Application of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging and Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Kidney Injury Associated with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. fMRI Protocol
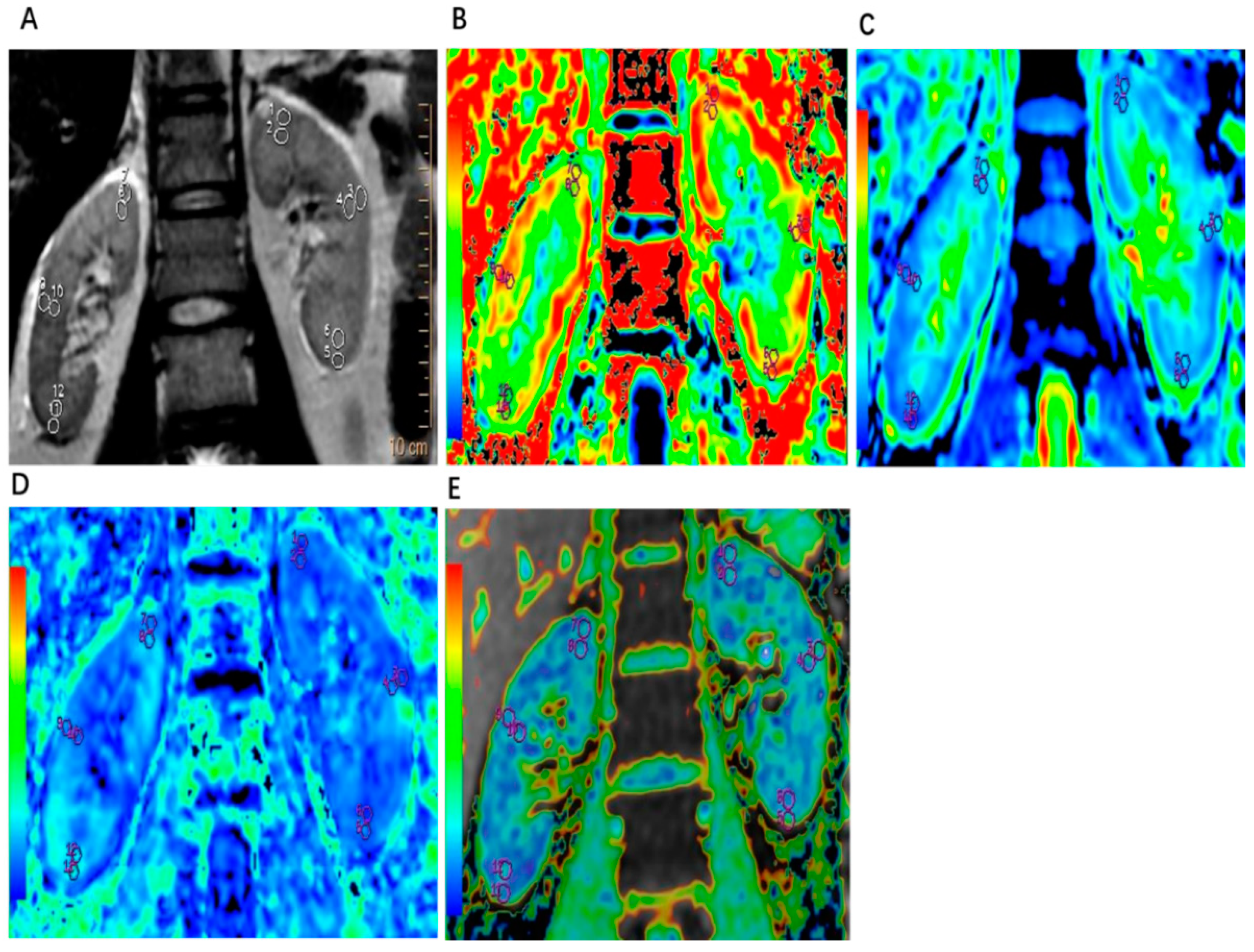
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and General Data of Patients with AAV
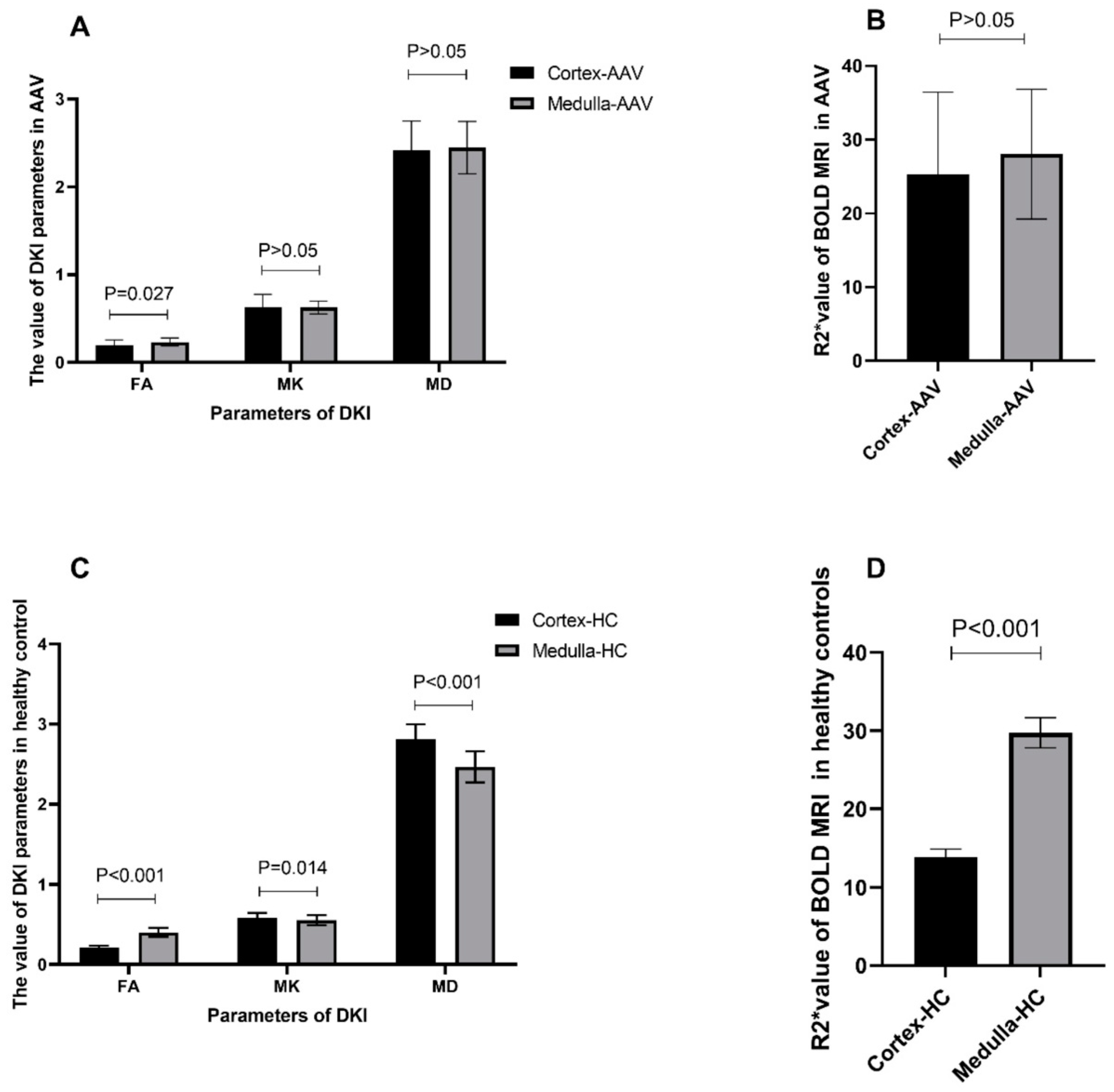
3.2. Comparison of Imaging Parameters of DKI and BOLD MRI between the Renal Cortex and Medulla
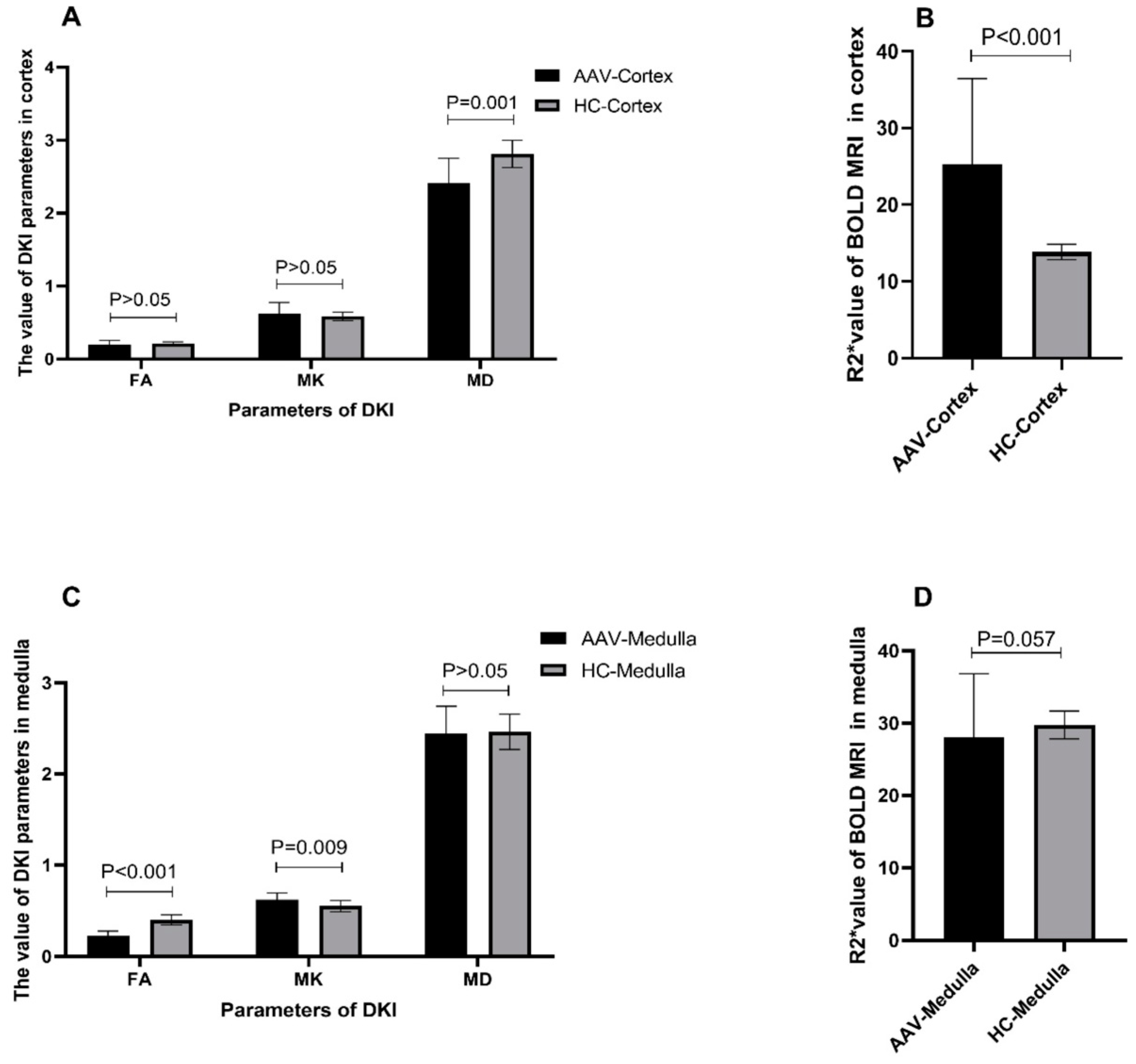
3.3. Comparison of fMRI Parameters between Patients with AAV and Healthy Controls
3.4. Association between fMRI Parameters and Clinicopathological Parameters of Patients with AAV
3.5. ROC Analysis of Diffusion Parameters
3.6. Follow-Up of Patients with AAV
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kronbichler, A.; Lee, K.H.; Denicolo, S.; Choi, D.; Lee, H.; Ahn, D.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.; Hwang, M.; et al. Immunopathogenesis of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geetha, D.; Jefferson, J.A. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Core Curriculum 2020. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroni, G.; Binda, V.; Leoni, A.; Raffiotta, F.; Quaglini, S.; Banfi, G.; Messa, P. Predictors of renal survival in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Validation of a histopatological classification schema and review of the literature. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33 (Suppl. S89), S56–S63. [Google Scholar]
- Hinojosa-Azaola, A.; Jiménez-González, A. Histopathologic classification of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated glomerulonephritis: Achievements, limitations, and perspectives. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 36, 1949–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.K.; Toussaint, N.D.; Elder, G.J.; Masterson, R.; Holt, S.G.; Robertson, P.L.; Ebeling, P.R.; Baldock, P.; Miller, R.C.; Rajapakse, C.S. Magnetic resonance imaging based assessment of bone microstructure as a non-invasive alternative to histomorphometry in patients with chronic kidney disease. Bone 2018, 114, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.-M.; Peng, X.; Wen, Y.; Ye, W.; Zheng, K.