Multi-Segment Extendable Soft Manipulator Driven by a Pneumatic–Tendon Coupling Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- A novel two-segment soft manipulator is proposed, driven by a pneumatic–tendon hybrid drive mechanism that enables extension, bending, and stiffness modulation. The design integrates off-the-shelf industrial components with 3D printing, reducing manufacturing complexity and cost. The segmented structure with differentiated stiffness effectively prevents motion coupling, ensuring stable control.
- (2)
- A hybrid control method fusing a physical prior with a data-driven approach is constructed. This method uses the PCC model to provide a structural prior that constrains the solution space, while a neural network precisely compensates for model deviations [1]. This strategy effectively avoids common issues in end-to-end learning, such as a lack of interpretability, strong data dependency, and slow convergence, thereby improving control accuracy.
2. Structural Design and Driving Principle of MSESM
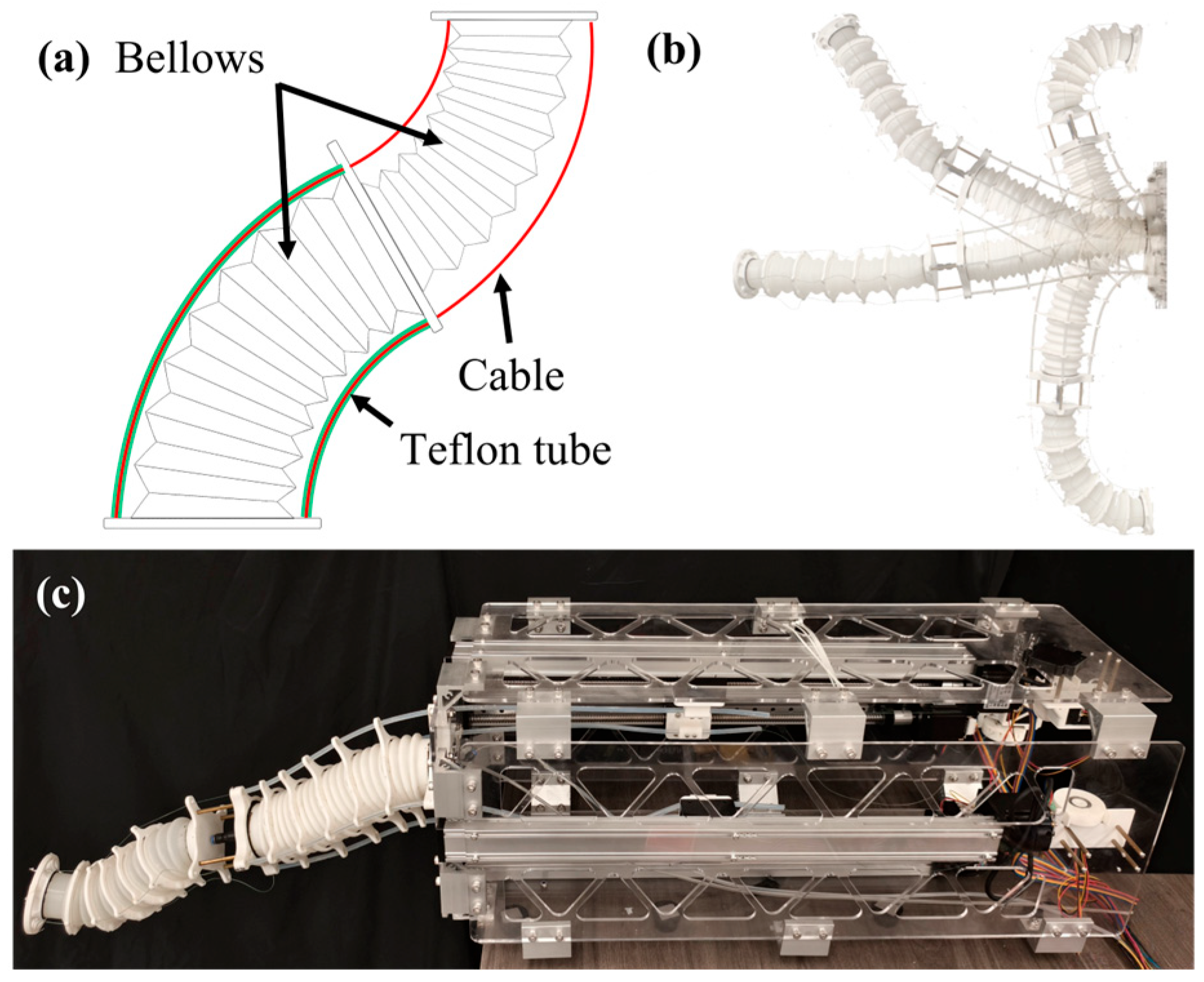
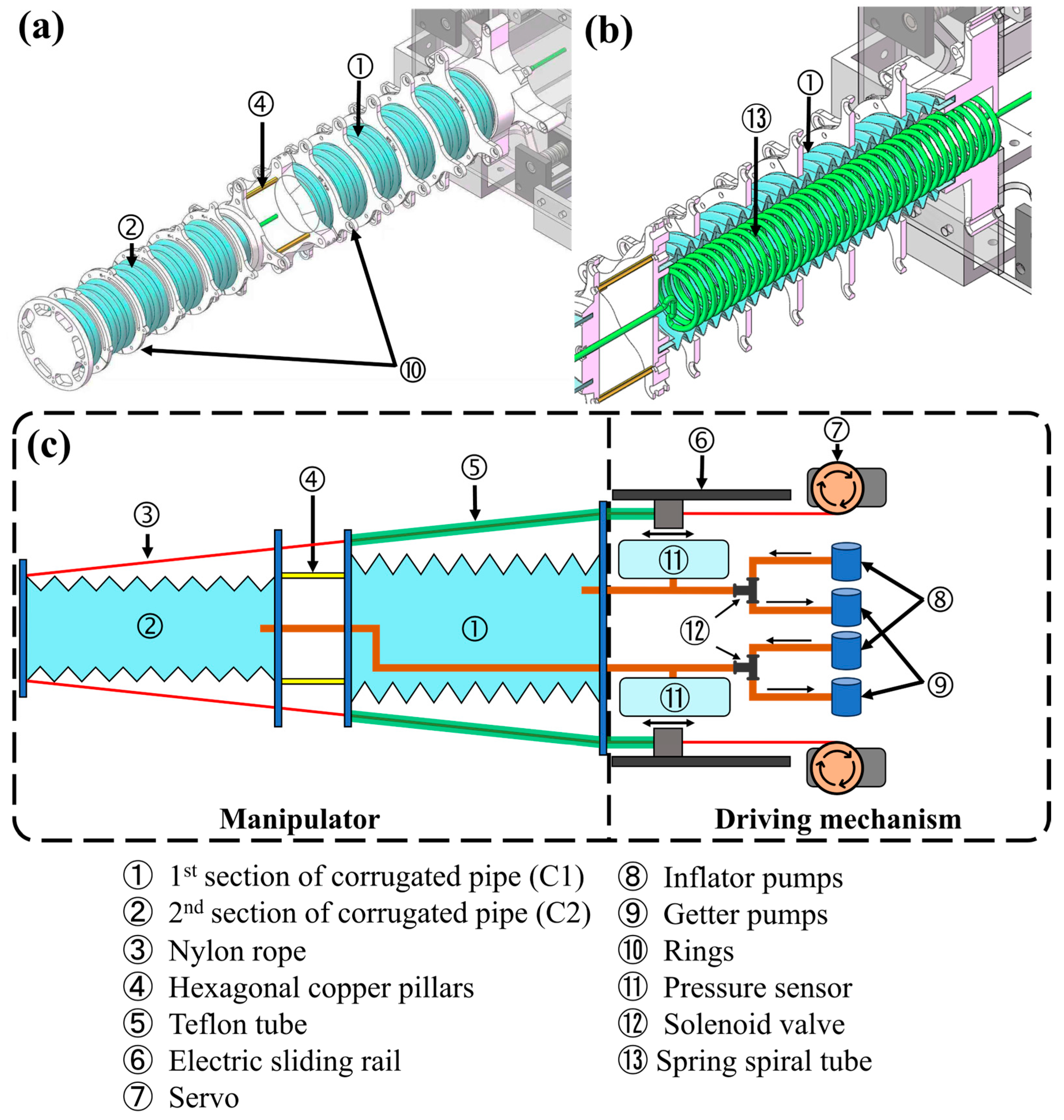
2.1. Mechanical Design of the MSESM
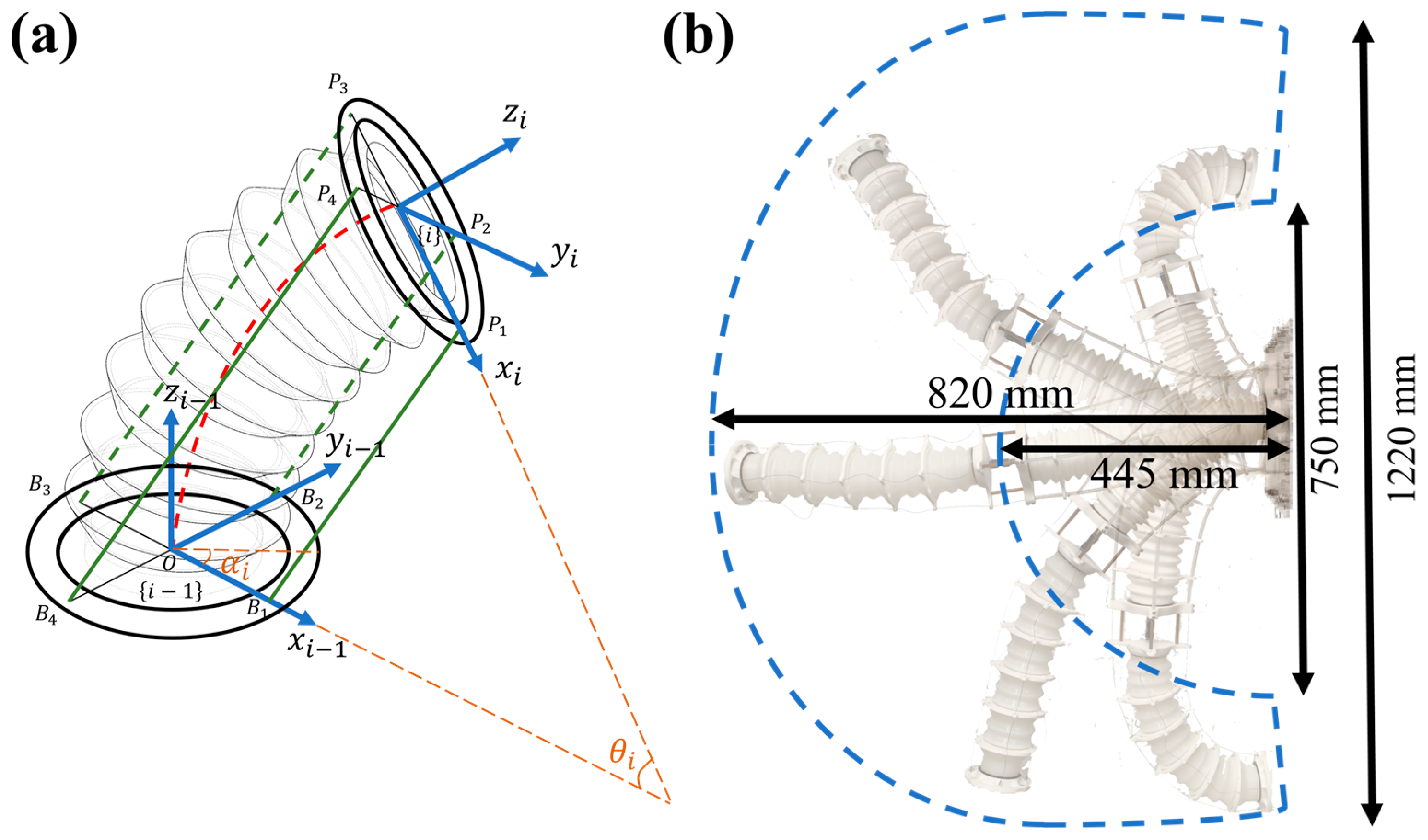
2.2. Forward and Inverse Kinematic Analysis of the MSESM End-Effector (And Avoiding Singularities in Inverse Kinematics)
2.3. Mapping and Decoupling Analysis Between Drive Space and Constant Curvature State Space
3. Experimental Characterization of the MSESM
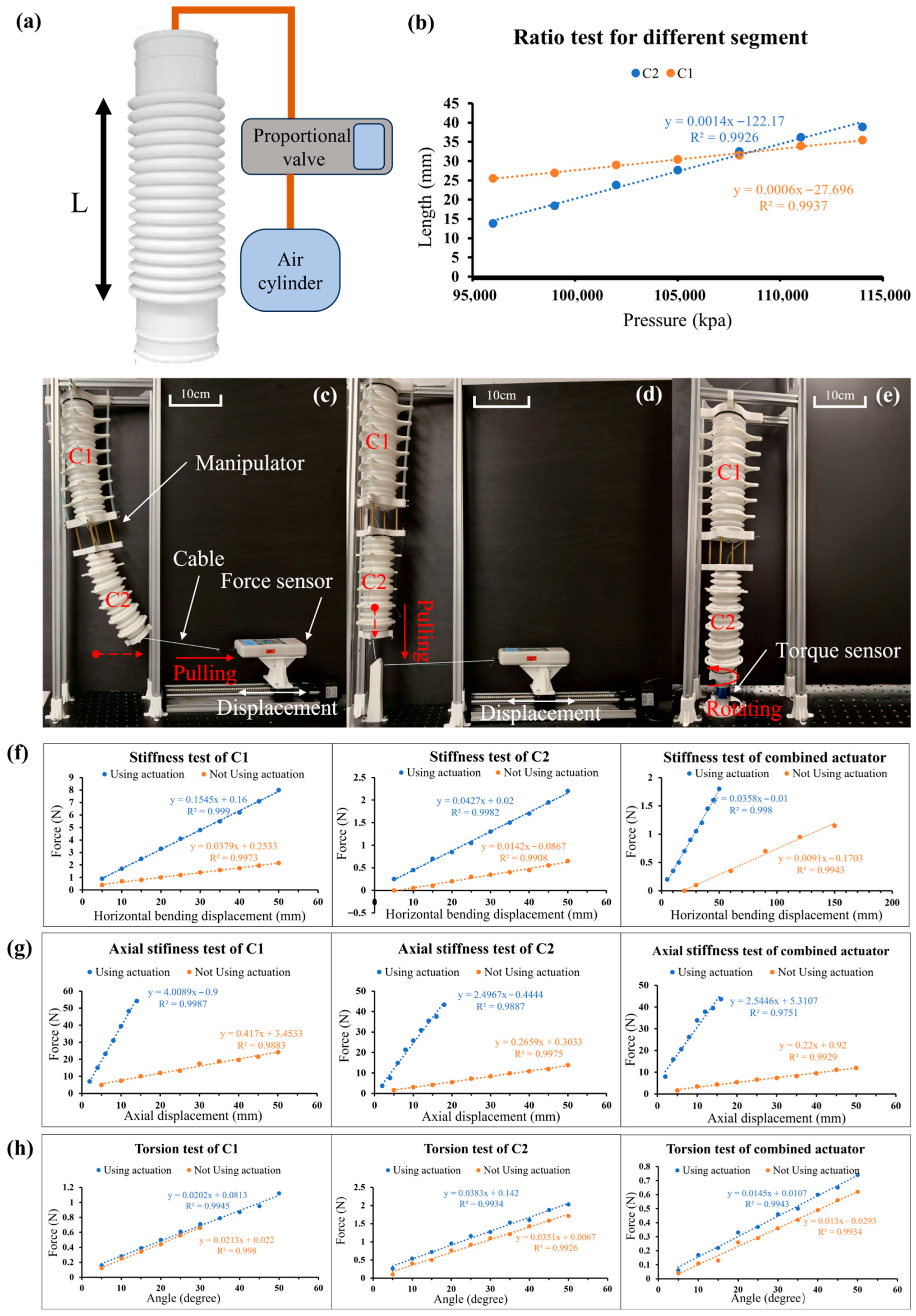
3.1. Extension Ratio Test
3.2. Stiffness Test of Different Segments
3.3. Axial Stiffness Test
3.4. Torsion Test
