Laser Scanners for High-Quality 3D and IR Imaging in Cultural Heritage Monitoring and Documentation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. ITR Technology and Systems
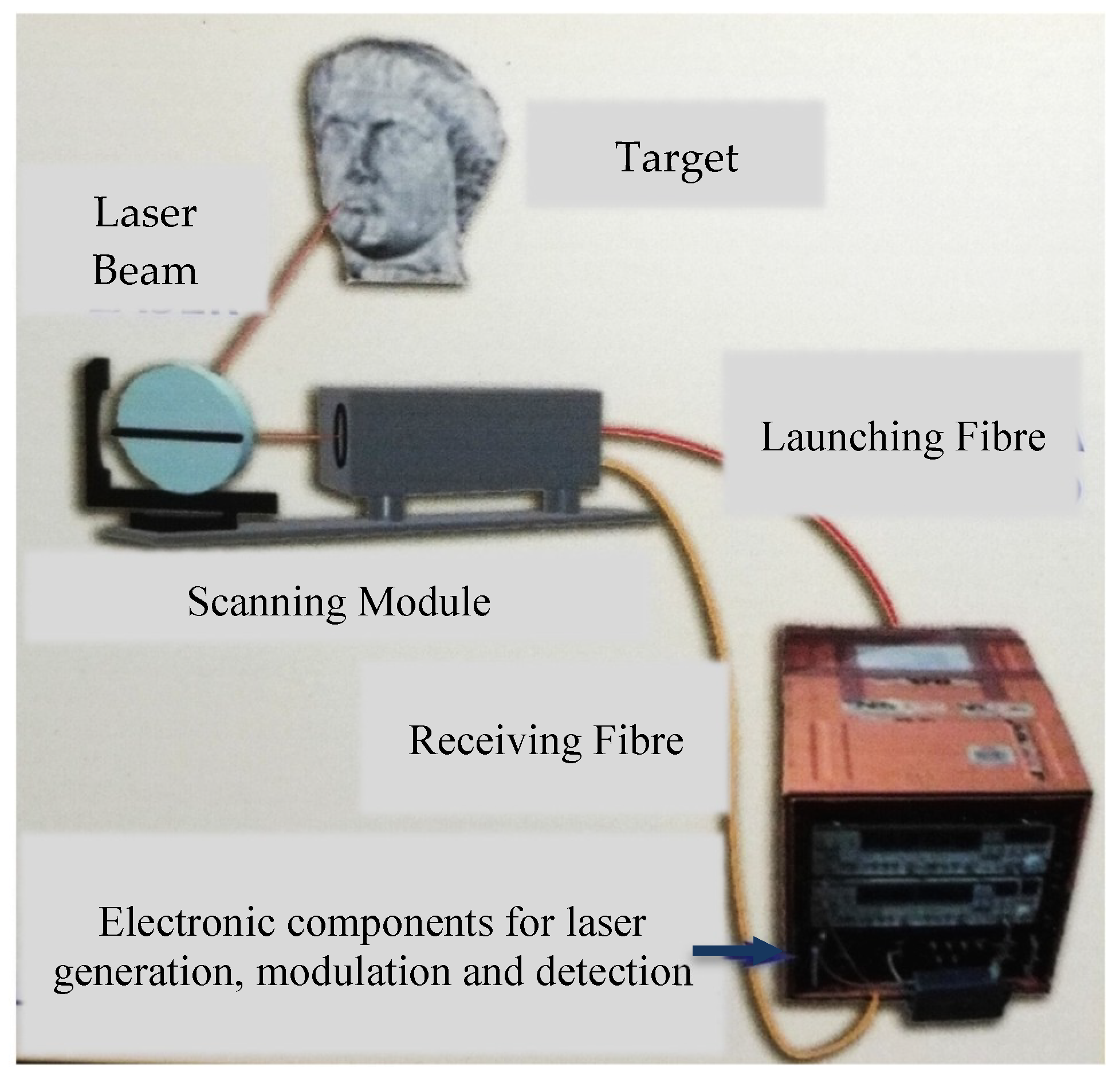
2.1. RGB-ITR Scanner
2.2. IR-ITR Prototype
2.3. Custom Software
2.3.1. ScanSystem
2.3.2. itrAnalyzer
3. Case Studies
3.1. In Situ Acquisitions
- Saint Brizio Chapel, Orvieto Cathedral (Viterbo, Italy);
- Greek Chapel, Priscilla Catacombs (Rome, Italy);
- Tower room, Saint Sebastian Gate, Aurelian Walls (Rome, Italy);
- Egyptian wood sarcophagus (Milan, Italy).
