Assessing Acetabular Index Angle in Infants: A Deep Learning-Based Novel Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Related Literature
1.1.1. Detection & Diagnosis Software Tools
1.1.2. Research Utilizing ML/DL-Based Methodologies
1.1.3. Research Gap
2. Materials and Methods
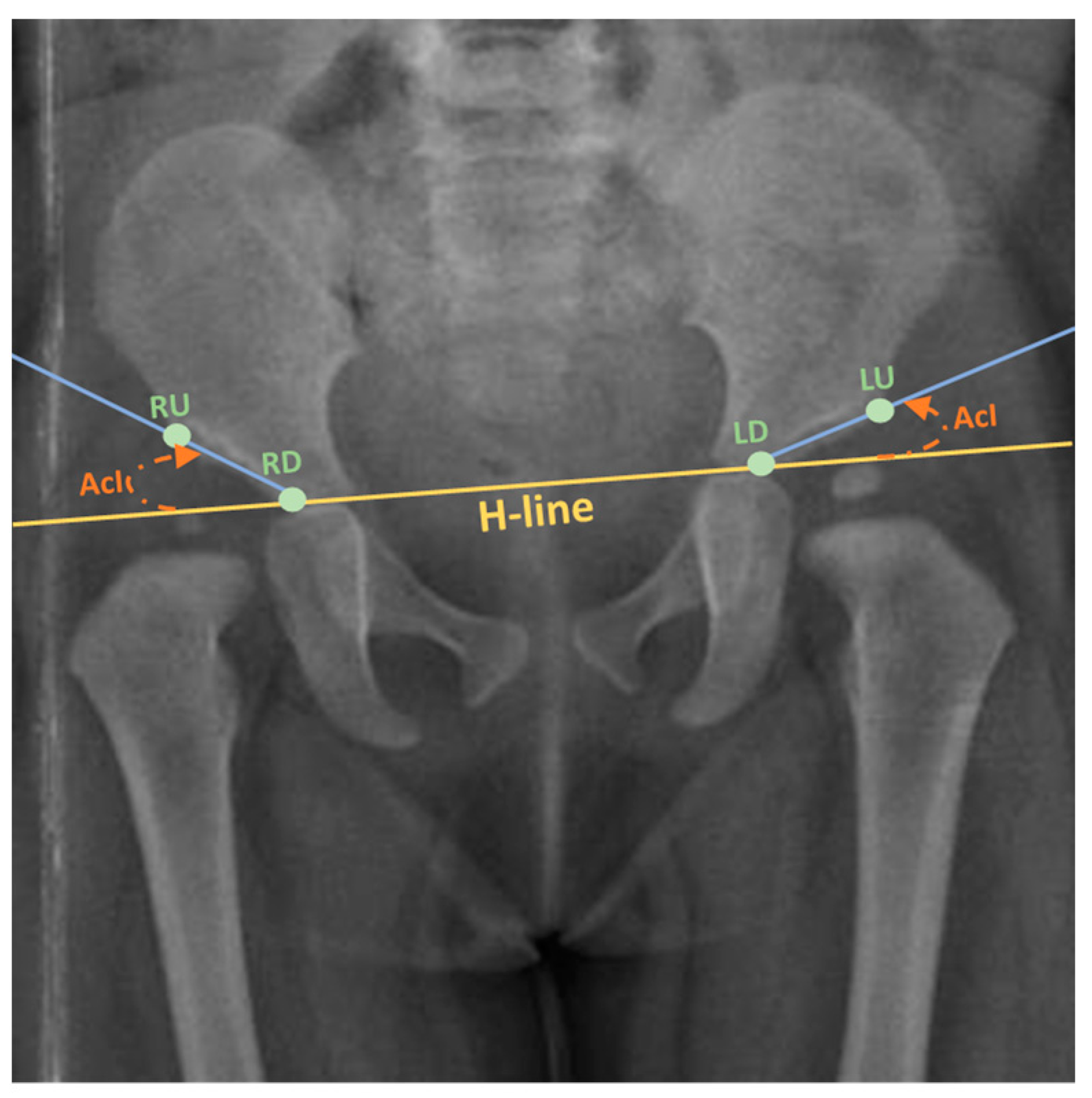
2.1. Data Annotation
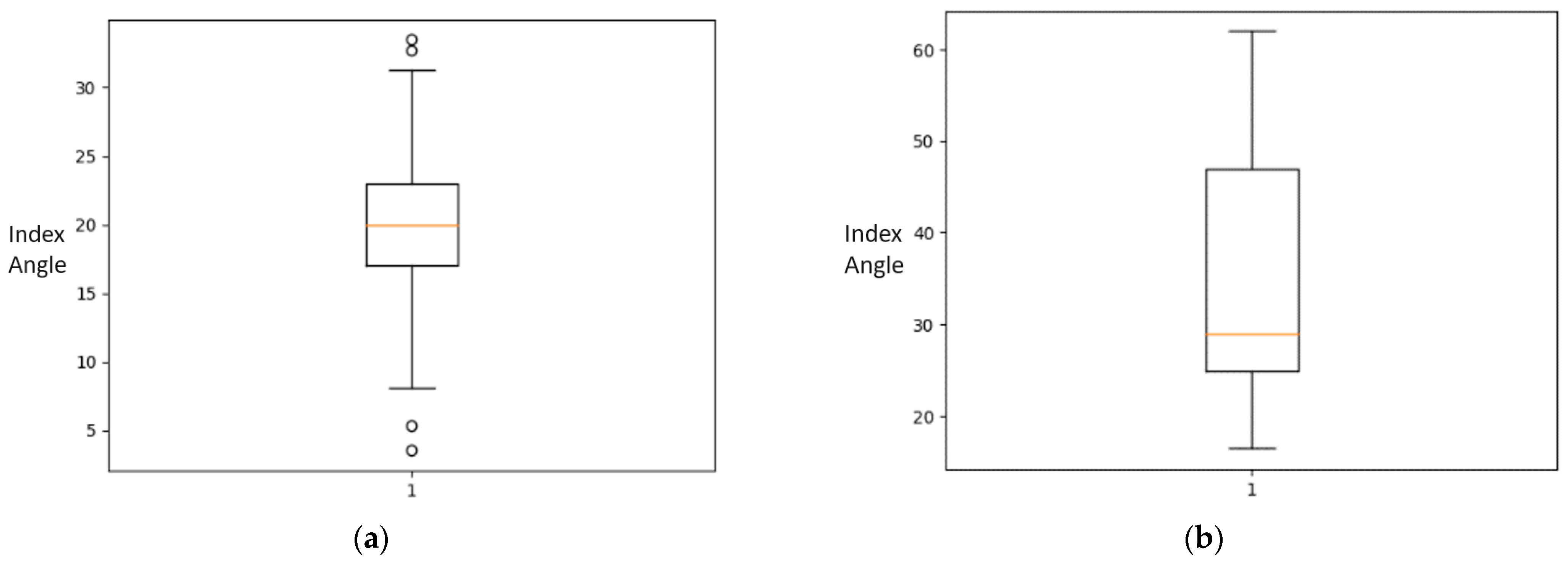
2.2. Statistical Analysis of the Dataset
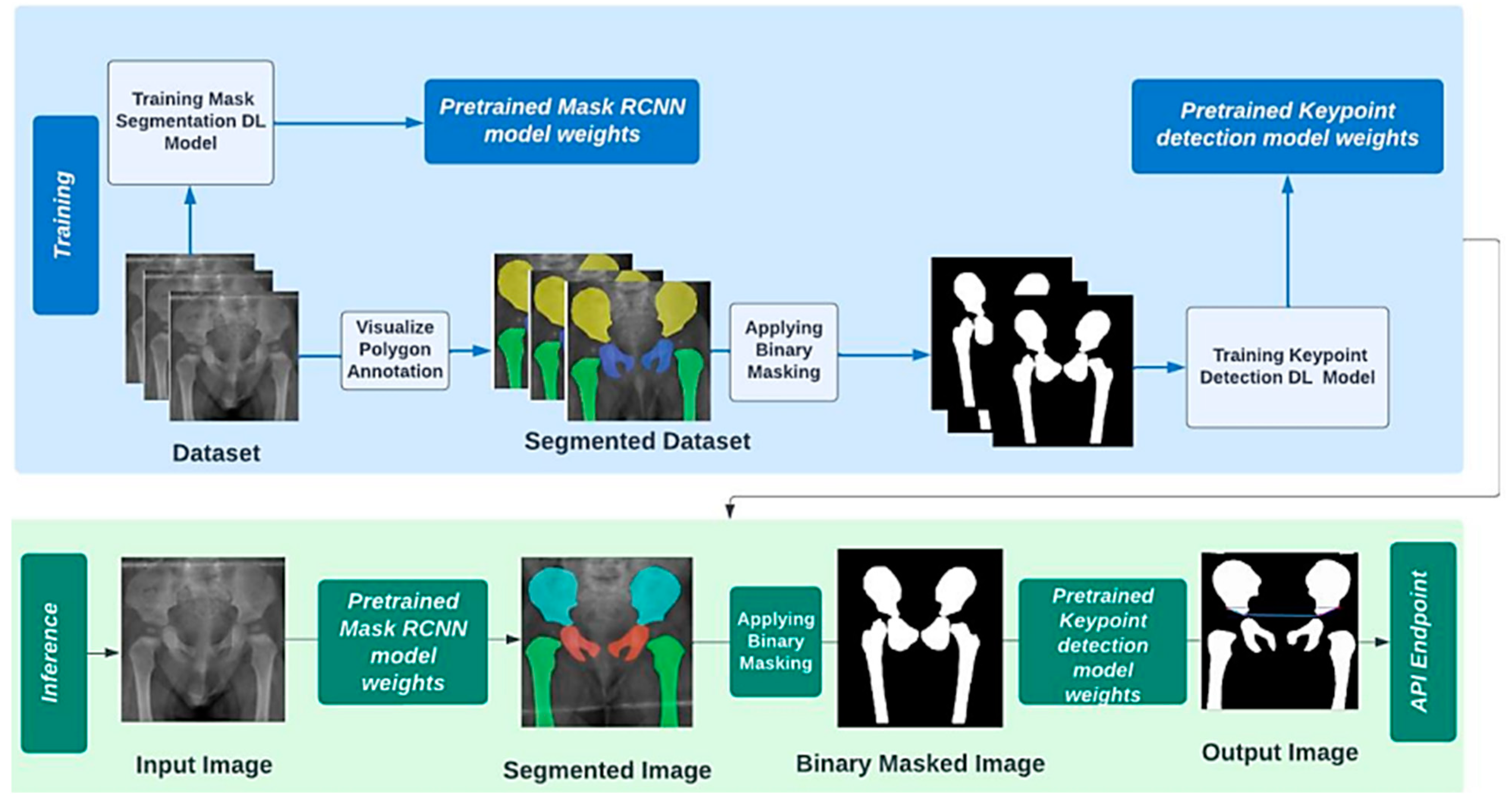
2.3. Operationl Framework
2.4. Experemintal Setup
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Landmarks Detection
