Application of Fisheries Acoustics: A Review of the Current State in Mexico and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Processing Software
Open-Source Software Options
| Software | Open Source | Project Administrator | Country of Origin | Programming Language | Availability | References, Contacts, and Repositories |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Echoview | No | Echoview | Australia | C++ | Request sales information from info@echoview.com | info@echoview.com |
| Echopype | Yes | The project is directed by Wu-Jung Lee and Emilio Mayorga, but there are other collaborators | United States | Python | https://pypi.org/project/echopype/, accessed on 16 July 2024. | https://github.com/leewujung https://github.com/emiliom leewj@uw.edu, accessed on 16 July 2024 |
| Large-Scale Survey System (LSSS) | MAREC—Institute of Marine Research (IMR) | Norway | Java | Request sales information from info@marec.no | [34] | |
| ESP3 | Yes | National Institute of Water and Atmospheric (NIWA) | New Zealand | Executable with a MATLAB license or with MATLAB Compiler Runtime (free) | https://sourceforge.net/, accessed on 4 September 2024 * You can subscribe to project updates to receive notification of new versions | Yoann.ladroit@niwa.co.nz Pablo.Escobar@niwa.co.nz |
| StoX | Yes | Institute of Marine Research (IMR) | Norway | Java | https://github.com/StoXProject/StoX/releases/tag/v4.0.0, accessed on 20 July 2024 | espen.johnsen@hi.no arnejh@hi.no |
| PyEcholab | Yes | Institute for Research in Environmental Science, University of Colorado, Boulder, and collaborators | United States | Python | https://github.com/CI-CMG/pyEchola/, accessed on 20 July 2024 | wcd.info@noaa.gov |
| EchoPy | Yes | Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) | France | Python | https://pypi.org/project/echopy/, accessed on 12 August 2024 | echopy@protonmail.com |
| ECOPAMPA | Yes | The Physics and Engineering Research Center of the Center of the Province of Buenos Aires (CIFICEN) | Argentina | Visual Studio 2010 | svillar@fio.unicen.edu.ar | |
| Matecho | Yes | Institut de Recherche pour le Développement (IRD) | France | Executable with a MATLAB license or with MATLAB Compiler Runtime (free) | https://git.outilsis.ird.fr/activeacoustics/matecho, accessed on 19 August 2024 | [22] |
| MOVIES + Movies-B | No | France | [32,35] | |||
| Echogram | Yes | Centro Interdisciplinario de Ciencias Marinas | Mexico | R | https://github.com/hvillalo/echogram, accessed on 26 August 2024 | hvillalo@inp.mx |
| Bergen Echo Integrator (BEI) | No | Institute of Marine Research (IMR) | Norway | C++ | [21,36] | |
| SONAR 4,5,6 | No | |||||
| MOVIES 3D | No | L’Institut Français de Recherche pour l’Exploitation de la Mer | France | http://flotte.ifremer.fr/Presentation-de-la-flotte/Logiciels-embarques/HERMES-MOVIES3D/Telechargem, accessed on 2 September 2024 |
4. Sampling Design
5. Frontiers for the Application of Acoustics
5.1. The Contribution of Acoustic Data to Ecosystem Studies
5.2. The Relevance of Acoustic Data for Marine Protected Areas and Endangered Species
5.3. Acoustic Assessment of Fishery Resources in Freshwater and Shallow Water
5.4. Target Strength
6. The Relevance of Time Series
6.1. Proportionality between Indices of Relative Abundance and Abundance
6.2. The Relevance of Density Time Series and Their Use as an Index of Relative Abundance
6.3. Hydroacoustic Data and Integrated Stock Assessment Models
| Package Name | Acronym | Does the Package Include a Population Dynamic Structure? | Is Uncertainty Assessed? | Does the Model Require Indices of Relative Abundance? | Is Documentation Available in the Form of a Peer-Reviewed Publication? | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age-structured Assessment Procedure | ASAP | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | [133] |
| C++ Algorithmic Stock Assessment Laboratory | CASAL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | [134] |
| Stock Synthesis Model | SSM | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | [114,135] |
| Assessment Method for Alaska | AMAK | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | [136] |
| Simple Stock Synthesis | SSS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | [137] |
| Extended Simple Stock Synthesis | XSSS | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | [138,139] |
| Woods Hole Assessment Model | WHAM | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | [140] |
| A Length-based, Age-structured Model | Multifan-CL | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | [141] |
7. Mexican Budget for Research
7.1. Acoustic Equipment and Instrumentation: Mexican Research Vessels
7.2. Investment in Human Resources
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dornan, T.; Fielding, S.; Saunders, R.A.; Genner, M.J. Large Mesopelagic Fish Biomass in the Southern Ocean Resolved by Acoustic Properties. Proc. R. Soc. B 2021, 289, 20211781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenevik, E.K.; Vølstad, J.H.; Høines, Å.; Aanes, S.; Óskarsson, G.J.; Jacobsen, J.A.; Tangen, Ø. Precision in Estimates of Density and Biomass of Norwegian Spring-Spawning Herring Based on Acoustic Surveys. Mar. Biol. Res. 2015, 11, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassermann, S.; Johnson, M.P. The Potential to Improve the Sustainability of Pelagic Fisheries in the Northeast Atlantic by Incorporating Individual Fish Behavior Into Acoustic Sampling. Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, V.; Mouget, A.; Perrot, Y.; Le Goff, L.; Thiriet, P.; Diogoul, N.; Feunteun, E.; Acou, A.; Brehmer, P. Insights from a Multibeam Echosounder to Survey Pelagic Fish Shoals and Their Spatio-Temporal Distribution in Ultra-Shallow Waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 264, 107705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domokos, R. On the Development of Acoustic Descriptors for Semi-Demersal Fish Identification to Support Monitoring Stocks. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Kiyomoto, S.; Kadota, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Yamanaka, H.; Kawauchi, Y.; Minami, K.; Miyashita, K. Assessment of Spatio-Temporal Variations of Macroalgal Canopies and Fish Schools before and after Coastal Desertification Using Acoustic Methods. Hydrobiologia 2023, 851, 1891–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Mukai, T.; Fujimori, Y.; Lida, K. Estimating the Sampling Efficiencies of a Framed Midwater Trawl and Ring Net for Zooplankton Using an Acoustic Method Net for Zooplankton Using an Acoustic Method. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2021, 29, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Z.-Z.; Chen, G.-B.; Zhang, P.; Qiu, Y.-S.; Yao, Z. Hydroacoustic Studies on the Commercially Important Squid Sthenoteuthis oualaniensis in the South China Sea. Fish. Res. 2015, 169, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cheng, J.; Tang, T.; Chen, J.; Li, G. Acoustic Target Strength of Jellyfish, Nemopilema nomurai, Measured at Multi-Frequency and Multi-Orientation. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2023, 2023, 6650863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkel, V.M.; Handegard, N.O.; Weber, T.C. Observing the Ocean Interior in Support of Integrated Management. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2016, 73, 1947–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit-Bird, K.J.; Lawson, G.L. Ecological Insights from Pelagic Habitats Acquired Using Active Acoustic Techniques. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2016, 8, 463–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.J.; Smith, S.J.; Lawton, P.; Anderson, J.T. Benthic Habitat Mapping: A Review of Progress towards Improved Understanding of the Spatial Ecology of the Seafloor Using Acoustic Techniques. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P.G.; Gerlotto, F.; Holliday, D.V.; Nakken, O.; Simmonds, E.J. Acoustic Applications in Fisheries Science: The ICES Contribution. ICES Mar. Sci. Symposia 2002, 215, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alverson, D.L. FAO Study Tour in USSR; US Fish and Wildlife Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1967; Sep No. 805.
