Investigating the Combined Impact of Water–Diesel Emulsion and Al2O3 Nanoparticles on the Performance and the Emissions from a Diesel Engine via the Design of Experiment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. The Experimental Strategy
2.2. Water Diesel Emulsion Fuel Preparation
2.3. Nanoparticles Characteristics and Aluminum Oxide Nanoparticles Blended Water Diesel Emulsion Fuel Preparation
2.4. Fuel Properties
2.5. Experimental Apparatus and Procedure
2.6. Measurement Uncertainty
2.7. RSM Modeling
3. Results and Discussions
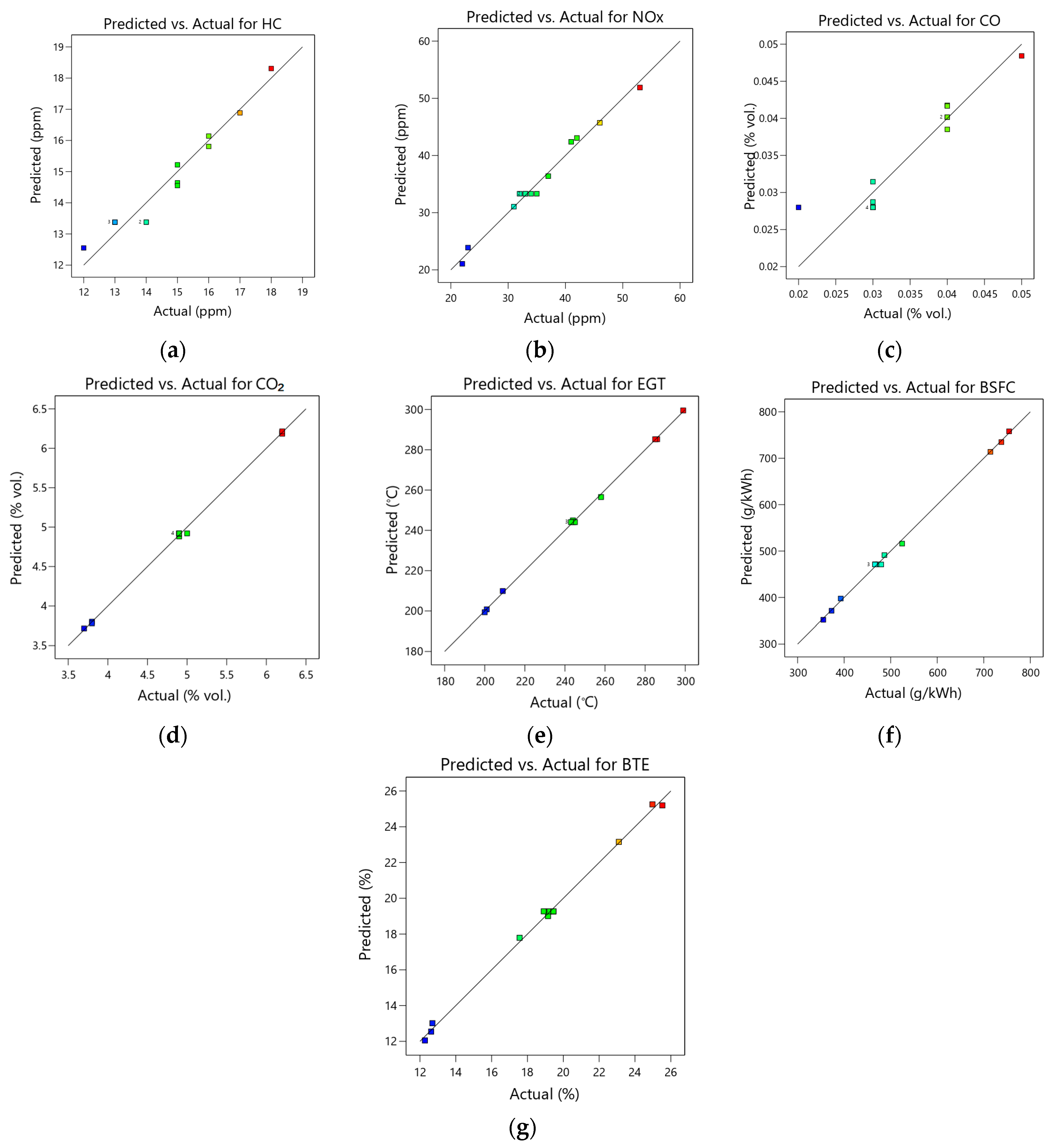
3.1. Models Assessment
3.2. Analysis of Emissions Characteristics
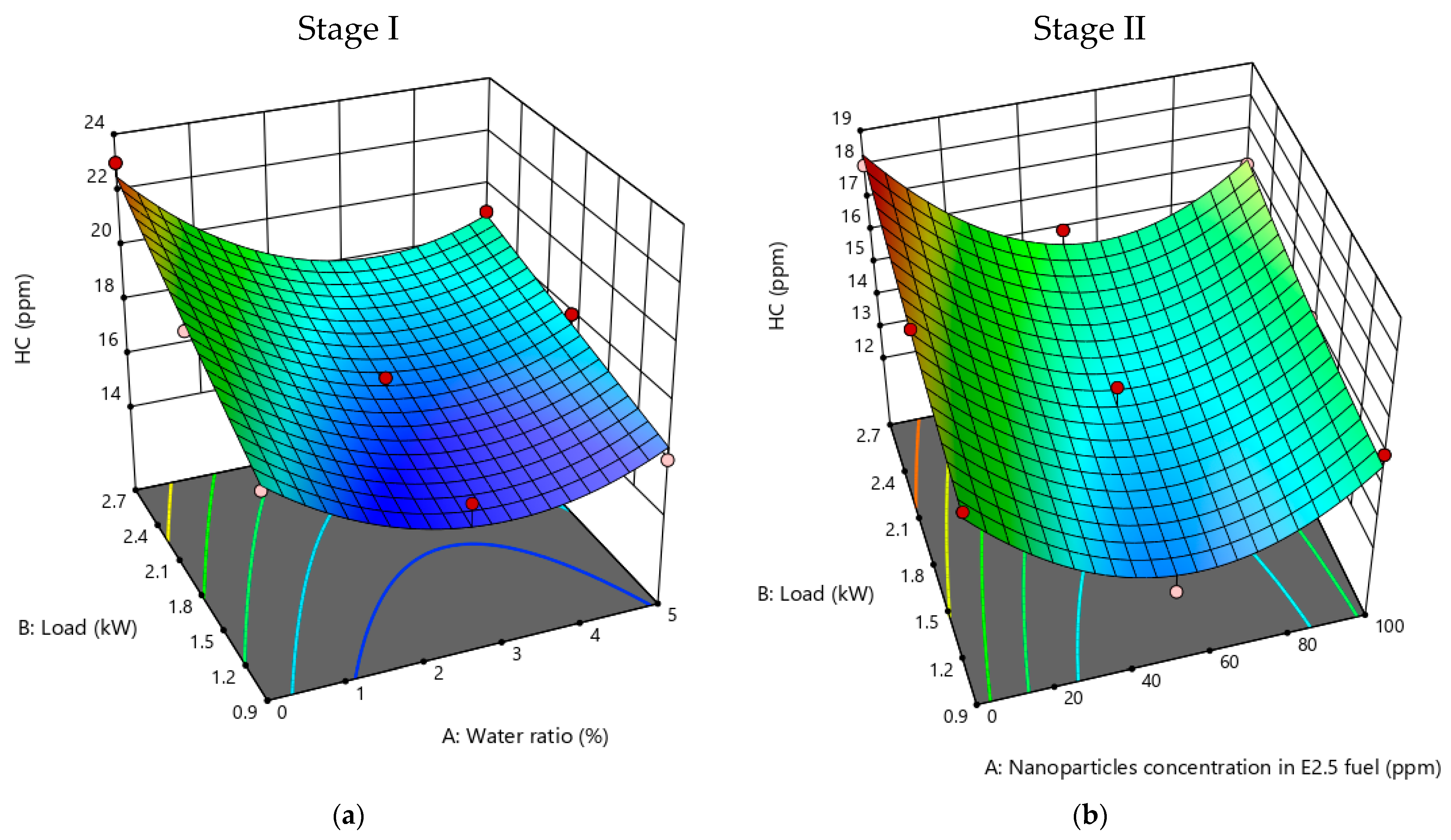
3.2.1. HC Emissions
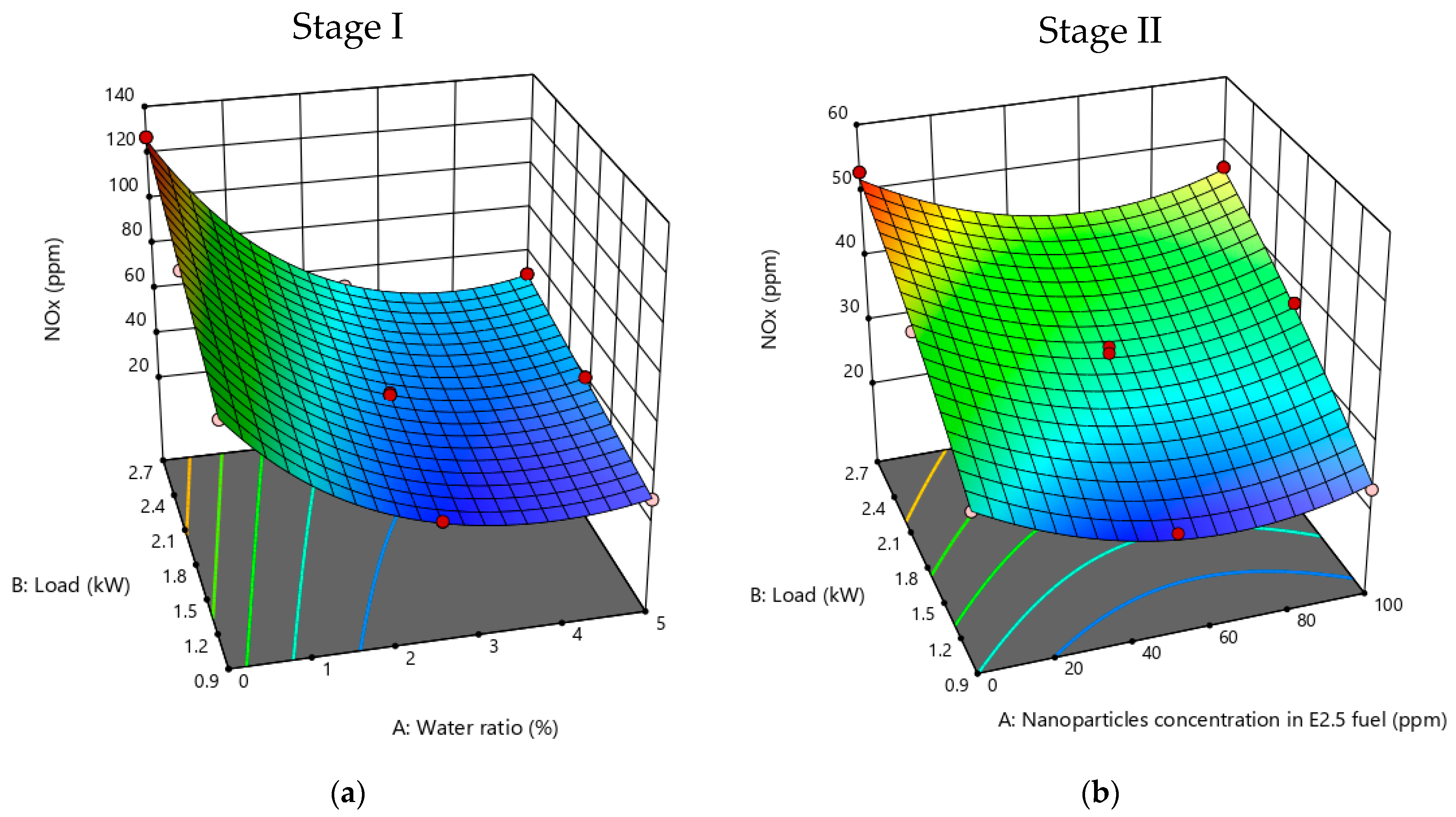
3.2.2. NOx Emissions
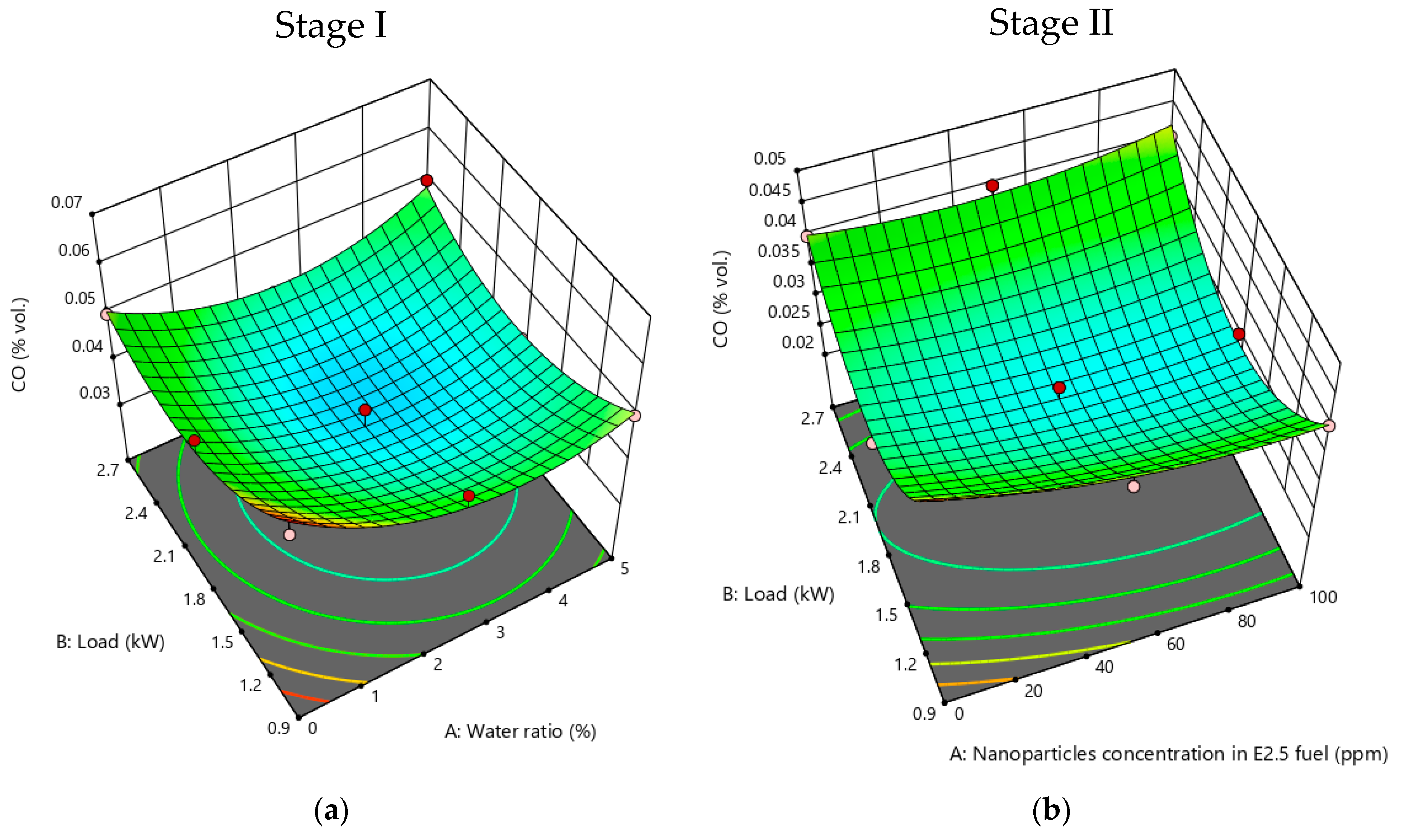
3.2.3. CO Emissions
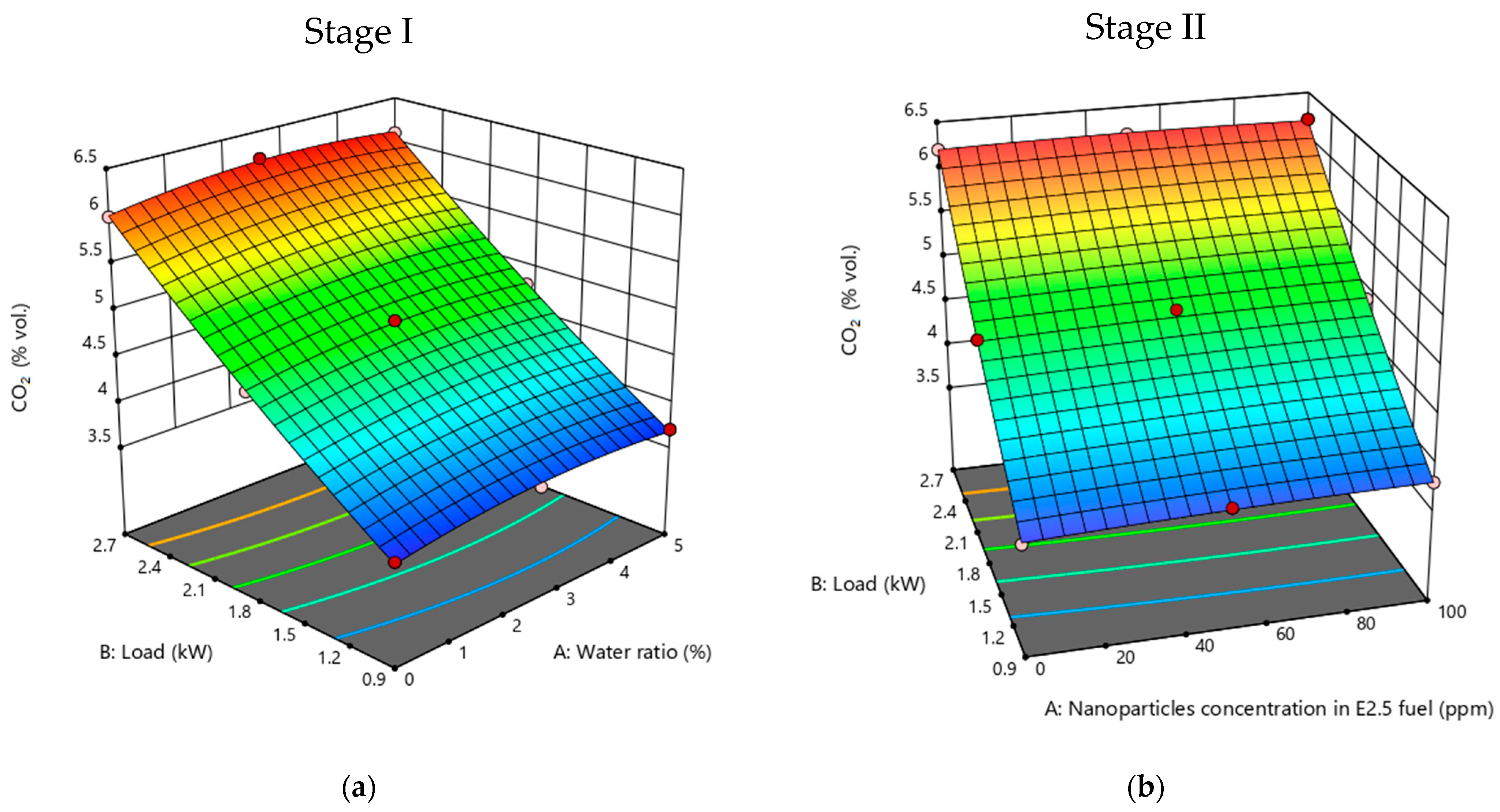
3.2.4. CO2 Emissions
3.3. Analysis of Engine Performance Parameters
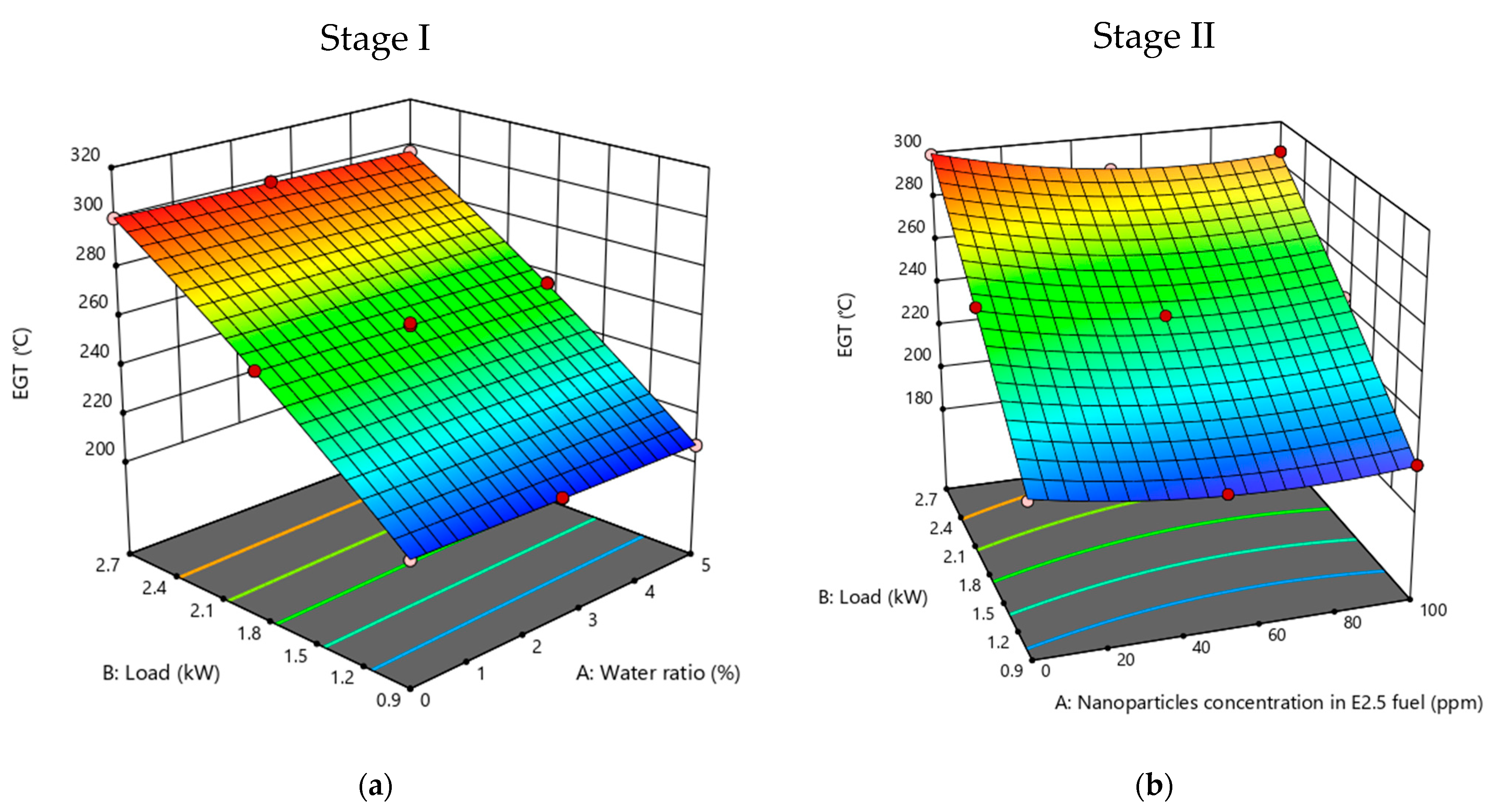
3.3.1. EGT
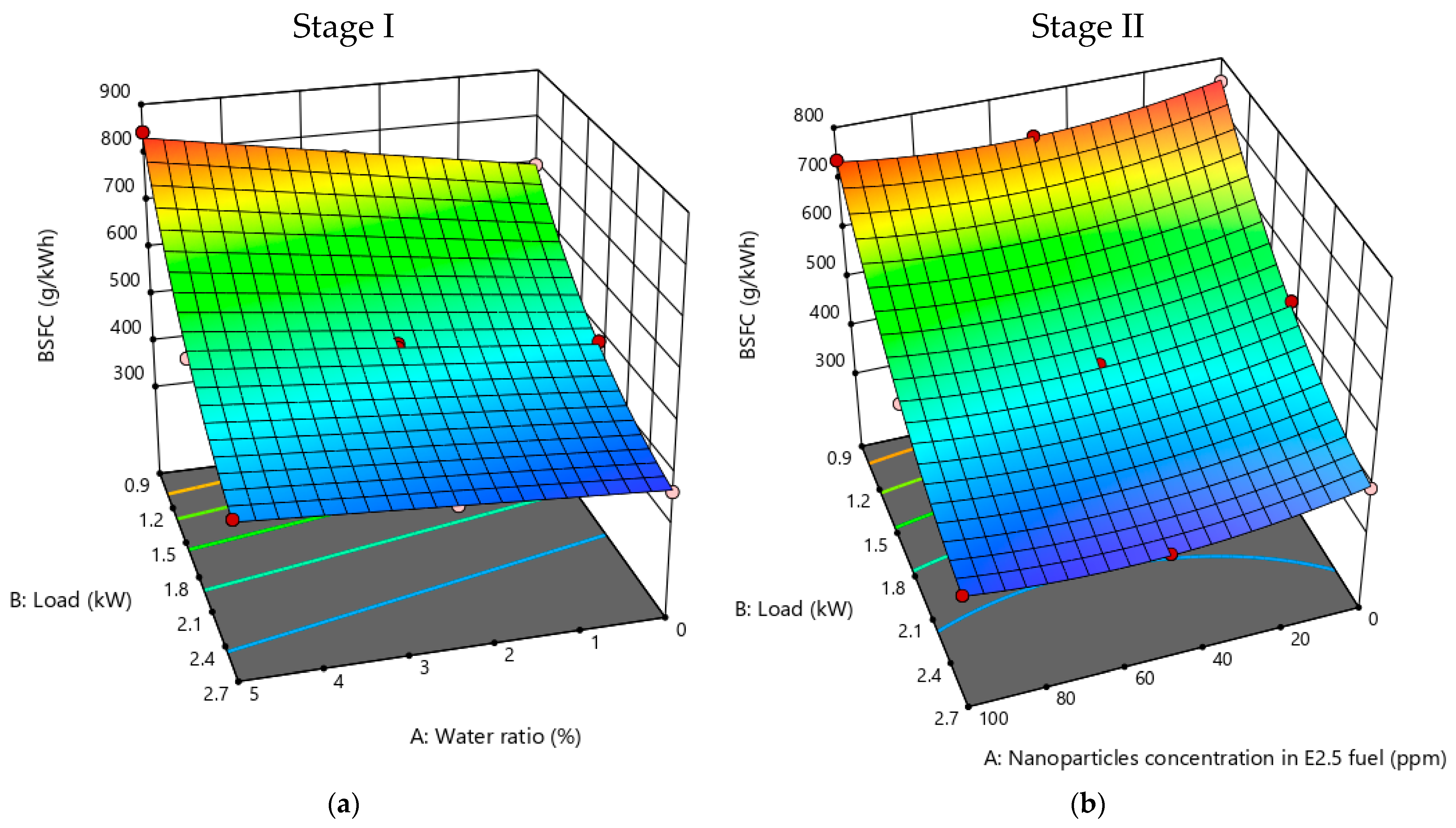
3.3.2. BSFC
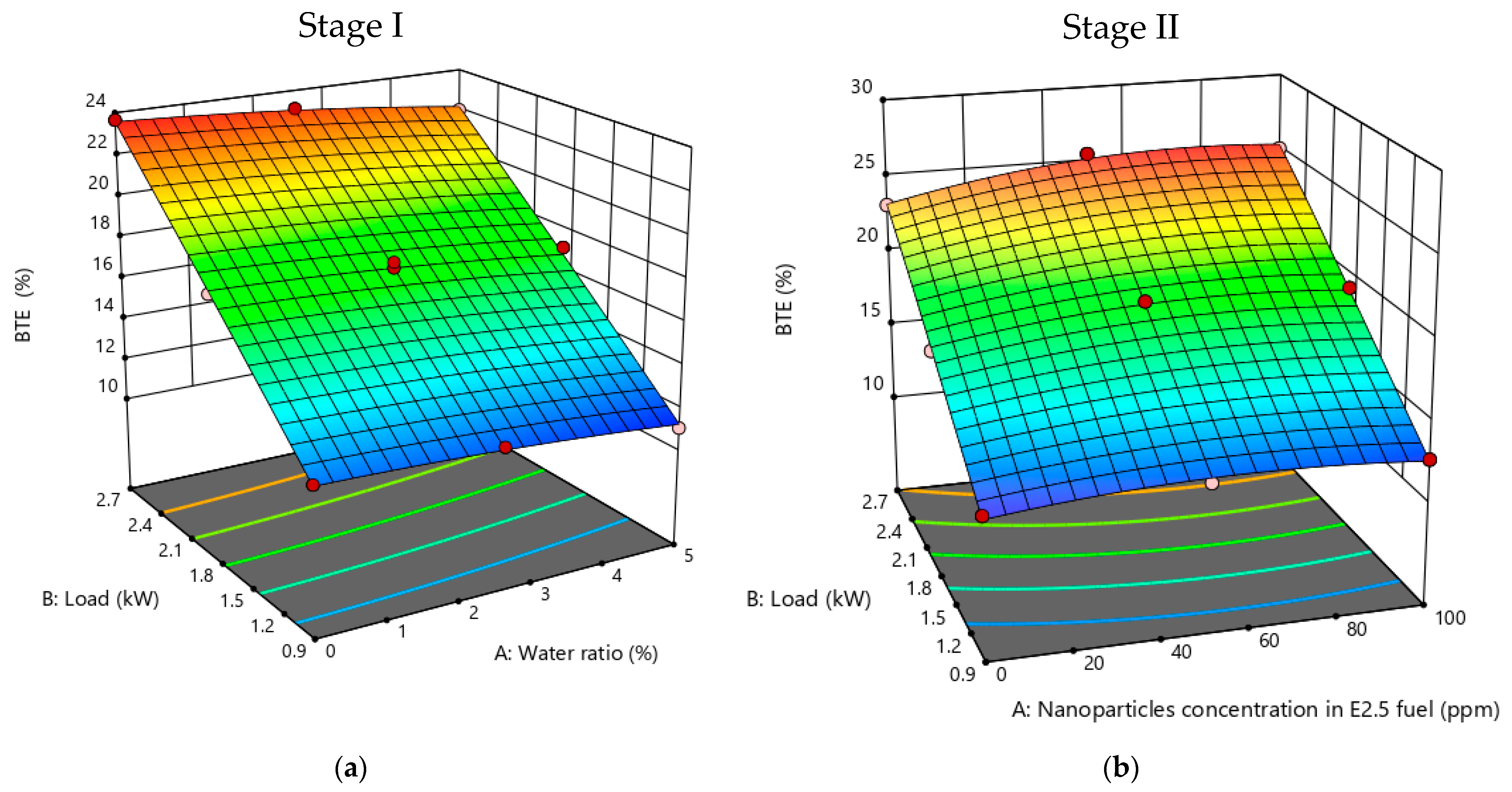
3.3.3. BTE
4. Conclusions
- Model analysis indicated the stability of each response model, with all p-values being less than 0.05. Additionally, HC, NOx, CO, CO2, EGT, BSFC, and BTE exhibited coefficient determination (R2) values of 0.9360, 0.9992, 0.8134, 0.9987, 0.9997, 0.9969, and 0.9976, respectively. The predicted R2 and adjusted R2 values differed by less than 0.2, signifying the robustness of both the model and the data.
- Performance analysis revealed that, due to the lower heating value of the emulsion, brake specific fuel consumption increased with an escalating water ratio, while brake thermal efficiency decreased.
- In terms of exhaust emissions analysis, the E2.5 fuel demonstrated average reductions of 60.18% for NOx, 16.62% for HC, and 21.56% for CO throughout engine loading compared to pure diesel fuel.
- Model analysis showed a p-value below 0.05 for every response model, with the corresponding R2 values for HC, NOx, CO, CO2, EGT, BSFC and BTE being 0.9443, 0.9867, 0.8315, 0.9989, 0.9994, 0.9986, and 0.9971, respectively. Additionally, the minimal difference between predicted R2 and adjusted R2 values (below 0.2) indicates the reliability of the models.
- Exhaust emissions analysis revealed that, on average, throughout engine loading, E2.5 + 50Al2O3 fuel accomplished a substantial reduction in NOx (69.70%), HC (33.37%), and CO (32.44%) compared to pure diesel fuel.
- Performance analysis indicated a 7.94% increase in brake thermal efficiency for E2.5 + 50Al2O3 compared to pure diesel fuel at maximum test load.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Okumuş, F.; Kaya, C.; Kökkülünk, G. NOX based comparative analysis of a CI engine fueled with water in diesel emulsion. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 6710–6729. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, A.; Mustafa, A.; Youssef, I.; Mourad, M. Assessment of Performance and Emissions Characteristics of Diesel Engine using Water Diesel Emulsion: A Review. Environ. Asia 2022, 15, 117–130. [Google Scholar]
