Shelf Life Study of Chilled Mullet (Mugil cephalus): Histamine Formation and Quality Degradation at Constant and Dynamic Storage Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Delivery and Preparation
2.2. Inoculation of Minced Mullet Flesh with M. morganii
Mathematical Modeling of M. morganii Growth and Histamine Formation
2.3. Shelf Life Evaluation of Mullet
2.3.1. Microbial Growth Determination
2.3.2. Sensory Evaluation
Total Volatile Basic Nitrogen (TVB-N) Determination
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
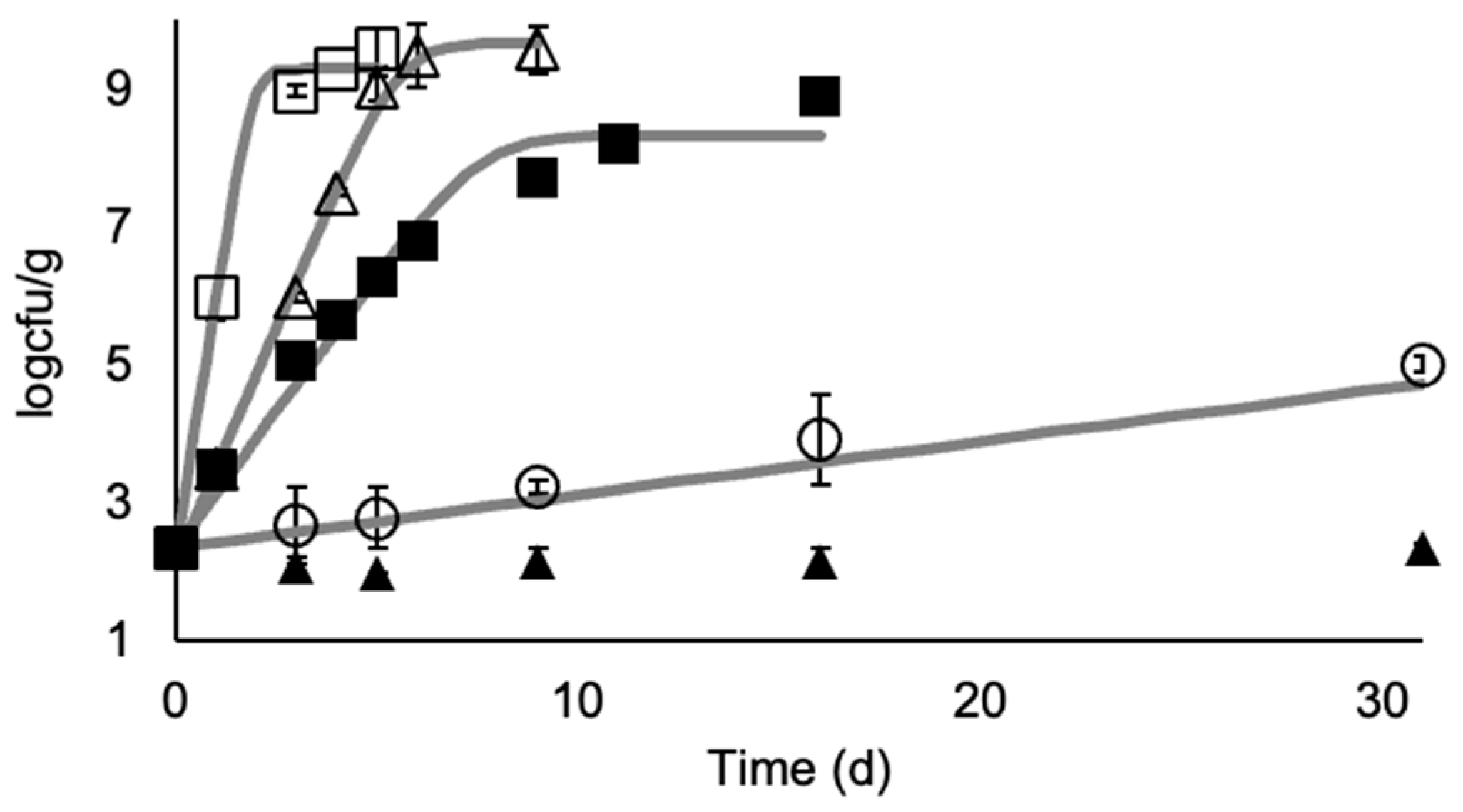
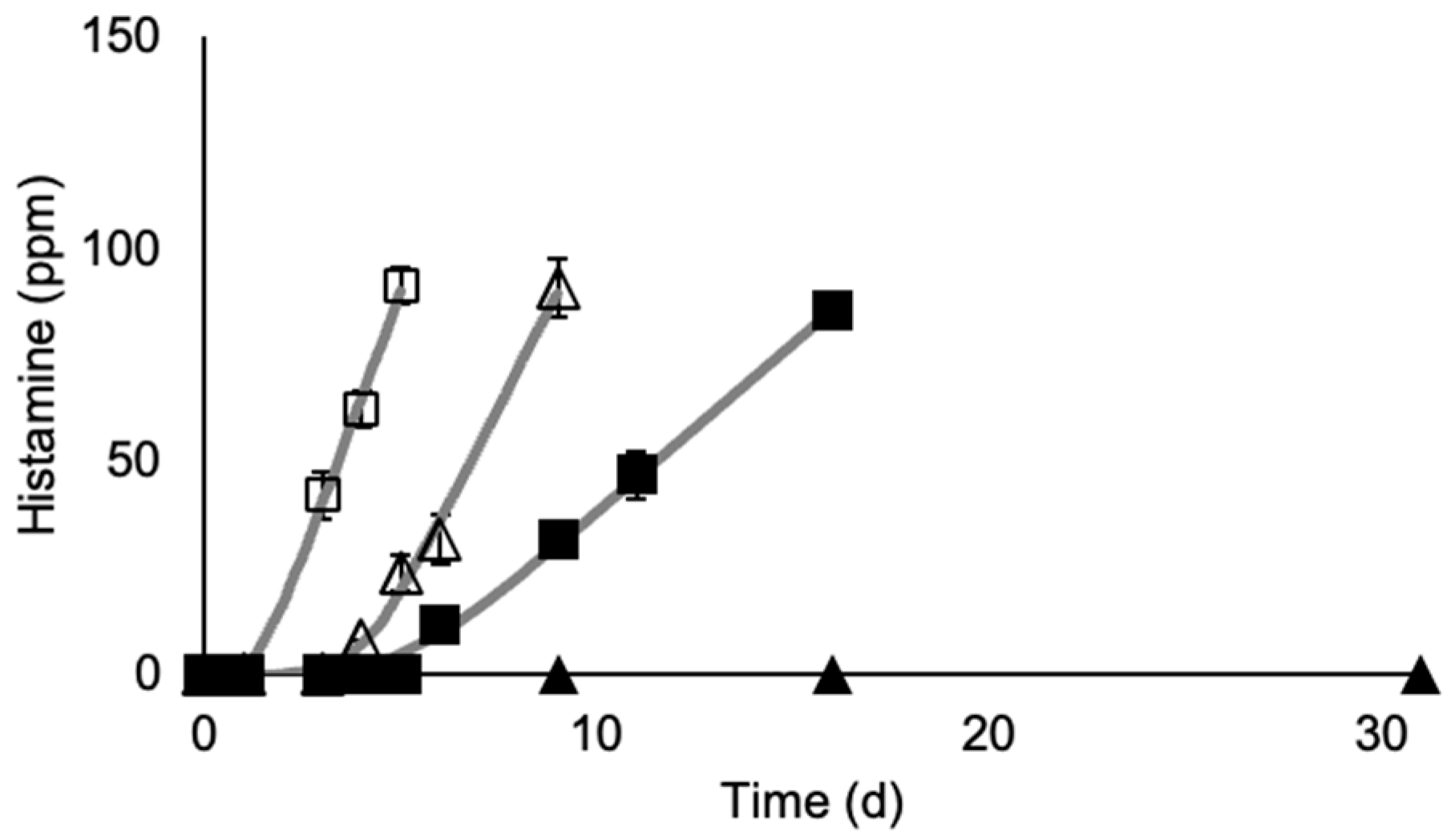
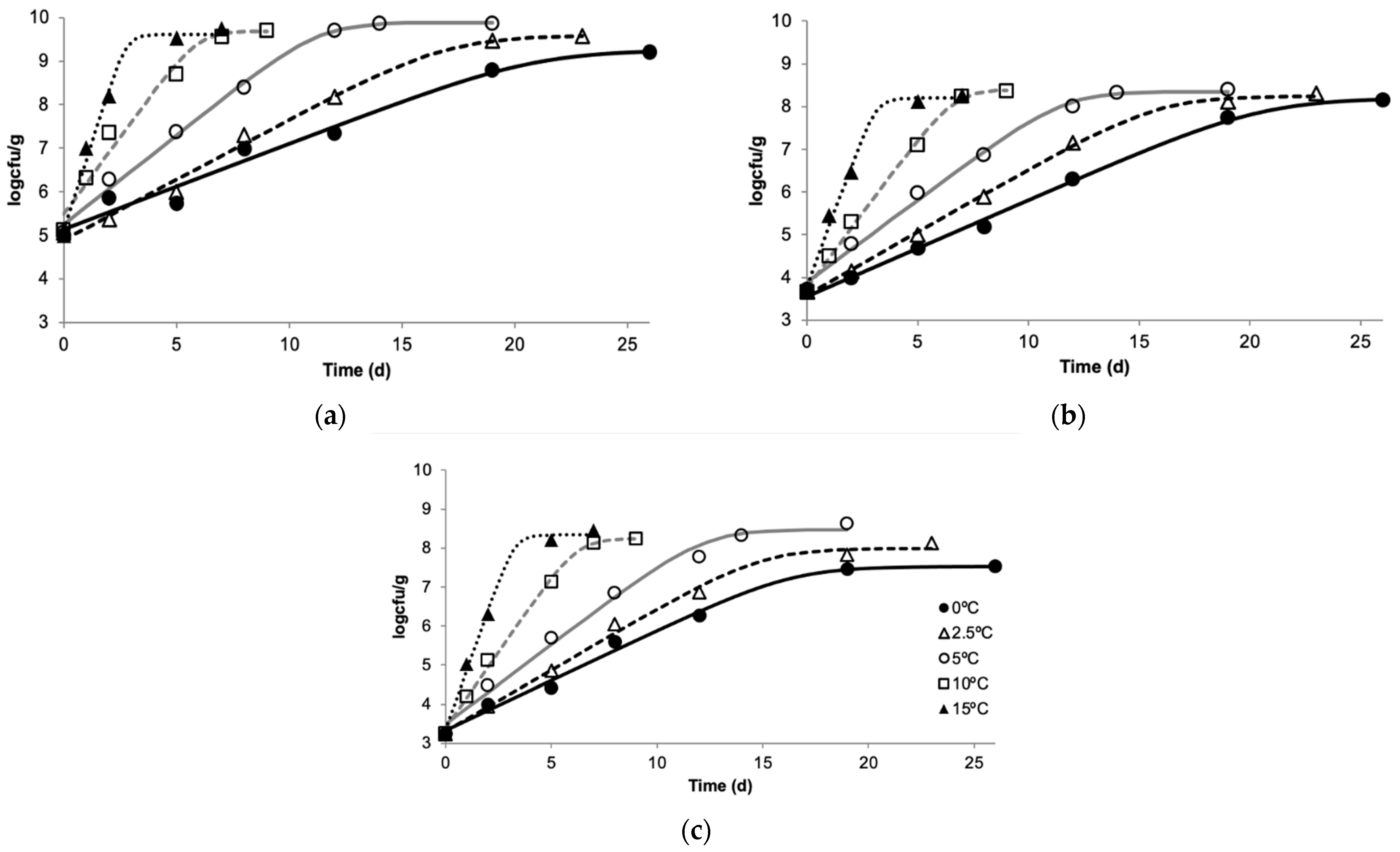
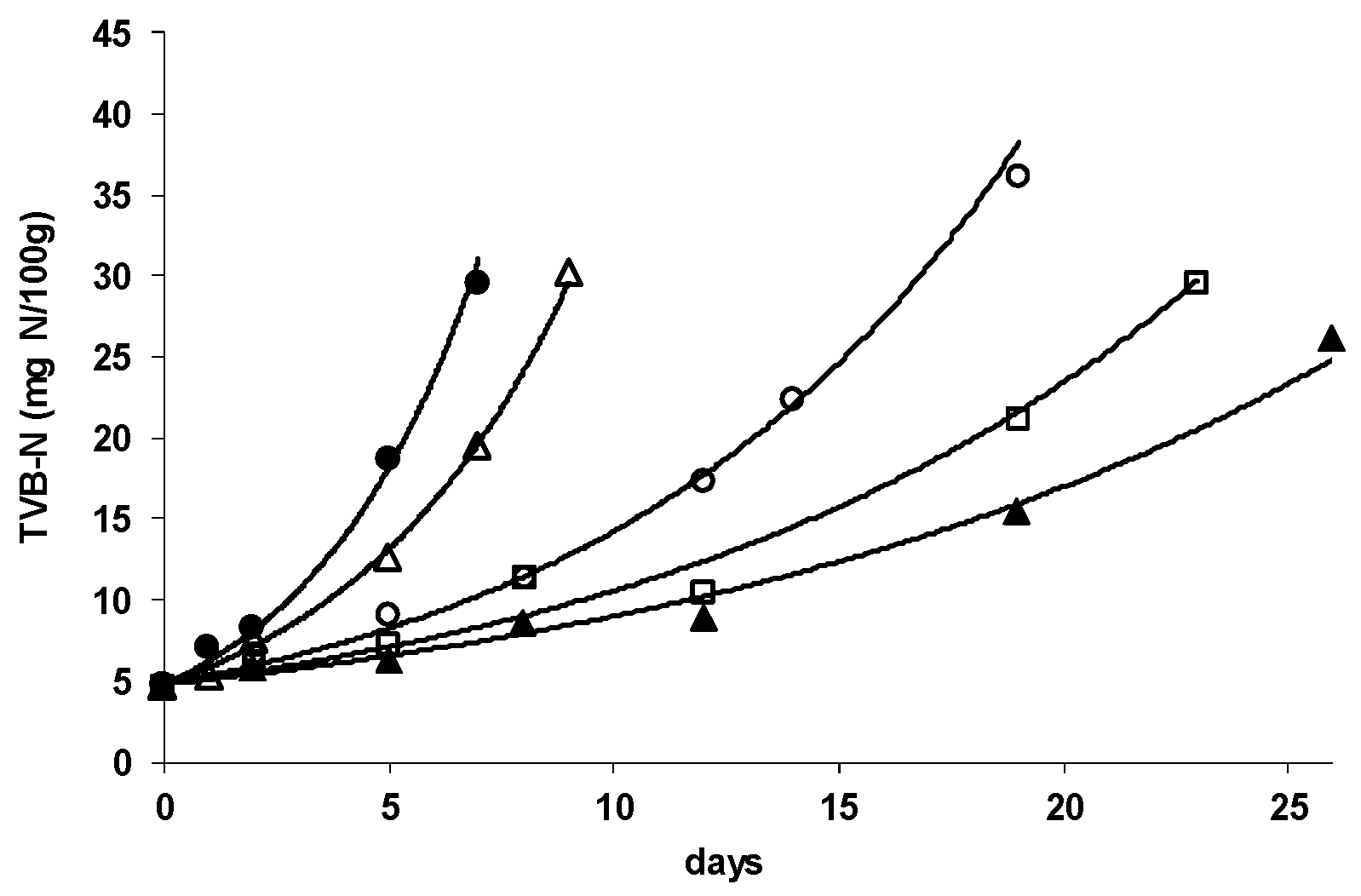
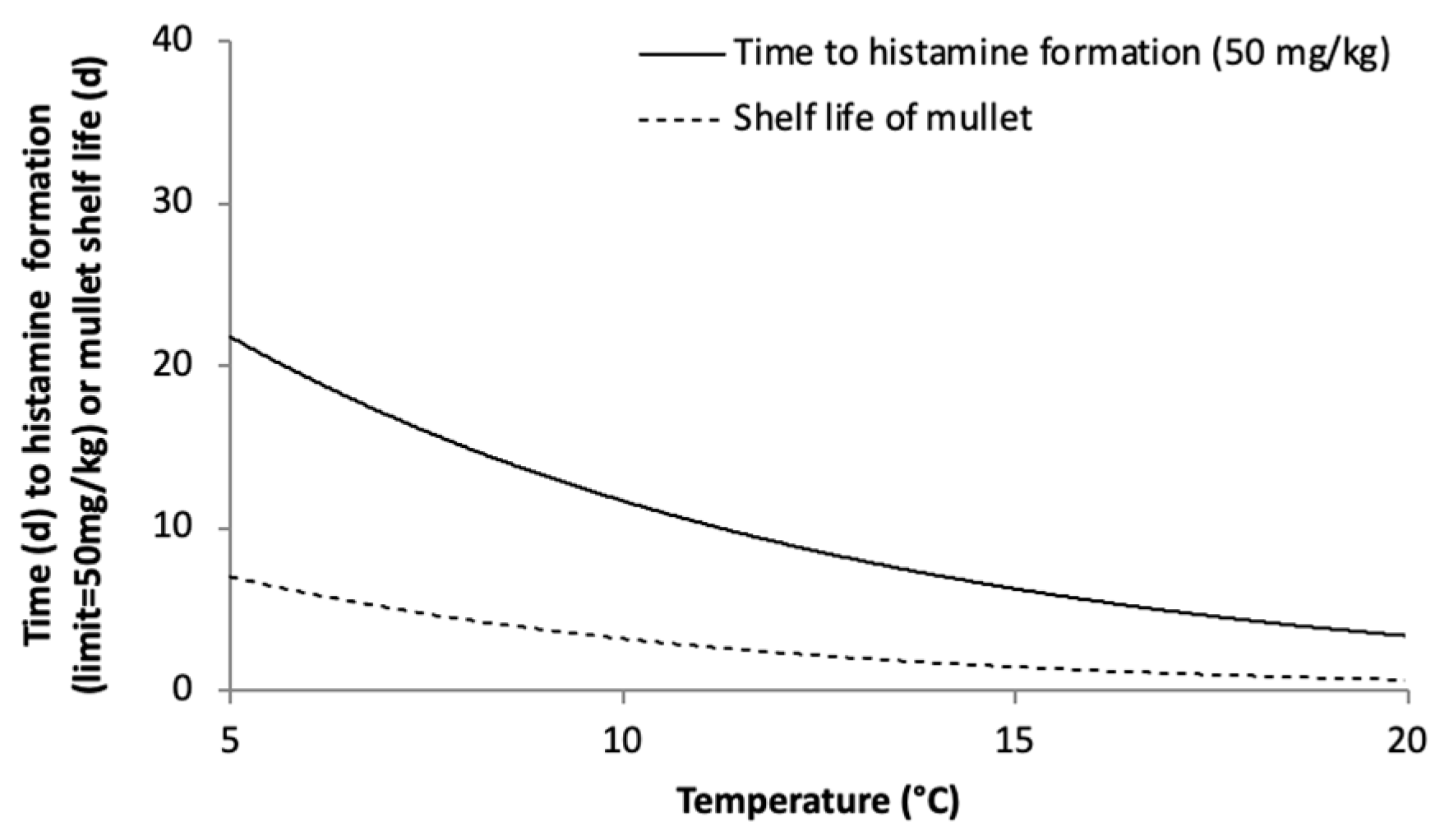
3.1. M. morganii Growth and Histamine Formation in Mullet
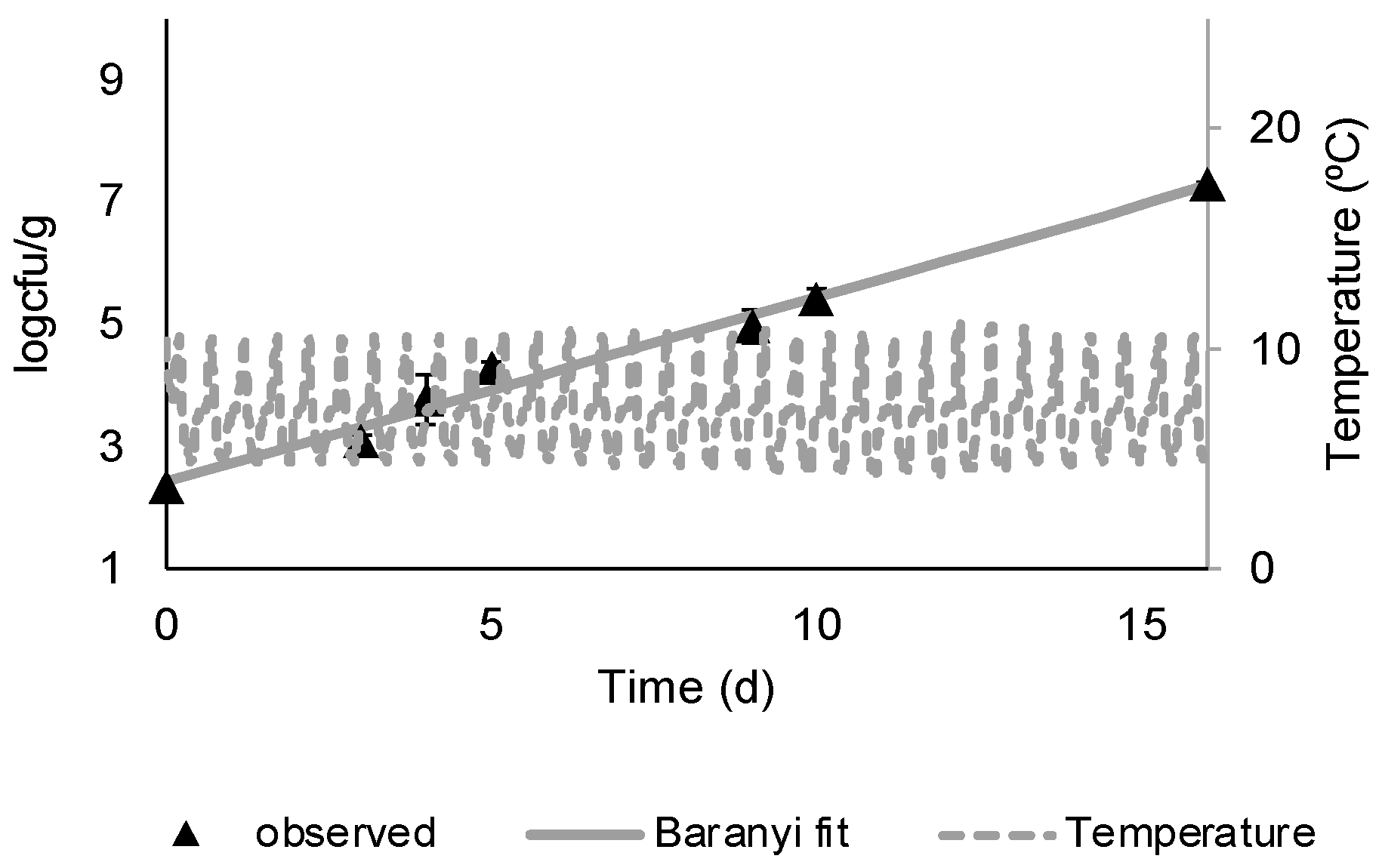
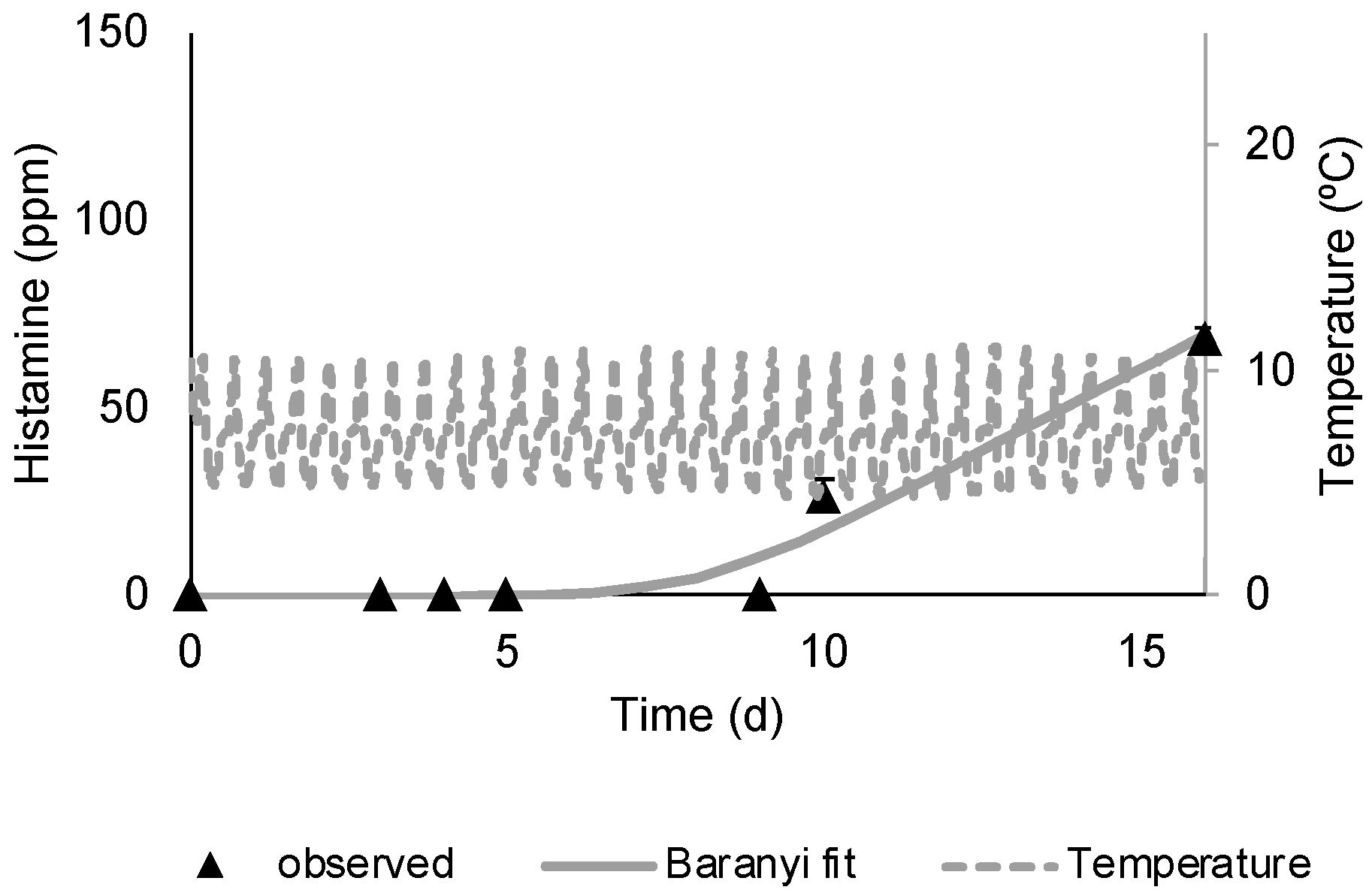
3.2. Shelf Life Evaluation of Chilled, Aerobically Packed Mullet
