Identifying Patients with Polycythemia Vera at Risk of Thrombosis after Hydroxyurea Initiation: The Polycythemia Vera—Advanced Integrated Models (PV-AIM) Project
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Ethics
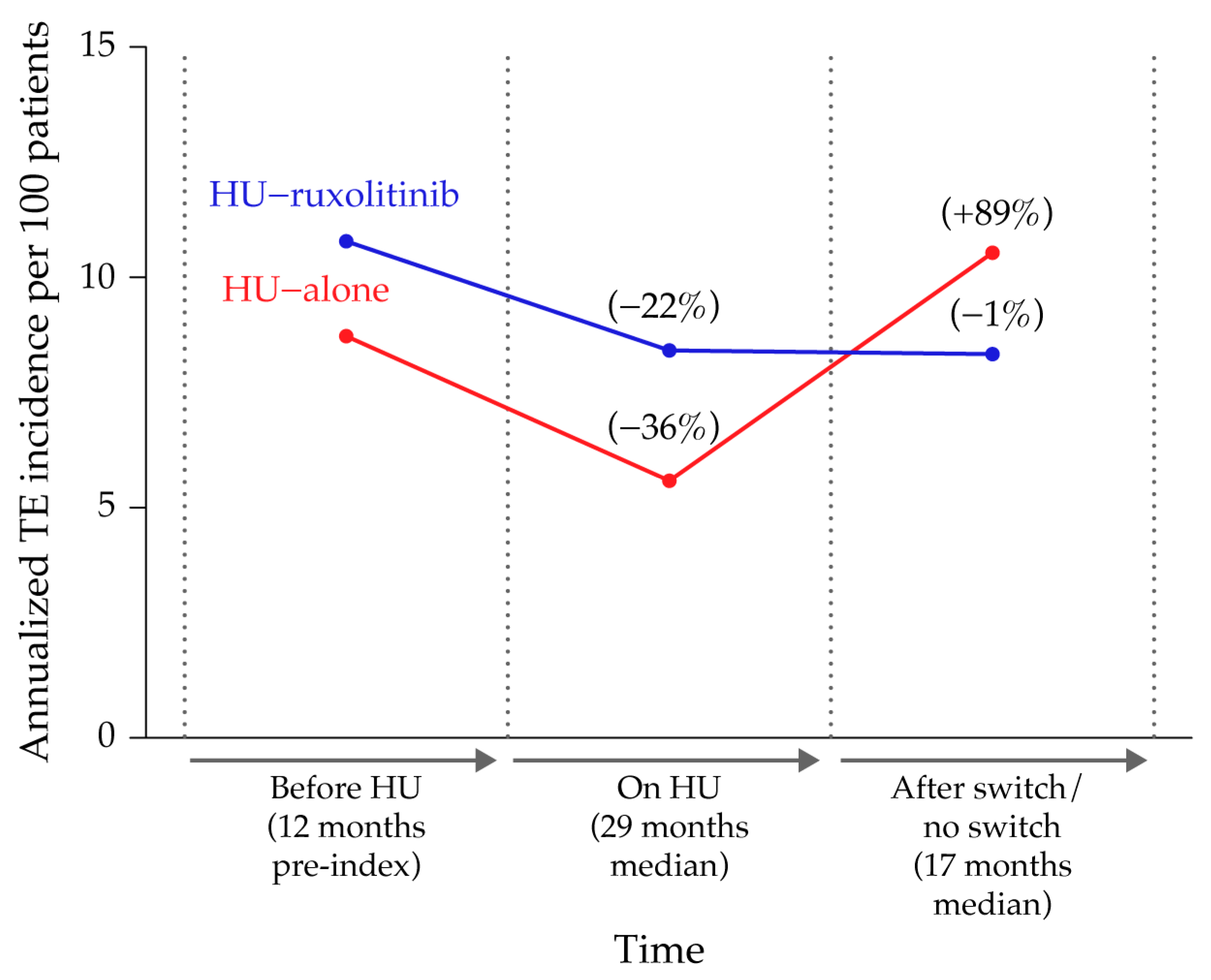
2.3. Annual Standardized Incidence Rate of TE in Patients with PV Treated with HU-Alone vs. HU-Ruxolitinib
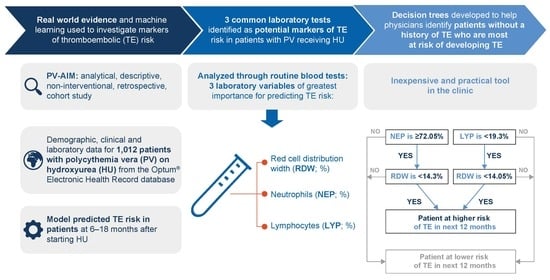
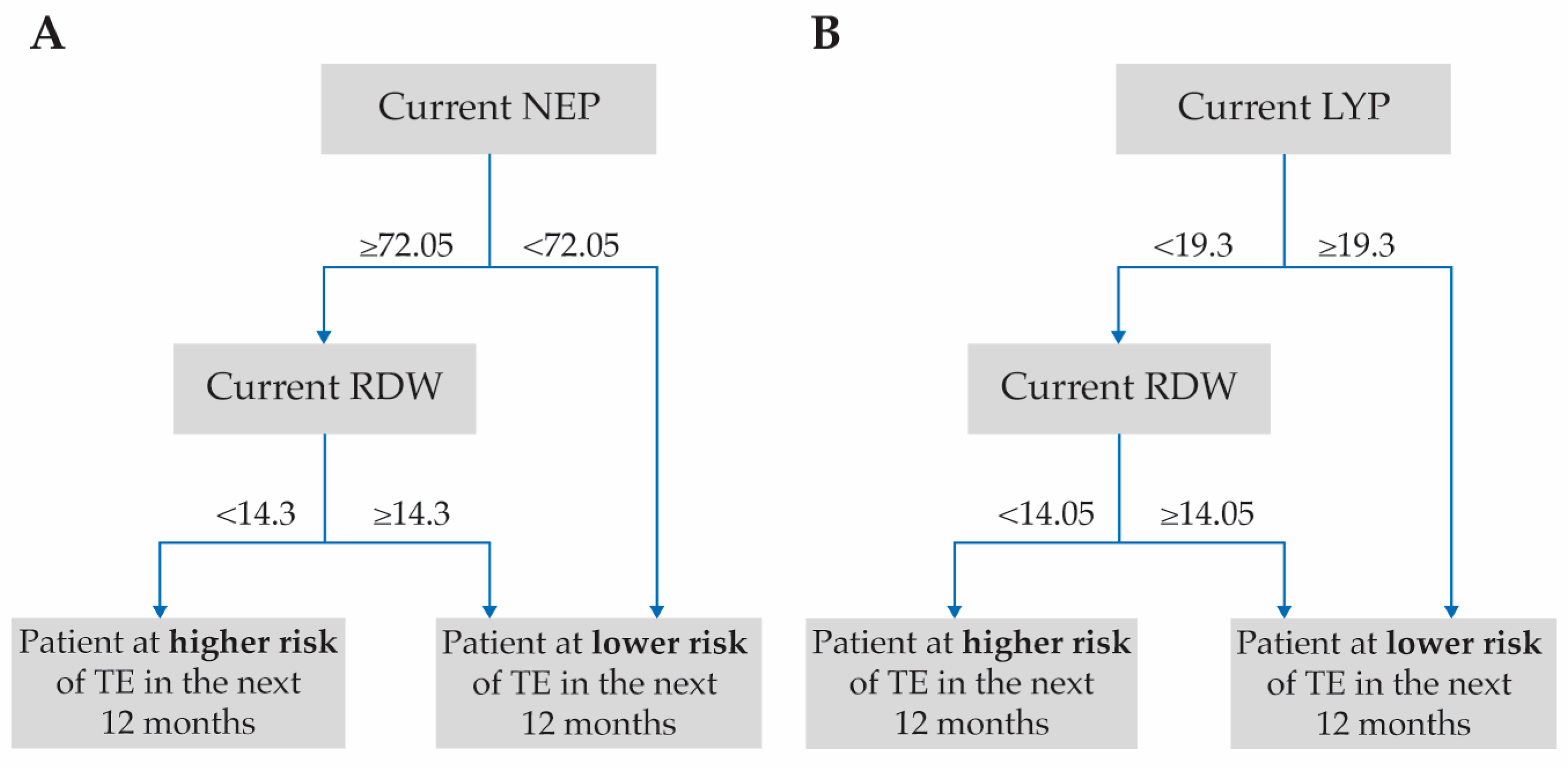
2.4. Prediction of TE in Patients with PV Receiving HU Using Machine Learning
2.5. External Validation of the Model Using an Independent Croatian Dataset
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Selection and Patient Characteristics
3.2. Annual Standardized IR of TE in PV Patients Treated with HU-Alone vs. HU-Ruxolitinib
3.3. Prediction of TE in Patients Receiving HU
3.4. Independent Validation of the RSF Model
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spivak, J.L. Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2168–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.; Griffin, L.; Robinson Harris, D. Polycythemia Vera: Rapid Evidence Review. Am. Fam. Physician 2021, 103, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reikvam, H.; Tiu, R.V. Venous thromboembolism in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Leukemia 2012, 26, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesshammer, M.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Besses, C. Thromboembolic events in polycythemia vera. Ann. Hematol. 2019, 98, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullin, M.F.; Harrison, C.N.; Ali, S.; Cargo, C.; Chen, F.; Ewing, J.; Garg, M.; Godfrey, A.; Knapper, S.; McLornan, D.P.; et al. A guideline for the diagnosis and management of polycythaemia vera. A British Society for Haematology Guideline. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 176–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tefferi, A.; Rumi, E.; Finazzi, G.; Gisslinger, H.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Rodeghiero, F.; Randi, M.L.; Vaidya, R.; Cazzola, M.; Rambaldi, A.; et al. Survival and prognosis among 1545 patients with contemporary polycythemia vera: An international study. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1874–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesa, R.A. New guidelines from the NCCN for polycythemia vera. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 15, 848–850. [Google Scholar]
