An Update of the Possible Applications of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Dentistry: A Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
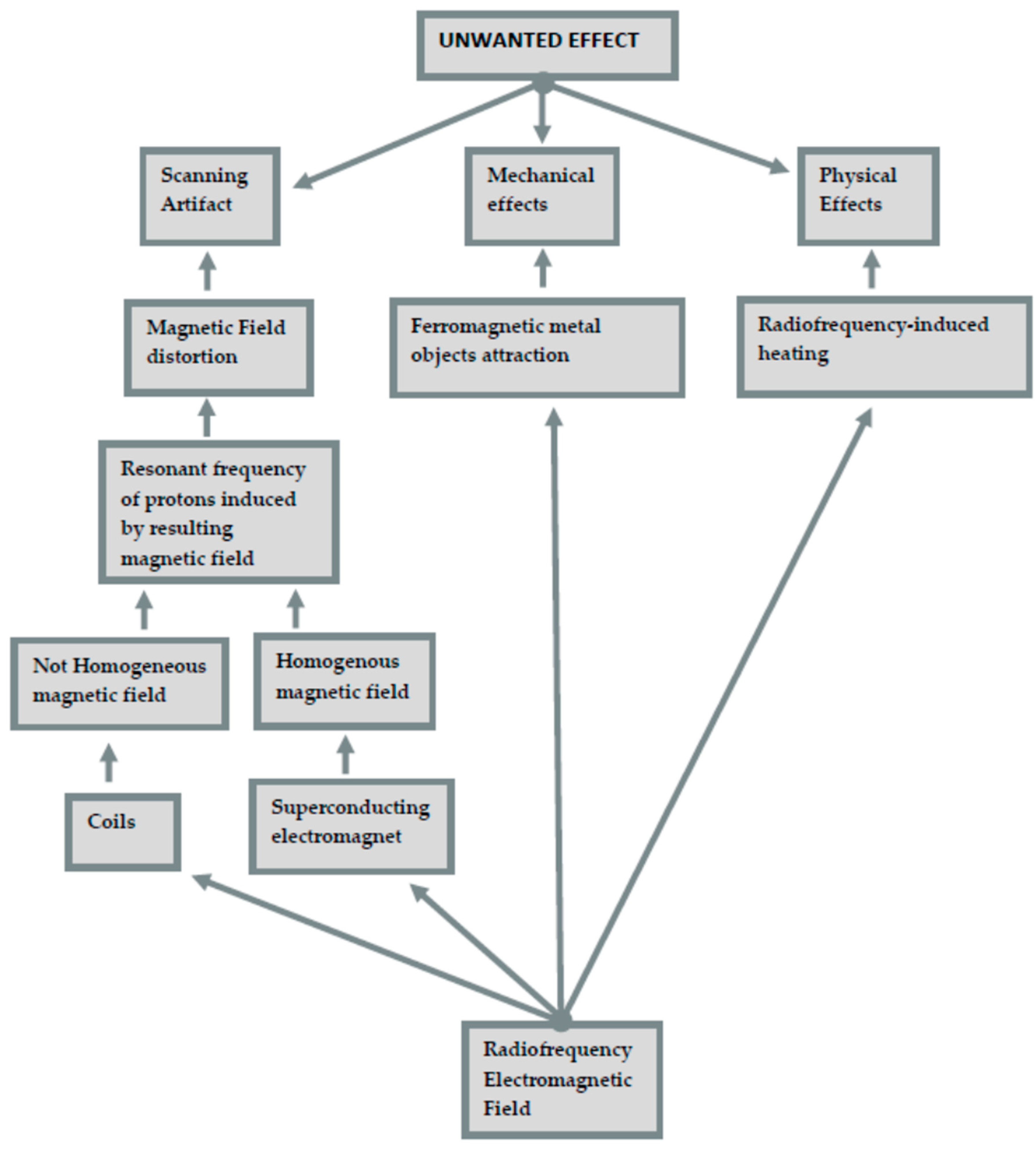
- Scanning artifact. These artifacts are defined by pixels that do not faithfully represent the tissue components studied. The shape of these artifacts depends on the scanning plane, whether it is axial or sagittal. The severity depends on the magnetic properties and position of the present metal; its orientation, shape, number; the homogeneity of the alloy; and the MRI sequence used. On this topic, the literature contains contradictory results, depending on where the attention has been focused on, whether that was gold content alloys, titanium, or a dental amalgam [9,10,11,12]. Distortion of the static magnetic field is generated from the difference in the magnetic susceptibility, as signal incoherence is generated by substances with different magnetic capacities.In addition to this typology, there are also artifacts caused by eddy currents, induced by alternating gradients and radiofrequency magnetic fields, which participate in generating distortions.
