Assessment of 18 Years of Genetic Marker-Assisted Selection and Augmentation of Native Walleye in the Upper New River, Virginia, USA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
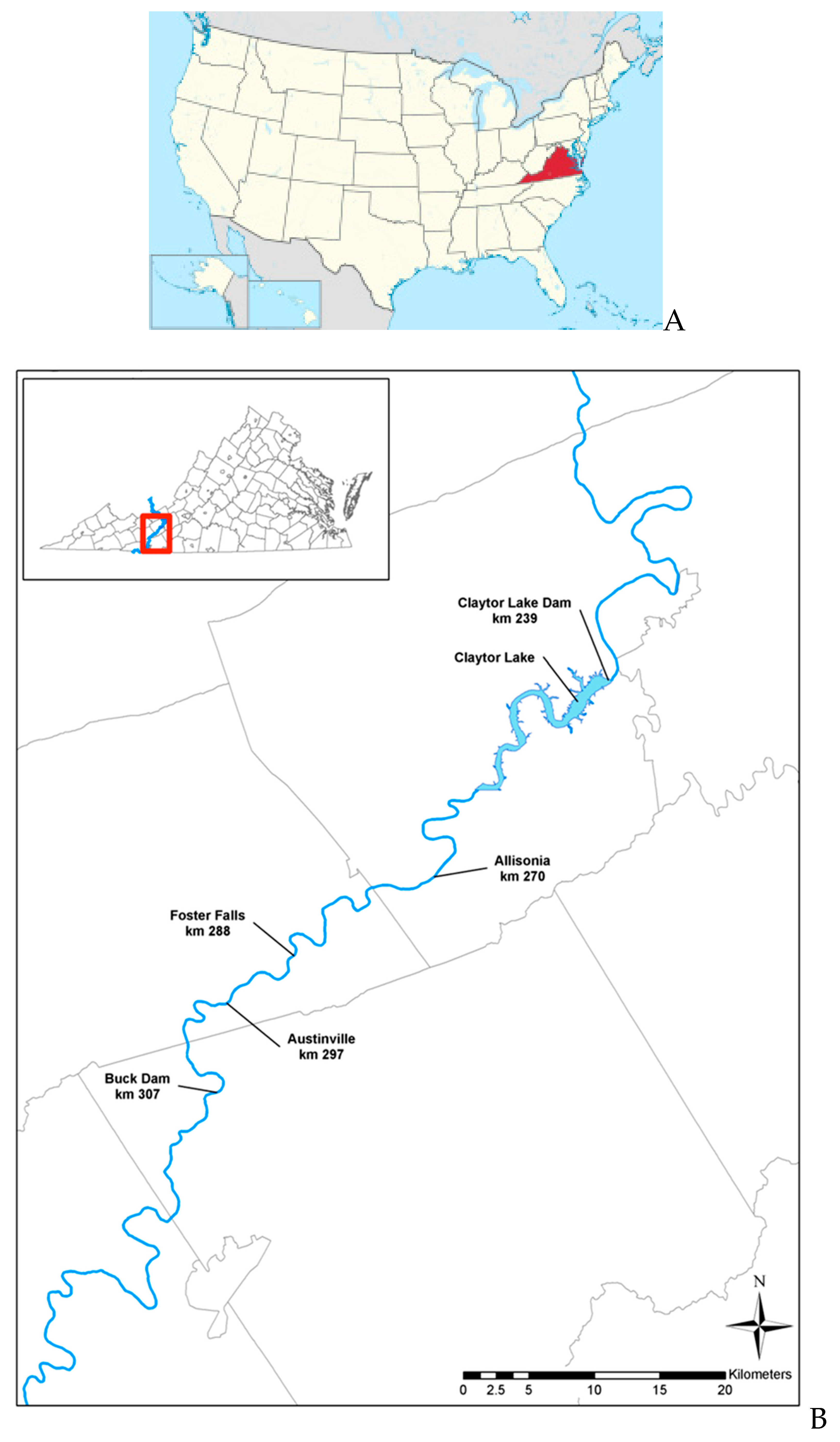
2.1. Study Area and Sampling
2.2. Molecular Methods
2.3. Evaluation of Hatchery-Based Augmentation
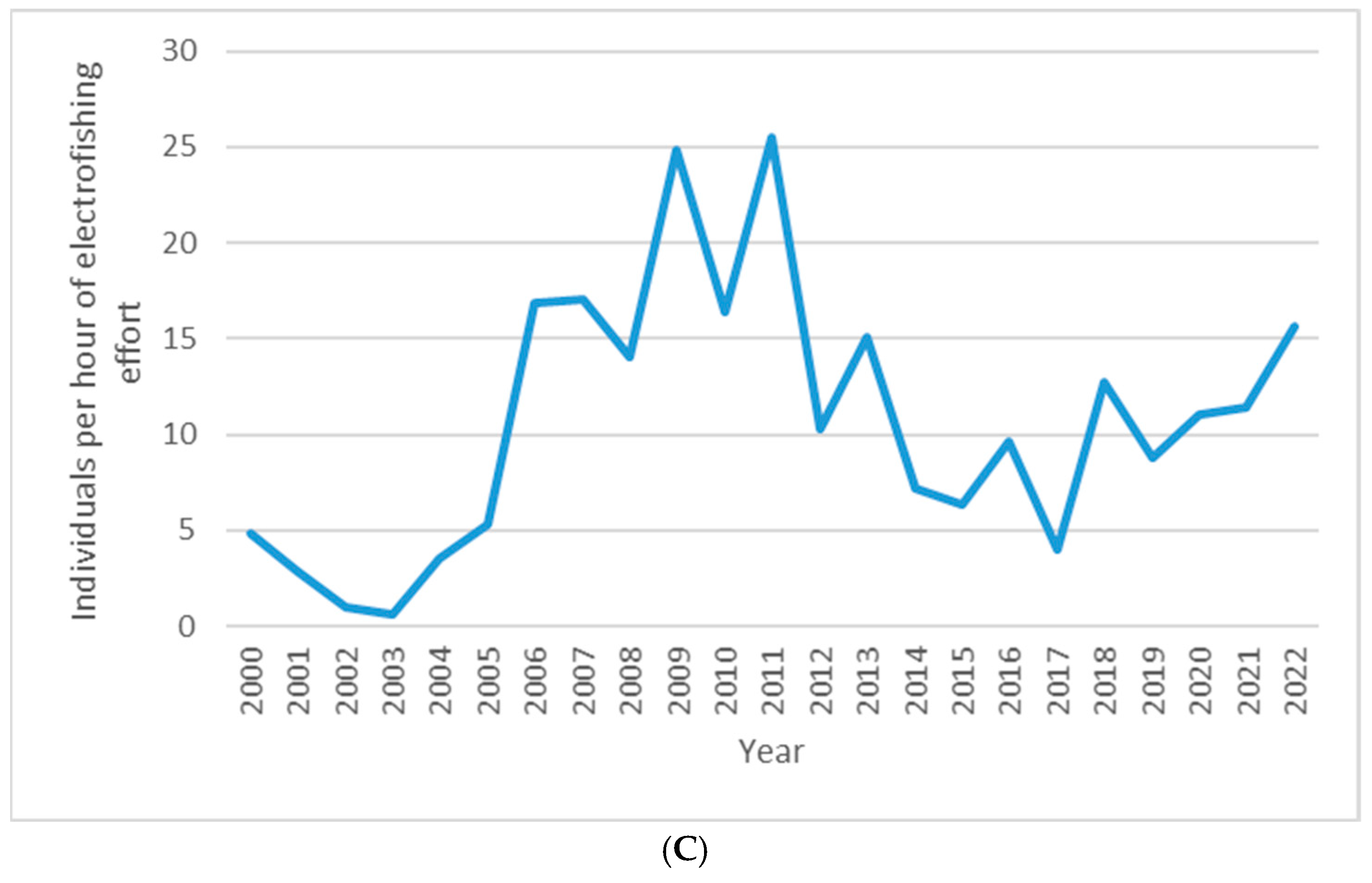
3. Results
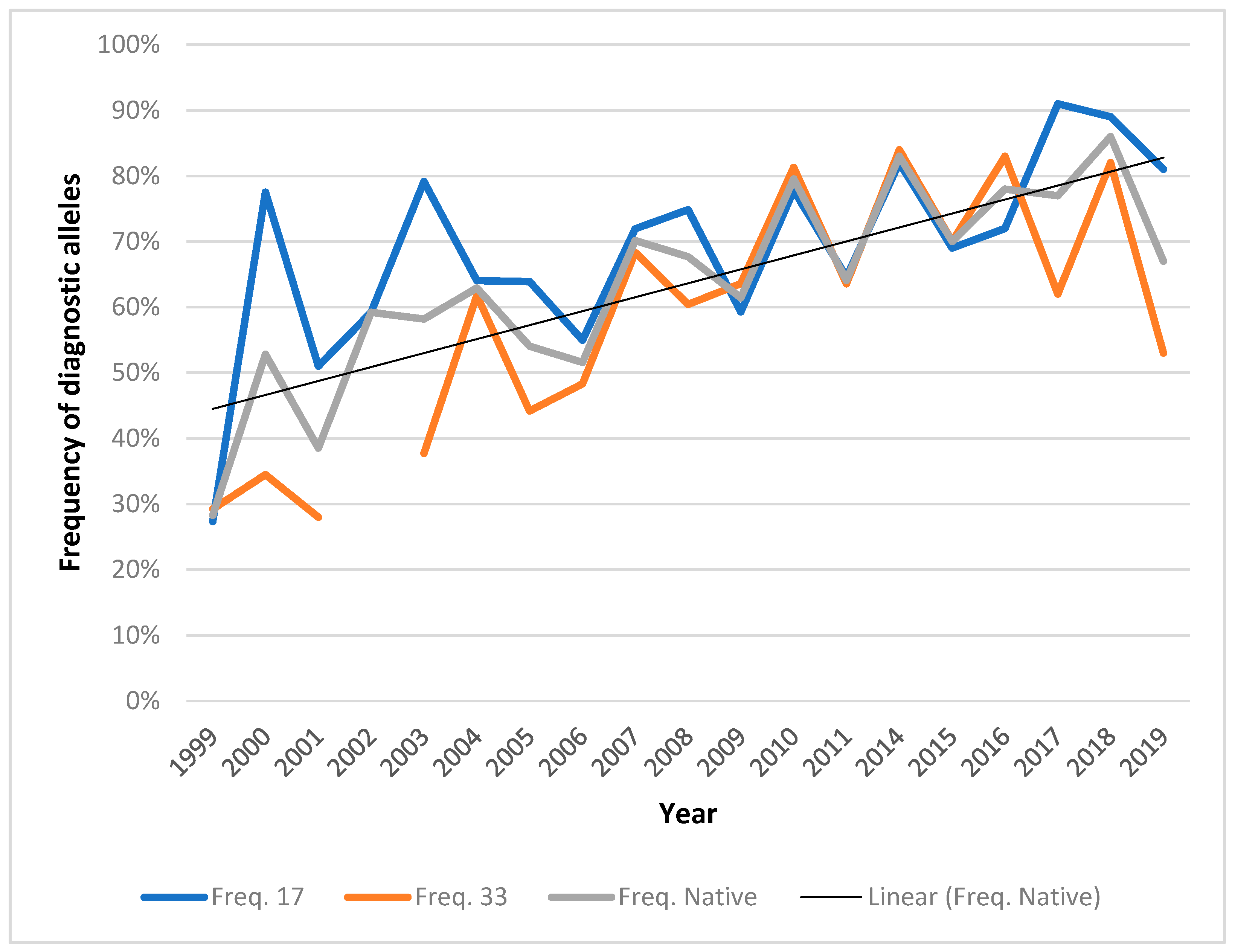
3.1. Marker-Assisted Selection
3.2. Augmentation of Upper New River Walleye
4. Discussion
4.1. MAS-Based Walleye Augmentation
4.2. Improving the MAS Protocol
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steinkoenig, E.; Hampton, T.; Reeser, S.; Greenlee, B. The walleye in Virginia. Virginia Wildl. 2001, 61, 10–26. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, S.J.; Palmer, G.; Hampton, T.; Wilson, D.; Harris, J. Differences in angler catch and exploitation of walleye from Virginia Waters. J. Southeast. Assoc. Fish Wildl. Agenc. 2014, 1, 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- McCotter, C.C. New River walleye: A late season bonus. Woods Waters Mag. 2006. Available online: https://woodsandwatersmagazine.com/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Ingram, B. The upper New’s mystery fish. Virginia Wildl. 2007, 67, 8–11. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, B.R.; Nielson, L.A.; Turner, B.J. Use of genetic tags to evaluate stocking success for reservoir walleyes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1983, 112, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, R.E.; Burkhead, N.M. Freshwater Fishes of Virginia; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, G.C. Genetic Characterization of Intermixed Walleye Stocks in Claytor Lake and the Upper New River, Virginia. Master’s Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, G.C.; Culver, M.; Dutton, D.; Murphy, B.R.; Hallerman, E.M.; Billington, N.; Williams, J. Genetic distinct walleye stocked in Claytor Lake and the Upper New River, Virginia. Proc. Southeast. Assoc. Fish. Wild. Agenc. 