Tendon Adaptations to Eccentric Exercise and the Implications for Older Adults
Abstract
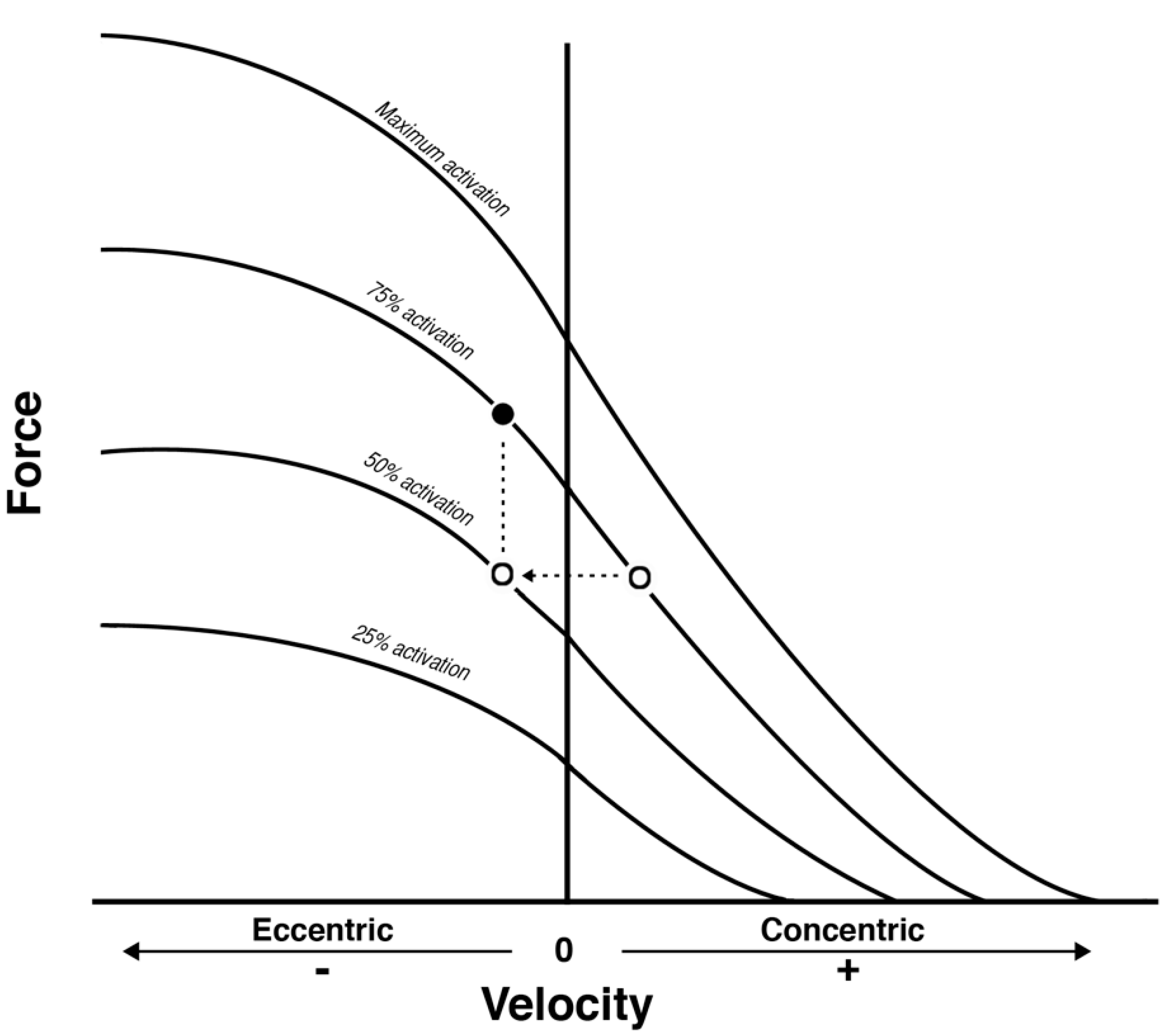
:1. Introduction
2. Eccentric Exercise and Tendon Adaptation
3. Are eccentric Contractions More Effective than Concentric for Tendon Adaptation?
4. Rationale of Using Eccentric Exercise for the Elderly Tendon
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franchi, M.V.; Reeves, N.D.; Narici, M.V. Skeletal Muscle Remodeling in Response to Eccentric vs. Concentric Loading: Morphological, Molecular, and Metabolic Adaptations. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, R.H.; Holm, L.; Malmgaard-Clausen, N.M.; Reitelseder, S.; Heinemeier, K.M.; Kjaer, M. Increase in tendon protein synthesis in response to insulin-like growth factor-I is preserved in elderly men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 116, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, B.F.; Olesen, J.L.; Hansen, M.; Døssing, S.; Crameri, R.M.; Welling, R.J.; Langberg, H.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Kjaer, M.; Babraj, J.A.; et al. Coordinated collagen and muscle protein synthesis in human patella tendon and quadriceps muscle after exercise. J. Physiol. 2005, 567, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, N.D.; Narici, M.V.; Maganaris, C.N. Strength training alters the viscoelastic properties of tendons in elderly humans. Muscle Nerve 2003, 28, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Seynnes, O.R.; Erskine, R.M.; Maganaris, C.N.; Longo, S.; Simoneau, E.M.; Grosset, J.F.; Narici, M.V. Training-induced changes in structural and mechanical properties of the patellar tendon are related to muscle hypertrophy but not to strength gains. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosset, J.; Breen, L.; Stewart, C.E.; Burgess, K.E.; Onambélé, G.L. Influence of exercise intensity on training-induced tendon mechanical properties changes in older individuals. Age 2014, 36, 9657. [Google Scholar]
- Malliaras, P.; Kamal, B.; Nowell, A.; Farley, T.; Dhamu, H.; Simpson, V.; Morrissey, D.; Langberg, H.; Maffulli, N.; Reeves, N.D. Patellar tendon adaptation in relation to load-intensity and contraction type. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 1893–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.I.; Maganaris, C.N.; Franchi, M.V.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.J.; Szewczyk, N.J.; Greenhaff, P.L.; Phillips, B.E.; Blackwell, J.I.; Boereboom, C.; et al. Muscle and Tendon Contributions to Reduced Rate of Torque Development in Healthy Older Males. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 539–545. [Google Scholar]
- Kongsgaard, M.; Reitelseder, S.; Pedersen, T.G.; Holm, L.; Aagaard, P.; Kjaer, M.; Magnusson, S.P. Region specific patellar tendon hypertrophy in humans following resistance training. Acta Physiol. 2007, 191, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couppé, C.; Svensson, R.B.; Grosset, J.-F.; Kovanen, V.; Nielsen, R.H.; Olsen, M.R.; Larsen, J.O.; Praet, S.F.E.; Skovgaard, D.; Hansen, M.; et al. Life-long endurance running is associated with reduced glycation and mechanical stress in connective tissue. Age 2014, 36, 9665. [Google Scholar]