3.2. Pipeline Landmark Detection
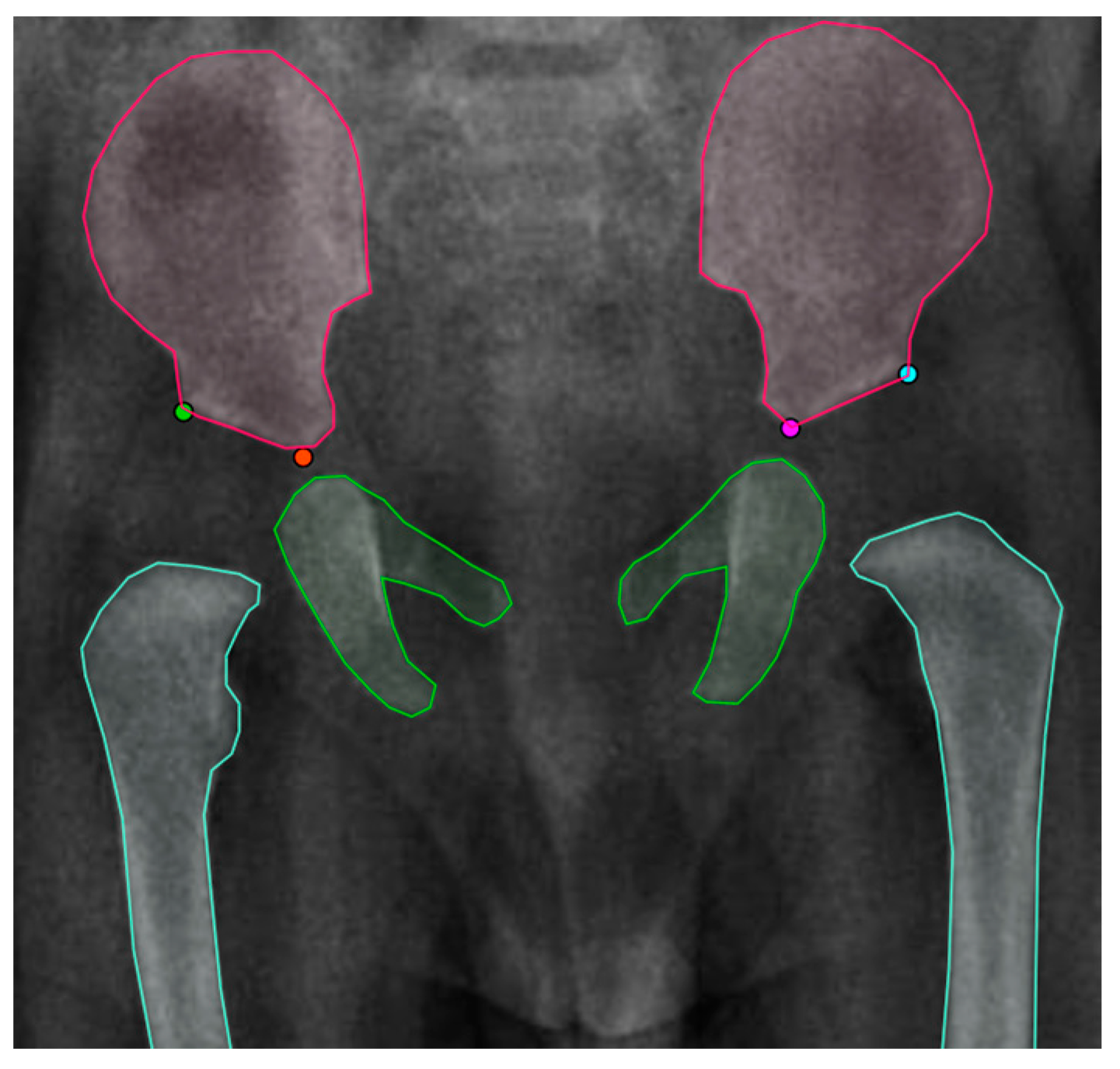
3.2.1. First Stage: Instance Segmentation
3.2.2. Second Stage: Landmark Detection
3.2.3. Performance Metrics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Fully annotating an open-source dataset [7] for instance segmentation and landmarks detection, which was published solely for binary classification task.
- Building an efficient deep-learning landmarks detection model with error margin of 2.402 ± 1.963° for the acetabular index angle measurement.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gambling, T.S.; Long, A. Psycho-social impact of developmental dysplasia of the hip and of differential access to early diagnosis and treatment: A narrative study of young adults. SAGE Open Med. 2019, 7, 2050312119836010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pun, S. Hip dysplasia in the young adult caused by residual childhood and adolescent-onset dysplasia. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2016, 9, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadat-Ali, M. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) in Saudi Arabia: Time to Wake up. A Systematic Review (1980–2018). Open J. Epidemiol. 2020, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhagopal, T.; De Cicco, F.L. Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip–NCBI Bookshelf; StatPearls: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2023; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563157/ (accessed on 25 September 2022).
- AAOS. Developmental Dislocation (Dysplasia) of the Hip (DDH). 2022. Available online: https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/developmental-dislocation-dysplasia-of-the-hip-ddh/ (accessed on 28 August 2023).