- Bhupinder Singh, D.; Andrews, F. A Literature Survey on the Subject of the Use of Acoustics in Fish Catching and Fish Study; Institute of Ocean Engineering, School of Engineering and Architecture, The Catholic University of America: Washington, DC, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Dragesund, O.; Midttun, L. Development of Acoustic Techniques in Norway for Fisheries Research and Commercial Fishing. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. Sect. B Biol. 1972, 73, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melcer-Zaiane, J.; García-Franco, W.; Mondragon-Corona, E.; Cota-Villavicencia, A. Estimación de Biomasa y Distribución de Peces Pelágicos Con Métodos Hidroacústicos En La Corriente de California Frente a La Costa Occidental de Baja California. In Proceedings of the Primer Simposium Nacional de Recursos Pesqueros Masivos de México, Ensenada, Mexico, 28–30 September 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Cotero-Altamirano, C.E.; Green-Ruiz, Y. Spawning Biomass of the Northern Anchovy (Engraulis mordax) in the Gulf of California during 1991; CalCOFI Reo: La Jolla, CA, USA, 1997; Volume 38. [Google Scholar]
- Diario Oficial de la Federación. Acuerdo Mediante el Cual Se da a Conocer la Actualización de la Carta Nacional Pesquera; Diario Oficial de la Federación: Cuauhtémoc, Mexico, 2021.
- Korneliussen, R.J.; Heggelund, Y.; Macaulay, G.; Patel, D.; Johnsen, E.; Eliassen, I.K. Acoustic Identification of Marine Species Using a Feature Library. Methods Oceanogr. 2016, 17, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, H.P. The Bergen Echo Integrator: An Introduction. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1990, 47, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, Y.; Brehmer, P.; Habasque, J.; Roudaut, G.; Behagle, N.; Sarré, A.; Lebourges-Dhaussy, A. Matecho: An Open-Source Tool for Processing Fisheries Acoustics Data. Acoust. Aust. 2018, 46, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballón, M.; Bertrand, A.; Lebourges-Dhaussy, A.; Gutiérrez, M.; Ayón, P.; Grados, D.; Gerlotto, F. Is There Enough Zooplankton to Feed Forage Fish Populations off Peru? An Acoustic (Positive) Answer. Prog. Oceanogr. 2011, 91, 360–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladroit, Y.; Escobar-Flores, P.C.; Schimel, A.C.G.; O’Driscoll, R.L. ESP3: An Open-Source Software for the Quantitative Processing of Hydro-Acoustic Data. Softwarex 2020, 12, 100581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, E.; Totland, A.; Skålevik, A.; Holmin, A.J.; Dingsør, G.E.; Fuglebakk, E.; Handegard, N.O. StoX: An Open Source Software for Marine Survey Analyses. MEE 2019, 10, 1523–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, S.; Madirolas, A.; Cabreira, A.G.; Rozenfeld, A.; Acosta, G.G. ECOPAMPA: A New Tool for Automatic Fish Schools Detection and Assessment from Echo Data. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-J.; Mayorga, E.; Setiawan, L.; Majeed, I.; Nguyen, K.; Staneva, V. Echopype: A Python Library for Interoperable and Scalable Processing of Water Column Sonar Data for Biological Information. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICES. Working Group on Fisheries Acoustics, Science and Technology (WGFAST); Scientific Reports; ICES: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020; Volume 2, p. 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, C.C.; Towler, R.; Anderson, C.; Cutter, R.; Jech, J.M. PyEcholab: An Open-Source, Python-Based Toolkit to Analyze Water-Column Echosounder Data. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 144, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Villalobos, H. Echogram: Echogram Visualisation and Analysis; R Package, Version 0.1.2; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=echogram (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- Weill, A.; Scalabrin, C.; Diner, N. MOVIES-B: An Acoustic Detection Description Software. Application to Shoal Species Classification. Aquat. Living Resour. 1993, 6, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D.G. Report on Echo Trace Classification. ICES Coop. Res. Rep. 2000, 238, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korneliussen, R.J.; Ona, E.; Eliassen, I.; Heggelund, Y.; Patel, R.; Godø, O.R.; Giertsen, C.; Patel, D.; Nornes, E.; Bekkvik, T.; et al. The Large Scale Survey System—LSSS. In Proceedings of the 29th Scandinavian Symposium on Physical Acoustics, Ustaosetm, Norway, 29 January–1 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, L.; Durand, C.; Marchalot, C.; Diner, N. Movies+ User Manual Version 4.3; Ifremer: Plouzané, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Korneliussen, R.J. Advances in Bergen Echo Integrator; ICES Cooperative Report; ICES: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1993; p. 12. [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds, E.J.; Williamson, N.J.; Gerlotto, F.; Aglen, A. Acoustic Survey Design and Analysis Procedure: A Comprehensive Review of Current Practice; ICES Cooperative Report; ICES: Copenhagen, Denmark, 1992; Volume 187. [Google Scholar]