- Attar, A.; Waghmare, J.; Mane, S. Water in diesel emulsion fuel: Production, properties, performance, and exhaust emission analysis. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2022, 13, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, B.; Cao, J.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. A new shift mechanism for micro-explosion of water-diesel emulsion droplets at different ambient temperatures. Appl. Energy 2022, 323, 119448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowrishankar, S.; Krishnasamy, A. Novel surfactants for stable biodiesel-water emulsions to improve performance and reduce exhaust emissions of a light-duty diesel engine. Fuel 2022, 330, 125562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, R.R.; Sharma, P.; Raj, P.; Keny, R.; Bhide, P.J.; Kumar, S.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Lohani, A.; Kumar, A.; Verma, A. Factors affecting emissions from diesel fuel and water-in-diesel emulsion. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2016, 38, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Roy, B. Influence of areca nut husk nano-additive on combustion, performance, and emission characteristics of compression ignition engine fuelled with plastic-grocery-bag derived oil-water-diesel emulsion. Energy 2023, 268, 126682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesharvani, S.; Chhabra, M.; Dwivedi, G.; Verma, T.N.; Pugazhendhi, A. Execution and emission characteristics of automotive compression ignition engine powered by cerium oxide nanoparticles doped water diesel emulsion fuel. Fuel 2023, 349, 128670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumuş, F.; Kökkülünk, G.; Kaya, C.; Aydın, Z. Thermodynamic assessment of water diesel emulsified fuel usage in a single cylinder diesel engine. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 3708–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, P.K.; Mandal, B.K. Optimization of water-emulsified diesel preparation and comparison of mechanical homogenization and ultrasonic dispersion methods to study CI engine performances. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 6566–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil, M.; Hemadri, V.B.; Swamy, M. Experimental investigation on impact of water in diesel emulsion in a single-cylinder research diesel engine. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2023, 44, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Yahya, W.; Ithnin, A.; Abd Kadir, H. Performance and emissions of diesel engine fuelled with water-in-diesel emulsion. J. Soc. Automot. Eng. Malays. 2017, 1, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmer, A.; Yamin, J.; Sakhrieh, A.; Hamdan, M. Engine performance using emulsified diesel fuel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2010, 51, 1708–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vali, R.H.; Wani, M.M. Optimal utilization of ZnO nanoparticles blended diesel-water emulsion by varying compression ratio of a VCR diesel engine. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Wei, J.; Chen, B.; Li, X.; Ying, D.; Gong, L.; Fang, W. Effect of nanoparticles on diesel engines driven by biodiesel and its blends: A review of 10 years of research. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 291, 117276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Wei, J. The combined effect of water and nanoparticles on diesel engine powered by biodiesel and its blends with diesel: A review. Fuel 2023, 343, 127940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wang, S.; Meng, B. The effects of nano-additives added to diesel-biodiesel fuel blends on combustion and emission characteristics of diesel engine: A review. Energies 2022, 15, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, J.S.; Anand, R. An experimental study in a CI engine using nanoadditive blended water–diesel emulsion fuel. Int. J. Green Energy 2011, 8, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, D.; Goyal, R. Effects of silicon dioxide nanoparticles on the performance and emission features at different injection timings using water diesel emulsified fuel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 205, 112379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MD, A.; Hemadri, V.; Swamy, M. Impact of Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles Dispersed in Water in Diesel Emulsion in Reduction of Diesel Engine Exhaust Pollutants. Pollution 2022, 8, 579–593. [Google Scholar]