4. Construction of the “Prior Prediction and Data Correction” Residual Learning Architecture
4.1. Reasons for Choosing the Constant Curvature Model
4.2. Sampling and Neural Network Model Construction
5. Performance Demonstration of the MSESM
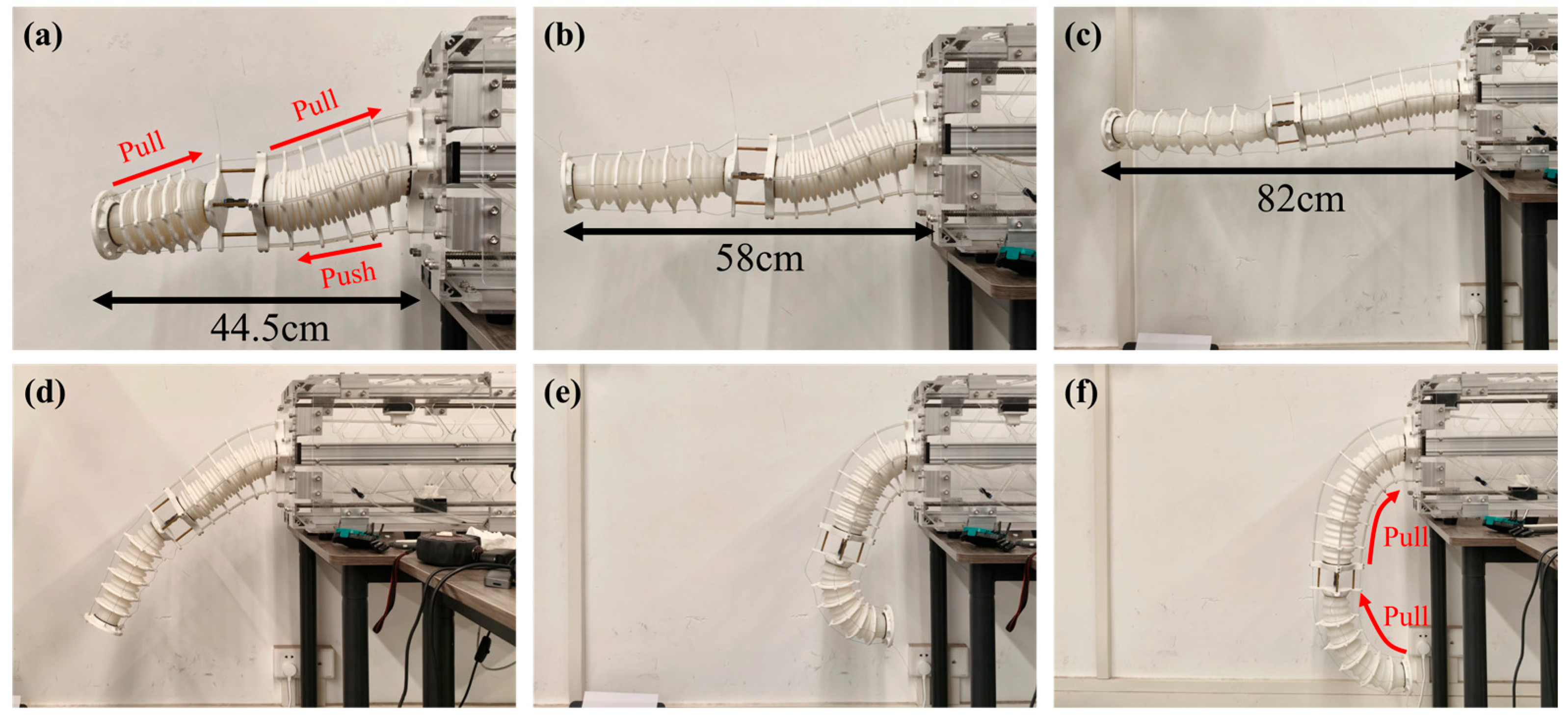
5.1. Multimodal Motion Performance Demonstration
5.2. Trajectory Tracking Experiment
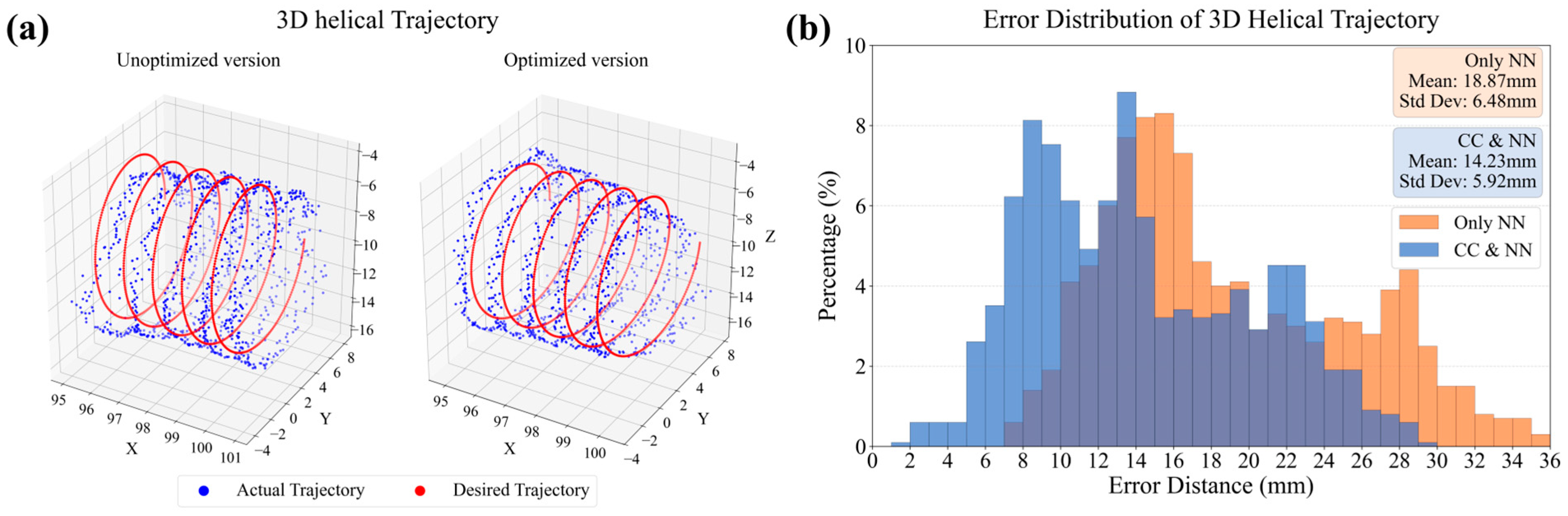
5.3. Three-Dimensional Helical Trajectory Tracking Experiment
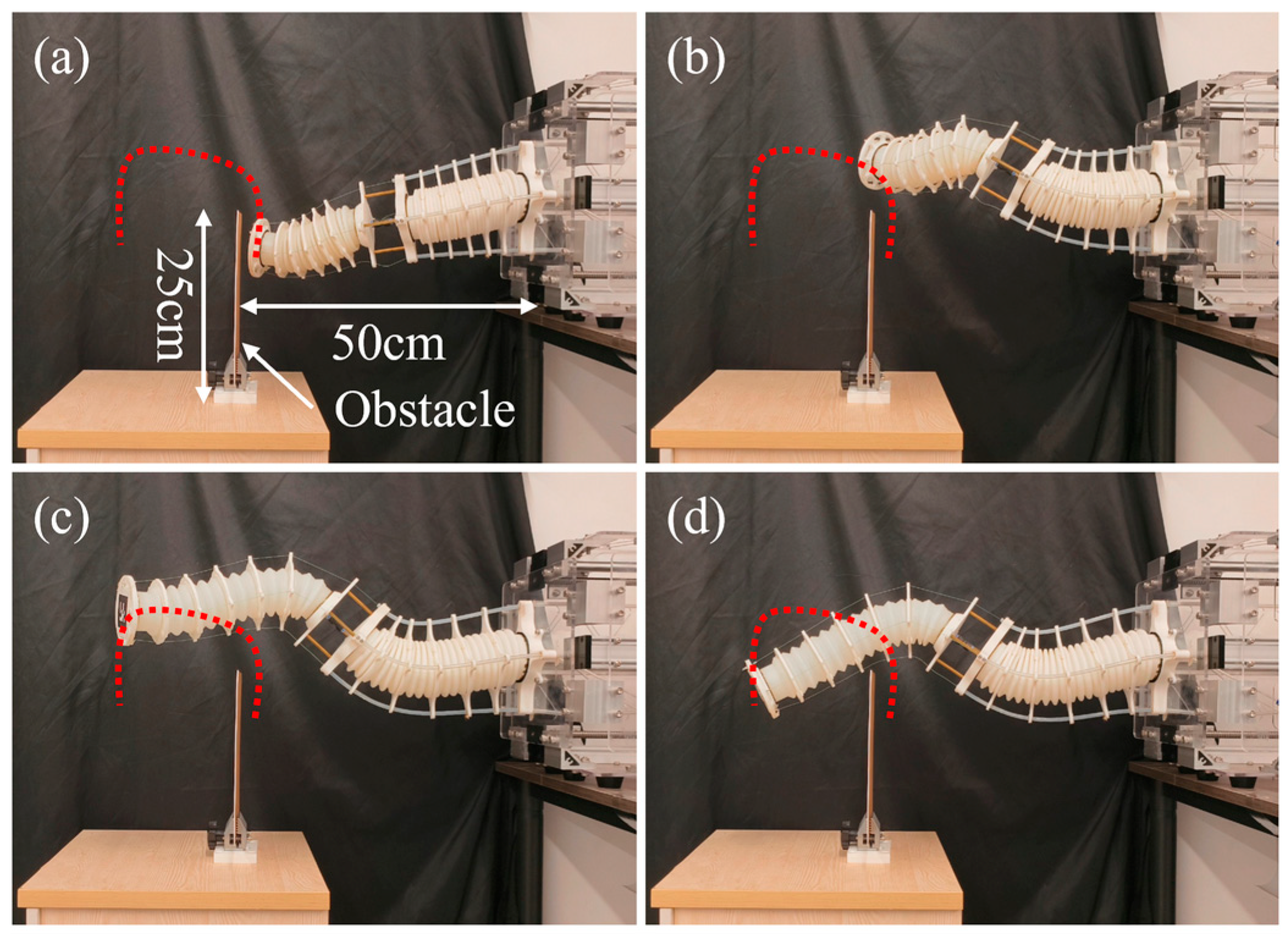
5.4. Obstacle Crossing Test
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MSESM | Multi-Segment Extendable Soft Manipulator |
References
- Burgner-Kahrs, J.; Rucker, D.C.; Choset, H. Continuum Robots for Medical Applications: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1261–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolachalama, S.; Lakshmanan, S. Continuum Robots for Manipulation Applications: A Survey. J. Robot. 2020, 2020, 4187048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Singh, P.; Krishna, C.M. Continuum Arm Robotic Manipulator: A Review. Univers. J. Mech. Eng. 2014, 2, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, Z.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, X.; Duo, Y.; Chen, B.; Kong, S.; Shao, Z.; Gong, Z.; et al. An Underwater Robotic System With a Soft Continuum Manipulator for Autonomous Aquatic Grasping. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2024, 29, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Kan, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Rajabi, H.; Wu, Z.; Peng, H.; Wu, J. A Preprogrammable Continuum Robot Inspired by Elephant Trunk for Dexterous Manipulation. Soft Robot. 