- Walline, P.D. Geostatistical Simulations of Eastern Bering Sea Walleye Pollock Spatial Distributions, to Estimate Sampling Precision. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2007, 64, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, D.; Lemberg, N.A. Variability of Line Intercept Density Estimates (A Simulation Study of the Variance of Hydroacoustic Biomass Estimates). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1981, 38, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, D.K.; Somerton, D.A. Review of Statistical Aspects of Survey Sampling for Marine Fisheries. Rev. Fish. Sci. 2007, 14, 245–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serrano, A.; Villalobos-Ortíz, H.; Nevárez-Martínez, M.O. A Probabilistic Procedure for Estimating an Optimal Echointegration Threshold Using the Expectation-Maximisation Algorithm. Aquat. Living Resour. 2018, 31, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enciso-Enciso, C.; Nevárez-Martínez, M.O.; Sánchez-Cárdenas, R.; Salcido-Guevara, L.A.; Minte-Vera, C.; Marín-Enriquez, E.; Hernández-Rivas, M. Assessment and Management of the Temperate Stock of Pacific Sardine (Sardinops sagax) in the South of California Current System. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 62, 102972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Rodríguez, U.; Villalobos, H.; Nevárez-Martínez, M.O. Acoustic Observations of the Vertical Distribution and Latitudinal Range of Small Pelagic Fish Schools in the Midriff Islands Region, Gulf of California, Mexico. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2018, 46, 989–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fréon, P.; Misund, O.A. Dynamics of Pelagic Fish Distribution and Behaviour: Effects on Fisheries and Stock Assessment; Fishing New Books, Blackwell Science Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1999; p. 348. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Bojórquez, E.; Nevárez-Martínez, M.O.; García-Alberto, G.; Villalobos, H.; Aguirre-Villaseñor, H.; Larios-Castro, E.; González-Peláez, S.S.; Arizmendi-Rodríguez, D.I.; Martínez-Zavala, M.A. Interaction Between Marine Fauna and the Small Pelagic Fishery in the Coastal Environment of the Gulf of California, Mexico. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 669176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonori, I.; Ticina, V.; Giannoulaki, M.; Hattab, T.; Iglesias, M.; Bonanno, A.; Costantini, I.; Canduci, G.; Machias, A.; Ventero, A.; et al. History of Hydroacoustic Surveys of Small Pelagic Fish Species in the European Mediterranean Sea. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2021, 22, 751–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salthaug, A.; Stenevik, K.E.; Vatnehol, S.; Anthonypillai, V.; Slotte, A. Distribution and Abundance of Norwegian Springspawning Herring during the Spawning Season in 2021; Survey Report; Institute of Marine Research: Bergen, Norway, 2021; ISSN 15036294. [Google Scholar]
- Cutter, G.R.; Demer, D.A. California Current Ecosystem Survey 2006 Acoustic Cruise Reports for NOAA FSV Oscar Dyson and NOAA FRV David Starr Jordan; NOAA Technical Memo; NOAA-SWFSC-415: 98; U.S. Department of Commerce: Washington, DC, USA, 2008.
- Demer, D.A.; Hewitt, R.P. Bias in Acoustic Biomass Estimates of Euphausia superba Due to Diel Vertical Migration. Deep Sea Res. I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1995, 42, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doray, M.; Badts, V.; Masse, J.; Huret, M.; Doremus, G.; Ptetitgas, P. Manual of Fisheries Survey Protocols 2014 PELGAS Surveys (PELagiques GAScogne); RBE/EMH 2014-01; Ifremer: Plouzane, France, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshimo, S. Spatial Distribution and Biomass of Pelagic Fish in the East China Sea in Summer, Based on Acoustic Surveys from 1997 to 2001. Fish. Sci. 2004, 70, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koslow, J. The Role of Acoustics in Ecosystem-Based Fishery Management. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2009, 66, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polovina, J.J. Model of a Coral Reef Ecosystem. Coral Reefs 1984, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Christensen, C.V.; Walters, C.J. Ecopath, Ecosim, and Ecospace as Tools for Evaluating Ecosystem Impact of Fisheries. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, J.C.; Danell, K. Terrestrial Trophic Dynamics in the Canadian Arctic. Can. J. Zool. 2003, 81, 827–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gascuel, D.; Pauly, D. EcoTroph: Modelling Marine Ecosystem Functioning and Impact of Fishing. Ecol. Model. 2009, 220, 2885–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, V.; Walters, C.; Pauly, D.; Forrest, R. Ecopath with Ecosim Version 6: User Guide; Fisheries Centre, University of British Columbia: Vancouver, BC, Canada; ICLARM: Penang, Malaysia, 2008; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, K.A.; Allen, J.I. End-To-End Models for the Analysis of Marine Ecosystems: Challenges, Issues, and Next Steps. Mar. Coast. Fish. 2010, 2, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handegard, N.O.; Buisson, L.; Brehmer, P.; Chalmers, S.J.; de Robertis, A.; Huse, G.; Kloser, R.; Macaulay, G.; Maury, O.; Ressler, P.H.; et al. Towards an Acoustic-Based Coupled Observation and Modelling System for Monitoring and Predicting Ecosystem Dynamics of the Open Ocean. Fish Fish. 2013, 14, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Monte-Luna, P.; Arreguín-Sánchez, F.; Lluch-Belda, D. Marine ecosystem analyses in the Gulf of Ulloa, Mexico: BAC meets Ecopath. In INCOFISH Ecosystem Models: Transiting from Ecopath to Ecospace; Le Quesne, W., Arreguín-Sánchez, F., Heymans, S., Eds.; Fisheries Centre Research Reports; University of British Columbia: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2007; Volume 15, pp. 114–133. [Google Scholar]
