler, A.B.; Lawrenson, P.R.; Weber, K., II; Elliott, J.M.; Wesselink, E.O.; Crossley, K.M.; Kemp, J.L.; Stewart, C.; Girdwood, M.; et al. The association between lateral hip muscle size/intramuscular fat infiltration and hip strength in active young adults with long standing hip/groin pain. Phys. Ther. Sport 2024, 65, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linge, J.; Petersson, M.; Forsgren, M.F.; Sanyal, A.J.; Dahlqvist Leinhard, O. Adverse muscle composition predicts all-cause mortality in the UK Biobank imaging study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2021, 12, 1513–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, K.; Ayers, C.; Butler, J.; Neeland, I.; Kritchevsky, S.; Pandey, A.; Barton, G.; Berry, J.D. Association between thigh muscle fat infiltration and incident heart failure: The Health ABC Study. Heart Fail. 2022, 10, 485–493. [Google Scholar]
- Farrow, M.; Biglands, J.; Tanner, S.F.; Clegg, A.; Brown, L.; Hensor, E.; O’Connor, P.; Emery, P.; Tan, A. The effect of ageing on skeletal muscle as assessed by quantitative MR imaging: An association with frailty and muscle strength. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2021, 33, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bas, J.; Ogier, A.C.; Le Troter, A.; Delmont, E.; Leporq, B.; Pini, L.; Guye, M.; Parlanti, A.; Lefebvre, M.-N.; Bendahan, D.; et al. Fat fraction distribution in lower limb muscles of patients with CMT1A: A quantitative MRI study. Neurology 2020, 94, e1480–e1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, Y.; Takashima, H. Clinical genetics of Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 68, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogna, C.; Cristiano, L.; Verdolotti, T.; Pichiecchio, A.; Cinnante, C.; Sansone, V.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Berardinelli, A.; Garibaldi, M.; Antonini, G.; et al. MRI patterns of muscle involvement in type 2 and 3 spinal muscular atrophy patients. J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 898–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, E.; García, A.; Combarros, O.; Berciano, J. Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease type 1A duplication: Spectrum of clinical and magnetic resonance imaging features in leg and foot muscles. Brain 2006, 129, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thukral, N.; Kaur, J.; Malik, M. A systematic review on foot muscle atrophy in patients with diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries. 2023, 43, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, J.W.; Menz, H.B.; Whittaker, G.A.; Landorf, K.B. Muscle function and muscle size differences in people with and without plantar heel pain: A systematic review. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2019, 49, 925–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulodi, N.; Azadinia, F.; Ebrahimi-Takamjani, I.; Atlasi, R.; Jalali, M.; Kamali, M. The functional capacity and morphological characteristics of the intrinsic foot muscles in subjects with Hallux Valgus deformity: A systematic review. Foot 2020, 45, 101706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franettovich Smith, M.M.; Elliott, J.M.; Al-Najjar, A.; Weber, K.A.; Hoggarth, M.A.; Vicenzino, B.; Hodges, P.W.; Collins, N.J. New insights into intrinsic foot muscle morphology and composition using ultra-high-field (7-Tesla) magnetic resonance imaging. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2021, 22, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.J.; Apple Jr, D.F.; Hillegass, E.A.; Dudley, G.A. Influence of complete spinal cord injury on skeletal muscle cross-sectional area within the first 6 months of injury. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1999, 80, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.D.; Craven, B.C.; Thabane, L.; Papaioannou, A.; Adachi, J.D.; Giangregorio, L.M. Does muscle atrophy and fatty infiltration plateau or persist in chronic spinal cord injury? J. Clin. Densitom. 2018, 21, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.C.; Weber, K.A.; Parrish, T.B.; Hornby, T.G.; Tysseling, V.M.; McPherson, J.G.; Wasielewski, M.; Elliott, J.M. Ambulatory function in motor incomplete spinal cord injury: A magnetic resonance imaging study of spinal cord edema and lower extremity muscle morphometry. Spinal Cord 2017, 55, 672–678. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, C.D.; Craven, B.; Thabane, L.; Laing, A.; Frank-Wilson, A.; Kontulainen, S.; Papaioannou, A.; Adachi, J.; Giangregorio, L. Lower-extremity muscle atrophy and fat infiltration after chronic spinal cord injury. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2015, 15, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Bekhet, A.H.; Jahan, A.M.; Bochkezanian, V.; Musselman, K.E.; Elsareih, A.A.; Gorgey, A.S. Effects of electrical stimulation training on body composition parameters after spinal cord injury: A systematic review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 103, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatas, M.P.; Lester, R.M.; Khan, M.R.; Gorgey, A.S. Semi-automated segmentation of magnetic resonance images for thigh skeletal muscle and fat using threshold technique after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1787. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mesbah, S.; Shalaby, A.M.; Stills, S.; Soliman, A.M.; Willhite, A.; Harkema, S.J.; Rejc, E.; El-Baz, A.S. Novel stochastic framework for automatic segmentation of human thigh MRI volumes and its applications in spinal cord injured individuals. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216487. [Google Scholar]
- Gillon, A.; Steel, C.; Cornwall, J.; Sheard, P. Increased nuclear permeability is a driver for age-related motoneuron loss. Geroscience 2020, 42, 833–847. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, T.M.; Schofield, M.R.; Cornwall, J.; Sheard, P.W. Modelling multilevel spatial behaviour in binary-mark muscle fibre configurations. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2019, 13, 1329–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, A.; Young, J.; Iliffe, S.; Rikkert, M.O.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in elderly people. Lancet 2013, 381, 752–762. [Google Scholar]
- Sierra, F. The emergence of geroscience as an interdisciplinary approach to the enhancement of health span and life span. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, N.; Elliott, J.M.; Weber, M.H.; Fehlings, M.G.; Fortin, M. Morphological Changes of Deep Extensor Neck Muscles in Relation to the Maximum Level of Cord Compression and Canal Compromise in Patients with Degenerative Cervical Myelopathy. Glob. Spine J. 2022, 14, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Burden of Disease (GBD). 2019. Available online: https://www.healthdata.org/research-analysis/gbd (accessed on 18 July 2023).
