Optimization Method of Human Posture Recognition Based on Kinect V2 Sensor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
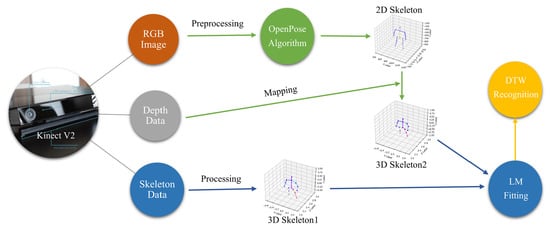
2. Skeletal Points Processing Method
2.1. Skeletal Points Information
2.2. Processing of Skeletal Points
3. Skeletal Points Fitting Method
3.1. Fitting Principle
3.2. LM Fitting Algorithm
4. Algorithm Testing and Analysis
4.1. Qualitative Analysis of Experimental Results
4.2. Human Action Analysis Based on DTW Algorithm
4.3. Quantitative Analysis of Experimental Results
5. Conclusions and Future Works
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lv, Z.; Poiesi, F.; Dong, Q.; Lloret, J.; Song, H. Deep Learning for Intelligent Human–Computer Interaction. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkov, I.; Kulkova, J.; Rohrbeck, R.; Menvielle, L.; Kaartemo, V.; Makkonen, H. Artificial intelligence-driven sustainable development: Examining organizational, technical, and processing approaches to achieving global goals. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 2253–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, H. Design of Bionic Robotic Hand Gesture Recognition System Based on Machine Vision. In Proceedings of the 2022 3rd International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning & International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications (CVIDL & ICCEA), Changchun, China, 20–22 May 2022; pp. 960–964. [Google Scholar]
- Çalışkan, A. Detecting human activity types from 3D posture data using deep learning models. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2023, 81, 104479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, D.W.; Gao, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J. Double-mode energy management for multi-energy system via distributed dynamic event-triggered Newton-Raphson algorithm. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2020, 11, 5339–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.A. Artificial intelligence assisted improved human-computer interactions for computer systems. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 101, 107950. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.L. Research on China’s Human-Computer Interaction Development Issues in the Field of Science and Technology Innovation. Ph.D. Thesis, Yan’an University, Yan’an, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, N.; Dong, M.; Zhao, J.; Wu, J.; Leung, V.C.M. Reconfigurable intelligent surface-assisted secure mobile edge computing networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 6647–6660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, K. A Survey of Human Body Action Recognition. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2014, 27, 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, W.; Pei, Q.; Wu, J.; Lin, X. Heterogeneous Computation and Resource Allocation for Wireless Powered Federated Edge Learning Systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2022, 70, 3220–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Tan, T.; Ning, H.; Hu, W. Silhouette analysis-based gait recognition for human identification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 1505–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, M.; Yu, M.; Jan, M.A.; Lan, D.; Taherkordi, A. Mobility-aware multi-hop task offloading for autonomous driving in vehicular edge computing and networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 2169–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shotton, J.; Sharp, T.; Kipman, A.; Fitzgibbon, A.; Finocchio, M.; Blake, A.; Cook, M.; Moore, R. Real-time human pose recognition in parts from single depth images. Commun. ACM 2013, 56, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Rui, X. Study on Edge Detection Method. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2006, 42, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, M.H. A Study to Wavelet Soft-Thresholding Algorithm with Application to SAR Image De-Noising. Ph.D. Thesis, Xiamen University, Xiamen, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Li, N. A random decision tree algorithm based on attribute significance. J. Hefei Univ. Technol. (Nat. Sci.) 2007, 6, 681–685. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chu, Z.; Xin, Y. Posture Recognition Technology Based on Kinect. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2020, 103, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Liu, L.; Pei, Q.; Li, K. Min-max cost optimization for efficient hierarchical federated learning in wireless edge networks. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2021, 33, 2687–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, S.; Luo, X. Towards Rehabilitation at Home After Total Knee Replacement. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2021, 26, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Shu, S. Intelligent Recognition of Physical Education Teachers’ Behaviors Using Kinect Sensors and Machine Learning. Sens. Mater. 2022, 34, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Gu, H.; Deng, W.; Xiao, Z.; Ren, X. ABL-TC: A lightweight design for network traffic classification empowered by deep learning. Neurocomputing 2022, 489, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Simon, T.; Wei, S.E.; Sheikh, Y. Realtime multi-person 2d pose estimation using part affinity fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7291–7299. [Google Scholar]
