The Bacillus velezensis CYS06 Strain Exhibits Promising Applications in Fighting Grass Carp Bacterial Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish, Bacterial Strains, and Culture Conditions
2.2. Antagonistic Activity
2.3. Identification of Antagonistic Strains
2.4. Extracellular Enzyme Activity
2.5. Genome Sequencing and Analysis
2.5.1. Genome Sequencing and Functional Annotation
2.5.2. Genome Evolution Analysis
2.5.3. Functional Gene
2.5.4. Risk-Associated Genes
2.6. Challenge Test
2.7. Biological Control
2.7.1. Resistance against A. hydrophila
2.7.2. Resistance against F. columnare
3. Results
3.1. Antagonistic Strain Screening and Identification
3.2. Extracellular Enzyme Activity
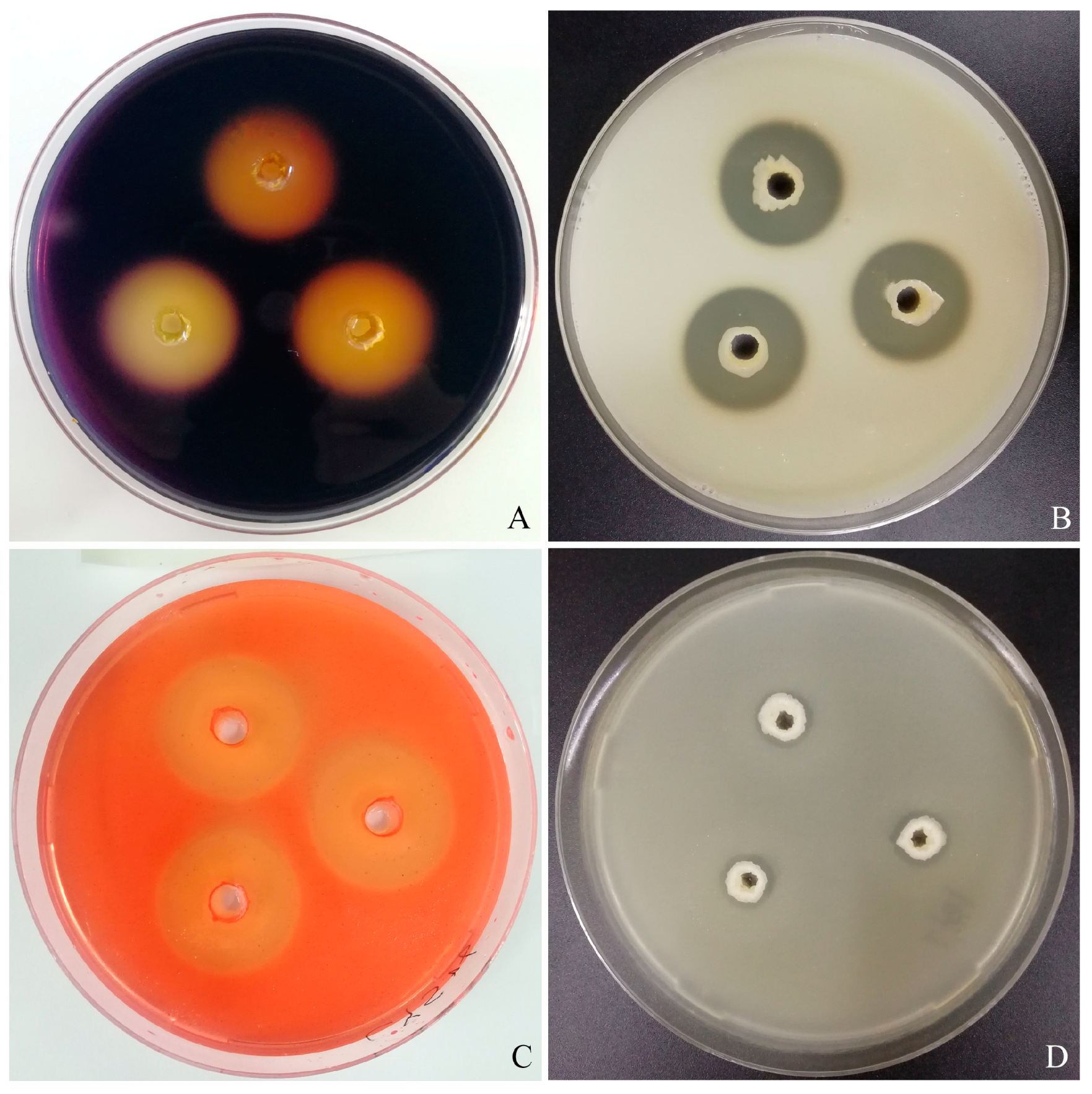
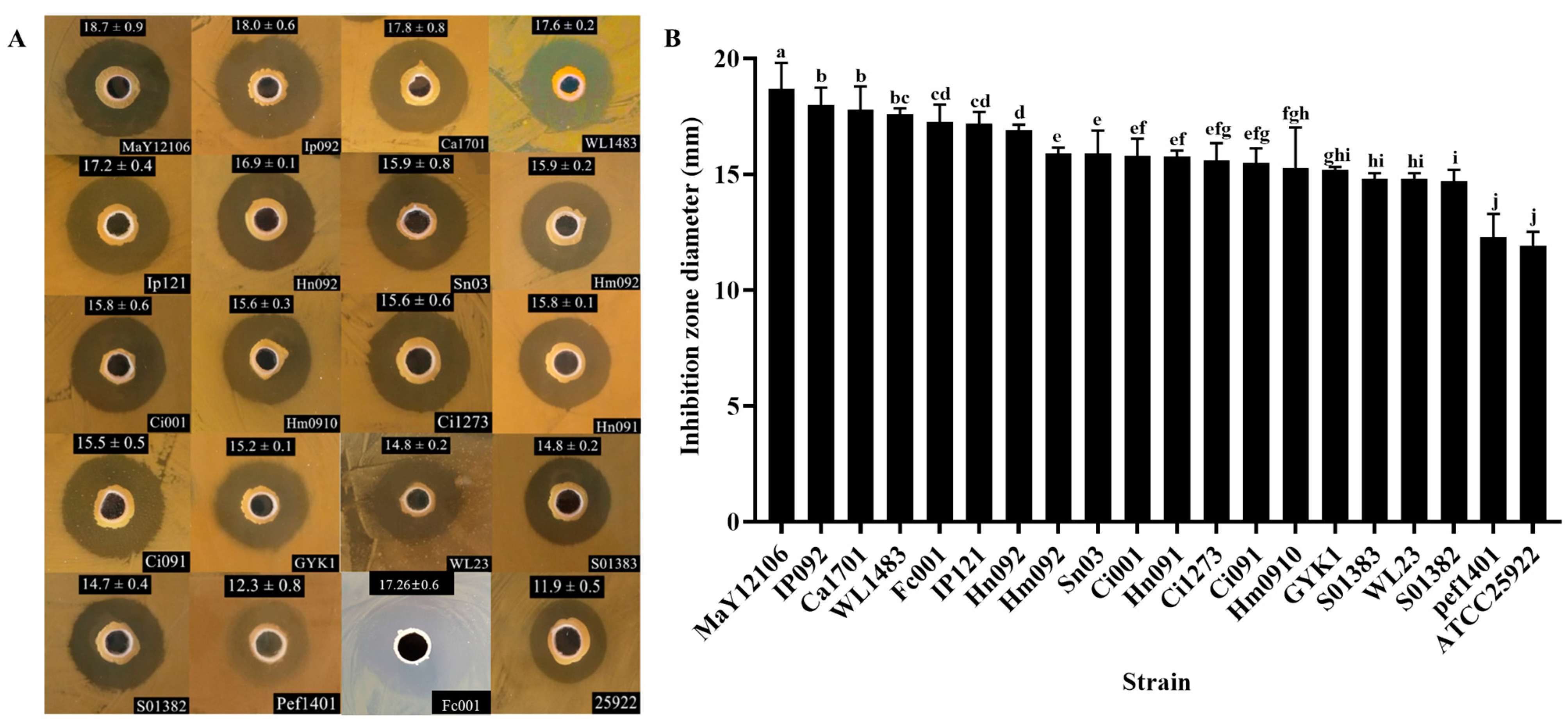
3.3. Antagonistic Activity
3.4. Genome Sequence Annotation and Functional Analysis
3.4.1. Sequence Assembly and Annotation
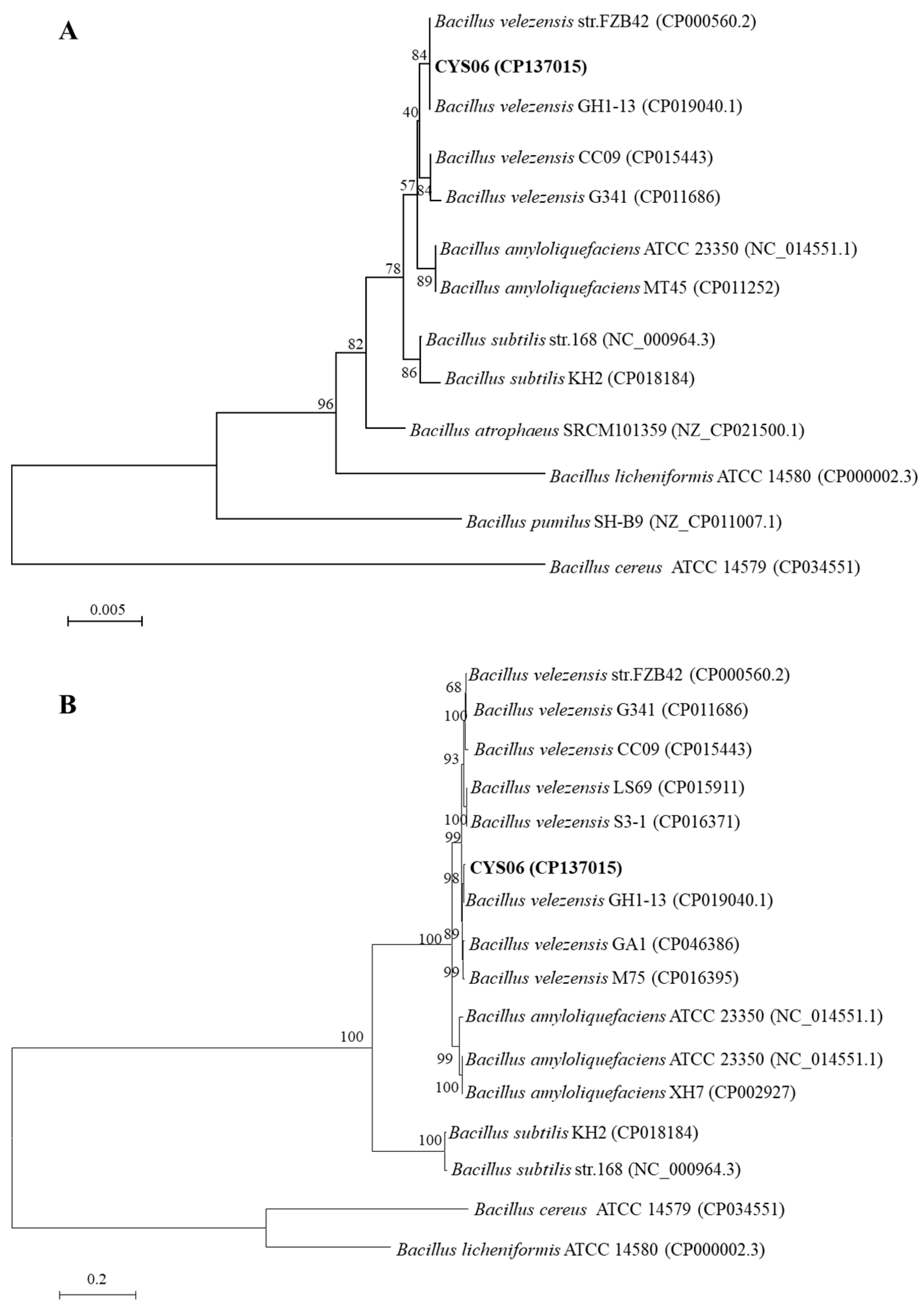
3.4.2. Taxonomic Status
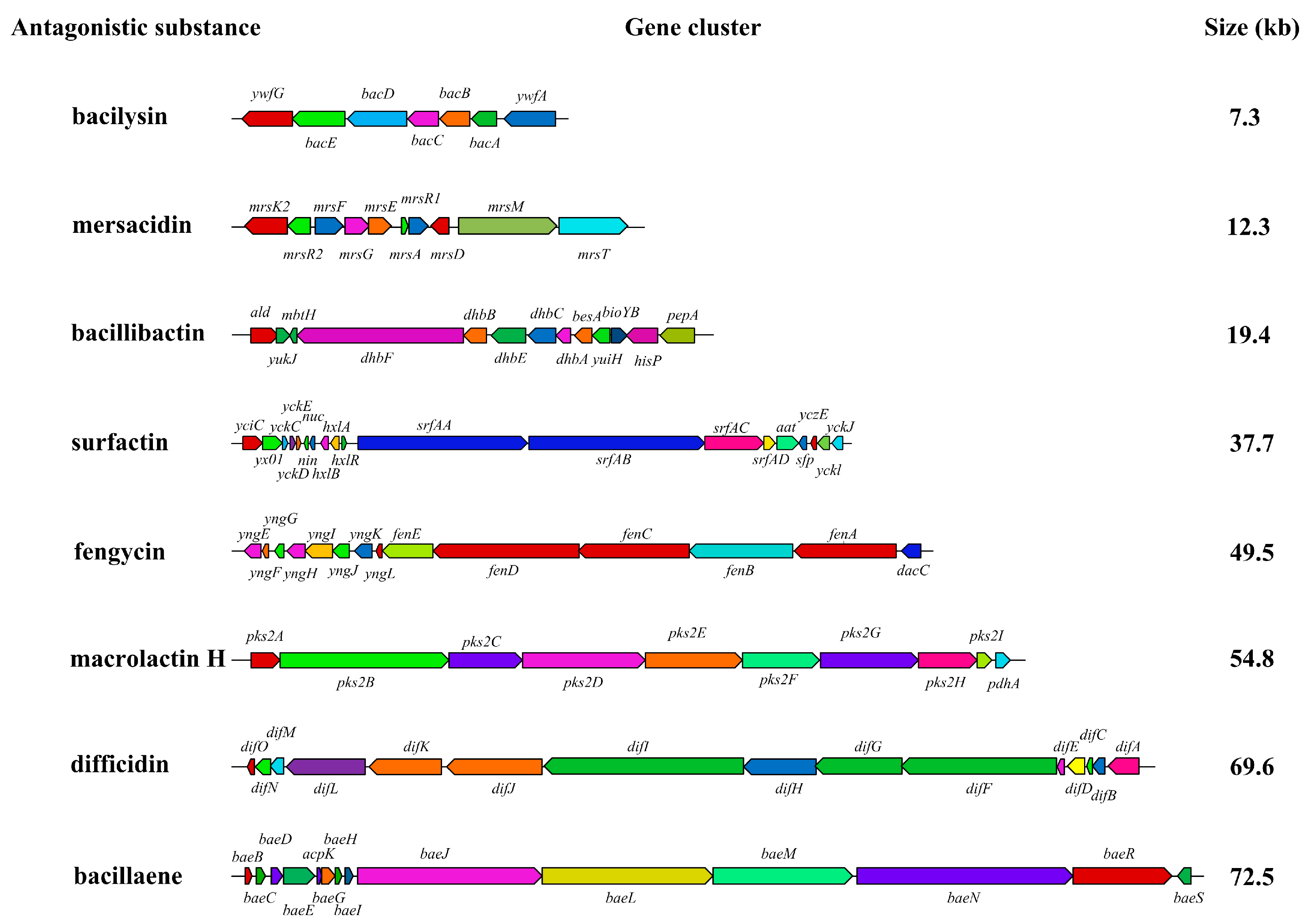
3.4.3. Antagonistic Substance Gene Clusters
3.4.4. CAZy Enzymes
3.4.5. Biogenic Amine and Toxin Encoding Genes
3.5. Challenge Test
3.6. Biocontrol Efficacy
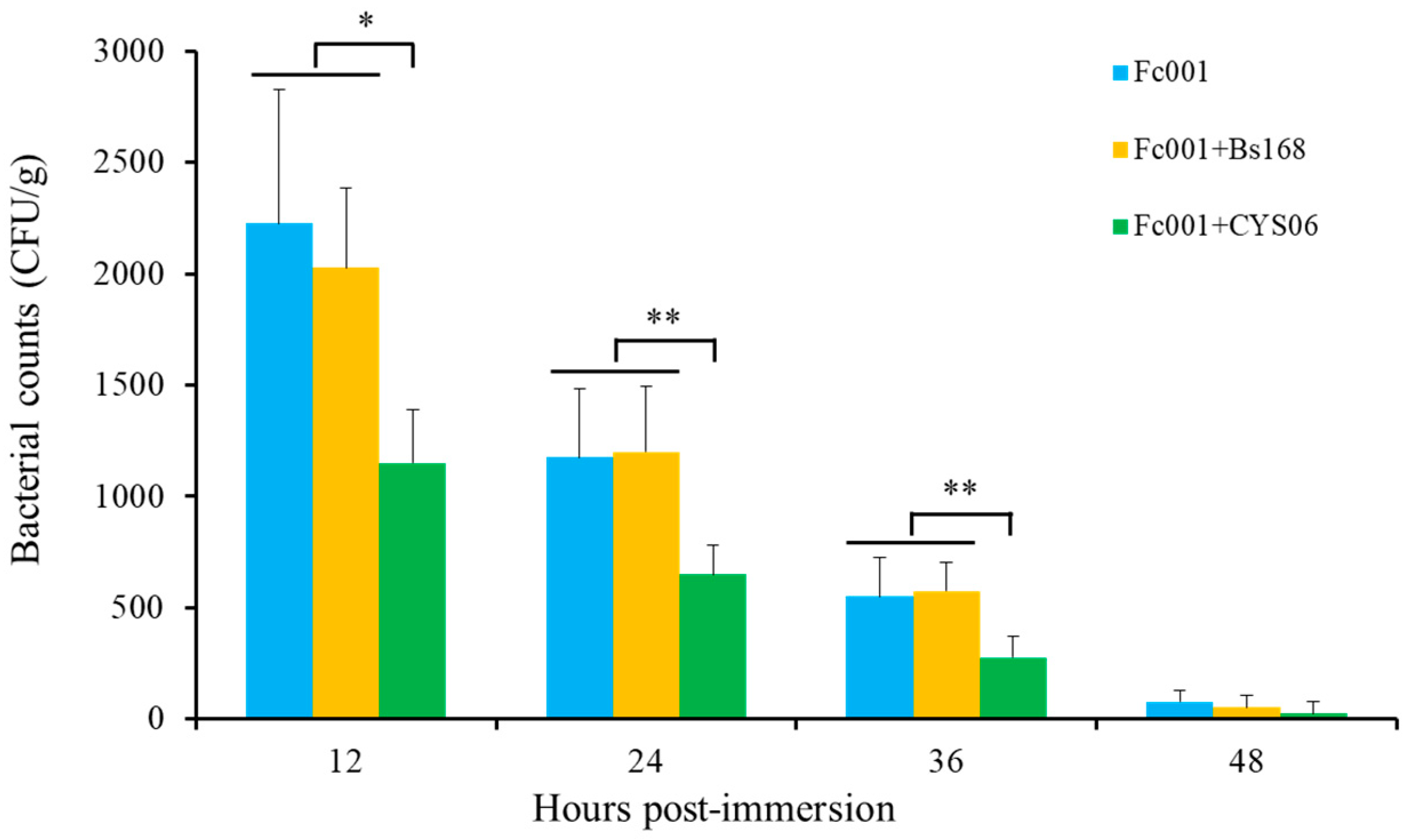
3.6.1. Resistance against A. hydrophila
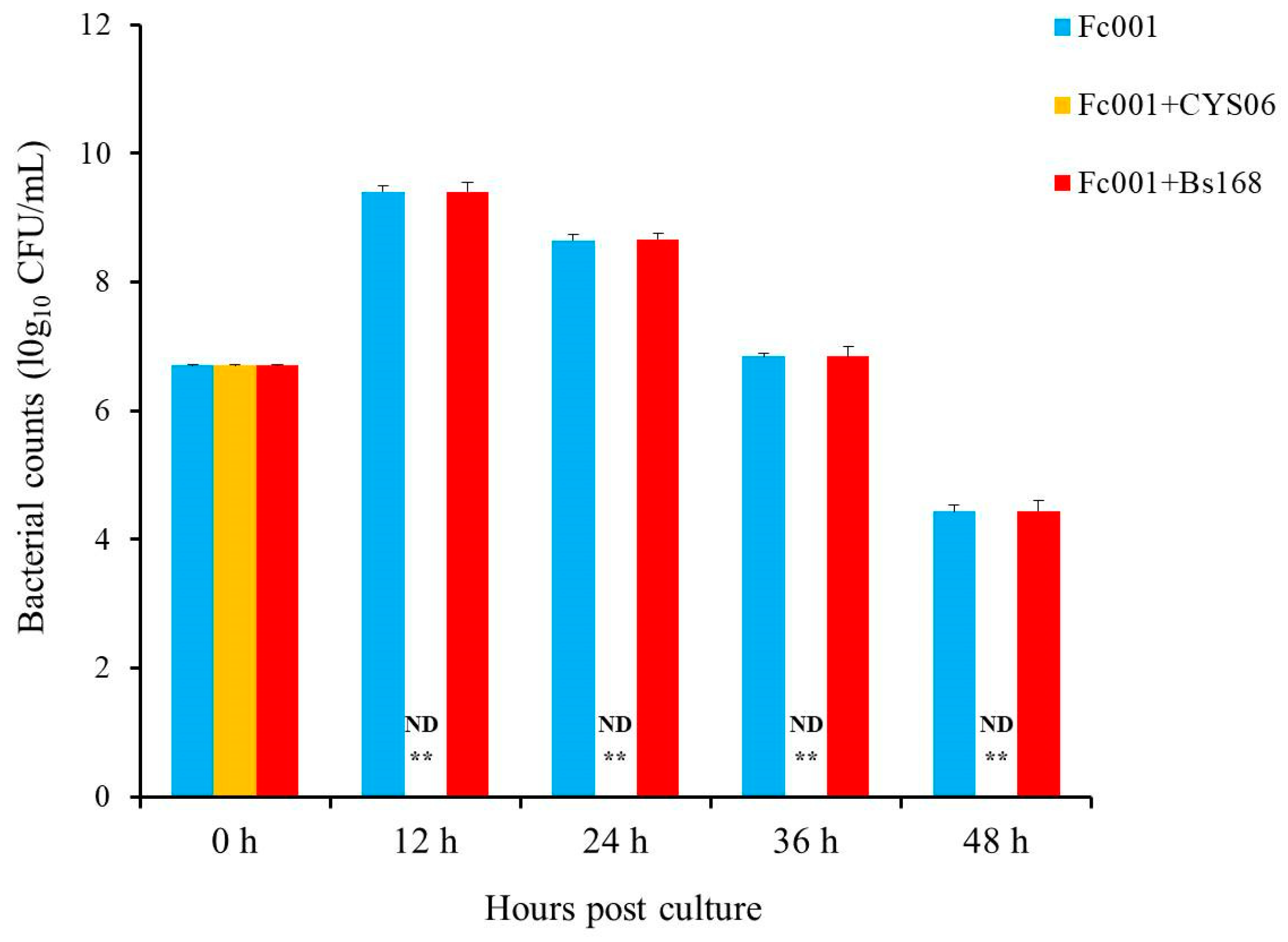
3.6.2. Resistance against F. columnare
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Xie, C. Biology and Ecology of Grass Carp in China: A Review and Synthesis. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2020, 40, 1379–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Lee, A.S.; Johnson, T.B.; Koops, M.A. Bioenergetics modelling of grass carp: Estimated individual consumption and population impacts in Great Lakes wetlands. J. Great Lakes Res. 2017, 43, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Gao, R.; Duan, Y.; Han, R.; Guo, W.; Dan, X.; Li, Y. Isolation and genetic characterization of Flavobacterium columnare from grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idellus, in China. Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhao, J.; Bo, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wu, K.; Gong, C. Aeromonas hydrophila induces intestinal inflammation in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): An experimental model. Aquaculture 2014, 434, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, A.; Wei, Z.; Hu, X.; Sun, J.; Pei, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Li, A.L. Isolation and Characterization of Acinetobacter lwoffii from the Intestine of Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2017, 69, 1411. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.N.; Zhao, Y.T.; Cao, S.L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.J. Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analyses of grass carp intestines after vaccination with a double-targeted DNA vaccine of Vibrio mimicus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 98, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Lian, Z.; Hu, X.; Lü, A.; Sun, J.; Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Yiksung, Y. First report of Vibrio vulnificus infection in grass carp Ctenopharyngodon idellus in China. Aquaculture 2019, 499, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.Y.; Xiao, L.Y.; Kou, H.Y.; Yang, C.G.; Guo, P.H.; He, W.; Tian, D.Y.; Wu, K.; Cheng, Z.K.; Song, X.H. Different routes of Aeromonas hydrophila infection lead to differential grass carp interleukin-17 family gene expression patterns during intestinal inflammation. Aquaculture 2020, 529, 735607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang, M.Q.; Shao, W.; Sheng, G.P. Antibiotic resistance and microbiota in the gut of Chinese four major freshwater carp from retail markets. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Qi, X.; Qu, S.; Ling, F.; Wang, G. Dietary supplementation of Bacillus velezensis B8 enhances immune response and resistance against Aeromonas veronii in grass carp. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2021, 115, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Wang, C.; Song, X.; Ding, X.; Wu, L.; Wu, H.; Gao, X.; Borriss, R. Bacillus velezensis FZB42 in 2018: The Gram-positive model strain for plant growth promotion and biocontrol. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Yang, C.; Wei, L.; Li, T.; Chen, X. Isolation and identification of an endophytic bacteria Bacillus velezensis 8-4 exhibiting biocontrol activity against potato scab. Biol. Control 2020, 141, 104156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.F.; Meng, J.F.; Tian, T.; Xiao, X.Q.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, Y.N. Endophytic Bacillus velezensis strain B-36 is a potential biocontrol agent against lotus rot caused by Fusarium oxysporum. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Heng, J.; Qin, S.; Bian, K. A comprehensive understanding of the biocontrol potential of Bacillus velezensis LM2303 against Fusarium head blight. PLoS ONE 2018, 6, e0198560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Liu, H.; Yu, L.; Zha, J.; Wang, J. Probiotic potential of Bacillus velezensis JW: Antimicrobial activity against fish pathogenic bacteria and immune enhancement effects on Carassius auratus. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 78, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, Y.; Ke, X.; Yi, M.; Liu, Z.; Han, X.; Shi, C.; Lu, M. Bacillus velezensis LF01: In vitro antimicrobial activity against fish pathogens, growth performance enhancement, and disease resistance against streptococcosis in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 9023–9035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.B.; Zhang, Z.; Zha, J.W.; Qu, S.Y.; Qi, X.Z.; Wang, G.X.; Ling, F. Effects of potential probiotic Bacillus velezensis K2 on growth, immunity and resistance to Vibrio harveyi infection of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus ♂ × E. fuscoguttatus ♀). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 93, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.P.; Pan, L.; Gong, L.; Yang, Y.H.; He, H.C.; Li, Y.P.; Peng, Y.N.; Li, D.J.; Yan, L.; Ding, X.Z.; et al. Interaction of a novel Bacillus velezensis (BvL03) against Aeromonas hydrophila in vitro and in vivo in grass carp. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 8987–8999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, L.; Ao, S.; Tang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Q.