Abstract
To understand the spatial temporal distribution characteristics of Illex argentinus caught by trawl fishing vessels in the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean and their relationship with key marine environmental factors, this study analyzed the temporal and spatial changes in the fishing ground center of trawl vessels at the ten-day scale from December 2019 to May 2022, combining Chinese trawl fishing log data marine environmental data with satellite remote sensing marine environmental data. Utilizing the Maxent model, ten-day intervals were used as the temporal scale, and ten marine environmental factors, including sea surface temperature, sea surface height, sea surface salinity, chlorophyll concentration, temperature at 50 m and 100 m depth, and the meridional and zonal velocities of ocean currents were quantitatively analyzed to explore the correlation between the spatial distribution of catch and environmental factors. The study reveals that the trawl fishing grounds for Illex argentinus are divided into southern and northern grounds. The southern grounds first appear near 45°20′ S in December, gradually moving southeastward in February and March. The northern grounds do not appear until April, near 42° S in the high seas. On the ten-day time scale, the central fishing grounds of Illex argentinus show significant spatial variability but minor interannual differences. The Maxent model results indicate that sea surface temperature and chlorophyll a concentration are the key environmental factors influencing the spatial and temporal variability of the high seas trawl fishing grounds for most of the time, with high environmental contribution rates during the fishing season. While the range of suitable habitats with an HSI > 0.6 identified by the Maxent model varies significantly between years, a pattern is observed where the range expands at the start and end of the fishing season and contracts during the peak fishing season. This suggests that a more concentrated range of suitable habitats is conducive to accurate predictions of trawl fishing grounds, enabling efficient fishing operations.
Key Contribution:
This study analyzed the spatiotemporal variations and the marine environmental factors influencing the dynamics of the Illex argentinus pelagic trawl fishery in the open sea; aiming to further enhance our understanding of this fishery. Prior to this work, most studies on this fishery were based on squid fishing data, with few focusing on trawl fisheries. This study provides valuable technical support for the operation of pelagic trawl fisheries in the southwest Atlantic Ocean.
1. Introduction
The Southwest Atlantic stands as one of the world’s premier fishing regions for cephalopods, with the primary high seas fishing grounds situated beyond Argentina’s 200-nautical-mile exclusive economic zone on the Patagonian Shelf. In this area, the confluence of the warm Brazilian Current from the north and the cold Malvinas Current from the south creates intricate and dynamic marine structures. The convergence of warm and cold currents also forms thermal fronts, with temperature fronts at different water depths being part of the vertical temperature structure. Thermal fronts and surrounding eddies contribute to higher fishery resources density, making this region one of the most active in the world’s oceans [1]. The Argentine shortfin squid (Illex argentinus), one of the main species in this area, is also a primary target for China’s distant-water fishing vessels. As a short-lived, single-generation species, this species responds rapidly to changes in the marine environment, making the distribution of its fishing grounds closely related to marine environmental changes. Belonging to the order Teuthoidea, family Ommastrephidae, and genus Illex, it is a pelagic species of short lifespan [2,3]. Throughout its life cycle, it allocates most of its energy to growth and a smaller portion to reproduction, continuously growing throughout its life. It is an important economic cephalopod resource in the Southwest Atlantic [4], occupying an intermediate position in the food chain [5]. The lifespan of this species is about one year, typically not exceeding 18 months. It preys on marine plankton and other small organisms while serving as food for larger marine predators. Rapid growth makes this resource widespread across the continental shelf and slope of the Southwest Atlantic, playing a significant role in the marine ecosystem. It preys on a variety of marine plankton and other small organisms, including crustaceans, cephalopods, Maurolicus muelleri, Merluccius hubbsi, and Euphausi sp. Simultaneously, as prey for larger marine predators, it is consumed by large size species such as tunas or cods. Additionally, there is evidence of cannibalism within this species. Its rapid growth facilitates a wide distribution across the entire continental shelf and slopes of the Southwest Atlantic, where it plays a crucial role in the marine ecosystem.
Extensive research, both domestically and internationally, has been conducted on the relationship between Illex argentinus resource fluctuations and marine environmental conditions, including predictions of fishing grounds [4,6], spatiotemporal distribution [2,7,8], and resource variability [9]. Liu [5] predicted the fishing grounds for Argentine shortfin squid by creating a habitat index model based on sea water temperatures at different depths. The model used a spatial resolution of 0.5° × 0.5° and implemented ten different weighting schemes for temperatures at various water layers, achieving effective predictions for the fishing grounds. Chen [6] utilized the maximum entropy model with data formatted at a 0.25° × 0.25° spatial resolution, setting the training and testing dataset ratio at 4:1. The study found that the distribution of the squid habitat mainly correlates with variations in SST and SSH. Cui [7] employed the GAM model with a monthly temporal resolution and a spatial resolution of 0.25° × 0.25°, conducting correlation analysis to study the impact of sea surface temperature and chlorophyll on the distribution of Argentine shortfin squid fishing grounds, discovering that changes in the center of the fishing grounds are more influenced by SST than by Chl-a. Li [8] assessed the resources of Argentine shortfin squid using the Bayesian statistical Schaefer model, suggesting that when the harvest rate is below 0.3, the resources can be maintained at a sustainably utilizable level.
Although there has been considerable research on Illex argentinus fishing grounds, almost all studies are based on squid jigging data [2,3,4,6,7], focusing on jigging fishing grounds. Research on trawl fishing grounds is scarce. In contrast to squid jigging operations, trawl fishing commenced later. China initiated squid jigging operations for this species in the Southwest Atlantic in 1997, and by 2014, the number of squid jigging vessels in the region had surpassed 400 [10]. China’s high seas trawling fishery for this squid began in 2008, with the number of trawl fishing vessels in this area now exceeding 50% of the total number of trawl vessels in the region. As China’s maritime fisheries strategy “goes global”, China has become one of the major distant-water fishing countries in the world [3], with trawling emerging as an important fishing method [11]. The operational areas of high seas jigging and trawling largely overlap, but trawl vessels operate outside the exclusive economic zones, while jigging vessels operate both inside and outside these zones. When operating outside exclusive economic zones, both types of vessels maintain a safe distance to avoid accidents. Trawl vessels generally operate near the boundary of the exclusive economic zones, and even if resources are abundant, high seas trawl vessels maintain a distance of 1 nautical mile from the boundary [12]. When ocean currents are strong and directions change frequently, it significantly affects jigging operations, while trawl vessels have the advantages of flexible operations, strong adaptability, and high production [13]. Therefore, the objective of our study is to utilize the Maxent model to analyze the high seas trawl fishing grounds of Illex argentinus in the Southwest Atlantic. We aim to reveal the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and variation patterns of these fishing grounds, and to identify the environmental factors that significantly contribute to the fishing grounds during different time periods. This research will better assist fishing vessels in exploiting Illex argentinus resources in the Southwest Atlantic by providing reasonable recommendations and scientific guidance for fishing operations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.1.1. Fishing Log Data
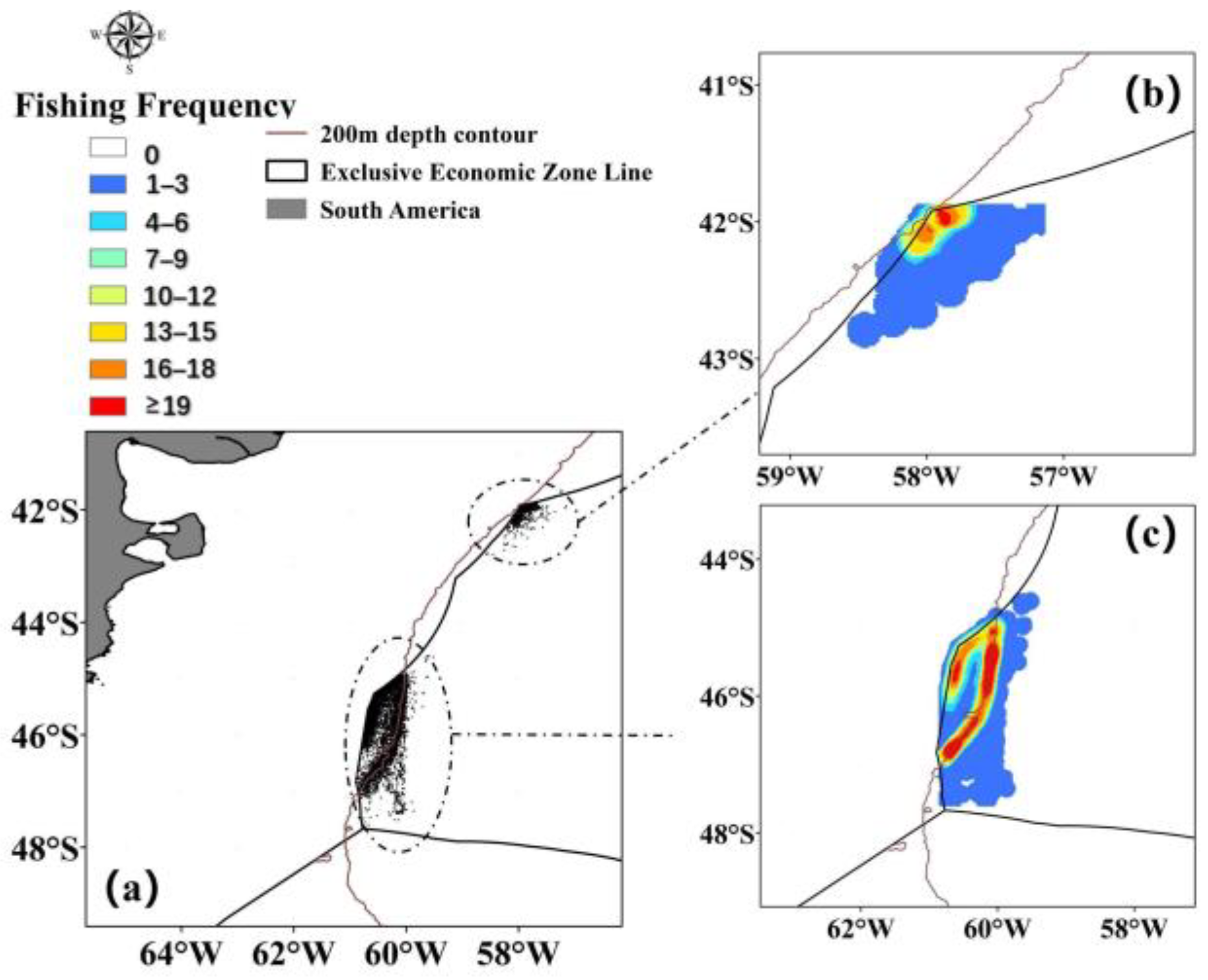
The trawl fishing data for Illex argentinus in the Southwest Atlantic was sourced from fishing logs recorded by a total of 34 high seas trawl vessels operating in the Southwest Atlantic from 2020 to 2022, including operation dates, locations, and catch volumes. The main fishing season for the squid spans from December to May of the following year, with trawl fishing operations primarily situated between 41° S~48° S and 57° W~61° W. The selected study area’s fishing data points and density are illustrated in Figure 1. Fishing logs, which are real-time records of trawler operations at sea including time, location, and catch yield, are inherently highly reliable due to their nature as direct documentation of fishing activities. Regarding the issues found in the fishing logs, we have removed obviously erroneous catch data and conducted preliminary verification with fishermen through satellite internet communication. This ensures that approximately 90% of the data is accurate. Additionally, the authors of this study are responsible members of the Chinese high seas trawl net technology group. They conduct annual data verification and quality assessment of fisheries data, which strongly guarantees the reliability of the fishing log data. This study, therefore, focuses on the fishery data within this specified region.