2023, 10, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Freris, N.M.; Wei, X. SpiRobs: Logarithmic Spiral-Shaped Robots for Versatile Grasping across Scales. Device 2025, 3, 100646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, D.; Zhao, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J. Design of a Bio-Inspired Extensible Continuum Manipulator with Variable Stiffness. J. Bionic Eng. 2025, 22, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.; Branson, D.T.; Zheng, T.; Guglielmino, E.; Caldwell, D.G. Design, Modeling and Control of a Pneumatically Actuated Manipulator Inspired by Biological Continuum Structures. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2013, 8, 036008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Han, L.; Zhu, X.; Xu, K. Development of a Dexterous Continuum Manipulator for Exploration and Inspection in Confined Spaces. Ind. Robot. 2016, 43, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takane, E.; Tadakuma, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Konyo, M.; Tadokoro, S. A Mechanical Approach to Realize Reflexive Omnidirectional Bending Motion for Pneumatic Continuum Robots. Robomech J. 2016, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Cao, L.; Liu, J. A Review of Soft Manipulator Research, Applications, and Opportunities. J. Field Robot. 2022, 39, 281–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, N.; Ge, L.; Gu, G. Dimension Optimization of Pneumatically Actuated Soft Continuum Manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 14–18 April 2019; IEEE: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2019; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, W.; Dong, X.; Mohammad, A.; Wang, M.; Axinte, D.; Norton, A. Design and Validation of a Novel Fuzzy-Logic-Based Static Feedback Controller for Tendon-Driven Continuum Robots. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2021, 26, 3010–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wang, T.; Fang, X.; Shi, Z. Design, Fabrication and Modeling Analysis of a Spiral Support Structure with Superelastic Ni-Ti Shape Memory Alloy for Continuum Robot. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 045007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.L.; Sikorski, J.; Ananthasuresh, G.K.; Venkiteswaran, V.K.; Misra, S. Design, Sensing, and Control of a Magnetic Compliant Continuum Manipulator. IEEE Trans. Med. Robot. Bionics 2022, 4, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Renda, F.; Le Gall, A.; Mocellin, L.; Bernabei, M.; Dangel, T.; Ciuti, G.; Cianchetti, M.; Stefanini, C. Data-Driven Methods Applied to Soft Robot Modeling and Control: A Review. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2025, 22, 2241–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadati, S.M.H.; Naghibi, S.E.; Shiva, A.; Walker, I.D.; Althoefer, K.; Nanayakkara, T. Mechanics of Continuum Manipulators, a Comparative Study of Five Methods with Experiments. In Towards Autonomous Robotic Systems; Gao, Y., Fallah, S., Jin, Y., Lekakou, C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 10454, pp. 686–702. ISBN 978-3-319-64106-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Hao, L.; Yang, H.; Xiang, C. Model-Free Tracking Control of Continuum Manipulators With Global Stability and Assigned Accuracy. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Kang, R.; Branson, D.T.; Dai, J.S. Model-Free Control for Continuum Robots Based on an Adaptive Kalman Filter. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, R.; Nishikawa, S.; Niiyama, R.; Kuniyoshi, Y. Model-Free Reinforcement Learning with Ensemble for a Soft Continuum Robot Arm. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 4th International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), New Haven, CT, USA, 12–16 April 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, N.; Yu, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, T. Model-Free Motion Control of Continuum Robots Based on a Zeroing Neurodynamic Approach. Neural Netw. 2021, 133, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Rong, Y.; Gu, G. High-Precision Dynamic Control of Soft Robots With the Physics-Learning Hybrid Modeling Approach. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2025, 30, 1658–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruder, D.; Bombara, D.; Wood, R.J. A Koopman-Based Residual Modeling Approach for the Control of a Soft Robot Arm. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2025, 44, 388–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.J.; Jones, B.A. Design and Kinematic Modeling of Constant Curvature Continuum Robots: A Review. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2010, 29, 1661–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Yang, G.; Zheng, T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Fang, Z. An Accuracy Enhancement Method for a Cable-Driven Continuum Robot With a Flexible Backbone. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 37474–37481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renda, F.; Cianchetti, M.; Giorelli, M.; Arienti, A.; Laschi, C. A 3D Steady-State Model of a Tendon-Driven Continuum Soft Manipulator Inspired by the Octopus Arm. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2012, 7, 025006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanfar, M.; Taki, S.; Sayadi, A.; Cecere, R.; Dargahi, J.; Hooshiar, A. Hyperelastic Modeling and Validation of Hybrid-Actuated Soft Robot with Pressure-Stiffening. Micromachines 2023, 14, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Kwok, K.-W. A Survey for Machine Learning-Based Control of Continuum Robots. Front. Robot. AI 2021, 8, 730330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Sadati, S.M.H.; Dong, X.; Mohammad, A.; Walker, I.D.; Bergeles, C.; Xu, K.; Axinte, D.A. Continuum Robots: An Overview. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Chen, X.; Freris, N.M. Dynamical Modeling and Control of Soft Robots with Non-Constant Curvature Deformation. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.07929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, Q.; Xiang, P.; Sun, D.; Xue, Y.; Jin, R.; Qiu, K.; Xiong, R.; Wang, Y.; Lu, H. A Survey on Design, Actuation, Modeling, and Control of Continuum Robot. Cyborg Bionic Syst. 2022, 2022, 9754697. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xiong, Q.; Sui, D.; Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, T.