- Godø, O.R.; Handegard, N.O.; Browman, H.I.; Macaulay, G.; Kaartvedt, S.; Giske, J.; Ona, E.; Huse, G.; Johnsen, E. Marine Ecosystem Acoustics (MEA): Quantifying Processes in the Sea at the Spatio-Temporal Scales on Which They Occur. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 2357–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, A.; Josse, E.; Bach, P.; Dagorn, L. Acoustics for Ecosystem Research: Lessons and Perspectives from a Scientific Programme Focusing on Tuna-Environment Relationships. Aquat. Living Resour. 2003, 16, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, M.A.; Tupper, B. Importance of Shallow Water Habitats for Demersal Fishes and Decapod Crustaceans in Penobscot Bay, Maine. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2002, 63, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collings, W.; McConnaughey, R.A. Acoustic Classification of the Sea Floor to Address Essential Fish Habitat and Marine Protected Area Requirements. In Proceedings of the Canadian Hydrographic Conference, Victoria, BC, Canada, 10–12 March 1998; pp. 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Kloser, R.J.; Penrose, J.D.; Butler, A.J. Multi-Beam Backscatter Measurements Used to Infer Seabed Habitats. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 1772–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamarche, G. Quantitative Characterization of Seafloor Substrate and Bedforms Using Advanced Processing of Multibeam Backscatter—Application to Cook Strait, New Zealand. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, S93–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutter, G.R.; Demer, D.A. Seabed Classification Using Surface Backscattering Strength versus Acoustic Frequency and Incidence Angle Measured with Vertical, Split-Beam Echosounders. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 71, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Siwabessy, J.W.; Tseng, Y.-T.; Gavrilov, A.N. Seabed Habitat Mapping in Coastal Waters Using a Normal Incident Acoustic Technique. In Proceedings of the Acoustics, Gold Coast, Australia, 3–5 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Gastauer, S.; Scoulding, B.; Parsons, M. An Unsupervised Acoustic Description of Fish Schools and the Seabed in Three Fishing Regions within the Northern Demersal Scalefish Fishery (NDSF, Western Australia). Acoust. Aust. 2017, 45, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, T.J.; Kalikoski, D.; Short, K.; Varkey, D.; Pramod, G. An Evaluation of Progress in Implementing Ecosystem-Based Management of Fisheries in 33 Countries. Mar. Policy 2009, 33, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Zarate, M.V.; Arreguín-Sánchez, F.; López-Martínez, J.; Lluch-Cota, S.E. Ecosystem Trophic Structure and Energy Flux in the Northern Gulf of California, México. Ecol. Model. 2004, 174, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreguín-Sánchez, F.; Arcos, E.; Chávez, E.A. Flows of Biomass and Structure in an Exploited Benthic Ecosystem in the Gulf of California, Mexico. Ecol. Model. 2002, 156, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Luis, R.; Salinas-Zavala, C.A.; Koch, V.; Del Monte-Luna, P.; Morales-Zarate, M.V. Importance of Jumbo Squid Dosidicus gigas (Orbigny, 1835) in the Pelagic Ecosystem of the Central Gulf of California. Ecol. Model. 2008, 218, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Zarate, M.V.; Lopez-Ramírez, J.A.; Salinas-Zavala, C.A. Loggerhead Marine Turtle (Caretta caretta) Ecological Facts from a Trophic Relationship Model in a Hot Spot Fishery Area: Gulf of Ulloa, Mexico. Ecol. Model. 2021, 439, 109327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez- Gutiérrez, J.; Robinson, C.J. Tidal Current Transport of Epibenthic Swarms of the Euphausiid Nyctiphanes simplex in a Shallow, Subtropical Bay on Baja California Peninsula, México. Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 2006, 320, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.J.; Anislado, V.; Ramos, P. Shoaling Fish and Red Crab Behaviour Related to Tidal Variations in Bahía Magdalena, México. Deep Sea Res. II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2004, 51, 767–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursella, L.; Pensieri, S.; Pallás-Sanz, E.; Herzka, S.Z.; Bozzano, R.; Tenreiro, M.; Cardin, V.; Candela, J.; Sheinbaum, J. Diel, Lunar and Seasonal Vertical Migration in the Deep Western Gulf of Mexico Evidenced from a Long-Term Data Series of Acoustic Backscatter. Prog. Oceanogr. 2021, 195, 102562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portner, E.J.; Benoit-Bird, K.J.; Hazen, E.L.; Waluk, C.M.; Robinson, C.J.; Gómez-Gutiérrez, J.; Gilly, W.F. Decline and Recovery of Pelagic Acoustic Backscatter Following El Niño Events in the Gulf of California, Mexico. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 206, 102823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmiento-Lezcano, A.N.; Busquets-Vass, G.; Rubio-Rodríguez, U.; Pilar Olivar, M.; Peña, M.; Medina-Suárez, I.; González-Rodríguez, E.; Gómez- Gutiérrez, J.; Robinson, C.J.; Hernández-León, S. Active Flux Seasonality of the Small Dominant Migratory Crustaceans and Mesopelagic Fishes in the Gulf of California during June and October. Prog. Oceanogr. 