- Marchioli, R.; Finazzi, G.; Specchia, G.; Cacciola, R.; Cavazzina, R.; Cilloni, D.; De Stefano, V.; Elli, E.; Iurlo, A.; Latagliata, R.; et al. Cardiovascular events and intensity of treatment in polycythemia vera. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbui, T.; Masciulli, A.; Marfisi, M.R.; Tognoni, G.; Finazzi, G.; Rambaldi, A.; Vannucchi, A. White blood cell counts and thrombosis in polycythemia vera: A subanalysis of the CYTO-PV study. Blood 2015, 126, 560–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Larrán, A.; Kerguelen, A.; Hernández-Boluda, J.C.; Pérez-Encinas, M.; Ferrer-Marín, F.; Bárez, A.; Martínez-López, J.; Cuevas, B.; Mata, M.I.; García-Gutiérrez, V.; et al. Frequency and prognostic value of resistance/intolerance to hydroxycarbamide in 890 patients with polycythaemia vera. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 172, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Larrán, A.; Pérez-Encinas, M.; Ferrer-Marín, F.; Hernández-Boluda, J.C.; Ramírez, M.J.; Martínez-López, J.; Magro, E.; Cruz, Y.; Mata, M.I.; Aragües, P.; et al. Risk of thrombosis according to need of phlebotomies in patients with polycythemia vera treated with hydroxyurea. Haematologica 2017, 102, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masciulli, A.; Ferrari, A.; Carobbio, A.; Ghirardi, A.; Barbui, T. Ruxolitinib for the prevention of thrombosis in polycythemia vera: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passamonti, F.; Griesshammer, M.; Palandri, F.; Egyed, M.; Benevolo, G.; Devos, T.; Callum, J.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Sivgin, S.; Bensasson, C.; et al. Ruxolitinib for the treatment of inadequately controlled polycythaemia vera without splenomegaly (RESPONSE-2): A randomised, open-label, phase 3b study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuelson, B.T.; Vesely, S.K.; Chai-Adisaksopha, C.; Scott, B.L.; Crowther, M.; Garcia, D. The impact of ruxolitinib on thrombosis in patients with polycythemia vera and myelofibrosis: A meta-analysis. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2016, 27, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingam, S.; Flatow-Trujillo, L.; Andritsos, L.A.; Arana Yi, C. Ruxolitinib in the Treatment of Polycythemia Vera: An Update on Health-Related Quality of Life and Patient-Reported Outcomes. J. Blood Med. 2019, 10, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shouval, R.; Fein, J.A.; Savani, B.; Mohty, M.; Nagler, A. Machine learning and artificial intelligence in haematology. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 192, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radakovich, N.; Nagy, M.; Nazha, A. Machine learning in haematological malignancies. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e541–e550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.; Imai, K.; King, G.; Stuart, E.A. MatchIt: Nonparametric preprocessing for parametric causal inference. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 42, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Carobbio, A.; Masciulli, A.; Ghirardi, A.; Finazzi, G.; De Stefano, V.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Barbui, T. Clinical outcomes under hydroxyurea treatment in polycythemia vera: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Haematologica 2019, 104, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, V.; Rossi, E.; Carobbio, A.; Ghirardi, A.; Betti, S.; Finazzi, G.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Barbui, T. Hydroxyurea prevents arterial and late venous thrombotic recurrences in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms but fails in the splanchnic venous district. Pooled analysis of 1500 cases. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Larrán, A.; Díaz-González, A.; Such, E.; Mora, E.; Andrade-Campos, M.; García-Hernández, C.; Gómez-Casares, M.T.; García-Gutiérrez, V.; Carreño-Tarragona, G.; Garrote, M.; et al. Genomic characterization of patients with polycythemia vera developing resistance to hydroxyurea. Leukemia 2021, 35, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannucchi, A.M.; Kiladjian, J.J.; Griesshammer, M.; Masszi, T.; Durrant, S.; Passamonti, F.; Harrison, C.N.; Pane, F.; Zachee, P.; Mesa, R.; et al. Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia vera. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiladjian, J.J.; Zachee, P.; Hino, M.; Pane, F.; Masszi, T.; Harrison, C.N.; Mesa, R.; Miller, C.B.; Passamonti, F.; Durrant, S.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib versus best available therapy in polycythaemia vera (RESPONSE): 5-year follow up of a phase 3 study. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e226–e237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Larrán, A.; Garrote, M.; Ferrer-Marín, F.; Pérez-Encinas, M.; Mata-Vazquez, M.I.; Bellosillo, B.; Arellano-Rodrigo, E.; Gómez, M.; García, R.; García-Gutiérrez, V.; et al. Real-world analysis of main clinical outcomes in patients with polycythemia vera treated with ruxolitinib or best available therapy after developing resistance/intolerance to hydroxyurea. Cancer 2022, 128, 2441–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.; Nangalia, J.; Boucher, R.; Jackson, A.; Yap, C.; O’Sullivan, J.; Fox, S.; Ailts, I.; Dueck, A.; Geyer, H.; et al. Ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for polycythemia vera intolerant or resistant to hydroxycarbamide in a randomized trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carobbio, A.; Ferrari, A.; Masciulli, A.; Ghirardi, A.; Barosi, G.; Barbui, T. Leukocytosis and thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 1729–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Zhao, R. Associations of lymphocyte percentage and red blood cell distribution width with risk of lung cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, B.