- Mechanical effects (magnetically induced displacement). The most immediate risk associated with the MR environment is the attraction between the MRI device (a magnet) and ferromagnetic metal objects. The magnetic field is strong enough to pull heavy objects towards the scanner at a very high velocity, this is also known as “the projectile effect”. Patients at the highest risk are those with metals not belonging to medical devices (e.g., projectiles, piercings, welding droplets), and among patients with medical devices, those with pacemakers, cochlear implants, neurostimulators, and infusion pumps are at risk.The complications related to RMI can cause malfunction, dislocation, and soft tissue burns (due to the absorption of radiofrequency energy).
- Physical effects (radiofrequency heating). Metallic objects in the human body, such as pacemakers, cochlear implants, neurostimulators, and infusion pumps, before human tissues themselves, can undergo radiofrequency-induced heating. In addition, the batteries of medical devices can also be subject to rapid discharge.Unwanted effects and the mechanisms that generate them are shown in Figure 1.
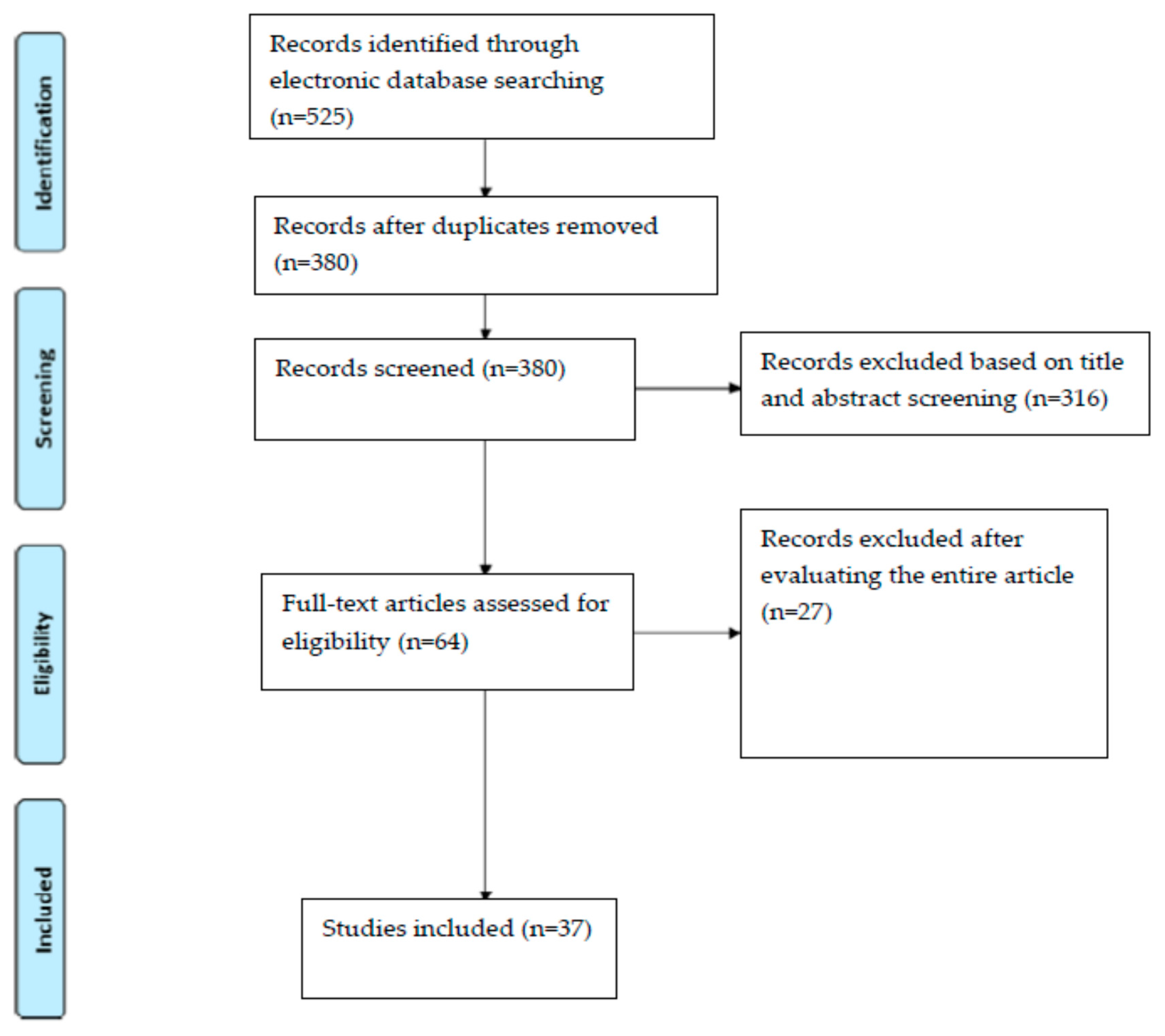
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Fundamental Parameters in MRI
4.2. Apical Periodontitis Diagnosis
4.3. Evaluation of Dental Fractures
4.4. Endodontics, Endodontic Anatomy and Conservative Dentistry
4.5. Implantology
4.6. Maxillary Sinus Diagnosis and Surgery
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valenti-Obino, F.; di Nardo, D.; Quero, L.; Miccoli, G.; Gambarini, G.; Testarelli, L.; Galli, M. Symmetry of root and root canal morphology of mandibular incisors: A cone-beam computed tomography study in vivo. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2019, 11, e527–e533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauwels, R.; Araki, K.; Siewerdsen, J.H.; Thongvigitmanee, S.S. Technical aspects of dental CBCT: State of the art. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2015, 44, 20140224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chogle, S.; Zuaitar, M.; Sarkis, R.; Saadoun, M.; Mecham, A.; Zhao, Y. The Recommendation of Cone-beam Computed Tomography and Its Effect on Endodontic Diagnosis and Treatment Planning. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, F.; di Carlo, G.; Saccucci, M.; Tombolini, V.; Polimeni, A. Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography in Children: Clinical Effectiveness and Cancer Risk due to Radiation Exposure. Oncology 2019, 96, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nardo, D.; Gambarini, G.; Capuani, S.; Testarelli, L. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Endodontics: A Review. J. Endod. 2018, 44, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piancino, M.G.; Cirillo, S.; Frongia, G.; Cena, F.; Bracco, A.A.; Dalmasso, P.; Bracco, P. Sensitivity of magnetic resonance imaging and computed axiography in the diagnosis of temporomandibular joint disorders in a selected patient population. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2012, 25, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, K.Y.; Hu, M.; Yu, Q.; Yang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Long, X.; Zhang, Z.G.; Liu, H.C. Experts consensus on MRI examination specification and diagnostic criteria of temporomandibular joint disc displacement. Chin. J. Stomatol. 2020, 55, 608–612. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Mabray, M.C.; Cha, S. Current Clinical Brain Tumor Imaging. Neurosurgery 2017, 81, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chockattu, S.J.; Suryakant, D.B.; Thakur, S. Unwanted effects due to interactions between dental materials and magnetic resonance imaging: A review of the literature. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2018, 43, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, B.A.; Worters, P.W.; Pauly, K.B.; Pauly, J.M.; Koch, K.M.; Gold, G.E. Metal-Induced Artifacts in MRI. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 197, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stradiotti, P.; Curti, A.; Castellazzi, G.; Zerbi, A. Metal-related artifacts in instrumented spine. Techniques for reducing artifacts in CT and MRI: State of the art. Eur. Spine J. 2009, 18, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilgenfeld, T.; Prager, M.; Schwindling, F.S.; Jende, J.M.; Rammelsberg, P.; Bendszus, M.; Heiland, S.; Juerchott, A. Protocol for the Evaluation of MRI Artifacts Caused by Metal Implants to Assess the Suitability of Implants and the Vulnerability of Pulse Sequences. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 17, e57394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kajima, Y.; Takaichi, A.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Hanawa, T.; Wakabayashi, N.; Kawasaki, A. Influence of magnetic susceptibility and volume on MRI artifacts produced by low magnetic susceptibility Zr-14Nb alloy and dental alloys. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prager, M.; Heiland, S.; Gareis, D.; Hilgenfeld, T.; Bendszus, M.; Gaudino, C. Dental MRI using a dedicated RF-coil at 3 Tesla. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinke, T.; Daboul, A.; Maron, J.; Gredes, T.; Puls, R.; Jaghsi, A.; Biffar, R. Artifacts in Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography Caused by Dental Materials. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roser, C.; Hilgenfeld, T.; Sen, S.; Badrow, T.; Zingler, S.; Heiland, S.; Bendszus, M.; Lux, C.J.; Juerchott, A. Evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging artifacts caused by fixed orthodontic CAD/CAM retainers—An in vitro study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geibel, M.-A.; Gelißen, B.; Bracher, A.-K.; Rasche, V. Artifact Properties of Dental Ceramic and Titanium Implants in MRI. RöFo Fortschr. Geb. Röntgenstrahlen Bildgeb. Verfahr. 2018, 191, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tymofiyeva, O.; Vaegler, S.; Rottner, K.; Boldt, J.; Hopfgartner, A.J.; Proff, P.C.; Richter, E.-J.; Jakob, P.M. Influence of dental materials on dental MRI. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2013, 42, 20120271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hilgenfeld, T.; Prager, M.; Heil, A.; Schwindling, F.S.; Nittka, M.; Grodzki, D.; Rammelsberg, P.; Bendszus, M.; Heiland, S. PETRA, MSVAT-SPACE and SEMAC sequences for metal artefact reduction in dental MR imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 5104–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duttenhoefer, F.; Mertens, M.E.; Vizkelety, J.; Gremse, F.; Stadelmann, V.A.; Sauerbier, S. Magnetic resonance imaging in zirconia-based dental implantology. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2015, 26, 1195–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ 2009, 21, 339:b2535. [Google Scholar]