- Seynnes, O.R.; Kamandulis, S.; Kairaitis, R.; Helland, C.; Campbell, E.; Brazaitis, M.; Skurvydas, A.; Narici, M.V. Effect of androgenic-anabolic steroids and heavy strength training on patellar tendon morphological and mechanical properties. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiesinger, H.P.; Kosters, A.; Muller, E.; Seynnes, O.R. Effects of Increased Loading on in Vivo Tendon Properties: A Systematic Review. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1885–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohm, S.; Mersmann, F.; Arampatzis, A. Human tendon adaptation in response to mechanical loading: A systematic review and meta-analysis of exercise intervention studies on healthy adults. Sports Med. Open 2015, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, S.P.; Kjaer, M. The impact of loading, unloading, ageing and injury on the human tendon. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arampatzis, A.; Karamanidis, K.; Albracht, K. Adaptational responses of the human Achilles tendon by modulation of the applied cyclic strain magnitude. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 2743–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lavagnino, M.; Arnoczky, S.; Tian, T.; Vaupel, Z. Effect of Amplitude and Frequency of Cyclic Tensile Strain on the Inhibition of MMP-1 mRNA Expression in Tendon Cells: An In Vitro Study. Connect. Tissue Res. 2007, 44, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couppé, C.; Svensson, R.B.; Silbernagel, K.G.; Langberg, H.; Magnusson, S.P. Eccentric or Concentric Exercises for the Treatment of Tendinopathies? J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2015, 45, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frizziero, A.; Trainito, S.; Oliva, F.; Nicoli Aldini, N.; Masiero, S.; Maffulli, N. The role of eccentric exercise in sport injuries rehabilitation. Br. Med. Bull. 2014, 110, 47–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jayaseelan, D.J.; Mischke, J.J.; Strazzulla, R.L. Eccentric Exercise for Achilles Tendinopathy: A Narrative Review and Clinical Decision-Making Considerations. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2019, 4, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahieu, N.N.; Mcnair, P.; Cools, A.; D’Haen, C.; Vandermeulen, K.; Witvrouw, E. Effect of eccentric training on the plantar flexor muscle-tendon tissue properties. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfredson, H.; Pietilä, T.; Jonsson, P.; Lorentzon, R. Heavy-Load Eccentric Calf Muscle Training For the Treatment of Chronic Achilles Tendinosis. Am. J. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrissey, D.; Roskilly, A.; Twycross-Lewis, R.; Isinkaye, T.; Screen, H.; Woledge, R.; Bader, D. The effect of eccentric and concentric calf muscle training on Achilles tendon stiffness. Clin. Rehabil. 2011, 25, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclay, J.; Martin, A.; Duclay, A.; Cometti, G.; Pousson, M. Behaviour of fascicles and the myotendinous junction of human medial gastrocnemius following eccentric strength training. Muscle Nerve 2009, 39, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geremia, J.M.; Baroni, B.M.; Bobbert, M.F.; Bini, R.R.; Lanferdini, F.J.; Vaz, M.A. Effects of high loading by eccentric triceps surae training on Achilles tendon properties in humans. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 118, 1725–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemeier, K.M.; Olesen, J.L.; Haddad, F.; Langberg, H.; Kjaer, M.; Baldwin, K.M.; Schjerling, P. Expression of collagen and related growth factors in rat tendon and skeletal muscle in response to specific contraction types. J. Physiol. 2007, 582, 1303–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemeier, K.M.; Olesen, J.L.; Schjerling, P.; Haddad, F.; Langberg, H.; Baldwin, K.M.; Kjaer, M. Short-term strength training and the expression of myostatin and IGF-I isoforms in rat muscle and tendon: Differential effects of specific contraction types. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 102, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaux, J.F.; Drion, P.; Libertiaux, V.; Colige, A.; Hoffmann, A.; Nusgens, B.; Besançon, B.; Forthomme, B.; Le Goff, C.; Franzen, R.; et al. Eccentric training improves tendon biomechanical properties: A rat model. J. Orthop. Res. 2013, 31, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, K.; Yata, H. Effects of Concentric and Eccentric Training on the Stiffness and Blood Circulation of the Patellar Tendon. Sports Med. Int. Open 2017, 1, E43–E49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reeves, N.D.; Maganaris, C.N.; Longo, S.; Narici, M.V. Differential adaptations to eccentric versus conventional resistance training in older humans. Exp. Physiol. 2009, 94, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farup, J.; Rahbek, S.K.; Vendelbo, M.H.; Matzon, A.; Hindhede, J.; Bejder, A.; Ringgard, S.; Vissing, K. Whey protein hydrolysate augments tendon and muscle hypertrophy independent of resistance exercise contraction mode. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2013, 24, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.J. Contribution of elastic tissues to the mechanics and energetics of muscle function during movement. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiesinger, H.P.; Rieder, F.; Kösters, A.; Müller, E.; Seynnes, O.R. Sport-specific capacity to use elastic energy in the patellar and Achilles tendons of elite athletes. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjær, M. Role of extracellular matrix in adaptation of tendon and skeletal muscle to mechanical loading. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 649–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onambele, G.L.; Narici, M.V.; Maganaris, C.N. Calf muscle-tendon properties and postural balance in old age. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 100, 2048–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojsen-Møller, J.; Magnusson, S.P.; Rasmussen, L.R.; Kjaer, M.; Aagaard, P.; Ras-, L.R. Muscle performance during maximal isometric and dynamic contractions is influenced by the stiffness of the tendinous structures. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hakkinen, K.; Newton, R.U.; Gordon, S.E.; Mccormick, M.; Volek, J.S.; Nindl, B.C.; Gotshalk, L.A.; Campbell, W.W.; Evans, W.J.; Hakkinen, A.; et al. Changes in Muscle Morphology, Electromyographic Activity, and Force Production Characteristics During Progressive Strength Training in Young and Older Men. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 1998, 53, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suetta, C.; Hvid, L.G.; Justesen, L.; Christensen, U.; Neergaard, K.; Simonsen, L.; Ortenblad, N.; Magnusson, S.P.; Kjaer, M.; Aagaard, P. Effects of aging on human skeletal muscle after immobilization and retraining. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reeves, N.D.; Maganaris, C.N.; Narici, M.V. Effect of strength training on human patella tendon mechanical properties of older individuals. J. Physiol. 2003, 548, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rees, J.D.; Lichtwark, G.A.; Wolman, R.L.; Wilson, A.M. The mechanism for efficacy of eccentric loading in Achilles tendon injury; an in vivo study in humans. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 1493–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henriksen, M.; Aaboe, J.; Bliddal, H.; Langberg, H. Biomechanical characteristics of the eccentric Achilles tendon exercise. J. Biomech. 