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Qin, T.; Qu, S.; Pan, L.; Sun, X.; Shi, Z.; Huang, H.; et al. RBC distribution width predicts thrombosis risk in polycythemia vera. Leukemia 2022, 36, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carobbio, A.; Vannucchi, A.M.; De Stefano, V.; Masciulli, A.; Guglielmelli, P.; Loscocco, G.G.; Ramundo, F.; Rossi, E.; Kanthi, Y.; Tefferi, A.; et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a novel predictor of venous thrombosis in polycythemia vera. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerds, A.T.; Mesa, R.A.; Burke, J.M.; Grunwald, M.R.; Stein, B.L.; Scherber, R.; Yu, J.; Hamer-Maansson, J.E.; Oh, S. A real-world evaluation of the association between elevated blood counts and thrombotic events in polycythemia vera (analysis of data from the REVEAL study). Blood 2021, 138, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, S.; Yu, J.; Paranagama, D.; Shrestha, S.; Wang, L.; Baser, O.; Scherber, R. Elevated White Blood Cell Levels and Thrombotic Events in Patients with Polycythemia Vera: A Real-World Analysis of Veterans Health Administration Data. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020, 20, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrukh, F.; Guglielmelli, P.; Loscocco, G.G.; Pardanani, A.; Hanson, C.A.; De Stefano, V.; Barbui, T.; Gangat, N.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Tefferi, A. Deciphering the individual contribution of absolute neutrophil and monocyte counts to thrombosis risk in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, E35–E37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elli, E.M.; Baratè, C.; Mendicino, F.; Palandri, F.; Palumbo, G.A. Mechanisms Underlying the Anti-inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Activity of Ruxolitinib. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezende, S.M.; Lijfering, W.M.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Cannegieter, S.C. Red cell distribution width and blood monocytes are associated with an increased risk of venous thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 227. [Google Scholar]
- Krečak, I.; Krečak, F.; Gverić-Krečak, V. High red blood cell distribution width might predict thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2020, 80, 102368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.H.; Patel, H.R.; Higgins, J.M. Modulation of red blood cell population dynamics is a fundamental homeostatic response to disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2015, 90, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, S.; Santoro, M.; Accurso, V.; Agliastro, G.; Raso, S.; Di Piazza, F.; Perez, A.; Bono, M.; Russo, A.; Siragusa, S. Cardiovascular Risk in Polycythemia Vera: Thrombotic Risk and Survival: Can Cytoreductive Therapy Be Useful in Patients with Low-Risk Polycythemia Vera with Cardiovascular Risk Factors? Oncol. Res. Treat. 