[18F]FDG PET/CT: Lung Nodule Evaluation in Patients Affected by Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Objectives
2.2. Study Design and Patients Selection
2.3. [18F]FDG-PET/CT
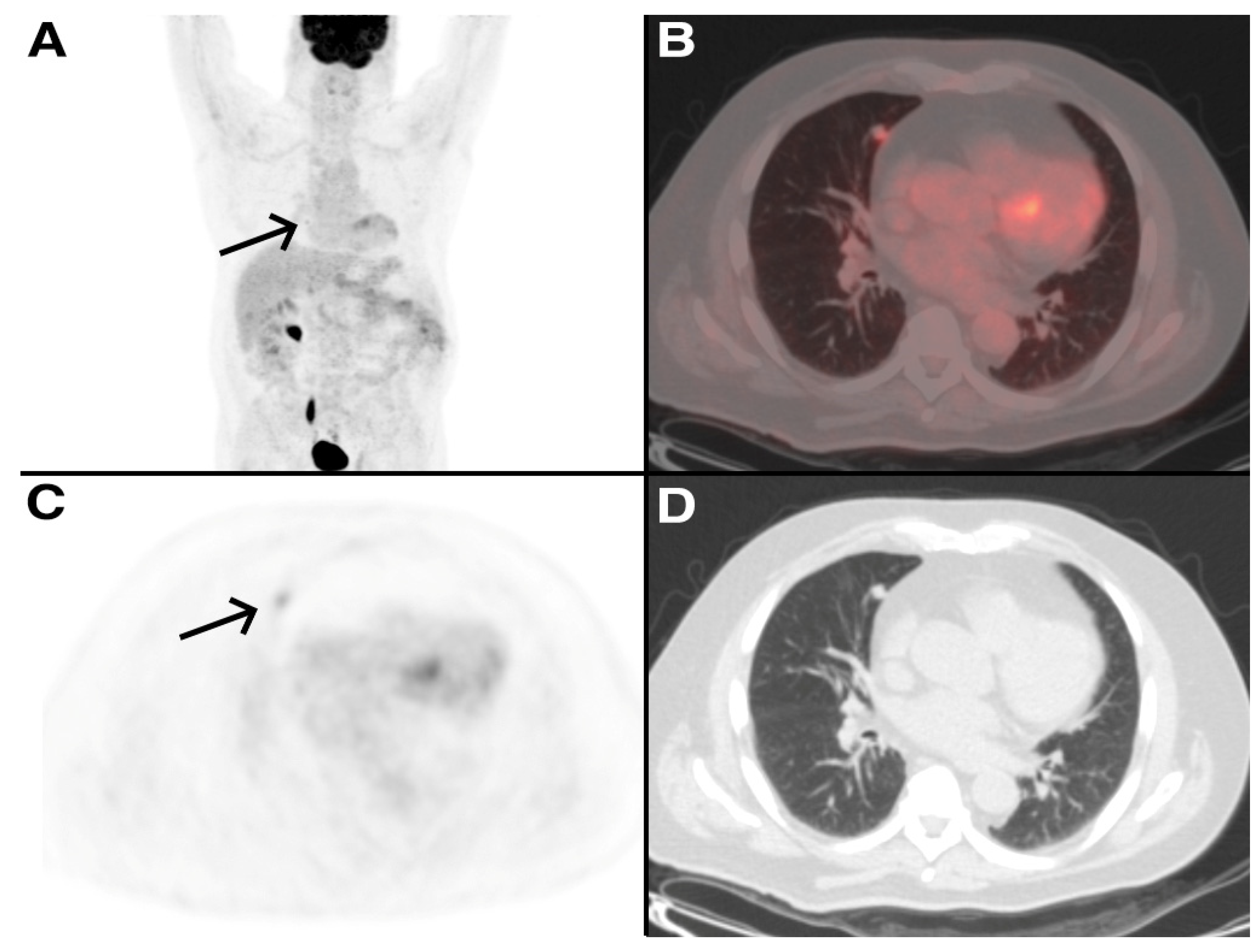
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Population
3.2. PET Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Escudier, B.; Porta, C.; Schmidinger, M.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Bex, A.; Khoo, V.; Grünwald, V.; Gillessen, S.; Horwich, A.; ESMO Guidelines Committee. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 706–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridge, C.A.; Pua, B.B.; Madoff, D.C. Epidemiology and staging of renal cell carcinoma. Semin. Interv. Radiol. 2014, 31, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Tomczak, P.; Michaelson, M.D.; Bukowski, R.M.; Oudard, S.; Negrier, S.; Szczylik, C.; Pili, R.; Bjarnason, G.A.; et al. Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3584–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Brussel, J.P.; Mickisch, G.H. Prognostic factors in renal cell and bladder cancer. BJU Int. 1999, 83, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanigan, R.C.; Campbell, S.C.; Clark, J.I.; Picken, M.M. Metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2003, 4, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, N.; Gore, M.E.; Sohaib, S.A. Imaging in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 189, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzen, N.K.; Kim, H.L.; Figlin, R.A.; Belldegrun, A.S. Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent disease. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 30, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhail, N.S.; Urbain, J.L.; Albani, J.M.; Kanvinde, M.H.; Rice, T.W.; Novick, A.C.; Mekhail, T.M.; Olencki, T.E.; Elson, P.; Bukowski, R.M. F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in the evaluation of distant metastases from renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3995–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ghesani, N.V.; Zuckier, L.S. Physiology and pathophysiology of incidental findings detected on FDG-PET scintigraphy. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2010, 40, 294–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boellaard, R.; Delgado-Bolton, R.; Oyen, W.J.; Giammarile, F.; Tatsch, K.; Eschner, W.; Verzijlbergen, F.J.; Barrington, S.F.; Pike, L.C.; Weber, W.A.; et al. FDG PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging: Version 2.0. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 328–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.E.; White, R.L., Jr.; Zuger, J.H.; Sasser, H.C.; Teigland, C.M. Clinical use of fluorodeoxyglucose F 18 positron emission tomography for detection of renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, J.; Drake, T.; Matthews, H.; Jenkins, J.; Tang, S.; Doherty, J.; Chan, K.; Dawe, H.; Thomas, T.; Kearley, S.; et al. Chest computed tomography for staging renal tumours: Validation and simplification of a risk prediction model from a large contemporary retrospective cohort. BJU Int. 2020, 125, 561–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzoli, A.; Milano, S.; Cancarini, G.; Zanotelli, T.; Cosciani Cunico, S. Surgery of lung metastases in renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Urol. 1995, 75, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, I.; Avril, N.; Bomanji, J.; Chowdhury, S.; Rockall, A.; Sahdev, A.; Nathan, P.; Wilson, P.; Shamash, J.; Sharpe, K.; et al. Sequential FDG-PET/CT as a biomarker of response to Sunitinib in metastatic clear cell renal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 6021–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.C.; Maloof, J.; Gunel, E. Probability of malignancy in solitary pulmonary nodules using fluorine-18-FDG and PET. J. Nucl. Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nucl. Med. 1996, 37, 943–948. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.H.; Shiau, Y.C.; Shen, Y.Y.; Kao, A.; Lin, C.C.; Lee, C.C. Differentiating solitary pulmonary metastases in patients with renal cell carcinomas by 18F-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography--a preliminary report. Urol. Int. 2003, 71, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahmadawy, M.A.; Elazab, M.S.S.; Ahmed, S.; Salama, M. Diagnostic value of F-18 FDG PET/CT for local and distant disease relapse surveillance in surgically treated RCC patients: Can it aid in establishing consensus follow up strategy? Nucl. Med. Review. Cent. East. Eur. 2018, 21, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, M.K.; Fletcher, J.; Iannettoni, M.D.; Lynch, W.R.; Midthun, D.E.; Naidich, D.P.; Ost, D.E.; American College of Chest Physicians. Evaluation of patients with pulmonary nodules: When is it lung cancer? ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest 2007, 132 (Suppl. 3), 108S–130S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. The Place of FDG PET/CT in Renal Cell Carcinoma: Value and Limitations. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Variable | Level | Overall (n = 67) |
|---|---|---|
| Age at the date of PET (y), median (IQR) | 66 (58–73) | |
| Gender, n (%) | Female | 19 (28.4) |
| Male | 48 (71.6) | |
| Type of primary therapy, n (%) | No surgery | 2 (3.0) |
| Total nephrectomy | 53 (79.1) | |
| Partial nephrectomy | 4 (6.0) | |
| Enucleation | 8 (11.9) | |
| Type of lung surgery, n (%) | Wedge resection | 35 (52.2) |
| Lobectomy | 29 (43.3) | |
| Pneumonectomy | 3 (4.5) | |
| Number of lesions, n (%) | 1 | 42 (62.7) |
| 2 | 16 (23.9) | |
| 3 | 5 (7.5) | |
| 4 | 2 (3.0) | |
| 5 | 2 (3.0) | |
| Lung histology, n (%) * | RCC metastasis | 57 (53.3) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 35 (32.7) | |