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X. Probiotic potential of Bacillus velezensis: Antimicrobial activity against non-O1 Vibrio cholerae and immune enhancement effects on Macrobrachium nipponense. Aquaculture 2021, 541, 736817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, C.; Wan, F.; Onchari, M.M.; Yin, X.; Tian, B.; Zhang, J.; Bai, Q.; Luo, C. Enhance the biocontrol efficiency of Bacillus velezensis Bs916 for white spot syndrome virus in crayfish by overproduction of cyclic lipopeptide locillomycin. Aquaculture 2023, 573, 739596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbee, M.F.; Ali, M.S.; Choi, J.; Hwang, B.S.; Jeong, S.C.; Baek, K. Bacillus velezensis: A valuable member of bioactive molecules within plant microbiomes. Molecules 2019, 24, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Jiang, H.; Ma, K.; Wang, X.; Liang, S.; Cai, Y.; Jing, Y.; Tian, B.; Shi, X. Genome sequencing and analysis of Bacillus velezensis VJH504 reveal biocontrol mechanism against cucumber Fusarium wilt. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1279695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaid, D.S.; Cai, S.; Hu, C.; Li, Z.; Li, Y. Comparative genome analysis reveals phylogenetic identity of Bacillus velezensis HNA3 and genomic insights into its plant growth promotion and biocontrol effects. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02169-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.H.; Liao, M.J.; Wang, H.K.; Zheng, M.Z.; Xu, J.J.; Guo, J.H. Bacillus velezensis, a potential and efficient biocontrol agent in control of pepper gray mold caused by Botrytis cinerea. Biol. Control 2018, 126, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zeng, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yin, J.; Ren, Y.; Shi, C. Use of high-resolution melting curve analysis to differentiate vaccine and wild type strains of grass carp reovirus genotype II. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 256, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.F.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Li, A.H. Development of a multiplex PCR assay for rapid and simultaneous detection of four genera of fish pathogenic bacteria. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 59, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.F.; Xiong, X.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Gao, Y.X.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Q.; Shi, C.B. Bacillus velezensis WLYS23 strain possesses antagonistic activity against hybrid snakehead bacterial pathogens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 131, 3056–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 11, 112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; Locascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki, E.P.; Eddy, S.R. Infernal 1.1: 100-fold faster RNA homology searches. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2933–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrocki, E.P.; Burge, S.W.; Bateman, A.; Daub, J.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Floden, E.W.; Gardner, P.P.; Jones, T.A.; Tate, J.; et al. Rfam 12.0: Updates to the RNA families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D130–D137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, R.; Chu, J.S.; Wang, K.; Pei, J.; Chen, N. GenBlastA: Enabling BLAST to identify homologous gene sequences. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birney, E.; Clamp, M.; Durbin, R. GeneWise and Genomewise. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.; Kim, Y.O.; Park, S.C.; Chun, J. OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1100–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auch, A.F.; Von, J.M.; Klenk, H.P.; Göker, M. Digital DNA-DNA hybridization for microbial species delineation by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2010, 2, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, G.; Li, X.; Liu, Z. Growth, immune response, antioxidant capability, and disease resistance of juvenile Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fed Bacillus velezensis V4 and Rhodotorula mucilaginosa compound. Aquaculture 2019, 500, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Nagao, J.; Zendo, T.; Sonomoto, K. Antimicrobial mechanism of lantibiotics. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Miao, L.L.; Li, E.W.; Sun, G.X.; Liu, Z.P. Characterization and mechanism of anti-Aeromonas salmonicida activity of a marine probiotic strain, Bacillus velezensis V4. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 3759–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurlow, C.M.; Williams, M.A.; Carrias, A.; Ran, C.; Newman, M.; Tweedie, J.; Allison, E.; Jescovitch, L.N.; Wilson, A.E.; Terhune, J.S.; et al. Bacillus velezensis AP193 exerts probiotic effects in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) and reduces aquaculture pond eutrophication. Aquaculture 2019, 503, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, G.; Kong, H.; Kim, N.; Lee, S.; Sul, S.; Jeong, D.W.; Lee, J.H. Antibiotic susceptibility of Bacillus velezensis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2022, 369, fnac017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Strain | Species | Host |
|---|---|---|
| MaY12106 | Aeromonas hydrophila | Megalobrama amblycephala |
| GYK1 | Aeromonas hydrophila | Mandarin fish (Siniperca chuatsi) |
| Ip092 | Aeromonas hydrophila | Channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) |
| Ci001 | Aeromonas hydrophila | Grass carp (C. idella) |
| Hm092 | Aeromonas hydrophila | Silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) |
| Hm0910 | Aeromonas hydrophila | Silver carp (H. molitrix) |
| Ca1701 | Aeromonas hydrophila | Crucian carp (C. auratus) |
| Hn091 | Aeromonas hydrophila | Bighead carp (Hypopthalmichthys nobilis) |
| Hn092 | Aeromonas veronii | Bighead carp (H. nobilis) |
| Ci091 | Aeromonas veronii | Grass carp (C. idella) |
| Ci1273 | Aeromonas jandaei | Grass carp (C. idella) |
| Ip121 | Aeromonas jandaei | Channel catfish (I. punctatus) |
| WL1483 | Aeromonas schubertii | Hybrid snakehead (Channa argus × C. maculate) |
| WL23 | Aeromonas schubertii | Hybrid snakehead (C. argus × C. maculate) |
| So1382 | Aeromonas aquariorum | Red drum (Sciaenops ocellatus) |
| So1383 | Aeromonas aquariorum | Red drum (S. ocellatus) |
| Pef1401 | Edwardsiella ictaluri | Yellow catfish (Tachysurus fulvidraco) |
| Fc001 | Flavobacterium columnare | Grass carp (C. idella) |
| Sn03 | Streptococcus iniae | Nile tilapia (O. niloticus) |