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pal, M.; Ketema, A.; Anberber, M.; Dutta, Y. Microbial quality of fish and fish products. Bev. Food World 2016, 43, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, S. The use of a tea polyphenol dips to extend the shelf life of silver-carp (Hypophthalmicthys molitrix) during storage in ice. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houicher, A.; Bensid, A.; Regenstein, J.M.; Ozogul, F. Control of biogenic amine production and bacterial growth in fish and seafood products using phytochemicals as biopreservatives: A review. Food Biosci. 2021, 39, 100807. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Jimenez-Colmenero, F. Biogenic amines in seafood products. In Handbook of Seafood and Seafood Products Analysis; Nollet, L.M.L., Toldora, F., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group, CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 833–850. [Google Scholar]
- Enache, E.; Kataoka, A.I.; Black, D.G.; Weddig, L.; Hayman, M.; Bjornsdottir-butler, K. Heat Resistance of Histamine-Producing Bacteria in Irradiated Tuna Loins. J. Food Prot. 2013, 76, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Møller, C.O.D.A.; Ücok, E.F.; Rattray, F.P. Histamine forming behavior of bacterial isolates from aged cheese. Food Res. Int. 2019, 128, 108719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakila, R.J.; Vijayalakshmi, K.; Jeyasekaran, G. Changes in histamine and volatile amines in six commercially important species of fish of the Thoothukkudi coast of Tamil Nadu, India stored at ambient temperature. Food Chem. 2003, 82, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA [European Food Safety Authority]. Scientific opinion on risk based control of biogenic amine formation in fermented foods. Panel on Biological Hazards (BIOHAZ). EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2393–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehane, L.; Olley, J. Histamine fish poisoning revisited. Int. J. Syst. Microbiol. 