- Veza, I.; Spraggon, M.; Fattah, I.R.; Idris, M. Response surface methodology (RSM) for optimizing engine performance and emissions fueled with biofuel: Review of RSM for sustainability energy transition. Results Eng. 2023, 18, 101213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaq, L.; Abbas, M.M.; Waseem, A.; Jauhar, T.A.; Fayaz, H.; Kalam, M.; Soudagar, M.E.M.; Silitonga, A.; Ishtiaq, U. Influence of varying concentrations of TiO2 nanoparticles and engine speed on the performance and emissions of diesel engine operated on waste cooking oil biodiesel blends using response surface methodology. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, A.; Mourad, M.; Mustafa, A.; Youssef, I. Influence of aluminum oxide nanoparticles addition with diesel fuel on emissions and performance of engine generator set using response surface methodology. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2023, 19, 100389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, P.K.; Mandal, B.K. Experimental investigation on the combustion, performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine using water emulsified diesel prepared by ultrasonication. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmer, H.; Alahmer, A.; Alamayreh, M.I.; Alrbai, M.; Al-Rbaihat, R.; Al-Manea, A.; Alkhazaleh, R. Optimal water addition in emulsion diesel fuel using machine learning and sea-horse optimizer to minimize exhaust pollutants from diesel engine. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shenawy, E.; Elkelawy, M.; Bastawissi, H.A.-E.; Shams, M.M.; Panchal, H.; Sadasivuni, K.; Thakar, N. Investigation and performance analysis of water-diesel emulsion for improvement of performance and emission characteristics of partially premixed charge compression ignition (PPCCI) diesel engines. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2019, 36, 100546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, J.S.; Al Balushi, M. Performance and emission features of a light duty diesel engine generator powered with water-diesel emulsions. Eur. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2019, 2, 72–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ithnin, A.M.; Ahmad, M.A.; Bakar, M.A.A.; Rajoo, S.; Yahya, W.J. Combustion performance and emission analysis of diesel engine fuelled with water-in-diesel emulsion fuel made from low-grade diesel fuel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 90, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamam, M.Q.M.; Yahya, W.J.; Ithnin, A.M.; Abdullah, N.R.; Kadir, H.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Rahman, H.A.; Mansor, M.R.A.; Noge, H. Performance and emission studies of a common rail turbocharged diesel electric generator fueled with emulsifier free water/diesel emulsion. Energy 2023, 268, 126704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, M.; Mirjavadi, S.S.; Davari, E.; Seifi, M.R. The effect of water-diesel emulsion usage on a tractor engine performance and emission. Russ. Agric. Sci. 2016, 42, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Din, M.N.; Mishrif, M.R.; Gad, M.; Keshawy, M. Performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel engine using diesel nanoemulsions as alternative fuels. Egypt. J. Pet. 2019, 28, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmer, A. Influence of using emulsified diesel fuel on the performance and pollutants emitted from diesel engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 73, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, Z.U.; Usman, M.; Asim, M.; Kazim, A.H.; Farooq, M.; Umair, M.; Imtiaz, M.U.; Asim, S.S. Use of diesel and emulsified diesel in CI engine: A comparative analysis of engine characteristics. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 00368504211020930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selim, M.Y.; Ghannam, M.T. Performance and Engine Roughness of a Diesel Engine Running on Stabilized Water Diesel Emulsion; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, D.; Roy, B. Effects of plastic-grocery-bag derived oil-water-diesel emulsions on combustion, performance and emission characteristics, and exergoeconomic aspects of compression ignition engine. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 54, 102877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.; Shen, Y.; Shu, G.; Chen, G.; Xu, B.; Zhao, W. Influence of water emulsified diesel & oxygen-enriched air on diesel engine NO-smoke emissions and combustion characteristics. Energy 2013, 55, 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, M.Y.; Ghannam, M. Combustion study of stabilized water-in-diesel fuel emulsion. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2009, 32, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahd, M.E.A.; Wenming, Y.; Lee, P.; Chou, S.; Yap, C.R. Experimental investigation of the performance and emission characteristics of direct injection diesel engine by water emulsion diesel under varying engine load condition. Appl. Energy 2013, 102, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, D.; Goyal, R.; Jain, A.; Johnson, A.T. Modeling and optimization of stability aspects for water diesel emulsified fuel using response surface methodology. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2022, 44, 3055–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abed, K.; Gad, M.; El Morsi, A.; Sayed, M.; Elyazeed, S.A. Effect of biodiesel fuels on diesel engine emissions. Egypt. J. Pet. 2019, 28, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.; Gadhave, A.; Mane, S.; Waghmare, J. Analyzing the stability of the water-in-diesel fuel emulsion. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugeng, D.; Abrori, M.; Syafrinaldy, A.; Kadir, H.; Saputro, F.; Kusdi, B.; Bahiudddin, I.; Yahya, W. Determining water content of non-surfactant emulsion fuel using bomb-calorimeter. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, M.; Ismail, Y.; Mohamed, M. The influence of ethanol–gasoline blends on performance characteristics of engine generator set. Am. J. Eng. Res. 2017, 6, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El Fattah, S.F.; Ezzat, M.F.; Mourad, M.A.; Elkelawy, M.; Youssef, I.M. Experimental Investigation of the Performance and Exhaust Emissions of a Spark-Ignition Engine Operating with Different Proportional Blends of Gasoline and Water Ammonia Solution. J. Eng. Res. 2022, 5, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Khulief, S.; Aboul-Fotouh, T.M. Experimental investigation of upgraded diesel fuel with copper oxide nanoparticles on performance and emissions characteristics of diesel engine. J. Energy Power Eng. 2017, 11, 541–552. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahiem, E.E.; Hakim, Y.A.; Aboul-Fotouh, T.M.; Abd Elfattah, M. Improvement of diesel fuel to enhance engine performance and emissions using zinc oxide nanoparticle additive. Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alur, S.; Shivashimpi, M.; Akkoli, K.; Banapurmath, N.; Sakthivel, D.; Sonawane, Y.D.; Islam, S.; Sharma, P.; Khan, M.A.; Razak, A. Optimization and modelling of EGR rate and MIS for POME fuelled CRDI diesel engine. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2023, 49, 103170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Casseres, D.; Valencia-Ochoa, G.; Duarte-Forero, J. Experimental assessment of combustion performance in low-displacement stationary engines operating with biodiesel blends and hydroxy. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2021, 23, 100883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, M.A.; Santelli, R.E.; Oliveira, E.P.; Villar, L.S.; Escaleira, L.A. Response surface methodology (RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry. Talanta 2008, 76, 965–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simsek, S.; Uslu, S. Determination of a diesel engine operating parameters powered with canola, safflower and waste vegetable oil based biodiesel combination using response surface methodology (RSM). Fuel 2020, 270, 117496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, S.; Celik, M. Response surface methodology-based optimization of the amount of cerium dioxide (CeO2) to increase the performance and reduce emissions of a diesel engine fueled by cerium dioxide/diesel blends. Energy 2023, 266, 126403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, S.; Xiao, B.; Shen, L.; Wang, P.; Nie, X. Study on Diesel Engine Selective Catalytic Reduction Performance at Different Atmospheric Pressures Using the Response Surface Method. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 14549–14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uslu, S. Optimization of diesel engine operating parameters fueled with palm oil-diesel blend: Comparative evaluation between response surface methodology (RSM) and artificial neural network (ANN). Fuel 2020, 276, 117990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamoradi, T.; Kiasat, A.R.; Veisi, H.; Nobakht, V.; Besharati, Z.; Karmakar, B. MgO doped magnetic graphene derivative as a competent heterogeneous catalyst producing biofuels via transesterification: Process optimization through Response Surface Methodology (RSM). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfe, M.H.; Alidust, S.; Motallebi, M.; Toghraie, D. Investigation of different transfer functions for modeling the dynamic viscosity of hybrid nanolubricant containing MWCNTs and MgO nanoparticles using the response surface methodology (RSM). Tribol. Int. 2023, 183, 108370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakran, S.; Kaushal, R.; Bajpai, V.K. Experimental study and optimization of performance characteristics of compression ignition hydrogen engine with diesel pilot injection. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 33705–33718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, C.; Verma, T.N.; Dwivedi, G.; Verma, P. Energy-exergy analysis of diesel engine fueled with microalgae biodiesel-diesel blend. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dong, R.; Tan, D.; Zhang, B. Multi-objective optimization of performance characteristic of diesel particulate filter for a diesel engine by RSM-MOPSO during soot loading. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 177, 530–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization of Legal Metrology. Available online: https://www.oiml.org/en/files/pdf_r/r099-1-2-e08.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2023).