- Chmiel-Nowak, M. Acetabular Index. Radiology Reference Article. 2022. Available online: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/acetabular-index?lang=gb (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Fraiwan, M.; Al-Kofahi, N.; Hanatleh, O.; Ibnian, A. A Dataset of DDH X-ray Images. Available online: https://data.mendeley.com/datasets/jf3pv98m9g/2 (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Overhoff, H.M.; Lazovic, D.; Franke, J.; Jan, U.V. Automatic determination of the newborn’s femoral head from three-dimensional ultrasound image data. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overhoff, H.M.; Lazovic, D.; von Jan, U.; Heinze, P. Computer-based determination of the newborn’s femoral head coverage using three-dimensional ultrasound scans. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Including Subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishii, T.; Sugano, N.; Sato, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Miki, H.; Yoshikawa, H. Three-dimensional distribution of acetabular cartilage thickness in patients with hip dysplasia: A fully automated computational analysis of MR imaging. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2004, 12, 650–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Bashir, A.K.; Al-Abed, M.; Sharkh, F.M.A.; Kordeya, M.N.; Rousan, F.M. Algorithm for automatic angles measurement and screening for Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH). In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBS, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BoneView—GLEAMER—Medical-Grade AI for Radiology. GLEAMER—Medical-Grade AI for Radiology. 2022. Available online: https://www.gleamer.ai/solutions/boneview/ (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Carlisle, J.C.; Zebala, L.P.; Shia, D.S.; Hunt, D.; Morgan, P.M.; Prather, H.; Wright, R.W.; Steger-May, K.; Clohisy, J.C. Reliability of various observers in determining common radiographic parameters of adult hip structural anatomy. Iowa Orthop. J. 2011, 31, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Maarek, R.; Hermann, A.-L.; Kammoun, A.; Marchi, A.; Khelifi-Touhami, M.R.; Collin, M.; Jaillard, A.; Kompel, A.J.; Hayashi, D.; et al. Assessment of an artificial intelligence aid for the detection of appendicular skeletal fractures in children and young adults by senior and junior radiologists. Pediatr. Radiol. 2022, 52, 2215–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IB Lab LAMA CE. 2022. Available online: https://www.imagebiopsy.com/product/lama-ce?utm_lang=en (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- IB Lab HIPPO CE. 2022. Available online: https://www.imagebiopsy.com/product/hippo-ce?utm_lang=en (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- ImageBiopsy Lab—Products CE, FDA. 2022. Available online: https://www.imagebiopsy.com/products?utm_lang=en (accessed on 4 October 2022).
- Thompson, P.; Perry, D.C.; Cootes, T.F.; Lindner, C. Automation of clinical measurements on radiographs of children’s hips. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2022 25th International Conference, Singapore, 18–22 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, G.; Liang, Y.; Shi, Q.; Cui, B.; Chang, X.; Qiu, Z.; Zhao, X. Computer-Aided System Application Value for Assessing Hip Development. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 587161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xie, H.; Tan, Q.; Wu, H.; Liu, C.; Zhang, S.; Mao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Multi-task hourglass network for online automatic diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip. World Wide Web 2022, 26, 539–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhong, L.; Huang, H.; Liu, H.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, H.; Yang, W.; Qin, M.; et al. Auxiliary diagnosis of developmental dysplasia of the hip by automated detection of Sharp’s angle on standardized anteroposterior pelvic radiographs. Medicine 2019, 98, e18500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Shu, L.; Gong, P.; Huang, C.; Xu, J.; Zhao, J.; Shu, Q.; Zhu, M.; Qi, G.; Zhao, G.; et al. A Deep-Learning Aided Diagnostic System in Assessing Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip on Pediatric Pelvic Radiographs. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 9, 785480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H. Sensors & Transducers the Novel Computer Aided Diagnostic System on Medical Images for Parameter Calculation. 2021. Available online: http://www.sensorsportal.com (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Zhang, S.C.; Sun, J.; Liu, C.B.; Fang, J.H.; Xie, H.T.; Ning, B. Clinical application of artificial intelligence-assisted diagnosis using anteroposterior pelvic radiographs in children with developmental dysplasia of the hip. Bone Jt. J. 2020, 102, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraiwan, M.; Al-Kofahi, N.; Ibnian, A.; Hanatleh, O. Detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip in X-ray images using deep transfer learning. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2022, 22, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S.; Jeon, K.; Cho, Y.J.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, S.B.; Choi, G.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y.H.; Cheon, J.-E.; Kim, W.S.; et al. Diagnostic performance of a new convolutional neural network algorithm for detecting developmental dysplasia of the hip on anteroposterior radiographs. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaremko, J.L.; Hareendranathan, A.; Bolouri, S.E.S.; Frey, R.F.; Dulai, S.; Bailey, A.L. AI aided workflow for hip dysplasia screening using ultrasound in primary care clinics. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xie, H.; Zhang, S.; Mao, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Misshapen Pelvis Landmark Detection with Local-Global Feature Learning for Diagnosing Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 3944–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xie, H.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y. Misshapen Pelvis Landmark Detection by Spatial Local Correlation Mining for Diagnosing Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2019: 22nd International Conference, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; Proceedings, Part VI. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N. Improving early detection of developmental dysplasia of the hip through general practitioner assessment and surveillance. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2018, 47, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A. Memetic computing based numerical solution to Troesch problem. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 37, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musleh, D.; Alotaibi, M.; Alhaidari, F.; Rahman, A.; Mohammad, R.M. Intrusion Detection System Using Feature Extraction with Machine Learning Algorithms in IoT. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2023, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den, H.; Ito, J.; Kokaze, A. Diagnostic accuracy of a deep learning model using YOLOv5 for detecting developmental dysplasia of the hip on radiography images. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.U.; Khan, S.; Mehmood, S.; Khan, M.A.; Rahman, A.-U.; Hwang, S.O. IoMT-Based Osteosarcoma Cancer Detection in Histopathology Images Using Transfer Learning Empowered with Blockchain, Fog Computing, and Edge Computing. Sensors 2022, 22, 5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.U.; Nasir, M.U.; Gollapalli, M.; Zubair, M.; Saleem, M.A.; Mehmood, S.; Khan, M.A.; Mosavi, A. Advance Genome Disorder Prediction Model Empowered with Deep Learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 70317–70328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Computer Vision Annotation Tool. Available online: https://www.cvat.ai/ (accessed on 13 February 2023).