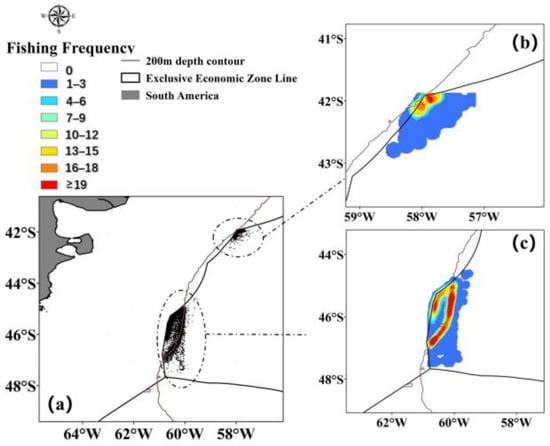
Figure 1.
Statistics (a) and heatmap (b,c) of operational data points for Illex argentinus high seas trawl fishing grounds ((b) is northern fishing ground and (c) is southern fishing ground).
2.1.2. Marine Environmental Data
Numerous marine environmental factors influence the variability of Illex argentinus fishing grounds. Water temperature affects the development and metabolism of organisms, salinity influences the osmotic balance within organisms, chlorophyll is an indicator of primary productivity in seawater, and sea surface height and ocean currents affect the distribution and migration of plankton and Illex argentinus. Research [5] indicates that this squid population typically inhabits areas within the 200 m depth contour, and, as shown in Figure 1, most of the southern fishing grounds are located within this depth contour. Considering the maximum data coverage, the marine environmental data selected for this study are divided into chlorophyll (Chl-a) data, sea surface temperature (SST) data, sea surface height (SSH) data, and sea surface salinity (SSS) data; 50 m water temperature, 50 m ocean current zonal velocity data (50 m zv), and 50 m meridional velocity data (50 m mv); and 100 m water temperature data, 100 m ocean current zonal velocity data (100 m zv), and 100 m meridional velocity data (100 m mv). Chlorophyll (Chl-a) data are downloaded from the website (https://coastwatch.pfeg.noaa.gov (24 October 2023)), while the other data are sourced from the Asia-Pacific Data Research Center (http://apdrc.soest.hawaii.edu/las_ofes/v6/dataset?catitem=71 (30 October 2023)). In this study, the selected research area ranges from 35° S to 55° S and from 50° W to 70° W, with a temporal resolution of ten days.
2.2. Data Processing Methods
2.2.1. Center of Fishing Grounds Processing
The fishing log data from December 2019 to May 2022 were divided into three annual segments, defining the previous year’s December and January to May of the following year as the fishing season for that year. For example, December 2019 to May 2020 was defined as the 2020 fishing season. The data were then divided into 18 parts according to the ten days of each month (beginning ten days, middle ten days, and end ten days), such as Jan/B indicating the beginning ten days of January. For each segment corresponding to a grid, the average fishing effort was calculated as the fishing effort for that grid, and the spatial center of the average fishing efforts for each time period was calculated. The formula for calculating the center of fishing grounds is given by Equation (1):
In the formula, X and Y represent the longitude and latitude coordinates of the center of the fishing operations, respectively. Xi refers to the latitude of the ith grid with a non-zero fishing effort, Yi refers to the longitude of the ith grid with a non-zero fishing effort, and Ci represents the fishing effort of the ith grid with a non-zero fishing effort [14].
2.2.2. CPUE Processing
In this study, the CPUE is standardized for calculation. Within each ten-day period, the average catch of Illex argentinus per net is determined as a standardized measure of fishing efficiency. The calculation formula is provided by Equation (2):
In the formula, CPUEt represents the catch quantity per unit of fishing effort, Catcht is the total catch in each ten-day period, Effortt represents the number of fishing nets deployed at the operation location, and t represents the ten-day period.
2.2.3. Maxent Model
The Maxent model is a species distribution model based on the maximum entropy algorithm, which is a machine learning method for predicting “unknown distributions” based on “current presence” [15]. The Maxent model, based on the principle of maximum entropy, predicts potential species habitats by deriving the most unbiased distribution from incomplete environmental and distributional data. In this study, the Maxent model version used was MAXENT 3.4.1, with the software available for download at (http://biodiversityinformatics.amnh.org/open_source/Maxent/ (24 November 2023)) [16]. First, we imported the downloaded NetCDF format data of SST, SSS, SSH, Chl-a, 50 m, and 100 m water temperatures, and the meridional and zonal velocities of ocean currents at 50 m and 100 m from the fishing season of 2020–2022 into ArcGIS 10.5. We started by preprocessing to integrate them into spatial resolution raster data of 0.1° × 0.1°, ensuring consistency in spatial dimensions across all environmental data. Then, we exported the data as ASCII format data, and used this ASCII data as the environmental layer input into the Maxent model for further computation. After the computation, the sum of environmental contribution rates for ten environmental factors at the same time amounted to 100. If one or more environmental factors had a high contribution rate, it indicated that these were significant environmental factors affecting the species during that time. A 0.1° grid represents a spatial distance of approximately 6 nautical miles, while the trawling distance for a single trawl operation is 15–20 nautical miles. This means that a 0.1° grid resolution can effectively represent the relationship between the trawl fishing grounds and the marine environment when aggregating data. If a 0.5° grid resolution were used, it would have been too coarse, ignoring some of the optimal marine environmental factors of the fishing grounds, which could lead to biased research results. Using a 0.25° grid resolution was also an option, but it was still not as detailed and accurate in reflecting the optimal marine environmental factors of the fishing grounds as the 0.1° resolution. Therefore, this paper adopted a 0.1-degree grid, a smaller-scale spatial resolution grid dataset. Before running the Maxent model, the maximum number of iterations was set to 5000, the replicated run type was set to Bootstrap, and the output format was set to Logistic. During the computation, 75% of the Argentine shortfin squid distribution data were used as the training data for building the model, while the remaining 25% served as the validation data for testing the model’s accuracy. The computation was repeated 30 times. The operation was set to repeat 30 times to eliminate repetitiveness and randomness. The Maxent model used the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis method to evaluate model accuracy. This method plots a curve with the false-positive rate (the rate at which species are incorrectly predicted to be present) on the x-axis and the true positive rate (the rate at which species are correctly predicted to be present) on the y-axis. The area under the curve (AUC) is used as an indicator of model accuracy; the closer the AUC value is to 1, the higher the accuracy of the model [17,18,19].
The distribution maps output by the model for each ten-day period were exported in ASCII format and imported into ArcGIS 10.2 for visual analysis. Because the output of the Maxent model is in Logistic format, with the presence probability of a species in each area ranging from 0 to 1, the Habitat Suitability Index (HSI) is defined based on these probabilities, and then manually categorized. When HSI > 0.6, the area was considered a highly suitable habitat for Illex argentinus trawl fishing grounds; when 0.6 ≥ HSI > 0.2, the area was considered a moderately suitable habitat [20]; and when HSI ≤ 0.2, the area was considered a lowly suitable habitat for the squid trawl fishing grounds [21]. The two environmental factors with the highest contribution rates each month were selected as key environmental factors, and their response curves and suitable ranges were plotted to analyze the response of the squid trawl fishing grounds to environmental factors on a ten-day scale [22,23]. In the data input phase, we first eliminated points where the catch was zero. Additionally, some data points had incorrect geographic coordinates, possibly due to errors during the fishing operations or during data entry, resulting in positions within Exclusive Economic Zones (EEZ). We removed these points based on the coordinates of the EEZ boundaries. These steps significantly reduced the impact of irrelevant and erroneous data on the model. Since the Maxent model does not reflect changes in yield or Catch per Unit Effort (CPUE), separate calculations for CPUE were also performed. The results from these calculations were then compared with the Habitat Suitability Index (HSI) outcomes derived from the Maxent model to study the relationship between changes in the quantity of high HSI areas and fluctuations in CPUE.