2020, 43, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbui, T.; Vannucchi, A.M.; Carobbio, A.; Rumi, E.; Finazzi, G.; Gisslinger, H.; Ruggeri, M.; Randi, M.L.; Cazzola, M.; Rambaldi, A.; et al. The effect of arterial hypertension on thrombosis in low-risk polycythemia vera. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, E5–E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Feature | Patient Data Extracted from the Optum® EHR Database |
|---|---|
| Demographics | Age at index, gender, race, ethnicity, region, division |
| History | Thromboembolic event (TE) history a, number of phlebolotomy procedures |
| Laboratory values b | Hematocrit (Hct), white blood cell count (WBC), platelet count (Plt), red blood cell distribution width (RDW), lymphocyte percentage (LYP), hemoglobin (HGB), neutrophil percentage (NEP) |
| Anticoagulant/ antiplatelet drugs used/prescribed a | Apixaban, Rivaroxaban, Edoxaban, Dabigatran warfarin, UFH (unfractioned heparins), LMWH (low molecular weight heparins, e.g., Enoxaparin, Nadroparin), Fondaparinux, Acetylsalicylic acid, Ticlopidine, Clopidogrel, Radugrel (prasugrel), Cangrelor, Abciximab (anti GpIIb/IIIa), Abciximab |
| Observations b | Respiratory (RSP), heart rate (HRT), pulse (PLS), weight (WGT), height (HGT), body mass index (BMI), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), alcohol a, smoking a |
| Characteristics | Optum® EHR Dataset (n = 1012) | Croatian Dataset (n = 100) |
|---|---|---|
| Females (%) | 51 | 45 |
| Age (years), median (IQR) | 73 (64–80) | 65 (56–72) |
| JAK2-V617F mutation, n | - | 100 |
| Palpable splenomegaly (%) | - | 23 |
| History of thrombosis (%) | 16.1 | 32 |
| Arterial hypertension (%) | 68.8 | 79 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 13.7 | 16 |
| Hyperlipidemia (%) | 15.9 | 16 |
| Smoking (%) | 12.8 | 17 |
| Anticoagulant or antiplatelet use a (%) | 48 (3 to 6 months)/ 93 (anytime) | 81 (anytime) |
| Leukocytes (×109/L), median (IQR) | 7.7 (5.9–10.3) | 7.2 (6.0–11.7) |
| Granulocytes (×109/L), median (IQR) | - | 3.8 (2.8–5.4) |
| Neutrophils (%), median (IQR) | 70 (62–78) | 68 (60–78) |
| Lymphocytes (%), median (IQR) | 19.5 (13.0–26.3) | 22 (14.8–30) |
| Platelets (×109/L), median (IQR) | 278 (203–381) | 269 (200–454) |
| Hematocrit (%), median (IQR) | 43 (39.7–46.3) | 42 (40–46) |
| Hemoglobin (g/L), median (IQR) | 140 (130–151) | 144 (129–154) |
| RDW (%), median (IQR) | 17.0 (14.5–19.3) | 16.0 (14.3–17.5) |