2006, 60, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, G.C.; Williams, J.; Scott, M.; Finne, K.; Johnson, N.; Dutton, D.; Murphy, B.R.; Hallerman, E.M. Genetic marker-assisted restoration of the presumptive native walleye fishery in the New River, Virginia and West Virginia. Proc. Annu. Conf. Southeast. Assoc. Fish. Wildl. Agenc. 2007, 61, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Borer, S.; Miller, L.M.; Kapuscinski, A.R. Microsatellites in walleye Stizostedion vitreum. Mol. Ecol. 1999, 8, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, M.J.; Bozek, M.A.; Newby, J.R.; Newman, S.P.; Staggs, M.D. Factors affecting recruitment of walleyes in Escanaba Lake, Wisconsin, 1958–1996. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 1998, 18, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozek, M.A.; Baccante, D.A.; Lester, N.P. Walleye and sauger life history. In Biology, Management, and Culture of Walleye and Sauger; Barton, B., Ed.; American Fisheries Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2011; pp. 233–301. [Google Scholar]
- Baccante, D.A.; Colby, P.J. Harvest, density and reproductive characteristics of North American walleye populations. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 1996, 33, 601–615. [Google Scholar]
- Chevalier, J.R. Changes in walleye (Stizostedion vitreum vitreum) population in Rainy Lake and factors in abundance, 1924–1975. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1977, 34, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, T.D., Jr.; Hansen, M.J.; Carpenter, S.R. Development of a regional stock–recruitment model for understanding factors affecting walleye recruitment in northern Wisconsin lakes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2003, 132, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forney, J.L. Evidence of inter- and intraspecific competition as factors regulating walleye (Stizostedion vitreum vitreum) biomass in Oneida Lake, New York. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1977, 34, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madenjian, C.P.; Tyson, J.T.; Knight, R.L.; Kershner, M.W.; Hansen, M.J. First-year growth, recruitment, and maturity of walleyes in western Lake Erie. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1996, 125, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielder, D.G.; Schaeffer, J.S.; Thomas, M.V. Environmental and ecological conditions surrounding the production of large year classes of walleye (Sander vitreus) in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2007, 33 (Suppl. S1), 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nate, N.A.; Bozek, M.A.; Hansen, M.J.; Hewett, S.W. Variation in walleye abundance with lake size and recruitment source. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2000, 20, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serns, S.L. Influence of various factors on density and growth of age-0 walleyes in Escanaba Lake, Wisconsin, 1958–1980. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1982, 111, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quist, M.C.; Guy, C.S.; Bernot, R.J.; Stephen, J.L. Factors related to growth and survival of larval walleyes: Implications for recruitment in a southern Great Plains reservoir. Fish. Res. 2004, 67, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, G.J.; Carpenter, S.R.; Gaeta, J.W.; Hennessy, J.M.; Vander Zanden, M.J. Predicting walleye recruitment as a tool for prioritizing management actions. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 72, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honsey, A.E.; Feiner, Z.S.; Hansen, G.J. Drivers of walleye recruitment in Minnesota’s large lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 77, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, C.A.; Murphy, D.J.; Lohner, R.N.; Sepulveda-Villet, O.J.; Haponski, A.E. Signatures of vicariance, postglacial dispersal and spawning philopatry: Population genetics of the walleye Sander vitreus. Mol. Ecol. 2009, 18, 3411–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, M.G. A comparison of zygote survival of native and non-native walleye stocks in two Georgian Bay rivers. Environ. Biol. Fish. 1993, 38, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, M.J.; Claussen, J.E.; Philipp, D.P. Evidence for heritable preferences for spawning habitat between two walleye populations. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1996, 125, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepien, C.A.; Farber, J.E. Population genetic structure, phylogeography and spawning philopatry in walleye (Stizostedion vitreum) from mitochondrial DNA control region sequences. Mol. Ecol. 1998, 7, 1757–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, W.E.; Bacigalupi, M.D.; Adelman, I.R.; Miller, L.M.; Kapuscinski, A.R. Determination of relative survival of two stocked walleye populations and resident natural-origin fish by microsatellite DNA parentage assignment. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.B.; Hilling, C.D.; Orth, D.J. Egg Size Variation Among Walleye in Virginia; Department of Fish and Wildlife Conservation, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2018; Unpublished Manuscript. [Google Scholar]
- Olsen, J.B.; Bentzen, P.; Banks, M.A.; Shaklee, J.B.; Young, S. Microsatellites reveal population identity of individual pink salmon to allow supportive breeding of a population at risk of extinction. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2000, 129, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matala, A.P.; French, R.; Olsen, E.; Ardren, W.R. Ecotype distinctions among steelhead in Hood River, Oregon, allow real-time genetic assignment of conservation broodstocks. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2009, 138, 1490–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.T. WVDNR Fisheries Management Plan: Native Walleye in the New River; West Virginia Department of Natural Resources: Charleston, WV, USA, 2012; 6p. [Google Scholar]
- Dreves, D.P.; Baker, D.; Cummins, E.; Frey, K.; Harrala, J.; Middleton, R.; Ross, J.; Williams, J. Conservation and Management Plan for the Native Walleye of Kentucky; Fisheries Division; Kentucky Department of Fish and Wildlife Resources: Frankfort, KY, USA, 2014; 16p. [Google Scholar]
- Berkman, L.K.; Titus, C.L.; Thomas, D.R.; Fluker, B.L.; Cieslewicz, P.; Knuth, D.; Koppelman, J.B.; Eggert, L.S. Genetic differences among the Interior Highlands walleye (Sander vitreus) with mitochondrial and nuclear markers indicate the need for updated stocking practices. Conserv. Genet. 2023, 24, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.C. Genetic Marker-Assisted Management of Virginia Sport fishes. Master’s Thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2019. Available online: https://vtechworks.lib.vt.edu/bitstream/handle/10919/98505/Harris_SC_T_2020.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 26 May 2022).