2000, 58, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsironi, T.; Lougovois, V.; Simou, V.N.; Mexi, A.; Koussissis, S.; Tsakali, E.; Papatheodorou, S.A.; Stefanou, V.; Van Impe, J.; Houhoula, D. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) for the Determination of Fish Flesh Microbiota. J. Food Res. 2019, 8, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisani, M.; Mancusi, R.; Cecchini, M.; Costanza, C.; Prearo, M. Detection and Characterization of Histamine-Producing Strains of Photobacterium damselae subsp. damselae Isolated from Mullets. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Yang, F.; Deng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, Y.; Ye, H.; Zhong, J.; Wang, Z. A Dual-Mode Method Based on Aptamer Recognition and Time-Resolved Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer for Histamine Detection in Fish. Molecules 2022, 27, 8711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Wei, C.I.; Clemens, R.A.; An, H. Histamine accumulation in seafoods and its control to prevent outbreaks of scombroid poisoning. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2008, 13, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emborg, J.; Dalgaard, P. Growth, inactivation and histamine formation of Morganella psychrotolerans and Morganella morganii—Development and evaluation of predictive models. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 128, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eschenbach, A.C.V.U.S. Food and Drug administration. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2011, 12, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/WHO [Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization]. Public Health Risks of Histamine and Other Biogenic Amines from Fish and Fishery Products. Meeting Report. 2013. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240691919 (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- Crosetti, D.; Blaber, S. Biology, Ecology and Culture of Grey Mullet (Mugilidae); CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cossu, P.; Mura, L.; Scarpa, F.; Lai, T.; Sanna, D.; Azzena, I.; Fois, N.; Casu, M. Genetic patterns in Mugil cephalus and implications for fisheries and aquaculture management. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Judez, S.; Duncan, N. Feeding habits and the influence of pellet diameter on the feeding responses of the flathead grey mullet (Mugil cephalus) in captivity. Anim. Feed Sci. 2022, 290, 115368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurma Rao, R.; Ramesh Babu, K. Reproductive biology of the flathead grey mullet, Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus, 1758) from Krishna Estuarine Region, East Coast of Andhra Pradesh, India. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2016, 4, 483–488. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, M.A. Mugil cephalus. In Cultured Aquatic Species Fact Sheets; Crespi, V., Ed.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2009; Available online: https://www.fao.org/fishery/docs/DOCUMENT/aquaculture/CulturedSpecies/file/en/en_flatheadgreymullet.htm (accessed on 28 October 2023).