3.1.1. Saint Brizio Chapel in Orvieto Cathedral
3.1.2. Greek Chapel in Priscilla Catacombs
3.1.3. Tower Room in Saint Sebastian Gate of the Aurelian Walls
3.1.4. Egyptian Wooden Sarcophagus
3.2. Laboratory Tests
4. Results
4.1. 3D Modelling and Image Enhancement
4.2. Infrared Imaging
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anno Europeo del Patrimonio Culturale 2018. Available online: https://europa.eu/cultural-heritage/about_it (accessed on June 2018).
- Stylianidis, E.; Remondino, F. 3D Recording, Documentation and Management of Cultural Heritage; Whittles Publishing: Dunbeath, UK, 2016; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fioravanti, M.; Mecca, S. The Safeguard of Cultural Heritage. A Challenge from the Past for the Europe of Tomorrow; Firenze University Press: Florence, Italy, 2012; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Whitmore, P.M.; Bernstein, J.; Khandekar, N.; Carlson, J.; Koestler, R.; Wheeler, G.S.; National Science Foundation (U.S.). Division of Human Resource Development; Andrew W. Mellon Foundation. Conservation Science Research: Activities, Needs, and Funding Opportunities; National Science Foundation: Arlington, VA, USA, 2005.
- Georgopoulos, A.; Stathopoulou, E.K. Data Acquisition for 3D Geometric Recording: State of the Art and Recent Innovations; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, M.; Robson, S. 3D colour imaging for cultural heritage artefacts. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 38, 288–292. [Google Scholar]
- Remondino, F.; Rizzi, A.; Jimenez, B.; Agugiaro, G.; Baratti, G.; De Amicis, R. The Etruscans in 3D: From Space to Underground Underwater Camera Calibration View Project iTour-Intelligent Transport System for Optimized URban Trips View Project the Etruscans in 3D: From Space to Underground; Czech Technical University in Prague: Praha, Czechia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Remondino, F. Image-based 3D modelling: A review. Photogramm. Rec. 2006, 21, 269–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehler, W.; Marbs, A. 3D Scanning and Photogrammetry for Heritage Recording: A Comparison. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Gävle, Sweden, 7–9 June 2004; pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzi, A.; Voltolini, F.; Remondino, F.; Girardi, S. Optical Measurement Techniques for the Digital Preservation, Documentation and Analysis of Cultural Heritage. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2007, 36, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Blais, F. Review of 20 years of range sensor development. J. Electron. Imaging 2004, 13, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santos, P.; Ritz, M.; Fuhrmann, C.; Fellner, D. 3D mass digitization: A milestone for archeological documentation. Virtual Archaeol. Rev. 2017, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosché, F.; Forster, A.; Valero, E. 3D Surveying Technologies and Applications: Point Clouds and Beyond Historic Digital Survey II-Project Extension: Digital Data Acquisition and Processing for Historic Building Fabric Condition Survey; Interpretation, Machine Learning and Scan to BIM View; Heriot-Watt University: Edinburgh, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzi, A.; Voltolini, F.; Girardi, S.; Gonzo, L.; Remondino, F.; Kessler-irst, F.B. Digital Preservation, Documentation and Analysis of Paintings, Monuments and Large Cultural Heritage with Infrared Technology, Digital Cameras and Range Sensors. In Proceedings of the XXI International CIPA Symposium, Athens, Greece, 1–6 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Guarnieri, A.; Pirotti, F.; Pontin, M.; Vettore, A. Combined 3D Surveying Techniques for Structural Analysis Applications; ISPRS Archives: Mestre-Venice, Italy, 2005; Volume 36. [Google Scholar]
- Pieraccini, M.; Guidi, G.; Atzeni, C. 3D digitizing of cultural heritage. J. Cult. Herit. 2001, 2, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micoli, L.; Guidi, G.; Angheleddu, D.; Russo, M. A multidisciplinary approach to 3D survey and reconstruction of historical buildings. In Proceedings of 2013 Digital Heritage International Congress (Federating 19th Int’l VSMM, 10th Eurographics GCH, & 2nd UNESCO Memory of the World Conferences; Plus Special Sessions from CAA, Arqueológica 2.0, Space2Place, ICOMOS ICIP & CIPA, EU Projects, et al.). UNESCO/IEEE/EG; IEEE: Marseille, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Remondino, F. Heritage recording and 3D modeling with photogrammetry and 3D scanning. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 1104–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hain, M.; Bartl, J.; Jacko, V. Multispectral analysis of cultural heritage artefacts. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2003, 3, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Del Pozo, S.; Rodríguez-Gonzálvez, P.; Sánchez-Aparicio, L.J.; Muñoz-Nieto, A. Multispectral Imaging in Cultural Heritage Conservation. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2017, XLII-2/W5, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, R.; Fovo, A.D.; Striova, J.; Pezzati, L.; Pampaloni, E.; Raffaelli, M.; Barucci, M. Application of non-invasive optical monitoring methodologies to follow and record painting cleaning processes. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2015, 121, 957–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Saunders, D.; Cupitt, J. A new multispectral imaging system for examining paintings. J. Imaging Sci. Technol. 2005, 49, 551–562. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, E.M. Imaging Techniques in Conservation. J. Conserv. Mus. Stud. 2013, 10, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siltanen, S.; Robson, S.; MacDonald, L.; Garside, D.; Evans, R. Spectral and 3D cultural heritage documentation using a modified camera. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, XLII-2, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar]
- Cosentino, A. Infrared Technical Photography for Art. E-Preserv. Sci. 2016, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Cosentino, A. Multispectral imaging system using 12 interference filters for mapping pigments. Conserv. Patrim. 2015, 21, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vitorino, T.; Casini, A.; Cucci, C.; Marcello, P.; Stefani, L. When It Is Not Only About Color: The Importance of Hyperspectral Imaging Applied to the Investigation of Paintings. In Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop, CCIW 2017, Milan, Italy, 29–31 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- De Collibus, M.F.; Fornetti, G.; Guarneri, M.; Paglia, E.; Poggi, C.; Ricci, R. ITR: An AM laser range finding system for 3D imaging and multi-sensor data integration. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Sensing Technology, Palmerston North, New Zealand, 21–23 November 2005; pp. 641–646. [Google Scholar]
- Fantoni, R.; Almaviva, S.; Caneve, L.; Caponero, M.; Colao, F.; de Collibus, M.F.; Fiorani, L.; Fornetti, G.; Francucci, M.; Guarneri, M.; et al. Laser scanners for remote diagnostic and virtual fruition of cultural heritage. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2017, 49, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneve, L.; Guarneri, M.; Lai, A.; Spizzichino, V.; Ceccarelli, S.; Mazzei, B. Non-Destructive Laser Based Techniques for Biodegradation Analysis in Cultural Heritage; Aipnd: Turin, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, R.; de Dominicis, L.; de Collibus, M.F.; Fornetti, G. RGB-ITR: An amplitude-modulated 3D colour laser scanner for cultural heritage applications. In Proceedings of the Laser Conservation Artworks VIII International Conference, Sibiu, Romania, 21–15 September 2009; pp. 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Poujouly, S.P.; Journet, B. A twofold modulation frequency laser range finder. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Opt. 2002, 4, S356–S363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitzan, D.; Brain, A.E.; Duda, R.O. The Measurement and Use of Registered Reflectance and Range Data in Scene Analysis. Proc. IEEE 1977, 65, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarneri, M.; De Dominicis, L.; De Collibus, M.F.; Fornetti, G.; Francucci, M.; Nuvoli, M.; Danielis, A.; Mencattini, A. Imaging topological radar technology as a general purpose instrument for remote colorimetric assessment, structural security, cataloguing, and dissemination. Stud. Conserv. 2015, 60, S134–S142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielis, A.; Guarneri, M.; Francucci, M.; de Collibus, M.F.; Fornetti, G.; Mencattini, A. A Quadratic Model with Nonpolynomial Terms for Remote Colorimetric Calibration of 3D Laser Scanner Data Based on Piecewise Cubic Hermite Polynomials. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 606948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, M.; Cigola, M. Colorimetric Study on Optical Data from 3D Laser Scanner Prototype for Cultural Heritage Applications. In New Activities for Cultural Heritage; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 190–199. [Google Scholar]
- Oleari, C. Misurare il Colore; Hoepli: Milano, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zanchi, M. Signorelli; Dossier d’; Giunti: Firenze, Italy, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vasari, G. Le Vite Dei Più Eccellenti Pittori, Scultori e Architetti; Newton Compton Ed.: Roma, Italy, 2016; pp. 550–567. [Google Scholar]
- Grussenmeyer, P.; Landes, T.; Boegtle, T.; Ringle, K. Comparison methods of terrestrial laser scanning, photogrammetry and tacheometry data for recording of cultural heritage buildings. ISPRS Congr. 2008, 37, 213–218. [Google Scholar]
- Catacombe di Priscilla. Available online: http://www.catacombepriscilla.com/ (accessed on July 2018).