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Chen, L. Diffusional kurtosis imaging in assessing renal function and pathology of IgA nephropathy: A preliminary clinical study. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 818–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, R.F.; Wang, H.Q.; Yang, L.; Jin, K.P.; Xie, Y.H.; Chen, C.Z.; Zeng, M.S. Diffusion kurtosis imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging in assessment of liver fibrosis stage and necroinflammatory activity. Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Jensen, J.H.; Ramani, A.; Helpern, J.A. Three-dimensional characterization of non-gaussian water diffusion in humans using diffusion kurtosis imaging. NMR Biomed. 2006, 19, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pentang, G.; Lanzman, R.S.; Heusch, P.; Müller-Lutz, A.; Blondin, D.; Antoch, G.; Wittsack, H.-J. Diffusion kurtosis imaging of the human kidney: A feasibility study. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 32, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruijm, M.; Milani, B.; Pivin, E.; Podhajska, A.; Vogt, B.; Stuber, M.; Burnier, M. Reduced cortical oxygenation predicts a progressive decline of renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2018, 93, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-P.; Thacker, J.M.; Li, W.; Hack, B.; Wang, C.; Kohn, O.; Sprague, S.M.; Prasad, P.V. Medullary Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent MRI Index (R2*) is Associated with Annual Loss of Kidney Function in Moderate CKD. Am. J. Nephrol. 2020, 51, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, H.; Mohamed, E.; Soni, N.; Yadav, P.; Jain, M.; Bhadauria, D.; Kaul, A.; Prasad, N.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, R. Role of Blood Oxygen Level-dependent MRI in Differentiation of Acute Renal Allograft Dysfunction. Indian J. Nephrol. 2018, 28, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gloviczki, M.L.; Glockner, J.F.; Lerman, L.O.; McKusick, M.A.; Misra, S.; Grande, J.P.; Textor, S.C. Preserved oxygenation despite reduced blood flow in poststenotic kidneys in human atherosclerotic renal artery stenosis. Hypertension 2010, 55, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yan, T.; Jia, J.; Li, D.; Wei, L.; Shang, W.; Shi, H. Detection of renal hypoxia configuration in patients with lupus nephritis: A primary study using blood oxygen level-dependent MR imaging. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 2032–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berden, A.E.; Ferrario, F.; Hagen, E.C.; Jayne, D.R.; Jennette, J.C.; Joh, K.; Neumann, I.; Noël, L.-H.; Pusey, C.D.; Waldherr, R.; et al. Histopathologic classification of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 Revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajema, I.M.; Hagen, E.C.; Hansen, B.E.; Hermans, J.; Noel, L.H.; Waldherr, R.; Ferrario, F.; Van Der Woude, F.J.; Bruijn, J.A. The renal histopathology in systemic vasculitis: An international survey study of inter- and intra-observer agreement. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 1996, 11, 1989–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajema, I.M.; Hagen, E.C.; Hermans, J.; Noël, L.-H.; Waldherr, R.; Ferrario, F.; van der Woude, F.J.; Bruijn, J.A.; For The Ec/Bcr Project For ANCA-Assay Standardisation. Kidney biopsy as a predictor for renal outcome in ANCA-associated necrotizing glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1999, 56, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauer, H.A.; Bajema, I.M.; Van Houwelingen, H.C.; Ferrario, F.; Noël, L.-H.; Waldherr, R.; Jayne, D.R.; Rasmussen, N.; Bruijn, J.A.; Hagen, E.C. Renal histology in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Differences between diagnostic and serologic subgroups. Kidney Int. 2002, 61, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, L.; Pan, D.; Liang, C.; Liu, Z. MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion in normal human kidney: A diffusional kurtosis imaging study. NMR Biomed. 2015, 28, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Nachman, P.H. ANCA Glomerulonephritis and Vasculitis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 1680–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, T.; Hu, J.; Jing, Z.; Jian, S. Noninvasive evaluation of early diabetic nephropathy using diffusion kurtosis imaging: An experimental study. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 2281–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Ding, Y.; Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Fu, C.; Zeng, M.; Zhou, J. Pathological assessment of chronic kidney disease with DWI: Is there an added value for diffusion kurtosis imaging? J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 54, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.H.; Helpern, J.A. MRI quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by kurtosis analysis. NMR Biomed. 