| Squamous carcinoma | 7 (6.5) | |
| Other tumors | 8 (7.5) | |
| Sum of the lesions size (mm), median (IQR) | 19 (12–33) |
| Histopathological Result | Diagnostic Performance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No RCC Lung Met | RCC Lung Met | Total | SE (95% CI) | SP (95% CI) | |
| PET/CT qualitative analysis | 49.1% (35.6–62.7%) | 10.0% (3.3–21.8%) | |||
| Negative | 5 | 29 | 34 | ||
| Positive | 45 | 28 | 73 | ||
| Lung SUV max | 33.3% (21.4–47.1%) | 26.0% (14.6–40.3%) | |||
| <2 (Negative) | 13 | 38 | 51 | ||
| ≥2 (Positive) | 37 | 19 | 56 | ||
| Total | 50 | 57 | 107 | ||
| Variable | Histopathological Result | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No Metastasis (n = 50) | Metastasis (n = 57) | ||
| Lung SUVmax, median (IQR) | 4.79 (1.96–10.5) | 1.58 (0.80–3.32) | <0.001 |
| Lung MTV (cm3), median (IQR) | 1.49 (0.49–4.60) | 0.12 (0.00–1.47) | <0.001 |
| Lung TLG, median (IQR) | 5.64 (1.35–16.2) | 0.05 (0.00–3.25) | <0.001 |
| Histopathological Result | Diagnostic Performance | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No RCC Lung Met | RCC Lung Met | Total | SE (95% CI) | SP (95% CI) | |
| PET/CT lung result | 30.6% (16.4–48.1%) | 20.0% (2.5–55.6%) | |||
| Negative | 2 | 25 | 27 | ||
| Positive | 8 | 11 | 19 | ||
| Lung SUV max | 11.1% (3.1–26.1%) | 50.0% (18.7–81.3%) | |||
| <2 (Negative) | 5 | 32 | 37 | ||
| ≥2 (Positive) | 5 | 4 | 9 | ||
| Total | 10 | 36 | 46 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Airò Farulla, L.S.; Travaini, L.L.; Cuomo, M.; Galetta, D.; Mattana, F.; Frassoni, S.; Buonsanti, G.; Muraglia, L.; Zuccotti, G.A.; Bagnardi, V.; et al. [18F]FDG PET/CT: Lung Nodule Evaluation in Patients Affected by Renal Cell Carcinoma. Tomography 2023, 9, 387-397. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010031
Airò Farulla LS, Travaini LL, Cuomo M, Galetta D, Mattana F, Frassoni S, Buonsanti G, Muraglia L, Zuccotti GA, Bagnardi V, et al. [18F]FDG PET/CT: Lung Nodule Evaluation in Patients Affected by Renal Cell Carcinoma. Tomography. 2023; 9(1):387-397. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010031
Chicago/Turabian StyleAirò Farulla, Lighea Simona, Laura Lavinia Travaini, Mariarosaria Cuomo, Domenico Galetta, Francesco Mattana, Samuele Frassoni, Giuseppe Buonsanti, Lorenzo Muraglia, Giulia Anna Zuccotti, Vincenzo Bagnardi, and et al. 2023. "[18F]FDG PET/CT: Lung Nodule Evaluation in Patients Affected by Renal Cell Carcinoma" Tomography 9, no. 1: 387-397. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010031
APA StyleAirò Farulla, L. S., Travaini, L. L., Cuomo, M., Galetta, D., Mattana, F., Frassoni, S., Buonsanti, G., Muraglia, L., Zuccotti, G. A., Bagnardi, V., Spaggiari, L., & Ceci, F. (2023). [18F]FDG PET/CT: Lung Nodule Evaluation in Patients Affected by Renal Cell Carcinoma. Tomography, 9(1), 387-397. https://doi.org/10.3390/tomography9010031