- Mehta, R.N.; Chakraborty, M.; Parikh, P.A. Nanofuels: Combustion, engine performance and emissions. Fuel 2014, 120, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.R.; Muthukkumar, T.; Krishnamoorthy, V.; Saravanan, S. A comparative evaluation and optimization of performance and emission characteristics of a DI diesel engine fueled with n-propanol/diesel, n-butanol/diesel and n-pentanol/diesel blends using response surface methodology. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61869–61890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Youssef, I.; Mourad, M. Impact of Ethanol-Gasoline Blends on Exhaust Emissions, Noise and Vibration Characteristics of Single Cylinder Spark Ignition Engine. Minia J. Eng. Technol. (MJET) 2018, 38, 275–283. [Google Scholar]
- Venkanna, B.; Venkataramana Reddy, C. Direct injection diesel engine performance, emission, and combustion characteristics using diesel fuel, nonedible honne oil methyl ester, and blends with diesel fuel. Int. J. Energy Res. 2012, 36, 1247–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.; Ghobadian, B.; Najafi, G.; Hoseini, S.; Mofijur, M.; Mazlan, M. Impact of water–biodiesel–diesel nano-emulsion fuel on performance parameters and diesel engine emission. Fuel 2020, 280, 118576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annamalai, M.; Dhinesh, B.; Nanthagopal, K.; SivaramaKrishnan, P.; Lalvani, J.I.J.; Parthasarathy, M.; Annamalai, K. An assessment on performance, combustion and emission behavior of a diesel engine powered by ceria nanoparticle blended emulsified biofuel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 123, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhik Basha, J.; Anand, R. Effects of nanoparticle additive in the water-diesel emulsion fuel on the performance, emission and combustion characteristics of a diesel engine. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2012, 59, 164–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneswaran, R.; Balasubramanian, D.; Sastha, B.S. Performance, emission and combustion characteristics of unmodified diesel engine with titanium dioxide (TiO2) nano particle along with water-in-diesel emulsion fuel. Fuel 2021, 285, 119115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, M.; Sundaram, N.S.; Thasthagir, M.H.S. Effect of aluminium oxide nanoparticles blended pongamia methyl ester on performance, combustion and emission characteristics of diesel engine. Renew. Energy 2018, 116, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yin, Z.; Wang, C.; Lv, G.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, H. Impact of aluminium oxide nanoparticles as an additive in diesel-methanol blends on a modern DI diesel engine. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 185, 116372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, K.; Kumar, G. Impact of 1-Hexanol/diesel blends on combustion, performance and emission characteristics of CRDI CI mini truck engine under the influence of EGR. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 217, 113003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayad, M.A.; Sobhi, M.; Chaichan, M.T.; Badawy, T.; Abdul-Lateef, W.E.; Dhahad, H.A.; Yusaf, T.; Isahak, W.N.R.W.; Takriff, M.S.; Al-Amiery, A.A. Reducing Soot Nanoparticles and NOX Emissions in CRDI Diesel Engine by Incorporating TiO2 Nano-Additives into Biodiesel Blends and Using High Rate of EGR. Energies 2023, 16, 3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanjani, A.; Sobati, M.A. Performance and emission of a diesel engine using different water/waste fish oil (WFO) biodiesel/diesel emulsion fuels: Optimization of fuel formulation via response surface methodology (RSM). Fuel 2021, 288, 119662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha, H.; Khalife, E.; Tabatabaei, M.; Aghbashlo, M.; Khanali, M.; Mohammadi, P.; Shojaei, T.R.; Soltanian, S. Effects of aqueous carbon nanoparticles as a novel nanoadditive in water-emulsified diesel/biodiesel blends on performance and emissions parameters of a diesel engine. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 196, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R.; Dhiman, V.D. Effect of hybrid nanoparticles MgO and Al2O3 added water-in-diesel emulsion fueled diesel engine using hybrid deep neural network-based spotted hyena optimization. Heat Transf. 2022, 51, 5748–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutak, W.; Jamrozik, A.; Grab-Rogaliński, K. Evaluation of Combustion Stability and Exhaust Emissions of a Stationary Compression Ignition Engine Powered by Diesel/n-Butanol and RME Biodiesel/n-Butanol Blends. Energies 2023, 16, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Raheman, H.; Machavaram, R. Performance of a diesel engine with water emulsified diesel prepared with optimized process parameters. Int. J. Green Energy 2019, 16, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaram, A.; Prabhu, N.; Praveen Kumar, R.; Navaneethakrishnan, G.; Palanisamy, R.; AboRas, K.M.; Bajaj, M.; Djidimbele, R.; Dieudonné, K.K.; Vinodhan, V.L. Performance Analysis of Compression Ignition Engines Using Emulsion Fuel Blended with Aluminium Oxide Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2023, 2023, 3988117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Mozafari-Vanani, L.; Dehghani-Soufi, M.; Jahanbakhshi, A. Effect of alumina nanoparticles as additive with diesel–biodiesel blends on performance and emission characteristic of a six-cylinder diesel engine using response surface methodology (RSM). Energy Convers. Manag. X 2021, 11, 100091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, M.; Issa, M.; Ilinca, A. Experimental underperformance detection of a fixed-speed diesel–electric generator based on exhaust gas emissions. Energies 2023, 16, 3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, M.; Sayin, C.; Canakci, M. The impact of fuel injection pressure on the exhaust emissions of a direct injection diesel engine fueled with biodiesel–diesel fuel blends. Fuel 2012, 95, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, A.B.; Abdullah, M. Performance and NOx emissions of a diesel engine fueled with biodiesel-diesel-water nanoemulsions. Fuel Process. Technol. 