2010, 23, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Padhani, A.R.; Chenevert, T.L.; Koh, D.; De Keyzer, F.; Taouli, B.; Le Bihan, D. Body diffusion kurtosis imaging: Basic principles, applications, and considerations for clinical practice. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 42, 1190–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.-Z.; Guo, L.-F.; Gao, G.-H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.-Z.; Yuan, Z.-G. Magnetic Resonance Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging versus Diffusion -Weighted Imaging in Evaluating the Pathological Grade of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5147–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.-Y.; Feng, Y.-Z.; Liu, X.-L.; Ye, Y.-J.; Hu, J.-J.; Cai, X.-R. Diffusional kurtosis imaging of kidneys in patients with hyperuricemia: Initial study. Acta Radiol. 2020, 61, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surowiecka, A.; Frączek, M.; Mruk, B.; Matejak-Górska, M.; Walecki, J.; Durlik, M.; Sklinda, K. Normal Pancreas Graft Appearance in Magnetic Resonance Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI). Med. Sci. Monit. 2020, 26, e920262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrelli, P.; Cavaliere, C.; Basso, L.; Soricelli, A.; Salvatore, M.; Aiello, M. Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Kidney: Design and Evaluation of a Reliable Processing Pipeline. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Kumar, V.; Koteshwara, P. Role of Diffusion Tensor Imaging in renal parenchymal changes. Indian J. Radiol. Imaging 2018, 28, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lin, Y.; Ge, X.; Liu, G.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Wu, G.; Chen, S.; Xu, J.; Suo, S. Multiparameter diffusion-weighted imaging for characterizing pathological patterns in lupus nephritis patients: A preliminary study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Zhou, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y. Application of BOLD-MRI in the classification of renal function in chronic kidney disease. Abdom Radiol. 