The Validation of Antibodies Suitable for Flow Cytometric Analysis and Immunopeptidomics of Peptide–MHC Complexes in the Outbred Swiss Albino Mouse Strain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. MHC Cell Surface Staining
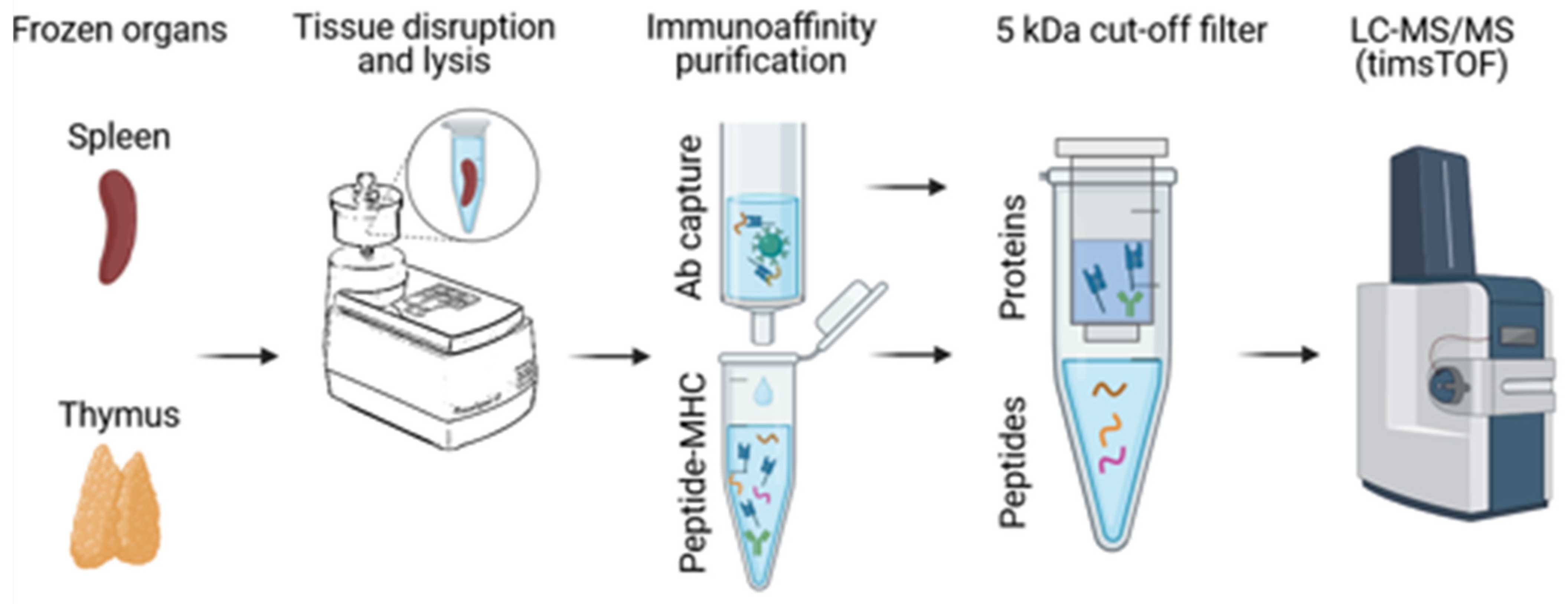
2.3. Small Scale Immunoaffinity Purification
2.4. Mass Spectrometry
2.5. LC-MS/MS Data Analysis
3. Results
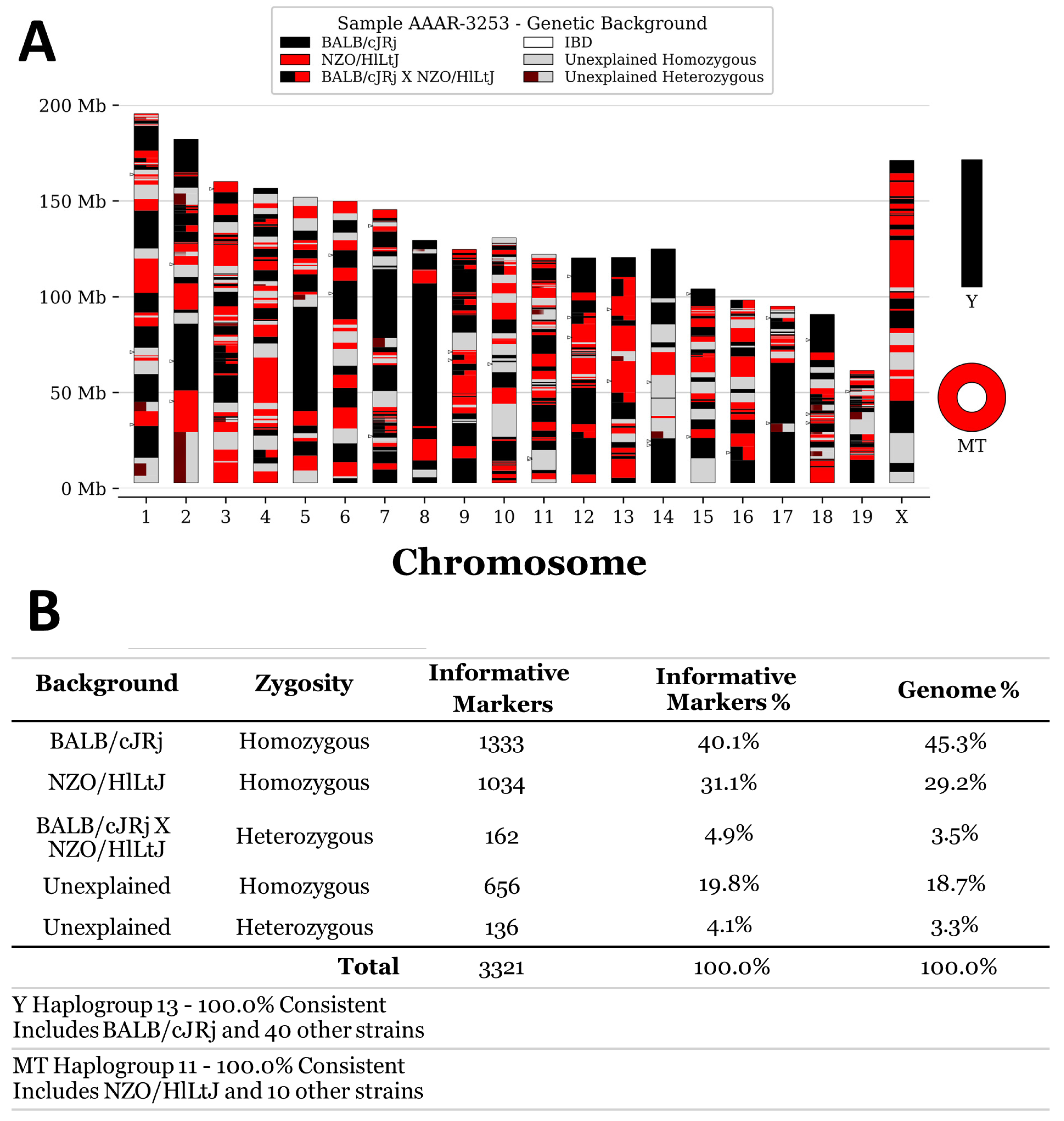
3.1. SNP Genotyping of Swiss Mice
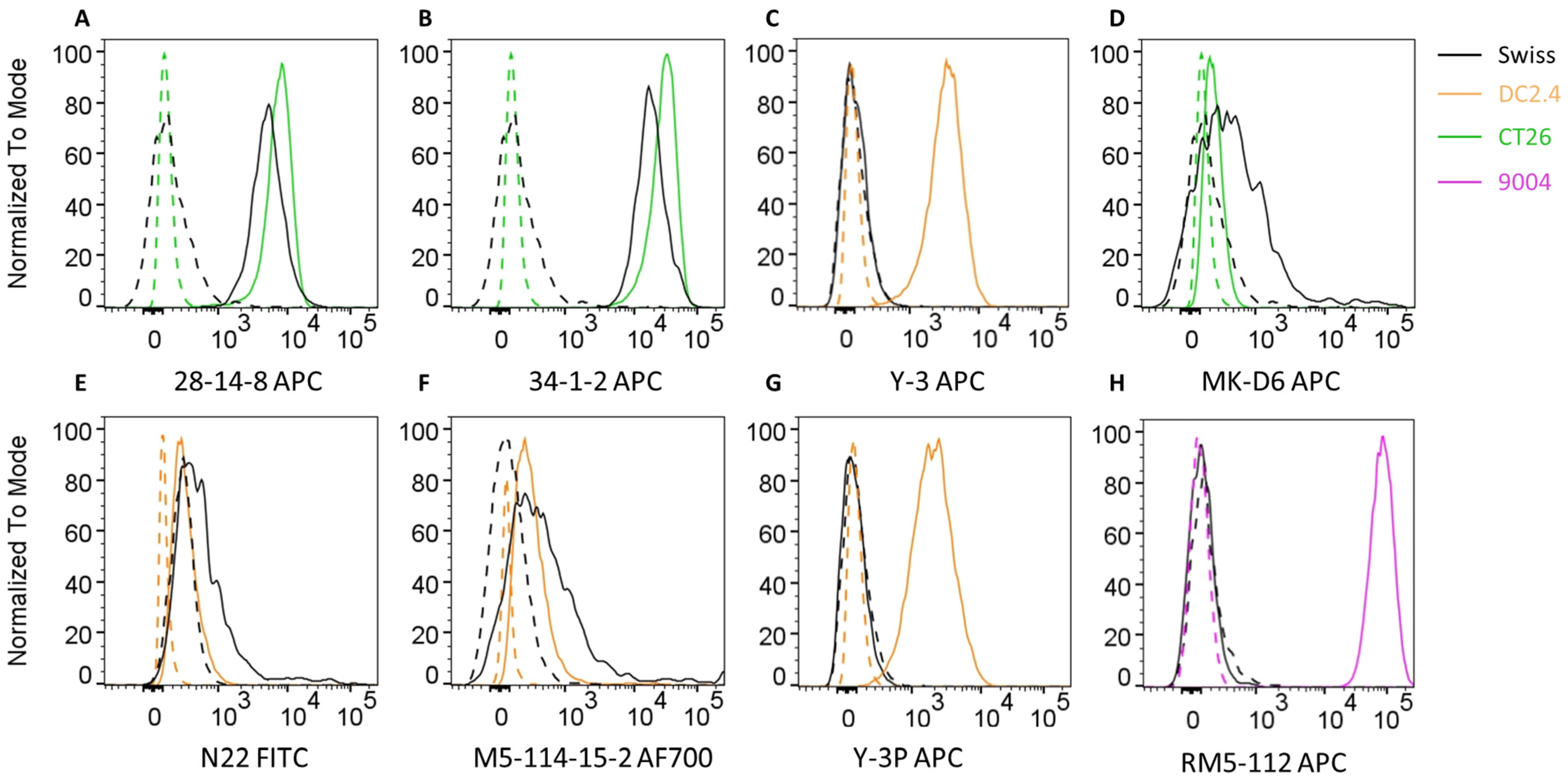
3.2. Identification of Established Anti-MHC Antibody Clones Capable of Cross-Reactivity with Swiss Cells
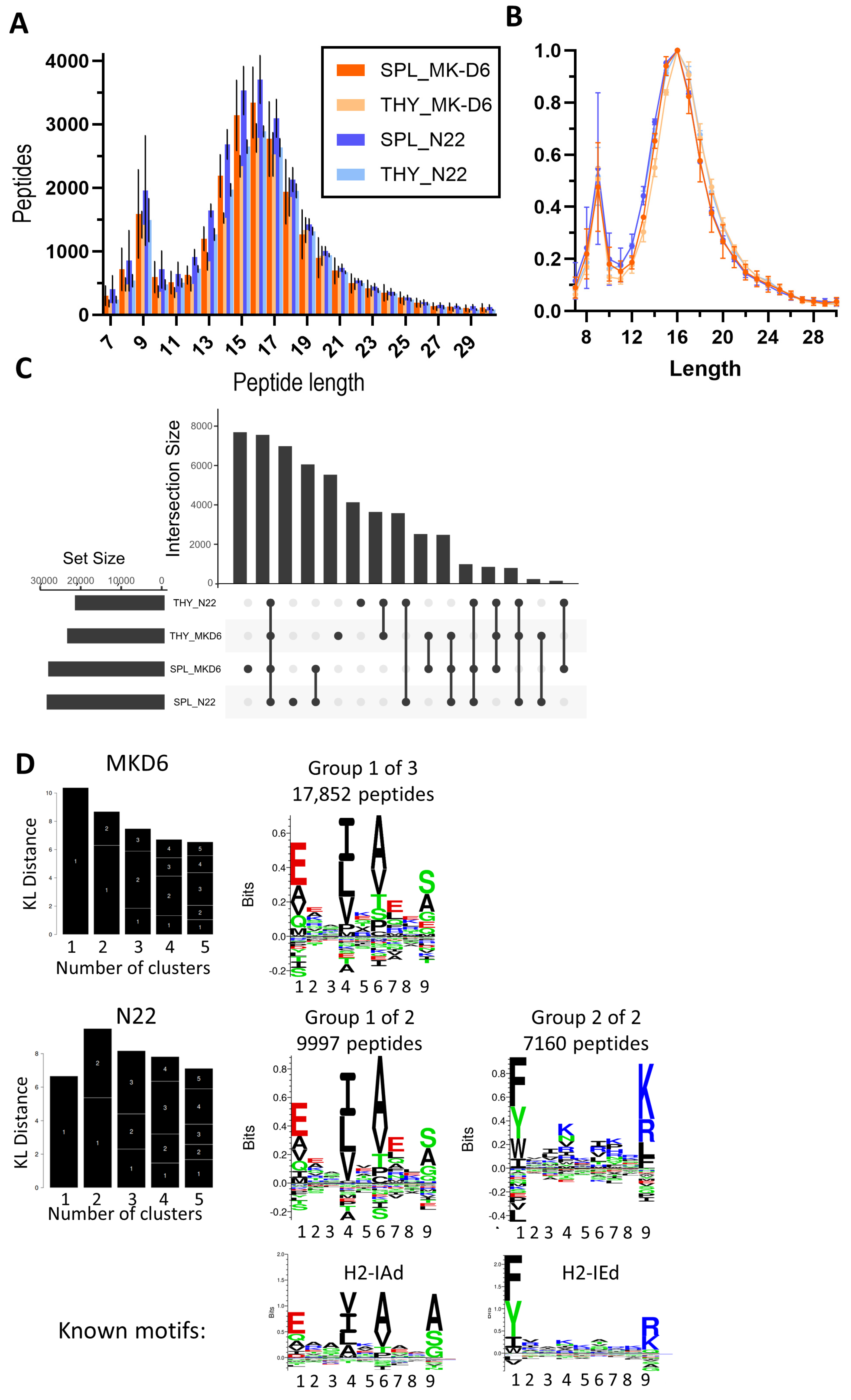
3.3. Immunopeptidomic Analysis in Swiss Mice
3.4. Comparison of the Thymus- and Spleen-Derived Immunopeptidomes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Purcell, A.W.; Ramarathinam, S.H.; Ternette, N. Mass spectrometry-based identification of MHC-bound peptides for immunopeptidomics. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1687–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, M.C.; O’Brien, S.J. Genetic variance of laboratory outbred Swiss mice. Nature 1980, 283, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreatta, M.; Nielsen, M. Gapped sequence alignment using artificial neural networks: Application to the MHC class I system. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadros, D.M.; Eggenschwiler, S.; Racle, J.; Gfeller, D. The MHC Motif Atlas: A database of MHC binding specificities and ligands. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D428–D437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Chesson, C.; Hope, R. Genetic variation within and between strains of outbred Swiss mice. Lab. Anim. 1993, 27, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigmon, J.S.; Blanchard, M.W.; Baric, R.S.; Bell, T.A.; Brennan, J.; Brockmann, G.A.; Burks, A.W.; Calabrese, J.M.; Caron, K.M.; Cheney, R.E.; et al. Content and Performance of the MiniMUGA Genotyping Array: A New Tool To Improve Rigor and Reproducibility in Mouse Research. Genetics 2020, 216, 905–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escher, C.; Reiter, L.; MacLean, B.; Ossola, R.; Herzog, F.; Chilton, J.; MacCoss, M.J.; Rinner, O. Using iRT, a normalized retention time for more targeted measurement of peptides. Proteomics 2012, 12, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, P.R.; Fehring, J.; Revote, J.; Pandey, K.; Shahbazy, M.; Scull, K.E.; Ramarathinam, S.H.; Faridi, P.; Croft, N.P.; Braun, A.; et al. Immunolyser: A web-based computational pipeline for analysing and mining immunopeptidomic data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 1678–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynisson, B.; Barra, C.; Kaabinejadian, S.; Hildebrand, W.H.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M. Improved Prediction of MHC II Antigen Presentation through Integration and Motif Deconvolution of Mass Spectrometry MHC Eluted Ligand Data. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2304–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozato, K.; Hansen, T.H.; Sachs, D.H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse MHC antigens. II. Antibodies to the H-2Ld antigen, the products of a third polymorphic locus of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. J. Immunol. 