2022, 208, 102894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crain, C.M.; Halpern, B.S.; Beck, M.W.; Kappel, C.V. Understanding and Managing Human Threats to the Coastal Marine Environment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1162, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortíz-Lozano, L.; Olivera-Vázquez, L.; Espejel, I. Legal Protection of Ecosystem Services Provided by Marine Protected Areas in Mexico. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2017, 138, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rife, A.N.; Erisman, B.; Sanchez, A.; Aburto-Oropeza, O. When Good Intentions Are Not Enough... Insights on Networks of “Paper Park” Marine Protected Areas. Conserv. Lett. 2013, 6, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburto-Oropeza, O.; Erisman, B.; Galland, G.R.; Mascareñas-Osorio, I.; Sala, E.; Ezcurra, E. Large Recovery of Fish Biomass in a No-Take Marine Reserve. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelleher, G.; Phillips, A. Guidelines for Marine Protected Areas; IUCN: Gland, Switzerland; Cambridge, UK, 1999; pp. 24–107. [Google Scholar]
- Bloomfield, H.J.; Sweeting, C.; Mill, A.C.; Stead, S.M.; Polunin, N.V.C. No-Trawl Area Impacts: Perceptions, Compliance and Fish Abundances. Environ. Conserv. 2012, 9, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, N.A.; Barrett, N.; Lawrence, E.; Hulls, J.; Dambacher, J.M.; Nichol, S.; Williams, A.; Hayes, K.R. Quantifying Fish Assemblages in Large, Offshore Marine Protected Areas: An Australian Case Study. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, R.M.; Wendt, D.E.; Barnes, C.L.; Marks, C.I.; Malone, D.; Waltz, G.; Schmidt, K.T.; Chiu, J.; Launer, A.L.; Hall, N.C.; et al. Variation in Responses of Fishes across Multiple Reserves within a Network of Marine Protected Areas in Temperate Waters. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egerton, J.P.; Turner, J.; LeVay, L.; Mascareñas-Osorio, I.; Aburto-Oropeza, O. Hydroacoustics as a Tool to Examine the Effects of Marine Protected Areas and Habitat Type on Marine Fish Communities. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatat, J.; Bez, N.; Habasque, J.; Lebourges-Dhaussy, A.; Lopes, C.; Roudaut, G.; Simier, M.; Travassos, P.; Vargas, G.; Bertrand, A. Comprehensive Spatial Distribution of Tropical Fish Assemblages from Multifrequency Acoustics and Video Fulfils the Island Mass Effect Framework. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalobos-Ortíz, H.; Zwolinski, J.P.; Godínez-Pérez, C.A.; González-Máynez, V.E.; Mayorga-Martínez, M.; Michaels, W.L.; Palacios-Higuera, M.S.; Rubio-Rodríguez, U.; Sarmiento-Lezcano, A.N.; Demer, D.A. A Practical Approach to Monitoring Marine Protected Areas. Oceanography 2021, 4, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.R.; Wilson, C.D.; de Robertis, A.; Rooper, C.N.; Weber, T.; Butler, J.L. Evaluation of Rockfish Abundance in Untrawlable Habitat: Combining Acoustic and Complementary Sampling Tools. Fish. Bull. 2012, 110, 332–343. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, J.; Wei, Q.; Du, H.; Li, J.; Ye, H. Are River Protected Areas Sufficient for Fish Conservation? Implications from Large-Scale Hydroacoustic Surveys in the Middle Reach of the Yangtze River. BMC Ecol. 2019, 19, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayorga-Martínez, M.; Bello-Pineda, J.; Perales-Valdivia, H.; Pérez-España, H.; Heyman, W. Characterizing Geomorphology of Mesophotic Coral Reef Ecosystems in the Southwestern Gulf of Mexico: Implications for Conservation and Management. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 639359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros-Montemayor, A.M.; Vincent, A. Science, Society, and Flagship Species: Social and Political History as Keys to Conservation Outcomes in the Gulf of California. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Anda Montañez, J.A.; García-de-León, F.J.; Zenteno-Savín, T.; Balart-Paez, E.; Méndez-Rodríguez, L.C.; Bocanegra-Castillo, N.; Martínez-Aguilar, S.; Campos-Dávila, L.; Román-Rodríguez, M.J.; Valenzuela-Quiñones, F.; et al. Estado de Salud y Estatus de Conservación de La(s) Población(Es) de Totoaba (Totoaba macdonaldi) En El Golfo de California: Una Especie En Peligro de Extinción; Proyecto No. HK050; Centro de Investigaciones Biológicas del Noroeste, S.C. La Paz, Baja California Sur. Informe Final, SNIB-CONABIO: Tlalpan, México, 2013; p. 113. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, A.; Cooke, S.J.; Deines, A.M.; Bower, S.D.; Bunnell, D.B.; Cowx, I.G.; Nguyen, V.M.; Nohner, J.; Phouthavong, K.; Riley, B.; et al. The Social, Economic, and Environmental Importance of Inland Fish and Fisheries. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollom, R.A.; Rose, G.A. A Global Review of the Spatial, Taxonomic, and Temporal Scope of Freshwater Fisheries Hydroacoustics Research. Environ. Rev. 2016, 24, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, E.O.; Guillard, J.; Schneider, P.; Caballero-Caballero, P.I.; Gerlotto, F. Hydroacoustic Surveys as Contribution to the Study of Spawning Aggregations of Nassau Grouper (Epinephelus striatus) in the Yucatan. In Proceedings of the IEEE/OES Acoustics in Underwater Geosciences Symposium, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 24–26 July 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowell, T.J.; Demer, D.A.; Aburto-Oropeza, O.; Cota-Nieto, J.J.; Hyde, J.R.; Erisman, B.E. Estimating Fish Abundance at Spawning Aggregations from Courtship Sound Levels. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Chen, L.; Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Kang, M. Spatiotemporal Distribution and Species Composition of Fish Assemblages in the Transitional Zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Water 2020, 12, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, J.; MacLennan, D.N. Fisheries Acoustics: Theory and Practice, 2nd ed.; Blackwell Science Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2005; p. 472. [Google Scholar]