2013, 109, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, G.; Ji, C.; Wang, S.; Hong, C.; Meng, H.; Yang, J.; Su, F. Experimental study on Miller cycle hydrogen-enriched ammonia engine by rich-burn strategy. Fuel 2023, 350, 128899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srithar, K.; Balasubramanian, K.A.; Pavendan, V.; Kumar, B.A. Experimental investigations on mixing of two biodiesels blended with diesel as alternative fuel for diesel engines. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2017, 29, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheman, H.; Ghadge, S. Performance of compression ignition engine with mahua (Madhuca indica) biodiesel. Fuel 2007, 86, 2568–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, P.; Senthilkumar, M. Simultaneous reduction of emissions as well as fuel consumption in CI engine using water and nanoparticles in diesel-biodiesel blend. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 43, 1500–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodi, F.; Zare, A.; Arora, P.; Stevanovic, S.; Ristovski, Z.; Brown, R.J.; Bodisco, T. Engine performance characteristics using microalgae derived dioctyl phthalate biofuel during cold, preheated and hot engine operation. Fuel 2023, 344, 128162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.P.; Prasad, L.S.V. Combined influence of compression ratio and exhaust gas recirculation on the diverse characteristics of the diesel engine fueled with novel palmyra biodiesel blend. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2022, 14, 100185. [Google Scholar]
- An, H.; Yang, W.; Chou, S.; Chua, K. Combustion and emissions characteristics of diesel engine fueled by biodiesel at partial load conditions. Appl. Energy 2012, 99, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

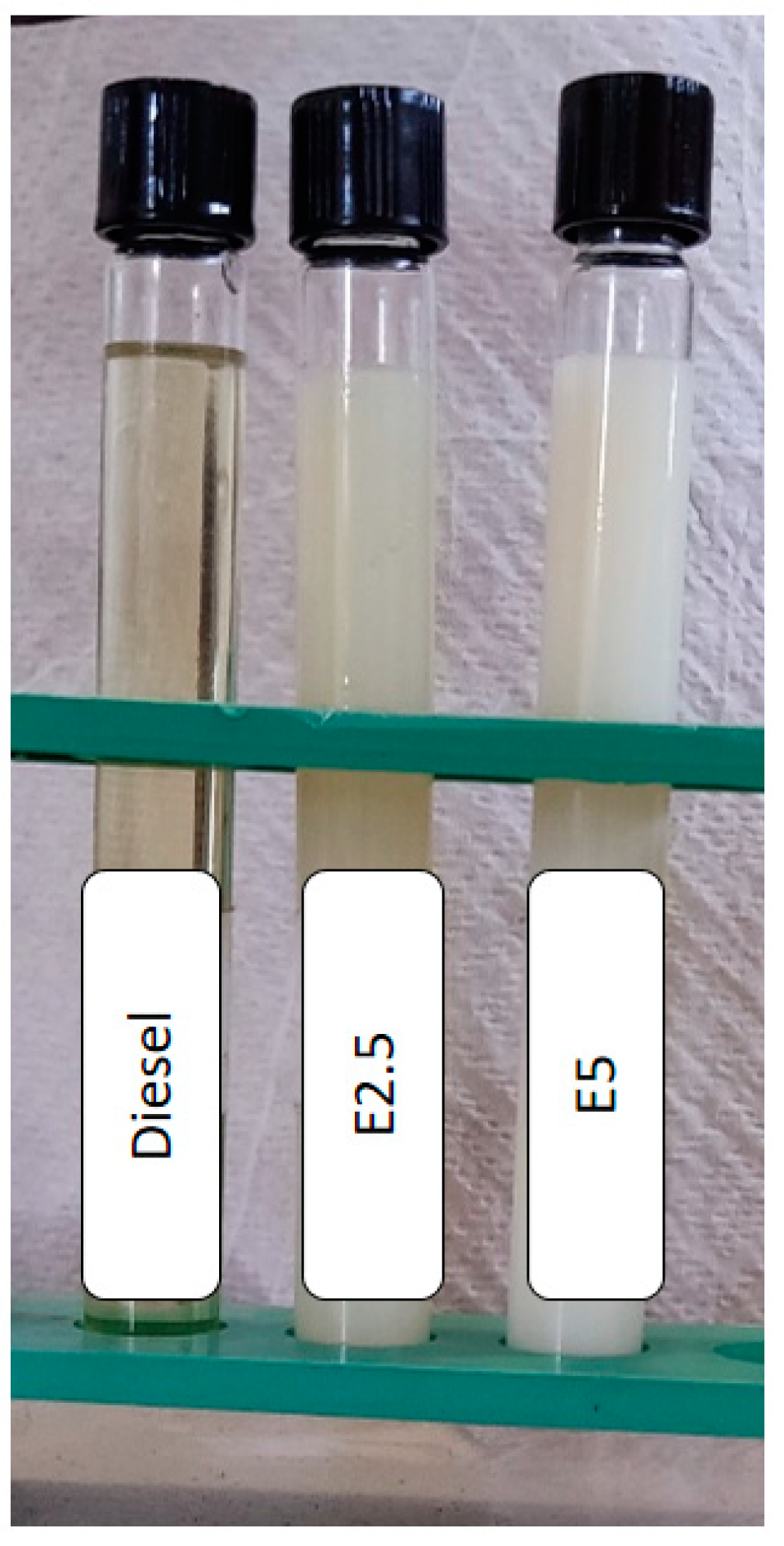

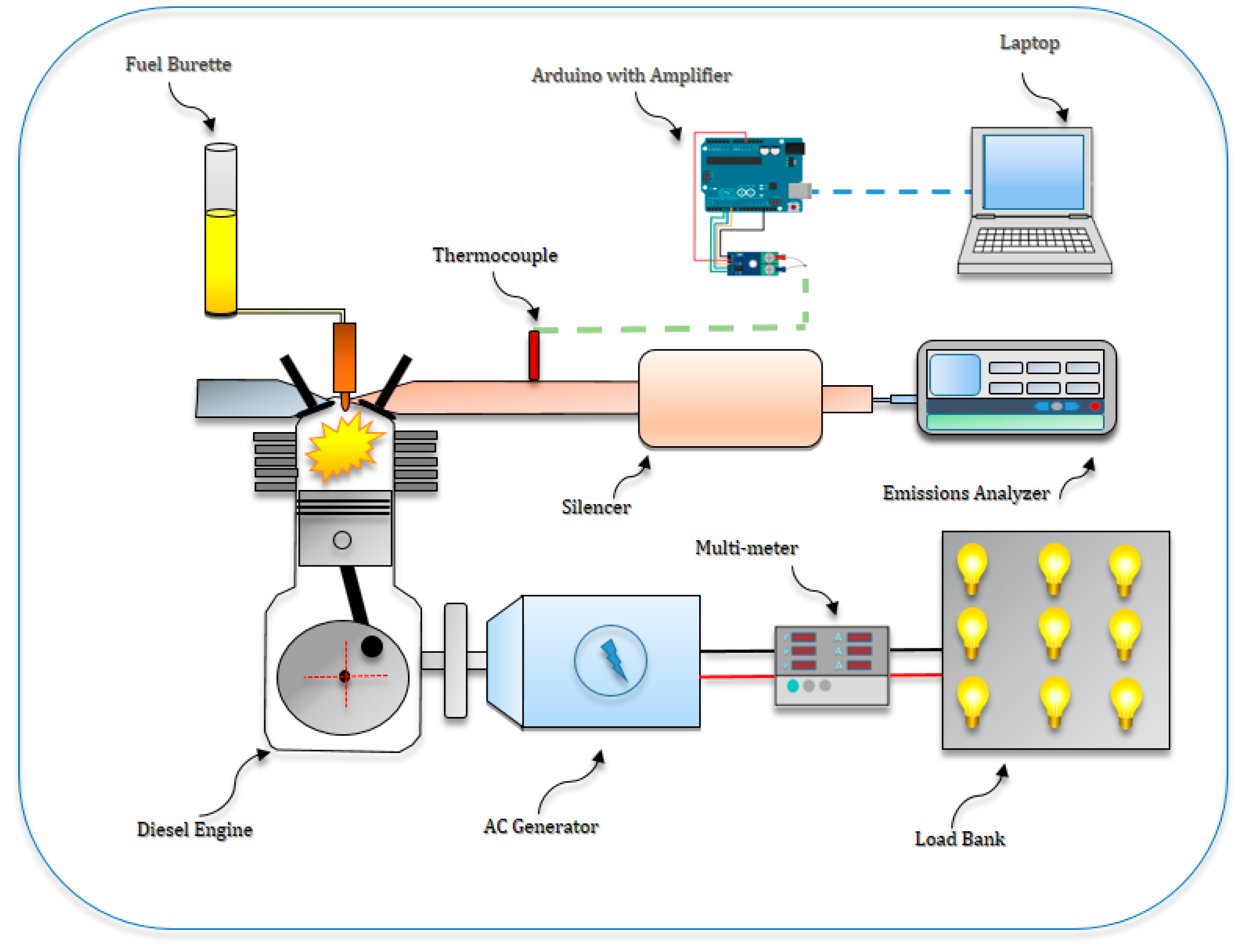
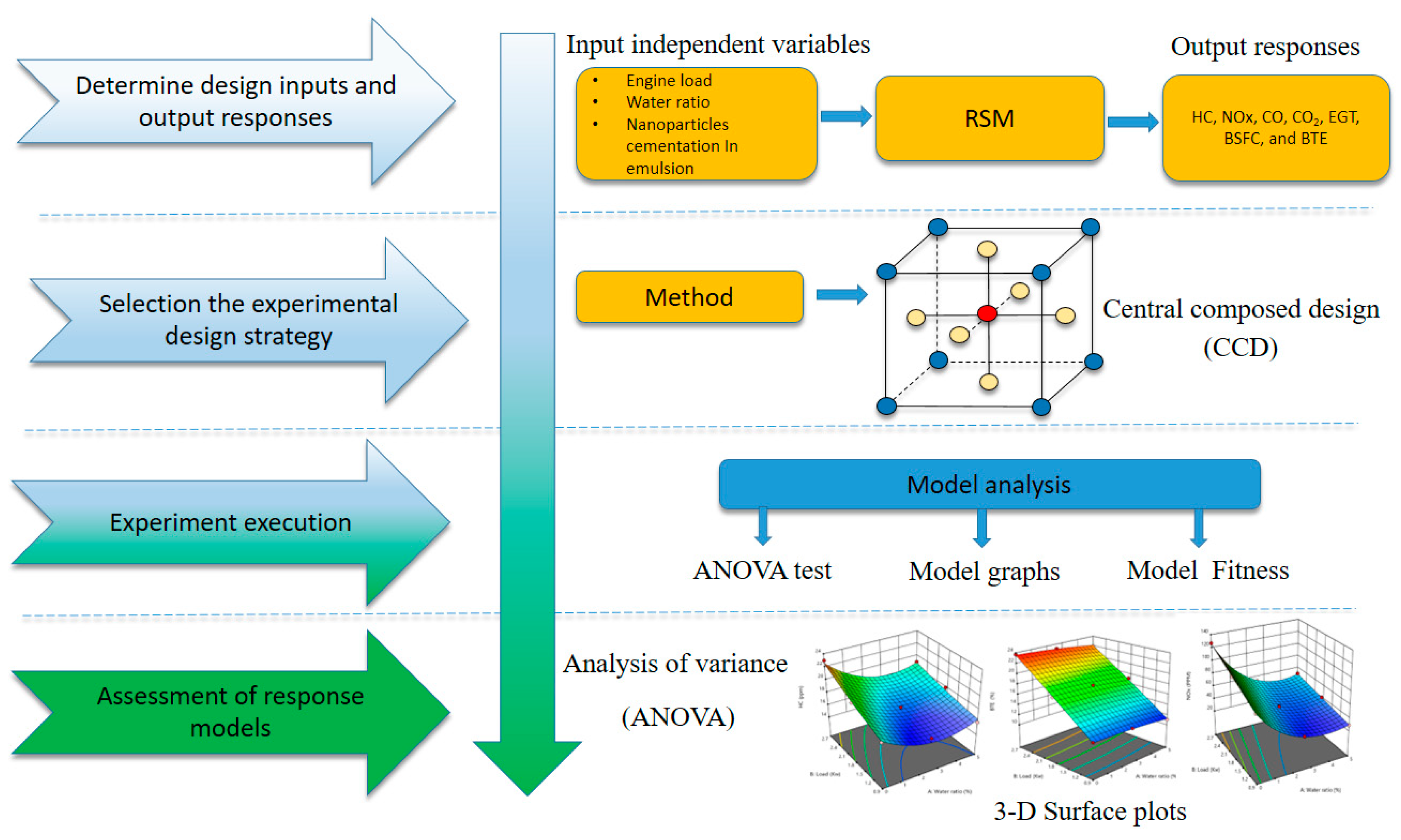

| Item | Specification |
|---|---|
| Chemical name | Aluminum oxide (Al2O3) |
| Manufacturer | Nanotech, Egypt |
| Physical Property | Value |
|---|---|
| 829 | |
| 45 | |
| 2.8 | |
| ( | 42,000 |
| No. | Fuel Designation | Water (%) by Vol. | Span 20 (%) by Vol. | Diesel Fuel (%) by Vol. | Density kg/m3 | Heating Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | E2.5 | 2.5 | 3 | 94.5 | 839.365 | 39,690 |
| 2 | E5 | 5 | 3 | 92 | 843.64 | 38,640 |
| Engine | Type | Single Cylinder, Four-Stroke Diesel Engine |
|---|---|---|
| Model | 5GF-SKM2 (Lister) | |
| Cooling system | Force air cooled | |
| Displacement | 406 cm3 | |
| Bore | ||
| Stroke lenght | 70 mm | |
| Rated power | ||
| Rated speed | 3000 rpm | |
| Start system | Electric start | |
| Generator | Type | AC generator with two-poles |
| Voltage | 220 VAC | |
| Frequency | ||
| Rated output | kW | |
| Maximum output | 5.5 kW |
| Emissions | Unit | Resolution | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO | vol | ||
| CO2 | vol. | ||
| HC | 1 | ||
| NOX | ppm | 1 | 0–5000 |
| Variable | Uncertainty [%] at Stage I | Uncertainty [%] at Stage II |
|---|---|---|
| NOX | ±0.8 | ±1.5% |
| HC | ±1.5 | ±1.8% |
| CO2 | ±0.4 | ±0.3% |
| CO | ±6.8 | ±7.1% |
| EGT | ±0.2% | ±0.1% |
| BSFC | ±0.6% | ±0.6 |
| BTE | ±0.6% | ±0.6% |
| U(overall) | ±7.1 | ±7.6 |
| Experimental Design Variables | Unit | Code | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (−1) | Central (0) | High (1) | |||
| Water ratio | % | 0 | 2.5 | 5 | |
| Engine load | 0.9 | 1.8 | 2.7 | ||
| Experimental Design Variables | Unit | Code | Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (−1) | Central (0) | High (1) | |||
| Nanoparticles concentration in E2.5 fuel | ppm | 0 | 50 | 100 | |
| Engine load | 0.9 | 1.8 | 2.7 | ||
| Input Variables | Emission Parameters | Performance Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run | Water Ratio (%) | Load (kW) | HC (ppm) | NOx (ppm) | CO (% Vol.) | CO2 (% Vol.) | EGT | BSFC (g/kWh) | BTE (%) |
| 1 | 2.5 | 2.7 | 18 | 53 | 0.04 | 6.2 | 299 | 392.7 | 23.10 |
| 2 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 17 | 42 | 0.03 | 4.9 | 256 | 524.6 | 17.29 |
| 3 | 5 | 2.7 | 19 | 50 | 0.05 | 6.1 | 297 | 424.5 | 21.95 |
| 4 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 16 | 42 | 0.04 | 4.8 | 257 | 516.5 | 17.56 |
| 5 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 17 | 42 | 0.03 | 4.9 | 256 | 508.7 | 17.83 |
| 6 | 2.5 | 0.9 | 16 | 31 | 0.05 | 3.7 | 209 | 754.5 | 12.02 |
| 7 | 0 | 1.8 | 20 | 104 | 0.05 | 4.7 | 259 | 480.6 | 17.84 |
| 8 | 5 | 0.9 | 16 | 29 | 0.05 | 3.7 | 207 | 843.6 | 11.04 |
| 9 | 0 | 0.9 | 18 | 83 | 0.06 | 3.6 | 210 | 698.1 | 12.28 |
| 10 | 0 | 2.7 | 23 | 127 | 0.05 | 6 | 300 | 362.4 | 23.65 |
| 11 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 16 | 41 | 0.04 | 4.9 | 258 | 516.5 | 17.56 |
| 12 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 17 | 43 | 0.04 | 4.9 | 257 | 524.6 | 17.29 |
| 13 | 5 | 1.8 | 18 | 40 | 0.04 | 4.8 | 256 | 544.3 | 17.12 |
| Input Variables | Emission Parameters | Performance Parameters | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run | Nanoparticles Conc. in E2.5 Fuel (ppm) | Load (kW) | HC (ppm) | NOx (ppm) | CO (% Vol.) | CO2 (% Vol.) | EGT °C | BSFC (g/kWh) | BTE (%) |