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y. Disturbance-Adaptive Tapered Soft Manipulator With Precise Motion Controller for Enhanced Task Performance. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2024, 40, 3581–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, Z.; Lu, Y.; Cao, H.; Zhou, J.; Tong, M.C.F.; Liu, Y.-H. Easy-to-Deploy Combined Nasal/Throat Swab Robot With Sampling Dexterity and Resistance to External Interference. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 9699–9706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, T.; Sui, D.; Lin, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, Y. A 3D Printed Variable Cross-Section Pneumatic Soft Manip-ulator with High-Precision Positioning Capability: Design and Control Implementation. Sens. Actuator A-Phys. 2022, 342, 113644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y. Design and Development of a Soft Robotic Manipulator. Int. J. Mech. Mater. Des. 2020, 16, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cases | Driving Cable Lengths (mm) | Joint Variables () | Poses of the End Platform |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 300, 300, 300, 300 | 0, 0, 0 | |
| 250, 250, 250, 250 | 0, 0, 0 | ||
| 2 | 266, 276, 294, 284 | 0.3, 0.5, 280 | |
| 196, 202, 205, 198 | −0.4, 0.2, 200 | ||
| 3 | 335, 335, 305, 305 | 0.8, −0.7, 320 | |
| 158, 168, 202, 192 | 0.5, 1.0, 180 |
| NN (m) | CC Combined with NN (m) | Reduction of Errors | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rectangular | 0.0165 | 0.0043 | 74.19% | 2.39 × 10−127 |
| Triangle | 0.0156 | 0.0084 | 46.27% | 1.37 × 10−150 |
| Circle | 0.0194 | 0.0076 | 60.84% | 7.87 × 10−77 |