- Visciano, P.; Schirone, M.; Paparella, A. An Overview of Histamine and Other Biogenic Amines in Fish and Fish Products. Foods 2020, 9, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silvestri, A.; Ferrari, E.; Gozzi, S.; Marchi, F.; Foschino, R. Determination of Temperature Dependent Growth Parameters in Psychrotrophic Pathogen Bacteria and Tentative Use of Mean Kinetic Temperature for the Microbiological Control of Food. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntzimani, A.; Angelakopoulos, R.; Stavropoulou, N.; Semenoglou, I.; Dermesonlouoglou, E.; Tsironi, T.; Moutou, K.; Taoukis, P. Seasonal pattern of the effect of slurry ice during catching and transportation on quality and shelf life of gilthead sea bream. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, K.G.; Hansen, T.B.; Knoechel, S. Growth of Heat-Treated Enterotoxin-Positive Clostridium perfringens and the Implications for Safe Cooling Rates. J. Food Prot. 2004, 67, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labbe, R.G.; Huang, T.H. Generation Times and Modeling of Enterotoxin-Positive and Enterotoxin-Negative Strains of Clostridium perfringens in Laboratory Media and Ground Beef. J. Food Prot. 1995, 58, 1303–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigehisa, T.; Nakagami, T.; Taji, S. Influence of heating and cooling rates on spore germination and growth of Clostridium perfringens in media and in roast beef. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi. 1985, 47, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranyi, J.; Roberts, T.A. Mathematics of predictive food microbiology. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1995, 26, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yimenu, S.M.; Koo, J.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.Y. Freshness-based real-time shelf-life estimation of packaged chicken meat under dynamic storage conditions. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 6921–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghollasi-Mood, F.; Mohsenzadeh, M.; Hoseindokht, M.R.; Varidi, M. Quality changes of air-packaged chicken meat stored under different temperature conditions and mathematical modelling for predicting microbial growth and shelf life. J. Food Saf. 2016, 37, e12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Labuza, T.P. Shelf life testing: Procedures and prediction methods. In Quality in Frozen Food; Erickson, M.C., Hung, Y.C., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: New York, NY, USA, 1997; p. 377. [Google Scholar]
- Botta, J.R. Sensory Evaluation: Freshness Quality Grading, Sensory Evaluation: Attribute Assessment. In Evaluation of Seafood Freshness Quality; John Wiley & Sons: Washington, DC, USA, 1996; pp. 145–185. ISBN 978-0-471-18580-2. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 8586; Sensory Analysis—Selection and Training of Sensory Assessors. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023.
- Pivarnik, L.; Ellis, P.; Wang, X.; Reilly, T. Standardization of the Ammonia Electrode Method for Evaluating Seafood Quality by Correlation to Sensory Analysis. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oscar, T.P. Validation of lag time and growth rate models for Salmonella Typhimurium: Acceptable prediction zone method. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Ben-Gigerey, B.; Barros-Velásquez, J.; Price, R.J.; An, H. Histamine and biogenic amine production by Morganella morganii isolated from temperature-abused albacore. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.; Kung, H.; Chen, T.; Tsai, Y. Hygienic quality, adulteration of pork and histamine production by Raoultella ornithinolytica in milkfish dumpling. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanki, M.; Yoda, T.; Tsukamoto, T.; Baba, E. Histidine Decarboxylases and their Role in Accumulation of Histamine in Tuna and Dried Saury. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2007, 73, 1467–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgaard, P.; Emborg, J.; Kjølby, A.; Sørensen, N.D.; Ballin, N.Z. Histamine and biogenic amines: Formation and importance in seafood. In Improving Seafood Products for the Consumer; Børresen, T., Ed.; British Welding Research Association: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 292–324. [Google Scholar]
- Gougouli, M.; Angelidis, A.S.; Koutsoumanis, K. A study on the kinetic behavior of Listeria monocytogenes in ice cream stored under static and dynamic chilling and freezing conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 97, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, T.; Dalgaard, P.; Tienungoon, S. Predictive modeling of the growth and survival of Listeria in fishery products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 62, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa Silva Andrade, S.; Teixeira Mársico, E.; de Oliveira Godoy, R.L.; Pacheco, S.; Maia Franco, R.; Borges Mano, S.; Adam Conte-Junior, C. Chemical Quality Indexes of Mullet (Mugil platanus) Stored on Ice. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti, R. Storage Characteristics and Histamine Content of Fish Stored at Tropical Ambient Temperature. Fish. Technol. 2002, 39, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, H.F.; Chien, L.T.; Liao, H.J.; Lin, C.S.; Liaw, E.T.; Chen, W.C.; Tsai, Y.H. Chemical characterisation and histamine-forming bacteria in salted mullet roe products. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visciano, P.; Schirone, M.; Tofalo, R.; Suzzi, G. Histamine poisoning and control measures in fish and fishery products. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Drug Administration (FDA). Fish and Fishery Products Hazards and Controls Guidance, 4th ed.; Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition: Rockville, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Tsironi, T.; Houhoula, D.; Taoukis, P. Hurdle technology for fish preservation. Fish. Aguac. 2020, 5, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ghareeb, W.R.; Elhelaly, A.E.; Abdallah, K.M.E.; El-Sherbiny, H.M.M.; Darwish, W.S. Formation of biogenic amines in fish: Dietary intakes and health risk assessment. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3123–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadia, M.H.M.; Khalil, M.K.M.; Abdel-Nabey, A.A.; Abo Samaha, O.R. Changes in Sensory and Microbiological Quality Indices of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) and Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus) During Ice Storage. Alex. Sci. Exch. J. 1997, 38, 433–445. [Google Scholar]
- Pilavtepe-Celik, M.; Yagiz, Y.; Marshall, M.R.; Balaban, M.O. Correlation of Mullet (Mugil cephalus) Fillet Color Changes with Chemical and Sensory Attributes during Storage at 0 °C. J. Aquat. Food Prod. Technol. 2021, 30, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özogul, Y.; Gulsum, Ö.; Özogul, F.; Kuley, E.; Polat, A. Freshness Assessment of European eel (Anguilla anguilla) by sensory, chemical and microbiological methods. Food Chem. 2005, 92, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, G.; Badalucco, C. Combining ozone and modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) to maximize shelf-life and quality of striped, red mullet (Mullus surmuletus). LWT 2012, 47, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntzimani, A.; Angelakopoulos, R.; Semenoglou, I.; Dermesonlouoglou, E.; Tsironi, T.; Moutou, K.; Taoukis, P. Slurry ice as an alternative cooling medium for fish harvesting and transportation: Study of the effect on seabass flesh quality and shelf life. Aquac. Fish. 2023, 8, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Temperature (°C) | k (d−1) |
|---|---|
| 0 | - |
| 5 | 0.098 ± 0.008 |
| 10 | 0.792 ± 0.071 |
| 15 | 1.355 ± 0.064 |
| 20 | 3.615 ± 0.442 |
| Temperature (°C) | k (d−1) | λ (d) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | - | - |
| 5 | - | - |
| 10 | 7.946 ± 0.465 | 4.921 ± 0.515 |
| 15 | 17.883 ± 3.218 | 3.964 ± 0.277 |
| 20 | 25.021 ± 2.233 | 1.328 ± 0.281 |
| Temperature (°C) | kTVC (d−1) | kPseudomonas (d−1) | kEnterobacteriaceae (d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.225 ± 0.031 | 0.198 ± 0.044 | 0.215 ± 0.026 |
| 2.5 | 0.314 ± 0.035 | 0.294 ± 0.030 | 0.276 ± 0.028 |
| 5 | 0.411 ± 0.042 | 0.383 ± 0.052 | 0.409 ± 0.039 |
| 10 | 0.782 ± 0.056 | 0.693 ± 0.041 | 0.708 ± 0.053 |
| 15 | 1.624 ± 0.295 | 1.393 ± 0.126 | 1.533 ± 0.237 |
| Ea (kJ/mol) | kref (Tref = 4 °C) (d−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| TVC | 89.9 ± 6.7 | 0.344 ± 0.042 |
| Pseudomonas spp. | 79.2 ± 7.4 | 0.355 ± 0.051 |
| Enterobacteriaceae | 79.4 ± 8.2 | 0.389 ± 0.770 |
| Temperature (°C) | kodor (d−1) | kappearance (d−1) | kov.impression (d−1) | kTVBN (d−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.249 ± 0.012 | 0.218 ± 0.017 | 0.251 ± 0.030 | 0.063 ± 0.007 |
| 2.5 | 0.352 ± 0.009 | 0.318 ± 0.026 | 0.357 ± 0.019 | 0.079 ± 0.008 |
| 5 | 0.564 ± 0.021 | 0.512 ± 0.045 | 0.566 ± 0.027 | 0.109 ± 0.009 |
| 10 | 1.074 ± 0.082 | 0.882 ± 0.113 | 1.088 ± 0.032 | 0.202 ± 0.016 |
| 15 | 1.518 ± 0.101 | 1.232 ± 0.098 | 1.554 ± 0.143 | 0.267 ± 0.022 |
| Ea (kJ/mol) | kref (Tref = 4 °C) (d−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | 76.1 ± 5.6 | 0.393 ± 0.024 |
| Odor | 80.9 ± 8.4 | 0.447 ± 0.033 |
| overall impression | 81.4 ± 9.8 | 0.452 ± 0.056 |
| TVBN | 65.8 ± 8.2 | 0.132 ± 0.015 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ntzimani, A.; Papamichail, E.; Dermesonlouoglou, E.; Tsironi, T.; Taoukis, P. Shelf Life Study of Chilled Mullet (Mugil cephalus): Histamine Formation and Quality Degradation at Constant and Dynamic Storage Conditions. Fishes 2024, 9, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9120480
Ntzimani A, Papamichail E, Dermesonlouoglou E, Tsironi T, Taoukis P. Shelf Life Study of Chilled Mullet (Mugil cephalus): Histamine Formation and Quality Degradation at Constant and Dynamic Storage Conditions. Fishes. 2024; 9(12):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9120480
Chicago/Turabian StyleNtzimani, Athina, Eirini Papamichail, Efimia Dermesonlouoglou, Theofania Tsironi, and Petros Taoukis. 2024. "Shelf Life Study of Chilled Mullet (Mugil cephalus): Histamine Formation and Quality Degradation at Constant and Dynamic Storage Conditions" Fishes 9, no. 12: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9120480
APA StyleNtzimani, A., Papamichail, E., Dermesonlouoglou, E., Tsironi, T., & Taoukis, P. (2024). Shelf Life Study of Chilled Mullet (Mugil cephalus): Histamine Formation and Quality Degradation at Constant and Dynamic Storage Conditions. Fishes, 9(12), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/fishes9120480