| Type | Number/Copy |
|---|---|
| Genome size (bp) | 3,914,159 |
| GC content (%) | 46.59 |
| Coding sequences | 3692 |
| 16S rRNA | 9 |
| 23S rRNA | 9 |
| 5S rRNA | 9 |
| tRNA | 86 |
| ncRNA | 42 |
| pseudogene | 7 |
| CRISPR | 9 |
| Genomic island | 7 |
| Prophage | 2 |
| Strain (GenBank Accession No.) | CYS06 Strain | |
|---|---|---|
| ANI (%) | DDH (%) | |
| Bacillus velezensis GH1-13 (CP019040) | 99.46 | 96.00 |
| Bacillus velezensis BvL03 (CP041192) | 99.13 | 93.10 |
| Bacillus velezensis M75 (CP016395) | 98.68 | 88.80 |
| Bacillus velezensis G341 (CP011686) | 97.81 | 81.40 |
| Bacillus velezensis FZB42 (CP000560) | 97.73 | 80.90 |
| Bacillus velezensis LS69 (CP015911) | 97.69 | 79.80 |
| Bacillus velezensis WLYS23 (CP055160) | 97.64 | 79.80 |
| Bacillus velezensis LG37 (CP023341) | 97.63 | 79.80 |
| Bacillus amyloliquefaciens ATCC 23350 (NC_014551) | 94.17 | 56.00 |
| Bacillus amyloliquefaciens MT45 (CP011252) | 94.02 | 55.60 |
| Bacillus subtilis str. 168 (NC_000964) | 76.89 | 20.90 |
| Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 14,580 (NC_006270) | 72.76 | 20.20 |
| Bacillus cereus ATCC 14,579 (CP034551) | 68.28 | 34.00 |
| Bacillus pumilus SH-B9 (CP011007) | 70.51 | 19.40 |
| CAZymes Families | Gene Subfamilies (Number) |
|---|---|
| Glycoside Hydrolases, GHs | GH1 (3); GH3 (1); GH4 (4); GH5 (1); GH11 (1); GH13 (4); GH16 (1); GH18 (2); GH23 (3); GH26 (1); GH30 (2); GH32 (3); GH43 (4); GH46 (1); GH51 (2); GH53 (1); GH68 (1); GH73 (2); GH76 (1); GH109 (4); GH126 (1) |
| Glycosyl Transferases, GTs | GT1 (3); GT2 (14); GT4 (8); GT8 (1); GT19 (1); GT26 (1); GT28 (3); GT46 (2); GT51 (4); GT83 (2) |
| Carbohydrate Esterases, CEs | CE1 (8); CE3 (2); CE4 (7); CE6 (1); CE7 (2); CE9 (3); CE10 (4); CE12 (2); CE14 (4) |
| Polysaccharide Lyases, PLs | PL1 (2); PL9 (1) |
| Auxiliary Activities, AAs | AA4 (1); AA6 (1); AA7 (4); AA10 (1) |
| Carbohydrate-Binding Modules, CBMs | CBM2 (1); CBM3 (1); CBM6 (1); CBM12 (1); CBM26 (1); CBM37 (1); CBM50 (25) |
| Enzymes of Biogenic Amine | Biogenic Amine | GenBank Accession No. a | CYS06 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tyrosine decarboxylase | Tyramine | JH792376 | Negative |