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Fishing Ground Centers
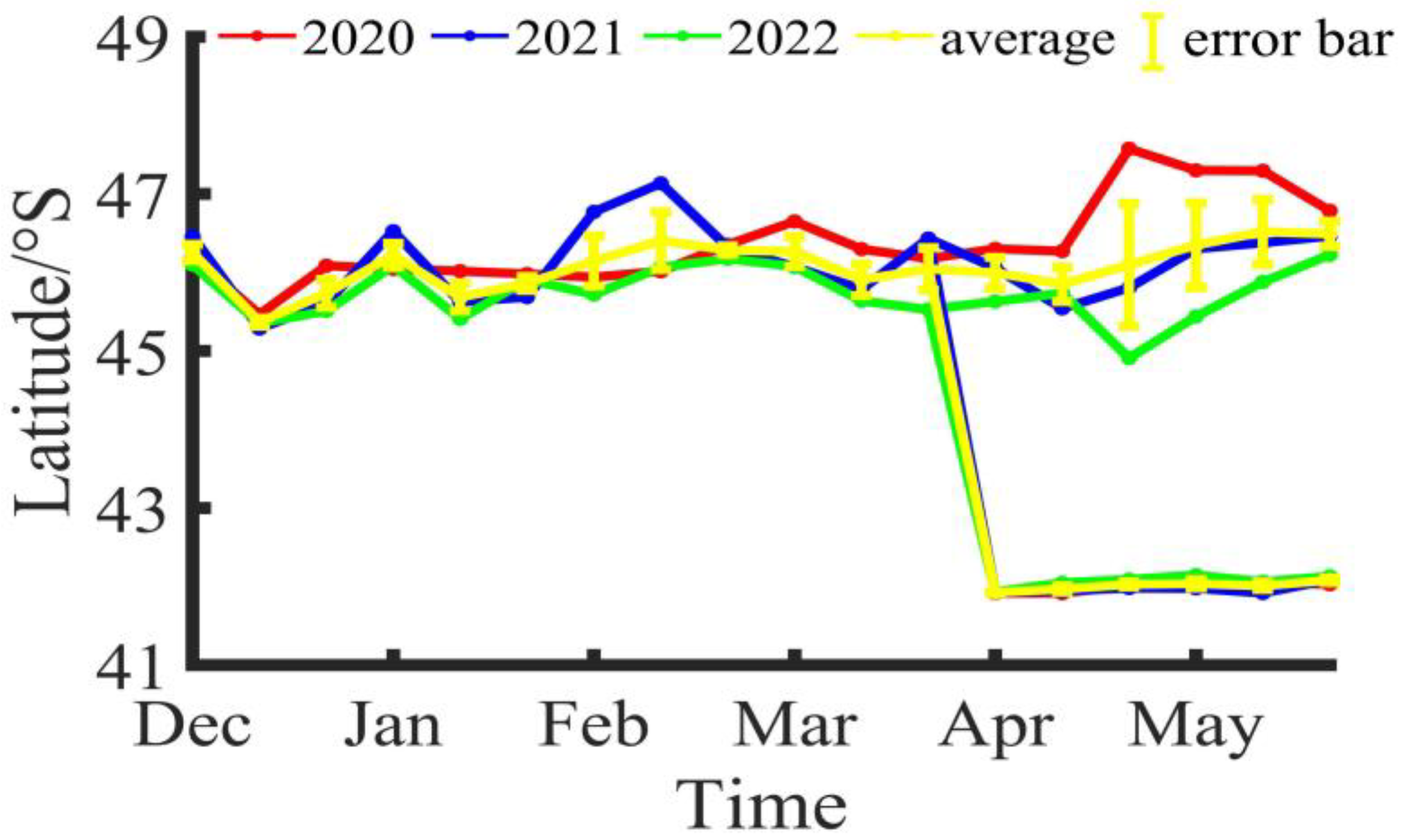
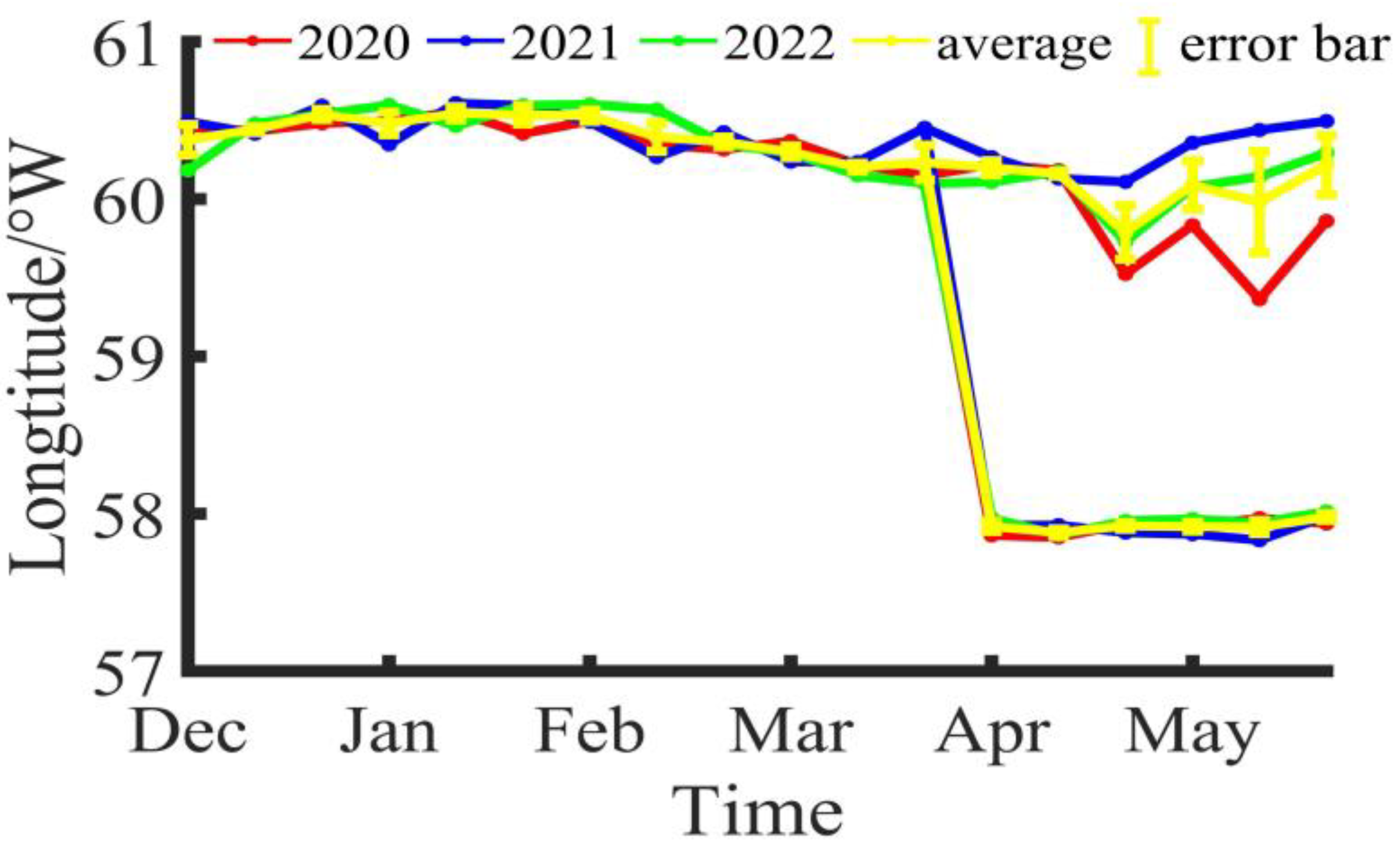
During the fishing season of Illex argentinus in the Southwestern Atlantic from 2020 to 2022, the longitude and latitude variations of the fishing center of trawl vessels are shown in Figure 2 and Figure 3. Based on the three-year average, the fishing operation center of the southern fishing grounds was at 60°23′ W, 46°15′ S in Dec/B, moved to 60°26′ W, 45°22′ S in Dec/M, and shifted to 60°32′ W, 45°44′ S in Dec/E; the fishing operation center in Jan/B was at 60°29′ W, 46°13′ S, moved to 60°32′ W, 45°41′ S in Jan/M, and was located at 60°32′ W, 45°52′ S in Jan/E; in Feb/B, the fishing operation center was at 60°32′ W, 46°8′ S, moved to 60°23′ W, 46°25′ S in Feb/M, and was positioned at 60°22′ W, 47°17′ S in Feb/E; in Mar/B, the fishing operation center was at 60°2′ W, 46°16′ S, moved to 60°1′ W, 45°55′ S in Mar/M, and was located at 60°14′ W, 46°3′ S in Mar/E; in Apr/B, the fishing operation center was at 60°1′ W, 46°0′ S, moved to 60°10′ W, 45°51′ S in Apr/M, and was positioned at 59°47′ W, 46°1′ S in Apr/E; in May/B, the fishing operation center was at 60°5′ W, 46°21′ S, moved to 59°39′ W, 47°11′ S in May/M, and was located at 60°13′ W, 46°29′ S in May/E. Overall, the southern fishing grounds show a trend of decreasing longitude and increasing latitude during the fishing season, shifting towards the southeast direction. For the northern fishing grounds, trawl vessels did not start operations until April. In Apr/B, the fishing operation center was at 57°55′ W, 41°55′ S, moved to 57°53′ W, 41°58′ S in Apr/M, and was positioned at 57°55′ W, 42°2′ S in Apr/E; in May/B, the fishing operation center was at 57°55′ W, 42°2′ S, moved to 57°54′ W, 42°1′ S in May/M, and was located at 57°59′ W, 42°5′ S in May/E. Compared to the southern fishing grounds, the position of the northern fishing grounds is relatively stable, mainly fluctuating around 57°55′ W, 42°0′ S.
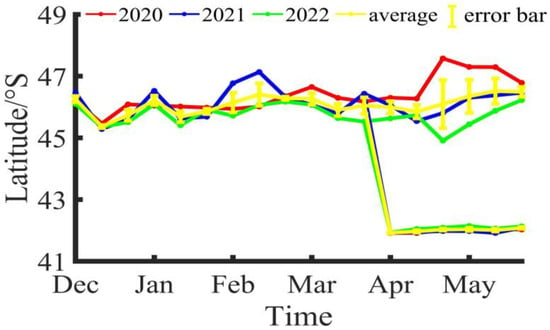
Figure 2.
The latitude variation of the fishing center for Illex argentinus trawl grounds.
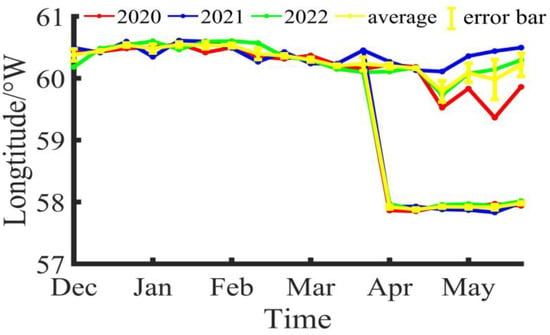
Figure 3.
The longitude variation of the fishing center for Illex argentinus trawl grounds.