| 1 | 50 | 2.7 | 15 | 41 | 0.04 | 6.2 | 285 | 355.3 | 25.53 |
| 2 | 50 | 1.8 | 14 | 33 | 0.03 | 4.9 | 244 | 466.3 | 19.45 |
| 3 | 100 | 2.7 | 16 | 46 | 0.04 | 6.2 | 286 | 373.1 | 24.97 |
| 4 | 50 | 1.8 | 14 | 33 | 0.02 | 4.9 | 244 | 466.3 | 19.45 |
| 5 | 50 | 1.8 | 13 | 32 | 0.03 | 4.9 | 243 | 479.6 | 18.91 |
| 6 | 50 | 0.9 | 12 | 22 | 0.04 | 3.8 | 200 | 714.4 | 12.70 |
| 7 | 0 | 1.8 | 17 | 42 | 0.03 | 4.9 | 258 | 524.6 | 17.56 |
| 8 | 100 | 0.9 | 15 | 23 | 0.04 | 3.8 | 201 | 737.9 | 12.63 |
| 9 | 0 | 0.9 | 16 | 31 | 0.05 | 3.7 | 209 | 754.5 | 12.28 |
| 10 | 0 | 2.7 | 18 | 53 | 0.04 | 6.2 | 299 | 392.7 | 23.10 |
| 11 | 50 | 1.8 | 13 | 34 | 0.03 | 5 | 245 | 466.3 | 19.45 |
| 12 | 50 | 1.8 | 13 | 35 | 0.03 | 4.9 | 244 | 472.9 | 19.18 |
| 13 | 100 | 1.8 | 15 | 37 | 0.03 | 4.9 | 244 | 486.6 | 19.15 |
| Response | Emission Parameters | Performance Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC | NOx | CO | CO2 | BSFC | BTE | ||
| p-value | 0.0172 | ||||||
| F value (Lack of Fit) | 1.24 | 1.94 | 0.2036 | 0.6590 | 0.4729 | 3.59 | 1.64 |
| Coefficient of Determination (R2) | 0.9360 | 0.9992 | 0.8134 | 0.9987 | 0.9997 | 0.9969 | 0.9976 |
| Adjusted (R2) | 0.9040 | 0.9987 | 0.6801 | 0.9977 | 0.9995 | 0.9946 | 0.9959 |
| Predicted (R2) | 0.7465 | 0.9950 | 0.5246 | 0.9944 | 0.9991 | 0.9771 | 0.9859 |
| Adequate Precision | 19.2006 | 131.7593 | 7.4351 | 92.5698 | 185.965 | 67.0173 | 71.1875 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.0713 | 0.0646 | 0.0119 | 0.0413 | 0.7361 | 0.2129 | 0.2551 |
| Mean | 4.21 | 7.28 | 0.2084 | 4.86 | 255.46 | 23.19 | 17.43 |
| Response | Emission Parameters | Performance Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HC | NOx | CO | CO2 | BSFC | BTE | ||
| -value | 0.0003 | 0.0123 | |||||
| F value (Lack of Fit) | 0.9432 | 1.66 | 0.1535 | 0.2807 | 3.41 | 1.50 | 2.67 |
| Coefficient of Determination (R2) | 0.9443 | 0.9867 | 0.8315 | 0.9989 | 0.9994 | 0.9986 | 0.9971 |
| Adjusted () | 0.9045 | 0.9772 | 0.7112 | 0.9981 | 0.9989 | 0.9976 | 0.9950 |
| Predicted () | 0.7187 | 0.9175 | 0.6024 | 0.9968 | 0.9954 | 0.9919 | 0.9788 |
| Adequate Precision | 15.6600 | 35.1651 | 6.8548 | 98.8349 | 145.399 | 91.1282 | 63.3320 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.5410 | 1.29 | 0.0113 | 0.0372 | 0.0323 | 6.56 | 0.0361 |
| Mean | 14.69 | 35.54 | 0.1849 | 4.95 | 15.67 | 514.65 | 4.31 |
| Quadratic Model | Equation | Transformation | Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| HC (ppm) | (6) | Square Root | Sqrt (HC) = 4.08742 − 0.151511 × A + 0.192455 × B − 0.048573 × AB + 0.264602 × A2 |
| NOx (ppm) | (7) | Square Root | Sqrt (NOx) = 6.47996 − 1.96619 × A + 0.926207 × B − 0.118273 × AB + 1.78284 × A2 − 0.0545217 × B2 |
| CO (% vol.) | (8) | Square Root | Sqrt (CO) = 0.190024 − 0.0074915 × A −0.0074915 × B + 0.00533554 × AB + 0.019923 × A2 + 0.019923 × B2 |
| CO2 (% vol.) | (9) | None | CO2 = 4.87586 + 0.05 × A + 1.21667 × B + 1.05542 × 10−15 × AB −0.115517 × A2 + 0.0844828 × B2 |
| °C | (10) | None | EGT = 256.966 − 1.5 × A + 45 × B + 9.15884× 10−14 × AB + 0.12069 × A2 − 3.37931 × B2 |
| BSFC (g/kWh) | (11) | Square Root | Sqrt (BSFC) = 22.726 + 0.932899 × A − 3.91319 × B − 0.264493 × AB − 0.00613766 × A2 + 1.00993 × B2 |
| BTE (%) | (12) | None | BTE = 17.5473 − 0.609208 × A + 5.55921 × B − 0.117002 × AB 0.174233 × A2 − 0.0908004 × B2 |
| Quadratic Model | Equation | Transformation | Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| HC (ppm) | (13) | None | (HC) = 13.3793 − 0.833333 × A + 1 × B − 0.25 × AB + 2.67241 × A2 + 0.172414 × B2 |
| NOx (ppm) | (14) | None | (NOx) = 33.3103 − 3.33333 × A + 10.6667 × B + 0.25 × AB + 6.41379 × A2 − 1.58621 × B2 |
| CO (% vol.) | (15) | Square Root | Sqrt (CO) = 0.166911 − 0.00393447 × A − 0.00393447 × B + 0.0059017 × AB + 0.00613707 × A2 + 0.032932 × B2 |
| CO2 (% vol.) | (16) | None | CO2 = 4.92069 + 0.0166667 × A + 1.21667 × B − 0.025 × AB − 0.0224138 × A2 + 0.0775862 × B2 |
| °C | (17) | Square Root | Sqrt (EGT) = 15.6237 − 0.183558 × A + 1.38478 × B − 0.0251741 × AB + 0.209543 × A2 − 0.119857 × B2 |
| BSFC (g/kWh) | (18) | None | BSFC = 0471.064 − 12.3718 × A − 180.953 × B − 0.763 × AB + 32.6036 × A2 + 61.8281 × B2 |
| BTE (%) | (19) | Square Root | Sqrt (BTE) = 4.38965 + 0.0709963 × A + 0.705923 × B + 0.0355258 × AB − 0.101044 × A2 − 0.0761533 × B2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mostafa, A.; Mourad, M.; Mustafa, A.; Youssef, I. Investigating the Combined Impact of Water–Diesel Emulsion and Al2O3 Nanoparticles on the Performance and the Emissions from a Diesel Engine via the Design of Experiment. Designs 2024, 8, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8010003
Mostafa A, Mourad M, Mustafa A, Youssef I. Investigating the Combined Impact of Water–Diesel Emulsion and Al2O3 Nanoparticles on the Performance and the Emissions from a Diesel Engine via the Design of Experiment. Designs. 2024; 8(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleMostafa, A., M. Mourad, Ahmad Mustafa, and I. Youssef. 2024. "Investigating the Combined Impact of Water–Diesel Emulsion and Al2O3 Nanoparticles on the Performance and the Emissions from a Diesel Engine via the Design of Experiment" Designs 8, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8010003
APA StyleMostafa, A., Mourad, M., Mustafa, A., & Youssef, I. (2024). Investigating the Combined Impact of Water–Diesel Emulsion and Al2O3 Nanoparticles on the Performance and the Emissions from a Diesel Engine via the Design of Experiment. Designs, 8(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/designs8010003