| Rank | Variable Name | Score |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TE history (yes/no) | 0.16 |
| 2 | Median BMI | 0.08 |
| 3 | Median DBP | 0.065 |
| 4 | Median weight | 0.064 |
| 5 | Median NEP | 0.059 |
| 6 | Median WBC | 0.059 |
| 7 | Median LYP | 0.058 |
| 8 | Use of anticoagulant/antiplatelet therapy | 0.058 |
| 9 | Age at index | 0.054 |
| 10 | Median RDW | 0.053 |
| Interaction | Cohort | Synergy a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable 1 | Variable 2 | Expected p Value | Observed p Value | Score | |
| NEP | RDW | Without TE history | 1.80 × 10−3 | 8.30 × 10−6 | 223.11 |
| LYP | RDW | Without TE history | 1.30 × 10−4 | 7.10 × 10−7 | 177.27 |
| DBP | Weight | Without TE history | 3.50 × 10−3 | 4.30 × 10−4 | 8.16 |
| Weight | RDW | Without TE history | 4.10 × 10−4 | 8.40 × 10−5 | 4.92 |
| LYP | RDW | All | 9.70 × 10−6 | 2.10 × 10−6 | 4.70 |
| BMI | Anticoagulant/ antiplatelet | Without TE history | 7.60 × 10−5 | 1.70 × 10−5 | 4.43 |
| WBC | RDW | With TE history | 1.40 × 10−2 | 4.80 × 10−3 | 2.88 |
| BMI | RDW | All | 1.90 × 10−3 | 7.00 × 10−4 | 2.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verstovsek, S.; Krečak, I.; Heidel, F.H.; De Stefano, V.; Bryan, K.; Zuurman, M.W.; Zaiac, M.; Morelli, M.; Smyth, A.; Redondo, S.; et al. Identifying Patients with Polycythemia Vera at Risk of Thrombosis after Hydroxyurea Initiation: The Polycythemia Vera—Advanced Integrated Models (PV-AIM) Project. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071925
Verstovsek S, Krečak I, Heidel FH, De Stefano V, Bryan K, Zuurman MW, Zaiac M, Morelli M, Smyth A, Redondo S, et al. Identifying Patients with Polycythemia Vera at Risk of Thrombosis after Hydroxyurea Initiation: The Polycythemia Vera—Advanced Integrated Models (PV-AIM) Project. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071925
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerstovsek, Srdan, Ivan Krečak, Florian H. Heidel, Valerio De Stefano, Kenneth Bryan, Mike W. Zuurman, Michael Zaiac, Mara Morelli, Aoife Smyth, Santiago Redondo, and et al. 2023. "Identifying Patients with Polycythemia Vera at Risk of Thrombosis after Hydroxyurea Initiation: The Polycythemia Vera—Advanced Integrated Models (PV-AIM) Project" Biomedicines 11, no. 7: 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071925
APA StyleVerstovsek, S., Krečak, I., Heidel, F. H., De Stefano, V., Bryan, K., Zuurman, M. W., Zaiac, M., Morelli, M., Smyth, A., Redondo, S., Bigan, E., Ruhl, M., Meier, C., Beffy, M., & Kiladjian, J.-J. (2023). Identifying Patients with Polycythemia Vera at Risk of Thrombosis after Hydroxyurea Initiation: The Polycythemia Vera—Advanced Integrated Models (PV-AIM) Project. Biomedicines, 11(7), 1925. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071925