- Love, R. Measurements of Fish Target Strength: A Review. Fish. Bull. 1971, 69, 703–715. [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan, D.N. Acoustical Measurement of Fish Abundance. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1990, 87, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ona, E. Physiological Factors Causing Natural Variations in Acoustic Target Strength of Fish. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1990, 70, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foote, K.G. Averaging of Fish Target Strength Functions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 67, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Setiazi, H.; Yuk, P.-S. Fisheries Hydroacoustic Assessment: A Bibliometric Analysis and Direction for Future Research towards a Blue Economy. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 60, 102838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICES. Report of the Workshop on Survey Design and Data Analysis (WKSAD). In Proceedings of the Workshop on Survey Design and Analysis [WKSAD], Sète, France, 9–13 May 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Trenkel, V.M.; Berger, L.; Bourguignon, S.; Doray, M.; Fablet, R.; Massé, J.; Mazauric, V.; Poncelet, C.; Quemener, G.; Scalabrin, C.; et al. Overview of Recent Progress in Fisheries Acoustics Made by Ifremer with Examples from the Bay of Biscay. Aquat. Living Resour. 2009, 22, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
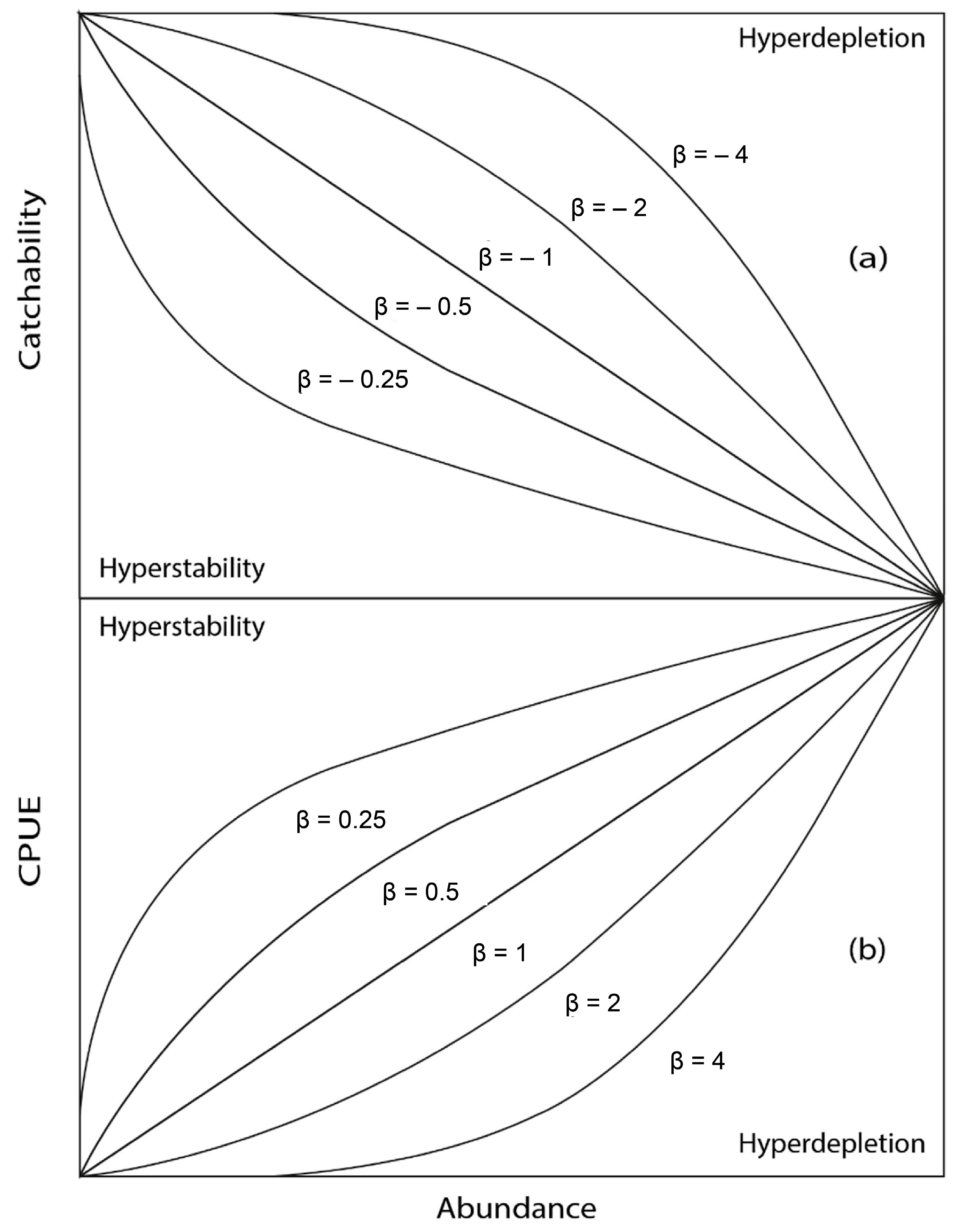
- Harley, S.J.; Myers, R.A.; Dunn, A. Is Catch-per-Unit-Effort Proportional to Abundance? Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 1760–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Aguilar, S.; de Anda-Montañez, J.A.; Arreguín-Sánchez, F. Constant Harvest Rate for the Pacific Sardine (Sardinops caeruleus) Fishery in the Gulf of California Based on Catchability-at-Length Estimations. Fish. Res. 2009, 99, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csirke, J. Small Schoalling Pelagic Fish Stocks. In Fish Population Dynamics, 2nd ed.; Gulland, J.A., Ed.; John Wiley: London, UK, 1988; pp. 271–302. [Google Scholar]
- Arreguín-Sánchez, F. Catchability: A Key Parameter for Fish Stock Assessment. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 1996, 6, 221–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilborn, R.; Walters, C.J. Quantitative Fisheries Stock Assessment: Choice, Dynamics and Uncertainty; Chapman and Hall: Boston, MA, USA, 1992; p. 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methot, R.D., Jr. Synthesis Model: An Adaptable Framework for Analysis of Diverse Stock Assessment Data. Bull. Int. North Pac. Fish. Comm. 1990, 50, 259–277. [Google Scholar]
- Fournier, D.; Archibald, C.P. A General Theory for Analyzing Catch at Age Data. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1982, 39, 1195–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polacheck, T.; Hilborn, R.; Punt, A. Fitting Surplus Production Models: Comparing Methods and Measuring Uncertainty. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1993, 50, 2597–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, D.N.; Fernandes, P.G.; Dalen, J. A Consistent Approach to Definitions and Symbols in Fisheries Acoustics. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 59, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddon, M. Modelling and Quantitative Methods in Fisheries, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall: Boston, MA, USA; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Petitgas, P. Geostatistics in Fisheries Survey Design and Stock Assessment: Models, Variances and Applications. Fish Fish. 2001, 2, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, L.G.S.; Rose, G.A. Using Geostatistics to Quantify Seasonal Distribution and Aggregation Patterns of Fishes: An Example of Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennington, M. Some Statistical Techniques for Estimating Abundance Indices from Trawl Surveys. Fish. Bull. 1986, 84, 519–525. [Google Scholar]
- Syrjala, S.E. Critique on the Use of the Delta Distribution for the Analysis of Trawl Survey Data. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2020, 57, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, G.; Hampton, I. A Stratifid Random Transect Design for Acoustic Surveys of Fish Stock. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1990, 47, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, N. Biomass and Reproduction of Pacific Sardine (Sardinops sagax) off the Pacific Northwestern United States, 2003–2005. Fish. Bull. 2010, 108, 174–192. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, N.G.-H.; Hunter, J.R.; Moser, H.G.; Smith, P.E. A Daily Fecundity Reduction Method of Biomass Estimation with Application to Dover Sole Microstomus pacificus. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1993, 53, 842–863. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, N.G.-H.; Green-Ruiz, Y.A.; Cervantes, M.J. Egg Production and Spawning Biomass of Pacific Sardine (Sardinops sagax) in 1994, Determined by the Daily Egg Production Method. Calif. Coop. Ocean Fish. Investig. Rep. 1996, 37, 160–174. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, L.; Konno, E.S.; Pertierra, J.P. Status of Pacific Mackerel and Trends in Biomass, 1978–1993. Calif. Coop. Ocean Fish. Investig. Rep. 1994, 35, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Conser, R.J.; Kevin, T.H.; Crone, P.R.; Lo, N.G.-H.; Berger, D. Stock Assessment of Pacific Sardine with Management Recommendations for 2003 Executive Summary; Pacific Fishery Management Council: Portland, OR, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson, L.; Lo, N.G.-H.; Barnes, J. A Biomass-Based Assessment Model for Northern Anchovy, Engraulis mordax. Fish. Bull. 1994, 92, 711–724. [Google Scholar]
- Green-Ruiz, Y.A.; Cotero-Altamirano, C.E. Spawning Biomass of the Northern Anchovy (Engraulis Mordax) in the Gulf of California during 1992. Cienc. Pesq. 2009, 17, 27–96. [Google Scholar]
- Nevárez-Martínez, M.O.; Morales-Bojórquez, E.; De Los Angeles Martínez-Zavala, M.; Villalobos-Ortíz, H.; Luquin-Covarrubias, M.; González-Máynez, V.E.; López-Martínez, J.; Santos-Molina, J.P.; Ornelas-Vargas, A.; Delgado-Vnces, F. An Integrated Catch-at-Age Model for Analyzing the Variability in Biomass of Pacific Sardine (Sardinops sagax) from the Gulf of California, Mexico. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 940083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, G.L.; Rose, G.A. The Importance of Detectability to Acoustic Surveys of Semi-Demersal Fish. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1999, 56, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legault, C.; Restrepo, V.R. A Flexible Forward Age-Structured Assessment Program. ICCAT. Col. Vol. Sci. Pap. 1998, 49, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Bull, B.; Francis, R.; Dunn, A. CASAL (C++ Algorithmic Stock Assessment Laboratory) CASAL User Manual v2.30-2012/03/21; NIWA Technical Report; NIWA: Auckland, New Zealand, 2012; p. 135. [Google Scholar]
- Methot, R.D., Jr.; Wetzel, C.R. Stock Synthesis: A Biological and Statistical Framework for Fish Stock Assessment and Fishery Management. Fish. Res. 2013, 142, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anon. Assessment Model for Alaska Description of GUI and Instructions. 2015. Available online: https://github.com/NMFS-toolbox/AMAK/blob/master/docs/AMAK%20Documentation.pdf (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- Cope, J. Implementing a Statistical Catch-at-Age Model (Stock Synthesis) as a Tool for Deriving Overfishing Limits in Data-Limited Situations. Fish. Res. 2013, 142, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, J.; MacCall, A.; Monk, M. Data-Moderate Stock Assessments for Brown, China, Copper, Sharpchin, Stripetail, and Yellowtail Rockfishes and English and Rex Soles in 2013; Pacific Fishery Management Council: Portland, OR, USA, 2015; Volume 97220, p. 298. [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, C.R.; Punt, A.E. Performance of a Fisheries Catch-at-Age Model (Stock Synthesis) in Datalimited Situations. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, B.C.; Miller, T.J. The Woods Hole Assessment Model (WHAM): A General State-Space Assessment Framework That Incorporates Time- and Age-Varying Processes via Random Effects and Links to Environmental Covariates. Fish. Res. 2021, 240, 105967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, D.; Hampton, J.; Sibert, J.R. MULTIFAN-CL: A Length-Based, Age-Structured Model for Fisheries Stock Assessment, with Application to South Pacific Albacore, Thunnus Alalunga. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1998, 55, 2105–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit-Bird, K.J.; Welch, T.P.; Waluk, C.M.; Barth, J.A.; Wangen, I.; McGill, P.; Okuda, C.; Hollinger, G.A.; Sato, M.; McCammon, S. Equipping an Underwater Glider with a New Echosounder to Explore Ocean Ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2018, 16, 734–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulon, C.; Le Meaux, O.; Vincent-Falquet, R.; Guillard, J. Hydroacoustic Autonomous Boat for Remote Fish Detection in LakE (HARLE), an Unmanned Autonomous Surface Vehicle to Monitor Fish Populations in Lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2021, 19, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, E.; Gjøsæter, H.; Prozorkevich, D.; Shamray, E.; Dolgov, A.; Skern-Mauritzen, M.; Stiansen, J.E.; Kovalev, Y.; Sunnana, K. From Single Species Surveys towards Monitoring of the Barents Sea Ecosystem. Prog. Oceanogr. 2018, 166, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Peña, V.; Lluch-Cota, S.E.; Chavez, F.P.; Lluch-Belda, D.; Morales-Bojórquez, E.; Ponce-Díaz, G. Is There a Future in the Sustainability Certification of Sardine and Anchovy Fisheries? Fisheries 2020, 45, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diario Oficial de La Federación. Plan de Manejo Pesquero Para La Pesquería de Pelágicos Menores (Sardina, Anchovetas, Macarela y Afines) Del Noroeste de México; Diario Oficial de La Federación: Cuauhtémoc, Mexico, 2012.
- Diario Oficial de La Federación. NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-003-SAG/PESC-2018; Diario Oficial de La Federación: Cuauhtémoc, México, 2019.