1980, 125, 2473–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrow, S.O.; Flaherty, L.; Sachs, D.H. Serologic cross-reactivity between Class I MHC molecules and an H-2-linked differentiation antigen as detected by monoclonal antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 1984, 159, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kappler, J.W.; Skidmore, B.; White, J.; Marrack, P. Antigen-inducible, H-2-restricted, interleukin-2-producing T cell hybridomas. Lack of independent antigen and H-2 recognition. J. Exp. Med. 1981, 153, 1198–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metlay, J.P.; Witmer-Pack, M.D.; Agger, R.; Crowley, M.T.; Lawless, D.; Steinman, R.M. The distinct leukocyte integrins of mouse spleen dendritic cells as identified with new hamster monoclonal antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 1990, 171, 1753–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunstein, N.S.; Germain, R.N.; Loney, K.; Berkowitz, N. Structurally interdependent and independent regions of allelic polymorphism in class II MHC molecules. Implications for Ia function and evolution. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Dorf, M.E.; Springer, T.A. A shared alloantigenic determinant on Ia antigens encoded by the I-A and I-E subregions: Evidence for I region gene duplication. J. Immunol. 1981, 127, 2488–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, G.R.; Pascoe, V.; d’Apice, A.J.; Seymour, A.E. Expression of HLA-DR, -DQ, and -DP antigens on renal tubular cells during rejection episodes. Transplant. Proc. 1986, 18, 293–297. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, A.; Rowntree, L.C.; Huang, Z.; Pandey, K.; Thuesen, N.; Li, C.; Petersen, J.; Littler, D.R.; Raji, S.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; et al. Mapping the immunopeptidome of seven SARS-CoV-2 antigens across common HLA haplotypes. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, G.A.; Genari, A.B.; Assis, A.F.; Monteleone-Cassiano, A.C.; Donadi, E.A.; Oliveira, E.H.; Duarte, M.J.; Machado, M.V.; Tanaka, P.P.; Mascarenhas, R. The Thymus as a Mirror of the Body’s Gene Expression. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2025, 1471, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelson, D.A.; Mathis, D. Thymic Mimetic Cells: Ontogeny as Immunology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 40, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, M.; Glaros, D.; Khoury, G.; Jay, G. Alternative RNA splicing in expression of the H-2K gene. Nature 1983, 306, 602–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Delarbre, C.; Kress, M.; Kourilsky, P.; Gachelin, G. An H-2K gene of the tw32 mutant at the T/t complex is a close parent of an H-2Kq gene. Immunogenetics 1985, 21, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Antibody | Species Origin/Isotype | Source | Catalogue Number | Amount Used/Dilution Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28-14-8 | Mouse/IgG2a | In-house | HB-27 | 2 μg |