- Idiyatullin, D.; Corum, C.A.; Nixdorf, D.R.; Garwood, M. Intraoral approach for imaging teeth using the transverse B 1 field components of an occlusally oriented loop coil. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 72, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr. Aetiology of root canal treatment failure: Why well-treated teeth can fail. Int. Endod. J. 2001, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nair, P. Pathogenesis of Apical Periodontitis and the Causes of Endodontic Failures. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2004, 15, 348–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, L.; Umorin, M.; Augsburger, R.A.; Glickman, G.N.; Jalali, P. Periradicular Lesions in Cancellous Bone Can Be Detected Radiographically. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Rôças, I.N.; Ricucci, D.; Hülsmann, M. Causes and management of post-treatment apical periodontitis. Br. Dent. J. 2014, 216, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lizio, G.; Salizzoni, E.; Coe, M.; Gatto, M.R.; Asioli, S.; Balbi, T.; Pelliccioni, G.A. Differential diagnosis between a granuloma and radicular cyst: Effectiveness of magnetic resonance imaging. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 1077–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricucci, D.; Mannocci, F.; Ford, T.R. A study of periapical lesions correlating the presence of a radiopaque lamina with his-tological findings. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricucci, D.; Rôças, I.N.; Hernández, S.; Siqueira, J.F., Jr. “True” Versus “Bay” Apical Cysts: Clinical, Radiographic, Histopathologic, and Histobacteriologic Features. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juerchott, A.; Pfefferle, T.; Flechtenmacher, C.; Mente, J.; Bendszus, M.; Heiland, S.; Hilgenfeld, T. Differentiation of periapical granulomas and cysts by using dental MRI: A pilot study. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2018, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.M.; Ricucci, D.; Lin, J.; Rosenberg, P.A. Nonsurgical Root Canal Therapy of Large Cyst-like Inflammatory Periapical Lesions and Inflammatory Apical Cysts. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geibel, M.A.; Schreiber, E.S.; Bracher, A.K.; Hell, E.; Ulrici, J.; Sailer, L.K.; Ozpeynirci, Y.; Rasche, V. Assessment of Apical Periodontitis by MRI: A Feasibility Study. RöFo Fortschr. Geb. Röntgenstrahlen Bildgeb. Verfahr. 2015, 187, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schestatsky, R.; Dartora, G.; Felberg, R.; Spazzin, A.O.; Sarkis-Onofre, R.; Bacchi, A.; Pereira, G.K.R. Do endodontic retreatment techniques influence the fracture strength of endodontically treated teeth? A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 90, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuurmans, T.J.; Nixdorf, D.R.; Idiyatullin, D.S.; Law, A.S.; Barsness, B.D.; Roach, S.H.; Gaalaas, L. Accuracy and Reliability of Root Crack and Fracture Detection in Teeth Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J. Endod. 2019, 45, 750–755.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seracchiani, M.; Miccoli, G.; Di Nardo, D.; Zanza, A.; Cantore, M.; Gambarini, G.; Testarelli, L. Effect of Flexural Stress on Torsional Resistance of NiTi Instruments. J. Endod. 2021, 47, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambarini, G.; Miccoli, G.; D’Angelo, M.; Seracchiani, M.; Obino, F.V.; Reda, R.; Testarelli, L. The relevance of operative torque and torsional resistance of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: A preliminary clinical investigation. Saudi Endod. J. 2020, 10, 260–264. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzoni, A.; Pacifici, A.; Zanza, A.; Giudice, A.; Reda, R.; Testarelli, L.; Gambarini, G.; Pacifici, L. Assessment of Real-Time Operative Torque during Nickel-Titanium Instrumentation with Different Lubricants. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambarini, G.; Seracchiani, M.; Zanza, A.; Miccoli, G.; Del Giudice, A.; Testarelli, L. Influence of shaft length on torsional behavior of endodontic nickel-titanium instruments. Odontology 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanasiewicz, M. Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Endodontic Treatment Prediction. J. Med. Imaging Radiat. Sci. 2010, 41, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracher, A.-K.; Hofmann, C.; Bornstedt, A.; Hell, E.; Janke, F.; Ulrici, J.; Haller, B.; Geibel, M.-A.; Rasche, V. Ultrashort echo time (UTE) MRI for the assessment of caries lesions. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2013, 42, 20120321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, C.; Scrimgeour, S.; Chudek, J.; Hunter, G.; Mackay, R. Application of Magnetic Resonance Microimaging to the Study of Dental Caries. Caries Res. 1999, 34, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploder, O.; Partik, B.; Rand, T.; Fock, N.; Voracek, M.; Undt, G.; Baumann, A. Reperfusion of autotransplanted teeth—comparison of clinical measurements by means of dental magnetic resonance imaging. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontology 2001, 92, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, M.; Akamine, A. The Application of Tissue Engineering to Regeneration of Pulp and Dentin in Endodontics. J. Endod. 2005, 31, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Annibali, S.; Bellavia, D.; Ottolenghi, L.; Cicconetti, A.; Cristalli, M.P.; Quaranta, R.; Pilloni, A. Micro-CT and PET analysis of bone regeneration induced by biodegradable scaffolds as carriers for dental pulp stem cells in a rat model of calvarial “critical size” defect: Preliminary data. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part. B Appl. Biomater. 2013, 102, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assaf, A.T.; Zrnc, T.A.; Remus, C.C.; Khokale, A.; Habermann, C.R.; Schulze, D.; Fiehler, J.; Heiland, M.; Sedlacik, J.; Friedrich, R.E. Early detection of pulp necrosis and dental vitality after traumatic dental injuries in children and adolescents by 3-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging. J. Cranio Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlacik, J.; Kutzner, D.; Khokale, A.; Schulze, D.; Fiehler, J.; Celik, T.; Gareis, D.; Smeets, R.; Friedrich, R.E.; Heiland, M.; et al. Optimized 14 + 1 receive coil array and position system for 3D high-resolution MRI of dental and maxillomandibular structures. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol. 2016, 45, 20150177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seracchiani, M.; Miccoli, G.; Reda, R.; Zanza, A.; Valenti Obino, F.; Bhandi, S.; Gambarini, G.; Testarelli, L. A Comprehensive In Vitro Comparison of Mechanical Properties of Two Rotary Endodontic Instruments. World J. Dent. 2020, 11, 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Probst, F.A.; Schweiger, J.; Stumbaum, M.J.; Karampinos, D.; Burian, E.; Probst, M. Magnetic resonance imaging based comput-er-guided dental implant surgery—A clinical pilot study. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2020, 22, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambarini, G.; Plotino, G.; Grande, N.M.; Testarelli, L.; Prencipe, M.; Messineo, D.; Fratini, L.; D’Ambrosio, F. Differential diagnosis of endodontic-related inferior alveolar nerve paraesthesia with cone beam computed tomography: A case report. Int. Endod. J. 2010, 44, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bari, R.; Coronelli, R.; Cicconetti, A. Intraosseous vascularization of anterior mandible: A radiographic analysis. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2014, 25, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnieri, R.; Miccoli, G.; Reda, R.; Mazzoni, A.; Di Nardo, D.; Testarelli, L. Laser microgrooved vs. machined healing abutment disconnection/reconnection: A comparative clinical, radiographical and biochemical study with split-mouth design. Int. J. Implant. Dent. 2021, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgenfeld, T.; Kästel, T.; Heil, A.; Rammelsberg, P.; Heiland, S.; Bendszus, M.; Schwindling, F.S. High-resolution dental magnetic resonance imaging for planning palatal graft surgery—A clinical pilot study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktuna Belgin, C.; Colak, M.; Adiguzel, O.; Akkus, Z.; Orhan, K. Three-dimensional evaluation of maxillary sinus volume in different age and sex groups using CBCT. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wang, C.-S.; Huang, Q.; Cui, S.-J.; Li, Y.-C.; Wang, X.-Y. CT and MRI diagnosis of lesions in unilateral maxillary sinus. Chin. J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 48, 895–900. [Google Scholar]
- Panou, E.; Motro, M.; Ateş, M.; Acar, A.; Erverdi, N. Dimensional changes of maxillary sinuses and pharyngeal airway in Class III patients undergoing bimaxillary orthognathic surgery. Angle Orthod. 2013, 83, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, M.; Kavak, R.P. Season, Age and Sex-Related Differences in Incidental Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Paranasal Sinuses in Adults. Turk. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 57, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.U.; Rao, G.V.; Kumar, D.R.; Sravya, T.; Sivaranjani, Y.; Kumar, M.P. Age and gender assessment through three-dimensional morphometric analysis of maxillary sinus using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Forensic Dent. Sci. 2017, 9, 46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butaric, L.N.; Wadle, M.; Gascon, J. Pediatric Imaging, Neurocognition and Genetics Study. Anatomical Variation in Maxillary Sinus Ostium Positioning: Implications for Nasal-Sinus Disease. Anat. Rec. 2019, 302, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.-P.; Li, C.-X.; Cao, Y.; Singh, S.; Zhong, R. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumour of the maxillary sinus: CT and MRI findings. Clin. Radiol. 2012, 67, e53–e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurino, F.A.R.; Gil Choi, I.G.; Kim, J.H.; Gialain, I.O.; Ferraço, R.; Haetinger, R.G.; Pinhata-Baptista, O.H.; Abdala-Junior, R.; Costa, C.; Cortes, A.R.G. Correlation between magnetic resonance imaging and cone-beam computed tomography for maxillary sinus graft assessment. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2020, 50, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munhoz, L.; Júnior, R.A.; Arita, E.S. The value of the apparent diffusion coefficient calculated from diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging scans in the differentiation of maxillary sinus inflammatory diseases. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2019, 127, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chen, K.C.; Gao, Y.; Shi, F.; Liao, S.; Li, G.; Shen, S.G.F.; Yan, J.; Lee, P.K.M.; Chow, B.; et al. Automated bone segmentation from dental CBCT images using patch-based sparse representation and convex optimization. Med. Phys. 2014, 41, 043503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hua, X.S. Landmarks Detection with Anatomical Constraints for Total Hip Arthroplasty Preoperative Measurements. In Part I, Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2020, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; Martel, A.L., Abolmaesumi, P., Stoyanov, D., Mateus, D., Zuluaga, M.A., Zhou, S.K., Racoceanu, D., Joskowicz, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 12264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jiao, Z.; Gao, X. An Attention-Guided Deep Regression Model for Landmark Detection in Cephalograms. In Proceedings of the Languages and Compilers for Parallel Computing, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 540–548. [Google Scholar]