- Segal, Y.; Ofer, H.; Lenka, L. Using EfficientNet-B7 (CNN), variational auto encoder (VAE) and Siamese twins’ networks to evaluate human exercises as super objects in a TSSCI images. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.K. Joint Stable Detection and Interactive Application System Based on RGB-D. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, T.; Yang, X.; Xu, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Xu, G. Trajectory Planning of Upper Limb Rehabilitation Robot Based on Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 2020 17th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR), Kyoto, Japan, 22–26 June 2020; pp. 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.L.; Chang, C.C. Simple method integrating OpenPose and RGB-D camera for identifying 3D body landmark locations in various postures. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2022, 91, 103354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yang, R.; Gu, H.; Zhao, W.; Chen, C.; Wan, S. Multi-objective optimization for resource allocation in vehicular cloud computing networks. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 25536–25545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Gu, H.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, N. Multi-dimensional resource allocation in distributed data centers using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2022, 20, 1817–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.C. Research on The Commonness of the One Hand Shot on the Shoulder of the Active NBA Top Shooters. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Sport University, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Segal, Y.; Yona, Y.; Danan, O.; Birman, R.; Hadar, O.; Kutilek, P.; Hejda, J.; Hourova, M.; Kral, P.; Lhotska, L.; et al. Camera Setup and OpenPose Software without GPU for Calibration and Recording in Telerehabilitation Use. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on e-Health and Bioengineering (EHB), Iasi, Romania, 18–19 November 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]








| Dimensions | Traditional ML Method | Deep Learning Method | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Modal Fusion | Unimodal (RGB/Skeleton) | Multimodal independent processing | Multimodal dynamic alignment |
| Feature Extraction | Manual design of time-domain statistics | Automatic extraction but spatiotemporal coupling | DTW-driven decoupling mechanism for spatiotemporal features |
| Labeling Cost | Manual frame-by-frame labeling | Requires 10w+ labeled samples | Zero labeling |
| Optimization mechanism | Static hyperparameter | Global gradient descent | Multi-stage optimization of LM guidance |
| Occlusion Robustness | Data Enhancement Compensation | Eigenspace interpolation | Multi-source complementarity |
| Schemes | MPJPE (mm) | DTW Cumulative Deviation | Abnormal Frame Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LM + DTW | 49.8 | 1.27 | 4.8 |
| LM only | 68.7 | 3.15 | 12.5 |
| DTW only | 61.2 | 2.84 | 9.1 |
| LM + Euclidean | 57.8 | 2.09 | 6.7 |
| Action | Number of People | Number of Actions | Number of Correct Recognitions | Recognition Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| shoulder lateral press | 30 | 20 | 578 | 96.3 |
| shoulder press | 30 | 20 | 570 | 95 |
| Arnold press | 30 | 20 | 522 | 87 |
| deep squat | 30 | 20 | 512 | 85.3 |
| deadlift | 30 | 20 | 546 | 91 |
| Action | Number of People | Number of Actions | Number of Correct Recognitions | Recognition Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| shoulder lateral press | 30 | 20 | 594 | 99 |
| shoulder press | 30 | 20 | 592 | 98.7 |
| Arnold press | 30 | 20 | 566 | 94.3 |
| deep squat | 30 | 20 | 550 | 91.7 |
| deadlift | 30 | 20 | 576 | 96 |
| Action | Kinect Algorithm | Ours | z Value | p Value | Significant or Not |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| shoulder lateral press | 96.3% | 99.0% | −3.52 | 0.0004 | yes |
| shoulder press | 95.0% | 98.7% | −3.94 | <0.001 | yes |
| Arnold press | 87.0% | 94.3% | −5.11 | <0.001 | yes |
| deep squat | 85.3% | 91.7% | −4.22 | <0.001 | yes |
| deadlift | 91.0% | 96.0% | −3.71 | 0.0002 | yes |
| Action | Accuracy (%) | SD(σ) | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| shoulder lateral press | 99.0% | ±0.41 | [98.6%, 99.4%] | <0.001 |
| shoulder press | 98.7% | ±0.43 | [98.3%, 99.1%] | <0.001 |
| Arnold press | 94.3% | ±0.93 | [93.4%, 95.2%] | <0.001 |
| deep squat | 91.7% | ±1.12 | [90.6%, 92.8%] | <0.001 |
| deadlift | 96.0% | ±0.78 | [95.2%, 96.8%] | <0.001 |
| Distance (m) | Kinect Algorithm | Recognition Rate (%) | Ours | Recognition Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 | 189 | 63 | 213 | 71 |
| 2.0 | 278 | 92.67 | 286 | 95.33 |
| 3.0 | 300 | 100 | 300 | 100 |
| 3.5 | 286 | 95.33 | 300 | 100 |
| 4.0 | 254 | 84.67 | 273 | 91 |
| 4.5 | 102 | 34 | 125 | 41.67 |
| Angel (°) | Kinect Algorithm | Recognition Rate (%) | Ours | Recognition Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 300 | 100 | 300 | 100 |
| 30 | 289 | 96.33 | 300 | 100 |
| 45 | 256 | 85.33 | 287 | 95.67 |
| 60 | 213 | 71 | 264 | 88 |
| 90 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 300 | 100 | 300 | 100 |
| No. | Kinect Recognition Speed (s) | OpenPose Recognition Speed (s) | Ours (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.57612 | 1.11011 | 1.04361 |
| 2 | 0.60053 | 1.09477 | 1.01948 |
| 3 | 0.59206 | 1.08447 | 1.03209 |
| 4 | 0.54681 | 1.13548 | 1.04618 |
| 5 | 0.61435 | 1.22148 | 1.09143 |
| 6 | 0.55164 | 1.30686 | 1.20437 |
| 7 | 0.59631 | 1.24357 | 1.03421 |
| 8 | 0.60321 | 1.04312 | 1.08437 |
| 9 | 0.57619 | 1.08342 | 1.07681 |
| 10 | 0.60746 | 1.13465 | 1.12648 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Li, H.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Y. Optimization Method of Human Posture Recognition Based on Kinect V2 Sensor. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040254
Li H, Li H, Qin Y, Liu Y. Optimization Method of Human Posture Recognition Based on Kinect V2 Sensor. Biomimetics. 2025; 10(4):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040254
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hang, Hao Li, Ying Qin, and Yiming Liu. 2025. "Optimization Method of Human Posture Recognition Based on Kinect V2 Sensor" Biomimetics 10, no. 4: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040254
APA StyleLi, H., Li, H., Qin, Y., & Liu, Y. (2025). Optimization Method of Human Posture Recognition Based on Kinect V2 Sensor. Biomimetics, 10(4), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics10040254