| 34-1-2 | Mouse/IgG2a | In-house | HB-79 | 2 μg |
| MK-D6 | Mouse/IgG2a | In-house | HB-3 | 2 μg |
| N22 | Hamster/IgG | In-house | HB-225 | 2 μg |
| RM5-112 | Mouse/IgG2a | In-house | N/A | 2 μg |
| Y-3 | Mouse/IgG2a | In-house | HB-176 | 2 μg |
| Y-3P | Mouse/IgG2a | In-house | HB-183 | 2 μg |
| M5-114-15-2 Alexa Fluor 700 | Rat/IgG2b | eBioscience | 56-5321-82 | 0.04 μg |
| CD4 PeCy7 | Mouse/IgG2a | BD Biosciences | 348799 | 1:500 dilution |
| CD16/CD32 | Rat/IgG2b | BD Biosciences | 553142 | 1:200 dilution |
| APC ((F(ab’)2-Goat anti-Mouse IgG) | Goat/IgG | eBioscience | 17-4010-82 | 1:1000 dilution |
| FITC (Goat anti-hamster (Armenian) IgG) | Goat/polyclonal IgG | BioLegend | 405502 | 1:200 dilution |
| Thymus—Top 10 Unique Source Proteins | Spleen—Top 10 Unique Source Proteins |
|---|---|
| Phospholipase D1 | Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member E |
| Major urinary protein (various) | Complement receptor type 2 |
| Keratin, type II cytoskeletal | Ig kappa chain V-III region |
| Protein TBATA (Thymus, Brain And Testes Associated) | Paired box protein Pax-5 |
| Thymus-specific serine protease | Trem-like transcript 2 protein |
| Beta-casein | Alpha-synuclein |
| Epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 | Fc receptor-like protein 1 |
| Proteoglycan 4 | 40S ribosomal protein S25 |
| Desmoglein-2 | Acidic leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member A |