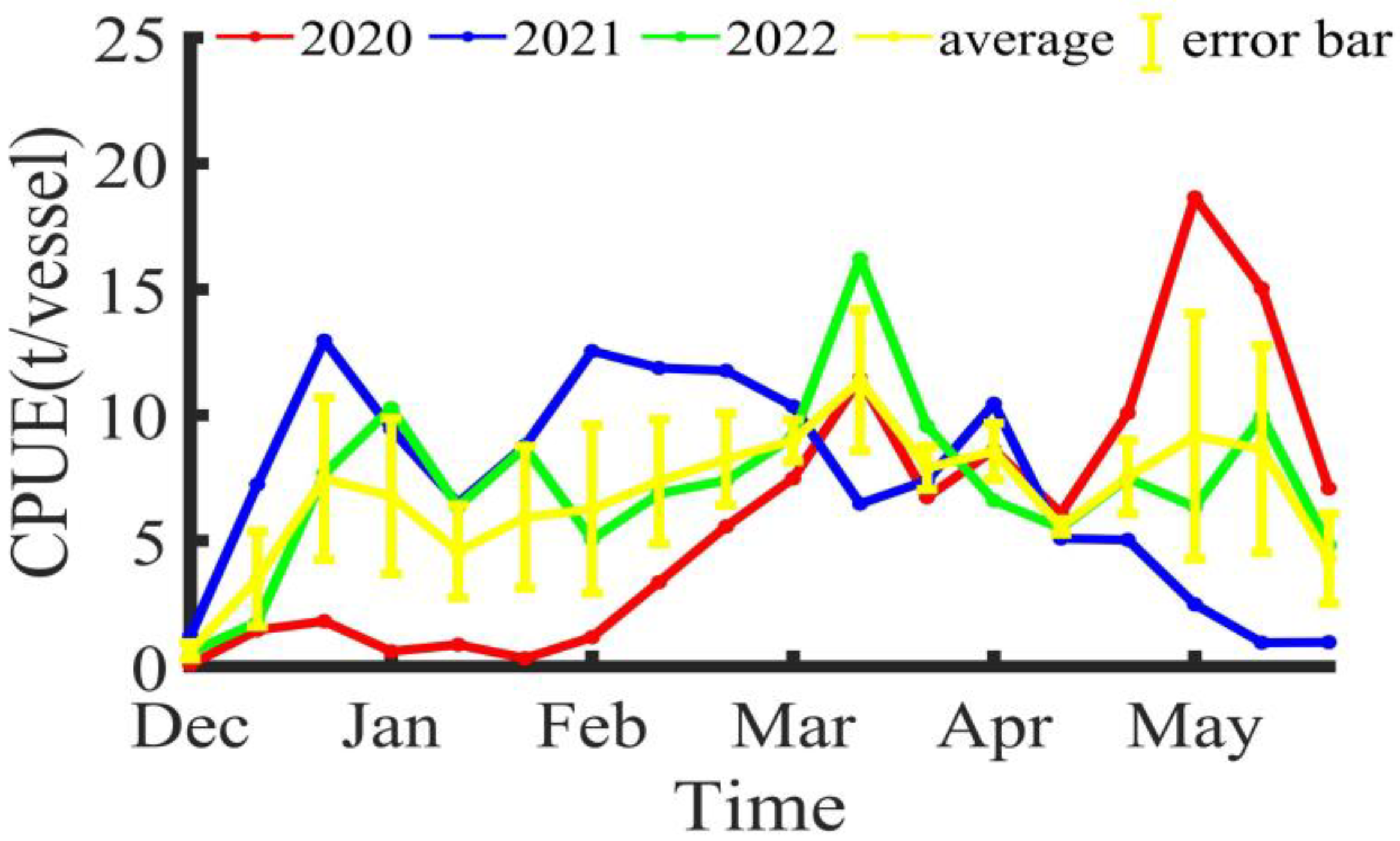
The CPUE within the Illex argentinus trawl fishing grounds, as shown in Figure 4, varies each year but also demonstrates common trends. At the start of the fishing season, the CPUE shows an upward trend, reaching a peak around Mar/M. From the middle ten days of March to the middle ten days of April, the CPUE shows a downward trend, before rising again after the middle ten days of April.
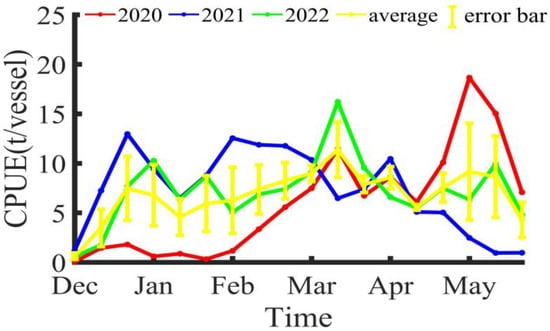
Figure 4.
The variation in CPUE for Illex argentinus trawl grounds.
3.2. Characteristics of Potential Habitat Distribution
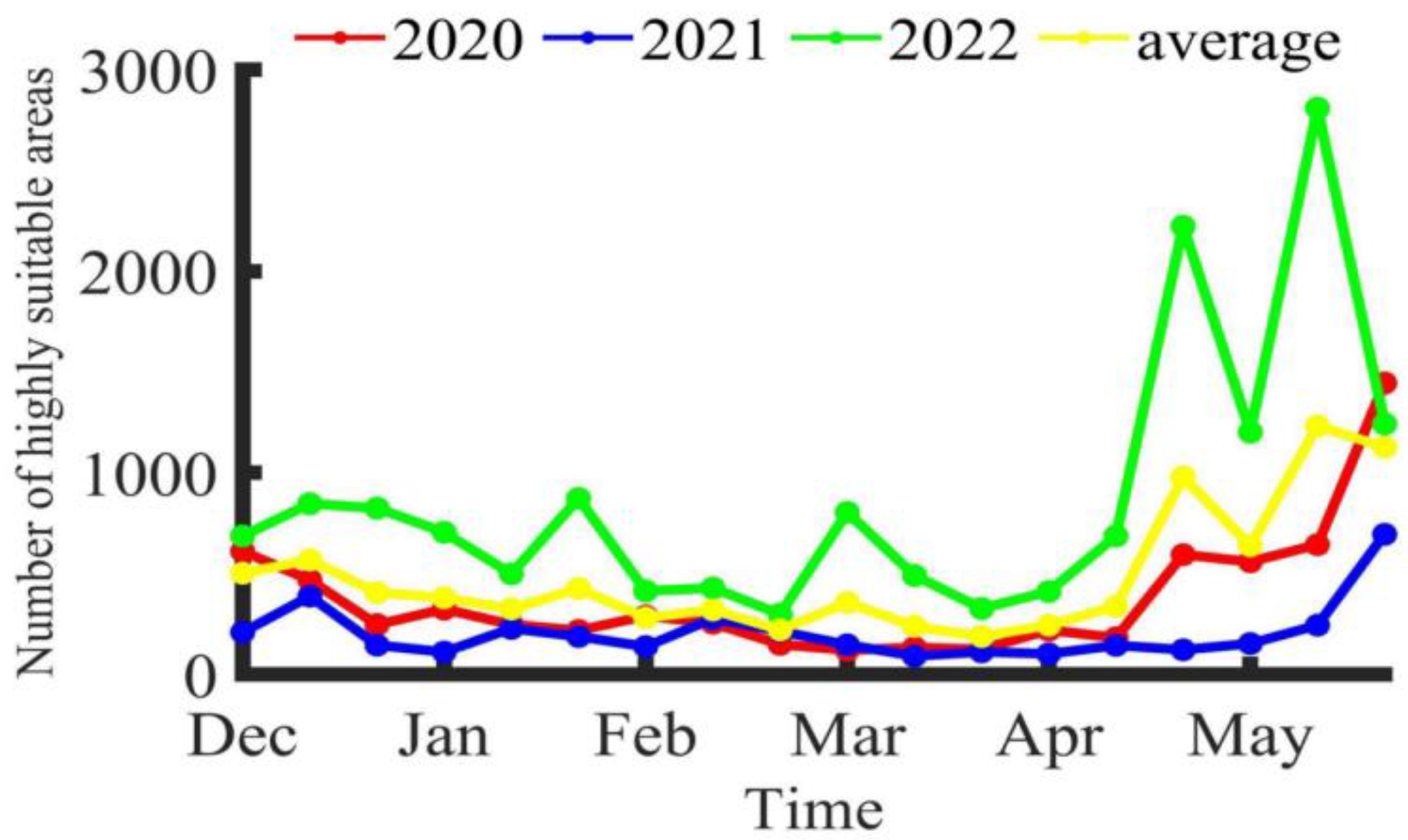
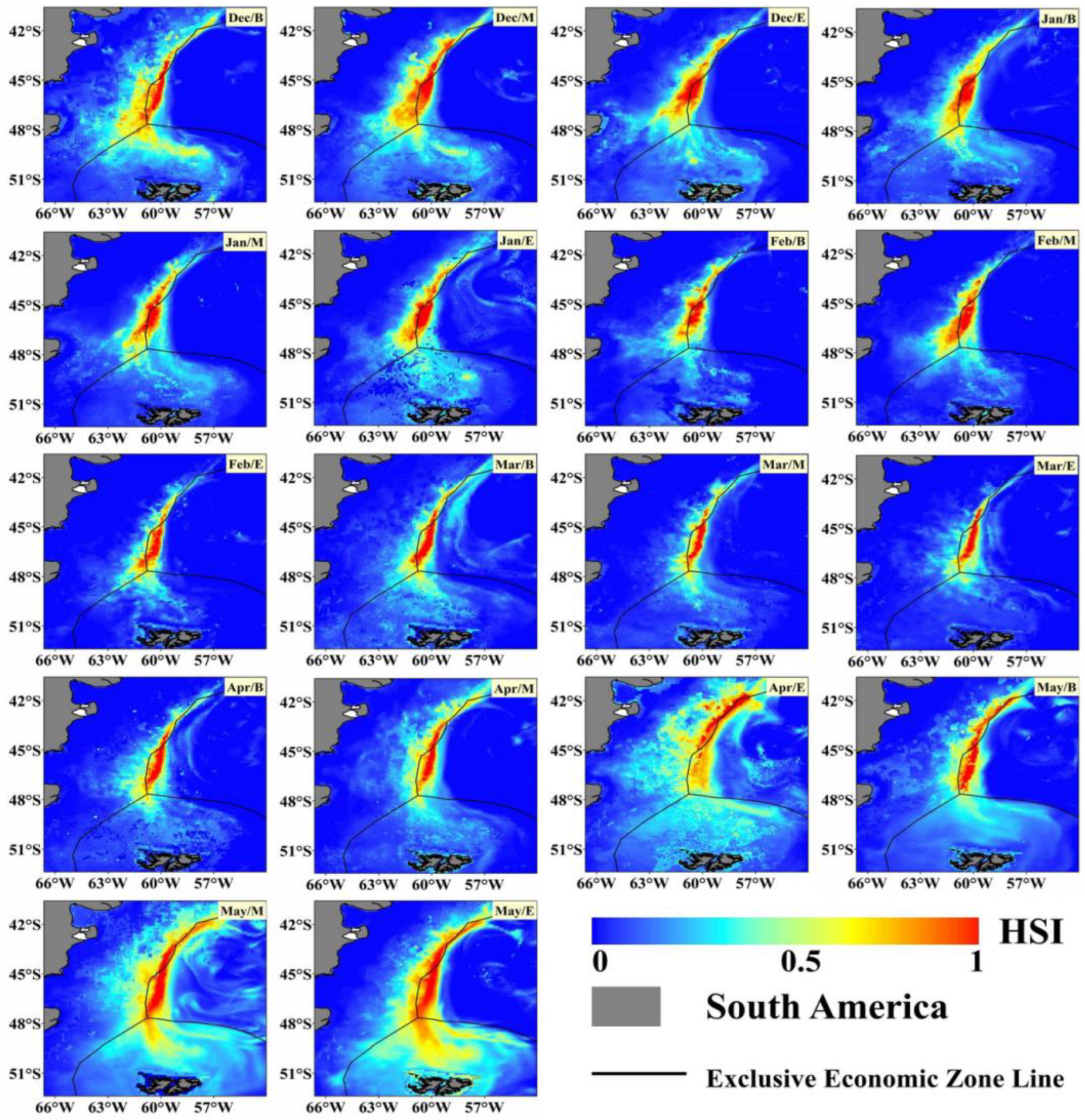
Using the Maxent model, the potential habitat distribution of Illex argentinus trawl fishing grounds was simulated for each ten-day period. The number of 0.1° × 0.1° areas with an HSI greater than 0.6 (indicating highly suitable areas) was counted, with the results shown in Figure 5. These HSI results from the Maxent model were then visualized using ArcGIS 10.2, calculating the averages over three years, as presented in Figure 6. From 2020 to 2022, during the fishing season, the trawl fishing grounds exhibit a band-like distribution, primarily concentrated between 58°48° S. Initially, at the start of the fishing season, the highly suitable areas for trawl fishing are concentrated around the 60° W, 45° S exclusive economic zone line, continuing until Feb/E. Simultaneously, the most suitable areas for trawl fishing gradually extend along the exclusive economic zone line both northward and southward. Since Chinese trawl vessels operate exclusively outside the exclusive economic zone line, the operation center remains between 45° S~47° S and 60° W~61° W, without moving northward. By April, as the highly suitable areas extend beyond the 42° S exclusive economic zone line, some Chinese trawl vessels start to operate in this area, forming three distinct fishing grounds: a northern ground near the 42° S exclusive economic zone line, a central ground east of the 45° S exclusive economic zone line, and a southern ground near the 47° S exclusive economic zone line.