- Kannan, A.; Hodgson, A.; Mulpuri, K.; Garbi, R. Uncertainty Estimation for Assessment of 3D US Scan Adequacy and DDH Metric Reliability. In Uncertainty for Safe Utilization of Machine Learning in Medical Imaging, and Graphs in Biomedical Image Analysis: Second International Workshop, UNSURE 2020, and Third International Workshop, GRAIL 2020; Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2020, Lima, Peru, October 8 2020. Proceedings; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, E.; Smith, N.; Watson, D.; Hassan, T.; Neupane, K. Early Screening of DDH Using SVM Classification; SoutheastCon: Huntsville, AL, USA, 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.S.; Rahman, A.; AlGhamdi, F.; AlDakheel, S.; Hakami, H.; AlJumah, A.; AlIbrahim, Z.; Youldash, M.; Alam Khan, M.A.; Basheer Ahmed, M.I. Joint Diagnosis of Pneumonia, COVID-19, and Tuberculosis from Chest X-ray Images: A Deep Learning Approach. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-W.; Ye, H.-U.; Lee, K.-J.; Jang, W.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Hwang, S.-M.; Heo, Y.-R. Accuracy of New Deep Learning Model-Based Segmentation and Key-Point Multi-Detection Method for Ultrasonographic Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) Screening. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basheer Ahmed, M.I.; Zaghdoud, R.; Ahmed, M.S.; Sendi, R.; Alsharif, S.; Alabdulkarim, J.; Albin Saad, B.A.; Alsabt, R.; Rahman, A.; Krishnasamy, G. A Real-Time Computer Vision Based Approach to Detection and Classification of Traffic Incidents. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2023, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Pan, X.; Zhang, H.; Luo, D.; Cheng, H.; Xiao, K. The lateral center-edge angle as radiographic selection criteria for periacetabular osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip in patients aged above 13 years. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020, 21, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, S.L.; Dolan, L.A. Proximal femoral growth disturbance in developmental dysplasia of the hip: What do we know? J. Child. Orthop. 2018, 12, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, M.U.; Zubair, M.; Ghazal, T.M.; Khan, M.F.; Ahmad, M.; Rahman, A.-u.; Hamadi, H.A.; Khan, M.A.; Mansoor, W. Kidney Cancer Prediction Empowered with Blockchain Security Using Transfer Learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 7483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ref. | Dataset Size | Methods | Performance | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [18] | 400 | Random Forest Regression Voting Model | Point-to-point error: 2.72 mm | Lack of implementation details for reproducibility. |
| [20] | 9369 | Multi-Task Hourglass Network with Encoder-Decoder | Landmarks Pixel Error: 4.67 ± 5.3 ACI Angle Error: 2.776 ± 2.381° | Extreme diversity of bone morphology in these X-ray images due to large age range |
| [21] | 11,574 | Mask R-CNN built on FPN and ResNet101 | AI measurement: 40.36 ± 4.15° Surgeons’ measurement: 39.59 ± 6.87° | Solely assessing sharp angle |
| [22] | 1398 | Mask R-CNN, HRNet, ResNet50 for segmentation, keypoint detection, and classification respectively. | Landmarks Mean Euclidean distance error: 4.653 | Lack of integration with clinical practice |
| [23] | 321 | Mask R-CNN for segmentation | Base Angles Difference: 1.81° | Solely used Ultrasound scans Lack of implementation details for keypoint detection model |