| Histidine decarboxylase | Histamine | AB553281.1 | Negative |
| Agmatine deiminase | Putrescine | NZ_GL635753.1 | Negative |
| Arginine decarboxylase | Putrescine | CP010005.1 | Negative |
| Arginine deiminase | Putrescine | CP009651.1 | Negative |
| Putrescine carbamoyltransferase | Putrescine | NZ_CAPG01000089.1 | Negative |
| N-carbamoylputrescine amidase | Putrescine | CP002394 | Negative |
| Ornithine carbamoyltransferase | Putrescine | CP000764.1 | Negative |
| Spermidine synthase | Spermidine | CP010052.1 | Positive |
| S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase | Spermidine | CP010052.1 | Positive |
| Enterotoxin | Major Encoding Genes | Reference a | CYS06 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cereulide | cesA, cesH, cesP, cesB, cesC, cesD | DQ360825.1 | Negative |
| Enterotoxin T | bacT | D17312.1 | Negative |
| Hemolysin BL | hbA, hblB, hblC, hblD | AJ007794.1 | Negative |
| Non-hemolytic enterotoxin | nheA, nheB, nheC | Y19005.2 | Negative |
| Cytotoxin K | cytK | AJ277962.1 | Negative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Jiang, D.; Ren, Y.; Shi, C.; Wang, Y.; Yin, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D. The Bacillus velezensis CYS06 Strain Exhibits Promising Applications in Fighting Grass Carp Bacterial Diseases. Fishes 2024, 9, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010007
Liu L, Jiang D, Ren Y, Shi C, Wang Y, Yin J, Wang Q, Zhang D. The Bacillus velezensis CYS06 Strain Exhibits Promising Applications in Fighting Grass Carp Bacterial Diseases. Fishes. 2024; 9(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lijuan, Dongdong Jiang, Yan Ren, Cunbin Shi, Yajun Wang, Jiyuan Yin, Qing Wang, and Defeng Zhang. 2024. "The Bacillus velezensis CYS06 Strain Exhibits Promising Applications in Fighting Grass Carp Bacterial Diseases" Fishes 9, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010007
APA StyleLiu, L., Jiang, D., Ren, Y., Shi, C., Wang, Y., Yin, J., Wang, Q., & Zhang, D. (2024). The Bacillus velezensis CYS06 Strain Exhibits Promising Applications in Fighting Grass Carp Bacterial Diseases. Fishes, 9(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9010007