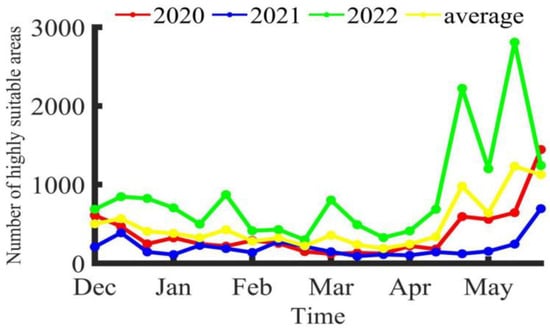
Figure 5.
Trend of changes in the number of highly suitable areas for Illex argentinus trawl fishing grounds.
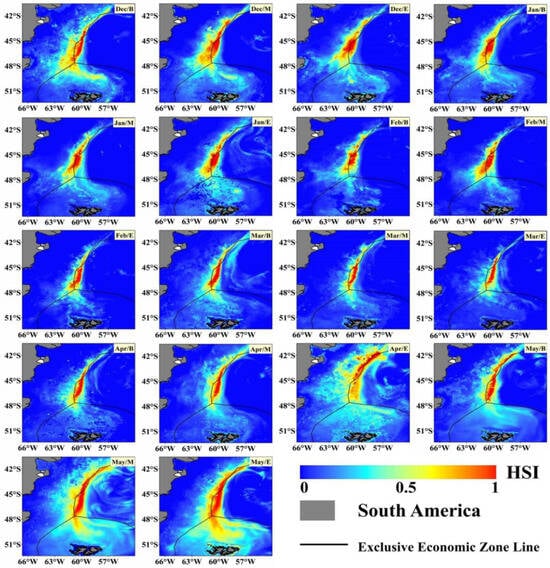
Figure 6.
Distribution of potential HSI for Illex argentinus trawl fishing grounds.
3.3. Response to Key Environmental Factors
Based on the Maxent model simulation results, the contribution rates of environmental factors for each ten-day period are detailed in Table 1. The findings indicate different impacts of environmental factors on the trawl fishing ground centers over time. Thus, the two environmental factors with the highest contribution rates in each ten-day period were identified as key factors. According to Table 1, SST and Chl-a are the key environmental factors influencing the trawl fishing ground centers in the early phase of the fishing season. From the beginning ten days of December to the beginning ten days of March, the combined contribution rates of these two factors exceed 70%, underscoring their significance. From the middle ten days of March to the middle ten days of April, the contribution rate of 50 m water temperature begins to rise, alternating with SSH and Chl-a as key factors. Entering May, several environmental factors, such as 100 m water temperature and SSH, start to exert a significant influence, suggesting a more pronounced joint constraint on the trawl fishing ground centers by a variety of environmental factors at this time. SST is identified as a key factor in 17 out of the 18 ten-day periods, while Chl-a is identified in 12 periods, highlighting their predominant influence on the Illex argentinus trawl fishing grounds. Other factors including sea surface height (SSH), 50 m st, and 100 m st, among others, are also important environmental factors.

Table 1.
Contribution rates of environmental factors in the Illex argentinus yrawl gishing grounds during the fishing season from 2020 to 2022.
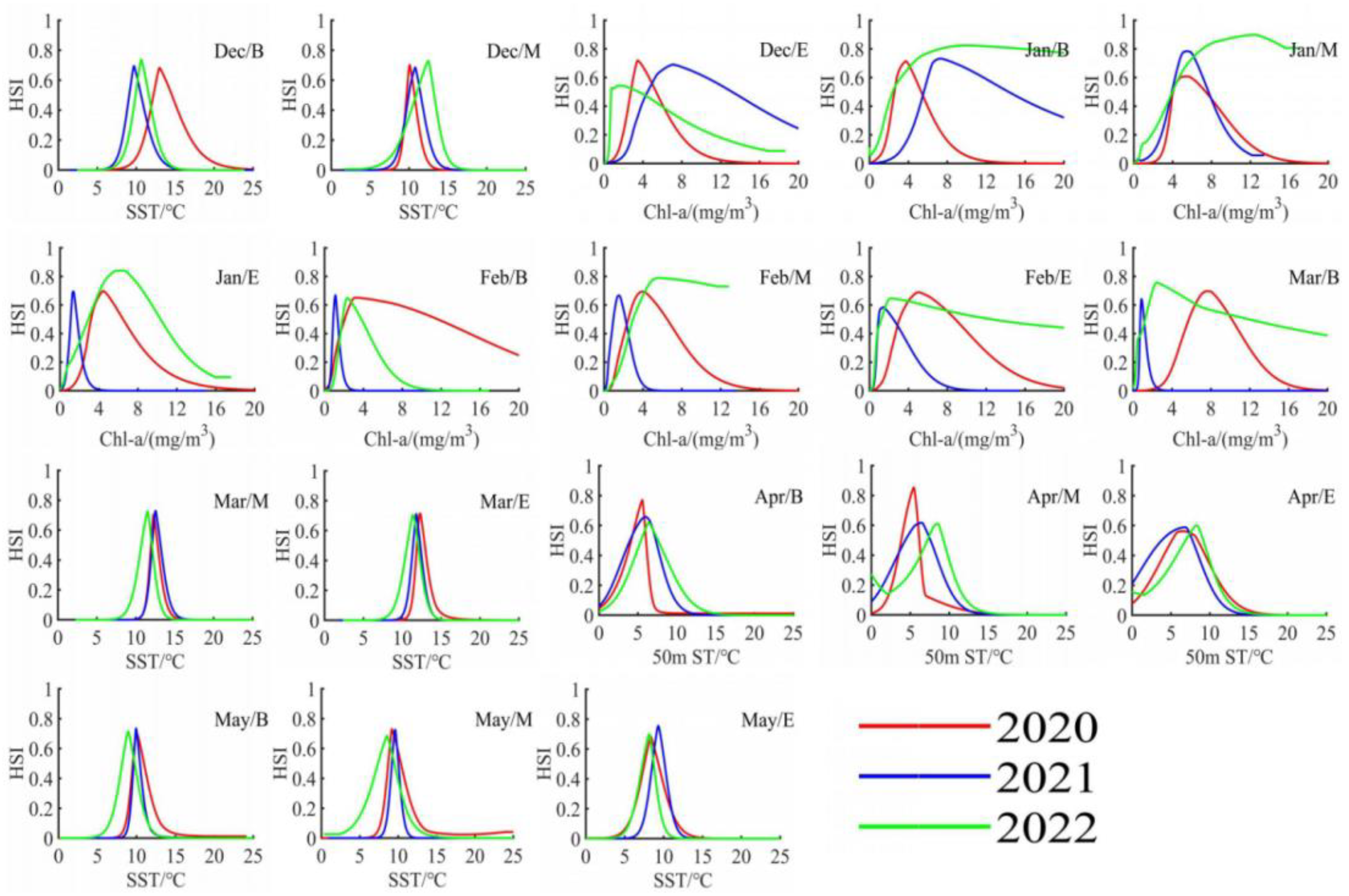
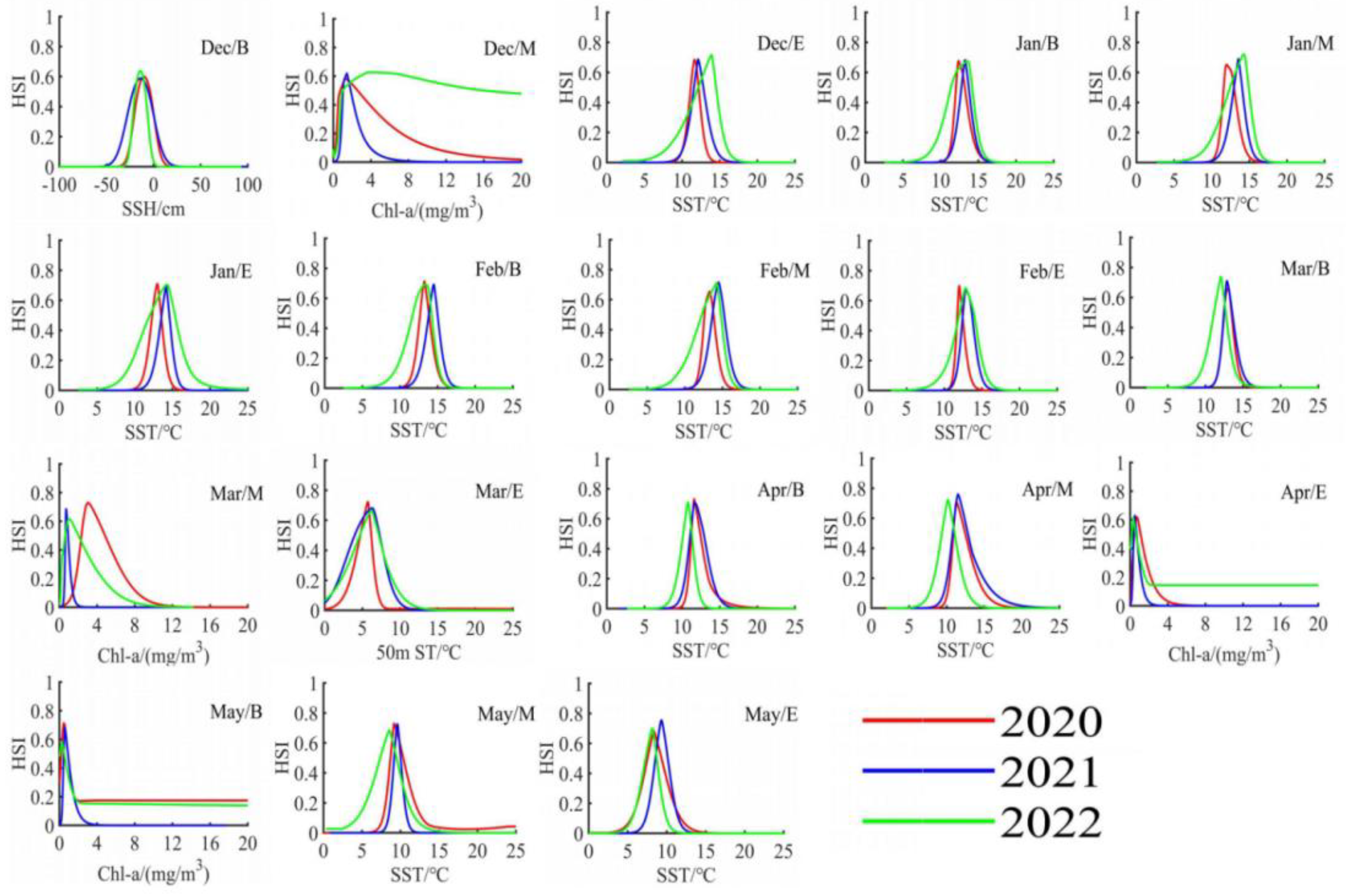
Based on the determination of key environmental factors in each ten-day period, we utilized MATLAB software to visualize the DAT format data exported from the MAXENT model, as shown in Figure 7 and Figure 8. By analyzing the response of the Illex argentinus trawl fishing grounds’ HSI to the key environmental factors in each ten-day period, we determined the optimal ranges for two key environmental factors during the fishing season over the three years, as summarized in Table 2. The accuracy of the fitting results is presented in Table 3, with precision exceeding 0.95 for each time period.