2019, 44, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.; Liao, Y.; Cui, K.; Tao, Y. Noninvasive evaluation of renal oxygenation in children with chronic kidney disease using blood-oxygen-level-dependent magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr. Radiol. 2020, 50, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yang, M.; Jiang, Z.; Ding, J.; Di, J.; Cui, L. Renal Hypoxia: An Important Prognostic Marker in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Nephrol. 2018, 48, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.V. Evaluation of intra-renal oxygenation by BOLD MRI. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2006, 103, c58–c65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaani, S.; Fussner, L.A.; Brodsky, S.; Meara, A.S.; Jayne, D. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: An Update. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, H.; Doi, S.; Nakashima, A.; Ike, T.; Maeoka, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Doi, T.; Masaki, T. Klotho overexpression protects against renal aging along with suppression of transforming growth factor-β1 signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2021, 321, F799–F811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Total number of patients | 20 |
| Male/Female | 8/12 |
| Age (years) | 55.8 ± 11.5 |
| Height (cm) | 159.5 ± 8.8 |
| Weight (kg) | 59.4 ± 7.6 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 79.2 ± 10.1 |
| Systolic pressure (mmHg) | 133.8 ± 20.5 |
| Diastolic pressure (mmHg) | 77.5 ± 11.0 |
| Edema of the face or lower limbs | 10/20 |
| Hemoptysis | 4/20 |
| Renal involvement | 20/20 |
| Pulmonary involvement | 6/20 |
| c-ANCA-positive | 0/20 |
| p-ANCA-positive | 19/20 |
| Hemoglobulin (g/L) | 92.0 ± 19.9 |
| White blood cell count (×109/L) | 10.0 ± 5.3 |
| Platelet (×109/L) | 216.9 ± 101.3 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 31.6 ± 5.9 |
| Globulin (g/L) | 25.7 ± 9.1 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mmol/L) | 17.8 ± 7.2 |
| Creatinine (μmoI/L) | 366.0 ± 203.9 |
| Evaluated glomerular filtration rate (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 15.41 (17.943) |
| Uric acid (μmol/L) | 399.1 ± 103.1 |
| Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score | 19.0 ± 4.1 |
| Group reaching the end point of follow-up (9 patients) | |
| FA (cortex/medulla) | 0.209 ± 0.064/0.228 ± 0.033 |