| Materials | Artifacts and Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Orthodontics | NiTi arch wires | Major distortions |
| Stainless-steel brackets | Major distortions | |
| Endodontics | Resin-based sealer | No distortions |
| Gutta-percha | No distortions | |
| Implant and Prostheses | Implants | Major distortions |
| Removable prostheses | Major distortions, and possibility of movement | |
| Gold crowns | No distortions | |
| Metal crowns | Minor distortions | |
| Zirconia | Confilicting results | |
| Ceramic | No distortions | |
| Restorative Dentistry | Glass ionomer cements | Major distortions |
| Composite resins | Major distortions | |
| Polycarboxylate | Minor distortions | |
| Zinc phosphate-based cement | Minor distortions | |
| Modified dimethacrylates | Minor distortions | |
| Amalgam | Minor distortions |
| Title | Possible Applications | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic resonance imaging based computer-guided dental implant surgery—A clinical pilot study | Implantology | 2020 |
| Evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging for diagnostic purposes in operative dentistry—a systematic review | Endodontics, conservative dentistry, and anatomy | 2019 |
| Virtual implant planning and fully guided implant surgery using magnetic resonance imaging—Proof of principle | Implantology | 2020 |
| Magnetic resonance imaging artifacts produced by dental implants with different geometries | Implantology | 2020 |
| Magnetic resonance imaging in endodontics: a literature review | Endodontics | 2017 |
| Magnetic resonance imaging artefacts and fixed orthodontic attachments | Orthodontics (artefacts) | 2015 |
| Human tooth and root canal morphology reconstruction using magnetic resonance imaging | Endodontics, anatomy | 2015 |
| MRI for Dental Applications | Endodontics, oral surgery, anatomy | 2018 |
| Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Endodontics: A Review | Endodontics, conservative denstistry, anatomy, oral surgery | 2018 |
| Magnetic resonance imaging in zirconia-based dental implantology | Implantology | 2014 |
| High-resolution dental MRI for planning palatal graft surgery—a clinical pilot study | Surgery | 2018 |
| Correlation between magnetic resonance imaging and cone-beam computed tomography for maxillary sinus graft assessment | Surgery, maxillary sinus, implantology | 2020 |
| Differentiation of periapical granulomas and cysts by using dental MRI: a pilot study | Surgery, endodontics | 2018 |
| Assessment of signal-to-noise ratio and contrast-to-noise ratio in 3 T magnetic resonance imaging in the presence of zirconium, titanium, and titanium-zirconium alloy implants | Surgery, implantology | 2019 |
| Dental Materials and Magnetic Resonance Imaging | Artefacts | 1991 |
| Differential diagnosis between a granuloma and radicular cyst: Effectiveness of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) | Surgery, endodontics | 2018 |
| Unwanted effects due to interactions between dental materials and magnetic resonance imaging: a review of the literature | Artefacts | 2018 |
| Accuracy and Reliability of Root Crack and Fracture Detection in Teeth Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging | Endodontics, conservative dentistry | 2019 |
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Endodontic Treatment Prediction | Endodontics | 2010 |