2009, 42, 2702–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, S.; Morrissey, D.; Woledge, R.C.; Bader, D.L.; Screen, H.R.C. Eccentric and Concentric Exercise of the Triceps Surae: An in Vivo Study of Dynamic Muscle and Tendon Biomechanical Parameters. J. Appl. Biomech. 2015, 31, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, V.; Piazzesi, G. The contractile response during steady lengthening of stimulated frog muscle fibres. J. Physiol. 1990, 431, 141–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigland-Ritchie, B.; Woods, J.J. Integrated electromyogram and oxygen uptake during positive and negative work. J. Physiol. 1976, 260, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boengler, K.; Kosiol, M.; Mayr, M.; Schulz, R.; Rohrbach, S. Mitochondria and ageing: Role in heart, skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 349–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, K.E.; Jubrias, S.A.; Esselman, P.C. Oxidative capacity and ageing in human muscle. J. Physiol. 2000, 526, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaStayo, P.; Marcus, R.; Dibble, L.; Frajacomo, F.; Lindstedt, S. Eccentric exercise in rehabilitation: Safety, feasibility, and application. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 116, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, W.K.; Taivassalo, T.; Narici, M.V.; Franchi, M.V. Eccentric Exercise and the Critically Ill Patient. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roig, M.; Macintyre, D.L.; Eng, J.J.; Narici, M.V.; Maganaris, C.N.; Reid, W.D. Preservation of eccentric strength in older adults: Evidence, mechanisms and implications for training and rehabilitation. Exp. Gerontol. 2010, 45, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gluchowski, A.; Harris, N.; Dulson, D.; Cronin, J. Chronic Eccentric Exercise and the Older Adult. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1413–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyldahl, R.D.; Chen, T.C.; Nosaka, K. Mechanisms and Mediators of the Skeletal Muscle Repeated Bout Effect. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2017, 45, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovering, R.M.; Brooks, S.V. Eccentric exercise in aging and diseased skeletal muscle: Good or bad? J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 116, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quinlan, J.I.; Narici, M.V.; Reeves, N.D.; Franchi, M.V. Tendon Adaptations to Eccentric Exercise and the Implications for Older Adults. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2019, 4, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk4030060
Quinlan JI, Narici MV, Reeves ND, Franchi MV. Tendon Adaptations to Eccentric Exercise and the Implications for Older Adults. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology. 2019; 4(3):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk4030060
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuinlan, Jonathan I, Marco V Narici, Neil D Reeves, and Martino V Franchi. 2019. "Tendon Adaptations to Eccentric Exercise and the Implications for Older Adults" Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology 4, no. 3: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk4030060
APA StyleQuinlan, J. I., Narici, M. V., Reeves, N. D., & Franchi, M. V. (2019). Tendon Adaptations to Eccentric Exercise and the Implications for Older Adults. Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology, 4(3), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfmk4030060