| MK (cortex/medulla) | 0.669 ± 0.202/0.663 ± 0.075 |
| MD (cortex/medulla) | 2.315 ± 0.437/2.44 ± 0.386 |
| R2* (cortex/medulla) | 27.278 ± 13.276/25.126 ± 6.449 |
| Group not reaching the end point of follow-up (10 patients) | |
| FA (cortex/medulla) | 0.182 ± 0.053/0.232 ± 0.054 |
| MK (cortex/medulla) | 0.580 ± 0.094/0.604 ± 0.057 |
| MD (cortex/medulla) | 2.514 ± 0.185/2.452 ± 0.207 |
| R2* (cortex/medulla) | 24.62 ± 8.813/30.85 ± 10.02 |
| Parameters | Renal Cortex | Renal Medulla | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK | MD | FA | R2* | MK | MD | FA | R2* | |
| Age (year) | −0.004 | 0.078 | 0.015 | 0.242 | 0.05912 | −0.117 | 0.181 | 0.469 * |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | −0.502 * | 0.238 | 0.337 | 0.199 | −0.513 * | −0.023 | 0.311 | 0.043 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 0.146 | 0.171 | 0.159 | 0.173 | 0.357 | 0.382 | 0.151 | 0.110 |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 0.328 | 0.179 | 0.002 | 0.113 | 0.591 ** | 0.419 | 0.077 | 0.084 |
| e-GFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | −0.363 | −0.198 | 0.028 | 0.140 | −0.539 * | −0.342 | 0.002 | 0.122 |
| BVAS | 0.408 | −0.344 | 0.333 | 0.029 | 0.372 | −0.186 | 0.124 | 0.157 |
| Percentage of crescents | 0.927 ** | −0.630 | 0.062 | 0.488 | 0.741 | −0.519 | −0.395 | 0.488 |
| Percentage of cellular crescents | −0.374 | 0.906 ** | −0.394 | 0.317 | 0.197 | 0.512 | −0.374 | 0.698 |
| Percentage of cell fiber crescents | 0.239 | 0.717 | 0.418 | 0.562 | −0.120 | 0.837 * | −0.717 | 0.358 |
| Percentage of fibrous crescents | 0.374 | −0.217 | 0.158 | 0.082 | 0.158 | −0.906 ** | −0.158 | 0.027 |
| Percentage of tubular atrophy | 0.126 | 0.456 | 0.141 | 0.072 | −0.141 | 0.488 | 0.355 | 0.159 |
| Percentage of interstitial fibrosis | 0.126 | 0.456 | 0.141 | 0.072 | −0.141 | 0.488 | 0.355 | 0.159 |
| Items | Cutoff Value | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discriminating AAV renal injury from HCs | ||||
| MK value of the renal cortex | >0.64 | 31.58 | 91.67 | 0.57 |
| MK value of the renal medulla | >0.59 | 63.16 | 83.33 | 0.77 |
| MD value of the renal cortex | <2.51 | 63.16 | 98.00 | 0.87 |
| MD value of the renal medulla | <2.31 | 36.84 | 83.33 | 0.54 |
| FA value of the renal cortex | <0.19 | 52.63 | 91.67 | 0.60 |
| FA value of the renal medulla | <0.29 | 94.74 | 100.00 | 0.99 |