- Felson, D.T.; Lawrence, R.C.; Dieppe, P.A.; Hirsch, R.; Helmick, C.G.; Jordan, J.M.; Kington, R.S.; Lane, N.E.; Nevitt, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Osteoarthritis: New insights. Part 1: The disease and its risk factors. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 133, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culvenor, A.G.; Wirth, W.; Roth, M.; Hunter, D.J.; Eckstein, F. Predictive capacity of thigh muscle strength in symptomatic and/or radiographic knee osteoarthritis progression–data from the FNIH OA biomarkers consortium. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2016, 95, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemnitz, J.; Wirth, W.; Eckstein, F.; Culvenor, A.G. The role of thigh muscle and adipose tissue in knee osteoarthritis progression in women: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 1190–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajer, B.; Dolatshahi, M.; Moradi, K.; Najafzadeh, N.; Eng, J.; Zikria, B.; Wan, M.; Cao, X.; Roemer, F.W.; Guermazi, A.; et al. Role of thigh muscle changes in knee osteoarthritis outcomes: Osteoarthritis initiative data. Radiology 2022, 305, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, H.; Poulsen, P.L.; Mogensen, C.E.; Jakobsen, J. Isokinetic muscle strength in long-term IDDM patients in relation to diabetic complications. Diabetes 1996, 45, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A. Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Med. Clin. N. Am 2004, 88, 787–835. [Google Scholar]
- Monaco, C.M.; Perry, C.G.; Hawke, T.J. Diabetic Myopathy: Current molecular understanding of this novel neuromuscular disorder. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2017, 30, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Haehling, S.; Anker, S.D. Prevalence, incidence and clinical impact of cachexia: Facts and numbers—Update 2014. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2014, 5, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordes, M.; Larsson, L.; Engstrand, L.; Löhr, J.-M. Pancreatic cancer cachexia: Three dimensions of a complex syndrome. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1623–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milsom, I.; Gyhagen, M. The prevalence of urinary incontinence. Climacteric 2019, 22, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharucha, A.E.; Knowles, C.H.; Mack, I.; Malcolm, A.; Oblizajek, N.; Rao, S.; Scott, S.M.; Shin, A.; Enck, P. Faecal incontinence in adults. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2022, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.-S.; Sivakumaran, Y.; Nassar, N.; Gladman, M.A. Fecal incontinence: Community prevalence and associated factors—A systematic review. Dis. Colon Rectum 2015, 58, 1194–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.D. Pelvic organ prolapse. BMJ 2016, 354, i3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharucha, A.; Fletcher, J.; Harper, C.; Hough, D.; Daube, J.; Stevens, C.; Seide, B.; Riederer, S.; Zinsmeister, A. Relationship between symptoms and disordered continence mechanisms in women with idiopathic faecal incontinence. Gut 2005, 54, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, D.R. The human genome project—An overview. Med. Res. Rev. 2000, 20, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McKay, M.J.; Weber, K.A., II; Wesselink, E.O.; Smith, Z.A.; Abbott, R.; Anderson, D.B.; Ashton-James, C.E.; Atyeo, J.; Beach, A.J.; Burns, J.; et al. MuscleMap: An Open-Source, Community-Supported Consortium for Whole-Body Quantitative MRI of Muscle. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10110262
McKay MJ, Weber KA II, Wesselink EO, Smith ZA, Abbott R, Anderson DB, Ashton-James CE, Atyeo J, Beach AJ, Burns J, et al. MuscleMap: An Open-Source, Community-Supported Consortium for Whole-Body Quantitative MRI of Muscle. Journal of Imaging. 2024; 10(11):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10110262
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcKay, Marnee J., Kenneth A. Weber, II, Evert O. Wesselink, Zachary A. Smith, Rebecca Abbott, David B. Anderson, Claire E. Ashton-James, John Atyeo, Aaron J. Beach, Joshua Burns, and et al. 2024. "MuscleMap: An Open-Source, Community-Supported Consortium for Whole-Body Quantitative MRI of Muscle" Journal of Imaging 10, no. 11: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10110262
APA StyleMcKay, M. J., Weber, K. A., II, Wesselink, E. O., Smith, Z. A., Abbott, R., Anderson, D. B., Ashton-James, C. E., Atyeo, J., Beach, A. J., Burns, J., Clarke, S., Collins, N. J., Coppieters, M. W., Cornwall, J., Crawford, R. J., De Martino, E., Dunn, A. G., Eyles, J. P., Feng, H. J., ... Elliott, J. M. (2024). MuscleMap: An Open-Source, Community-Supported Consortium for Whole-Body Quantitative MRI of Muscle. Journal of Imaging, 10(11), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging10110262