- Scatigno, C.; Gaudenzi, S.; Sammartino, M.P.; Visco, G. A microclimate study on hypogea environments of ancient roman building. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zammit, G.; Sánchez-Moral, S.; Albertano, P. Bacterially mediated mineralisation processes lead to biodeterioration of artworks in Maltese catacombs. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 2773–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Systems Standford Research, “About Lock-In Amplifiers”; Application Note, No. 408; Stanford Research Systems, Inc.: Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 1–9.
- Montesanti, A. Le Mura Aureliane. Storia Della Cinta Difensiva di Roma. Available online: http://www.instoria.it/home/mura_aureliane_I.htm (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Cardilli, L.; Coarelli, F.; Pietrangeli, C.; Sartorio, G.P. Mura e Porte di Roma Antica Roma; Editore Colombo: Roma, Italy, 1995. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Thorlabs. Laser Viewing Cards; Thorlabs: Newton, NJ, USA, 2014; p. 19180. [Google Scholar]
- Guarneri, M.; Ceccarelli, S.; Ciaffi, M. Multi-wavelengths 3D laser scanner for investigation and reconstruction of 19th century charcoal inscriptions. In Proceedings of the IMEKO International Conference on Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage, Lecce, Italy, 23–25 October 2017; pp. 161–165. [Google Scholar]















| Target | Acquisition Time | Minimum Angular Step | Distance Target/System | Critical Issues |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The San Brizio Chapel | ~26 h (day and night) | 0.14 mrad | 4 ÷ 9 m | Excessive brightness |
| The Greek Chapel | ~190 h (day and night) | 0.07 ÷ 0.035 mrad | 3 ÷ 6 m | High humidity and reduced working space |
| The Saint Sebastian Gate | ~130 h (day and night) | 0.14 ÷ 0.07 mrad | 5 ÷ 11 m | Excessive brightness and small inscriptions |
| Egyptian sarcophagus | ~70 h (day and night) | 0.07 mrad | Less than 3 m | Irregular surface and reduced distance |
| Watercolor canvas | 1 h and 45 min | 0.035 mrad | 10 m | Unknown layering and watercolor |
| Acrylics canvas | 40 min | 0.035 mrad | 5 m | Unknown layering and acrylic colors |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceccarelli, S.; Guarneri, M.; Ferri de Collibus, M.; Francucci, M.; Ciaffi, M.; Danielis, A. Laser Scanners for High-Quality 3D and IR Imaging in Cultural Heritage Monitoring and Documentation. J. Imaging 2018, 4, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging4110130
Ceccarelli S, Guarneri M, Ferri de Collibus M, Francucci M, Ciaffi M, Danielis A. Laser Scanners for High-Quality 3D and IR Imaging in Cultural Heritage Monitoring and Documentation. Journal of Imaging. 2018; 4(11):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging4110130
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeccarelli, Sofia, Massimiliano Guarneri, Mario Ferri de Collibus, Massimo Francucci, Massimiliano Ciaffi, and Alessandro Danielis. 2018. "Laser Scanners for High-Quality 3D and IR Imaging in Cultural Heritage Monitoring and Documentation" Journal of Imaging 4, no. 11: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging4110130
APA StyleCeccarelli, S., Guarneri, M., Ferri de Collibus, M., Francucci, M., Ciaffi, M., & Danielis, A. (2018). Laser Scanners for High-Quality 3D and IR Imaging in Cultural Heritage Monitoring and Documentation. Journal of Imaging, 4(11), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging4110130