| [24] | 10,219 | FR-DDH network with ResNet-101 for feature map and spatial information extraction | Bland–Altman 95% limits of agreement for AcI: −4.733° | Extreme diversity of bone morphology in X-ray images for wide age range Lack of integration with clinical practice |
| [28] | 10,000 | CNN—Pyramid Non-local UNet (PN-UNet) | Average point-to-point error: 9.286 µm | Local dataset with manual annotations |
| Five Number Summary | ||
|---|---|---|
| DDH Angle | Minimum | 16.442 |
| Q1 | 24.869 | |
| Median | 28.931 | |
| Q3 | 47.278 | |
| Maximum | 61.932 | |
| IQR | 22.409 | |
| Normal Angle | Minimum | 3.498 |
| Q1 | 16.968 | |
| Median | 19.947 | |
| Q3 | 22.976 | |
| Maximum | 33.479 | |
| IQR | 6.008 | |
| Model Hyperparameters | |
|---|---|
| RPN Batch Size | 256 |
| Roi Heads Batch Size | 128 |
| Base Learning Rate | 0.00075 |
| Maximum Iteration | 2500 |
| Weight Decay | 0.0001 |
| Batch Size | 4 |
| Model | RMSE | AcI Error | Pixel Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline ResNet50 | 7.108 | 4.3705 ± 3.565 | 7.141 ± 6.7355 |
| Pipelined ResNet50 | 3.408 | 3.3275 ± 2.94 | 4.266 ± 3.545 |
| Baseline Keypoint RCNN | 2.9 | 2.955 ± 2.51 | 3.309 ± 2.410 |
| Pipelined Keypoint RCNN | 2.7 | 2.402 ± 1.963 | 2.862 ± 2.392 |
| Pipelined Keypoint RCNN with Binary Mask Segmentation: Pixel Error | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Median | Mean ± Std | |
| Landmark RU | 2.582 | 1.908 | 2.204 | 2.582 ± 1.908 |
| Landmark RD | 3.287 | 2.947 | 2.35 | 3.287 ± 2.947 |
| Landmark LU | 3.584 | 3.107 | 2.656 | 3.584 ± 3.107 |
| Landmark LD | 1.993 | 1.607 | 1.552 | 1.993 ± 1.607 |
| Avg | 2.862 | 2.392 | 2.190 | 2.862 ± 2.392 |
| Pipelined Keypoint RCNN with Binary Mask Segmentation: AcI Measurement Error Rate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std | Median | Mean ± Std | |
| Left | 2.127 | 1.732 | 1.996 | 2.127 ± 1.732 |
| Right | 2.676 | 2.194 | 2.37 | 2.676 ± 2.194 |
| Avg | 2.402 | 1.963 | 2.183 | 2.402 ± 1.963 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jan, F.; Rahman, A.; Busaleh, R.; Alwarthan, H.; Aljaser, S.; Al-Towailib, S.; Alshammari, S.; Alhindi, K.R.; Almogbil, A.; Bubshait, D.A.; et al. Assessing Acetabular Index Angle in Infants: A Deep Learning-Based Novel Approach. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9110242
Jan F, Rahman A, Busaleh R, Alwarthan H, Aljaser S, Al-Towailib S, Alshammari S, Alhindi KR, Almogbil A, Bubshait DA, et al. Assessing Acetabular Index Angle in Infants: A Deep Learning-Based Novel Approach. Journal of Imaging. 2023; 9(11):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9110242
Chicago/Turabian StyleJan, Farmanullah, Atta Rahman, Roaa Busaleh, Haya Alwarthan, Samar Aljaser, Sukainah Al-Towailib, Safiyah Alshammari, Khadeejah Rasheed Alhindi, Asrar Almogbil, Dalal A. Bubshait, and et al. 2023. "Assessing Acetabular Index Angle in Infants: A Deep Learning-Based Novel Approach" Journal of Imaging 9, no. 11: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9110242
APA StyleJan, F., Rahman, A., Busaleh, R., Alwarthan, H., Aljaser, S., Al-Towailib, S., Alshammari, S., Alhindi, K. R., Almogbil, A., Bubshait, D. A., & Ahmed, M. I. B. (2023). Assessing Acetabular Index Angle in Infants: A Deep Learning-Based Novel Approach. Journal of Imaging, 9(11), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/jimaging9110242