| The value of the apparent diffusion coefficient calculated from diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images in the differentiation of maxillary sinus infiammatory diseases | Maxillary sinus | 2018 |
| Season, Age and Sex-Related Differences in Incidental Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Paranasal Sinuses in Adults | Maxillary sinus | 2019 |
| Anatomical variation in maxillary sinus ostium positioning: implications for nasal-sinus disease | Maxillary sinus | 2018 |
| Metal-induced artifacts in MRI | Artefacts | 2011 |
| Protocol for the Evaluation of MRI Artifacts Caused by Metal Implants to Assess the Suitability of Implants and the Vul-nerability of Pulse Sequences | Artefacts | 2018 |
| Influence of magnetic susceptibility and volume on MRI artifacts produced by low magnetic susceptibility Zr-14Nb alloy and dental alloys | Artefacts | 2019 |
| Dental MRI using a dedicated RF-coil at 3 Tesla | Artefacts | 2015 |
| Artifacts in magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography caused by dental materials | Artefacts | 2012 |
| Evaluation of magnetic resonance imaging artifacts caused by fixed orthodontic CAD/CAM retainers-an in vitro study | Artefacts, | 2012 |
| Artifact Properties of Dental Ceramic and Titanium Implants in MRI | Artefacts | 2018 |
| PETRA, MSVAT-SPACE and SEMAC sequences for metal artefact reduction in dental MR imaging | Artefacts | 2017 |
| Magnetic resonance imaging in zirconia-based dental implantology | Artefacts, implantology | 2015 |
| Assessment of apical periodontitis by MRI: a feasibility study | Surgery, endodontics | 2015 |
| Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Endodontic Treatment Prediction | Endodontics | 2011 |
| Ultrashort echo time (UTE) MRI for the assessment of caries lesions | Endodontics, conservative dentistry | 2013 |
| Reperfusion of autotransplanted teeth--comparison of clinical measurements by means of dental magnetic resonance im-aging | Endodontics, surgery | 2013 |
| Early detection of pulp necrosis and dental vitality after traumatic dental injuries in children and adolescents by 3-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging | Endodontics | 2015 |
| Optimized 14 + 1 receive coil array and position system for 3D high-resolution MRI of dental and maxillomandibular structures | Endodontics | 2016 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reda, R.; Zanza, A.; Mazzoni, A.; Cicconetti, A.; Testarelli, L.; Di Nardo, D. An Update of the Possible Applications of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Dentistry: A Literature Review. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging7050075
Reda R, Zanza A, Mazzoni A, Cicconetti A, Testarelli L, Di Nardo D. An Update of the Possible Applications of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Dentistry: A Literature Review. Journal of Imaging. 2021; 7(5):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging7050075
Chicago/Turabian StyleReda, Rodolfo, Alessio Zanza, Alessandro Mazzoni, Andrea Cicconetti, Luca Testarelli, and Dario Di Nardo. 2021. "An Update of the Possible Applications of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Dentistry: A Literature Review" Journal of Imaging 7, no. 5: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging7050075
APA StyleReda, R., Zanza, A., Mazzoni, A., Cicconetti, A., Testarelli, L., & Di Nardo, D. (2021). An Update of the Possible Applications of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Dentistry: A Literature Review. Journal of Imaging, 7(5), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging7050075