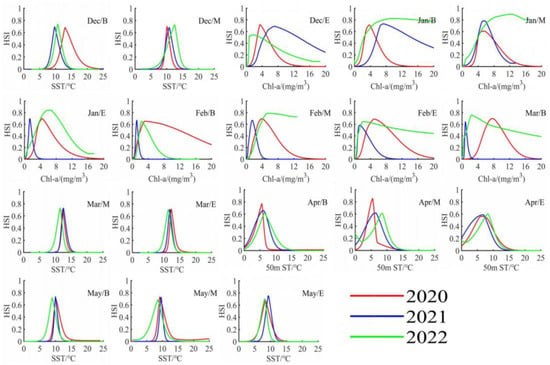
Figure 7.
Response curves of the most important environmental factors to the center of the Argentine Illex argentinus trawl grounds in the Southwest Atlantic during the fishing season from 2020 to 2022.
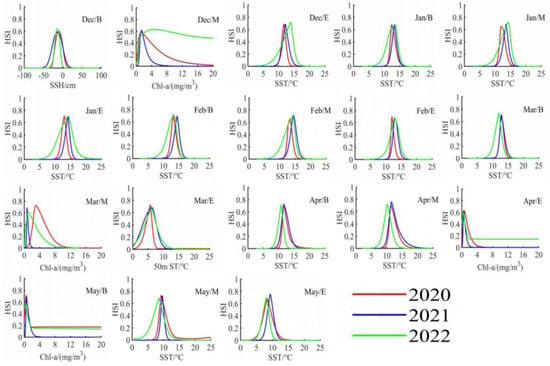
Figure 8.
Response curves of the secondary important environmental factors to the center of the Argentine Illex argentinus trawl grounds in the Southwest Atlantic during the fishing season from 2020 to 2022.

Table 2.
Key environmental factors and their optimal ranges for Illex argentinus high seas trawl fishing grounds in each ten-day period.

Table 3.
Statistical results of the Maxent model for the Argentine Illex argentinus from 2020 to 2022.
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Illex argentinus High Seas Trawl Fishing Grounds
A small amount of research [2] has found that the fishing yields of Illex argentinus in the Southwest Atlantic are distributed across latitudes between 40.5° S to 42.5° S and 44.5° S to 48.5° S, and longitudes between 60° W to 61° W. Analysis of the centroids of the fishing grounds indicates that the trawling areas for this species can be divided into southern and northern zones. The southern zone spans 45° S to 48° S in latitude and 60° W to 62° W in longitude, and is active throughout the fishing season. On the other hand, the northern zone, located between 41° S to 43° S and 58° W to 60° W, starts operations later, only beginning in early April. This pattern aligns with the migration routes of Illex argentinus, a species native to the continental shelf, which begins migrating from the Argentine EEZ to international waters in early December. From January to March, activity primarily occurs in the southern fishing grounds. In late March, some vessels start fishing in the northern grounds, with operations continuing there until June, while others remain in the southern waters.
According to the average fishing data from trawl fishing boats from 2020 to 2022, at the beginning of the fishing season, the operational center of the southern fishing grounds was around 60°23′ W, 46°15′ S. Over time, the center of the fishing grounds tended to shift southeastward. The seabed is deeper in the southeast direction compared to the initial position, indicating that as the Illex argentinus populations mature, parts of them prefer to gather in deeper waters. This is consistent with the findings that the contribution rates of the environmental factors at 50 m and 100 m water depth gradually increase over time. Cui [8] also found a trend of the fishing grounds’ center moving eastward from February to May in his study of this species from 2016 to 2018. Chen and Zhao [24] found that from January to April, the squid’s jigging fishing grounds mainly concentrated between 44° S and 46° S, 60° W and 62° W, and mainly near 42° S in May. These studies prove that there is a certain overlap in space between the high seas trawl fishing grounds and jigging fishing grounds of the squid. This study shows that the trend in the potential habitat changes of the trawl fishing grounds is similar to the actually spatiotemporal distribution of the fishing grounds, initially appearing near 45° S, then gradually expanding southward and northward, reaching the northern high seas fishing grounds in April, where high seas trawl fishing boats begin operations, and the southern habitats also expand southeastward over time, which corresponds with the changing pattern of the fishing grounds’ center. Although the number of highly suitable areas (HSI > 0.6) varies significantly between years, there is a common pattern: during or around periods of higher CPUE, the number of highly suitable areas tends to increase, indicating that high Illex argentinus trawl fishery yields require better habitats. However, it is also found that at the beginning and end of the fishing season, the number of highly suitable areas is often more than in the same year, while the CPUE values are lower, suggesting that too many highly suitable areas can cause the squid to disperse, which is not conducive to high-yield operations. Conversely, during the high CPUE period from January to April, fewer highly suitable areas help concentrate the squid, which is more favorable for operations. The overall greater number of highly suitable areas in 2022, without a corresponding increase in CPUE, also proves this point.
4.2. Environmental Factors Affecting the High Seas Trawl Fishing Grounds for Illex argentinus
4.2.1. The Impact of SST on the Fishing Grounds
The location of the fishing grounds is influenced by changes in the marine environment. Illex argentinus is a warm-water species that predominantly inhabits the confluence of the Brazil Warm Current and the Falkland Cold Current off the Argentine continental shelf. The intersection of these currents creates ideal conditions for productive fishing grounds. During years when the Brazil Warm Current is strong, the squid’s growth and foraging range expand accordingly. Chen [7] suggests that the 12 °C isotherm can be used as an indicator of the strength of the Brazil Warm Current and as a marker for locating the central fishing grounds. According to the contribution rates of environmental factors during the fishing seasons from 2020 to 2022, although key factors varied over different periods (Table 1), all key environmental factors shared a common characteristic: Sea Surface Temperature (SST) consistently had a high environmental contribution rate, appearing as a key factor 17 times, indicating that SST is an important factor affecting the variability of Illex argentinus trawl fishing grounds. This is consistent with previous research findings. Temperature is one of the main factors affecting marine biological activities [8], influencing fish aggregation, migration timing and routes, and the location and shift of fishing grounds [25]. As a short-lived species, this species’ fishing grounds are particularly sensitive to changes in SST [26], making SST also a viable indicator for predicting this squid’s trawl fishing grounds in the Southwest Atlantic. Between mid-December and mid-March, SST and Chl-a are the two most crucial environmental factors affecting the Illex argentinus trawl fishing grounds, with their combined contribution rates exceeding 60% for most of this period, reaching as high as 84.7%. During this time, the optimal SST range affecting this species’ trawl fishing grounds is 10.1 °C to 14.6 °C. Within this optimal SST range, the biomass of this species generally increases with rising temperatures up to the optimal range, beyond which biomass decreases with further temperature increases. This study’s findings on SST calculations share similarities with many previous studies on the squid jigging fishing grounds, proving a high reliability of this research. Wu [3] used data from Chinese squid jigging operations in 2006 to find that the optimal sea surface temperature for Illex argentinus fishing grounds in the Southwest Atlantic was 7 °C to 15 °C; Tang [27] combined squid jigging data from 2002 to 2014 and used a GAM model to determine that the optimal sea surface temperature for squid fishing grounds in the Southwest Atlantic was 9 °C to 14 °C; He [28] used GAM and Maxent models to analyze squid jigging data and found that the optimal temperature ranges for Illex argentinus fishing grounds were 7 °C to 9 °C and 13 °C to 16 °C, respectively, and also noted that this fishery’s catches were higher in January, February, April, and May, which is similar to the CPUE trend shown in the trawl fishery. Zhang [29] analyzed the center of jigging fishing grounds and changes in sea surface temperature, finding that the optimal temperature range from January to May was 7.8 °C to 14.8 °C. Throughout the trawling fishing season, the optimal SST range is 8.2 °C to 14.6 °C, similarly to the jigging fishery ground. These studies all indicate that both squid jigging and trawl fishing grounds for this squid are significantly influenced by SST.