- Chu, D.; Parker-Stetter, S.; Hufnagle, L., Jr.; Thomas, R.; Getsiv-Clemons, J.; Gauthier, S.; Stanley, C. 2018 Unmanned Surface Vehicle (Saildrone) Acoustic Survey off the West Coasts of the United States and Canada. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2019 MTS/IEEE, Seattle, WA, USA, 27–31 October 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Robertis, A.; Lawrence-Slavas, N.; Jenkins, R.; Wangen, I.; Mordy, C.W.; Meinig, C.; Levine, M.; Peacock, D.; Tabisola, H. Long-Term Measurements of Fish Backscatter from Saildrone Unmanned Surface Vehicles and Comparison with Observations from a Noise-Reduced Research Vessel. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 76, 2459–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
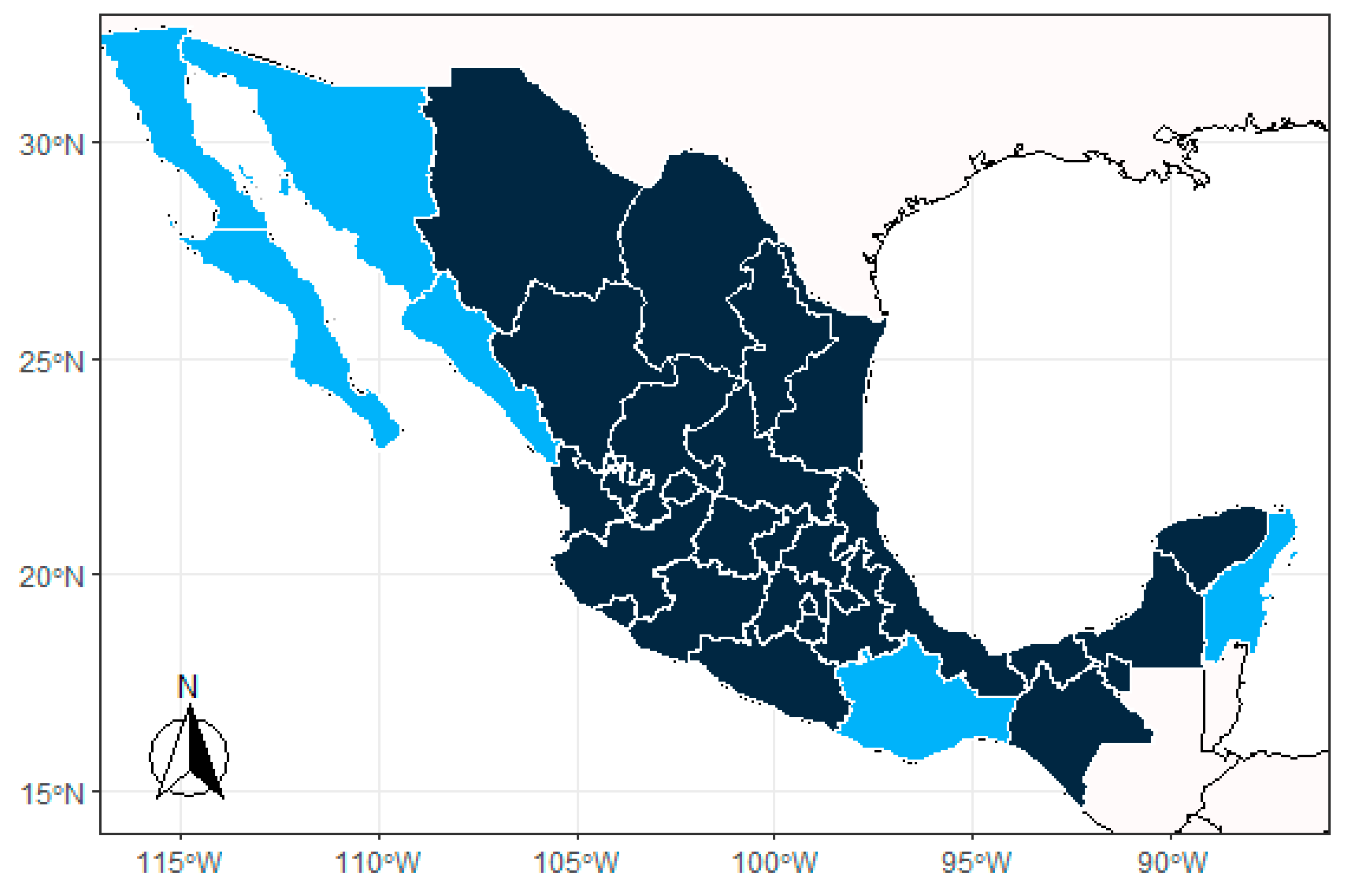

| Platforms | Institution | Echosounder System | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| RV BIP XI Autonomy: 22 days | IMIPAS | EK60 | Split-beam transducer ES38-12 (resonant frequency: 38 kHz; beamwidth: 11.94°) Split-beam transducer ES120-7C (resonant frequency: 120 kHz; beamwidth: 7.61°) Source: manuel.nevarez@imipas.gob.mx |
| RV Dr. Jorge Carranza Fraser Autonomy: 60 days | IMIPAS | EK60 | Split-beam transducer ES18 312 (resonant frequency: 18 kHz; beamwidth: 10.53°) Split-beam transducer ES38-B 312 (resonant frequency: 38 kHz; beamwidth: 6.79°) Split-beam transducer ES70-7C 312-204154 (side) (resonant frequency: 70 kHz; beamwidth: 7.12°) Split-beam transducer ES70-7C 312-204154 (resonant frequency: 70 kHz; beamwidth: 7.12°) Split-beam transducer ES120-7C 312-204022 (resonant frequency: 120 kHz; beamwidth: 7.29°) Split-beam transducer ES200-7C 312-200841 (side and down) (resonant frequency: 200 kHz; beamwidth: 7.45°) Source: https://www.gob.mx/agricultura/colima/articulos/conoce-nuestro-buque-de-investigacion-dr-jorge-carranza-fraser?idiom=es, accessed on 4 September 2024 |
| RV El Puma Autonomy: 30 days | UNAM | EK60 | Frequency: 38 kHz Frequency: 120 kHz Source: https://buques.cic.unam.mx/el-puma/equipo-puma/, accessed on 4 September 2024 |
| RV Justo Sierra Autonomy: 30 days | UNAM | EK80 | Wide-band split-beam transducer ES38-7 Resonant frequency: 38 kHz Beamwidth: 7° Source: https://buques.cic.unam.mx/justo-sierra/equipo-js/, accessed on 4 September 2024 |
| Swing steel arm | CICIMAR | EK80 | Combi transducer ES38-18/200-18C Nominal frequency Low: 38 kHz High: 200 kHz Beamwidth: 18° Source: hvillalo@ipn.mx |
| Swing steel arm | IMIPAS | EK80 | Wide-band split-beam transducer ES38-7 Resonant frequency: 38 kHz Beamwidth: 7.5° Source: manuel.nevarez@imipas.gob.mx |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Máynez, V.E.; Morales-Bojórquez, E.; Nevárez-Martínez, M.O.; Villalobos, H. Application of Fisheries Acoustics: A Review of the Current State in Mexico and Future Perspectives. Fishes 2024, 9, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9100387
González-Máynez VE, Morales-Bojórquez E, Nevárez-Martínez MO, Villalobos H. Application of Fisheries Acoustics: A Review of the Current State in Mexico and Future Perspectives. Fishes. 2024; 9(10):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9100387
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Máynez, Violeta E., Enrique Morales-Bojórquez, Manuel O. Nevárez-Martínez, and Héctor Villalobos. 2024. "Application of Fisheries Acoustics: A Review of the Current State in Mexico and Future Perspectives" Fishes 9, no. 10: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9100387
APA StyleGonzález-Máynez, V. E., Morales-Bojórquez, E., Nevárez-Martínez, M. O., & Villalobos, H. (2024). Application of Fisheries Acoustics: A Review of the Current State in Mexico and Future Perspectives. Fishes, 9(10), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9100387