| Centroid Deviation (m) | Maximum Centroid Deviation (m) | DTW (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rectangular (Unoptimized) | 0.0020 | 0.0162 | 0.0433 |
| Triangle (Unoptimized) | 0.0018 | 0.0087 | 0.0355 |
| Circle (Unoptimized) | 0.0056 | 0.0395 | 0.0698 |
| Rectangular (Unoptimized) | 0.0026 | 0.0091 | 0.0433 |
| Triangle (Unoptimized) | 0.0018 | 0.0072 | 0.0361 |
| Circle (Unoptimized) | 0.0017 | 0.0080 | 0.0360 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Zeng, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Ling, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Multi-Segment Extendable Soft Manipulator Driven by a Pneumatic–Tendon Coupling Mechanism. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10100643
Yang H, Zeng Y, Zhong Z, Chen Z, Zhou J, Ling Z, Chen Y, Li Y. Multi-Segment Extendable Soft Manipulator Driven by a Pneumatic–Tendon Coupling Mechanism. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(10):643. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10100643
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hongxi, Yufeng Zeng, Zeyu Zhong, Zhiyan Chen, Junxi Zhou, Zhicheng Ling, Ye Chen, and Yunquan Li. 2025. "Multi-Segment Extendable Soft Manipulator Driven by a Pneumatic–Tendon Coupling Mechanism" Biomimetics 10, no. 10: 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10100643
APA StyleYang, H., Zeng, Y., Zhong, Z., Chen, Z., Zhou, J., Ling, Z., Chen, Y., & Li, Y. (2025). Multi-Segment Extendable Soft Manipulator Driven by a Pneumatic–Tendon Coupling Mechanism. Biomimetics, 10(10), 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10100643