| Pro-adrenomedullin | Tyrosine-protein kinase SYK |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chung, S.; Knox-Johnson, I.G.; Gazzard, S.E.; Song, R.; Le, N.H.; Cullen-McEwen, L.A.; Bertram, J.F.; Purcell, A.W.; Braun, A. The Validation of Antibodies Suitable for Flow Cytometric Analysis and Immunopeptidomics of Peptide–MHC Complexes in the Outbred Swiss Albino Mouse Strain. Methods Protoc. 2025, 8, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8030043
Chung S, Knox-Johnson IG, Gazzard SE, Song R, Le NH, Cullen-McEwen LA, Bertram JF, Purcell AW, Braun A. The Validation of Antibodies Suitable for Flow Cytometric Analysis and Immunopeptidomics of Peptide–MHC Complexes in the Outbred Swiss Albino Mouse Strain. Methods and Protocols. 2025; 8(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8030043
Chicago/Turabian StyleChung, Shanzou, Isambard G. Knox-Johnson, Sarah E. Gazzard, Runqiu Song, Ngoc H. Le, Luise A. Cullen-McEwen, John F. Bertram, Anthony W. Purcell, and Asolina Braun. 2025. "The Validation of Antibodies Suitable for Flow Cytometric Analysis and Immunopeptidomics of Peptide–MHC Complexes in the Outbred Swiss Albino Mouse Strain" Methods and Protocols 8, no. 3: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8030043
APA StyleChung, S., Knox-Johnson, I. G., Gazzard, S. E., Song, R., Le, N. H., Cullen-McEwen, L. A., Bertram, J. F., Purcell, A. W., & Braun, A. (2025). The Validation of Antibodies Suitable for Flow Cytometric Analysis and Immunopeptidomics of Peptide–MHC Complexes in the Outbred Swiss Albino Mouse Strain. Methods and Protocols, 8(3), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/mps8030043