4.2.2. Impact of Chlorophyll-a on Fishing Grounds
The concentration of chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) reflects the strength of marine primary productivity and serves as a fundamental indicator for estimating ocean productivity. It can be used to represent the quantity of phytoplankton in seawater [30]. Additionally, the reproductive capacity of Illex argentinus is significantly correlated with the concentration of chlorophyll in seawater [31]. In this study, we focused on the sea surface chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) data. According to the results from the Maxent model used in this research, Chl-a emerged as a key environmental factor influencing the Argentine shortfin squid trawling grounds in 12 out of the 18 periods analyzed. Among these, it appeared 10 times before Mar/E. After that, as the Southern Hemisphere enters autumn, the chlorophyll concentration decreases, but overall, from Mar/E to May/M, the areas with high chlorophyll concentration gradually diminish [32]. Despite this, the contribution rate of Chl-a remains above 10%. This species requires increasing amounts of bait as it grows, and the availability of small planktonic organisms for this species to prey upon decreases as phytoplankton becomes scarcer, indicating that it can still feed on large planktonic animals during this period. Currently, research finds that mature individuals of this species primarily feed on large planktonic animals [33]. However, after mid-May, when the chlorophyll concentration in seawater is low, it becomes difficult to directly utilize Chl-a data for research purposes, and its contribution rate also decreases. Unlike previous studies on squid fishing grounds, this study found that chlorophyll has a significant impact on trawl fishing grounds. From Dec/E to Mar/M, when the concentration of Chl-a in the area exceeds 0.9 mg/m3, there is a higher yield of this squid in the trawl fishing grounds of the open sea. In contrast, previous studies [3,8] on squid fishing grounds have found that the yield of squid is not significantly related to chlorophyll concentration, indicating that chlorophyll concentration is not the primary factor in the formation of the squid fishing grounds. In her study, Zheng [34] found that the concentration of Chl-a had little effect on the fishing effort of squid fishing vessels. In summary, although many previous studies have shown that the concentration of Chl-a in seawater has little effect on squid fishing for Illex argentinus, this study indicates that for open-sea trawl fishing grounds, Chl-a is one of the main key environmental factors affecting fishing ground changes. And Kininmonth [35] conducted a comprehensive analysis of chlorophyll-a concentration and plankton community data, revealing the complex interactions between primary productivity and trophic structure in the Baltic Sea ecosystem. The results showed that the seasonal variations in chlorophyll-a concentration were significantly correlated with the biomass of major plankton species. This finding is crucial for predicting changes in the food web and their impact on fish resources. Additionally, some studies have found that changes in Chl-a concentration can also affect the trajectories of fishing vessels [36].
4.2.3. The Impact of Other Environmental Factors on the Illex argentinus High Sea Trawl Fishing Grounds
In addition to SST and Chl-a, two main key environmental factors, SSH, 50-m water temperature, and 100-m water temperature also have significant impacts on the high sea trawl fishing grounds. Among them, SSH appeared as a key environmental factor twice, in Dec/B and May/E. Its optimal range was −14 to −9 cm in Dec/B and −16.1 to −9.3 cm in May/E. In other periods, including mid to Dec/E, Feb/B, Mar/M, and Apr/M to May/M, SSH’s contribution rate exceeded 10%, indicating that it is also one of the important factors influencing this squid open sea trawl fishing grounds. The Illex argentinus high sea trawl fishing grounds are located at the convergence of the cold Falkland Current and the warm Brazil Current, where the increase and decrease in SSH are believed to be related to the convergence and divergence of ocean currents [37] and also affect the heat balance [38]. Ding’s research [39] found that a sea level lower than the average sea level indicates upward replenishment of nutrient-rich bottom layers, which is conducive to the formation of good fishing grounds.
The contribution rate of the 50 m st and 100 m st is not high at the beginning of the fishing season, but it gradually increases over time. The 50 m st became a key environmental factor in four periods from Mar/E to Apr/E, while the 100 m st became a key environmental factor in May/M, with a contribution rate exceeding 10% in May/E. The changing trends of these two environmental factors also demonstrate that as Illex argentinus individuals mature, there is a tendency for their populations to gradually move to deeper waters. Liu’s team [1] also found in their offshore surveys that this species was mainly distributed in deep waters after March, whereas before that, they were mainly distributed in shallow waters. Meanwhile, the temperature in deep waters is lower than that in shallow waters. Hao’s research [4] found that individuals inhabiting lower temperature waters tend to be larger, further confirming this trend.
4.3. Results and Advantages of the Maxent Model
This study employed the Maxent model to investigate the relationship between changes in the Illex argentinus trawl fishing grounds in the Southwest Atlantic during the fishing seasons of 2020 to 2022 and marine environmental factors, simulating the potential distribution of their habitats. We set the maximum number of iterations to 5000 to enhance the model’s convergence, and we also configured the model to run 30 times to reduce errors caused by randomness. Upon comparison, it was found that the potential distribution of the squid trawl fishing grounds corresponds well with the actual trawl fishing boat locations. Additionally, according to the results in Table 3, the AUC measure of the models’ average precision is greater than 0.95, proving the reliability of the Maxent model results. Compared to previous habitat suitability index models and generalized additive models (GAM) for studying the distribution of this species, the Maxent model, based on a limited number of species distribution points and environmental factors, can effectively avoid the temporal and spatial limitations of fishery statistical data. It has been applied in studies on various species, including the South Pacific albacore [19], mackerel and sardines in the Northwest Pacific [40], and stem squid [22,41].
In reality, environmental factors affect Illex argentinus to varying degrees at different times, with key and non-key environmental contributors varying over time. Many studies on this species and environmental factors have neglected temporal variations in the environment, and these studies often consider only surface marine factors, overlooking the impact of deeper marine environments. This application of the Maxent model takes into account the correlations among environmental variables based on the biological characteristics of this species, calculating the contribution of each environmental variable to model efficacy, thus indicating the importance of each variable. Key environmental factors are identified based on their contribution rates during different periods, ignoring less impactful factors, which significantly enhances the scientific accuracy and reliability of environmental variable selection when forecasting this squid trawl fishing grounds [21]. For example, Yang [42] used the Maxent model to identify key environmental factors affecting the fishing grounds of hairtail in the South China Sea across different seasons. Zlateva Ivelina [43] and others applied the Maxent model to study the relationship between five species of fish in the Black Sea region of Bulgaria and environmental factors such as dissolved oxygen and SST. Therefore, based on the advantages of the Maxent model, this study applies it to analyze the spatiotemporal changes in the squid trawl fishing grounds, considering various marine environmental factors that could affect their distribution, and constructing potential distribution maps for the squid trawl fishing grounds using environmental data. This visually demonstrates the suitability differences of potential fishing grounds to changes in marine environmental factors. The contribution of key environmental factors to the Maxent model results determines their importance, enhancing the scientific selection of environmental factors for forecasting the squid trawl fishing, and improving the accuracy of fishing ground forecasts [23]. However, the Maxent model also has limitations: the study subject, Illex argentinus, exhibits varied group distributions and migratory characteristics [44], some individuals also migrate to the continental shelf and undergo seasonal migrations following changes in the concentration of planktonic organisms [45], and the data used in the Maxent model calculations are the currently available data [46]. The model’s results can only represent the distribution of the currently fished population, not the actual distribution across the entire sea area, making it more suitable for species with weaker migratory capabilities and simpler population structures. In future research, other marine environmental factors can be incorporated to explore their impact on the distribution of this species’ trawl fishing grounds, thereby enhancing understanding of the influence of marine environmental factors on the movement of fishing ground centers. Furthermore, although the Maxent model’s results in this study show high AUC values, and researchers generally believe that higher AUC values indicate a more accurate model, some scholars [47] argue that a high AUC value does not necessarily mean better fit, and human factors may interfere with the model’s computations.
5. Conclusions
This study utilized trawl data from the Southwest Atlantic Ocean between 2020 and 2022, employing the Maxent model to analyze changes in the distribution of Illex argentinus in comparison to previous studies on squid fishing grounds. The study investigated the contributions of various marine environmental factors to the variability of this squid trawl fishing grounds and identified their optimal ranges. In terms of model application, this study contrasted CPUE calculated from fishing logbook data with results from the Maxent model, addressing previous limitations of Maxent models that solely considered vessel positions. Additionally, the study demonstrated the reliability of its results with all AUC values exceeding 0.95.
The selection of ten marine environmental variables in this study allows for near real-time data acquisition, facilitating the establishment of operational fishing ground prediction models in future research. Moreover, the spatial resolution of 0.1° × 0.1° employed in this study is finer compared to the 0.25° × 0.25° and 0.5° × 0.5° resolutions used in previous studies. Similarly, employing a ten-day interval as a time scale is more detailed than using monthly or quarterly scales, and more distinguishable than using a weekly scale. Our study on the distribution of trawl fishing grounds for Illex argentinus not only enhances our understanding of their life history traits, including reproduction, foraging, and migration, but also helps fisheries managers establish more scientific catch quotas and seasonal opening times. This approach aims to prevent overfishing and ensure the long-term sustainable use of this squid resource. Additionally, this species is extremely sensitive to changes in the marine environment, making it a potential indicator for climate change or environmental monitoring based on variations in its fishing grounds. Economically, our findings provide vital technical support for Chinese distant-water fishing enterprises operating trawl fishing in the Southwest Atlantic. Understanding the distribution of fishing grounds can help optimize fishing strategies and increase fishing efficiency.