- Harris, S.C.; Palmer, G.; Stepien, C.A.; Hallerman, E.M. Population genetic differentiation of walleye (Sander vitreus) across the Eastern Highlands of the United States. Fishes 2024, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryman, N.; Laikre, L. Effects of supportive breeding on the genetically effective population size. Conserv. Biol. 1991, 5, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, T.; Saint-Laurent, R.; Bernatchez, L. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in the walleye (Stizostedion vitreum), and cross-species amplification within the family Percidae. Mol. Ecol. 1999, 8, 1960–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cena, C.J.; Morgan, G.E.; Malette, M.D.; Heath, D.D. Inbreeding, outbreeding and environmental effects on genetic diversity in 46 walleye (Sander vitreus) populations. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 303–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, M.M.; Kassler, T.W.; Phillip, D.P.; Schell, S.A. A genetic assessment of Ohio River walleyes. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2005, 134, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letcher, B.H.; King, T.L. Targeted stock identification using multilocus genotype ‘familyprinting’. Fish. Res. 1999, 43, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, A.J.; Schreck, C.B.; Hess, J.E.; Bohn, S.; O’Malley, K.G.; Peterson, J.T. Application of genetic stock identification and parentage-based tagging in a mixed-stock recreational Chinook salmon fishery. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2021, 41, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, C.A.; Hess, M.; Narum, S.; Campbell, M. Parentage-based tagging: Reviewing the implementation of a new tool for an old problem. Fisheries 2019, 44, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Silliman, K.; Lewis, M.; Johnson, S.; Kratina, G.; Rider, S.J.; Stepien, C.A.; Hallerman, E.M.; Beck, B.; Fuller, A.; et al. SNP analyses highlight a unique, imperiled southern walleye (Sander vitreus) in the Mobile River Basin. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 77, 1366–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Zipfel, K.; Hallerman, E.; Massure, W.; Euclide, P.; Welsh, A. Genomic evaluation of native walleye in the Appalachian region and the effects of stocking. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2023, 152, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.; Zipfel, K.; Welsh, A. Advancing conservation strategies for native Eastern Highlands-strain walleye Sander vitreus in West Virginia: Insights from genomic investigations and broodstock screening. Diversity 2024, 16, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euclide, P.T.; Larson, W.A.; Bootsma, M.; Miller, L.M.; Scribner, K.T.; Stott, W.; Wilson, C.C.; Latch, E.K. A new GTSeq resource to facilitate multijurisdictional research and management of walleye Sander vitreus. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
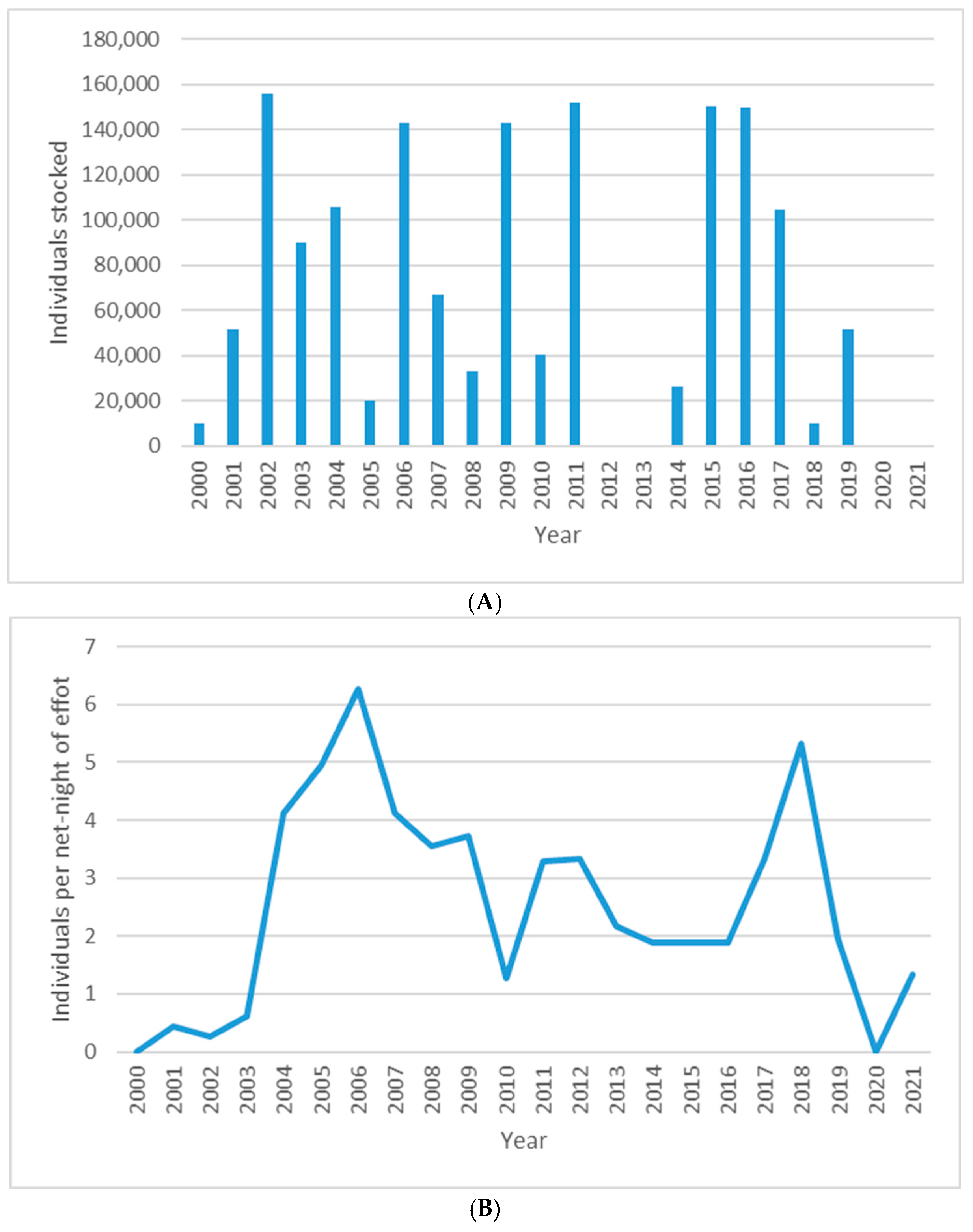
| Year | Females Spawned | Eggs Produced | Fry Stocked | Fingerlings Stocked | Locations Stocked | No. Stocked per km |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 9 | 0.5 million | - | 10,000 | Allisonia to Buck Dam | 283 |
| 2001 | 20 | 2.2 million | 500,000 | 51,840 | Allisonia to Buck Dam | 1463 |
| 2002 | 9 | 0.9 million | - | 156,200 | Allisonia to Fries Dam | 3031 |
| 2003 | 20 | 1.7 million | 100,000 | 90,080 | Allisonia to Fries Dam | 1748 |
| 2004 | 17 | 2.0 million | - | 106,000 | Allisonia to Fields Dam | 889 |
| 2005 | 23 | 2.5 million | - | 20,000 | Allisonia to Buck Dam | 564 |
| 2006 | 11 | 1.0 million | - | 143,000 | Allisonia to Fields Dam | 1200 |
| 2007 | 11 | 0.66 million | - | 67,140 | Allisonia to Buck Dam | 1895 |
| 2008 | 13 | 0.87 million | - | 33,250 | Allisonia to Buck Dam | 938 |
| 2009 | 17 | - | - | 143,000 | Allisonia to Fields Dam | 1200 |
| 2010 | 14 | - | - | 40,612 | Allisonia | N/A |
| 2011 | 14 | - | - | 151,912 | Allisonia to Fries Dam | 2948 |
| 2014 | 18 | - | - | 26,354 | Allisonia | N/A |
| 2015 | 17 | - | - | 150,100 | Allisonia to Fries Dam | 2913 |