| R2* value of the renal cortex | >15.42 | 90.00 | 93.33 | 0.95 |
| R2* value of the renal medulla | <28.64 | 70.00 | 80.00 | 0.69 |
| Discriminating AAV patients with Cr > 300 µmol from Cr < 300 µmol/L | ||||
| MK value of the renal cortex | >0.52 | 100.00 | 37.50 | 0.66 |
| MK value of the renal medulla | >0.59 | 81.82 | 75.00 | 0.81 |
| MD value of the renal cortex | >2.32 | 90.91 | 50.00 | 0.67 |
| MD value of the renal medulla | >2.49 | 54.55 | 87.50 | 0.77 |
| FA value of the renal cortex | <0.19 | 63.64 | 62.50 | 0.57 |
| FA value of the renal medulla | <0.22 | 54.55 | 75.00 | 0.61 |
| R2* value of the renal cortex | >29.29 | 33.33 | 87.50 | 0.55 |
| R2* value of the renal medulla | <27.72 | 66.67 | 62.50 | 0.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, W.; Yan, W.; Yi, J.; Cheng, L.; Luo, P.; Sun, J.; Gou, S.; Fu, P. Application of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging and Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Kidney Injury Associated with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Tomography 2024, 10, 970-982. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070073
Yu W, Yan W, Yi J, Cheng L, Luo P, Sun J, Gou S, Fu P. Application of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging and Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Kidney Injury Associated with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Tomography. 2024; 10(7):970-982. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070073
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Wenhui, Weijie Yan, Jing Yi, Lu Cheng, Peiyi Luo, Jiayu Sun, Shenju Gou, and Ping Fu. 2024. "Application of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging and Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Kidney Injury Associated with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis" Tomography 10, no. 7: 970-982. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070073
APA StyleYu, W., Yan, W., Yi, J., Cheng, L., Luo, P., Sun, J., Gou, S., & Fu, P. (2024). Application of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging and Blood Oxygen Level-Dependent Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Kidney Injury Associated with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Tomography, 10(7), 970-982. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography10070073