However, this study also has limitations. Illex argentinus species exhibits wide distribution and relatively complex population structure, potentially comprising multiple populations based on hatching seasons and spawning grounds. While this species is generally considered to lack genetic differentiation, there may still be relatively independent population habitats among different groups. Future research could benefit from detailed population subdivision of Illex argentinus for more accurate results. In addition to the environmental factors we studied, other elements could also affect the distribution of this squid, such as seafloor topography, which might influence habitat selection, and pollutants in the water, which could impact their feeding behaviors and survival rates. However, due to the difficulty in obtaining data on these factors, they were not included in our current study. Future research could benefit from collaborations with experts in marine biology or marine environmental sciences to further refine our results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: D.X., S.Y. and H.Z.; Data curation, D.X., Y.L. and Y.W.; Formal analysis, S.Y., H.Z. and Y.S.; Funding acquisition, K.J., H.Z. and Y.S.; Investigation, D.X., Y.L. and Y.S.; Methodology, D.X. and Y.W.; Project administration, H.Z.; Resources, D.X. and Y.L.; Software, D.X.; Supervision, K.J., H.Z. and Y.S.; Validation, D.X., Y.L., Y.W. and S.Y.; Visualization, D.X.; Writing—original draft, D.X.; Writing—review & editing, D.X., H.H. and H.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Financially supported by the particular Fund for Basic Scientific Research Business Expenses of the East China Sea Fisheries Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Fisheries Sciences at the Central Level for Public Welfare (2021M06); the Laoshan Laboratory (LSKJ202201803); the Laoshan Laboratory (No.LSKJ202201804); the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFD0901405, 2022YFC2807504); the Zhejiang Ocean Fishery Resources Exploration and Capture Project (CTZB-2022080076); Program on the Survey, Monitoring and Assessment of Global Fishery Resources (Comprehensive scientific survey of fisheries resources at the high seas) sponsored by the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable. Our study did not directly involve any live animal experiments.
Data Availability Statement
The original data supporting the conclusions of this article will be provided by the corresponding author. To obtain the original data, contact the corresponding author of this article.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to H. Zhang for his guidance and support on this research, and thanks to the other authors for their assistance in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, H.W.; Yu, W.; Chen, X.J. Research progress on the resources of Illex argentinus in the Southwest Atlantic and its environmental response. J. Fish. China 2020, 27, 1254–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.L.; Chen, X.J.; Wang, J.T. Study on the spatio-temporal distribution of Illex argentinus resources in the Southwest Atlantic. Mar. Sci. 2019, 43, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.M.; Yang, S.L.; Shen, J.H.; Zhou, W.F.; Zhang, J. Characteristics of Illex argentinus fishing grounds in the Southwest Atlantic. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 20, 1445–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Lu, H.J.; Liu, B.L.; Qian, W.G. Predicting Illex argentinus fishing grounds in the Southwest Atlantic using a habitat index. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2012, 21, 431–438. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.X. Study on the Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Illex argentinus Bottom Trawl. Diploma Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Yu, W.; Chen, X.J.; Zhu, W.B. Construction of Illex argentinus habitat model based on seawater temperature at different water layers. J. Dalian Ocean. Univ. 2021, 36, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chen, X.J. Analysis of Illex argentinus habitat distribution in the Southwest Atlantic based on the Maxent model. J. Fish. China 2016, 40, 893–902. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.C.; Xuan, W.D.; Wei, Q.Y.; Tao, Y.X.; Su, S.; Yu, Q.C.; Zhu, W.B. Analysis of spatiotemporal changes in Illex argentinus fishing grounds in the Southwest Atlantic based on SST and Chl-a. J. Zhejiang Ocean. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 42, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Chen, X.J.; Jin, Y. Assessment and management strategy evaluation of Illex argentinus resources based on a composite population. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2019, 28, 471–482. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, D.; Wang, L.; Fan, W.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.; Tang, F.; Zhang, S. Management of Illex argentinus fisheries resources and its implications for China. China Agric. Sci. Technol. Guide 2014, 16, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, J.N.; Li, R.G.; Lü, D.J.; Chang, Y.F.; Song, W.H. Survey of pair trawling near the coast of Uruguay in the Southwest Atlantic. Ocean. Dev. Manag. 2019, 36, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Sun, M. Composition of trawl catches and biological characteristics of main species on the Patagonian continental shelf in summer and autumn. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2014, 35, 8–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.J.; Chen, X.J.; Cao, J. Standardization of CPUE in the Chinese mainland Illex argentinus jig fishery based on the GLBM model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 5375–5384. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, J. Discussion on the relationship between Illex argentinus fishing grounds in the Southwest Atlantic and major marine environmental factors. J. Shanghai Fish. Univ. 2008, 17, 471–475. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.L.; Fan, X.M.; Tang, F.H.; Cheng, T.F.; Fan, W. Spatiotemporal distribution of kingfish fishing grounds in the Arabian Sea and its relationship with marine environment. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2019, 38, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Tian, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, L.S. Relationship between resource abundance distribution of Japanese mackerel in the Northwest Pacific and surface temperature and vertical temperature structure. J. Ocean. Univ. China (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2019, 49, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Feng, B.; Xu, L.X. Study and comparison of habitat indices for bigeye tuna in the Indian Ocean. J. Fish. China 2008, 2, 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.S. Study on the Habitat Simulation of Different Populations of Skipjack Tuna in the Central and Western Pacific Based on the MaxEnt Model. Diploma Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabia, I.D.; Saitoh, S.; Mugo, R.; Igarashi, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Usui, N.; Kamachi, M.; Awaji, T.; Seito, M. Seasonal potential fishing ground prediction of neon flying squid (Ommastrephes bartramii) in the western and central North Pacific. Fish. Oceanogr. 2015, 24, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.R.; Yang, X.M.; Tian, S.Q. Habitat prediction for longfin tuna in the South Pacific based on the MaxEnt model. J. Fish. China 2020, 27, 1222–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.X.; Chen, X.J.; Gao, F. Simulation of potential habitat distribution of squid in the Northwest Pacific based on the MaxEnt model. J. Fish. China 2020, 27, 336–345. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.N.; He, Y.; Yu, W.; Chen, X.J. Spatiotemporal distribution of jumbo flying squid habitat off Peru and their response differences to environmental factors. J. Fish. China 2021, 28, 658–672. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.P.; Yu, W.; Chen, X.J.; Zou, X.R. Study on the habitat of jack mackerel off the coast of Chile based on the MaxEnt model. J. Fish. China 2021, 28, 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.J.; Zhao, X.H. Preliminary study on the relationship between Illex argentinus yield distribution and surface temperature in the Southwest Atlantic. J. Dalian Fish. Univ. 2005, 3, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.L.; Chen, X.J. Preliminary study on the relationship between Illex argentinus yield distribution and surface temperature in the Southwest Atlantic in 2001. Mar. Fish. 2004, 4, 326–330. [Google Scholar]
- Waluda, C.; Rodhouse, P.; Podestá, G.; Trathan, P.; Pierce, G. Surface oceanography of the inferred hatching grounds of Illex argentinus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) and influences on recruitment variability. Mar. Biol. 2001, 139, 671–679. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.H.; Cui, X.S.; Fan, W.; Zhang, S.M.; Fan, X.M.; Wu, Y.M. Study on the relationship between squid resource abundance and marine environment in international waters. China Agric. Sci. Technol. Guide 2016, 18, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y. Study on the Relationship between Illex argentinus Resource Distribution and Environmental Factors and Fishing Ground Prediction. Diploma Thesis, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.P.; Chen, X.J. Relationship between Illex argentinus fishing grounds and water temperature. In Proceedings of the China Oceanographic Society. “Belt and Road” Strategy and Marine Science and Technology Innovation—Collection of Academic Papers of China Oceanographic Society 2015, Beijing, China, 26 October 2015; Volume 9. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Yuan, Q.; Huang, H.L.; Zhou, A.Z. Distribution characteristics of chlorophyll-a in squid fishing grounds in the North Pacific and its relationship with fishing grounds. Acta Oceanol. Sin. (Chin. Ed.) 2004, 6, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.Z.; Chen, Z.K.; Lin, D.M. The impact of marine environment on the reproductive characteristics of female Illex argentinus. South China Fish. Sci. 2024, 20, 130–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.M.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, T.F.; Wu, Y.M. Thematic map service for Illex argentinus fishing grounds in Southwest Atlantic Ocean. Computer Knowledge and Technology 2017, 13, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronkiewicz, A. Growth and life cycle of squid Illex argentinus from Patagonian and Falkland Shelf and Polish fishery of squid for this region, 1978–1985. Gdyn. Sea Fish. Inst. 1986, 27, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.L.; Wu, Y.M.; Fan, W. Distribution of chlorophyll-a in Illex argentinus fishing grounds in the Southwest Atlantic and its relationship with fishing grounds. Bull. Mar. Lake Res. 2011, 1, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kininmonth, S.; Blenckner, T.; Niiranen, S.; Watson, J.; Orio, A.; Casini, M.; Neuenfeldt, S.; Bartolino, V.; Hansson, M. Is Diversity the Missing Link in Coastal Fisheries Management? Diversity 2022, 14, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaihola, S.; Kininmonth, S. Environmental Factors Determine Tuna Fishing Vessels’ Behavior in Tonga. Fishes 2023, 8, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Gao, F.; Lei, L.; Guan, W.J.; Chen, X.J. Study on the forecasting model of Illex argentinus stock replenishment based on spawning ground environmental factors. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2014, 36, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Lu, H.J.; Chen, X.J. Comparison of forecasting models for Illex argentinus fishing grounds in the Southwest Atlantic based on different BP neural networks. J. Guangdong Ocean. Univ. 2017, 37, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Chen, X.J.; Wang, J.T. Comparison of suitable habitat models for Illex argentinus and their application in fishing ground forecasts. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2015, 36, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Fang, Z. Differences in habitat of Far Eastern pilchard and Japanese mackerel in the Northwest Pacific based on the MaxEnt model. J. Shanghai Ocean. Univ. 2023, 32, 806–817. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Fang, X.N.; Chen, X.J.; Zhang, Z. Monthly distribution of jumbo flying squid habitat in equatorial waters and its association with environmental factors. J. Fish. China 2022, 46, 2315–2329. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Dong, J.; Deng, Y. Suitable habitat of the scad fish (Decanters spp.) in Northern South China Sea predicted by MaxEnt model. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2024, 69, 103315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlateva, I.; Raykov, V.; Slabakova, V.; Stefanova, E.; Stefanova, K. Habitat suitability models of five keynote Bulgarian Black Sea fish species relative to specific abiotic and biotic factors. Oceanologia 2022, 64, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.J.; Chen, X.J.; Liu, B.L.; Gong, C.X. Advances in the study of the biology of Illex argentinus fisheries in the Southwest Atlantic. J. Guangdong Ocean. Univ. 2010, 30, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, N.E.; Ivanovic, M.L. Distribution and abundance of early life stages of squid (Illex argentinus) in the south-west Atlantic. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 1992, 49, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, J. Simulation of the spatial distribution of forest fires in Heilongjiang Province based on generalized linear models and the MaxEnt model. Ecol. J. 2013, 32, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Dudík, M. Modeling of Species Distributions with Maxent: New Extensions and a Comprehensive Evaluation. Ecography 2008, 31, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).