| 2016 | 24 | - | - | 150,000 | Allisonia to Fries Dam | 2911 |
| 2017 | 36 | - | - | 105,000 | Allisonia to Fries Dam | 2038 |
| 2018 | 30 | - | - | 10,000 | Allisonia to Buck Dam | 283 |
| 2019 | 23 | - | - | 51,840 | Allisonia to Buck Dam | 1463 |
| Citation | Trophy | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | New R./ Claytor Res. | Elsewhere | New R./ Claytor Res. | Elsewhere |
| 2000 | 24 | 85 | 3 | 0 |
| 2001 | 17 | 91 | 0 | 4 |
| 2002 | 18 | 106 | 7 | 2 |
| 2003 | 15 | 85 | 4 | 0 |
| 2004 | 18 | 94 | 3 | 1 |
| 2005 | 18 | 96 | 4 | 2 |
| 2006 | 20 | 60 | 2 | 3 |
| 2007 | 11 | 58 | 1 | 0 |
| 2008 | 20 | 75 | 3 | 0 |
| 2009 | 32 | 45 | 1 | 3 |
| 2010 | 45 | 57 | 1 | 3 |
| 2011 | 19 | 36 | 3 | 2 |
| 2012 | 20 | 21 | 4 | 1 |
| 2013 | 27 | 15 | 6 | 2 |
| 2014 | 23 | 15 | 3 | 3 |
| 2015 | 9 | 17 | 1 | 0 |
| 2016 | 11 | 20 | 1 | 2 |
| 2017 | 15 | 15 | 1 | 1 |
| 2018 | 14 | 12 | 1 | 1 |
| 2019 | 42 | 33 | 4 | 1 |
| Totals | 418 | 1036 | 53 | 31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harris, S.; Palmer, G.; Copeland, J.; Williams, J.; Hallerman, E. Assessment of 18 Years of Genetic Marker-Assisted Selection and Augmentation of Native Walleye in the Upper New River, Virginia, USA. Fishes 2025, 10, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030118
Harris S, Palmer G, Copeland J, Williams J, Hallerman E. Assessment of 18 Years of Genetic Marker-Assisted Selection and Augmentation of Native Walleye in the Upper New River, Virginia, USA. Fishes. 2025; 10(3):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030118
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarris, Sheila, George Palmer, John Copeland, Joe Williams, and Eric Hallerman. 2025. "Assessment of 18 Years of Genetic Marker-Assisted Selection and Augmentation of Native Walleye in the Upper New River, Virginia, USA" Fishes 10, no. 3: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030118
APA StyleHarris, S., Palmer, G., Copeland, J., Williams, J., & Hallerman, E. (2025). Assessment of 18 Years of Genetic Marker-Assisted Selection and Augmentation of Native Walleye in the Upper New River, Virginia, USA. Fishes, 10(3), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes10030118







